Memetic Strategy of Particle Swarm Optimization for One-Dimensional Magnetotelluric Inversions
Abstract
1. Introduction
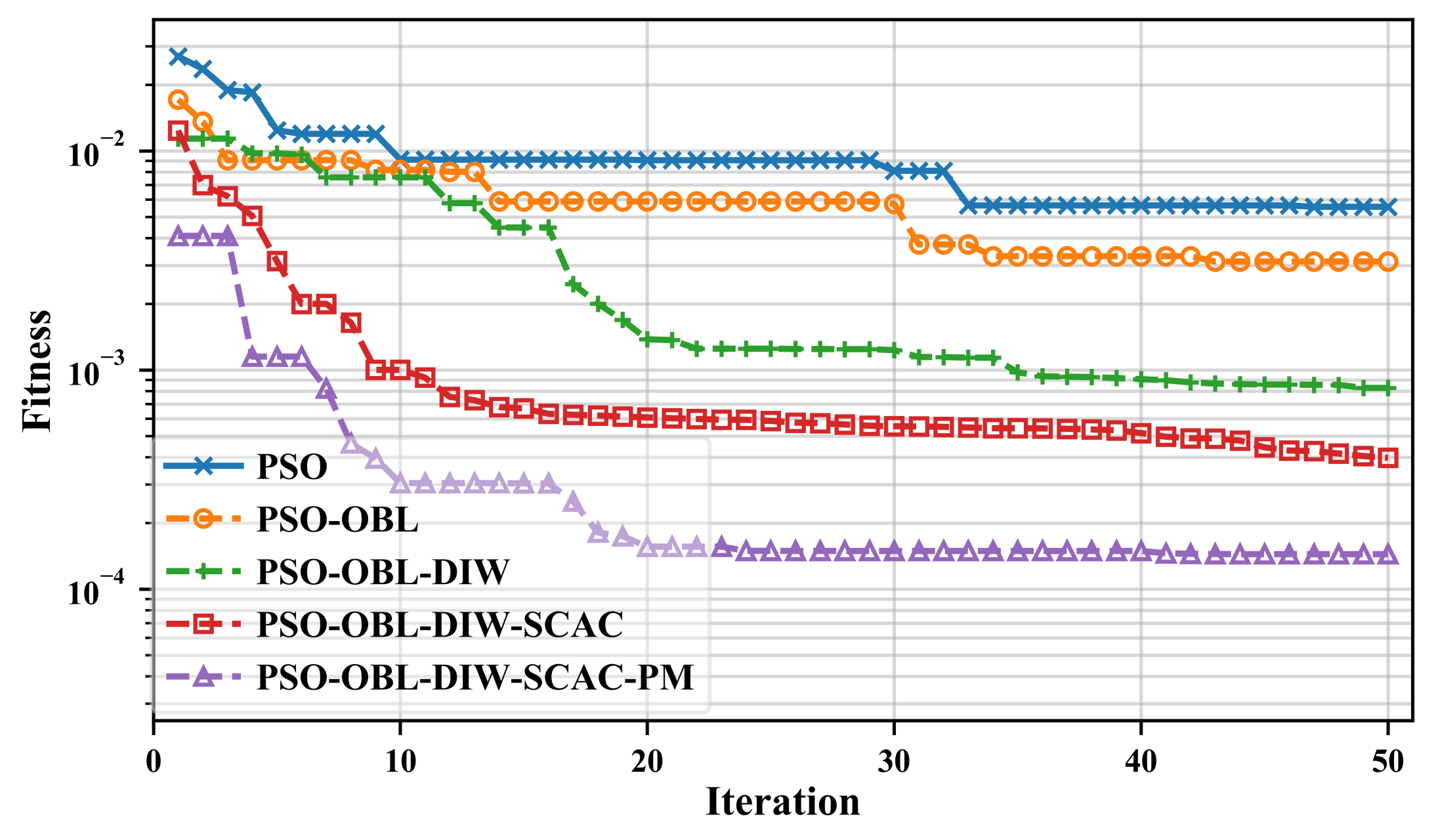
- We use opposition-based learning strategy to search for a suitable initial population of geoelectric model more accurately, the strategy can help to determine the appropriate global optimal search direction in the early stage and accelerate convergence.
- We use DIWs based on sine mapping to integrate empirical cognition of the previous inversion iterations, and this strategy can strengthen the optimization ability of MT inversions.
- We used sine-cosine acceleration coefficients to balance the influence of individual cognition and group cognition on the evolutionary process, this strategy can improve the global optimization capability, and convergence stability in the MT inversion process.
2. PSO for 1D MT Inversions
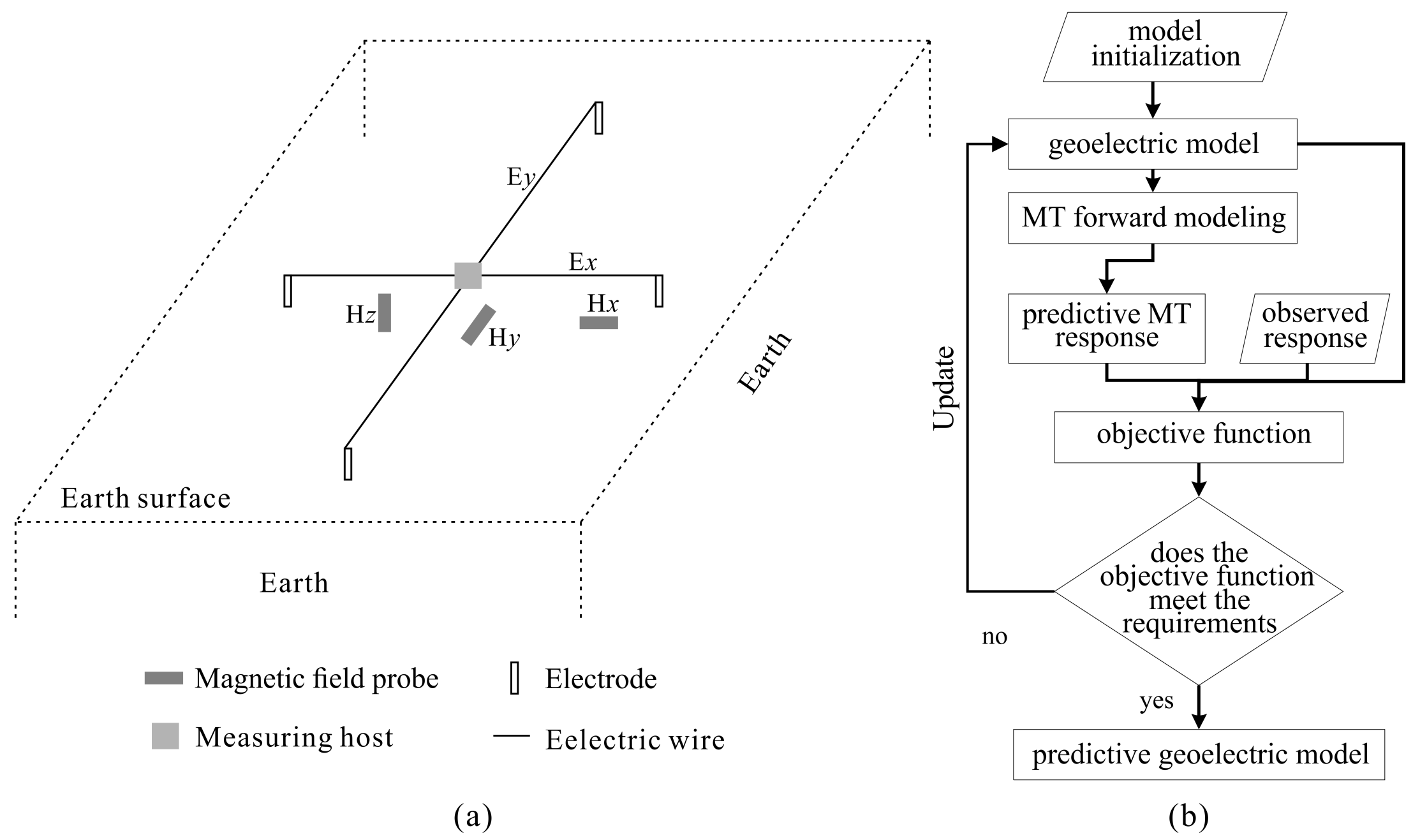
2.1. Forward Modeling
2.2. Inversions
2.3. PSO Optimization
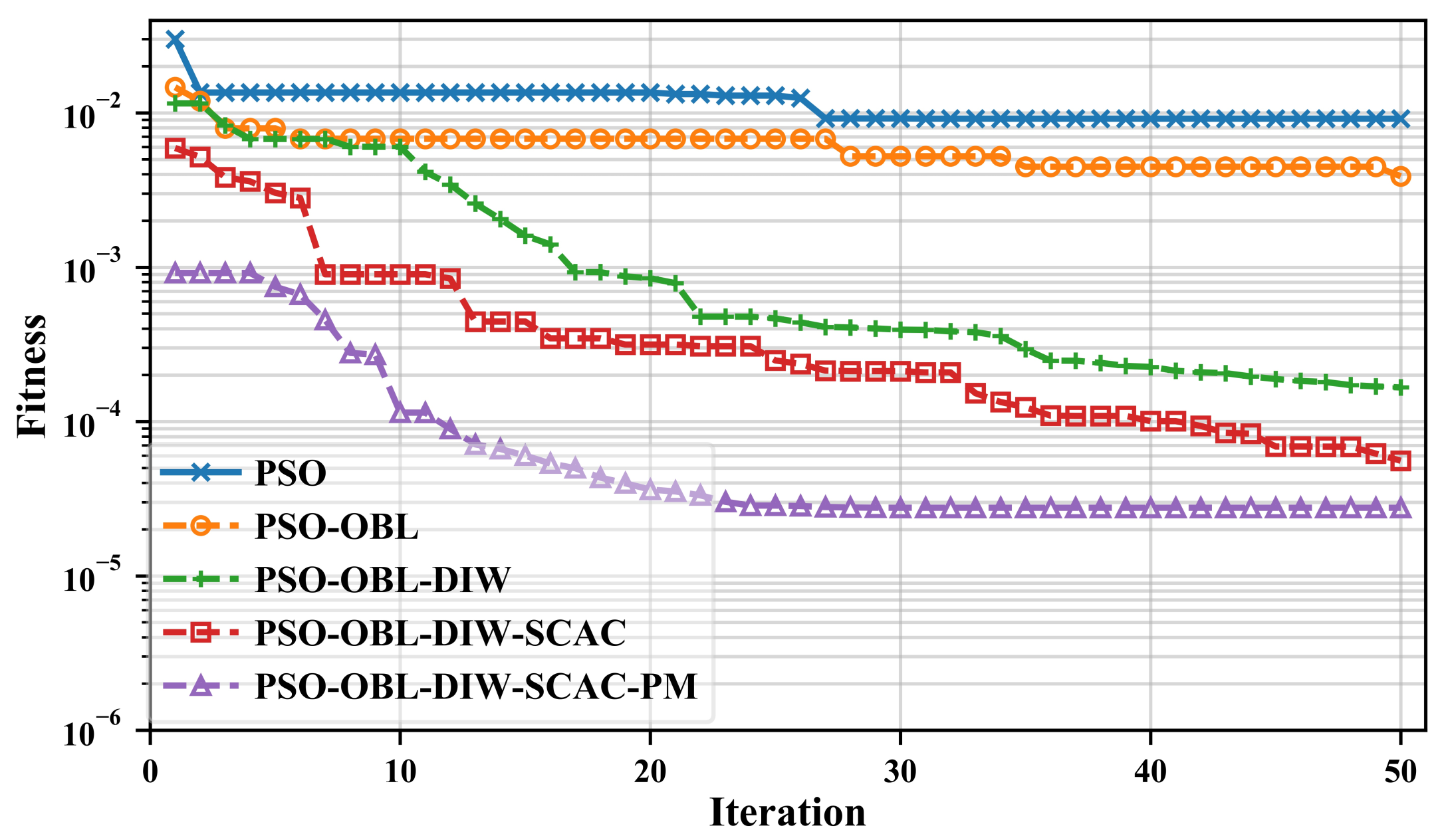
3. Memetic Strategies
3.1. Framework
3.2. Population Initialization
3.3. Dynamic Inertia Weight
3.4. Accelerating Evolution
3.5. Population Mutation
3.6. Fitness
4. Test Model
4.1. Three-Layer Model
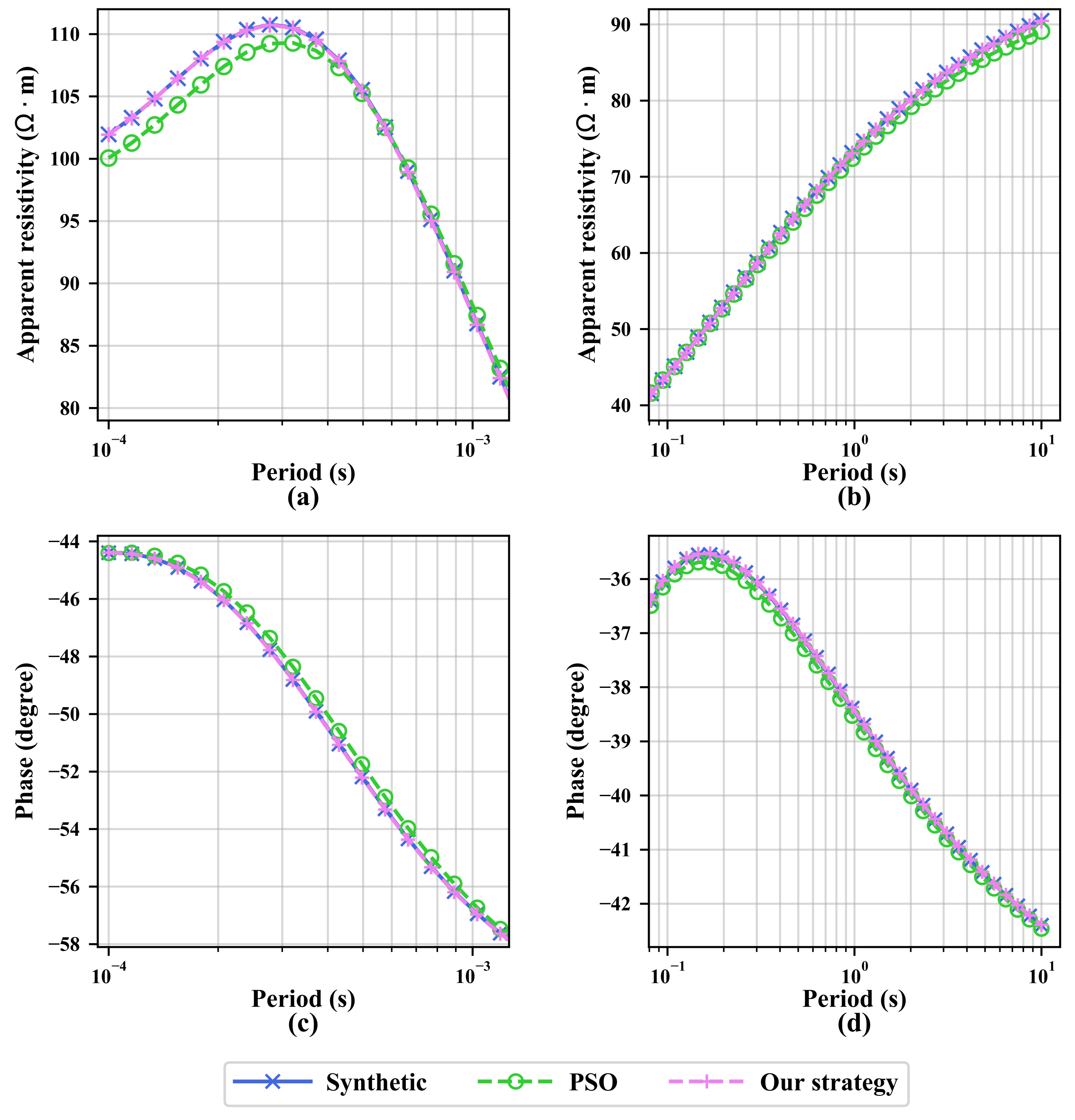
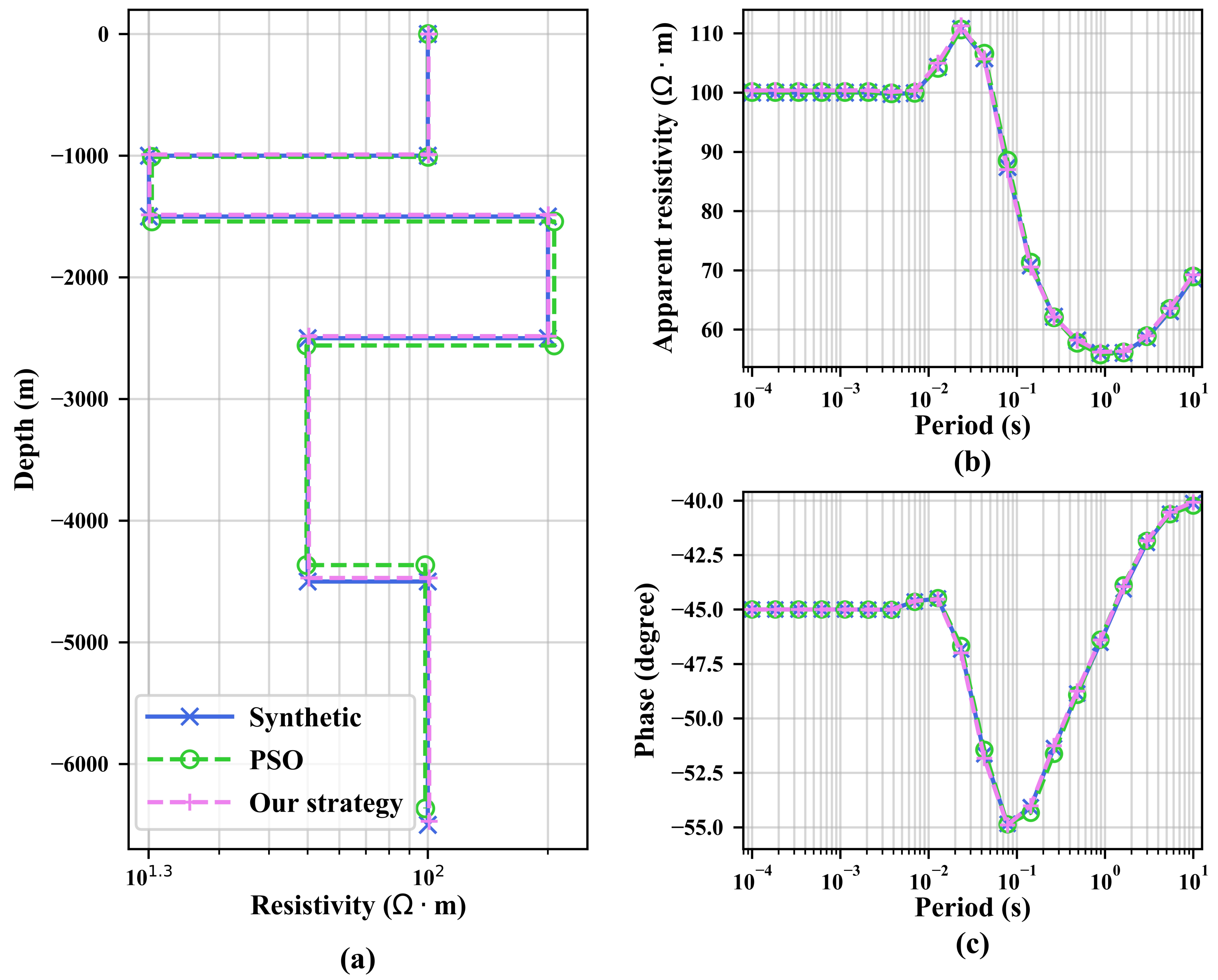
4.2. Five-Layer Model
5. Stability Evaluation
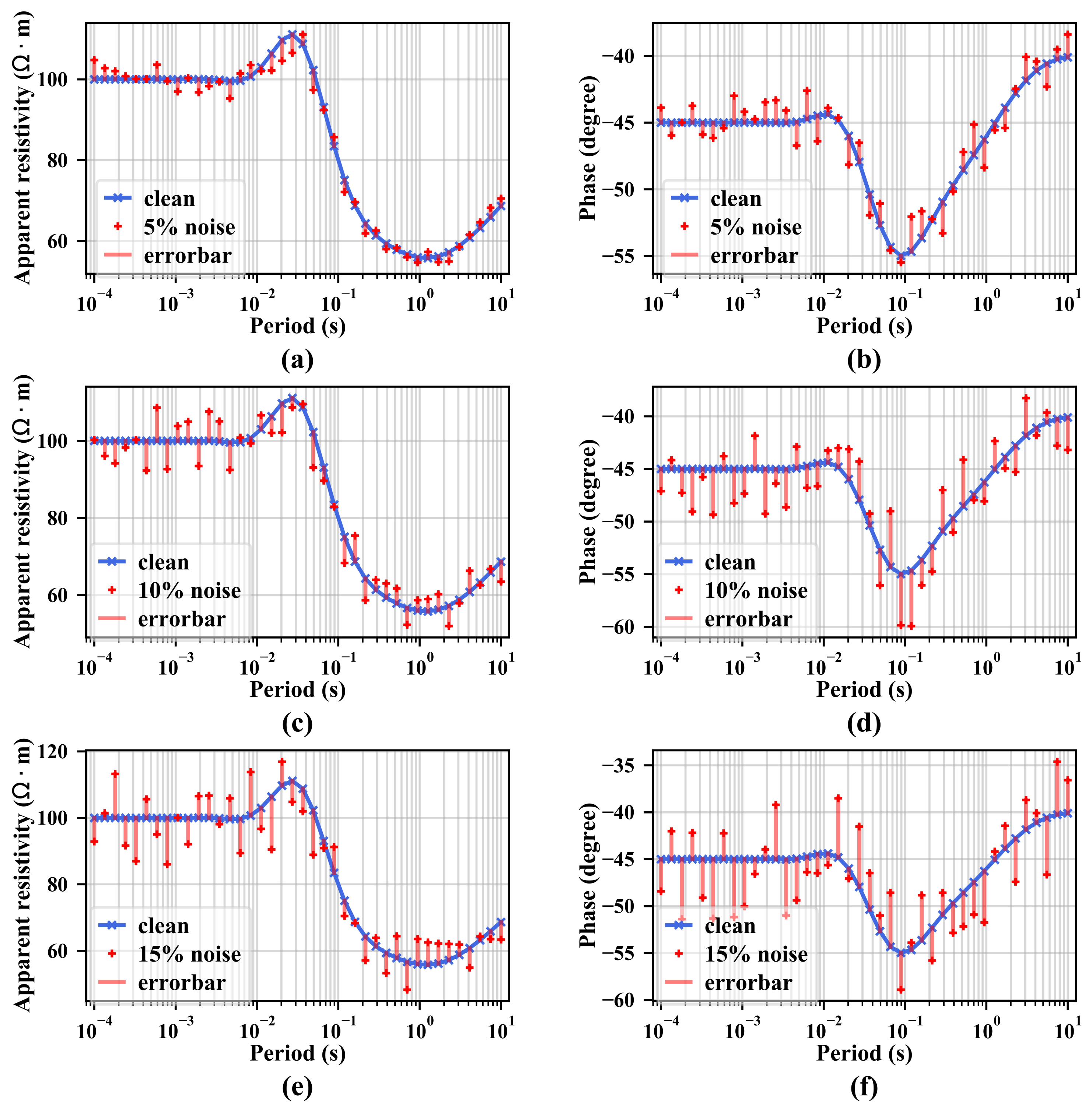
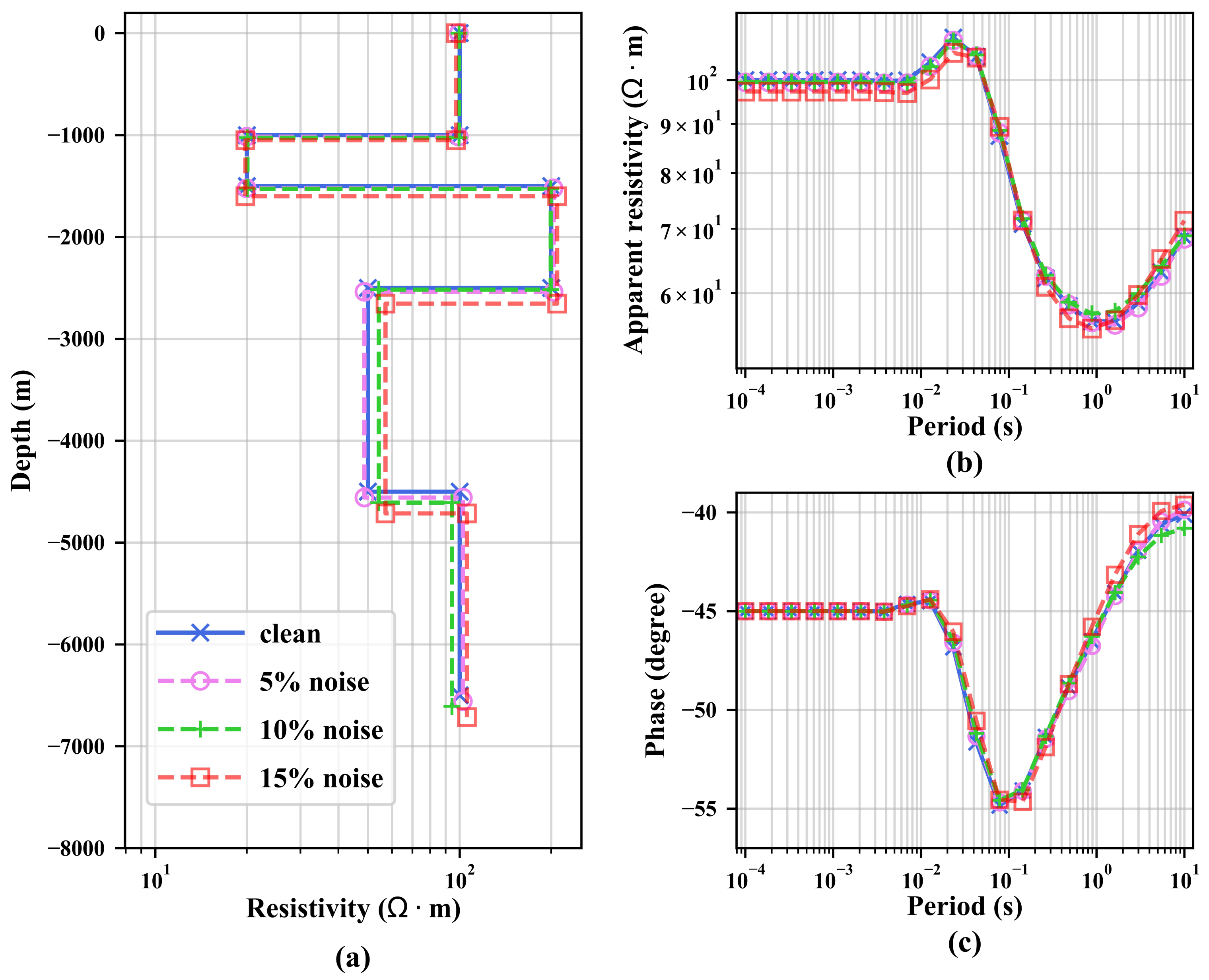
5.1. Noise Immunity Test
5.2. Real Application Data
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seillé, H.; Visser, G. Bayesian inversion of magnetotelluric data considering dimensionality discrepancies. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 223, 1565–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.Q. Special Issue on Electromagnetic Methods in Applied Geophysics—Introduction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1984, 22, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhdanov, M. Foundations of Geophysical Electromagnetic Theory and Methods; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ramananjaona, C.; MacGregor, L.; Andréis, D. Sensitivity and inversion of marine electromagnetic data in a vertically anisotropic stratified earth. Geophys. Prospect. 2011, 59, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordy, M.; Wannamaker, P.; Maris, V.; Cherkaev, E.; Hill, G. 3-D magnetotelluric inversion including topography using deformed hexahedral edge finite elements and direct solvers parallelized on SMP computers—Part I: Forward problem and parameter Jacobians. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 204, 74–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, S.C.; Parker, R.L.; Constable, C.G. Occam’s inversion: A practical algorithm for generating smooth model from electromagnetic sounding data. Geophysics 1987, 52, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Hu, X.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y.; Yu, N. Characterizing the 3D hydrogeological structure of a debris landslide using the transient electromagnetic method. J. Appl. Geophys. 2020, 175, 103991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, D.; Alexander, B.; King, M.; Heinson, G.; Kee, Y. Inverting magnetotelluric responses in a three-dimensional earth using fast forward approximations based on artificial neural networks. Comput. Geosci. 2019, 127, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grana, D.; Fjeldstad, T.; Omre, H. Bayesian Gaussian Mixture Linear Inversion for Geophysical Inverse Problems. Math. Geosci. 2017, 49, 493–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.G.; Tan, Y. Improving Metaheuristic Algorithms With Information Feedback Models. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 49, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.G.; Guo, L.; Gandomi, A.H.; Hao, G.S.; Wang, H. Chaotic Krill Herd algorithm. Inf. Sci. 2014, 274, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.P.; Biswas, A. Global nonlinear optimization for the estimation of static shift and interpretation of 1-D magnetotelluric sounding data. Ann. Geophys. 2011, 54, 249–264. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, E.; Guo, R.; Liu, J.; Ren, Z.; Dong, H. Efficient hierarchical trans-dimensional Bayesian inversion of magnetotelluric data. Geophys. J. Int. 2018, 213, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, J.D.C.; Sampaio, E.E.S. Magnetotelluric inversion of one- and two-dimensional synthetic data based on hybrid genetic algorithms. Acta Geophys. 2019, 67, 1365–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, F.; Santilano, A.; Godio, A. Particle Swarm Optimization of 2D Magnetotelluric data. Geophysics 2019, 84, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Obaiahnahatti, B. A Modified Particle Swarm Optimizer. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Evolutionary Computation, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–9 May 1998; Volume 6, pp. 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Jordehi, A.R. Time varying acceleration coefficients particle swarm optimisation (TVACPSO): A new optimisation algorithm for estimating parameters of PV cells and modules. Energy Conv. Manag. 2016, 129, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.F.; Tawhid, M.A. A hybrid particle swarm optimization and genetic algorithm with population partitioning for large scale optimization problems. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2017, 8, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, I.F.; Silva, I.R.D.M.; Goldbarg, E.F.G.; Monteiro, S.M.D.; Goldbarg, M.C. A PSO-inspired architecture to hybridise multi-objective metaheuristics. Memet. Comput. 2020, 12, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wong, W.K.; Tan, K.C. Competitive swarm optimizer with mutated agents for finding optimal designs for nonlinear regression models with multiple interacting factors. Memet. Comput. 2020, 12, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commer, M.; Newman, G.A. New advances in three-dimensional controlled-source electromagnetic inversion. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 172, 513–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Oldenburg, D.W.; Haber, E. 3-D inversion of airborne electromagnetic data parallelized and accelerated by local mesh and adaptive soundings. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 196, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdanov, M.S.; Uma, M.; Wilson, G.A.; Velikhov, E.P.; Black, N.; Gribenko, A.V. Iterative electromagnetic migration for 3D inversion of marine controlled: Ource electromagnetic data. Geophys. Prospect. 2011, 59, 1101–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siripunvaraporn, W. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion: An introductory guide for developers and users. Surv. Geophys. 2012, 33, 5–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Hu, X.; Li, J. Pseudo-3D constrained inversion of transient electromagnetic data for a polarizable SMS hydrothermal system in the Deep Sea. Stud. Geophys. Geod. 2018, 62, 512–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groothedlin, C.D.D.; Constable, S.C. Occam’s inversion to generate smooth, two-dimensional models from magnetotelluric data. Geophysics 1990, 55, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y. Full 3-D inversion of electromagnetic data on PC. J. Appl. Geophys. 2001, 46, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Srivastava, D.C.; Gupta, P.K. The genetic algorithm: A robust method for stress inversion. J. Struct. Geol. 2017, 94, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, F.; Cotta, C. Memetic algorithms and memetic computing optimization: A literature review. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2012, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tan, D.; Liu, L. Particle swarm optimization algorithm: An overview. Soft Comput. 2018, 22, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.F.; Chen, H.M.; Chen, J.H.; Hwang, S.F.; Ho, S.Y. MeSwarm: Memetic particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference, GECCO 2005, Washington, DC, USA, 25–29 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chiam, S.; Tan, K.; Al-Mamun, A. A memetic model of evolutionary PSO for computational finance applications. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 3695–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Lei, Y.X.; Guo, W.P.; Wang, C.; Cai, Y.Q.; Luo, W. A novel improved particle swarm optimization algorithm based on individual difference evolution. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2017, 57, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerc, M.; Kennedy, J. The particle swarm-explosion, stability, and convergence in a multidimensional complex space. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.; Deep, K.; Pant, M. Novel inertia weight strategies for particle swarm optimization. Memet. Comput. 2013, 5, 229–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hao, J.K.; Duval, B. Opposition-based Memetic Search for the Maximum Diversity Problem. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2017, 21, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, G.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Z. On Tchebycheff decomposition approaches for multiobjective evolutionary optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2017, 22, 226–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizhoosh, H.R. Opposition-based learning: A new scheme for machine intelligence. In Proceeding of the International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Modelling, Control and Automation and International Conference on Intelligent Agents, Web Technologies and Internet Commerce (CIMCA-IAWTIC’06), Vienna, Austria, 28–30 November 2005; Volume 1, pp. 695–701. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Sun, H.; Rahnamayan, S. Using opposition-based learning to enhance differential evolution: A comparative study. In Proceeding of the 2016 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Liu, F.; Qi, Y.; Gong, M.; Yin, M.; Li, L.; Jiao, L.; Wu, J. MOEA/D with opposition-based learning for multiobjective optimization problem. Neurocomputing 2014, 146, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, J.C.; Singh, P.; Saraswat, M.; Verma, A.; Jadon, S.S.; Abraham, A. Inertia weight strategies in particle swarm optimization. In Proceeding of the 2011 Third World Congress on Nature and Biologically Inspired Computing, Salamanca, Spain, 19–21 October 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 633–640. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, F.; Yin, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wan, F. A hybrid particle swarm optimizer with sine cosine acceleration coefficients. Inf. Sci. 2018, 422, 218–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.O.; Shamsuddin, S.M.; Abraham, A.; Qasem, S.N. Adaptive memetic method of multi-objective genetic evolutionary algorithm for backpropagation neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 4945–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beusekom, A.; Parker, R.; Bank, R.; Gill, P.; Constable, S. The 2-D magnetotelluric inverse problem solved with optimization. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 184, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

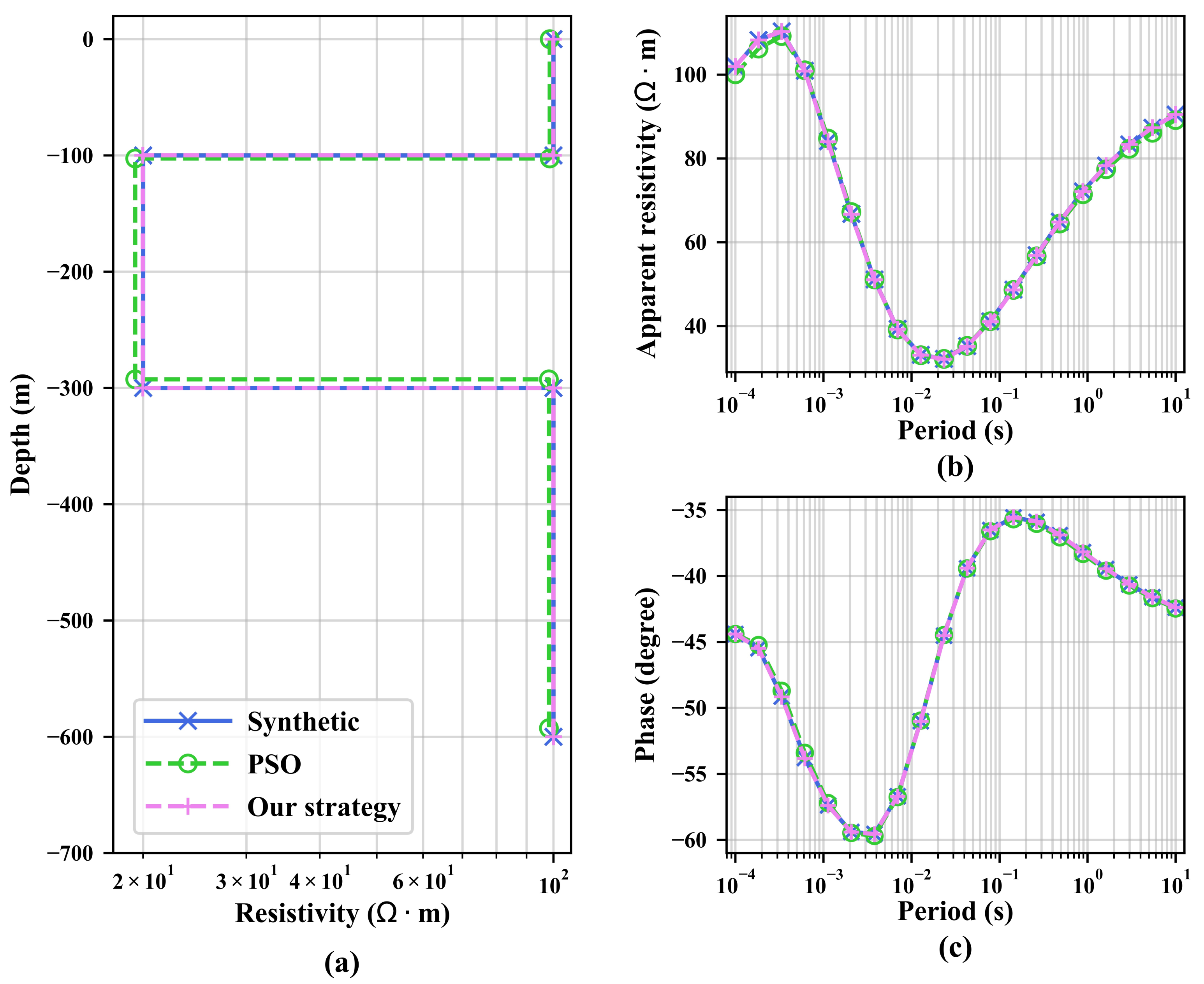



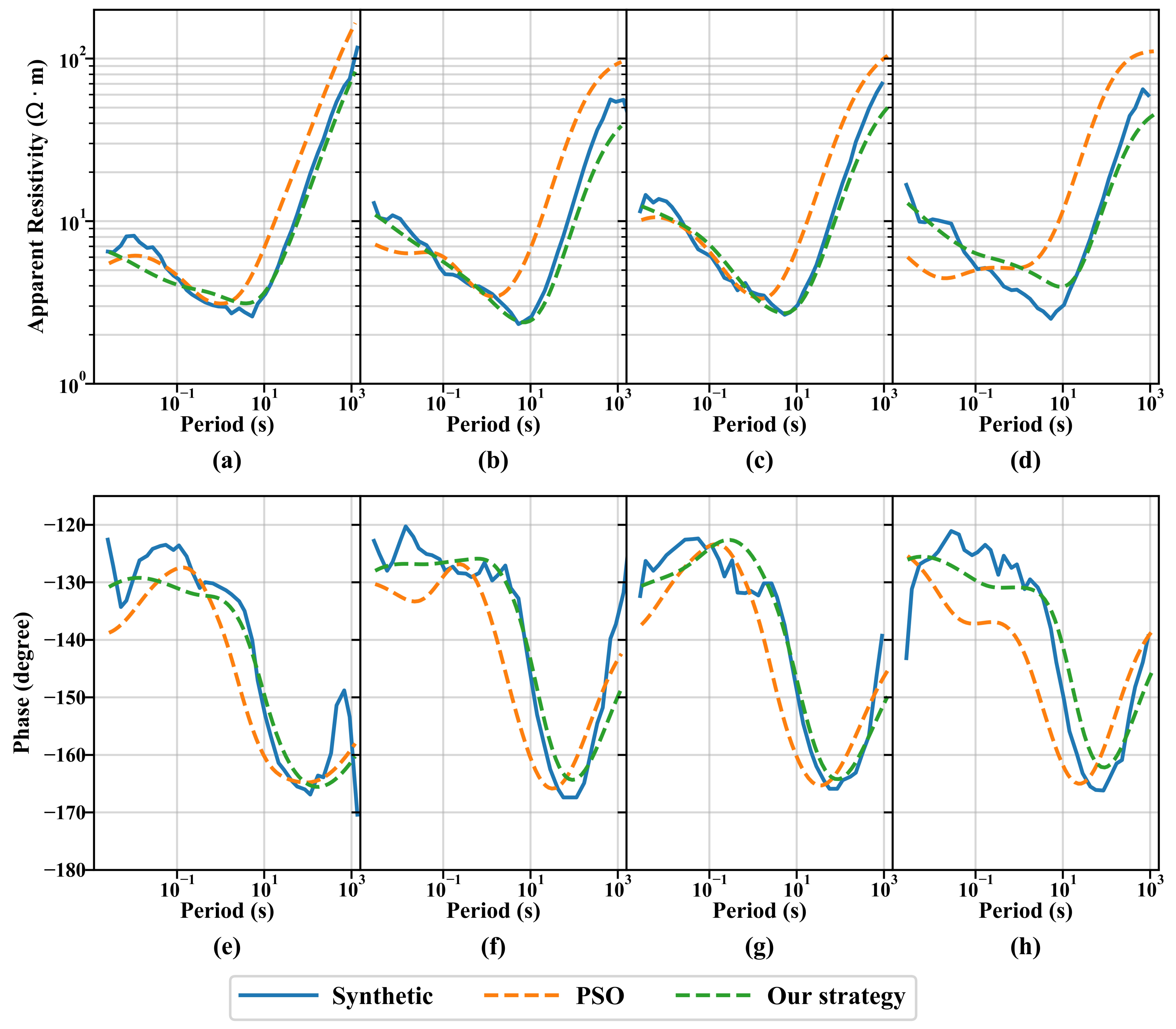
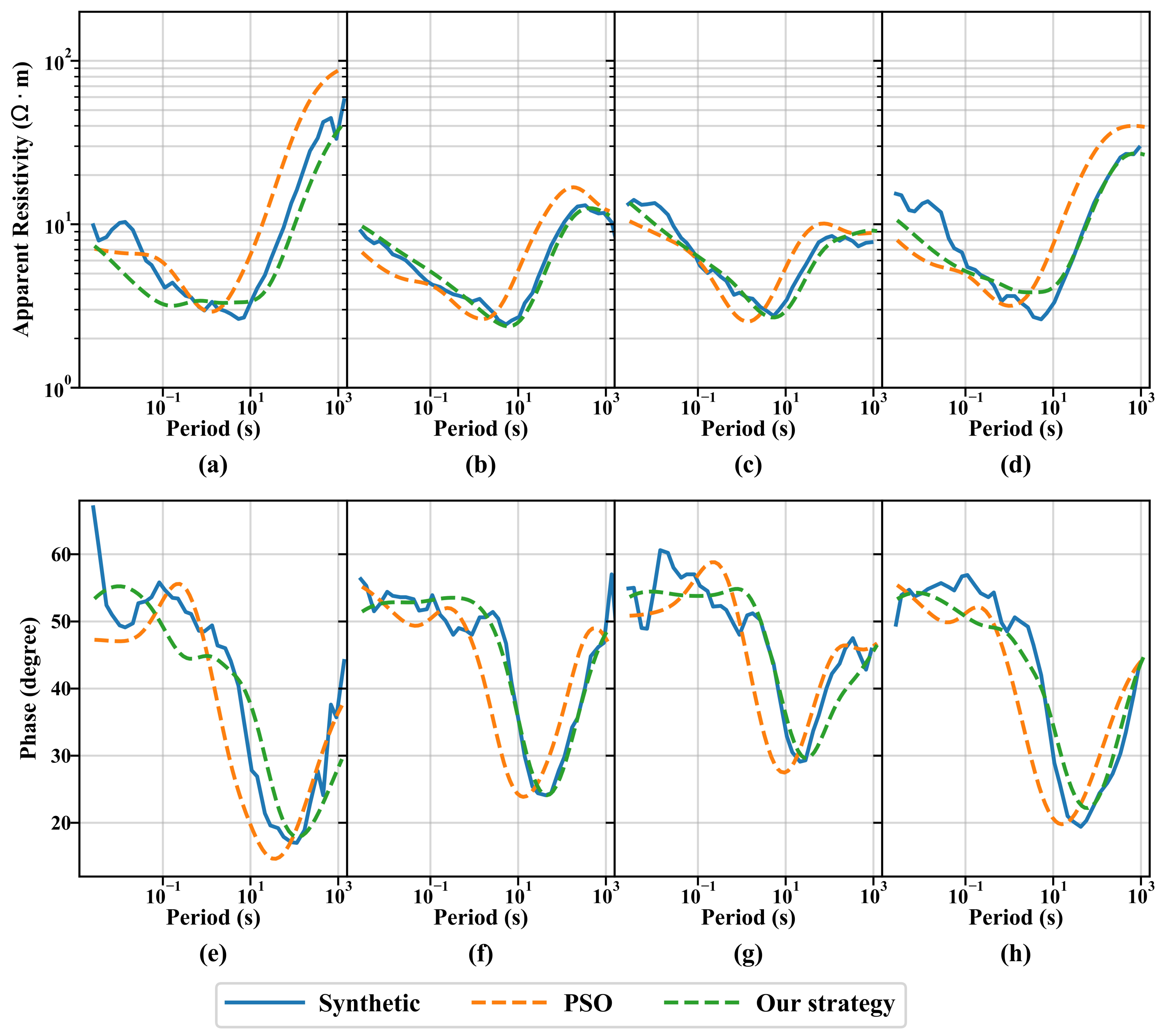
| (·m) | h(m) | Fitness | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supposed model | 100.00 | 20.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 200.00 | ||
| PSO | model | 98.61 | 19.38 | 98.27 | 102.58 | 189.95 | |
| misfit | 1.39 | 3.08 | 1.73 | 2.58 | 5.02 | ||
| SO-OBL | model | 99.84 | 20.42 | 100.12 | 97.36 | 205.08 | |
| misfit | 0.16 | 2.09 | 0.12 | 2.64 | 2.54 | ||
| PSO-OBL-DIW | model | 100.16 | 20.37 | 100.21 | 98.21 | 205.27 | |
| misfit | 0.16 | 1.87 | 0.21 | 1.78 | 2.64 | ||
| PSO-OBL-DIW-SCAC | model | 100.05 | 20.12 | 100.06 | 99.41 | 201.61 | |
| misfit | 0.05 | 0.58 | 0.06 | 0.59 | 0.81 | ||
| PSO-OBL-DIW-SCAC-PM | model | 99.96 | 19.97 | 100.03 | 200.15 | 99.86 | |
| misfit | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.14 | ||
| (·m) | h(m) | Fitness | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supposed model | 100.00 | 20.00 | 200.00 | 50.00 | 100.00 | 1000.00 | 500.00 | 1000.00 | 2000.00 | ||
| PSO | model | 100.11 | 20.34 | 207.38 | 49.67 | 98.51 | 1009.82 | 530 | 1019.5 | 1806.08 | |
| misfit | 0.11 | 1.68 | 3.69 | 0.67 | 1.49 | 0.98 | 6 | 1.95 | 9.7 | ||
| PSO-OBL | model | 99.79 | 20.21 | 200.52 | 48.3 | 100.81 | 973.19 | 483.79 | 968.88 | 1984.67 | |
| misfit | 0.21 | 1.04 | 0.26 | 3.39 | 0.81 | 2.68 | 3.24 | 3.11 | 0.77 | ||
| PSO-OBL-DIW | model | 99.53 | 19.96 | 195 | 50.4 | 98.03 | 1012.72 | 510.31 | 1008.9 | 1977.88 | |
| misfit | 0.47 | 0.22 | 2.5 | 0.79 | 1.97 | 1.27 | 2.06 | 0.89 | 1.11 | ||
| PSO-OBL-DIW-SCAC | model | 100 | 20.31 | 198.23 | 50.32 | 100.04 | 996.66 | 508.88 | 990.29 | 2021.54 | |
| misfit | 0 | 1.53 | 0.88 | 0.64 | 0.04 | 0.33 | 1.78 | 0.97 | 1.08 | ||
| PSO-OBL-DIW-SCAC-PM | model | 100.36 | 20.06 | 200.48 | 50.34 | 100.8 | 990.26 | 496.39 | 996.2 | 1988.36 | |
| misfit | 0.36 | 0.3 | 0.24 | 0.69 | 0.8 | 0.97 | 0.72 | 0.38 | 0.58 | ||
| (·m) | h(m) | Fitness | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supposed model | 100.00 | 20.00 | 100.00 | 200.00 | 100.00 | ||
| 5% noise | model | 100.42 | 19.98 | 100.8 | 100.25 | 197.8 | |
| misfit | 0.42 | 0.09 | 0.8 | 0.24 | 1.1 | ||
| 10% noise | model | 105.6 | 19.8 | 95.34 | 97.31 | 200.7 | |
| misfit | 5.6 | 0.98 | 4.66 | 2.69 | 0.36 | ||
| 15% noise | model | 109.44 | 19.4 | 96.43 | 96.72 | 189.6 | |
| misfit | 9.44 | 2.99 | 3.57 | 3.28 | 5.2 | ||
| (·m) | h(m) | Fitness | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supposed mode | 100.00 | 20.00 | 200.00 | 50.00 | 100.00 | 1000.00 | 500.00 | 1000.00 | 2000.00 | ||
| 5% noise | model | 99.47 | 19.98 | 203.61 | 48.63 | 102.5 | 1016.27 | 505.19 | 1017 | 2020.14 | 0.0241 |
| misfit | 0.53 | 0.12 | 1.81 | 2.73 | 2.5 | 1.63 | 1.038 | 1.7 | 1.01 | ||
| 10% noise | model | 99.54 | 20.09 | 199.34 | 54.21 | 94.39 | 1025.08 | 502.03 | 989.19 | 2091.82 | 0.0491 |
| misfit | 0.46 | 0.44 | 0.33 | 8.41 | 5.61 | 2.51 | 0.41 | 1.08 | 4.59 | ||
| 15% noise | model | 97.28 | 19.77 | 209.19 | 57.04 | 105.71 | 1050.71 | 549.93 | 1054.34 | 2058.1 | 0.077 |
| misfit | 2.71 | 1.13 | 4.6 | 14.08 | 5.71 | 5.07 | 9.99 | 5.43 | 2.91 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Gao, L.; Yu, N.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, E.; Feng, X. Memetic Strategy of Particle Swarm Optimization for One-Dimensional Magnetotelluric Inversions. Mathematics 2021, 9, 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9050519
Li R, Gao L, Yu N, Li J, Liu Y, Wang E, Feng X. Memetic Strategy of Particle Swarm Optimization for One-Dimensional Magnetotelluric Inversions. Mathematics. 2021; 9(5):519. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9050519
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ruiheng, Lei Gao, Nian Yu, Jianhua Li, Yang Liu, Enci Wang, and Xiao Feng. 2021. "Memetic Strategy of Particle Swarm Optimization for One-Dimensional Magnetotelluric Inversions" Mathematics 9, no. 5: 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9050519
APA StyleLi, R., Gao, L., Yu, N., Li, J., Liu, Y., Wang, E., & Feng, X. (2021). Memetic Strategy of Particle Swarm Optimization for One-Dimensional Magnetotelluric Inversions. Mathematics, 9(5), 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9050519






