Novel Design Framework for Dual-Band Frequency Selective Surfaces Using Multi-Variant Differential Evolution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Problem Definition
2.2. Optimization Process
2.3. MVDE Algorithm Description
2.4. Performance Evaluation
- Independent trials: 100;
- Iterations: 1000;
- Population: 100;
- Decision variables (solutions to the optimization problem): 30 and 50;
- Decision variables boundaries: [−10 10].
| Algorithm 1 Pseudocode of the Multi-Variant Differential Evolution Algorithm |
|
3. Optimization Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization Setup
- Independent trials: 10;
- Iterations: 200;
- Population: 50;
- Decision variables (solutions to the optimization problem): 10 (UC1), 11 (UC2, UC3).
- is the position vector for each member of the population of the utilized MVDE algorithm,
- (i = {2.45 GHz, 5.8 GHz}) is the system metric (magnitude of the reflection coefficient) of the designed EM structure at the specific frequencies of interest,
- is the threshold criterion for an acceptable solution of the optimization problem provided by the members of the population (in our case =−10 dB),
- is a positive number (multiplying factor in the objective function) that is triggered when the obtained solution is above the threshold criterion, and
- is the objective function of the optimization problem.
3.2. Unit Cell Results
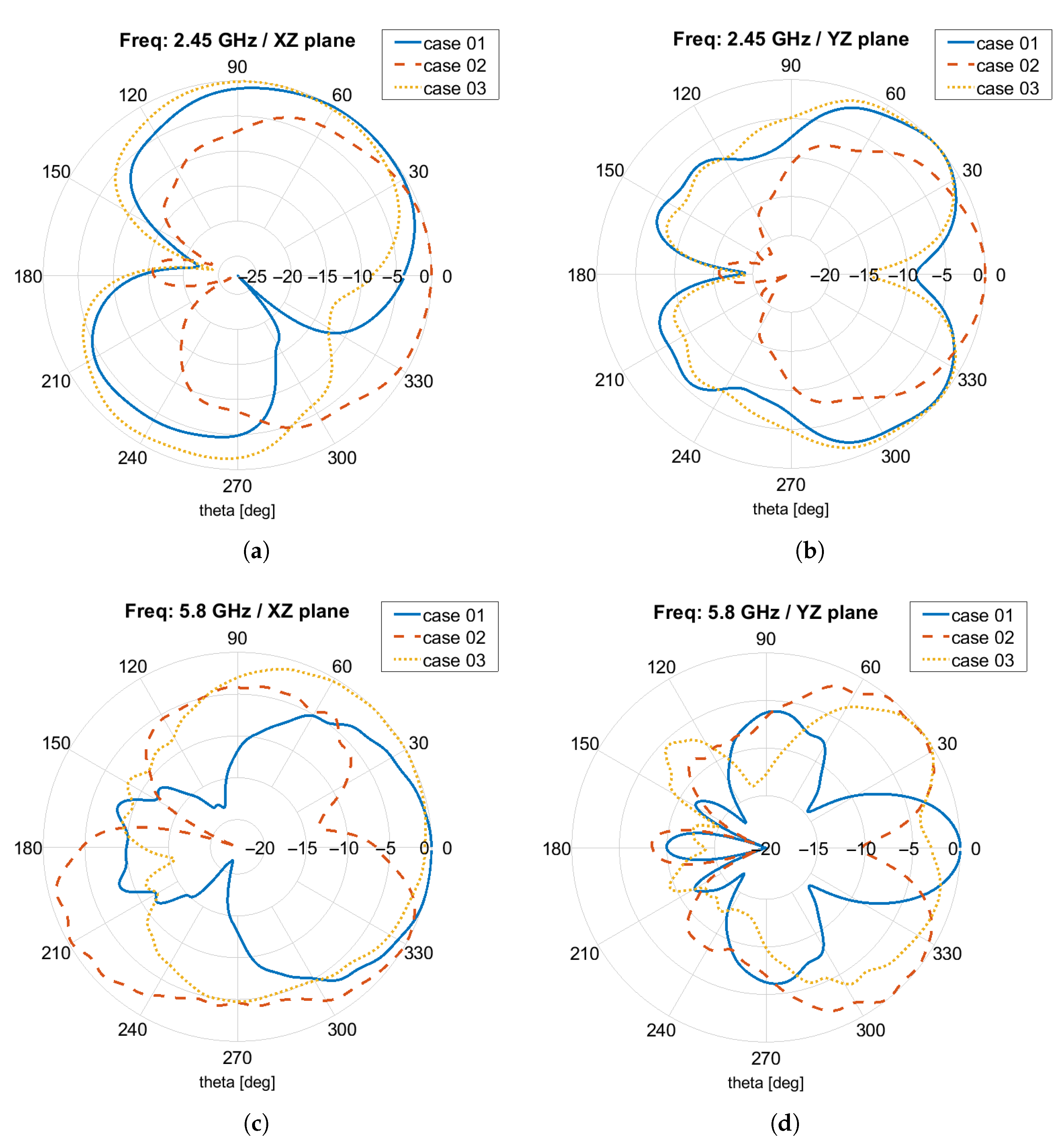
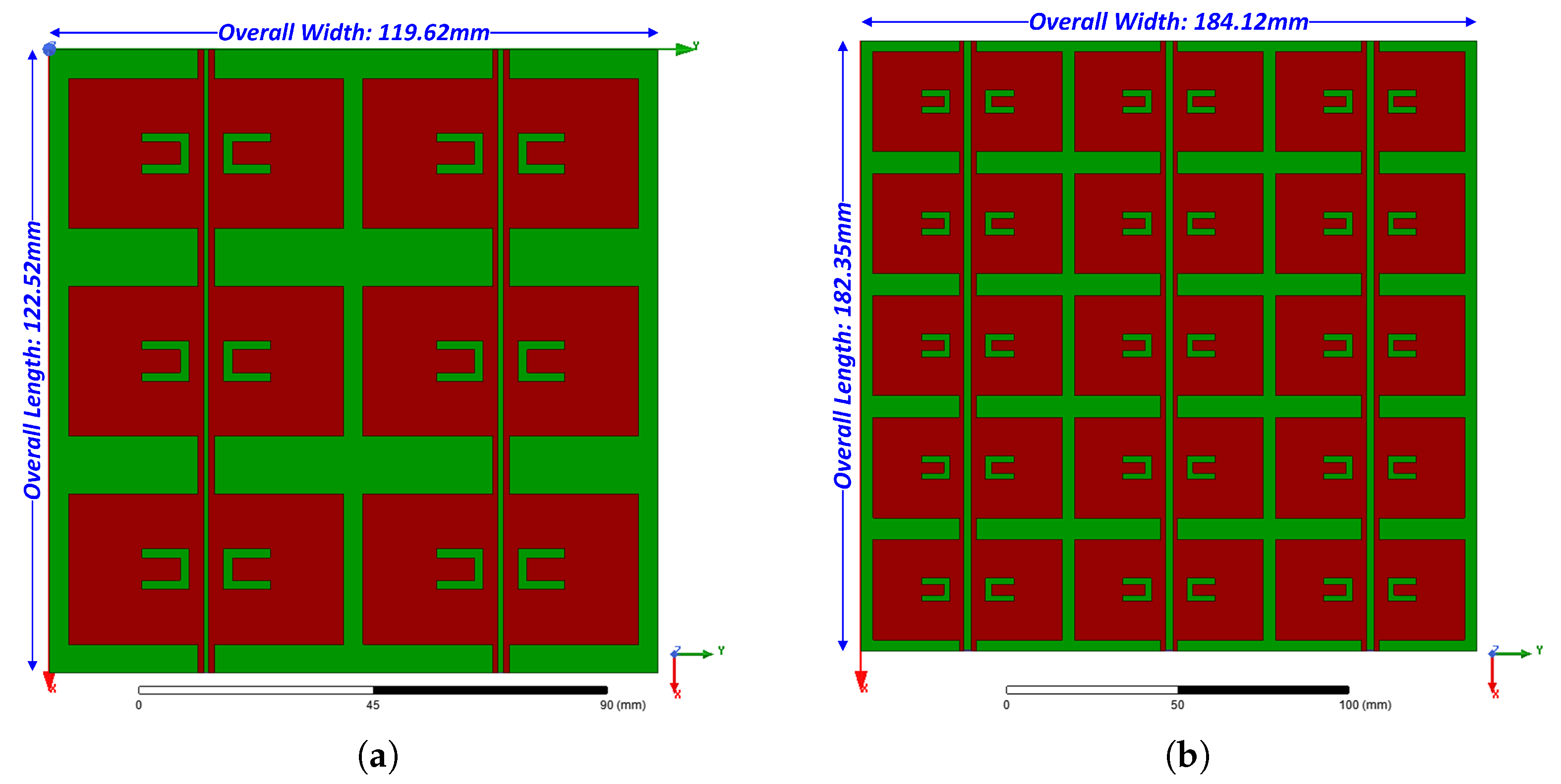
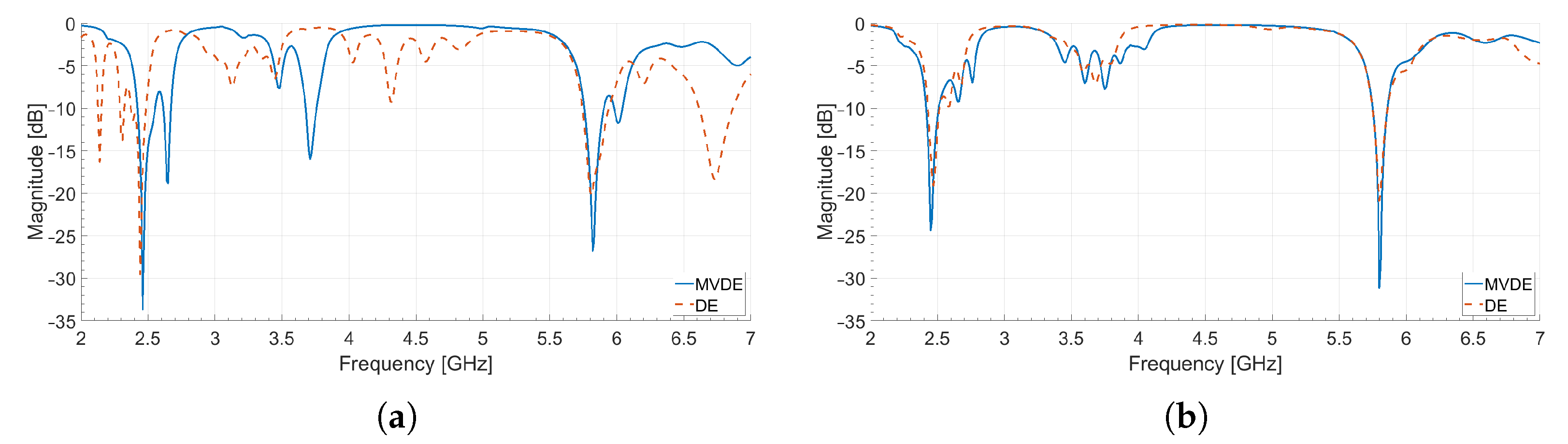
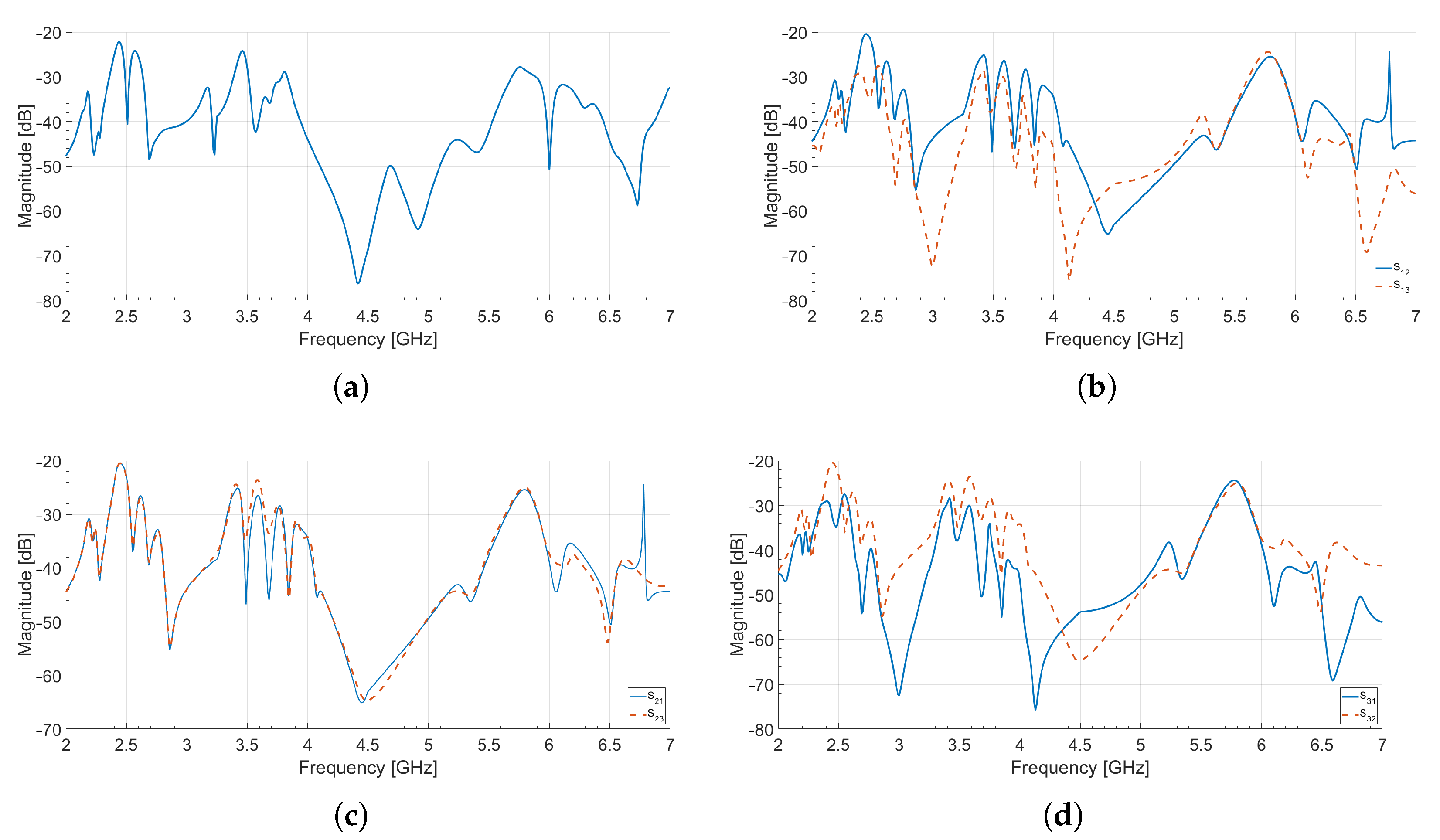
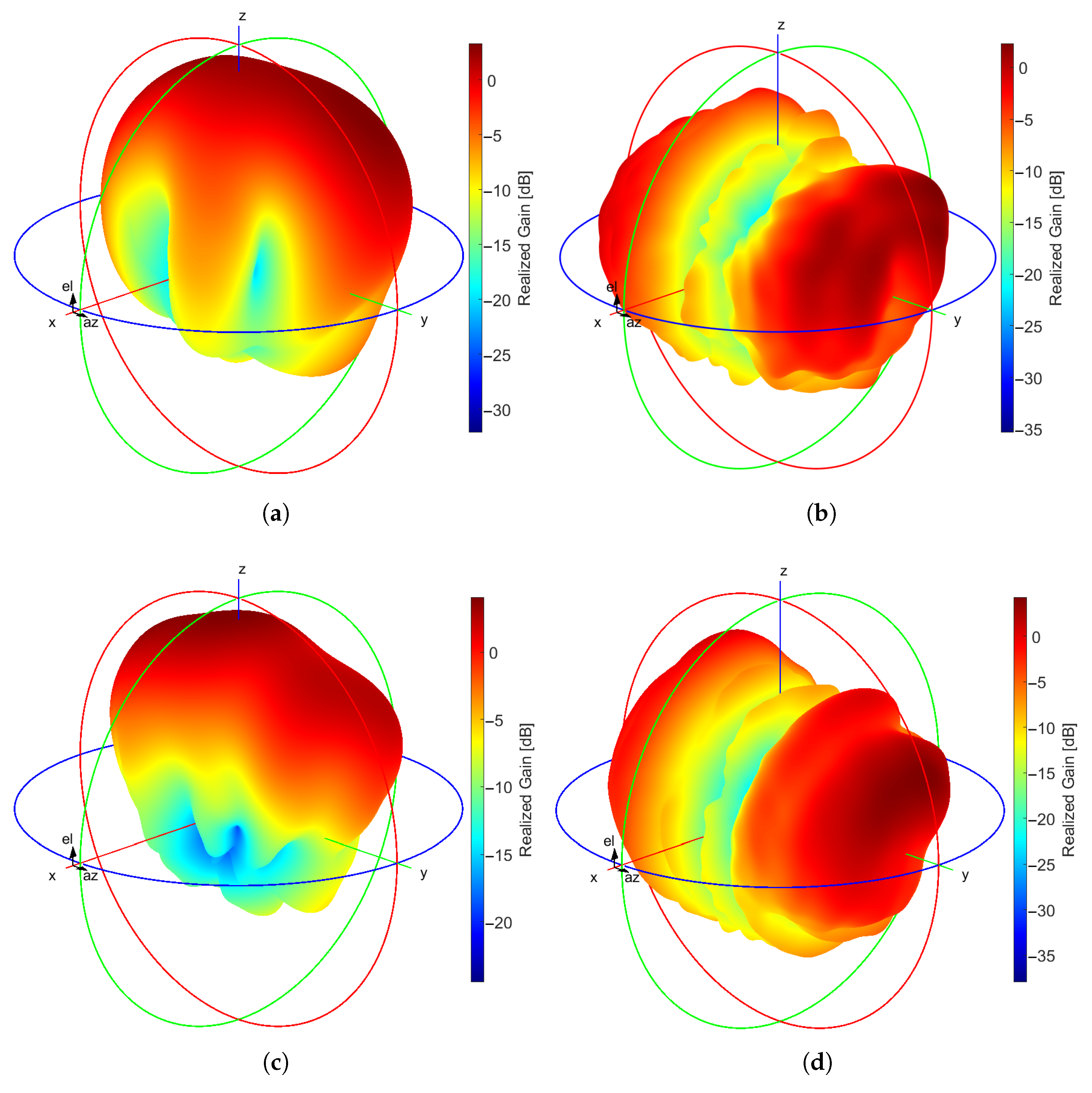
3.3. FSS Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACO | Ant Colony Optimization |
| BBO | Biogeography-Based Optimization |
| CMA-ES | Covariance Matrix Adaptation-Evolution Strategy |
| DE | Differential Evolution |
| EA | Evolutionary Algorithm |
| EH | Energy Harvesting |
| EM | Electromagnetic |
| FEM | Finite Element Method |
| FDTD | Finite Difference Time Domain |
| FSS | Frequency Selective Surface |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| GWO | Gray Wolf Optimizer |
| HHO | Harris Hawks Optimization |
| HPBW | Half Power Bandwidth |
| MFEM | Modular Finite Element Methods |
| MIMO | Multiple-Input Multiple-Output |
| MOLACO | Multi-Objective Lazy Ant Colony Optimization |
| MVDE | Multi Variant Differential Evolution |
| PCB | Printed Circuit Board |
| PDE | Partial Differential Equation |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| RF | Radio Frequency |
| SADE | Self-Adaptive Differential Evolution |
| WDO | Wind-Driven Optimization |
Appendix A. Benchmark Functions
- Ackley Function:where a = 20, b = 0.2, and c = 2, Dimensions: d, Global Minimum: at
- Griewank Function:Dimensions: d, Global Minimum: at
- Rastrigin Function:Dimensions: d, Global Minimum: at
- Schaffer No. 4:
- Schwefel Function:Dimensions: d, Global Minimum: at
- Sphere Function:
- Rozenbrock Function:Dimensions: d, Global Minimum: at
- De Jong Function No. 5:where , Dimensions: 2
- Hartmann 6D Function:where , , , Dimensions: 6, Global Minimum: at
- Powell Function:Dimensions: d, Global Minimum: at
References
- Saleem, R.; Bilal, M.; Chattha, H.T.; Ur Rehman, S.; Mushtaq, A.; Shafique, M.F. An FSS Based Multiband MIMO System Incorporating 3D Antennas for WLAN/WiMAX/5G Cellular and 5G Wi-Fi Applications. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 144732–144740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Pedersen, G.F. Dual-Band Structure Reused Antenna Based on Quasi-Elliptic Bandpass Frequency Selective Surface for 5G Application. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 7612–7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, J. The requirements, challenges, and technologies for 5G of terrestrial mobile telecommunication. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnson, E.; Sanguinetti, L.; Wymeersch, H.; Hoydis, J.; Marzetta, T.L. Massive MIMO is a reality—What is next?: Five promising research directions for antenna arrays. Digit. Signal Process. 2019, 94, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Joumayly, M.A.; Behdad, N. A Generalized Method for Synthesizing Low-Profile, Band-Pass Frequency Selective Surfaces With Non-Resonant Constituting Elements. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 4033–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, R.; Lee, J.R. Progress in frequency selective surface-based smart electromagnetic structures: A critical review. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 66, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basar, E.; Wen, M.; Mesleh, R.; Di Renzo, M.; Xiao, Y.; Haas, H. Index Modulation Techniques for Next-Generation Wireless Networks. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 16693–16746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, H.J.; Vullers, R.J.M. RF Energy Harvesting and Transport for Wireless Sensor Network Applications: Principles and Requirements. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 1410–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Vyas, R.; Bito, J.; Niotaki, K.; Collado, A.; Georgiadis, A.; Tentzeris, M.M. Ambient RF Energy-Harvesting Technologies for Self-Sustainable Standalone Wireless Sensor Platforms. Proc. IEEE 2014, 102, 1649–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, P.; Niyato, D.; Kim, D.I.; Han, Z. Wireless Networks With RF Energy Harvesting: A Contemporary Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 757–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgiadis, A.; Collado, A.; Tentzeris, M.M. Energy Harvesting: Technologies, Systems, and Challenges; EuMA High Frequency Technologies Series; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Yang, S.; Bai, J.; Fu, Y. Design of Absorptive/Transmissive Frequency-Selective Surface Based on Parallel Resonance. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 4897–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Bai, J.; Chen, L.; Fu, Y. A Miniaturized Absorptive Frequency Selective Surface. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranga, Y.; Matekovits, L.; Esselle, K.P.; Weily, A.R. Multioctave Frequency Selective Surface Reflector for Ultrawideband Antennas. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2011, 10, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pous, R.; Pozar, D. A frequency-selective surface using aperture-coupled microstrip patches. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1991, 39, 1763–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, T.K.; Lee, S.W. Tri-band frequency selective surface with circular ring elements. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1994, 42, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.K.; Lee, S.W. Multiband frequency selective surface with multiring patch elements. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1994, 42, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Romeu, J.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. Fractal FSS: A novel dual-band frequency selective surface. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2000, 48, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, P.S.; Parker, E.A.; Batchelor, J.C. An Active Annular Ring Frequency Selective Surface. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 3265–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, T.K. Four-band frequency selective surface with double-square-loop patch elements. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1994, 42, 1659–1663. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, K.R.; Singh, G.; Jyoti, R. A Simple Synthesis Technique of Single-Square-Loop Frequency Selective Surface. Prog. Electromagn. Res. B 2012, 45, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kesavan, A.; Karimian, R.; Denidni, T.A. A Novel Wideband Frequency Selective Surface for Millimeter-Wave Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 1711–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Tao, Y. Performance Improvement of a U-Slot Patch Antenna Using a Dual-Band Frequency Selective Surface With Modified Jerusalem Cross Elements. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 3482–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittra, R.; Chan, C.; Cwik, T. Techniques for analyzing frequency selective surfaces-a review. Proc. IEEE 1988, 76, 1593–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, G.I.; Ford, K.L.; Olsson, L.G.; Esselle, K.P.; Panagamuwa, C.J. Switchable Frequency Selective Surface for Reconfigurable Electromagnetic Architecture of Buildings. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanz-Izquierdo, B.; Parker, E.A.; Batchelor, J.C. Switchable Frequency Selective Slot Arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 2728–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, G.; Wu, Q.; Hua, J. A Novel Active Frequency Selective Surface With Wideband Tuning Range for EMC Purpose. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 4534–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.K.; Li, B.; Shen, Z. An overview of three-dimensional frequency-selective structures. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2014, 56, 43–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.G.; Shen, Z.; Feng, Q.Y.; Li, B. Tunable 3-D Bandpass Frequency-Selective Structure With Wide Tuning Range. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 3297–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Shen, Z.; Withayachumnankul, W.; Al-Sarawi, S.F.; Abbott, D. Varactor-Tunable Second-Order Bandpass Frequency-Selective Surface With Embedded Bias Network. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 1672–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sheikh, A.; Shen, Z. Design of Wideband Bandstop Frequency-Selective Structures Using Stacked Parallel Strip Line Arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 3401–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt, D.; Haase, K.; Hübler, A.; Ellinger, F. Bending and Folding Effect Study of Flexible Fully Printed and Late-Stage Codified Octagonal Chipless RFID Tags. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 2815–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turki, B.M.; Parker, E.T.A.; Wünscher, S.; Schubert, U.S.; Saunders, R.; Sanchez-Romaguera, V.; Ziai, M.A.; Yeates, S.G.; Batchelor, J.C. Significant Factors in the Inkjet Manufacture of Frequency-Selective Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 6, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Izquierdo, B.; Parker, E. 3D printing technique for fabrication of frequency selective structures for built environment. Electron. Lett. 2013, 49, 1117–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebrebrhan, M.; Aranda, F.; Walsh, G.; Ziegler, D.; Giardini, S.; Carlson, J.; Kimball, B.; Steeves, D.; Xia, Z.; Yu, S.; et al. Textile Frequency Selective Surface. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2017, 27, 989–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauraya, A.; Seager, R.; Whittow, W.; Zhang, S.; Vardaxoglou, Y. Embroidered Frequency Selective Surfaces on textiles for wearable applications. In Proceedings of the 2013 Loughborough Antennas Propagation Conference (LAPC), Loughborough, UK, 11–12 November 2013; pp. 388–391. [Google Scholar]
- Bossard, J.A.; Liang, X.; Li, L.; Yun, S.; Werner, D.H.; Weiner, B.; Mayer, T.S.; Cristman, P.F.; Diaz, A.; Khoo, I.C. Tunable Frequency Selective Surfaces and Negative-Zero-Positive Index Metamaterials Based on Liquid Crystals. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2008, 56, 1308–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayatpur, F.; Sarabandi, K. A Tunable Metamaterial Frequency-Selective Surface With Variable Modes of Operation. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2009, 57, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Eibert, T.F. A Multifunctional Metamaterial-Based Dual-Band Isotropic Frequency-Selective Surface. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 4042–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J. Broadband metamaterial absorber based on coupling resistive frequency selective surface. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 4675–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Dickie, R.; Cahill, R.; Gamble, H.; Ismail, Y.; Fusco, V.; Linton, D.; Grant, N.; Rea, S. Liquid Crystal Tunable mm Wave Frequency Selective Surface. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2007, 17, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yu, B.; Behdad, N. Liquid-Tunable Frequency Selective Surfaces. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2010, 20, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.J.; Zamora, A.; Chun, T.F.; Ohta, A.T.; Shiroma, W.A. A Wideband, Pressure-Driven, Liquid-Tunable Frequency Selective Surface. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2011, 21, 465–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Lim, S. Fluidically Reconfigurable Multifunctional Frequency-Selective Surface With Miniaturization Characteristic. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2018, 66, 3857–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Jornet, J.M.; Akyildiz, I.F.; Wu, Z.P. Mutual Coupling Reduction for Ultra-Dense Multi-Band Plasmonic Nano-Antenna Arrays Using Graphene-Based Frequency Selective Surface. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 33214–33225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lin, L.; Wu, L.S.; Yin, W.Y.; Mao, J.F. A Bandpass Graphene Frequency Selective Surface With Tunable Polarization Rotation for THz Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Sahu, A.; Panwar, R. Cascaded Graphene Frequency Selective Surface Integrated Tunable Broadband Terahertz Metamaterial Absorber. IEEE Photonics J. 2019, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.W.; Zhao, W.S.; Xie, H.; Hu, J.; Zhou, L.; Chen, W.; Gao, P.; Ye, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, H.S.; et al. Tunable THz Multiband Frequency-Selective Surface Based on Hybrid Metal–Graphene Structures. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2017, 16, 1132–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabandi, K.; Behdad, N. A Frequency Selective Surface With Miniaturized Elements. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2007, 55, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, M.; Behdad, N. A Second-Order Dual X-/Ka-Band Frequency Selective Surface. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2008, 18, 785–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.K.; Shen, Z. A Novel Band-Reject Frequency Selective Surface With Pseudo-Elliptic Response. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauman, M.; Saleem, R.; Rashid, A.K.; Shafique, M.F. A Miniaturized Flexible Frequency Selective Surface for X-Band Applications. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2016, 58, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holakouei, R.; Nourinia, J.; Ghobadi, C. A design approach for a dual-polarized, dual-band-reject frequency selective surface using a new Fractal element. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2007, 61, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Huang, C.; Chen, P.; Pu, M.; Ma, X.; Luo, X. A Beam Steering Horn Antenna Using Active Frequency Selective Surface. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 6218–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzwawi, G.H.; Elzwawi, H.H.; Tahseen, M.M.; Denidni, T.A. Frequency Selective Surface-Based Switched-Beamforming Antenna. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 48042–48050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euler, M.; Fusco, V.F. Frequency Selective Surface Using Nested Split Ring Slot Elements as a Lens With Mechanically Reconfigurable Beam Steering Capability. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 3417–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazegar, M.; Zheng, Y.; Kohler, C.; Maune, H.; Nikfalazar, M.; Binder, J.R.; Jakoby, R. Beam Steering Transmitarray Using Tunable Frequency Selective Surface With Integrated Ferroelectric Varactors. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 60, 5690–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, S.M.; Denidni, T.A. Pattern-Reconfigurable Antenna Using a Switchable Frequency Selective Surface With Improved Bandwidth. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 1148–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroo-Jazi, M.; Denidni, T.A. Electronically Sweeping-Beam Antenna Using a New Cylindrical Frequency-Selective Surface. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, N.; Liu, H.; Li, L. A Transplantable Frequency Selective Metasurface for High-Order Harmonic Suppression. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Momeni Hasan Abadi, S.M.A.; Li, M.; Behdad, N. Harmonic-Suppressed Miniaturized-Element Frequency Selective Surfaces With Higher Order Bandpass Responses. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 2562–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Parui, S.K. Performance Enhancement of a Dual-Band Monopole Antenna by Using a Frequency-Selective Surface-Based Corner Reflector. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 2165–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.C.; Hong, W.; Wu, K.; Tang, H.J.; Hao, Z.C.; Chen, J.X.; Zhou, H.X.; Zhou, H. Design of a Bandwidth-Enhanced Polarization Rotating Frequency Selective Surface. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kong, P.; Cheng, W.; Bao, W.; Yu, X.; Miao, L.; Jiang, J. Broadband tunability of polarization-insensitive absorber based on frequency selective surface. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Cao, Q.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y. An Improved Multifunctional Active Frequency Selective Surface. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 1854–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phon, R.; Ghosh, S.; Lim, S. Novel Multifunctional Reconfigurable Active Frequency Selective Surface. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 1709–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyrouz, S.; Perotto, G.; Visser, H.J. Frequency selective surface for radio frequency energy harvesting applications. IET Microwaves Antennas Propag. 2014, 8, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtari, R.; Baginski, M.; Dean, R. A 2.45-GHz frequency-selective rectenna for wireless energy harvesting. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2016, 58, 2508–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.; Sismeiro, L.; Ferreira, A.; Caldeirinha, R.F.; Fernandes, T.R.; Cuiñas, I. Hybrid FSS and Rectenna Design for Wireless Power Harvesting. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 2038–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosrati, M.; Dalili Oskouei, H.; Khalilpour, J. Parallel-series connected rectenna array using frequency selective surface (FSS) for power harvesting applications at 5.8 GHz. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2019, 29, e21819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkmen, F.; Almoneef, T.S.; Ramahi, O.M. Scalable Electromagnetic Energy Harvesting Using Frequency-Selective Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2018, 66, 2433–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkmen, F.; Ramahi, O.M. A Scalable, Dual-band Absorber Surface for Electromagnetic Energy Harvesting and Wireless Power Transfer. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021. (Early Access). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, P.; Benedetti, M.; Donelli, M.; Franceschini, D.; Massa, A. Evolutionary optimization as applied to inverse scattering problems. Inverse Probl. 2009, 25, 123003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goudos, S.K. Emerging Evolutionary Algorithms for Antennas and Wireless Communications; Electromagnetic Waves, SciTech Publishing, Incorporated: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, N.; Adeli, H. Nature-Inspired Computing: Physics-and Chemistry-Based Algorithms; Chapman and Hall/CRC: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. The whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 95, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Gandomi, A.H.; Mirjalili, S.Z.; Saremi, S.; Faris, H.; Mirjalili, S.M. Salp Swarm Algorithm: A bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2017, 114, 163–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Kar, A.K. Swarm intelligence: A review of algorithms. In Nature-Inspired Computing and Optimization; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 475–494. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, J.H. Genetic Algorithms. Sci. Am. 1992, 267, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, T. Evolutionary Algorithms in Theory and Practice: Evolution Strategies, Evolutionary Programming, Genetic Algorithms; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Storn, R.; Price, K. Differential Evolution—A Simple and Efficient Heuristic for global Optimization over Continuous Spaces. J. Glob. Optim. 1997, 11, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, A.; Suganthan, P. Self-adaptive differential evolution algorithm for numerical optimization. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Edinburgh, UK, 2–5 September 2005; Volume 2, pp. 1785–1791. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95—International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayraktar, Z.; Komurcu, M.; Bossard, J.A.; Werner, D.H. The Wind Driven Optimization Technique and its Application in Electromagnetics. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 2745–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.; Rahmat-Samii, V. Genetic algorithms in engineering electromagnetics. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 1997, 39, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rocca, P.; Oliveri, G.; Massa, A. Differential Evolution as Applied to Electromagnetics. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2011, 53, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudos, S.K.; Siakavara, K.; Samaras, T.; Vafiadis, E.E.; Sahalos, J.N. Self-Adaptive Differential Evolution Applied to Real-Valued Antenna and Microwave Design Problems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. Particle swarm optimization in electromagnetics. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2004, 52, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Luk, K.M. The Grey Wolf Optimizer and Its Applications in Electromagnetics. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 2186–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manara, G.; Monorchio, A.; Mittra, R. Frequency selective surface design based on genetic algorithm. Electron. Lett. 1999, 35, 1400–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bossard, J.; Werner, D.; Mayer, T.; Drupp, R. A novel design methodology for reconfigurable frequency selective surfaces using genetic algorithms. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2005, 53, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, S.; Mittra, R. Design of a frequency selective surface (FSS) with very low cross-polarization discrimination via the parallel micro-genetic algorithm (PMGA). IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2003, 51, 1664–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnakumar, K. Micro-genetic algorithms for stationary and non-stationary function optimization. Intelligent control and adaptive systems. Int. Soc. Opt. Photonics 1990, 1196, 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarty, S.; Mittra, R. Application of the micro-genetic algorithm to the design of spatial filters with frequency-selective surfaces embedded in dielectric media. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2002, 44, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, D.J.; Werner, D.H.; Wilhelm, M.J.; Church, K.H. Genetically engineered multiband high-impedance frequency selective surfaces. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2003, 38, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.; Mittra, R. On the analysis of frequency-selective surfaces using subdomain basis functions. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1990, 38, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, M.; Deguchi, H.; Tsuji, M.; Shigesawa, H. Multiband single-layer frequency selective surface designed by combination of genetic algorithm and geometry-refinement technique. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2004, 52, 2925–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, N.; Müller, S.D.; Koumoutsakos, P. Reducing the Time Complexity of the Derandomized Evolution Strategy with Covariance Matrix Adaptation (CMA-ES). Evol. Comput. 2003, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.F.; Qing, A.; Lee, C.K. Application of the differential-evolution strategy to the design of frequency-selective surfaces. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2005, 15, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.F.; Teo, P.T.; Qing, A.; Lee, C.K. Design of double-square-loop frequency-selective surfaces using differential evolution strategy coupled with equivalent-circuit model. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2005, 44, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, M.D.; Wang, X.; Werner, D.H. Flexible design of doubly periodic frequency selective surfaces with a prismatic mesh based FEBI simulation tool and CMA-ES. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), Spokane, WA, USA, 3–8 July 2011; pp. 1867–1870. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Xue, Z.H.; Li, W.M.; Ren, W.; Sheng, X.Q. Particle Swarm Optimization of frequency selective surface. CSQRWC 2012, 2012, 195–198. [Google Scholar]
- Genovesi, S.; Mittra, R.; Monorchio, A.; Manara, G. Particle Swarm Optimization for the Design of Frequency Selective Surfaces. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2006, 5, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalbakhsh, A.; Afzal, M.U.; Esselle, K.P.; Zeb, B.A. Multi-objective particle swarm optimization for the realization of a low profile bandpass frequency selective surface. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Hobart, TAS, Australia, 9–12 November 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Dorigo, M.; Birattari, M.; Stutzle, T. Ant colony optimization. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2006, 1, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.Z.; Werner, P.L.; Werner, D.H. Multi-Objective Lazy Ant Colony Optimization for Frequency Selective Surface Design. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Boston, MA, USA, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 2035–2036. [Google Scholar]
- Boursianis, A.D.; Salucci, M.; Koulouridis, S.; Georgiadis, A.; Tentzeris, M.; Goudos, S.K. Dual-Band Frequency Selective Surface Design Using Harris Hawks Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2021 10th International Conference on Modern Circuits and Systems Technologies (MOCAST), Thessaloniki, Greece, 5–7 July 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Heidari, A.A.; Mirjalili, S.; Faris, H.; Aljarah, I.; Mafarja, M.; Chen, H. Harris hawks optimization: Algorithm and applications. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 97, 849–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karban, P.; Pánek, D.; Orosz, T.; Petrášová, I.; Doležel, I. FEM based robust design optimization with Agros and Ārtap. Comput. Math. Appl. 2021, 81, 618–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.; Andrej, J.; Barker, A.; Bramwell, J.; Camier, J.S.; Cerveny, J.; Dobrev, V.; Dudouit, Y.; Fisher, A.; Kolev, T.; et al. MFEM: A modular finite element methods library. Comput. Math. Appl. 2021, 81, 42–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebig, T. openEMS—Open Electromagnetic Field Solver; University of Duisburg-Essen: Duisburg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.; Hemeida, A.M.; Alkhalaf, S.; Mohamed, A.A.; Senjyu, T. Multi-variant differential evolution algorithm for feature selection. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, A.; Mishrikey, M.; Hafner, C.; Vahldieck, R. Efficient Procedures for the Optimization of Frequency Selective Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2008, 56, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Cai, Z. Differential Evolution With Ranking-Based Mutation Operators. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 43, 2066–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, D. Biogeography-Based Optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2008, 12, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boursianis, A.D.; Papadopoulou, M.S.; Pierezan, J.; Mariani, V.C.; Coelho, L.S.; Sarigiannidis, P.; Koulouridis, S.; Goudos, S.K. Multiband Patch Antenna Design Using Nature-Inspired Optimization Method. IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag. 2021, 2, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagih, M.; Weddell, A.S.; Beeby, S. Rectennas for Radio-Frequency Energy Harvesting and Wireless Power Transfer: A Review of Antenna Design [Antenna Applications Corner]. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2020, 62, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
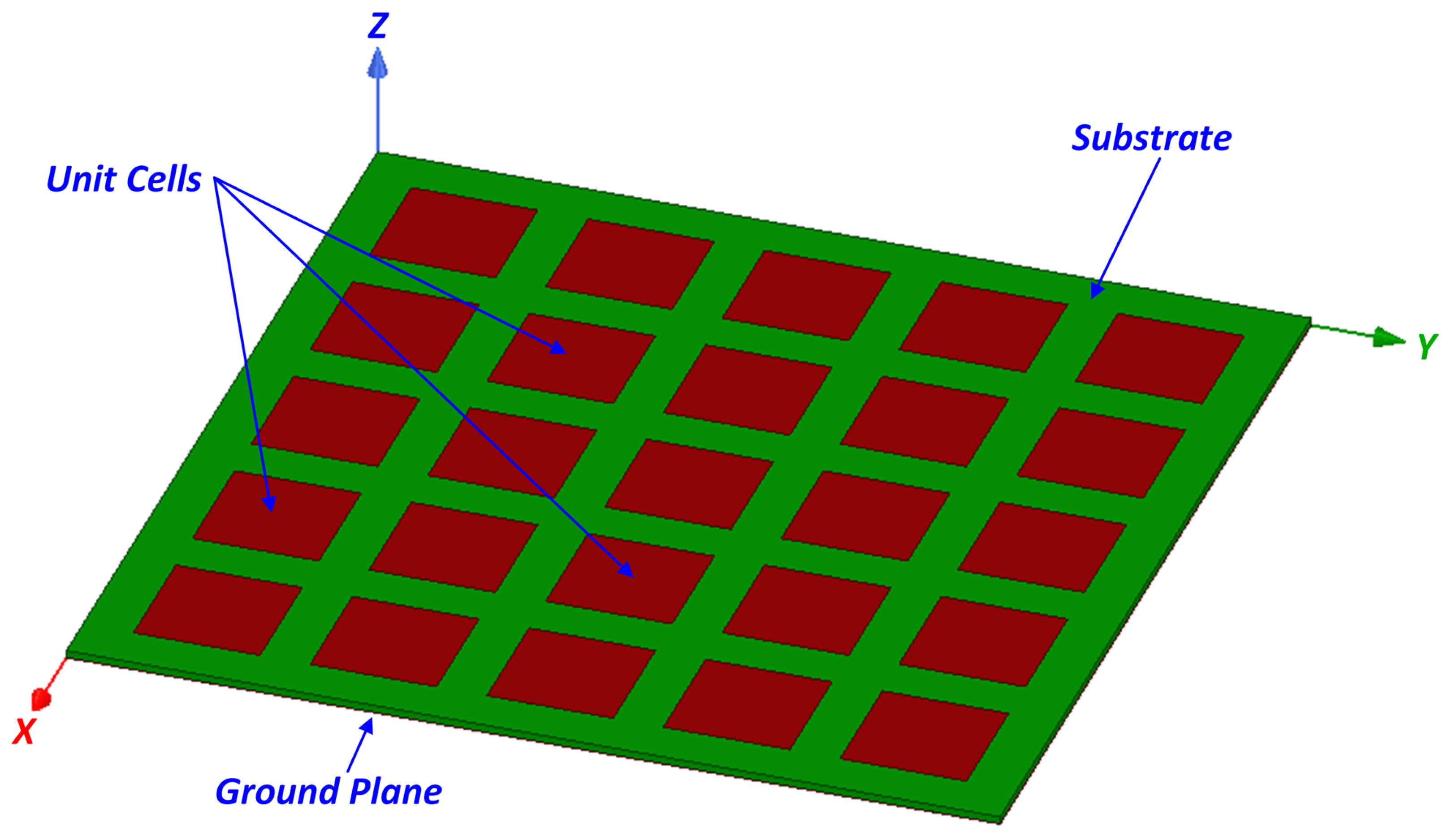


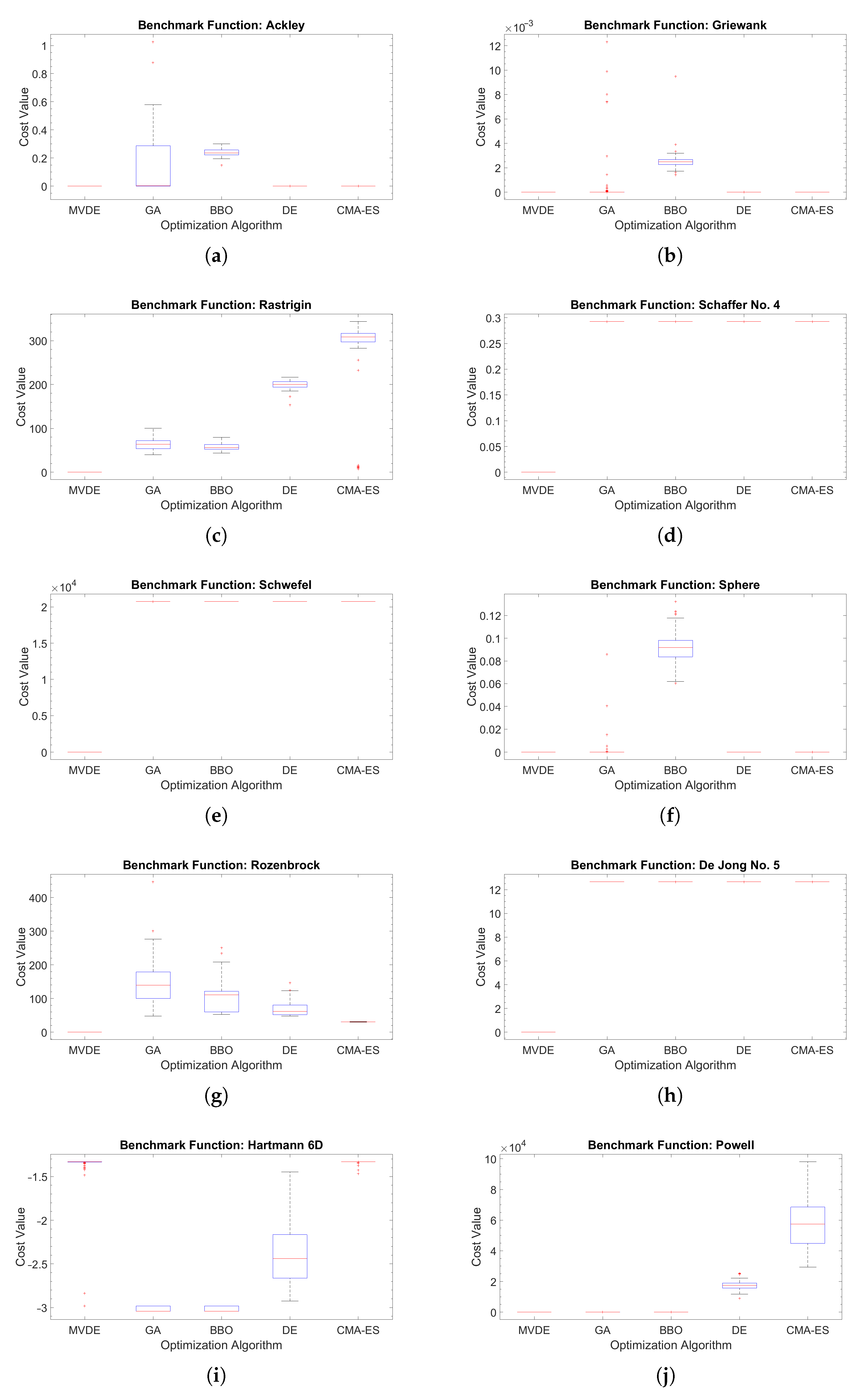

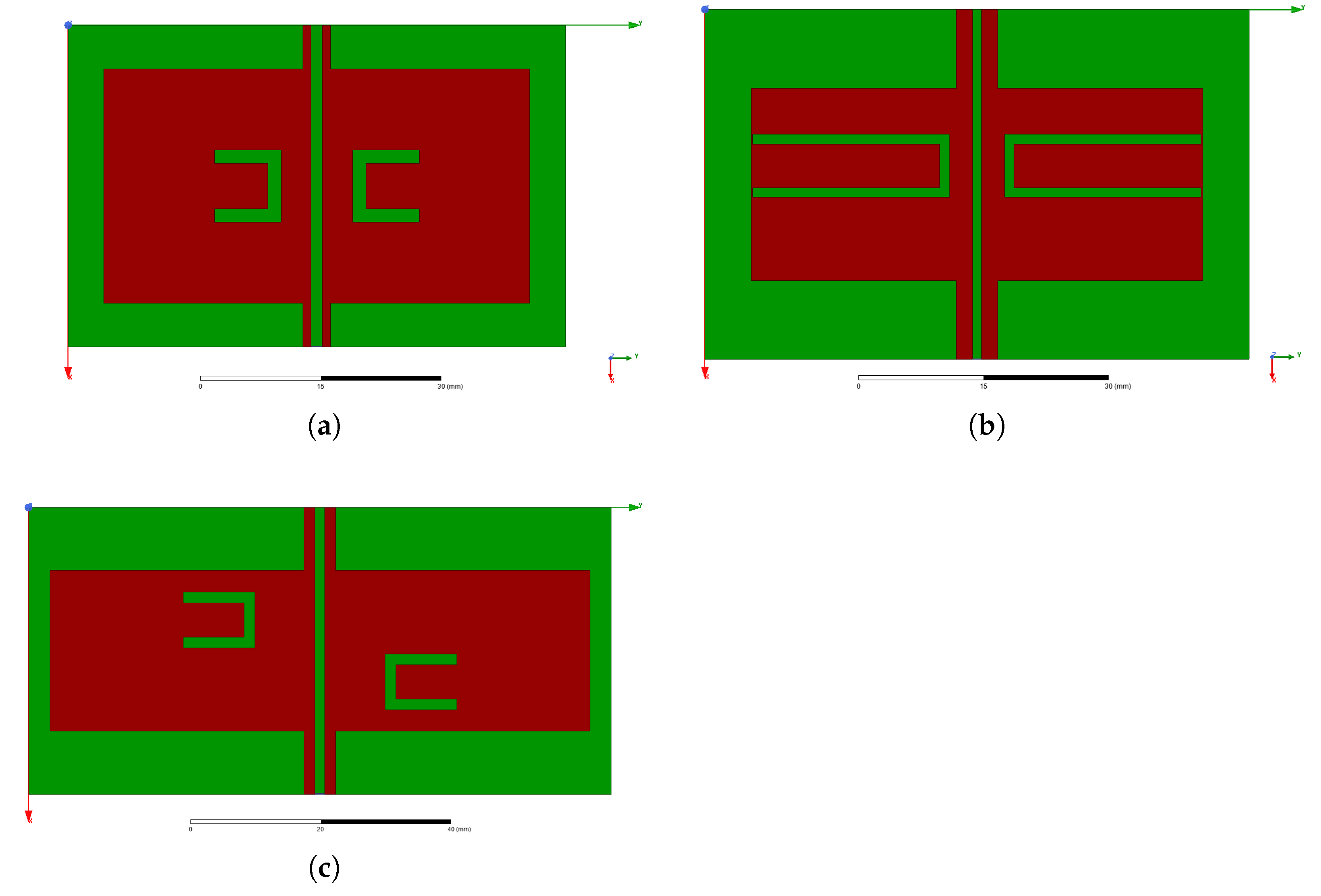
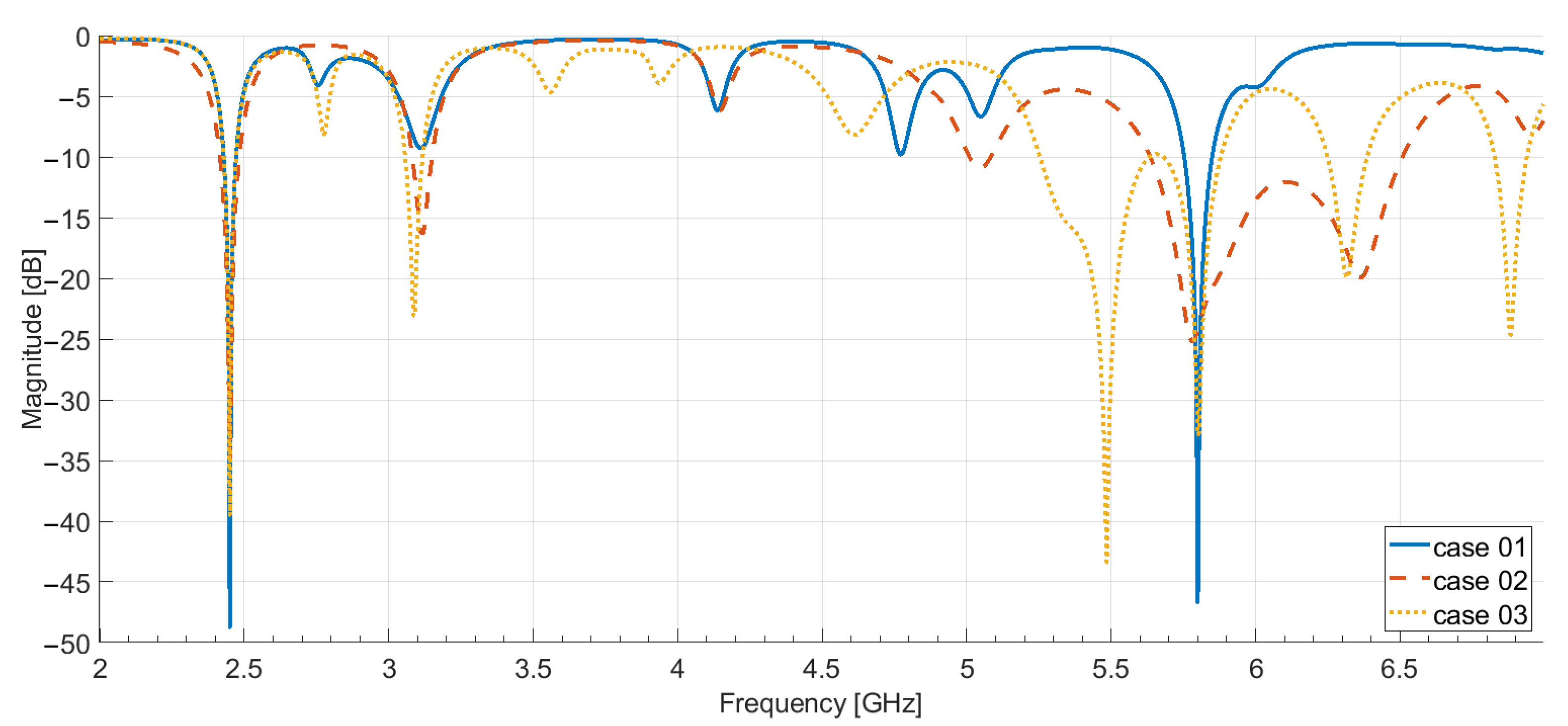

| MVDE | GA | BBO | DE | CMA-ES | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D = 30 | f1 | 0.000 | 7.994 | 2.902 | 1.262 | 3.997 |
| f2 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 6.224 | 3.886 | 0.000 | |
| f3 | 0.000 | 8.238 | 6.241 | 4.770 | 1.169 | |
| f4 | 0.000 | 2.926 | 2.926 | 2.926 | 2.926 | |
| f5 | 0.000 | 1.245 | 1.245 | 1.245 | 1.245 | |
| f6 | 0.000 | 1.606 | 1.061 | 3.438 | 1.242 | |
| f7 | 0.000 | 1.131 | 1.862 | 2.386 | 5.768 | |
| f8 | 0.000 | 1.267 | 1.267 | 1.267 | 1.267 | |
| f9 | −3.042 | −3.042 | −3.042 | −2.969 | −1.364 | |
| f10 | 0.000 | 6.950 | 4.350 | 1.429 | 9.343 | |
| D = 50 | f1 | 0.000 | 1.766 | 1.486 | 3.109 | 6.272 |
| f2 | 0.000 | 2.220 | 1.436 | 1.619 | 0.000 | |
| f3 | 0.000 | 3.980 | 4.341 | 1.541 | 6.965 | |
| f4 | 0.000 | 2.926 | 2.926 | 2.926 | 2.926 | |
| f5 | 0.000 | 2.075 | 2.075 | 2.075 | 2.075 | |
| f6 | 0.000 | 1.231 | 6.051 | 3.696 | 5.605 | |
| f7 | 0.000 | 4.747 | 5.266 | 4.739 | 2.966 | |
| f8 | 0.000 | 1.267 | 1.267 | 1.267 | 1.267 | |
| f9 | −2.981 | −3.042 | −3.042 | −2.925 | −1.465 | |
| f10 | 0.000 | 2.251 | 9.063 | 9.041 | 2.931 |
| Algorithm | MVDE | GA | BBO | DE | CMA-ES | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D = 30 | Friedman test | 1.20 | 2.75 | 3.55 | 2.95 | 3.55 |
| Normalized Ranking | 1 | 2 | 3.5 | 5 | 3.5 | |
| D = 50 | Friedman test | 1.25 | 3.10 | 3.80 | 3.85 | 4.00 |
| Normalized Ranking | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 2 |
| UCs | Decision Variables | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UC1 | Variable | |||||||||||
| Value | 29.78 | 25.30 | 5.55 | 4.56 | 9.14 | 8.49 | 1.70 | - | 3.80 | 1.01 | 1.47 | |
| UC2 | Variable | |||||||||||
| Value | 23.54 | 25.13 | 9.62 | 5.65 | 7.71 | 24.13 | 1.19 | 5.65 | 2.79 | 1.96 | 1.11 | |
| UC3 | Variable | |||||||||||
| Value | 25.22 | 39.85 | 9.88 | 3.35 | 8.73 | 11.23 | 1.70 | 3.40 | 9.44 | 1.72 | 1.54 | |
| UCs | Frequency: 2.45 GHz | Frequency: 5.8 GHz |
|---|---|---|
| UC1 | ||
| UC2 | ||
| UC3 |
| 3 × 2 FSS Design | 5 × 3 FSS Design | |
| MVDE | −33.71 dB @ 2.46 GHz −26.83 dB @ 5.82 GHz | −24.36 dB @ 2.45 GHz −31.15 dB @ 5.80 GHz |
| DE | −29.57 dB @ 2.44 GHz −20.24 dB @ 5.81 GHz | −19.12 dB @ 2.47 GHz −20.88 dB @ 5.80 GHz |
| Ref. | PCB Substrate | Unit Cell | Frequency Band | Layout | Occupied Area in | Reflection Coefficient | Reference Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [25] | FR-4 | Square Loop | Wi-Fi 2.45 GHz | 25 × 15 | 3.68 × 2.45 | −28 dB (max. value) | 3.05 GHz |
| [40] | Rigid Polyurethane Foam | Cross and Fractal Square Patch | 2–18 GHz | ∼ 13 × 13 | 7.64 × 7.64 | <−10 dB | 5.27–18 GHz |
| [67] | 0.12 mm = 3 | Gridded Square Loop | Wi-Fi 2.45 GHz | 3 × 3 5 × 5 | 1.79 × 1.79 2.98 × 2.98 | <−30 dB (for the unit cell) | 2.2 GHz |
| [69] | FR-4 | Single Patch | Wi-Fi 2.45 GHz | 4 × 3 | 2.94 × 2.21 | −33.52 dB | 2.45 GHz |
| [70] | FR-4 | Cross with 4 apertures | Wi-Fi 5.8 GHz | 7 × 7 | 2.00 × 2.00 | >−40 dB | 5.8 GHz |
| [71] | Rogers RO4003C | Pair of patches | Wi-Fi 2.45 GHz | 5 × 6 | 1.87 × 2.49 | <−20 dB | 2.45 GHz |
| [72] | Rogers RO4003C | Pair of Bow-tie dipoles | GSM-1800, Wi-Fi 2.45 GHz | 5 × 4 | 1.11 × 1.80 (single unit cell) | <−30 dB (for the rectifier) | ∼ 2.4 GHz |
| This work | FR-4 | Pair of U-slots | Wi-Fi 2.45 GHz Wi-Fi 5.8 GHz | 3 × 2: | 1.00 × 0.98 | −33.71 dB −26.83 dB | 2.46 GHz 5.82 GHz |
| 5 × 3: | 1.49 × 1.50 | −24.36 dB −31.15 dB | 2.45 GHz 5.8 GHz |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boursianis, A.D.; Papadopoulou, M.S.; Nikolaidis, S.; Sarigiannidis, P.; Psannis, K.; Georgiadis, A.; Tentzeris, M.M.; Goudos, S.K. Novel Design Framework for Dual-Band Frequency Selective Surfaces Using Multi-Variant Differential Evolution. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2381. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9192381
Boursianis AD, Papadopoulou MS, Nikolaidis S, Sarigiannidis P, Psannis K, Georgiadis A, Tentzeris MM, Goudos SK. Novel Design Framework for Dual-Band Frequency Selective Surfaces Using Multi-Variant Differential Evolution. Mathematics. 2021; 9(19):2381. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9192381
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoursianis, Achilles D., Maria S. Papadopoulou, Spyridon Nikolaidis, Panagiotis Sarigiannidis, Konstantinos Psannis, Apostolos Georgiadis, Manos M. Tentzeris, and Sotirios K. Goudos. 2021. "Novel Design Framework for Dual-Band Frequency Selective Surfaces Using Multi-Variant Differential Evolution" Mathematics 9, no. 19: 2381. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9192381
APA StyleBoursianis, A. D., Papadopoulou, M. S., Nikolaidis, S., Sarigiannidis, P., Psannis, K., Georgiadis, A., Tentzeris, M. M., & Goudos, S. K. (2021). Novel Design Framework for Dual-Band Frequency Selective Surfaces Using Multi-Variant Differential Evolution. Mathematics, 9(19), 2381. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9192381













