A New Method for Enantiomeric Determination of 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine and p-Methoxymethamphetamine in Human Urine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of the Packing Material of Capillary Immunoaffinity Columns (CIACs)
2.3. Preparation of CIACs
2.4. Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometric Equipment and Conditions
2.5. Sample Preparation
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- A Rule by the Drug Enforcement Administration on 06/25/2021, Schedules of Controlled Substances: Placement of para-Methoxymethamphetamine (PMMA) in Schedule I. The Daily Journal of United State Goverment 2021. Available online: https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2021/06/25/2021-13460/schedules-of-controlled-substances-placement-of-para-methoxymethamphetamine-pmma-in-schedule-i (accessed on 6 January 2022).
- Institute of Forensic Medicine, Ministry of Justice. 2020 Annual Report of Forensic Medicine Statistics in Taiwan. Available online: https://www.tpa.moj.gov.tw/292712/292713/292728/926527/post (accessed on 6 January 2022).
- Schwaninger, A.E.; Meyer, M.R.; Barnes, A.J.; Kolbrich-Spargo, E.A.; Gorelick, D.A.; Goodwin, R.S.; Huestis, M.A.; Maurer, H.H. Stereoselective urinary MDMA (ecstasy) and metabolites excretion kinetics following controlled MDMA administration to humans. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Curry, D.W.; Young, M.B.; Tran, A.N.; Daoud, G.E.; Howell, L.L. Separating the agony from ecstasy: R(–)-3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine has prosocial and therapeutic-like effects without signs of neurotoxicity in mice. Neuropharmacology 2018, 128, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, T.D.; Katz, J.L.; Ricaurte, G.A. Evaluation of the neurotoxicity of N-methyl-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-aminopropane (para-methoxymethamphetamine, PMMA). Brain Res. 1992, 589, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.; Dukat, M.; Malmusi, L.; Glennon, R.A. Stimulus Properties of PMMA: Effect of Optical Isomers and Conformational Restriction. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1999, 64, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emke, E.; Evans, S.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; de Voogt, P. Enantiomer profiling of high loads of amphetamine and MDMA in communal sewage: A Dutch perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castrignanò, E.; Yang, Z.; Bade, R.; Baz-Lomba, J.A.; Castiglioni, S.; Causanilles, A.; Covaci, A.; Gracia-Lor, E.; Hernandez, F.; Kinyua, J.; et al. Enantiomeric profiling of chiral illicit drugs in a pan-European study. Water Res. 2018, 130, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Archer, E.; Castrignanò, E.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Wolfaardt, G.M. Wastewater-based epidemiology and enantiomeric profiling for drugs of abuse in South African wastewaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Guo, C.; Chen, L.; Qiu, Z.; Yin, X.; Xu, J. Simultaneous enantioselective analysis of illicit drugs in wastewater and surface water by chiral LC-MS/MS: A pilot study on a wastewater treatment plant and its receiving river. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, L.F.; Yegles, M.; Chung, H.; Wennig, R. Sensitive, rapid and validated gas chromatography/negative ion chemical ionization-mass spectrometry assay including derivatisation with a novel chiral agent for the enantioselective quantification of amphetamine-type stimulants in hair. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 842, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, L.B.; Olsen, K.H.; Johansen, S.S. Chiral separation and quantification of R/S-amphetamine, R/S-methamphetamine, R/S-MDA, R/S-MDMA, and R/S-MDEA in whole blood by GC-EI-MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 842, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aasim, W.R.; Gan, S.H.; Tan, S.C. Development of a simultaneous liquid-liquid extraction and chiral derivatization method for stereospecific GC-MS analysis of amphetamine-type stimulants in human urine using fractional factorial design. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2008, 22, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.; Gonçalves, R.; Tiritan, M.E. Separation of Enantiomers Using Gas Chromatography: Application in Forensic Toxicology, Food and Environmental Analysis. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 51, 787–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, M.G.; Hägele, J.S. Separation of enantiomers and positional isomers of novel psychoactive substances in solid samples by chromatographic and electrophoretic techniques–A selective review. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1624, 461256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.; Santos, C. Chiral Drug Analysis in Forensic Chemistry: An Overview. Moleclues 2018, 23, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonçalves, R.; Ribeiro, C.; Cravo, S.; Cunha, S.C.; Pereira, J.A.; Fernandes, J.O.; Afonso, C.; Tiritan, M.E. Multi-residue method for enantioseparation of psychoactive substances and beta blockers by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1125, 121731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lua, A.C.; Chou, T.-Y. Preparation of immunoaffinity columns for direct enantiomeric separation of amphetamine and/or methamphetamine. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 967, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lua, A.C.; Sutono, Y.; Chou, T.-Y. Enantiomeric quantification of (S)-(+)-methamphetamine in urine by an immunoaffinity column and liquid chromatography–electrospray-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 576, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.Y.; Wang, C.K.; Lua, A.C.; Yang, H.H. A simple and high throughput parallel dual immunoaffinity liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry system for urine drug testing. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Suh, S.; Park, J.; In, M.K. Simultaneous Determination of Amphetamine-Related New Psychoactive Substances in Urine by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2018, 42, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). Mandatory Guidelines for Federal Workplace Drug Testing Programs; Final Rule, Federal Register January 23, 2017 (82 FR 7920). 2017. Available online: https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-2017-01-23/pdf/2017-00979.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2022).
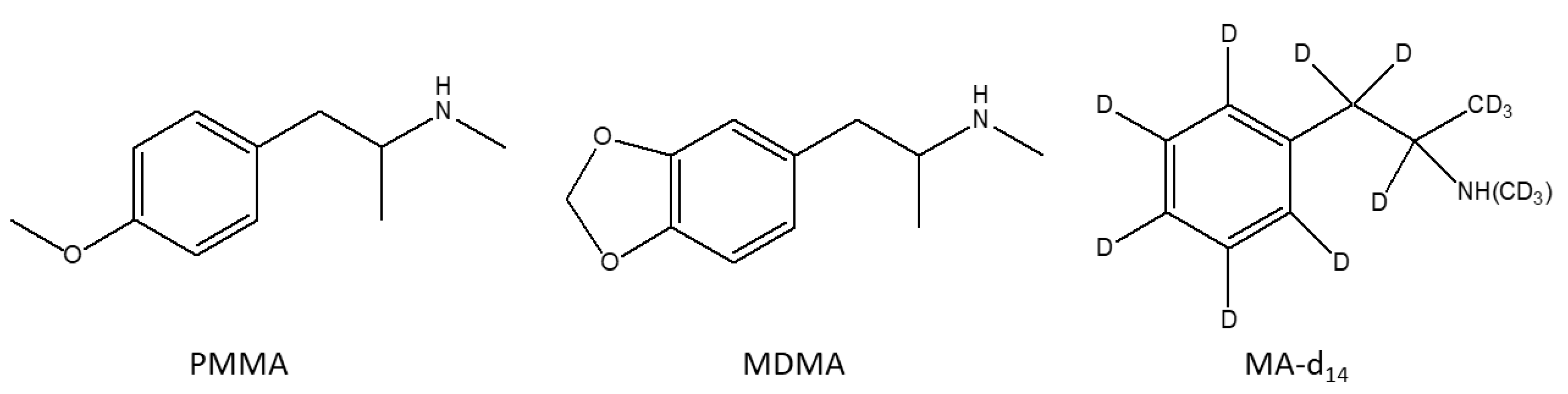
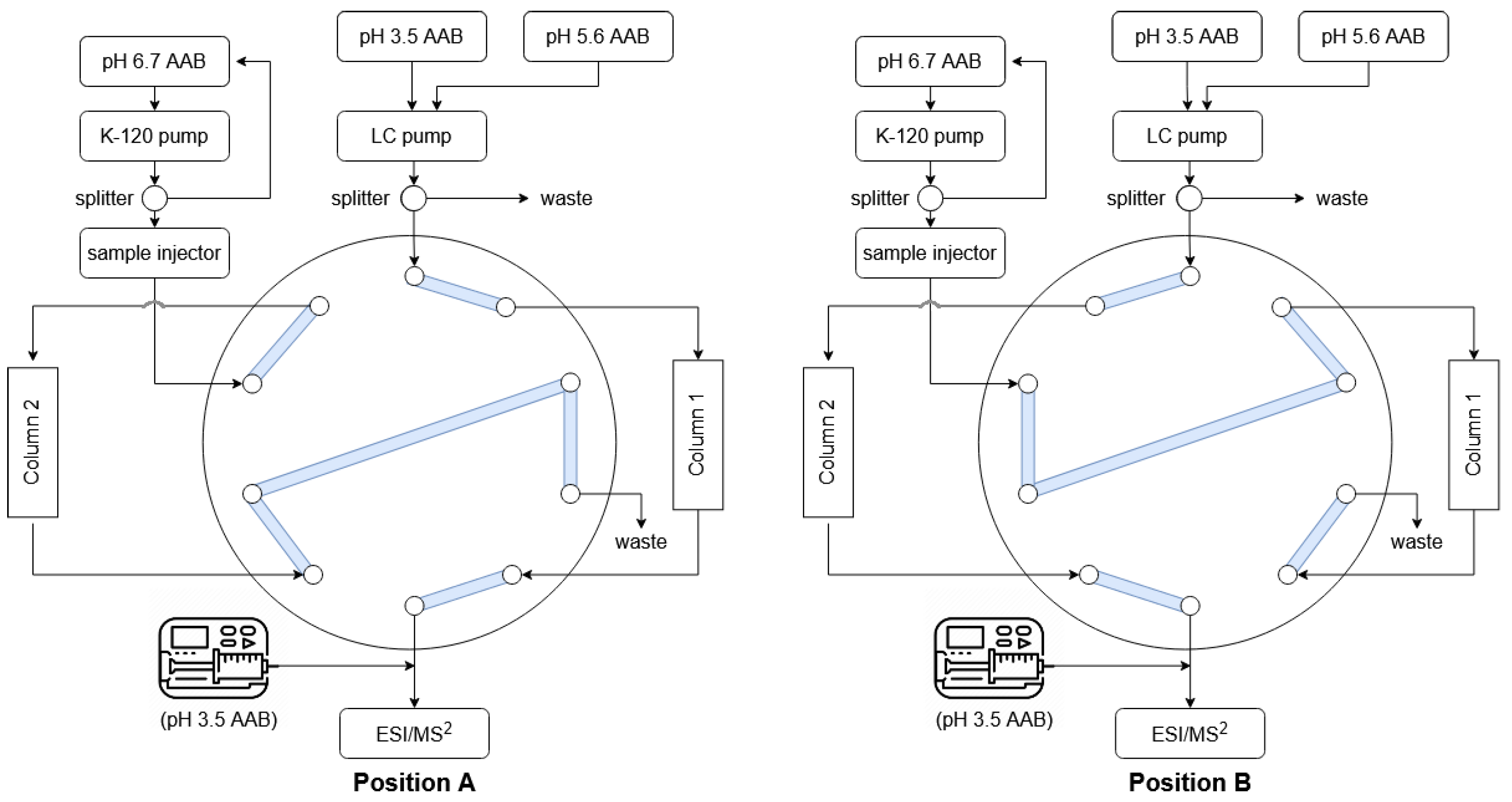
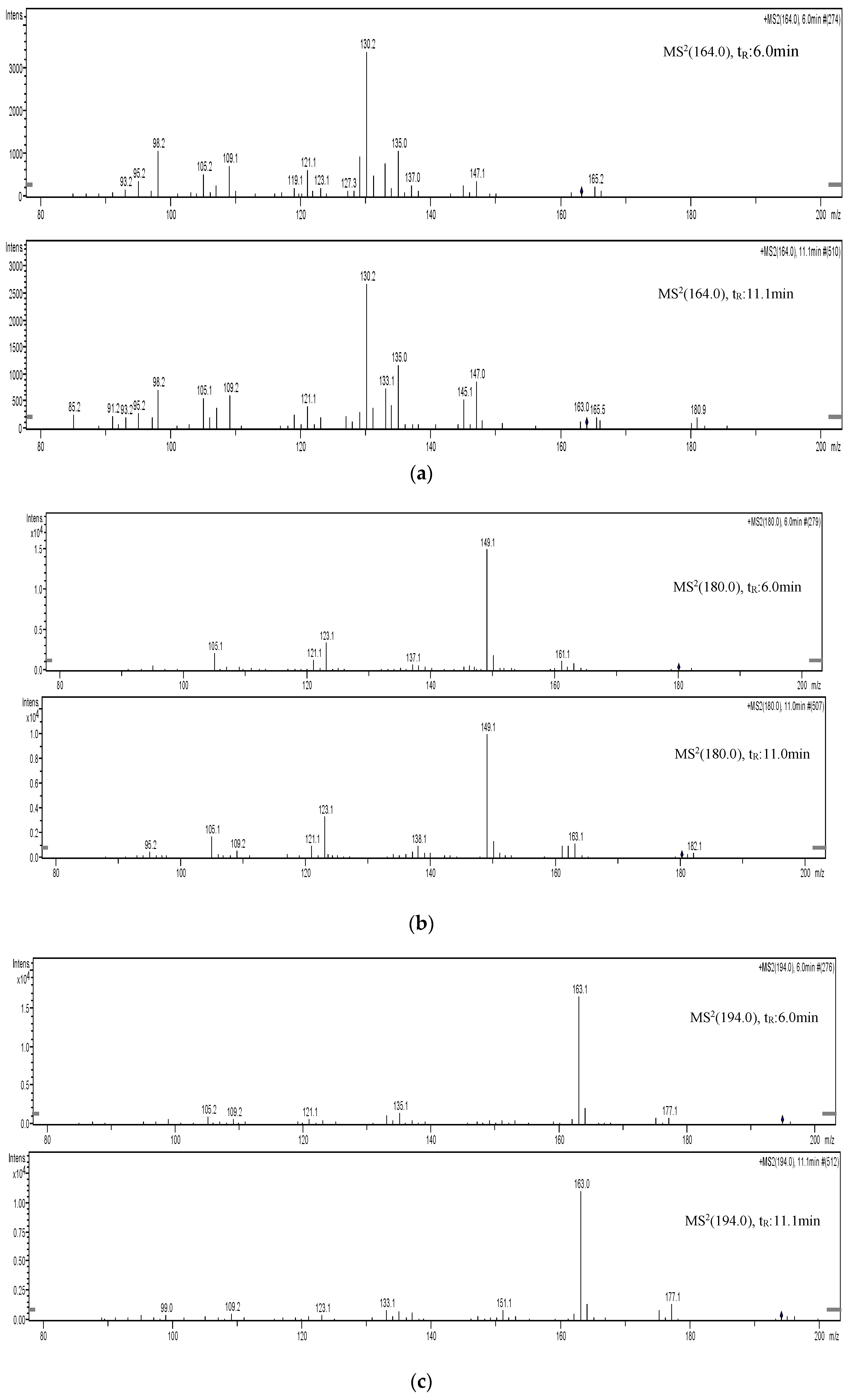
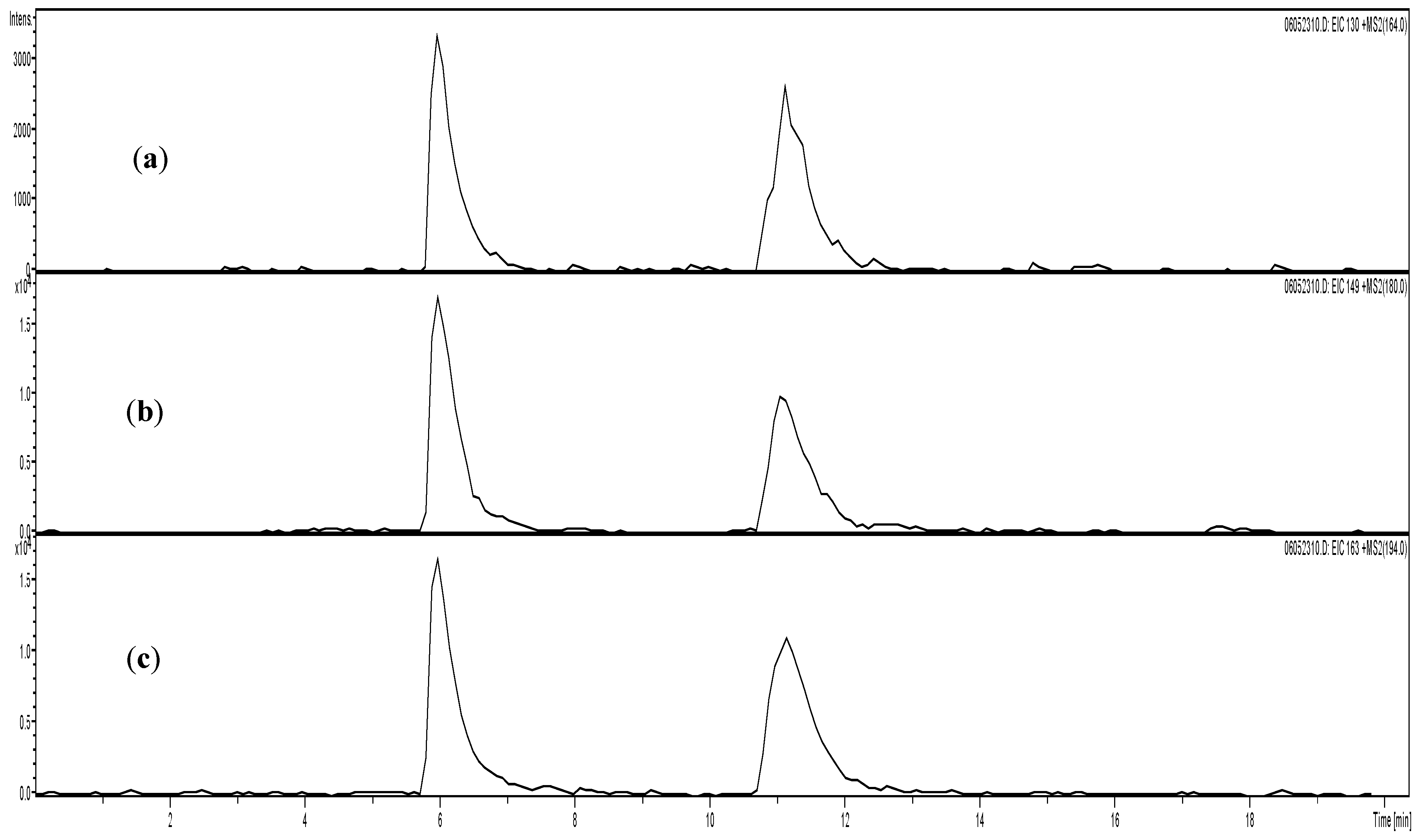
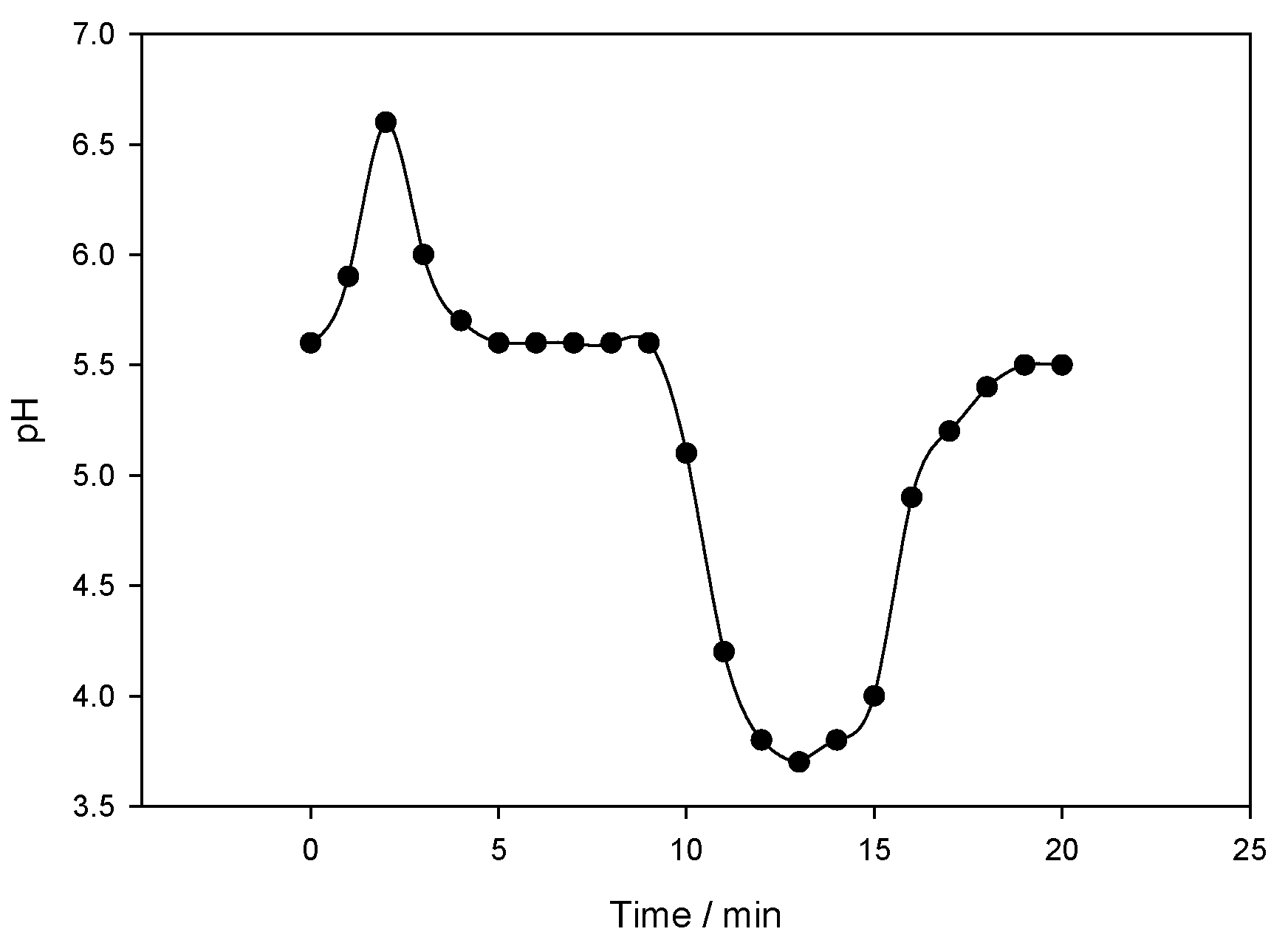
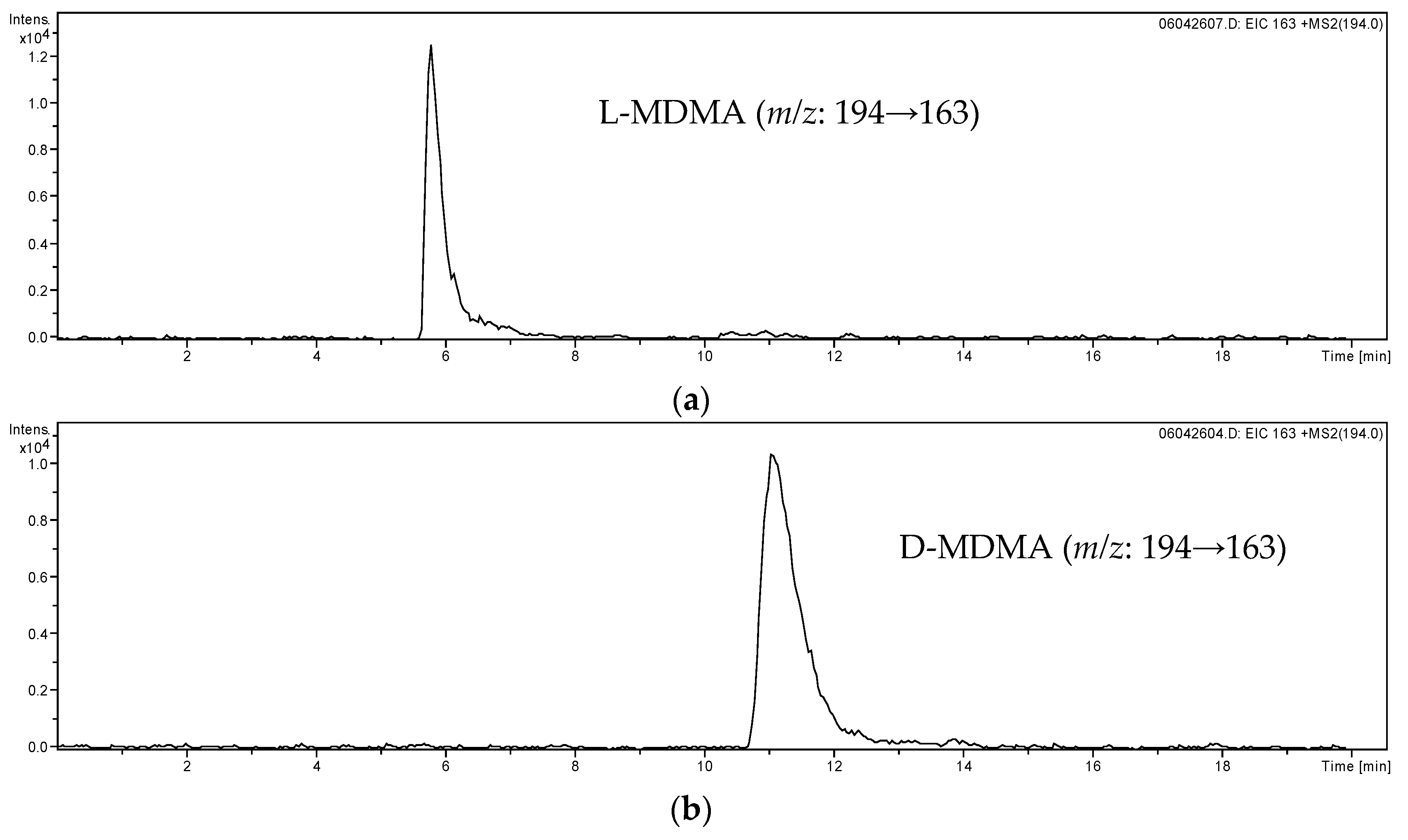
| Analytes | Regression Line | Correlation Coefficient (R2) | LOD a (ng/mL) | LOQ a (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D-PMMA | y = 4.87 × 10−3x + 3.33 × 10−3 | 0.9994 | 11.5 | 38.2 |
| L-PMMA | y = 4.03 × 10−3x + 8.33 × 10−3 | 0.9999 | 11.9 | 39.5 |
| D-MDMA | y = 8.91 × 10−3x − 3.64 × 10−2 | 1.0000 | 9.3 | 30.9 |
| L-MDMA | y = 5.96 × 10−3x − 7.05 × 10−3 | 0.9995 | 10.4 | 34.6 |
| Analytes | Concentration (ng/mL) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 100 | 250 | 400 | 500 | 50 | 100 | 250 | 400 | 500 | |
| Repeatability (RSD b %) | Accuracy (%) | |||||||||
| D-PMMA | 9.7 | 8.4 | 7.3 | 6.7 | 5.3 | 17.4 | 4.5 | −3.6 | −5.6 | −9.8 |
| L-PMMA | 4.0 | 13.1 | 8.9 | 9.0 | 7.9 | −9.4 | −5.1 | −0.2 | −2.9 | −8.8 |
| D-MDMA | 10.7 | 5.8 | 4.4 | 2.3 | 2.3 | −3.6 | 9.6 | −1.9 | 0.0 | 2.2 |
| L-MDMA | 8.3 | 7.2 | 5.3 | 8.1 | 7.9 | 12.4 | 19.7 | −3.9 | 3.8 | 2.2 |
| Analysis Technique | Sample Treatment | Linea Range (ng/mL) | LOD (ng/mL) | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMMA | LC-MS/MS | - | 50–500 (D) | 11.5 (D) | This work |
| 50–500 (L) | 11.9 (L) | ||||
| GC-MS | derivatization | 2–250 | 0.6 | [21] | |
| MDMA | LC-MS/MS | - | 50–500 (D) | 9.3 (D) | This work |
| 50–500 (L) | 10.4 (L) | ||||
| GC-MS | solid phase extraction and derivatization | 0.006–60 (D) | 1.7 (D) | [11] | |
| 0.005–60 (L) | 1.5 (L) | ||||
| GC-MS | derivatization | 5–500 | 1.7 | [13] | |
| GC-MS | solid phase extraction and derivatization | 0.0063–4 (D) | 0.0013 (D) | [17] | |
| 0.00156–4 (L) | 0.0021 (L) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.-J.; Wu, R.-J.; Yang, H.-H.; Lua, A.-C.; Tzeng, Y.-J.; Tuan, S.-H.; Chen, L.; Chou, T.-Y. A New Method for Enantiomeric Determination of 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine and p-Methoxymethamphetamine in Human Urine. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10020050
Chen W-J, Wu R-J, Yang H-H, Lua A-C, Tzeng Y-J, Tuan S-H, Chen L, Chou T-Y. A New Method for Enantiomeric Determination of 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine and p-Methoxymethamphetamine in Human Urine. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(2):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10020050
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wei-Jay, Ren-Jang Wu, Hsueh-Hui Yang, Ahai-Chang Lua, Yin-Jeh Tzeng, Shun-Hsing Tuan, Liang Chen, and Tsong-Yung Chou. 2022. "A New Method for Enantiomeric Determination of 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine and p-Methoxymethamphetamine in Human Urine" Chemosensors 10, no. 2: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10020050
APA StyleChen, W.-J., Wu, R.-J., Yang, H.-H., Lua, A.-C., Tzeng, Y.-J., Tuan, S.-H., Chen, L., & Chou, T.-Y. (2022). A New Method for Enantiomeric Determination of 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine and p-Methoxymethamphetamine in Human Urine. Chemosensors, 10(2), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10020050





