Abstract
This study carried out a comparative analysis of indicators of electricity consumption and CO2 emissions for four-pole induction motors (IMs) of efficiency classes IE3 and IE4 with a rated power of 2.2–200 kW in a variable speed pump unit. In addition, innovative IE4 converter-fed synchronous reluctance motors (SynRMs) were evaluated. The comparison was derived from the manufacturer’s specifications for the power drive systems (PDSs) at various rotational speeds and loads. The results showed that the emission indicators for IE3 class motors were significantly worse compared with IE4 class motors for low power ratings, which make up the vast majority of electric motors in service. This justifies expanding the mandatory power range for IE4 motors to at least 7.5–200 kW or even 0.75–200 kW, as it will dramatically contribute to the achievement of the new ambitious goals for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. In addition, the operational advantages of IE4 SynRMs over IE4 IMs were demonstrated, such as their simpler design and manufacturing technology at a price comparable to that of IE3 IMs.
1. Introduction
Recently, the European Union has set new ambitious targets to achieve a climate-neutral economy by 2050 according to the European Green Deal plan [1]. In addition, the Council of Europe has raised the target for reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 from the 1990 level of 40% to 55% [2]. The main greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide (CO2). The most modern methods of electricity generation result in CO2 emissions. Therefore, the CO2 emissions can be limited by reducing the electricity consumption of the most significant consumers [3,4]. Electric motors are the largest consumers of electricity. Reducing their consumption will have a significant positive impact on climate change mitigation. According to [5], electric motors consume about half of all electricity in the European Union, which is about 2000 TWh per year; the number of electric motors is about 8 billion; and the volume of associated annual greenhouse gas emissions is 800 MtCO2-eq. It is also known that electric motors account for approximately 53% of all electric power generated worldwide, or 10,700 TWh per year [6]. As a result, ever more stringent legal requirements for the energy efficiency of mains [7] and frequency-converter-powered motors [8] are being adopted.
In accordance with the European Commission Regulations 2009 and 2014 [9] of 1 January 2017, in the European Union, every direct-on-line motor with a power rating of 0.75–375 kW must be at least as efficient as the IE3 energy efficiency class, and the converter-fed motors must not be less efficient than the IE2 class. In 2019, these requirements were updated: in accordance with European Commission Regulation 2019 [10] of 1 July 2021; both motors with the mains supply and converter-fed motors from 0.75 to 1000 kW with the number of poles from 2 to 8 must correspond to at least IE3 class. In many other countries, the IE3 efficiency class has already been adopted as mandatory for newly installed motors, as Table 1 suggests [11,12]. Moreover, in accordance with [10], the European Union plans to adopt the IE4 class as mandatory for motors with a power rating from 75 to 200 kW with the number of poles from 2 to 6.

Table 1.
Adopting national regulations for the mandatory IE3 class.
It is known that electrically driven fluid-processing mechanisms such as pumps, fans, and compressors use about 70% of electric power consumed by all electric motors [6]. In this regard, reducing the energy consumption of pumping units becomes critical. There are many ways to reduce the energy consumption of a pump unit. For instance, it is well known that the reduction of their energy consumption is possible with the help of variable-speed drives (VSDs) [13]. A further improvement in the energy efficiency of a pump unit equipped with a VSD can be achieved through the use of a more energy-efficient electric motor.
2. Literature Review and Novelty of the Study
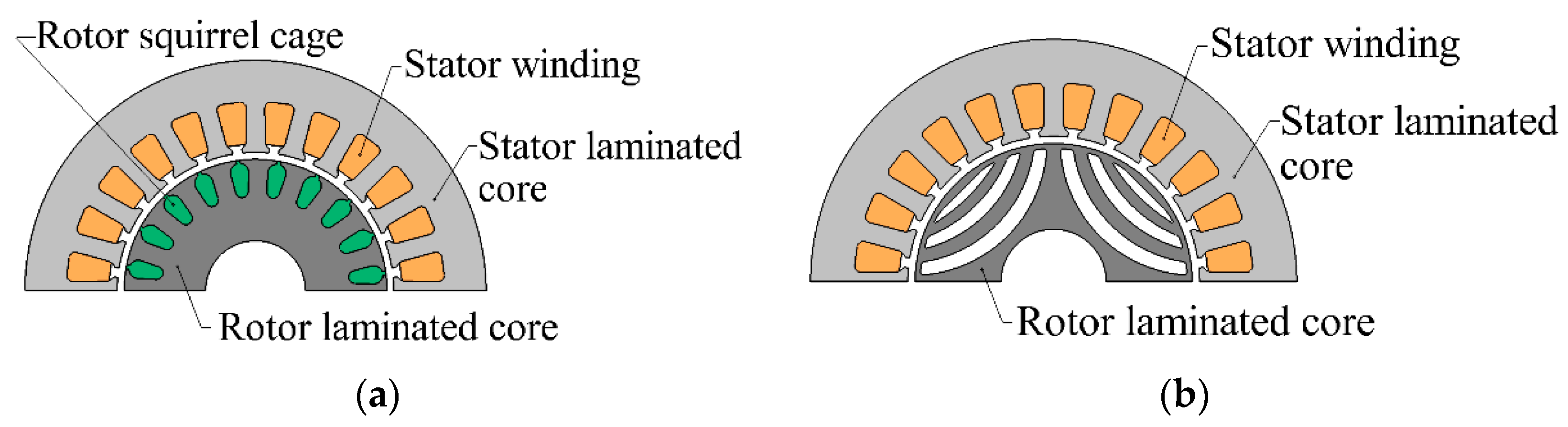
The energy efficiency of three-phase AC electric motors such as induction motors (IMs, Figure 1a), permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs), and synchronous reluctance motors (SynRMs, Figure 1b) has been extensively compared in previous studies.
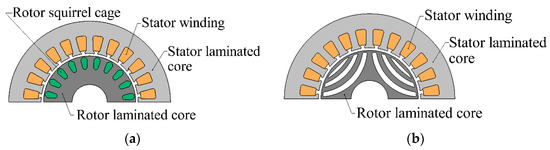
Figure 1.
Machine general design representations: (a) IM; (b) SynRM.
Some studies were not devoted to the analysis of pumps driven by VSDs, but to the analysis of pumps with motors powered directly from the mains. For instance, in [14], a comparison of the efficiency and power factor of the IE1-IE3 induction motors and a direct-on-line permanent magnet motor of the IE4 class was provided. It was concluded that direct-on-line PMSMs could be competitively capable with IMs in the power range of ≤15 kW due to significantly higher efficiency, despite their significantly higher cost. The article claimed that PMSMs cost 2.2–38 times more than IE2 IMs. However, it should be noted that the paper was published more than 7 years ago, motor manufacturers have further mastered PMSM production, and the market price of PMSMs has dropped significantly. In any case, it is shown that PMSMs can have a payback period of fewer than 3 years, even if their cost is 2.3 times higher than IE2 IMs.
In [15], the energy consumption of induction and direct-on-line permanent magnet motors of the IE3 and IE4 energy-efficiency classes and with a power rating of 2.2 kW was assessed for a pump application. A number of energy-efficiency metrics were compared for these motors, such as annual energy costs and lifetime energy costs, as well as cost savings. The study demonstrated that for maximum energy savings, it was necessary to ensure high motor efficiency not only under maximum flow conditions, but also under reduced flow conditions, which have the longest duration in the typical duty cycle of pumping systems with VSDs. In [16], the energy consumption and payback period of IE1 and IE2 induction motors with a rated power of 15 kW were compared. However, CO2 emissions were not evaluated in [12,13,14,15,16].
A number of papers were devoted to accessing the energy consumption of pump units controlled by VSDs. In [17], the dependencies of efficiency on speed and torque were determined for a pump drive based on 15 kW IMs of IE3 class, 15 and 18.5 kW SynRMs of IE4 class, and 15 kW PMSM of IE5 class. A typical pump load profile with a variable flow rate was considered. Annual energy indicators such as electricity consumption and cost, as well as electricity savings, were assessed. Paper [18] compared experimental data on the energy consumption of IE1 and IE2 IMs and an IE3 SynRM with a power rating of 45 kW in a pumping application. In [19], an IE2 IM and an IE5 SynRM with a power rating of 0.75 kW were compared in the case of a VSD pump application. In [20], an IM and SynRM with a power rating of 1.1 kW were considered in a pump unit with an approximately constant flow rate. The annual energy consumption, annual electricity costs, and annual cost savings were determined. In [21], efficiency maps for an 11 kW IM and SynRM were experimentally obtained and compared.
Paper [22] was devoted to the comparison of the service life of induction motors of various IE classes in various conditions; for example, with an asymmetric and distorted power supply. Paper [23] showed the effect of an overvoltage and undervoltage imbalance on the temperature and performance of IMs of the classes IE2, IE3, and IE4. Paper [24] presented issues related to motor protection, and compared a 7.5 kW IM and PMSM under various operating conditions: thermal steady state at full and partial load, starting, locked rotor, voltage unbalance, and undervoltage. Paper [25] developed and validated simple energy models for pump systems with a VSD drive. In [26], an estimate of energy savings for single pump systems for a storage fill application was developed using various control strategies.
All the previous studies mentioned above [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26] did not assess CO2 emissions. In addition, in [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24], the analyses were carried out only for one specific power rating of the pump and PDS, which did not allow the authors to draw conclusions about the energy savings, cost savings, and CO2 emissions for the wide range of power ratings commonly used in the industry.
Based on the literature overview presented above, it can be concluded that the energy efficiency metrics and CO2 emissions for IMs and SynRMs of the IE3 and IE4 classes over a wide range of power outputs in the application of variable speed pumps have not yet been investigated in previous studies.
This paper presents a comparative analysis of the main metrics of energy efficiency, cost savings, and CO2 emissions of PDSs with four-pole IMs of the IE3 and IE4 classes and SynRMs of the IE4 class with rated outputs of 2.2, 15, 75, 200 kW in a variable-speed pump unit. An analysis of PMSM metrics was not included in this study, as they are rarely used in variable speed pumps due to their higher cost compared to IMs and SynRMs. The main advantage of PMSMs is their reduced weight and dimensions, but this is not in demand in the considered application [20]. The authors believe that the converter-powered PMSMs are more suitable for use in applications such as traction and servo drives. The power ratings of 75 and 200 kW were selected for the analysis, as they are the upper and lower limits of the mandatory range of IE4 motors according to the directive [10].
For the comparative analysis, data from catalogues of pump manufacturers [27,28,29,30] and a typical flow-time diagram for the application under consideration were used. The pump characteristics from the catalogues were interpolated by the second-order polynomial, which was most often used in previous works [31,32,33]. The semianalytical pump model based on interpolation of catalogue data at the rated rotational speed is commonly used for pumping system analysis [15,33]. When analyzing pumping systems, methods of multicriteria optimization [34,35], statistical methods of reliability analysis [36], and neural networks [37] are also often used.
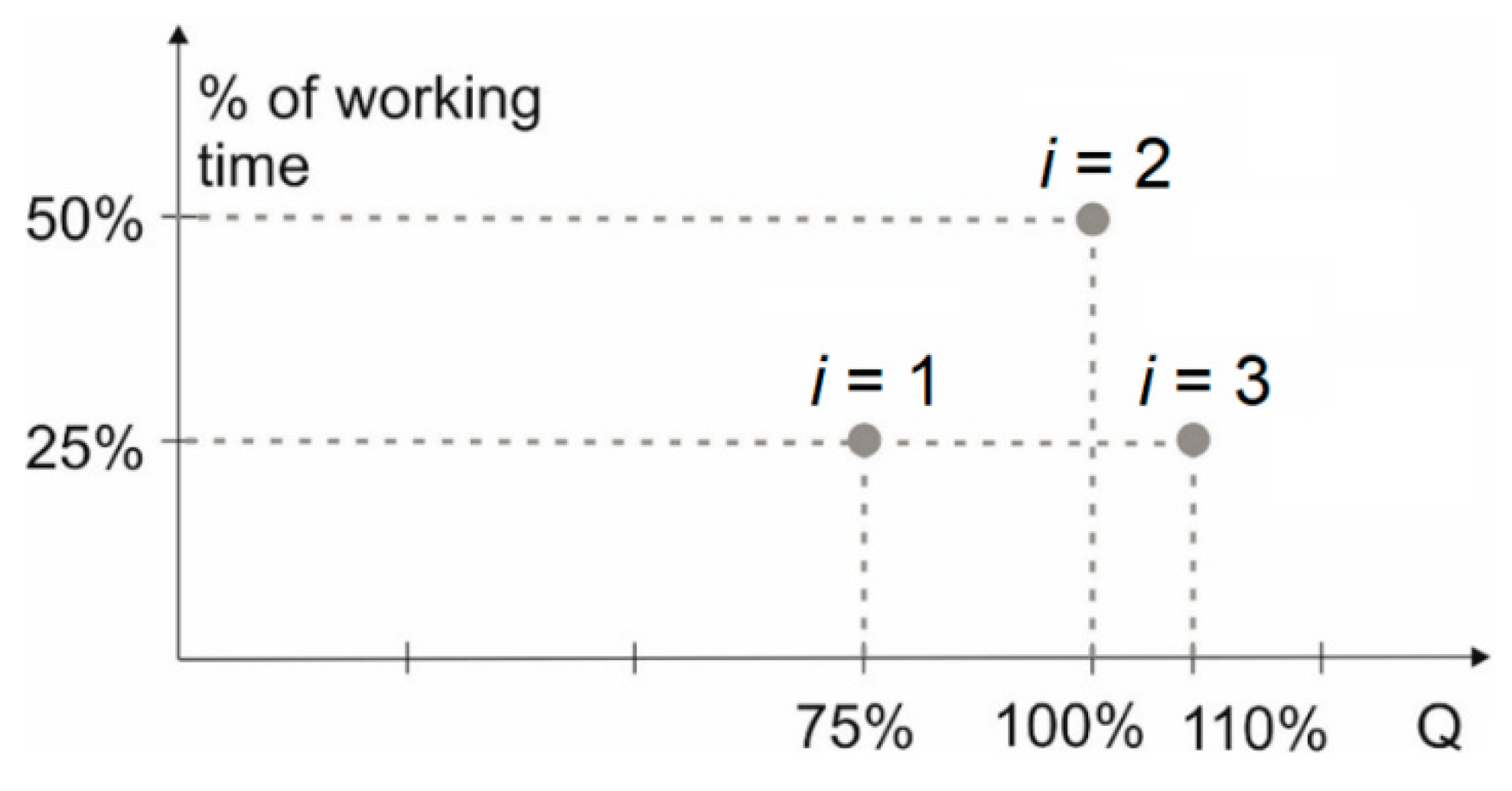
Typical pump operating conditions and flow-time diagrams are well described in the literature [38,39]. The flow-time diagram with the approximately constant flow rate given in [38,39] was selected for analysis as the most suitable for considered power range. As shown in Figure 2, it was considered: 75% flow for a quarter of the total duty cycle (below this case marked as i = 1, where i is the index of the duty cycle load point); 100% flow for half of the total duty cycle (i = 2); and 110% flow for another quarter of the total duty cycle (i = 3).
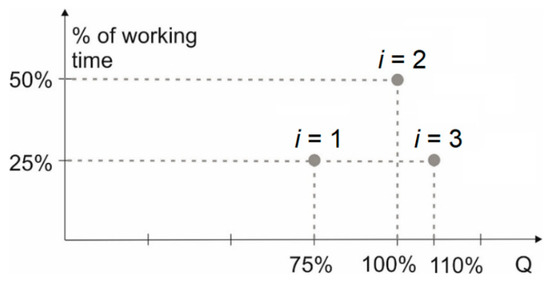
Figure 2.
Flow versus time for the constant flow pump units [38,39].
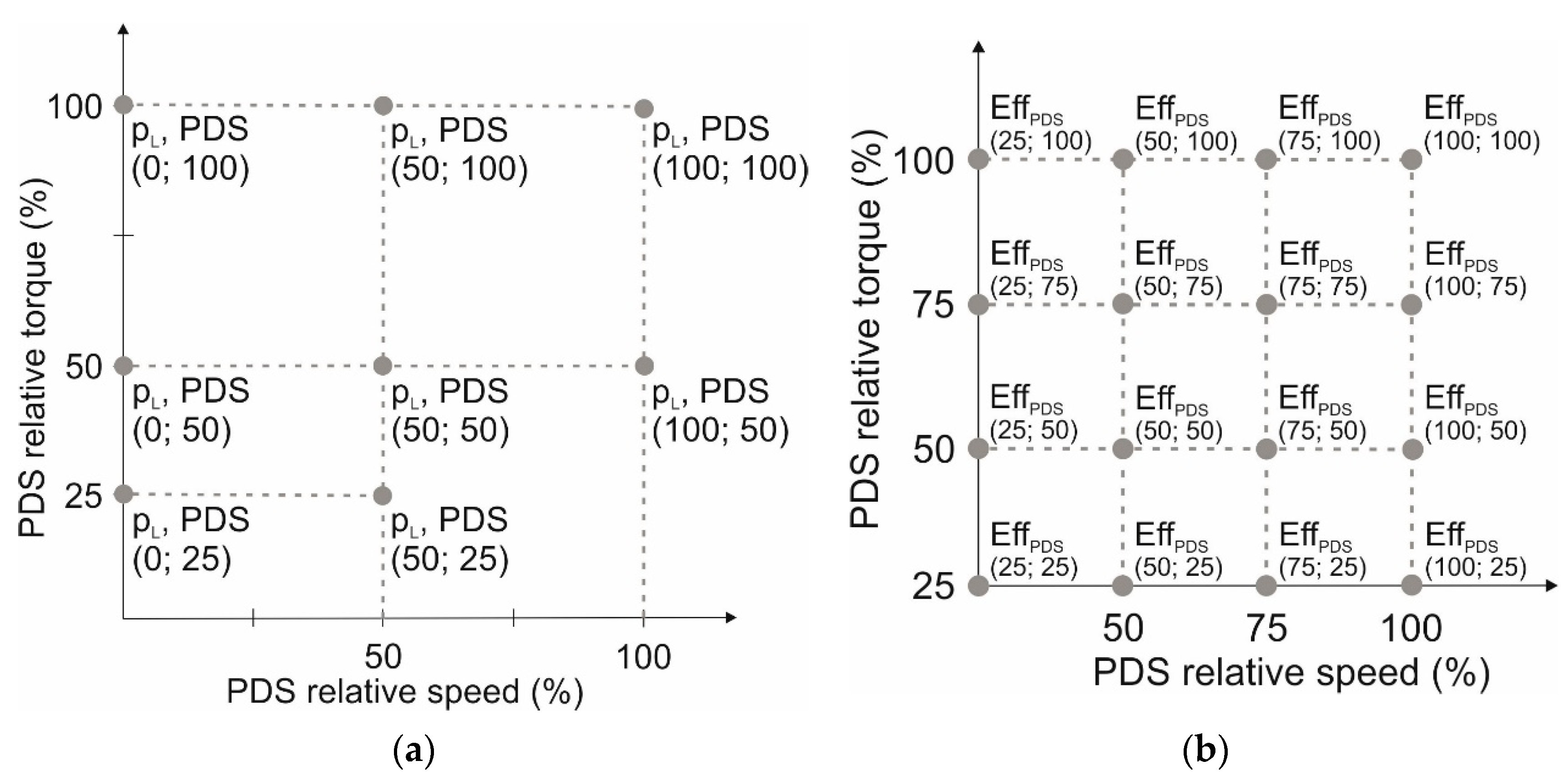
The PDS efficiency depends on the torque and rotational speed. We considered the PDS as a power drive system in terms of the standard IEC 61800-9-2: 2017 [40]. It consisted of a complete drive module (CDM) and an electric motor. The CDM included a frequency converter and protection devices. Nowadays, sensorless field-oriented control is commonly used as a method for controlling AC motors in applications that do not require high-precision control, such as pumps and fans [41]. According to [40], the PDS power loss measurement must be provided at eight loading points (Figure 3a). Values of the motor efficiency under variable speed operations and partial load conditions can be calculated, for example, according to [42], but this does not provide values for the entire PDS efficiency. Some manufacturers already provide such information; therefore, their experimental data were used for analysis as the most reliable source. Information on PDS loss at these eight points is available in the online application Sinasave [43]. Since the range of the power rating of the Siemens SynRM was limited to 45 kW, a PDS based on ABB’s SynRMs were considered for 75 and 200 kW ratings. Efficiency data for the ABB PDSs at 16 loading points (shown in Figure 3b) were provided in the manufacturer’s statements [44,45].
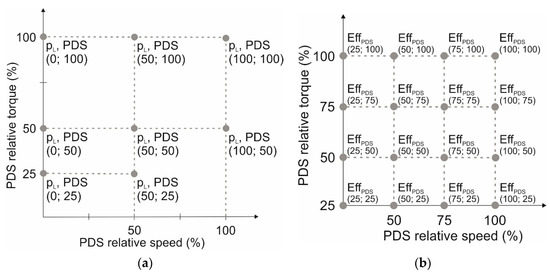
Figure 3.
Data formats for PDS efficiency interpolation: (a) Siemens (losses according to IEC 61800-9-2:2017 [40]; source: Sinasave software [43]); (b) ABB (efficiency; source: manufacturer’s statements [44,45]).
3. Evaluation of Pump and PDS Performances
Data from the Grundfos NB 50-200/210 [27], NB 80-315/305 [28], NB 150-400/375 [29], and NB 250-500/445 [30] pumps with the rated powers PRATE.pump consequently of 2.2, 15, 75, and 200 kW were considered in the analysis. All considered pumps had a rated rotational speed of 1450 rpm. The key parameters of these pumps at the best efficiency point (BEP) are specified in Table 2, where H is the pump head, Q is the pump flow rate, and η is the pump efficiency. Let us evaluate the power consumption of the PDS in combination with a pump of a certain power rating. First, a polynomial interpolation of the head-flow curve for the rated rotational speed was carried out according to Equation (1):

Table 2.
Nameplate data of pumps.
At nonrated rotational speed npump, according to the hydraulic affinity laws [33], which were applicable for the considered flow variation range (75…110%), the H-Q curve is described as:
The rotational speeds required to provide 75% and 110% of the rated flow were determined according to the reference control curve C(Q) [38], which was a straight line (3) passing through points (0, HBEP/2) and (QBEP, HBEP), where QBEP and HBEP are the flow and head of the pump in the BEP:
The rotational speed npump.i (in rpm) for each required value of a flow was determined by jointly solving Equations (2) and (3). Using the results of the pump operating performances (ni, Qi, Hi) and the manufacturer’s ISO efficiency curves [27,28,29,30], the pump efficiency ηpump.i was evaluated at each operating point considered (75, 100, and 110% of the rated flow). According to Equations (4) and (5), the motor mechanical power and torque were evaluated at i-th loading point:
where g = 9.81 m/s2; ρ = 1000 is the water density, kg/m3; and i = 1, 2, 3 (see Figure 1).
Pmech.i = ρ·g·Qi·Hi/ηpump.i.
Tpump.i = 9.55 Pmech.i/npump.i
The rated rotational speed nRATED.motor and rated torque TRATED.motor of the motors employed in the considered PDSs are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Catalogue data of motors.
In the case of the data format shown in Figure 3a, the loss of the m-th PDS at the i-th load point Ploss.i.m was calculated using two-dimensional interpolation of the initial loss points according to the methodology givenin [40]. In the case of the data format shown in Figure 3b, the traditional bilinear interpolation was used. The PDS efficiency ηPDS.i.m was determined using Equation (6):
ηPDS.i.m = Pmech.i/(Pmech.i + Ploss.i.m).
4. PDS Energy Consumption
The mechanical power obtained according to Equation (4) and the interpolated PDS efficiency were used to calculate the electrical power consumed from the grid (7):
P1.i.m = Pmech.i/ηPDS.i.m.
The annual electricity consumption of each PDS with the adopted flow-time diagram (Figure 2) of the pump unit was determined according to Equation (8):
where ti is the time of running the pump at each point of the flow-time diagram; and tΣ is the total duration of the daily operation of the pump (24 h).
The electricity cost was calculated using Equation (9):
where GT = EUR 0.1781/kWh is the electricity tariff for nonhousehold consumers in Germany in the first half of 2020, excluding VAT [46].
Cy.m = Ey.m·GT.
To compare the cost of energy consumed by different electric motors in a certain pump unit, the difference in the electricity cost relative to case m = 3 (PDS with the IE3 motor) was calculated as Equation (10):
Sy.3m = Cy.3 − Cy.m.
It is known that the service life of a pump unit is about 15–20 years, and the most significant contribution to the lifetime expenses of a pump is made by the cost of consumed electricity, which can exceed 50–60% of the total cost [47,48]. In this study, we assumed that the design life of the pump unit was n = 20 years.
The net present value (NPV) for the lifetime energy cost was calculated according to Equation (11):
where p = 0.02 is the assumed annual inflation rate; and y = 0.04 is the interest rate [47,48].
CLCCen.m = Cy.m/(1 + (y − p))n,
The lifetime cost savings of PDSs with different IE4 motors (m = 1, 2) compared to a PDS with IE3 motors (m = 3) was evaluated as:
ΔCLCCen.3m = CLCCen.3 − CLCCen.m.
5. Evaluation of CO2 Emission Intensity
The yearly CO2 emission intensity was evaluated according to Equation (13):
where EFE = 418.8 g/kW·h is the CO2 emission factor for electricity consumption for Germany [49].
CDEy.m = Ey.m·EFE.
The yearly avoided CO2 emissions were estimated as:
ΔCDEy.3m = CDEy.3 − CDEy.m.
The emission intensity estimation using Equations (13) and (14) did not take into account the total volume of emissions. CO2 emissions arise from the consumption of primary energy sources in power plants. Therefore, to assess the CO2 emissions associated with the electricity calculated by Equation (8), it was necessary to use the primary energy factor (PEF) characterizing the average efficiency of conversion of primary energy into the final one [50,51]. Therefore, the annual emission including PEF CDE*y.m and the corresponding avoided CO2 emissions ΔCDE*y.3m were evaluated as the follows:
where PEF = 2.2 is the primary energy factor evaluated.
CDE*y.m = CDEy.m PEF.
ΔCDE*y.3m = CDE*y.3 − CDE*y.m.
A default PEF value of 2.5 should be applied in accordance with directive 2012/27/EU [50]. However, recent studies indicated the need to revise this factor to 1.8–2.2 [52,53]. Based on this, PEF = 2.2 was adopted in this study.
6. Results and Discussions
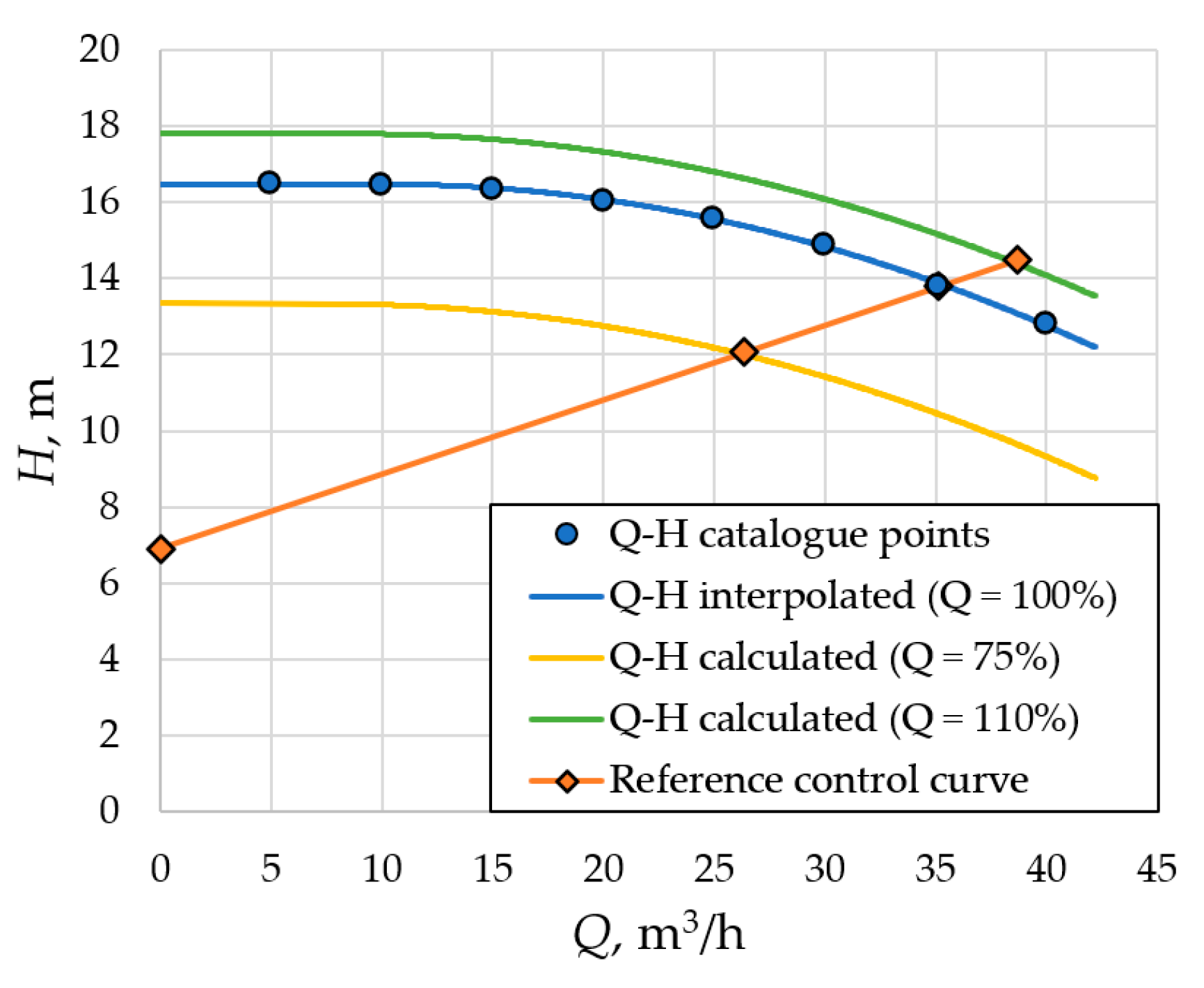
Figure 4 shows the catalogue points of the pump head-flow characteristic calculated according to Equation (2) head-flow curves and reference control curve for the 2.2 kW pump as an example. Table 4 shows the calculation results for the pump performances during the operating cycle. Table 5 shows the interpolated PDS efficiency at the pump operating points indicated in Figure 2 for the four power ratings considered.
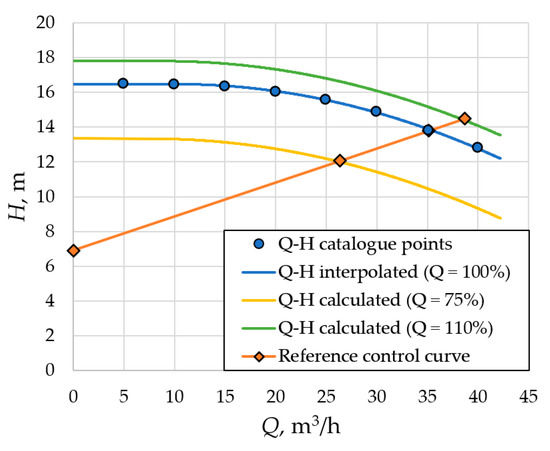
Figure 4.
Calculated head-flow curves of the pump at 75, 100, and 110% flow and initial points of the 2.2 kW pump, and reference control curve.

Table 4.
Performances of the pumps of different power ratings during the operating cycle.

Table 5.
Interpolated efficiencies of selected power drive systems.
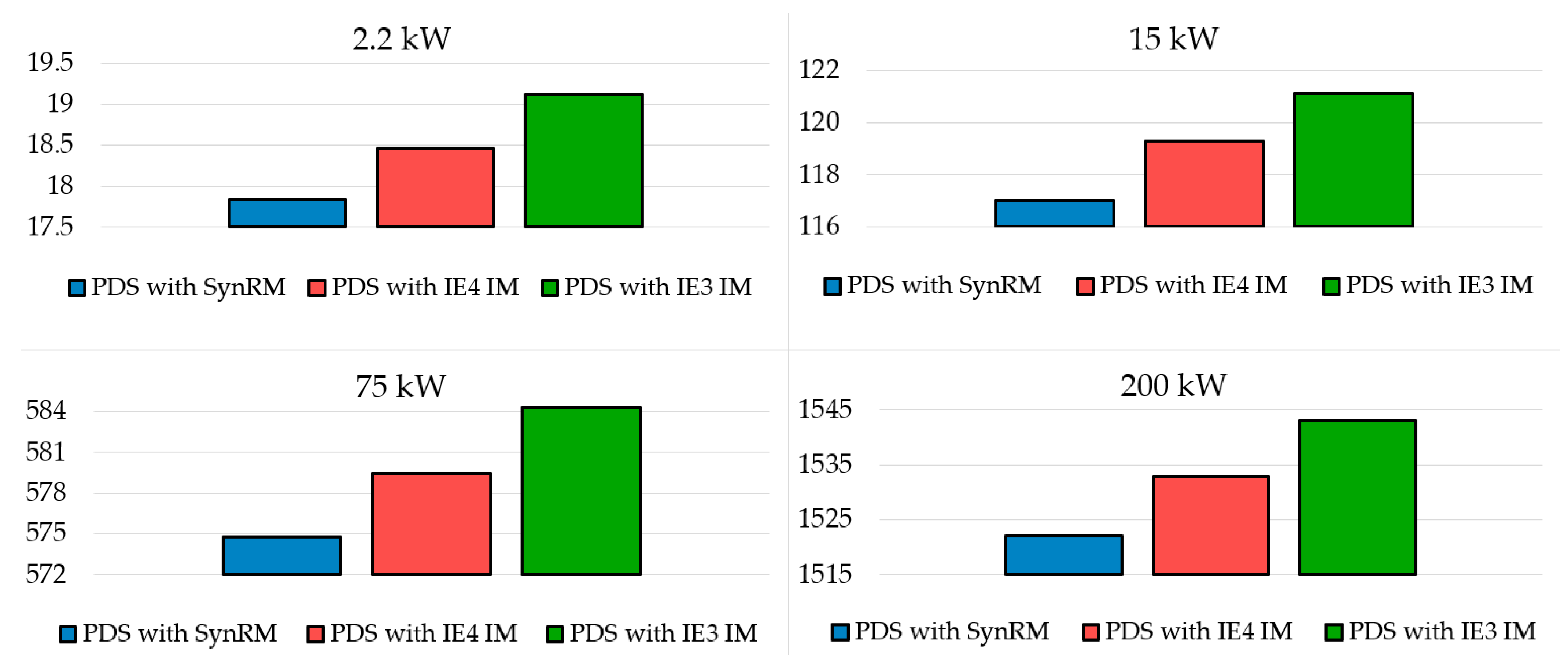
Table 6 summarizes the results of calculations using Equations (8)–(12). The annual energy consumption is shown in Figure 5. According to these results, the PDS based on SynRM demonstrated the lowest annual electricity consumption and the highest cost savings. Based on the annual Sy.3m and lifetime savings ΔCLCCen.3m, replacing the IE3 IM with the IE4 SynRM provided approximately 2 times more savings than replacing it with the IE4 IM for all power ratings considered. Table 7 summarizes the results for the CO2 emissions according to Equations (13)–(16). The results for CO2 emissions in Table 7 showed similar patterns; i.e., the PDS with IE4 SynRM allowed the highest avoided annual emissions: ΔCDEy.3m and ΔCDE*y.3m.

Table 6.
Results for the PDS electricity costs and cost savings.
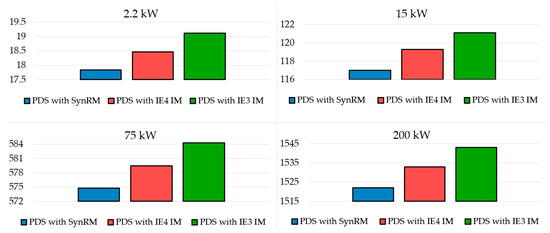
Figure 5.
Annual energy consumption (MW·h).

Table 7.
Results of calculating the annual CO2 emissions.
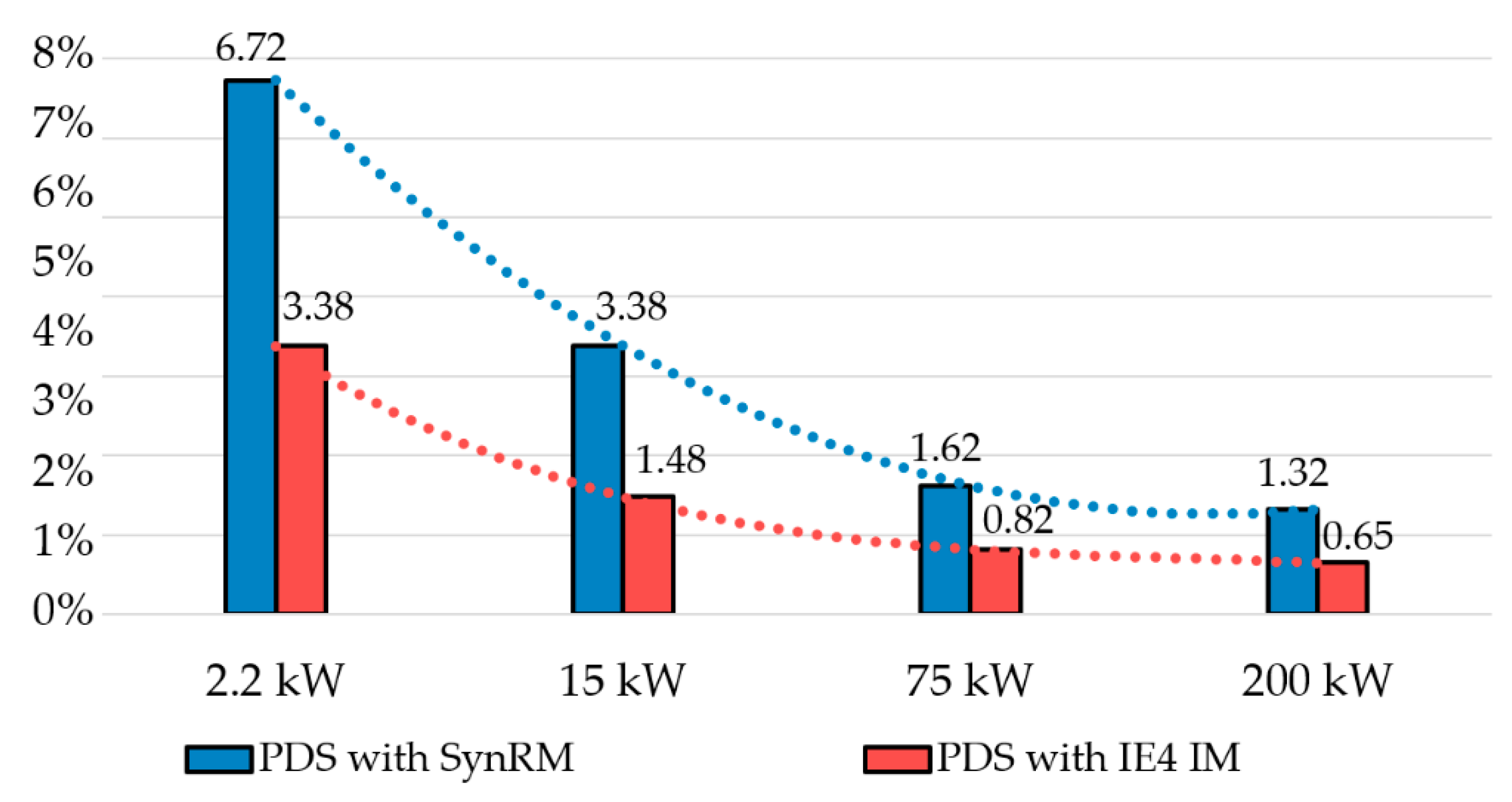
The percentages shown in Table 8 and Figure 6 were the same for the cost savings and avoided CO2 emissions.

Table 8.
Cost savings (avoided CO2 emissions, in%) relative to the PDS with an IE3 motor.
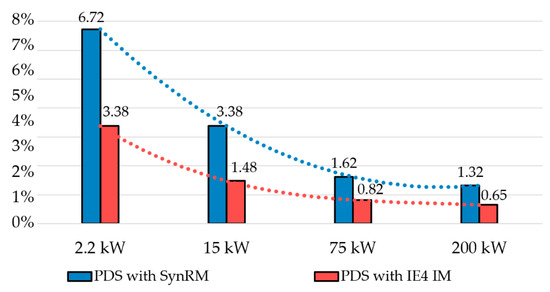
Figure 6.
Cost savings/avoided CO2 emissions (in %) for an output power range of 2.2–200 kW relative to the PDS with an IE3 motor.
As seen in Figure 6, the relative savings were about 5 times greater for low-power motors compared to high-power motors. Nevertheless, according to [54], for Europe, in the power range of 0.75–200 kW, the share of motors with rated power from 0.75 (1 hp) to 7.5 kW (10 hp) is 79.1%, and the share of motors with rated power from 7.5 (10 hp) to 75 kW (100 hp) is only 19.8%. Therefore, to fulfill the tasks of the European Green Deal, it is recommended to legislatively expand the mandatory power range for electric motors of the IE4 class to at least 7.5–200 kW, or even to 0.75–200 kW. However, the authors are aware that in the range of 0.75–7.5 kW, it is more difficult to achieve the IE4 class for induction motors [55].
Using the results shown in Table 8, the interpolation polynomials (17) for the PDS with SynRM and (18) for the PDS with IE4 IM were obtained, which can be used to calculate the cost savings, CS, % (avoided CO2 emissions taking into account the final energy, ΔCDE, %; avoided CO2 emissions taking into account the primary energy, ΔCDE*, %) for intermediate power ratings not specified in Table 8, without carrying out a detailed calculation using Equations (1)–(16).
CS SynRM = −0.02·P3 + 0.91·P2 − 5.93·P + 11.76,
CS IE4 IM = −0.125·P3 + 1.37·P2 − 5.135·P + 7.27.
7. Payback Period Assessment
Studies [56,57] described SynRMs of the IE4 class designed using the same stator as an IE3 IM. Based on this, the cost of the IE4 SynRM was taken to be equal to the cost of the IE3 IM. At the same time, the SynRM has a simpler rotor design (Figure 1), is more reliable, and requires fewer active materials for their production [58,59]. The SynRM was characterized by higher efficiencies at lower loads than IMs [55,59]. The IE4 energy efficiency class (and even IE5) for SynRM can be achieved relatively easily, without the use of expensive solutions typical for the class IE4 of IMs [55]: the use of copper conductors in the rotor, the use of higher-quality electrical steel, and an increase in the mass and volume of active materials, which, in turn, leads to an increase in the dimensions of the motor and, in some cases, the transition to the next frame size for the same rated power. Thus, the SynRM can be expected to cost no more than the IE3 class IM in mass production.
The disadvantages of SynRMs are that they have a slightly lower power factor than IMs [59], and therefore a slightly higher rated current. The current values of the considered electric motors, taken from the manufacturers’ catalogues, are shown in Table 9. The rated currents of the IE3 IM and the IE4 IM of the same power rating were approximately the same. The rated current of the IE4 SynRM was 15–33% higher than the IE3 IM, which was higher than the overcurrent limit usually provided by frequency converter manufacturers. Due to this, it is required to use a more expensive converter with a higher power rating when using a SynRM, in comparison with an IM. The cost of the converter turned out to be 10–40% higher, which led to an increase in the cost of the PDS.

Table 9.
Motor payback period.
Let us calculate the payback period of using a PDS based on a SynRM and IE4 IM instead of PDS based on IE3 IM, for two cases, according to Formulas (19) and (20), where Ciic.m is the turnkey costs of the m-th PDS, which are presented in Table 9. Formula (19) describes the calculation of the payback period for the case of a newly commissioned pump unit. Replacing the motor in a pump unit already put into operation is implied when calculating according to Formula (20):
Tm1 = (Ciic.m − Ciic.3)/Sy.3m,
Tm2 = Ciic.m/Sy.3m.
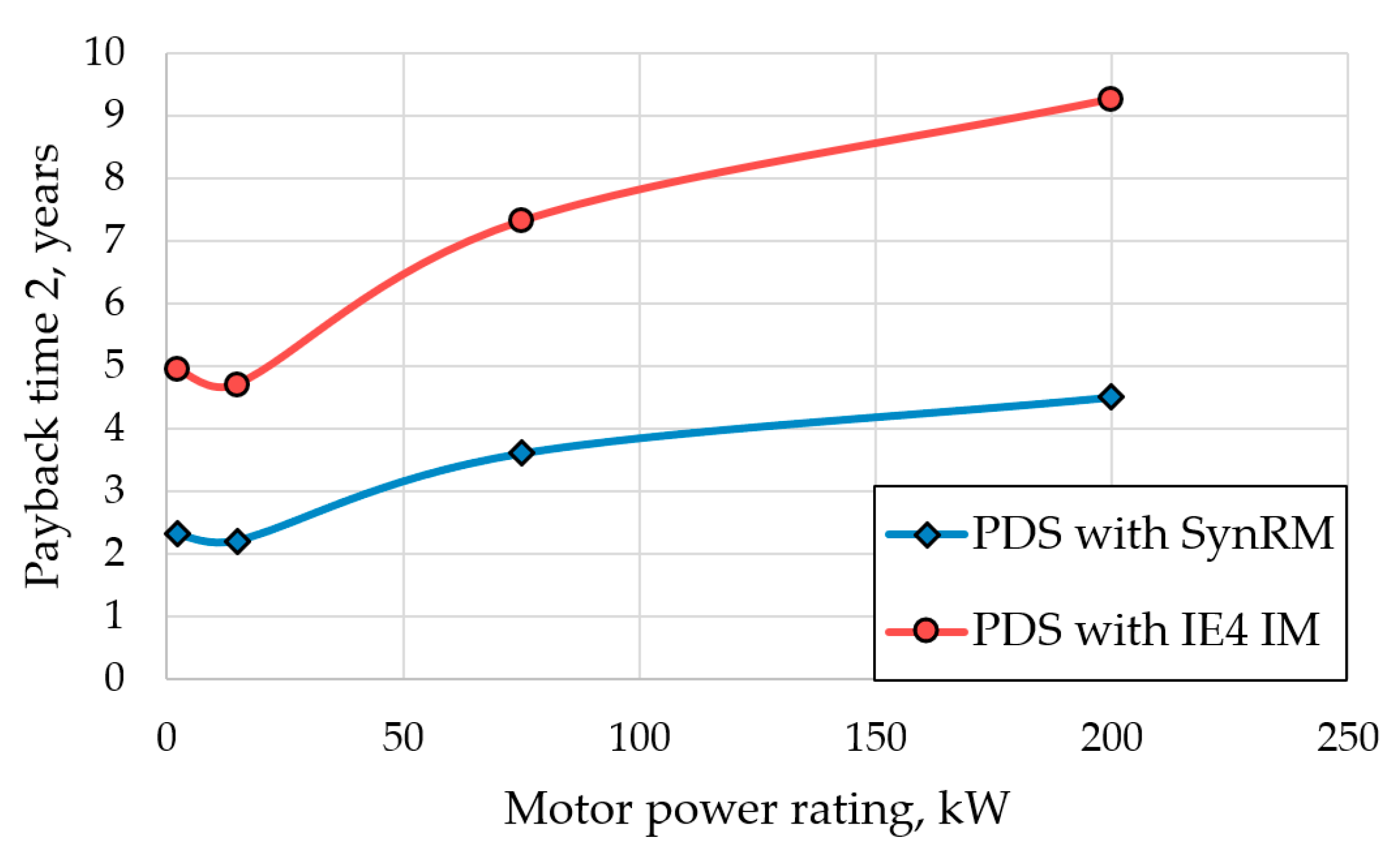
To evaluate the cost of frequency converters and IE3 class IMs, their market prices were taken from manufacturers’ websites [58,60]. It was assumed that the cost of the SynRM was the same as the cost of the IE3 IM. An analysis of recent studies [5,61,62,63] and available market prices showed that the difference in the turnkey price of motors of related energy efficiency classes was usually 15–30%. In this paper, it was assumed that the cost of the IE4 class IMs was 22.5% higher than the cost of the IE3 class IMs. Table 9 shows the assumed costs. For the considered power range, the cost of the frequency converter, as shown in Table 9, was 60–140% of the motor cost, and the difference in the price of the PDS based on SynRM and IM was in the range of −8–+5%. Based on the results in Table 9, it can be concluded that the PDSs with SynRM and IE4 IM had similar initial costs. However, despite this, the payback period of the SynRM turned out to be significantly shorter (Figure 7) due to the greater energy savings, Sy.3m.
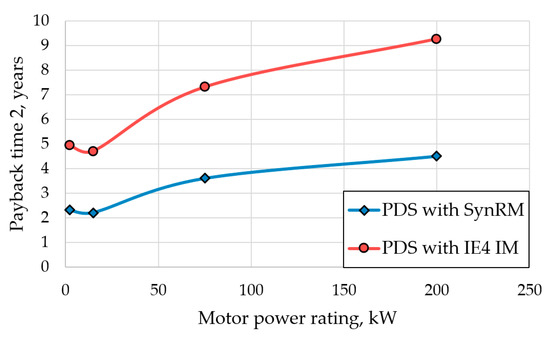
Figure 7.
Payback time versus motor power rating.
8. Conclusions
This study provided a comparative assessment of metrics of energy consumption and CO2 emission for various PDSs with a rated power in the range of 2.2–200 kW. The converter-fed PDSs with the IE3 IM, IE4 IM, and SynRM are considered. The analysis was based on extensive data from the technical specifications of the PDS [43,44,45] and pump manufacturers [27,28,29,30]. These data were processed using mathematical methods of polynomial and bilinear interpolation, regression, and a semianalytical model of a variable-speed pump unit. As a result of the analysis, the interpolating polynomials were constructed to evaluate the metrics of interest for any PDS from the entire considered power range.
This study showed that to achieve the goals of reducing greenhouse gas emissions, it is extremely important to use electric motors of higher energy-efficiency classes. The state of the art (IMs and SynRMs of the IE4 class) already allows effectively implementing the requirements of the European Commission [10], prescribing the mandatory use of IE4 class motors in the rated power range of 75–200 kW from 1 July 2023. The results showed that when replacing IE3 motors with IE4 motors, the largest reduction in CO2 emissions was shown by the low-power motors, which make up the vast majority of electric motors in service [54]. This justifies the mandatory use of IE4 motors for lower power ratings.
In addition, it was shown that the SynRMs of the IE4 class demonstrated significantly better indicators of reduction of CO2 emissions and energy savings than the IMs of the same energy-efficiency class. Moreover, SynRMs have several operational advantages, such as their simpler design and manufacturing technology, at a price comparable to the price of the IE3 IMs. As a result, when replacing an IE IM, the energy savings of an IE4 SynRM will be approximately 2 times higher, and the payback period will be approximately half that of the IE4 IM for the entire considered power range. At the same time, the influence of the SynRM’s lower power factor compared to IMs and the associated need for frequency converters with a higher power rating does not significantly affect the payback period.
According to the results of this study, in order to achieve the goals of the European Green Deal [1,2], it is recommended to legislatively expand the mandatory power range of electric motors of IE4 class from 75–200 kW to at least 7.5–200 kW.
In future work, the potential for significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions in other mass applications of electric machines will be investigated. For example, fans and compressors are in principle similar to pumps, but have different typical operating conditions. The subject of future work may be an assessment of the energy-saving potential, payback periods, and CO2 emissions for various typical operating profiles of such equipment. Moreover, a fast-growing quantity of electric vehicles also consumes an increasing share of electricity, which makes analysis in this area relevant.
In addition, on the basis of the developed model, it is possible to optimize the operating points of multipump units, which include pumps operating in parallel on the same pipeline.
Author Contributions
Conceptual approach, V.D. and V.P.; data curation V.D. and V.G.; calculations and modeling, V.G. and V.K.; writing of original draft, V.D., V.G., V.K. and V.P.; visualization, V.G. and V.K.; review and editing, V.D., V.G., V.K. and V.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was partially supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (through the basic part of the government mandate, Project No. FEUZ 2020-0060).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
In this article, for the analysis, the technical specifications of the manufacturers of electric motors and pumps were used [27,28,29,30,43,44,45].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- The European Green Deal. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/strategy/priorities-2019-2024/european-green-deal_en (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- European Council Meeting (10 and 11 December 2020)—Conclusions. EUCO 22/20 CO EUR 17 CONCL 8. Available online: https://www.consilium.europa.eu/media/47296/1011-12-20-euco-conclusions-en.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Chodakowska, E.; Nazarko, J. Assessing the performance of sustainable development goals of EU countries: Hard and soft data integration. Energies 2020, 13, 3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siksnelyte, I.; Zavadskas, E.K. Achievements of the European Union countries in seeking a sustainable electricity sector. Energies 2019, 12, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Commission Staff Working Document Impact Assessment Accompanying the Document Commission Regulation (EU) 2019/1781 Laying Down Ecodesign Requirements for Electric Motors and Variable Speed Drives Pursuant to Directive 2009/125/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council and Repealing Commission Regulation (EC) No 640/2009. SWD/2019/0343 Final. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/transparency/regdoc/rep/10102/2019/EN/SWD-2019-343-F1-EN-MAIN-PART-1.PDF (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Van Werkhoven, M.; Werle, R.; Brunner, C.U. 4E EMSA Policy guidelines for motor driven units: Pumps, fans and compressors. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Energy Efficiency in Motor Driven System (EEMODS’ 2017), Rome, Italy, 6–8 September 2017; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2018. Available online: http://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/bitstream/JRC110714/eemods_2017_proceedings_v11(1).pdf (accessed on 23 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Rotating Electrical Machines—Part 30-1: Efficiency Classes of Line Operated AC Motors (IE Code). IEC 60034-30-1/ Ed. 1; IEC: 2014-03. Available online: https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/136 (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Rotating Electrical Machines—Part 30-2: Efficiency Classes of Variable Speed AC Motors (IE-Code) IEC 60034-30-2/ IEC: 2016-12. Available online: https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/30830 (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- European Commission Regulation (EC), No. 640/2009 Implementing Directive 2005/32/ EC of the European Parliament and of the Council with Regard to Ecodesign Requirements for Electric Motors, (2009), Amended by Commission Regulation (EU) No 4/2014 of January 6, 2014. Document 32014R0004. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32014R0004 (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2019/1781 of 1 October 2019 Laying Down Ecodesign Requirements for Electric Motors and Variable Speed Drives Pursuant to Directive 2009/125/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, Amending Regulation (EC) No 641/2009 with Regard to Ecodesign Requirements for Glandless Standalone Circulators and Glandless Circulators Integrated in Products and Repealing Commission Regulation (EC) No 640/2009. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32019R1781&from=EN (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Efficiency Regulations for Motors: International Norms. NORD DRIVESYSTEMS Group, S4700 Part. No. 6069202 / 4019. Available online: https://www.nord.com/cms/media/documents/bw/S4700_6069202_4019_Screen.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- How International Standards for Electric Motor Systems Support Policies of Countries Using These in Their Regulations. Available online: https://www.iec.ch/government-regulators/electric-motors (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Shankar, V.K.A.; Umashankar, S.; Paramasivam, S.; Hanigovszki, N. A comprehensive review on energy efficiency enhancement initiatives in centrifugal pumping system. Appl. Energy 2016, 181, 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Ferreira, F.; Duarte, A. Technical and economical considerations on super high-efficiency three-phase motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 1274–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goman, V.; Oshurbekov, S.; Kazakbaev, V.; Prakht, V.; Dmitrievskii, V. Energy Efficiency analysis of fixed-speed pump drives with various types of motors. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oshurbekov, S.; Kazakbaev, V.; Prakht, V.; Dmitrievskii, V. Comparative study of energy consumption of 15 kW induction motors of IE1 and IE2 efficiency classes in pump applications. In Proceedings of the XI International Conference on Electrical Power Drive Systems (ICEPDS), Saint-Petersburg, Russia, 4–7 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahonen, T.; Orozco, S.M.; Ahola, J.; Tolvanen, J. Effect of electric motor efficiency and sizing on the energy efficiency in pumping systems. In Proceedings of the 18th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’16 ECCE Europe), Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–8 September 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rhyn, P.; Pretorius, J.H.C. Utilising high and premium efficiency three phase motors with VFDs in a public water supply system. In Proceedings of the IEEE 5th International Conference on Power Engineering, Energy and Electrical Drives (POWERENG), Riga, Latvia, 11–13 May 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safin, N.; Kazakbaev, V.; Prakht, V.; Dmitrievskii, V. Calculation of the efficiency and power consumption of induction IE2 and synchronous reluctance IE5 electric drives in the pump application based on the passport specification according to the IEC 60034-30-2. In Proceedings of the 25th International Workshop on Electric Drives: Optimization in Control of Electric Drives (IWED), Moscow, Russia, 31 January–2 February 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakbaev, V.; Prakht, V.; Dmitrievskii, V.; Ibrahim, M.N.; Oshurbekov, S.; Sarapulov, S. Efficiency analysis of low electric power drives employing induction and synchronous reluctance motors in pump applications. Energies 2019, 12, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rassolkin, A.; Heidari, H.; Kallaste, A.; Vaimann, T.; Acedo, J.P.; Romero-Cadaval, E. Efficiency map comparison of induction and synchronous reluctance motors. In Proceedings of the 26th International Workshop on Electric Drives: Improvement in Efficiency of Electric Drives (IWED), Moscow, Russia, 30 January–2 February 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.J.T.E.; Baoming, G.; De Almeida, A.T. Reliability and operation of high-efficiency induction motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 4628–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabora, J.M.; De Lima Tostes, M.E.; De Matos, E.O.; Bezerra, U.H.; Soares, T.M.; De Albuquerque, B.S. Assessing voltage unbalance conditions in IE2, IE3 and IE4 classes induction motors. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 186725–186739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.J.T.; Leprettre, B.; De Almeida, A.T. Comparison of protection requirements in IE2-IE3-and IE4-class motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 3603–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G. Data-driven energy models for existing VFD-motorpump systems. Sci. Technol. Built Environ. 2019, 25, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieninger, T.; Goppelt, F.; Schmidt-Vollus, R.; Schlucker, E. Energy-saving potential for centrifugal pump storage operation using optimized control schemes. Energy Effic. 2021, 14, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundfos Product Center: Technical Data and Curves NB 50-200/210 AF2ABAQE. Available online: https://product-selection.grundfos.com/products/nb-nbe-nbe-series-2000/nb/nb-50-200210-97837025?tab=variant-curves&pumpsystemid=1173717497 (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Grundfos Product Center: Technical Data and Curves NB 80-315/305 AF2ABAQE. Available online: https://product-selection.grundfos.com/products/nb-nbe-nbe-series-2000/nb/nb-80-315305-97839395?tab=variant-curves&pumpsystemid=1167816632 (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Grundfos Product Center: Technical Data and Curves NB 150-400/375 AF1ABAQE. Available online: https://product-selection.grundfos.com/products/nb-nbe-nbe-series-2000/nb/nb-150-400375-97837168?tab=variant-curves&pumpsystemid=1168447008 (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Grundfos Product Center: Technical Data and Curves NB 250-500/445 AF1ABAQE. Available online: https://product-selection.grundfos.com/products/nb-nbe-nbe-series-2000/nb/nb-250-500445-97921024?tab=variant-curves&pumpsystemid=1173934349 (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Tamminen, J.; Viholainen, J.; Ahonen, T.; Ahola, J.; Hammo, S.; Vakkilainen, E. Comparison of model-based flow rate estimation methods in frequency-converter-driven pumps and fans. Energy Effic. 2014, 7, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Liu, M. Development of simplified in-situ fan curve measurement method using the manufacturers fan curve. Build. Environ. 2012, 48, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelik, L. Centrifugal and Rotary Pumps. Fundamentals with Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Lai, Z.; Wu, D.; Wang, L. Optimization Research of Parallel Pump System for Improving Energy Efficiency. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2015, 141, 04014094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfaoui, J.; Rezk, H.; Al-Dhaifallah, M.; Elyes, F.; Abdelkader, M. Numerical Performance Evaluation of Solar Photovoltaic Water Pumping System under Partial Shading Condition using Modern Optimization. Mathematics 2019, 7, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goyal, N.; Ram, M.; Kumar, A.; Bisht, S.; Klochkov, Y. Reliability Measures and Profit Exploration of Windmill Water-Pumping Systems Incorporating Warranty and Two Types of Repair. Mathematics 2021, 9, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhaj Salem, M.; Fouladirad, M.; Deloux, E. Prognostic and Classification of Dynamic Degradation in a Mechanical System Using Variance Gamma Process. Mathematics 2021, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Extended Product Approach for Pumps, Copyright © 2021 by Europump. Published by Europump. Available online: http://europump.net/uploads/Extended%20Product%20Approach%20for%20Pumps%20-%20A%20Europump%20guide%20(27OCT2014).pdf (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Stoffel, B. Assessing the Energy Efficiency of Pumps and Pump Units. Background and Methodology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjustable Speed Electrical Power Drive Systems—Part 9-2: Ecodesign for Power Drive Systems, Motor Starters, Power Electronics and Their Driven Applications—Energy Efficiency Indicators for Power Drive Systems and Motor Starters; IEC 61800-9-2/Ed1; IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Pellegrino, G.; Bojoi, R.; Guglielmi, P. Unified Direct-Flux Vector Control for AC Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 2093–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Lau, J.; Zhang, B. A novel method to determine the motor efficiency under variable speed operations and partial load conditions. Appl. Energy 2015, 144, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SinaSave Energy Saving and Amortization, Siemens Online Tool. Available online: https://www.sinasave.siemens.com (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Manufacturer’s Statement ACS880-01 and IE4 SynRM Motor Package Efficiency. Drive: ACS880-01-202A-3, Motor: M3BL 280SMA, 3GBL282213-ADC, Pn 75 kW, 1500 rpm. Document No: FIVEN201506010267. Available online: https://library.e.abb.com/public/34f02c42d4b642b5888d22a429ef04c5/Manufacturers%20statement%20-%20IE4%20M3BL%20280SMA_ACS880_103A,%2075%20%20kW,%201500%20rpm.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Manufacturer’s Statement ACS880-01 and IE4 SynRM Motor Package Efficiency. Drive: ACS880-01-427A-3, Motor: M3BL 315MLA, 3GBL312413-ADC, Pn 200 kW, 1500 rpm. Document No: FIVEN201506010275. Available online: https://library.e.abb.com/public/c00bb6eb084a40b3912317e345a73fe0/Manufacturers%20statement%20-%20IE4%20M3BL%20315MLA_ACS880_427A,%20200%20%20kW,%201500%20rpm.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Eurostat Data for the Industrial Consumers in Germany. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Electricity_price_statistics#Electricity_prices_for_industrial_consumers (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Pump Life Cycle Costs: A Guide to LCC Analysis for Pumping Systems, Executive Summary. (2001) Hydraulic Institute (Parsippany, NJ); Europump (Brussels, Belgium); Office of Industrial Technologies Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy U.S. Department of Energy (Washington, DC). January 2001, pp. 1–19. Available online: https://searchworks.stanford.edu/view/4676735 (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Waghmode, L.; Sahasrabudhe, A. A comparative study of life cycle cost analysis of pumps. In Proceedings of the International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference (ASME 2010), Montreal, QC, Canada, 15–18 August 2010; Volume 6, pp. 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CO2 Intensity of Electricity Generation. European Environment Agency. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/co2-intensity-of-electricity-generation (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Directive 2012/27/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October 2012 on Energy Efficiency, Amending Directives 2009/125/EC and 2010/30/EU and Repealing Directives 2004/8/EC and 2006/32/EC. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A32012L0027 (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Wilby, M.R.; González, A.B.R.; Díaz, J.J.V. Empirical and dynamic primary energy factors. Energy 2014, 73, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Final Report. Evaluation of Primary Energy Factor Calculation Options for Electricity. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/energy/sites/ener/files/documents/final_report_pef_eed.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Tucki, K.; Orynycz, O.; Mitoraj-Wojtanek, M. Perspectives for Mitigation of CO2 Emission due to Development of Electromobility in Several Countries. Energies 2020, 13, 4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro Andrade, C.T.; Pontes, R.S.T. Economic analysis of Brazilian Policies for Energy Efficient Electric Motors. Energy Policy 2017, 106, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, A.T.; Ferreira, F.J.; Baoming, G. Beyond Induction Motors—Technology Trends to Move Up Efficiency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 2103–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, R.R.; Magnussen, F.; Sadarangani, C. Theoretical and Experimental Reevaluation of Synchronous Reluctance Machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrievskii, V.; Prakht, V.; Kazakbaev, V.; Pozdeev, A.; Oshurbekov, S. Development of a high efficient electric drive with synchronous reluctance motor. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Pattaya, Thailand, 25–28 October 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AC Electric Motor. Available online: https://www.acelectricmotor.co.uk/ (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Ozcelik, N.G.; Dogru, U.E.; Imeryuz, M.; Ergene, L.T. Synchronous Reluctance Motor vs. Induction Motor at Low-Power Industrial Applications: Design and Comparison. Energies 2019, 12, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Three Phase VFD Pricelist. Available online: http://www.gohz.com/three-phase-vfd (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Report on Study on International Efficiency (IE) Efficiency Classes for Low Voltage AC Motors. Available online: https://www.emsd.gov.hk/filemanager/en/content_764/Report%20on%20International%20Efficiency%20Efficiency%20Classes%20for%20Low%20Voltage%20AC%20Motors.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Fact Sheet, No. 29–New Motor Technologies November 2018. Available online: https://www.topmotors.ch/sites/default/files/2018-11/E_MB_29_Motor_technologies.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Almeida, A. Motor Systems Technology Developments. In Proceedings of the 8th Motor Summit for Energy Efficient Motor Driven Systems Powered by Impact Energy, Zurich, Switzerland, 14–15 November 2018; Available online: https://motorsummit.ch/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/MS18_proceedings.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2021).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).