Nanostructured Diamond Composites for Multifunctional Sensing Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
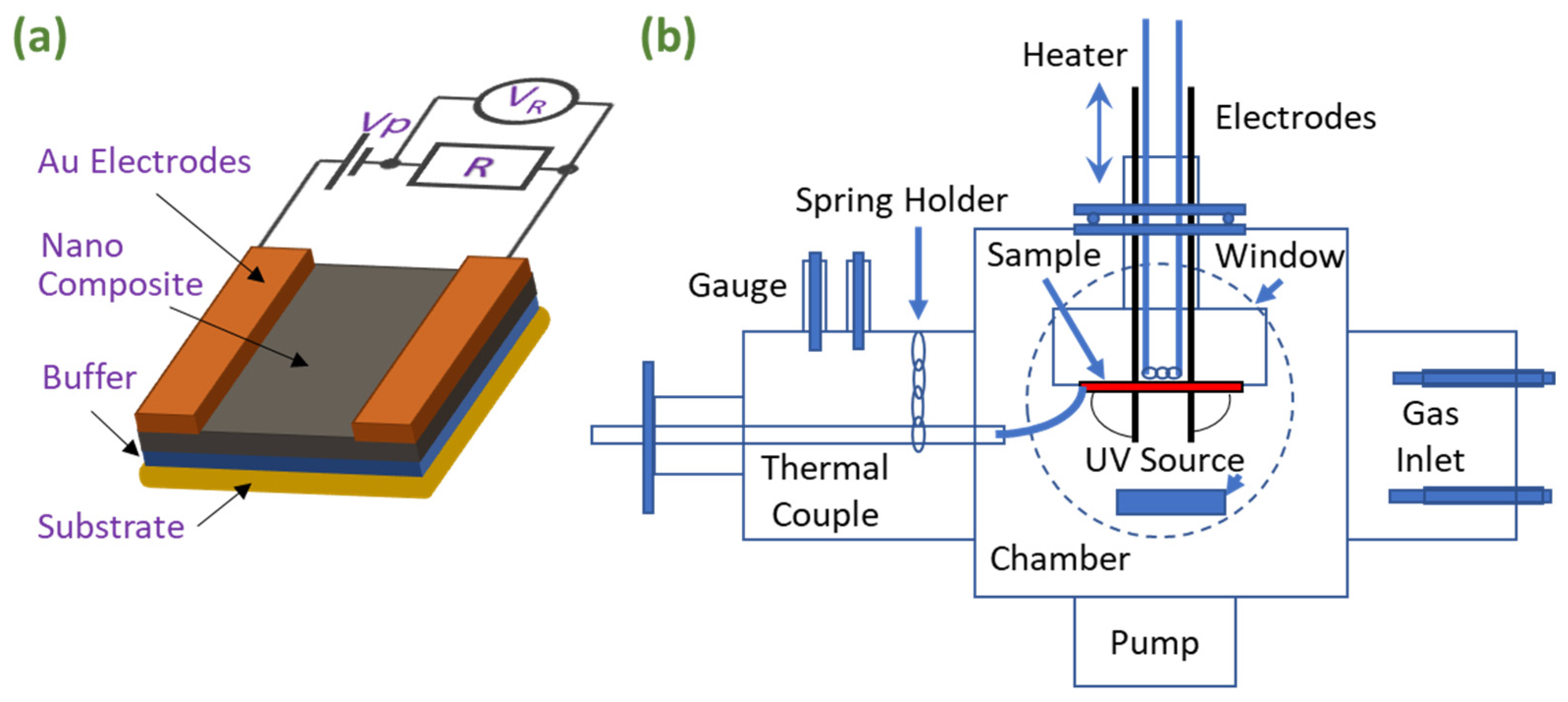
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
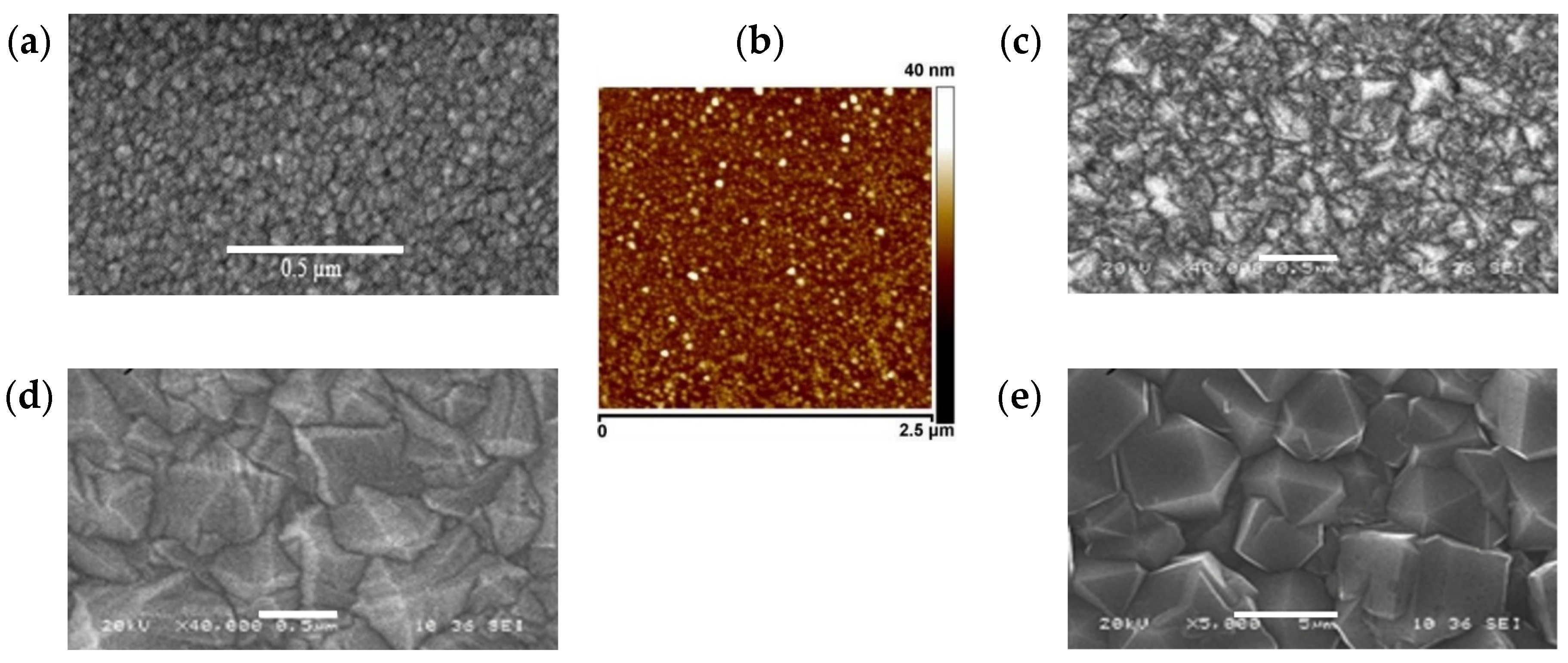
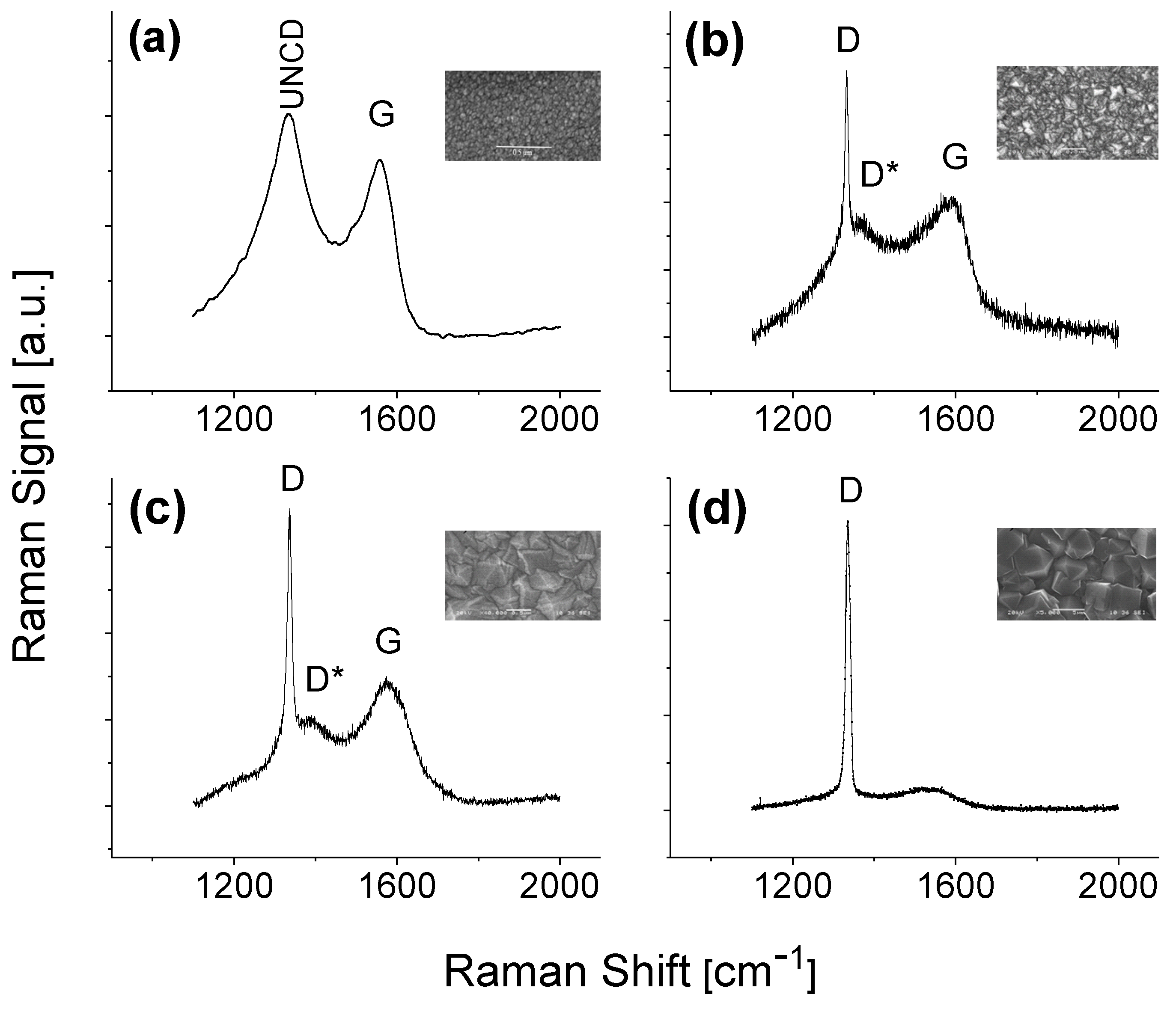
3.1. Material Characterizations
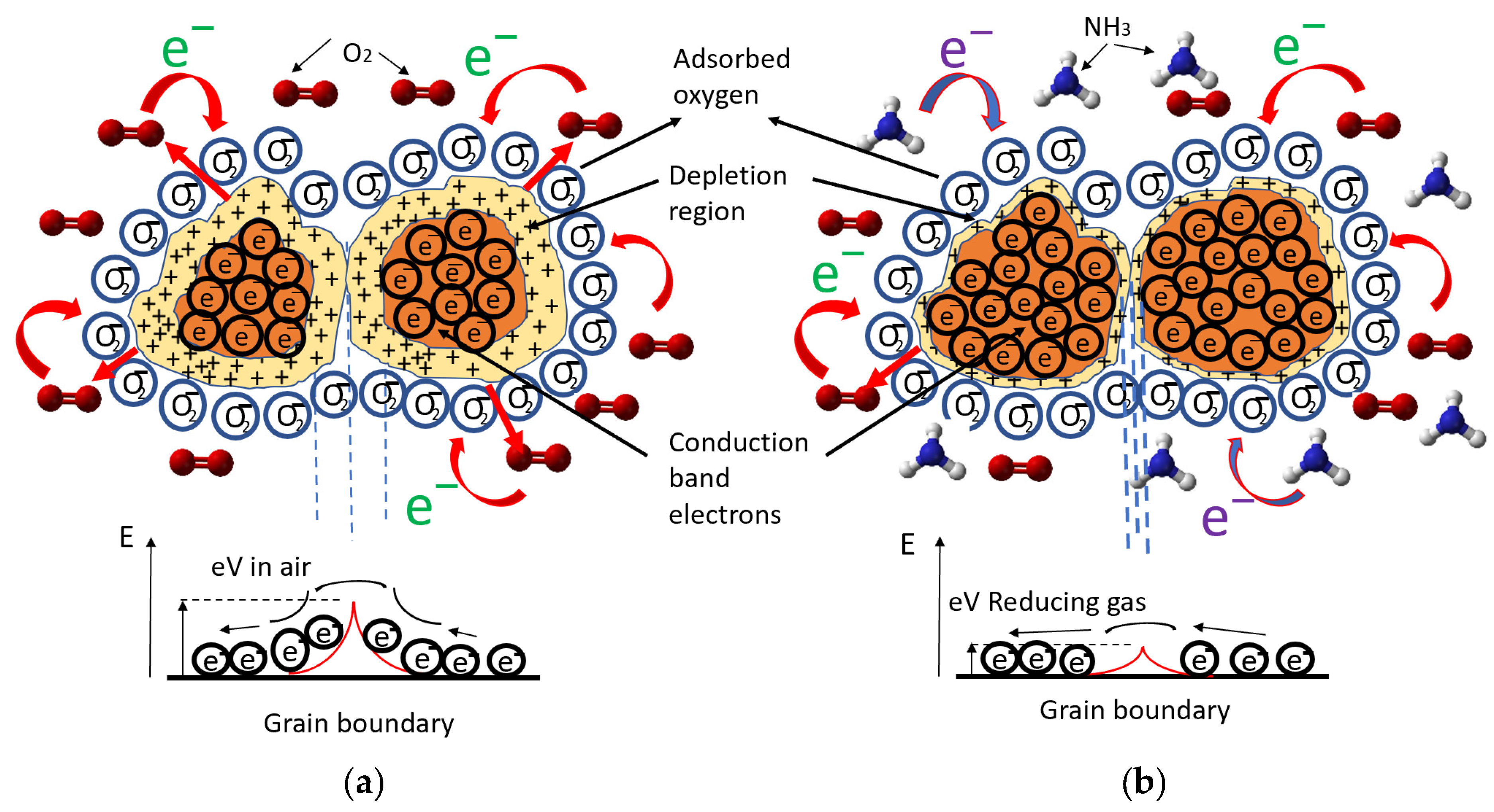
3.2. Electrical Properties
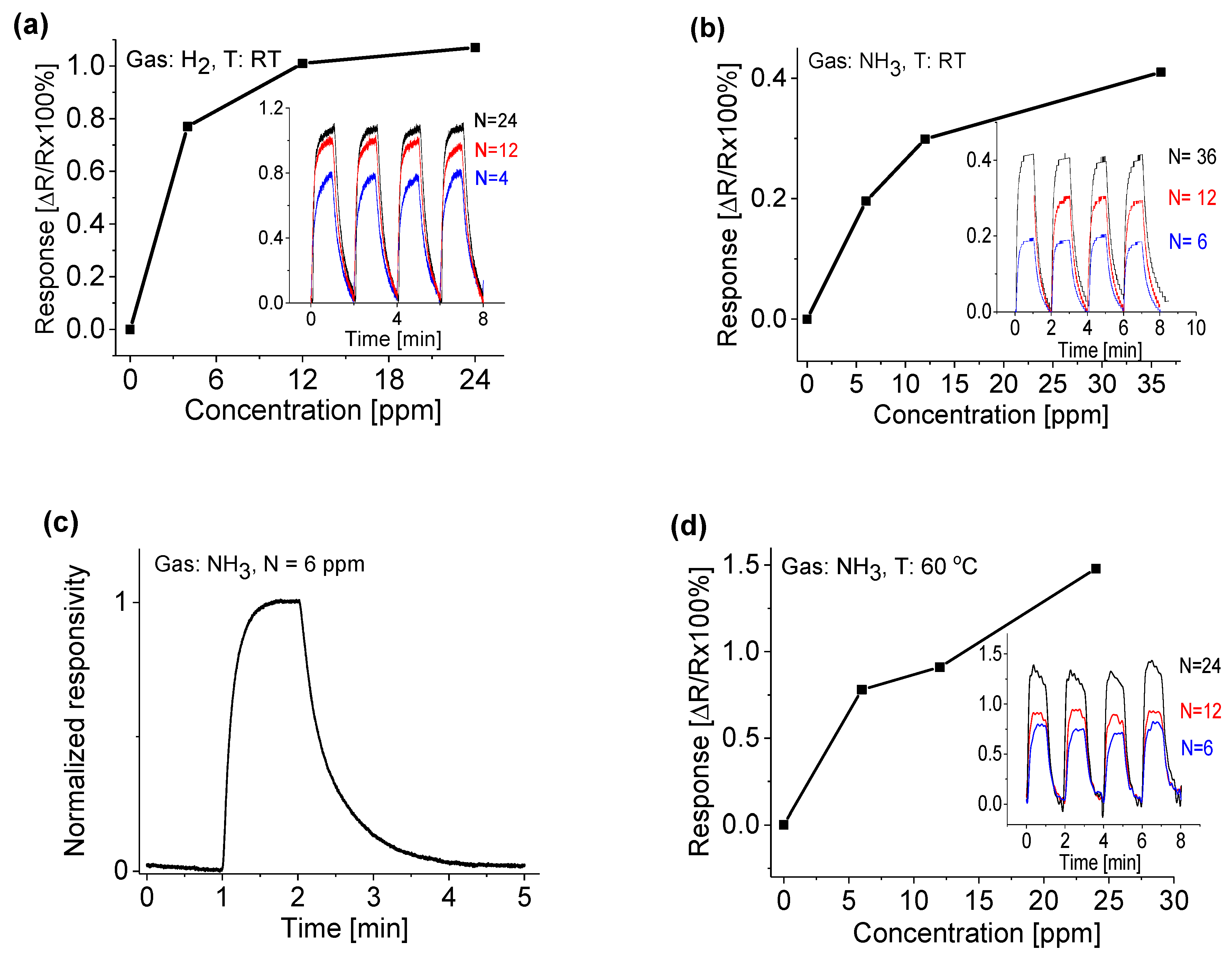
3.3. Response to Target Gases with Different Concentrations
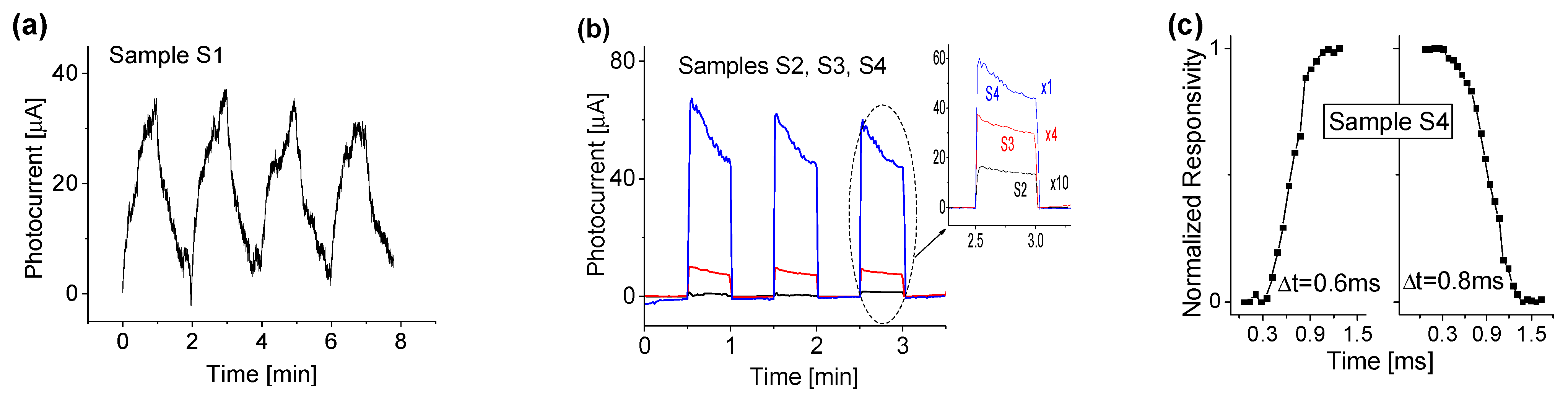
3.4. Response to Deep UV Illumination with Different Wavelengths
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Toni, A.M.; Habila, M.A.; Labis, J.P.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Alhoshan, M.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Zhang, F. Design, synthesis and applications of core–shell, hollow core, and nanorattle multifunctional nanostructures. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 2510–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarta, A.; Di Corato, R.; Manna, L.; Argentiere, S.; Cingolani, R.; Barbarella, G.; Pellegrino, T. Multifunctional nanostructures based on inorganic nanoparticles and oligothiophenes and their exploitation for cellular studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10545–10555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, J.Y.; Chowdhury, S.; Hollis, M.A.; Jena, D.; Johnson, N.M.; Jones, K.A.; Kaplar, R.J.; Rajan, S.; Van de Walle, C.G.; Bellotti, E.; et al. Ultrawide-Bandgap Semiconductors: Research Opportunities and Challenges. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 4, 1600501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokuno, Y.; Chayahara, A.; Yamada, H. Synthesis of large single crystal diamond plates by high rate homoepitaxial growth using microwave plasma CVD and lift-off process. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2008, 17, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, L.; Liao, M.; Sumiya, M. A comprehensive review of semiconductor ultraviolet photodetectors: From thin film to one-dimensional nanostructures. Sensors 2013, 13, 10482–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakaji, Y.; Kanasugi, M.; Maida, O.; Ito, T. Characterization of Diamond Ultraviolet Detectors Fabricated with High-Quality Singlecrystalline Chemical Vapor Deposition Films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 223511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, E.; De Sio, A. Diamond detectors for space applications. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2003, 514, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.R.; Wei, D.H.; BenDao, M.K.; Chen, W.E.; Liu, T.Y. Development of High-Performance UV Detector Using Nanocrystalline Diamond Thin Film. Int. J. Photoenergy 2014, 2014, 492152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Wang, L.J.; Huang, J.; Ma, Y.; Hu, G.; Zhu, X.F.; Xia, Y.B. Diamond film ultraviolet detectors with different diamond grain size. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 152, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallaire, A.; Achard, J.; Silva, F.; Brinza, O.; Gicquel, A. Growth of large size diamond single crystals by plasma assisted chemical vapour deposition: Recent achievements and remaining challenges. C. R. Phys. 2013, 14, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimanzadeh, R.; Naamoun, M.; Floriduz, A.; Khadar, R.A.; van Erp, R.; Matioli, E. Seed Dibbling Method for the Growth of High-Quality Diamond on GaN. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 43516–43523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Jang, T.H.; Gwon, J.U.; Kim, T.G.; Bae, M.K. Nitrogen-doping effect on single-crystal diamond synthesis by HFCVD. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2022, 36, 2242019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.E.; Windischmann, H. Developments in CVD-diamond synthesis during the past decade. MRS Bull. 1998, 23, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.F.; Wang, X.; Pacheco, E.; Feng, P.X. Ultrananocrystalline Diamond Nanowires: Fabrication, Characterization, and Sensor Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado-Meza, M.; Martínez-Rodríguez, G.; Tirado-Cantú, P.; Montijo-Valenzuela, E.E.; García-Gutiérrez, R. Synthesis and properties of electrically conductive/nitrogen grain boundaries incorporated ultrananocrystalline diamond (N-uncd) thin films grown by microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition (mpcvd). Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auciello, O.; Sumant, A.V. Status review of the science and technology of ultrananocrystalline diamond (UNCD™) films and application to multifunctional devices. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2010, 19, 699–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, A.R.; Auciello, O.; Gruen, D.M.; Jayatissa, A.; Sumant, A.; Tucek, J.; Mancini, D.C.; Moldovan, N.; Erdemir, A.; Ersoy, D.; et al. Ultrananocrystalline diamond thin films for MEMS and moving mechanical assembly devices. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2001, 10, 1952–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.F.; Pacheco, E.; Zhou, B.; Feng, P.X. Size-Dependent Electrical Transport Properties in Conducting Diamond Nanostripes. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Wang, X.; Aldalbahi, A.; Zhou, A.F. Methane induced electrical property change of nitrogen doped ultrananocrystalline diamond nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 233103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Li, Y.; Duan, S.; Chu, J.; Feng, P. Precise B-doped ultrananocrystalline diamond nanowire arrays for high performance of CO gas sensor. Mater. Lett. 2020, 265, 127404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, R.; Rivera, M.; Zhou, A.F.; Bromley, D.; Feng, P.X. Zero Bias, Super Sensitive and Broadband UV Photoconductor Based on Pt Nanoparticle Functionalized Ultrananocrystalline Diamond Nanowire Arrays. Def. Syst. Inf. Anal. Cent. (DSIAC) J. 2019, 6, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, A.F.; Velázquez, R.; Wang, X.; Feng, P.X. Nanoplasmonic 1D Diamond UV Photodetectors with High Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 38068–38074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Synthesis, Fabrication, Characterization and Application of Ultrananocrystalline Diamond Micro- and Nanosctructures. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Puerto Rico, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, O.A.; Zimmermann, T.; Kubovic, M.; Denisenko, A.; Kohn, E.; Jackman, R.B.; Gruen, D.M. Synthesis, Properties and Applications of Ultrananocrystalline Diamond; Gruen, D.M., Shenderova, O.A., Vul, A.Y., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 373–382. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ocola, L.E.; Divan, R.S.; Sumant, A.V. Nanopatterning of ultrananocrystalline diamond nanowires. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 075301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Ürgen, M. Surface morphology, growth rate and quality of diamond films synthesized in hot filament CVD system under various methane concentrations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 8420–8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birrell, J.; Gerbi, J.E.; Auciello, O.; Gibson, J.M.; Johnson, J.; Carlisle, J.A. Interpretation of the Raman spectra of ultrananocrystalline diamond. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2005, 14, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, O.A.; Daenen, M.; D’Haen, J.; Haenen, K.; Maes, J.; Moshchalkov, V.V.; Nesládek, M.; Gruen, D.M. Comparison of the growth and properties of ultrananocrystalline diamond and nanocrystalline diamond. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2006, 15, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Liu, K.; Ye, K.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H. Constructing Fe-MOF-derived Z-scheme photocatalysts with enhanced charge transport: Nanointerface and carbon sheath synergistic effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 25494–25502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, J.; Balogun, M.S.; Wang, P.; Tong, Y.; Huang, Y. Charge Relays via Dual Carbon-Actions on Nanostructured BiVO4 for High Performance Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2112738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.P.; Gurbuz, Y.; Davidson, J.L.; Kerns, D.V. A New Hydrogen Sensor Using a Polycrystalline Diamond-Based Schottky Diode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1994, 141, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.P.; Gurbuz, Y.; Davidson, J.L.; Kerns, D.V. A polycrystalline diamond thin-film-based hydrogen sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1995, 25, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbuz, Y.; Kang, W.P.; Davidson, J.L.; Kerns, D.V. Analyzing the mechanism of hydrogen adsorption effects on diamond based MIS hydrogen sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1996, 35, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.F.; Wang, X.; Feng, X.P. Nitrogen-doped Diamond Nanowire Gas Sensor for the Detection of Methane. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2020, 11, 20021473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.Y.; Chu, J.; Wang, L.D.; Duan, S.; Feng, P. Boron-doped diamond nanowires for CO gas sensing application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydova, M.; Kulha, P.; Laposa, A.; Hruska, K.; Demo, P.; Kromka, A. Gas sensing properties of nanocrystalline diamond at room temperature. Beilstein. J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 2339–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kočí, M.; Kromka, A.; Bouřa, A.; Szabó, O.; Husák, M. Hydrogen-Terminated Diamond Surface as a Gas Sensor: A Comparative Study of Its Sensitivities. Sensors 2021, 21, 5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbuz, Y.; Kang, W.P.; Davidson, J.L.; Kerns, D.V. Diamond microelectronic gas sensor for detection of benzene and toluene. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 99, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Sharma, N.; Srinivasan, P.; Kumar, S.; Balaguru Rayappan, J.B.; Kailasam, K. Heptazine based organic framework asa chemiresistive sensor for ammonia detection atroom temperature. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 18389–18395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yin, L.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, D.; Gao, R. Metal Oxide Gas Sensors: Sensitivity and Influencing Factors. Sensors 2010, 10, 2088–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khun Khun, K.; Mahajan, A.; Bedi, R.K. SnO2 thick films for room temperature gas sensing applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 124509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Xi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Rumyntseva, M.N.; Gaskov, A.M. Light enhanced VOCs sensing of WS2 microflakes based chemiresistive sensors powered by triboelectronic nangenerators. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 256, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmer, B.; Olthuis, W.; Van Den Berg, A. Ammonia sensors and their applications—A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 107, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydova, M.; Stuchlik, M.; Rezek, B.; Kromka, A. Temperature enhanced gas sensing properties of diamond films. Vacuum 2012, 86, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Ocola, L.E.; Chen, J. Reduced graphene oxide for room-temperature gas sensors. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 445502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, S.; Lu, G.; Chen, J. Nanocarbon-based gas sensors: Progress and challenges. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 5573–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Tao, L.M.; Deng, Y.C.; Wang, Q.H.; Song, W.G. Phosphorus doped graphene nanosheets for room temperature NH3 sensing. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 2269–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suehiro, J.; Zhou, G.; Hara, M. Fabrication of a carbon nanotube-based gas sensor using dielectrophoresis and its application for ammonia detection by impedance spectroscopy. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, L109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travlou, N.A.; Seredych, M.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Bandosz, T.J. Activated carbon-based gas sensors: Effects of surface features on the sensing mechanism. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 3821–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncea, O.; Casanova-Chafer, J.; Poinsot, D.; Ochmann, L.; Mboyi, C.D.; Nasrallah, H.O.; Llobet, E.; Makni, I.; El Atrous, M.; Brandès, S.; et al. Diamondoid Nanostructures as sp3-Carbon-Based Gas Sensors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 9933–9938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, F.; Makarov, V.; Weiner, B.; Morell, G. Solar-Blind Field-Emission Diamond Ultraviolet Detector. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 201605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balducci, A.; Marinellia, M.; Milani, E.; Morgada, M.E.; Tucciarone, A.; Verona-Rinati, G. Extreme Ultraviolet Single-Crystal Diamond Detectors by Chemical Vapor Deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 193509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teraji, T.; Yoshizaki, S.; Wada, H.; Hamada, M.; Ito, T. Highly Sensitive UV Photodetectors Fabricated Using High-Quality Single-Crystalline CVD Diamond Films. Diam. Relat. Mat. 2004, 13, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Wang, X.; Teraji, T.; Koizumi, S.; Koide, Y. Light Intensity Dependence of Photocurrent Gain in Single-Crystal Diamond Detectors. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 033304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Liu, B.; Zhao, J.; Shu, G.; Xu, X.; Yao, K.; Sun, M.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Su, Z.; et al. Application of back bias to interdigital-electrode structured diamond UV detector showing enhanced responsivity. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2019, 290, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeag, R.D.; Chan, S.M.; Jackman, R.B. Polycrystalline Diamond Photoconductive Device with High UV-Visible Discrimination. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995, 67, 2117–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yang, Z.; Yin, S.; Zeng, H. Al Plasmon-Enhanced Diamond Solar-Blind UV Photodetector by Coupling of Plasmon and Excitons. Mater. Technol. 2016, 31, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BenMoussa, A.; Soltani, A.; Haenen, K.; Kroth, U.; Mortet, V.; Barkad, H.A.; Bolsee, D.; Hermans, C.; Richter, M.; De Jaeger, J.C.; et al. New Developments on Diamond Photodetector for VUV Solar Observations. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2008, 23, 035026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.N.; Lu, Y.J.; Yang, X.; Tian, Y.Z.; Gao, C.J.; Sun, J.L.; Dong, L.; Zhang, F.; Hu, W.D.; Shan, C.X. Diamond-Based All-Carbon Photodetectors for Solar-Blind Imaging. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2018, 6, 1800068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koide, Y.; Liao, M.; Alvarez, J. Thermally stable solar-blind diamond UV photodetector. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2006, 15, 1962–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Wu, G.; Guo, W.; Wang, Y.; Cao, S.; Shang, K.; Han, W. Study on trapping center and trapping effect in MSM ultraviolet photo-detector on microcrystalline diamond film. Phys. Status Solidi 2010, 207, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatori, S.; Scotti, F.; Conte, G.; Rossi, M.C. Diamond-based UV photodetectors for high temperature applications. Electron. Lett. 1999, 35, 1768–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schühle, U.; Hochedez, J.F. Solar-blind UV detectors based on wide band gap semiconductors. In Observing Photons in Space; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 467–477. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco, E.; Zhou, B.; Aldalbahi, A.; Zhou, A.F.; Feng, P.X. Zero-biased and visible-blind UV photodetectors based on nitrogen-doped ultrananocrystalline diamond nanowires. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 3757–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, P.; Jia, P.; Cui, H.; Wang, L.; Duan, S. Performance Improvement of MoS2; Gas Sensor at Room Temperature. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2021, 68, 4644–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Pristine Nanocarbon Materials | Detected Gas Molecules | Responsivity and Operating Temperature | Response Time | Recover Time | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graphene (rGO) | H2 | 4.5% (160 ppm) | 20 s | 10 s | [45] |
| UNCD nanowire (Boron doping) | H2 | 20% (100 ppm) at 400 °C | - | - | [35] |
| Graphene film (CVD) | NH3 | 90% (1000 ppm) at 200 °C | 180 min | - | [46] |
| Pristine graphene (PG) (P-doping) | NH3 | 5.4% (100 ppm) | 2.23 min | 13.6 min | [47] |
| Multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) | NH3 | 10 ppm | ~100 s | - | [48] |
| Wood-based activated carbon | NH3 | 100–500 ppm | - | - | [49] |
| Diamondoid Nanostructures (H2P-DiamOH) | NH3 | 6% (25 ppm) at 100 °C | ~10 min | ~40 min | [50] |
| N-UNCD film | H2 | 0.084% per ppm at room temperature (RT) | 20 s | >64 s | This work |
| NH3 | 0.02% per ppm at room temperature (RT) | 18 s | ~64 s | This work | |
| NH3 | 0.07% per ppm at 60 °C | 16 s | >64 s | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, E.Y.; Pacheco, E.; Zhou, A.F.; Feng, P.X. Nanostructured Diamond Composites for Multifunctional Sensing Applications. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10110488
Li EY, Pacheco E, Zhou AF, Feng PX. Nanostructured Diamond Composites for Multifunctional Sensing Applications. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(11):488. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10110488
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Eric Y., Elluz Pacheco, Andrew F. Zhou, and Peter X. Feng. 2022. "Nanostructured Diamond Composites for Multifunctional Sensing Applications" Chemosensors 10, no. 11: 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10110488
APA StyleLi, E. Y., Pacheco, E., Zhou, A. F., & Feng, P. X. (2022). Nanostructured Diamond Composites for Multifunctional Sensing Applications. Chemosensors, 10(11), 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10110488









