Otitis Media and Obesity—An Unusual Relationship in Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
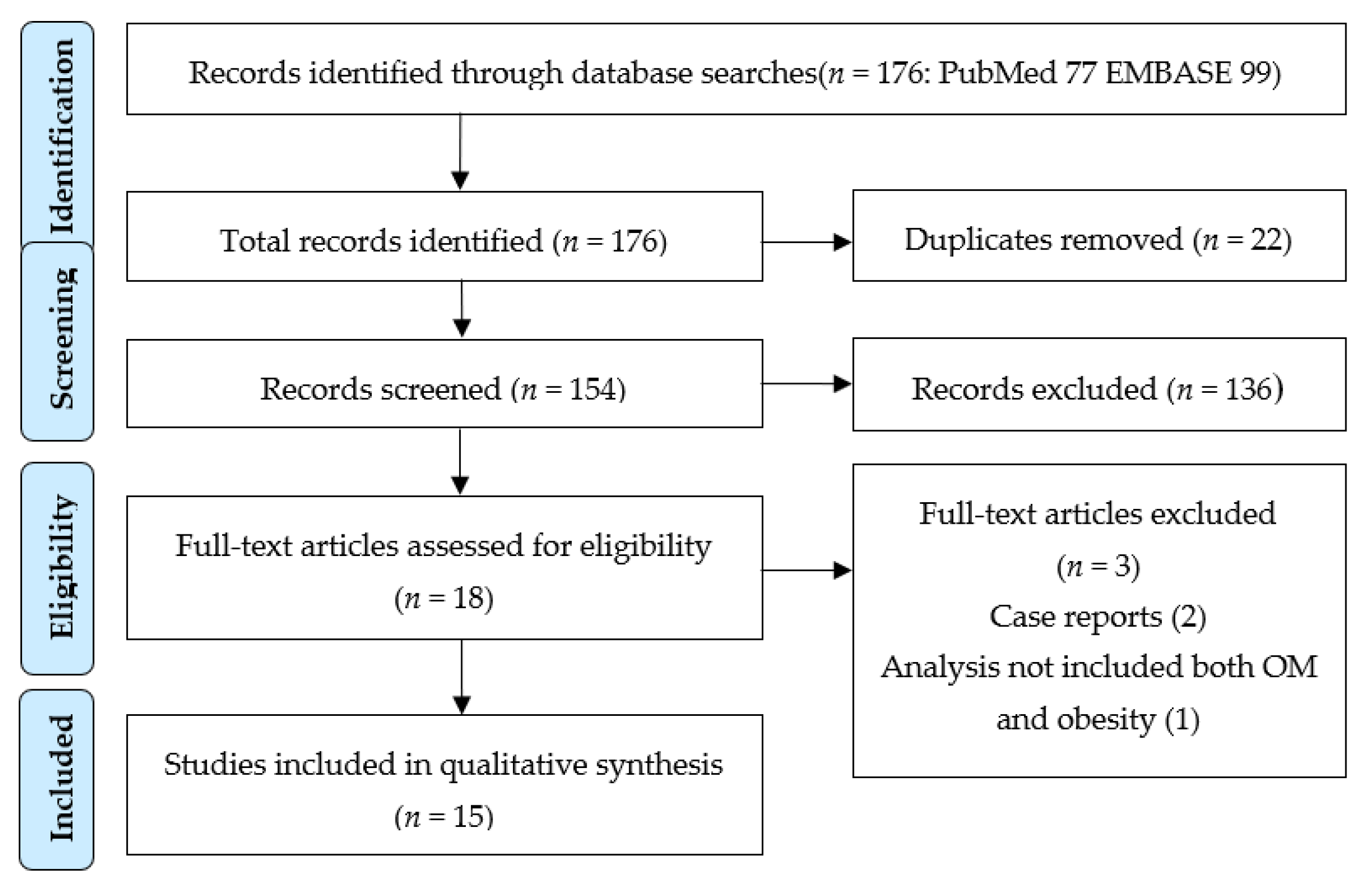
3.1. Search Results
3.2. OM—Obesity Relationship: The Impact of Obesity/Overweight on OM Development
3.3. OM—Obesity Relationship: The Impact of OM on the Overweight/Obesity Development
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berman, S. Otitis Media in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meherali, S.; Campbell, A.; Hartling, L.; Scott, S. Understanding Parents’ Experiences and Information Needs on Pediatric Acute Otitis Media: A Qualitative Study. J. Patient Exp. 2019, 6, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.K.C.; Wong, A.H.C. Acute otitis media in children. Recent Pat. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2017, 11, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Morris, M.; Pichichero, M.E. Epidemiology of Acute Otitis Media in the Postpneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine Era. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20170101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.; Marchisio, P.; Vergison, A.; Harriague, J.; Hausdorff, W.P.; Haggard, M. Impact of pneumococcal conjugate vaccination on otitis media: A systematic review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, C.M.; Fryar, C.D.; Carroll, M.D. Trends in Obesity and Severe Obesity Prevalence in US Youth and Adults by Sex and Age, 2007–2008 to 2015–2016. JAMA 2018, 319, 1723–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight Factsheet No. 311; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hales, C.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Ogden, C.L. Prevalence of Obesity among Adults and Youth: United States, 2015–2016. NCHS Data Brief. 2017, 288, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Deurenberg, P.; Weststrate, J.A.; Seidell, J.C. Body mass index as a measure of body fatness: Age- and sex-specific prediction formulas. Br. J. Nutr. 1991, 65, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group WHO child growth standards based on length/height, weight and age. Acta Paediatr. Suppl. 2006, 450, 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- de Onis, M.; Onyango, A.W.; Borghi, E.; Siyam, A.; Nishida, C.; Siekmann, J. Development of a WHO growth refer-ence for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull WHO 2007, 85, 660–667. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Arjmand, E.; Sidell, D. Role of Obesity in Otitis Media in Children. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.G.; Sim, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, H.-J. A high-fat diet is associated with otitis media with effusion. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 79, 2327–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peracchio, H.L.; Henebery, K.E.; Sharafi, M. Otitis media exposure associates with dietary preference and adi-posity: A community-based observational study of at-risk preschoolers. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 106, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, H.; Daly, K.; Davey, C.; Himes, J.; Synder, D.; Bartoshuk, L. Otitis media and associations with overweight status in toddlers. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 102, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogel, A.; Blissett, J. Associations between Otitis media, taste sensitivity and adiposity: Two studies across childhood. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 208, 112570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidell, D.; Shapiro, N.L.; Bhattacharyya, N. Obesity and the risk of chronic rhinosinusitis, allergic rhinitis, and acute otitis media in school-age children. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 2360–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijga, A.H.; Scholtens, S.; Bemelmans, W.J.E.; De Jongste, J.C.; Kerkhof, M.; Schipper, M.; Sanders, E.A.; Gerritsen, J.; Brunekreef, B.; Smit, H.S. Comorbidities of obesity in school children: A cross-sectional study in the PIAMA birth cohort. BMC Public Health 2010, 10, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibli, R.; Rubin, L.; Akons, H.; Shaoul, R. Morbidity of Overweight (>=85th Percentile) in the First 2 Years of Life. Pediatrics 2008, 122, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaraifi, A.K.; Alosfoor, M.A.; Alsaab, F. Impact of pediatric obesity on the prevalence and outcome of otitis media with effusion. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 133, 110005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçyiğit, M.; Çakabay, T.; Örtekin, S.G.; Akçay, T.; Özkaya, G.; Bezgin, S.Ü.; Yıldız, M.; Adalı, M.K. Association Between Endocrine Diseases and Serous Otitis Media in Children. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2017, 9, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, S.; Selimoğlu, E.; Cureoğlu, S.; Selimoğlu, M.A. Relationship between chronic otitis media with effusion and overweight or obesity in children. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2017, 131, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, I.H.; Park, D.C.; Kwon, C.; Yeo, S.G. Changes in taste function related to obesity and chronic otitis media with effusion. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 137, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, D.C.; Byun, J.Y.; Park, M.S.; Cha, C.I.; Yeo, S.G. The relationship between overweight and otitis media with effusion in children. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 35, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kim, J.B.; Park, D.C.; Cha, C.I.; Yeo, S.G. Relationship between pediatric obesity and otitis media with effusion. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 133, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kuhle, S.; Kirk, S.F.L.; Ohinmaa, A.; Urschitz, M.S.; Veugelers, P.J. The association between childhood overweight and obesity and otitis media. Pediatr. Obes. 2011, 7, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaberg, R.M.; Chadha, N.K.; Hubbard, B.J.; Gordon, K.A.; Allemang, B.A.; Harrison, B.J.; Papsin, B.C. Chorda tympani nerve function in children: Relationship to otitis media and body mass index. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 74, 1393–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Cha, S.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, S.K.; Chung, H.Y.; Yeo, J.H.; Kim, Y.I.; Yeo, S.G. Decreased Pattern-Recognition Receptor-Mediated Cytokine mRNA Expression in Obese Children With Otitis Media With Effusion. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 7, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielnik-Jurkiewicz, B.; Stankiewicz-Szymczak, W. Pro-inflammatory interleukins in middle ear effusions from atopic and non-atopic children with chronic otitis media with effusion. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 273, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottam, D.R.; Mattar, S.G.; Barinas-Mitchell, E. The chronic inflammatory hypothesis for the morbidity associ-ated with morbid obesity: Implications and effects of weight loss. Obes. Surg. 2004, 14, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Sánchez, A.; Madrigal-Santillán, E.; Bautista, M.; Esquivel-Soto, J.; Morales-González, Á.; Esquivel-Chirino, C.; Durante-Montiel, I.; Sánchez-Rivera, G.; Valadez-Vega, C.; Morales-González, J.A. Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3117–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, P. Obesity and respiratory infections: Does excess adiposity weigh down host defense? Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 26, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Yeo, S.G. Relationship between pediatric obesity and otitis media with effusion. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2009, 9, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibert, J.W.; Danner, C.J. Eustachian tube function and the middle ear. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2006, 39, 1221–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoshuk, L.M.; Duffy, V.B.; Hayes, J.E.; Moskowitz, H.R.; Snyder, D.J. Psychophysics of sweet and fat perception in obesity: Problems, solutions and new perspectives. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, A.; Babu, S.V.; Mohiyuddin, S.M.A.; Naseeruddin, K. Gustatory function in chronic otitis media (mucosal type) before and after tympanoplasty. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 274, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, C.L.; Carroll, M.D.; Lawman, H.G.; Fryar, C.D.; Kruszon-Moran, D.; Kit, B.K.; Flegal, K.M. Trends in Obesity Prevalence Among Children and Adolescents in the United States, 1988-1994 Through 2013-2014. JAMA 2016, 315, 2292–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Lawrence, J.M.; Dabelea, D.; Lawrence, J.M. Incidence trends of type 1 and type 2 diabetes among youths, 2002–2012. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, A.; Juszczyk, D.; van Jaarsveld, C.H.M.; Gulliford, M.C. Body Mass Index and Incident Type 1 and Type 2 Diabe-tes in Children and Young Adults: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Endocr. Soc. 2017, 1, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnus, M.C.; Olsen, S.F.; Granstrom, C.; Joner, G.; Skrivarhaug, T.; Svensson, J.; Johannesen, J.; Njolstad, P.; Magnus, P.; Stordal, K.; et al. Infant growth and risk of childhood-onset type 1 diabetes in children from 2 Scandinavian birth cohorts. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, e153759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernroth, M.L.; Fall, K.; Svennblad, B.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; Sjölander, A.; Almqvist, C.; Fall, T. Early Childhood Antibiotic Treatment for Otitis Media and Other Respiratory Tract Infections Is Associated With Risk of Type 1 Diabetes: A Nationwide Register-Based Study With Sibling Analysis. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavrilovici, C.; Oprea, L. Clinical ethics, research ethics and community ethics–the moral triad of nowadays society. Rev. Rom. Bioetic. 2013, 11, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
| Study, Publication Year, Country | Population Size | Population Age | Study Type | Type of Ear Infection | Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alaraifi, 2020, Saudi Arabia [20] | 112 | 2–18 | Case-control study | OME | BMI assessment, data from medical charts and electronic hospital system includinghistory of OME |
| Fogel, 2019, Birmingham (UK) [16] | 196 | 2–9 | Cross-sectional analysis | OM | BMI and waist-to-height ratio assessment, taste sensitivity evaluation (Short Sensory Profile questionnaire), Sucrose Detection Threshold |
| Koçyiğit, 2017, Turkey [21] | 918 | 3–15 | Case-control study | OME | Tympanometry, medical history |
| Kaya, 2017, Turkey [22] | 60 | 2–10 | Case-control study | COME | BMI and waist-to-height ratio assessment, tympanometry |
| Choi, 2015, Korea [13] | 4359 | 4–13 | Cross-sectional study | OME | BMI assessment, medical history, nutritional survey |
| Peracchio, 2012, United States [14] | 485 | 3–4 | Cross-sectional analysis | OM | BMI assessment, medical history, nutritional survey |
| Shin, 2011, Seoul, South Korea [23] | 42 | 3–7 | Prospective, case-control study | COME | BMI assessment, electrogustometry, history of previous AOM episodes |
| Nelson, 2011, Unitated States [15] | 596 | 2 | Cross sectional analysis based on a prospective cohort study | AOM | Waist-to-height ratio assessment, medical history |
| Kuhle, 2011, Nova Scotia, Canada [26] | 3399 | 10–13 | Prospective cohort study | Suppurative OM | BMI assessment, medical history |
| Seaberg, 2010, Canada [27] | 142 | 5–18 | Retrospective cohort study | AOM | BMI assessment, electrogustometry, history of previous AOM episodes |
| Wijga, 2010, Netherlands [18] | 3960 | 8 | Cross-sectional analysis | Ear infection | BMI assessment, questionnaires applied to parents including details about ear infection episodes |
| Shibli, 2008, Israel [19] | 2139 | ≤13 | Cross- sectional analysis | AOM | BMI assessment, questionnaires applied to parents regarding children’s diets and AOM episodes |
| Kim, 2007, Korea [25] | 155 | 2–7 | Prospective, nonrandomized, case-control study | OME | Assessment of BMI, serum triglycerides, and total cholesterol |
| Sidell, 2013, United States [17] | 42.1 million | 6–17 | Cross-Sectional Analysis | AOM | BMI assessment, medical history |
| Kim, 2011, Korea [24] | 140 | 2–7 | Case- control study | OME | Assessment of BMI, serum triglycerides, and total cholesterol |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gavrilovici, C.; Spoială, E.-L.; Ivanov, A.-V.; Mocanu, A.; Ștreangă, V.; Alecsa, M.-S.; Miron, I. Otitis Media and Obesity—An Unusual Relationship in Children. Healthcare 2021, 9, 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9040458
Gavrilovici C, Spoială E-L, Ivanov A-V, Mocanu A, Ștreangă V, Alecsa M-S, Miron I. Otitis Media and Obesity—An Unusual Relationship in Children. Healthcare. 2021; 9(4):458. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9040458
Chicago/Turabian StyleGavrilovici, Cristina, Elena-Lia Spoială, Anca-Viorica Ivanov, Adriana Mocanu, Violeta Ștreangă, Mirabela-Smaranda Alecsa, and Ingrith Miron. 2021. "Otitis Media and Obesity—An Unusual Relationship in Children" Healthcare 9, no. 4: 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9040458
APA StyleGavrilovici, C., Spoială, E.-L., Ivanov, A.-V., Mocanu, A., Ștreangă, V., Alecsa, M.-S., & Miron, I. (2021). Otitis Media and Obesity—An Unusual Relationship in Children. Healthcare, 9(4), 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9040458






