Evolving Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks for Early COVID-19 Detection in Chest X-ray Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- a system that efficiently discovers DL models with growing depths, with no constraints on number of layers, thus optimising performances;
- a fast optimisation phase, making this method suitable also in devices plagued by modest computational capabilities;
- an practical encoding strategy for the convolutional structures to be “evolved” that allow for a practical model quality evaluation.
- Section 2 reports the material and methods used in this study in terms of employed dataset and optimisation algorithm;
- Section 3 describes all the components forming the proposed system;
- Section 4 shows our results;
- Section 5 comments on the our achievements;
- Section 6 draws the conclusions of this study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. COVID-X-ray Dataset
2.2. The Neural Network
- Underfitting if the CNN is too small.
- Overfitting if the CNN is too large.
2.3. Biogeography-Based Optimisation
3. Our Evolutionary Framework for CNNs
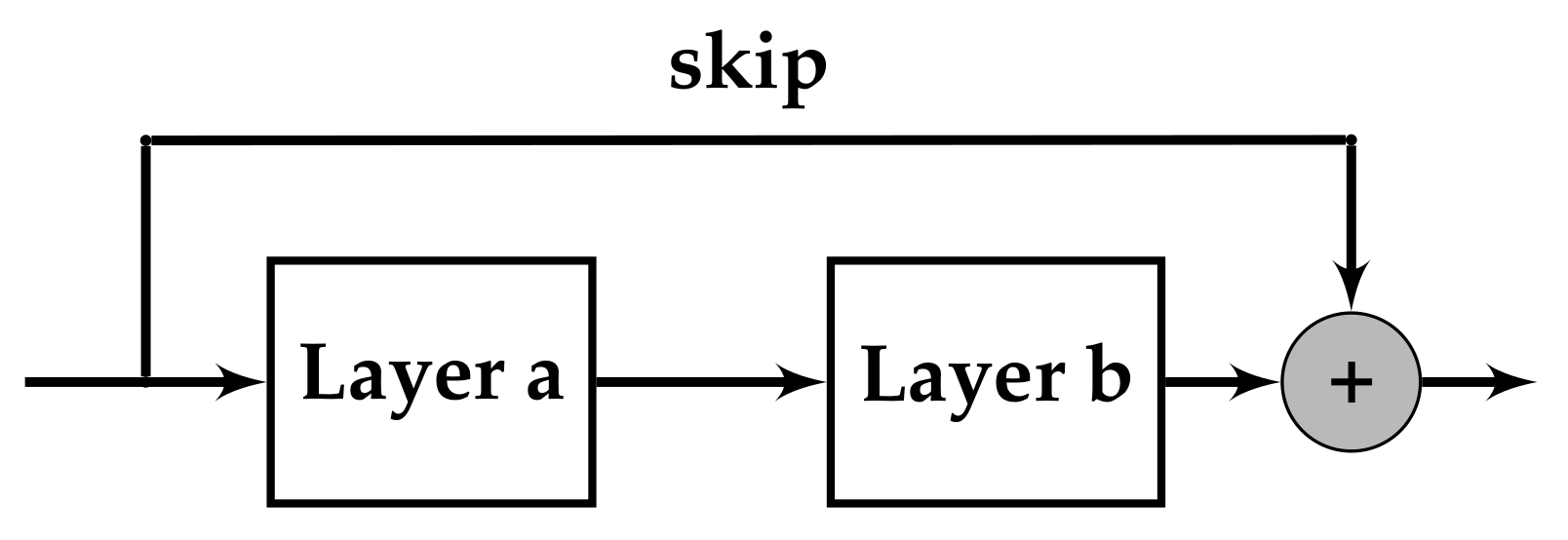
3.1. Encoding the Networks
3.2. Fitness Function Evaluation
3.3. Optimising the Layers
3.4. Convergence Test
4. Results
4.1. The Final Neural Network
4.2. Performance of the Designed Classifier
4.3. Comparison to Other Classifiers
4.4. Class Activation Mapping
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gabutti, G.; d’Anchera, E.; Sandri, F.; Savio, M.; Stefanati, A. Coronavirus: Update Related to the Current Outbreak of COVID-19. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2020, 9, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. What’s New in the Guidelines. 2021. Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/whats-new/ (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- Ün, M.K.; Avşar, E.; Akçalı, İ.D. An analytical method to create patient-specific deformed bone models using X-ray images and a healthy bone model. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 104, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toğaçar, M.; Ergen, B.; Cömert, Z. COVID-19 detection using deep learning models to exploit Social Mimic Optimization and structured chest X-ray images using fuzzy color and stacking approaches. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruesgas, L.; Álvarez Cuervo, R.; Valderrama-Gual, F.; Rojas-Sola, J.I. Projective geometric model for automatic determination of X-ray-emitting source of a standard radiographic system. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 99, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kengyelics, S.M.; Treadgold, L.A.; Davies, A.G. X-ray system simulation software tools for radiology and radiography education. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 93, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bielby, J.; Kuhn, S.; Colreavy-Donnelly, S.; Caraffini, F.; O’Connor, S.; Anastassi, Z.A. Identifying Parkinson’s Disease through the Classification of Audio Recording Data. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santucci, V.; Milani, A.; Caraffini, F. An Optimisation-Driven Prediction Method for Automated Diagnosis and Prognosis. Mathematics 2019, 7, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thurnhofer-Hemsi, K.; López-Rubio, E.; Roe-Vellve, N.; Molina-Cabello, M.A. Multiobjective optimization of deep neural networks with combinations of Lp-norm cost functions for 3D medical image super-resolution. Integr. Comput. Aided Eng. 2020, 27, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charte, F.; Rivera, A.J.; Martínez, F.; del Jesus, M.J. EvoAAA: An evolutionary methodology for automated neural autoencoder architecture search. Integr. Comput. Aided Eng. 2020, 27, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togo, R.; Watanabe, H.; Ogawa, T.; Haseyama, M. Deep convolutional neural network-based anomaly detection for organ classification in gastric X-ray examination. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 123, 103903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colreavy-Donnelly, S.; Caraffini, F.; Kuhn, S.; Gongora, M.; Florez-Lozano, J.; Parra, C. Shallow buried improvised explosive device detection via convolutional neural networks. Integr. Comput. Aided Eng. 2020, 27, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet, I.; Caraffini, F.; Peña, A.; Puerta, A.; Gongora, M. Oil Palm Detection via Deep Transfer Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasienica-Józkowy, J.; Knapik, M.; Cyganek, B. An ensemble deep learning method with optimized weights for drone-based water rescue and surveillance. Integr. Comput. Aided Eng. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamreras, S.; Boucheham, B.; Molina-Cabello, M.A.; Benitez-Rochel, R.; Lopez-Rubio, E. Content based image retrieval by ensembles of deep learning object classifiers. Integr. Comput. Aided Eng. 2020, 27, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, T.; Rahman, M.A.; Fattah, S.A. CovXNet: A multi-dilation convolutional neural network for automatic COVID-19 and other pneumonia detection from chest X-ray images with transferable multi-receptive feature optimization. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 122, 103869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, T.; Talo, M.; Yildirim, E.A.; Baloglu, U.B.; Yildirim, O.; Rajendra Acharya, U. Automated detection of COVID-19 cases using deep neural networks with X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, H.; Gupta, P.; Siddiqui, M.K.; Morales-Menendez, R.; Singh, V. Application of deep learning for fast detection of COVID-19 in X-Rays using nCOVnet. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 138, 109944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, I.D.; Mpesiana, T.A. Covid-19: Automatic detection from X-ray images utilizing transfer learning with convolutional neural networks. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 43, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, C.C. Neural Networks and Deep Learning. A Textbook; Springer International: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, K.; Huyen, A.; Lu, T. Deep Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.09645. [Google Scholar]
- Le, Q.V.; Ngiam, J.; Coates, A.; Lahiri, A.; Prochnow, B.; Ng, A.Y. On Optimization Methods for Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Bellevue, WA, USA, 28–2 July 2011; Omnipress: Madison, WI, USA, 2011; pp. 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Arulkumaran, K.; Deisenroth, M.P.; Brundage, M.; Bharath, A.A. Deep Reinforcement Learning: A Brief Survey. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2017, 34, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinyals, O.; Povey, D. Krylov Subspace Descent for Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, La Palma, Spain, 21–23 April 2012; Lawrence, N.D., Girolami, M., Eds.; PMLR: La Palma, Spain, 2012; Volume 22, pp. 1261–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Olshanskii, M.A.; Tyrtyshnikov, E.E. Krylov Subspace Methods. In Iterative Methods for Linear Systems: Theory and Applications; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, K. Deep Learning without Poor Local Minima. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 5–10 December 2015; pp. 586–594. [Google Scholar]
- Sutskever, I.; Martens, J.; Dahl, G.; Hinton, G. On the importance of initialization and momentum in deep learning. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–21 June 2013; Dasgupta, S., McAllester, D., Eds.; PMLR: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013; Volume 28, pp. 1139–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Jiang, H.; Ji, C.G.; Pan, Z. A modified butterfly optimization algorithm: An adaptive algorithm for global optimization and the support vector machine. Expert Syst. 2020, 38, e12642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, J.M.; Caraffini, F.; Homapour, E.; Santucci, V.; Milani, A. A Clustering System for Dynamic Data Streams Based on Metaheuristic Optimisation. Mathematics 2019, 7, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demirel, D.; Cetinsaya, B.; Halic, T.; Kockara, S.; Ahmadi, S. Partition-based optimization model for generative anatomy modeling language (POM-GAML). BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Dhir, C.S.; Lee, J. Hessian-Free Optimization for Learning Deep Multidimensional Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 18–23 December 2014; pp. 883–891. [Google Scholar]
- Florez-Lozano, J.; Caraffini, F.; Parra, C.; Gongora, M. Cooperative and distributed decision-making in a multi-agent perception system for improvised land mines detection. Inf. Fusion 2020, 64, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khishe, M.; Mosavi, M. Classification of underwater acoustical dataset using neural network trained by Chimp Optimization Algorithm. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 157, 107005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiben, A.E.; Smith, J.E. Introduction to Evolutionary Computation; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, K.O.; Clune, J.; Lehman, J.; Miikkulainen, R. Designing neural networks through neuroevolution. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2019, 1, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.Y.; Park, S.M.; Sim, K.B. Optimal hyperparameter tuning of convolutional neural networks based on the parameter-setting-free harmony search algorithm. Optik 2018, 172, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, G.; Papa, J.; Marana, A.; Scheirer, W.; Cox, D. Fine-Tuning Convolutional Neural Networks Using Harmony Search. In Progress in Pattern Recognition, Image Analysis, Computer Vision, and Applications; Pardo, A., Kittler, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 683–690. [Google Scholar]
- Bąk, S.; Carr, P.; Lalonde, J.F. Domain Adaptation Through Synthesis for Unsupervised Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2018, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 193–209. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Zheng, L.; Yan, C.; Yang, Y. Unsupervised Person Re-Identification: Clustering and Fine-Tuning. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Fu, Y.; Xiang, T.; Wang, W.; Qiu, J.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, Y.G.; Xue, X. Pose-Normalized Image Generation for Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2018, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 661–678. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Xue, B.; Zhang, M.; Yen, G.G.; Lv, J. Automatically Designing CNN Architectures Using the Genetic Algorithm for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 50, 3840–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young, S.R.; Rose, D.C.; Karnowski, T.P.; Lim, S.H.; Patton, R.M. Optimizing Deep Learning Hyper-Parameters through an Evolutionary Algorithm. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Machine Learning in High-Performance Computing Environments; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real, E.; Moore, S.; Selle, A.; Saxena, S.; Suematsu, Y.L.; Tan, J.; Le, Q.V.; Kurakin, A. Large-Scale Evolution of Image Classifiers. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; Volume 70, pp. 2902–2911. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.P.; Morrison, P.; Dao, L. COVID-19 Image Data Collection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:eess.IV/2003.11597. [Google Scholar]
- Minaee, S.; Kafieh, R.; Sonka, M.; Yazdani, S.; Soufi, G.J. Deep-covid: Predicting covid-19 from chest X-ray images using deep transfer learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.09363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvin, J.; Rajpurkar, P.; Ko, M.; Yu, Y.; Ciurea-Ilcus, S.; Chute, C.; Marklund, H.; Haghgoo, B.; Ball, R.; Shpanskaya, K.; et al. Chexpert: A large chest radiograph dataset with uncertainty labels and expert comparison. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2019, 33, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulodimos, A.; Doulamis, N.; Doulamis, A.; Protopapadakis, E. Deep Learning for Computer Vision: A Brief Review. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, 2018, 7068349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, H.; Hjelmervik, K.T. Classification of anti-submarine warfare sonar targets using a deep neural network. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2018 MTS/IEEE Charleston, Charleston, SC, USA, 22–25 October 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Tabassum, A.; Cui, J.; Xie, J.; Ho, J.; Agarwal, P.; Adhikari, B.; Prakash, B.A. DeepCOVID: An Operational Deep Learning-driven Framework for Explainable Real-time COVID-19 Forecasting. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.J.; Azimi-Sadjadi, M.R.; Kargl, S.G.; Zhao, Y.; Williams, K.L. Underwater Unexploded Ordnance (UXO) Classification Using a Matched Subspace Classifier With Adaptive Dictionaries. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2019, 44, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D. Biogeography-Based Optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2008, 12, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, J. Swarm Intelligence. In Handbook of Nature-Inspired and Innovative Computing: Integrating Classical Models with Emerging Technologies; Zomaya, A.Y., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 187–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraffini, F.; Santucci, V.; Milani, A. Evolutionary Computation & Swarm Intelligence; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yaman, A.; Iacca, G.; Caraffini, F. A comparison of three differential evolution strategies in terms of early convergence with different population sizes. In LeGO 2018–14th International Global Optimization Workshop; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2019; p. 020002. [Google Scholar]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Let a biogeography-based optimizer train your multi-layer perceptron. Inf. Sci. 2014, 269, 188–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanski, I. Metapopulation dynamics. Nature 1998, 396, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, A.; Higgins, K. Persistence of transients in spatially structured ecological models. Science 1994, 263, 1133–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H. An analysis of the equilibrium of migration models for biogeography-based optimization. Inf. Sci. 2010, 180, 3444–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D. Biogeography-Based Optimization. 2009. Available online: https://academic.csuohio.edu/simond/bbo/ (accessed on 27 April 2021).
- Xu, Q.S.; Liang, Y.Z. Monte Carlo cross validation. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 56, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Category | COVID-19 | Healthy |
|---|---|---|
| Training Set | 84 (420 after augmentation) | 2000 |
| Test Set | 100 | 3000 |
| Name | Acronym | Admissible Values |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Output Channels | NOC | 8, 16, 32, |
| 64, 128, 256, 512 | ||
| Convolution Kernel Size | CKS | , , |
| , , | ||
| Activation Type | AT | ReLU, Tanh |
| ELU, SELU | ||
| Include Pool | IP | Yes, No |
| Pooling Type | PT | Max pooling, |
| Average pooling | ||
| Batch Normalization | BN | Yes, No |
| Insert Skip | IS | Yes, No |
| Insert Layer | IL | Yes, No |
| Max immigration (I) | 1 |
| Max emigration (E) | 1 |
| Max mutation rate (M) | 0.02 |
| Layer | Type | No. Filters | Size | Stride | Resulting Dimension |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Convolution | 500 | |||
| 2 | Pooling | 500 | |||
| 3 | Convolution | 1000 | |||
| 4 | Convolution | 1000 | |||
| 5 | Convolution | 2000 | |||
| 6 | Pooling | 2000 | |||
| 7 | Convolution (padded) | 1181 | |||
| 8 | Convolution (padded) | 1181 | |||
| 9 | Convolution (padded) | 1181 | |||
| 10 | Convolution (padded) | 1181 | |||
| 11 | Convolution (padded) | 1181 | |||
| 12 | Convolution | 4000 | |||
| 13 | Fully connected (4000 nodes) | ||||
| 14 | Dropout (probability = ) | ||||
| 15 | Fully connected (4000 nodes) | ||||
| 16 | Dropout (probability = ) | ||||
| 17 | Fully connected (2 nodes) |
| Epoch | OptiDCNN | MSCAD | DeepCovid | DCNN | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | STD | Accuracy | STD | Accuracy | STD | Accuracy | STD | |
| 1 | 89.63 | N/A | 88.12 | 0.41 | 87.26 | 0.33 | 84.11 | 0.75 |
| 2 | 93.11 | N/A | 92.11 | 0.37 | 91.33 | 0.21 | 89.22 | 0.31 |
| 3 | 96.15 | N/A | 93.12 | 0.31 | 92.09 | 0.22 | 91.11 | 0.38 |
| 4 | 97.22 | N/A | 94.62 | 0.24 | 92.89 | 0.32 | 92.47 | 0.11 |
| 5 | 97.27 | N/A | 95.41 | 0.18 | 93.55 | 0.09 | 93.47 | 0.29 |
| 6 | 98.41 | N/A | 95.92 | 0.17 | 95.25 | 0.18 | 94.02 | 0.39 |
| 7 | 98.55 | N/A | 96.11 | 0.16 | 96.13 | 0.19 | 95.17 | 0.19 |
| 8 | 98.88 | N/A | 96.77 | 0.12 | 97.24 | 0.11 | 96.58 | 0.21 |
| 9 | 99.01 | N/A | 96.99 | 0.09 | 98.11 | 0.15 | 96.76 | 0.09 |
| 10 | 99.11 | N/A | 97.22 | 0.15 | 98.22 | 0.09 | 97.18 | 0.11 |
| Epoch | OptiDCNN | MSCAD | DeepCovid | DCNN | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | STD | Time | STD | Time | STD | Time | STD | |
| 1 | 99.11 | N/A | 102.23 | 1.01 | 102.08 | 0.89 | 102.11 | 0.77 |
| 2 | 201.04 | N/A | 236.03 | 8.54 | 255.11 | 1.54 | 268.47 | 4.33 |
| 3 | 302.62 | N/A | 347.41 | 2.32 | 387.55 | 2.28 | 299.17 | 0.53 |
| 4 | 355.13 | N/A | 421.45 | 2.01 | 521.27 | 2.18 | 443.49 | 0.65 |
| 5 | 461.11 | N/A | 582.47 | 3.96 | 533.26 | 1.32 | 601.77 | 3.09 |
| 6 | 555.22 | N/A | 692.75 | 1.23 | 611.75 | 5.96 | 721.22 | 2.01 |
| 7 | 645.39 | N/A | 797.02 | 1.02 | 725.68 | 4.15 | 836.75 | 2.25 |
| 8 | 747.55 | N/A | 854.43 | 1.74 | 805.74 | 4.02 | 1007.9 | 1.53 |
| 9 | 875.35 | N/A | 964.12 | 2.01 | 953.89 | 6.05 | 1125.57 | 5.07 |
| 10 | 934.54 | N/A | 1112.36 | 1.97 | 1211.34 | 1.33 | 1133.44 | 4.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khishe, M.; Caraffini, F.; Kuhn, S. Evolving Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks for Early COVID-19 Detection in Chest X-ray Images. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9091002
Khishe M, Caraffini F, Kuhn S. Evolving Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks for Early COVID-19 Detection in Chest X-ray Images. Mathematics. 2021; 9(9):1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9091002
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhishe, Mohammad, Fabio Caraffini, and Stefan Kuhn. 2021. "Evolving Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks for Early COVID-19 Detection in Chest X-ray Images" Mathematics 9, no. 9: 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9091002
APA StyleKhishe, M., Caraffini, F., & Kuhn, S. (2021). Evolving Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks for Early COVID-19 Detection in Chest X-ray Images. Mathematics, 9(9), 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9091002








