A Multi-Stage GAN for Multi-Organ Chest X-ray Image Generation and Segmentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Synthetic Image Generation
2.2. Image-to-Image Translation
2.3. Medical Image Generation
2.4. Organ Segmentation
3. Chest X-ray Generation
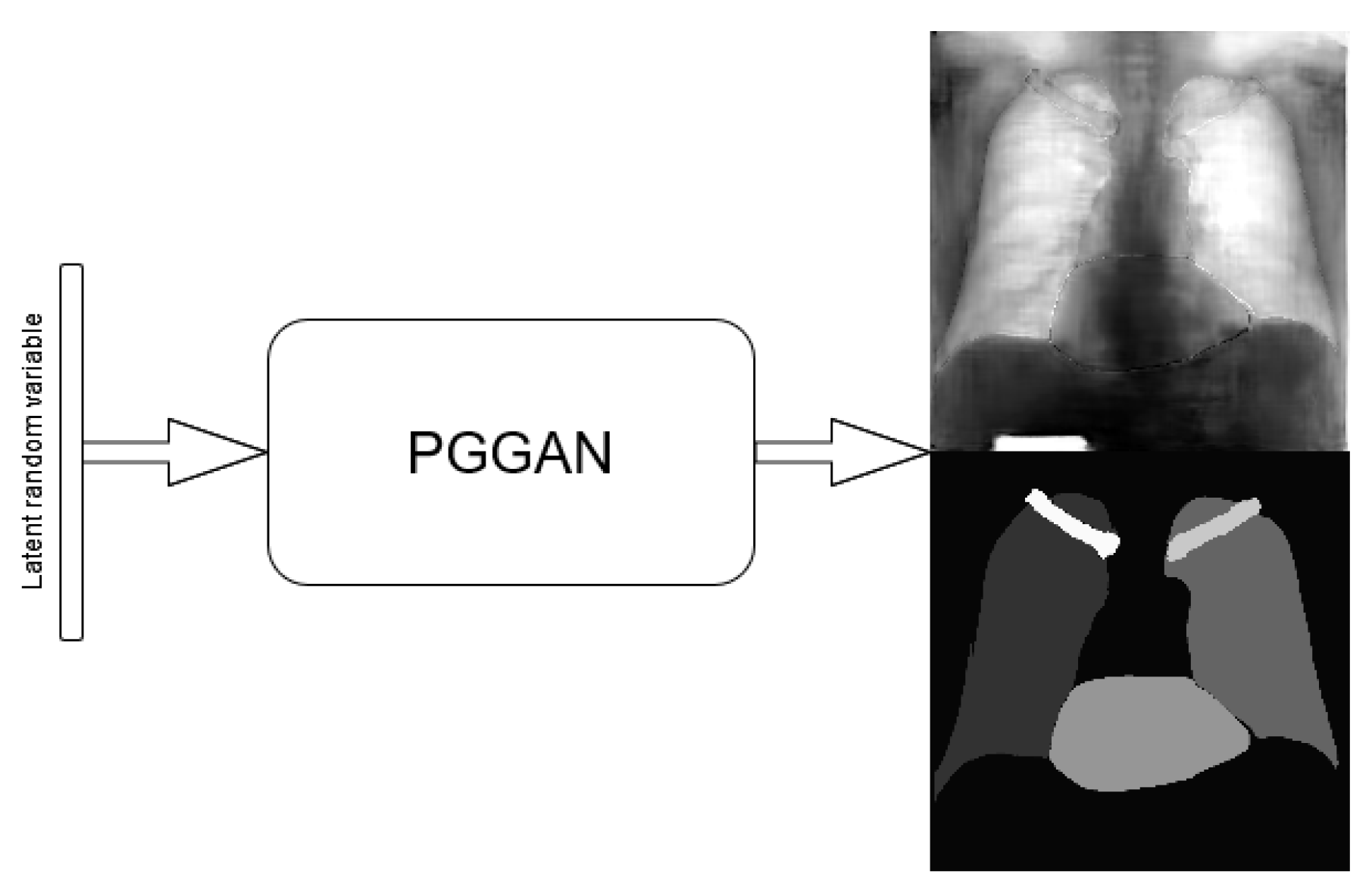
3.1. Single-Stage Method
3.2. Two-Stage Method
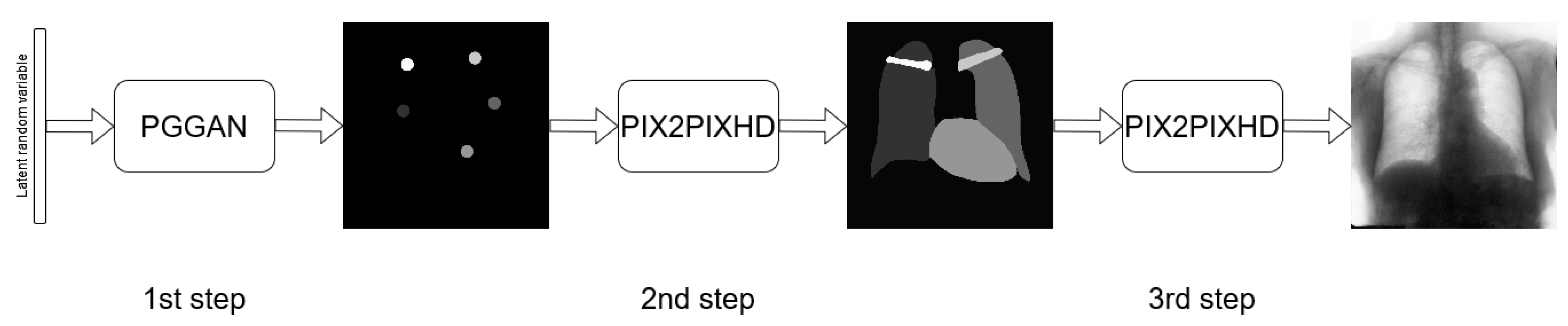
3.3. Three-Stage Method
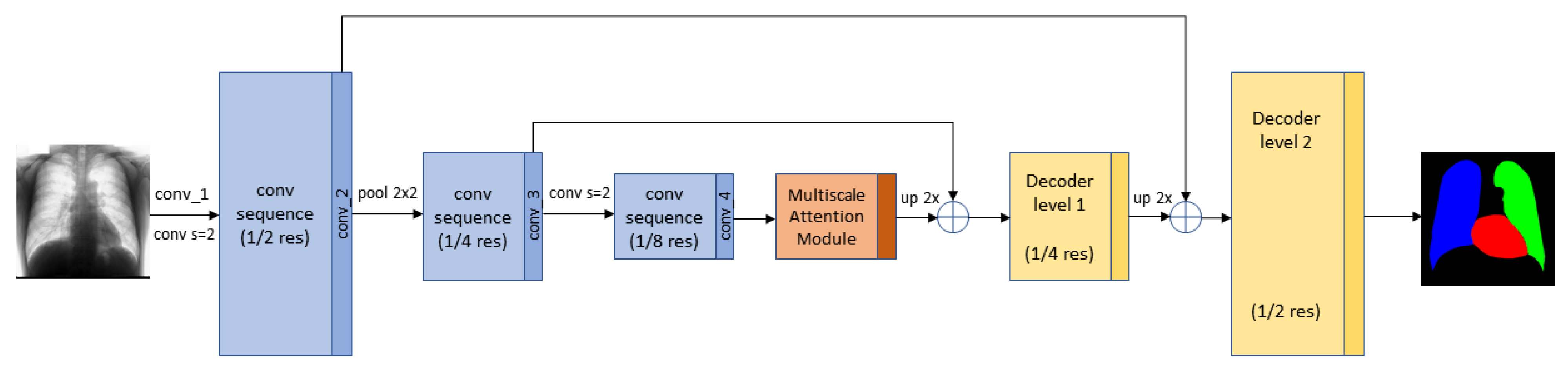
3.4. Segmentation Multiscale Attention Network
3.5. Training Details
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Quantitative Results
- REAL—only real images are used for training the semantic segmentation network;
- SINGLE-STAGE—the segmentation network uses the images generated by the single-stage method (Synth 1 in the tables) for training while real images are employed for fine-tuning (Finetune in the tables);
- TWO-STAGES—the images generated with the two-stage method are used to pre-train the segmentation network (Synth 2) while real images are used for fine-tuning;
- THREE-STAGE—the images generated with the three-stage method are used for training the segmentation network (Synth 3), while real images are employed for fine-tuning.
4.3. Comparison with Other Approaches
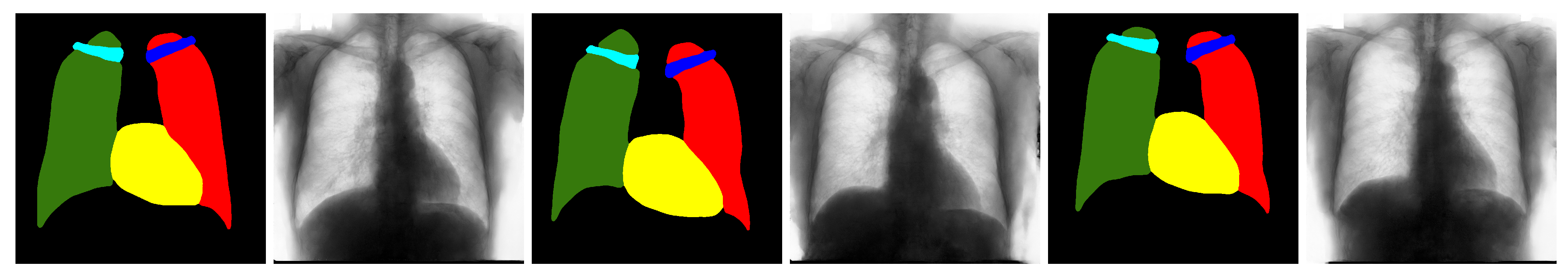
4.4. Qualitative Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mettler, F.A., Jr.; Huda, W.; Yoshizumi, T.T.; Mahesh, M. Effective doses in radiology and diagnostic nuclear medicine: A catalog. Radiology 2008, 248, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, E.; Hasan, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Lee, I.; Tamanna, T.; Parvez, M.Z. CoroDet: A deep learning based classification for COVID-19 detection using chest X-ray images. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 142, 110495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismael, A.M.; Şengür, A. Deep learning approaches for COVID-19 detection based on chest X-ray images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 164, 114054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.R.; Nayak, D.R.; Sinha, U.; Arora, V.; Pachori, R.B. Application of deep learning techniques for detection of COVID-19 cases using chest X-ray images: A comprehensive study. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 64, 102365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonechi, S.; Bianchini, M.; Bongini, P.; Ciano, G.; Giacomini, G.; Rosai, R.T.; Rossi, A.R.; Andreini, P. Fusion of Visual and Anamnestic Data for the Classification of Skin Lesions with Deep Learning. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Cristani, M., Prati, A., Lanz, O., Messelodi, S., Sebe, N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 11808, pp. 211–219. [Google Scholar]
- Van Ginneken, B.; Stegmann, M.B.; Loog, M. Segmentation of anatomical structures in chest radiographs using supervised methods: A comparative study on a public database. Med. Image Anal. 2006, 10, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, C.; Yao, D.; Shi, Y.; Song, Z. Computer-aided detection in chest radiography based on artificial intelligence: A survey. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teixeira, L.O.; Pereira, R.M.; Bertolini, D.; Oliveira, L.S.; Nanni, L.; Cavalcanti, G.D.; Costa, Y.M. Impact of lung segmentation on the diagnosis and explanation of COVID-19 in chest X-ray images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.09780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, T.; Aila, T.; Laine, S.; Lehtinen, J. Progressive growing of gans for improved quality, stability, and variation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.10196. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.C.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhu, J.Y.; Tao, A.; Kautz, J.; Catanzaro, B. High-resolution image synthesis and semantic manipulation with conditional gans. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8798–8807. [Google Scholar]
- Vapnik, V.N. Statistical Learning Theory; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Neyshabur, B.; Bhojanapalli, S.; Mcallester, D.; Srebro, N. Exploring Generalization in Deep Learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5947–5956. [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi, K.; Kaelbling, L.P.; Bengio, Y. Generalization in Deep Learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.05468. [Google Scholar]
- Bonechi, S.; Bianchini, M.; Scarselli, F.; Andreini, P. Weak supervision for generating pixel–level annotations in scene text segmentation. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 138, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreini, P.; Bonechi, S.; Bianchini, M.; Mecocci, A.; Scarselli, F.; Sodi, A. A two stage gan for high resolution retinal image generation and segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.12296. [Google Scholar]
- Andreini, P.; Bonechi, S.; Bianchini, M.; Mecocci, A.; Scarselli, F. Image generation by GAN and style transfer for agar plate image segmentation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 184, 105268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreini, P.; Bonechi, S.; Bianchini, M.; Mecocci, A.; Scarselli, F. A Deep Learning Approach to Bacterial Colony Segmentation. In Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning—ICANN 2018; Kůrková, V., Manolopoulos, Y., Hammer, B., Iliadis, L., Maglogiannis, I., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 522–533. [Google Scholar]
- Odena, A.; Olah, C.; Shlens, J. Conditional image synthesis with auxiliary classifier gans. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 2642–2651. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aila, T. A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 4401–4410. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aittala, M.; Hellsten, J.; Lehtinen, J.; Aila, T. Analyzing and improving the image quality of stylegan. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 8110–8119. [Google Scholar]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszár, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 22–25 July 2017; pp. 4681–4690. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, D.; Krahenbuhl, P.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Efros, A.A. Context encoders: Feature learning by inpainting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2536–2544. [Google Scholar]
- Gatys, L.A.; Ecker, A.S.; Bethge, M. A neural algorithm of artistic style. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1508.06576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.; Breuel, T.; Kautz, J. Unsupervised image-to-image translation networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.00848. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.Y.; Tuzel, O. Coupled generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.07536. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Tan, P.; Gong, M. Dualgan: Unsupervised dual learning for image-to-image translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2849–2857. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Koltun, V. Photographic image synthesis with cascaded refinement networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1511–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1784. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Zhang, R.; Pathak, D.; Darrell, T.; Efros, A.A.; Wang, O.; Shechtman, E. Toward multimodal image-to-image translation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.11586. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, X.; Chen, Q.; Jia, J.; Koltun, V. Semi-parametric image synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8808–8816. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.; Liu, M.Y.; Wang, T.C.; Zhu, J.Y. Semantic image synthesis with spatially-adaptive normalization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 2337–2346. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Wang, J.; Ding, X.; Huang, Y.; Paisley, J. An adversarial learning approach to medical image synthesis for lesion removal. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.10850. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Konukoglu, E. Unsupervised detection of lesions in brain mri using constrained adversarial auto-encoders. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.04972. [Google Scholar]
- Schlegl, T.; Seeböck, P.; Waldstein, S.M.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Langs, G. Unsupervised Anomaly Detection with Generative Adversarial Networks to Guide Marker Discovery. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.05921. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Jian, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S. Deform-GAN:An Unsupervised Learning Model for Deformable Registration. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.11430. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Cao, X.; Xue, Z.; Yap, P.; Shen, D. Adversarial Similarity Network for Evaluating Image Alignment in Deep Learning Based Registration. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2018—21st International Conference, Granada, Spain, 16–20 September 2018; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Frangi, A.F., Schnabel, J.A., Davatzikos, C., Alberola-López, C., Fichtinger, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Proceedings, Part I; Volume 11070, pp. 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, C.; Ozdemir, F.; Profanter, R.; Vishnevsky, V.; Konukoglu, E.; Goksel, O. Generative Adversarial Networks for MR-CT Deformable Image Registration. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.07349. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, X.; Walia, E.; Babyn, P. Unsupervised and semi-supervised learning with categorical generative adversarial networks assisted by wasserstein distance for dermoscopy image classification. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03700. [Google Scholar]
- Madani, A.; Moradi, M.; Karargyris, A.; Syeda-Mahmood, T. Semi-supervised learning with generative adversarial networks for chest X-ray classification with ability of data domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018; pp. 1038–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Lecouat, B.; Chang, K.; Foo, C.S.; Unnikrishnan, B.; Brown, J.M.; Zenati, H.; Beers, A.; Chandrasekhar, V.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Krishnaswamy, P. Semi-Supervised Deep Learning for Abnormality Classification in Retinal Images. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.07832. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Shen, L. cC-GAN: A robust transfer-learning framework for HEp-2 specimen image segmentation. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 14048–14058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhang, H.; Long, L.R.; Huang, X. Segan: Adversarial network with multi-scale l 1 loss for medical image segmentation. Neuroinformatics 2018, 16, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frid-Adar, M.; Diamant, I.; Klang, E.; Amitai, M.; Goldberger, J.; Greenspan, H. GAN-based synthetic medical image augmentation for increased CNN performance in liver lesion classification. Neurocomputing 2018, 321, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.; Tang, Y.; Eric, I.; Chang, C.; Fan, Y.; Lai, M.; Xu, Y. Unsupervised learning for cell-level visual representation in histopathology images with generative adversarial networks. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 23, 1316–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srivastav, D.; Bajpai, A.; Srivastava, P. Improved Classification for Pneumonia Detection using Transfer Learning with GAN based Synthetic Image Augmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 11th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence), Noida, India, 28–29 January 2021; pp. 433–437. [Google Scholar]
- Candemir, S.; Jaeger, S.; Palaniappan, K.; Musco, J.P.; Singh, R.K.; Xue, Z.; Karargyris, A.; Antani, S.; Thoma, G.; McDonald, C.J. Lung segmentation in chest radiographs using anatomical atlases with nonrigid registration. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2013, 33, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boykov, Y.; Funka-Lea, G. Graph cuts and efficient ND image segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2006, 70, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Candemir, S.; Akgül, Y.S. Statistical significance based graph cut regularization for medical image segmentation. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2011, 19, 957–972. [Google Scholar]
- Boykov, Y.; Jolly, M. Interactive graph cuts for optimal boundary and region segmentation of objects in nd images. In Proceedings of the Eighth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–14 July 2001; pp. 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yang, X.; Shen, D. Hierarchical lung field segmentation with joint shape and appearance sparse learning. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2014, 33, 1761–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibragimov, B.; Likar, B.; Pernuš, F.; Vrtovec, T. Accurate landmark-based segmentation by incorporating landmark misdetections. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 13th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Prague, Czech Republic, 13–16 April 2016; pp. 1072–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Novikov, A.A.; Lenis, D.; Major, D.; Hladůvka, J.; Wimmer, M.; Bühler, K. Fully Convolutional Architectures for Multiclass Segmentation in Chest Radiographs. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2018, 37, 1865–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C. Segmentation of multiple structures in chest radiographs using multi-task fully convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the Scandinavian Conference on Image Analysis, Tromsø, Norway, 12–14 June 2017; pp. 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, H.; dos Santos, J. Deep transfer learning for segmentation of anatomical structures in chest radiographs. In Proceedings of the 2018 31st SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images (SIBGRAPI), Paraná, Brazil, 29 October–1 November 2018; pp. 204–211. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, J.; Zhang, Y. Towards robust lung segmentation in chest radiographs with deep learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.12638. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, W.; Dong, N.; Wang, Z.; Liang, X.; Zhang, H.; Xing, E.P. Scan: Structure correcting adversarial network for organ segmentation in chest x-rays. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 263–273. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Savalle, P.A. Untangling local and global deformations in deep convolutional networks for image classification and sliding window detection. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.0296. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Shiraishi, J.; Katsuragawa, S.; Ikezoe, J.; Matsumoto, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Komatsu, K.i.; Matsui, M.; Fujita, H.; Kodera, Y.; Doi, K. Development of a digital image database for chest radiographs with and without a lung nodule: Receiver operating characteristic analysis of radiologists’ detection of pulmonary nodules. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 174, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Real | Three-Stage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synth 3 | Finetune | |||
| J | Left Lung | 96.10 | 95.30 | 96.22 |
| Heart | 90.78 | 87.25 | 91.11 | |
| Right Lung | 96.85 | 96.15 | 96.79 | |
| Average | 94.58 | 92.90 | 94.71 | |
| DSC | Left Lung | 98.01 | 97.6 | 98.07 |
| Heart | 95.17 | 93.19 | 95.35 | |
| Right Lung | 98.40 | 98.04 | 98.37 | |
| Average | 97.19 | 96.28 | 97.26 | |
| Real | Single-Stage | Two-Stage | Three-Stage | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synth 1 | Finetune | Synth 2 | Finetune | Synth 3 | Finetune | |||
| J | Left Lung | 93.70 | 55.59 | 74.11 | 94.91 | 94.4 | 94.96 | 95.29 |
| Heart | 85.50 | 0.07 | 37.47 | 86.98 | 85.21 | 87.27 | 87.47 | |
| Right Lung | 93.70 | 52.78 | 79.99 | 95.90 | 95.44 | 95.90 | 95.92 | |
| Average | 90.97 | 36.15 | 63.86 | 92.60 | 91.68 | 92.71 | 92.89 | |
| DSC | Left Lung | 96.75 | 71.46 | 85.13 | 97.39 | 97.12 | 97.42 | 97.59 |
| Heart | 92.18 | 0.13 | 54.51 | 93.04 | 92.02 | 93.20 | 93.32 | |
| Right Lung | 96.74 | 69.09 | 88.89 | 97.91 | 97.66 | 97.90 | 97.92 | |
| Average | 95.22 | 46.89 | 76.18 | 96.11 | 95.60 | 96.17 | 96.28 | |
| Method | Image Size | Augmentation | Evaluation Scheme | Lungs | Heart | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSC | J | DSC | J | ||||
| Human expert [6] | No | - | - | 94.6 | - | 87.8 | |
| U-Net [60] | No | 5-fold CV | - | 95.9 | - | 89.9 | |
| InvertedNet [58] | No | 3-fold CV | 97.4 | 95 | 93.7 | 88.2 | |
| SegNet [62] | No | 5-fold CV | 97.9 | 95.5 | 94.4 | 89.6 | |
| FCN [62] | No | 5-fold CV | 97.4 | 95 | 94.2 | 89.2 | |
| SCAN [58] | No | training/test split (209/38) | 97.3 | 94.7 | 92.7 | 86.6 | |
| Our three-stage method | Yes | official split | 98.2 | 96.5 | 95.36 | 91.1 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciano, G.; Andreini, P.; Mazzierli, T.; Bianchini, M.; Scarselli, F. A Multi-Stage GAN for Multi-Organ Chest X-ray Image Generation and Segmentation. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2896. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9222896
Ciano G, Andreini P, Mazzierli T, Bianchini M, Scarselli F. A Multi-Stage GAN for Multi-Organ Chest X-ray Image Generation and Segmentation. Mathematics. 2021; 9(22):2896. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9222896
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiano, Giorgio, Paolo Andreini, Tommaso Mazzierli, Monica Bianchini, and Franco Scarselli. 2021. "A Multi-Stage GAN for Multi-Organ Chest X-ray Image Generation and Segmentation" Mathematics 9, no. 22: 2896. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9222896
APA StyleCiano, G., Andreini, P., Mazzierli, T., Bianchini, M., & Scarselli, F. (2021). A Multi-Stage GAN for Multi-Organ Chest X-ray Image Generation and Segmentation. Mathematics, 9(22), 2896. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9222896






