Finite Element Study for Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) Tangent Hyperbolic Nanofluid Flow over a Faster/Slower Stretching Wedge with Activation Energy
Abstract
1. Introduction
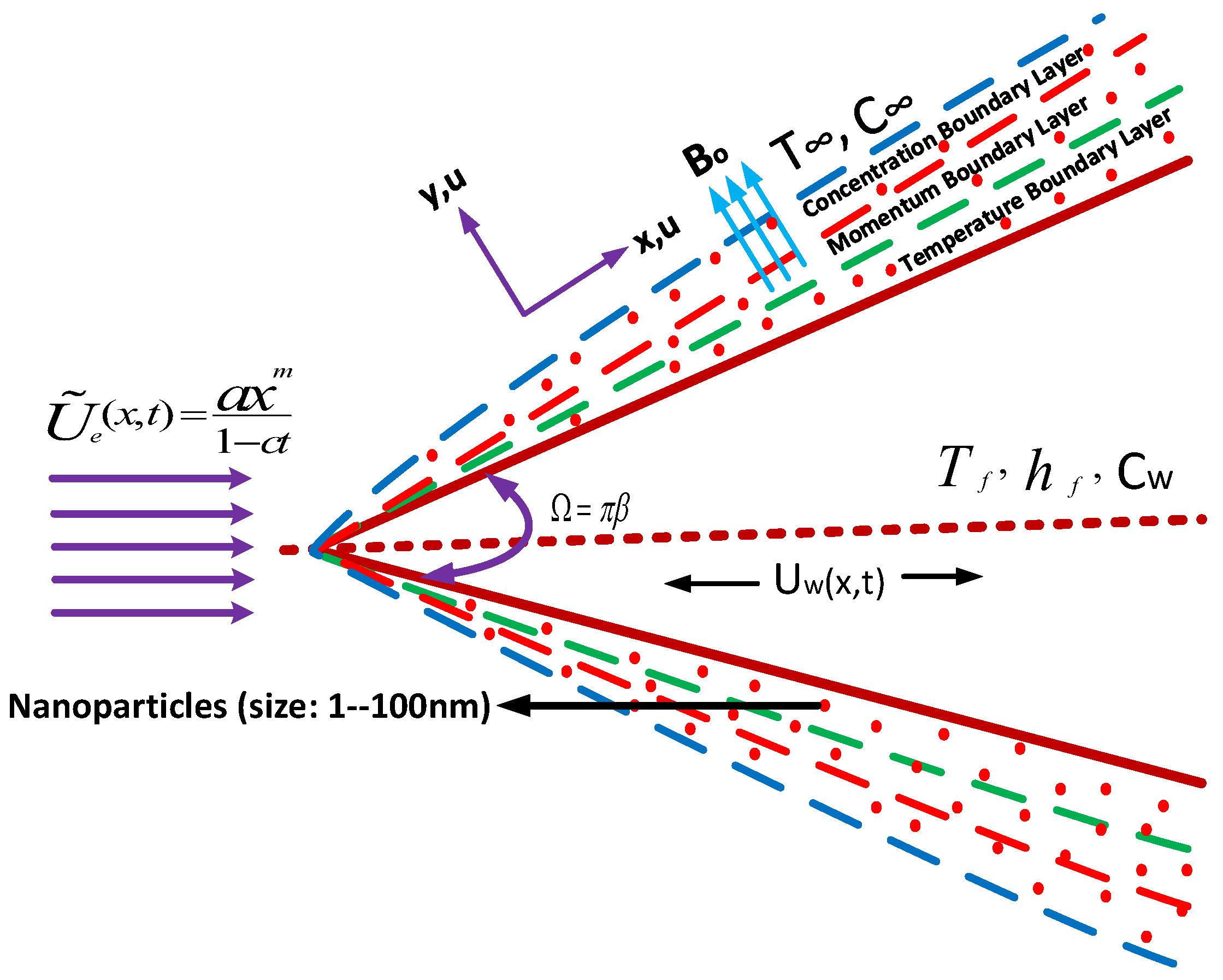
2. Physical Model and Mathematical Formulation
2.1. Tangent Hyperbolic Constitutive Model
2.2. Statement of the Problem
3. Finite Element Solutions
3.1. Variational-Formulations
3.2. Formulation of Finite-Element

4. Results And Discussion
5. Conclusions
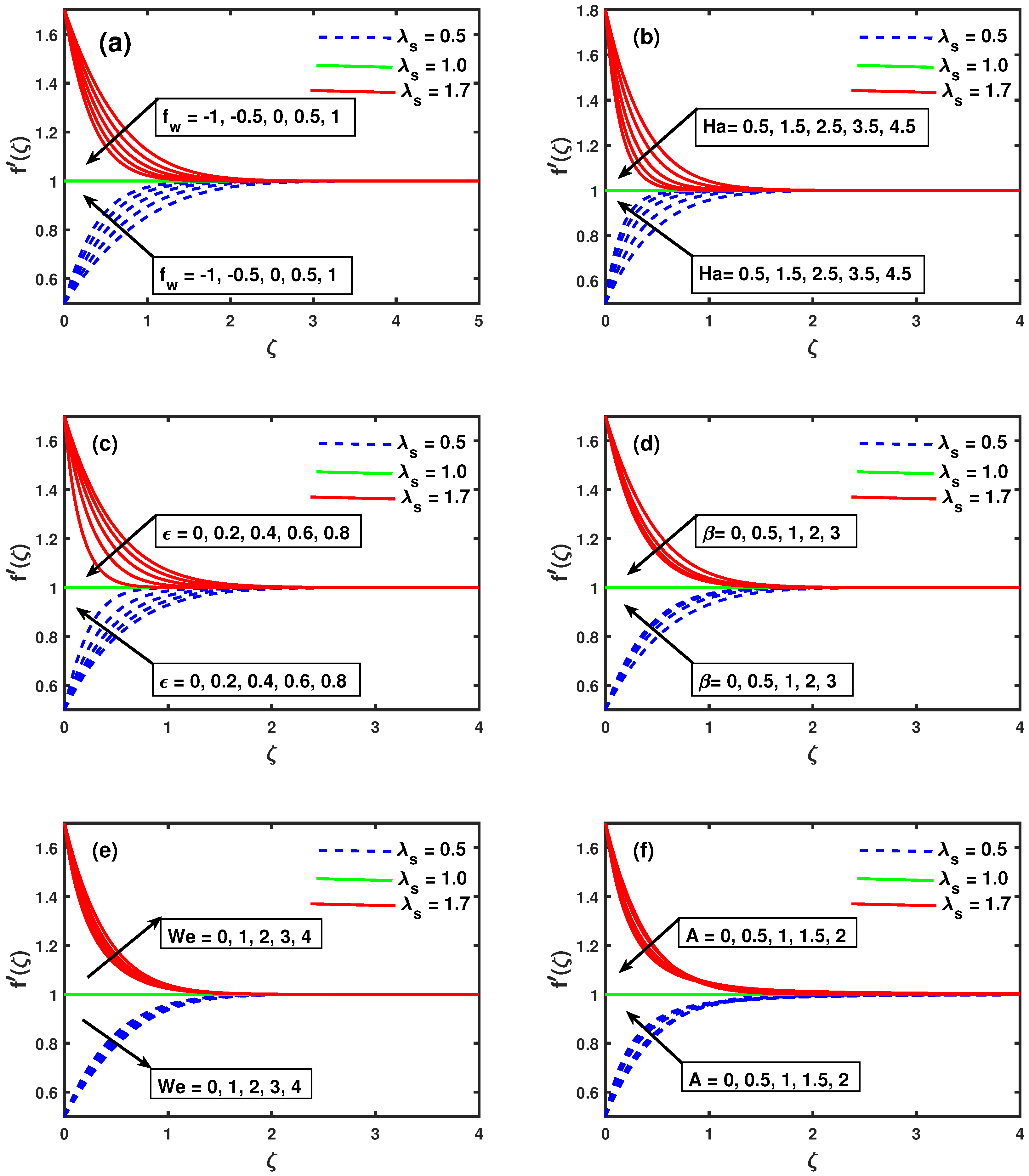
- Increased injection parameter makes the flow faster, whereas the suction causes the speed of flow to slow.
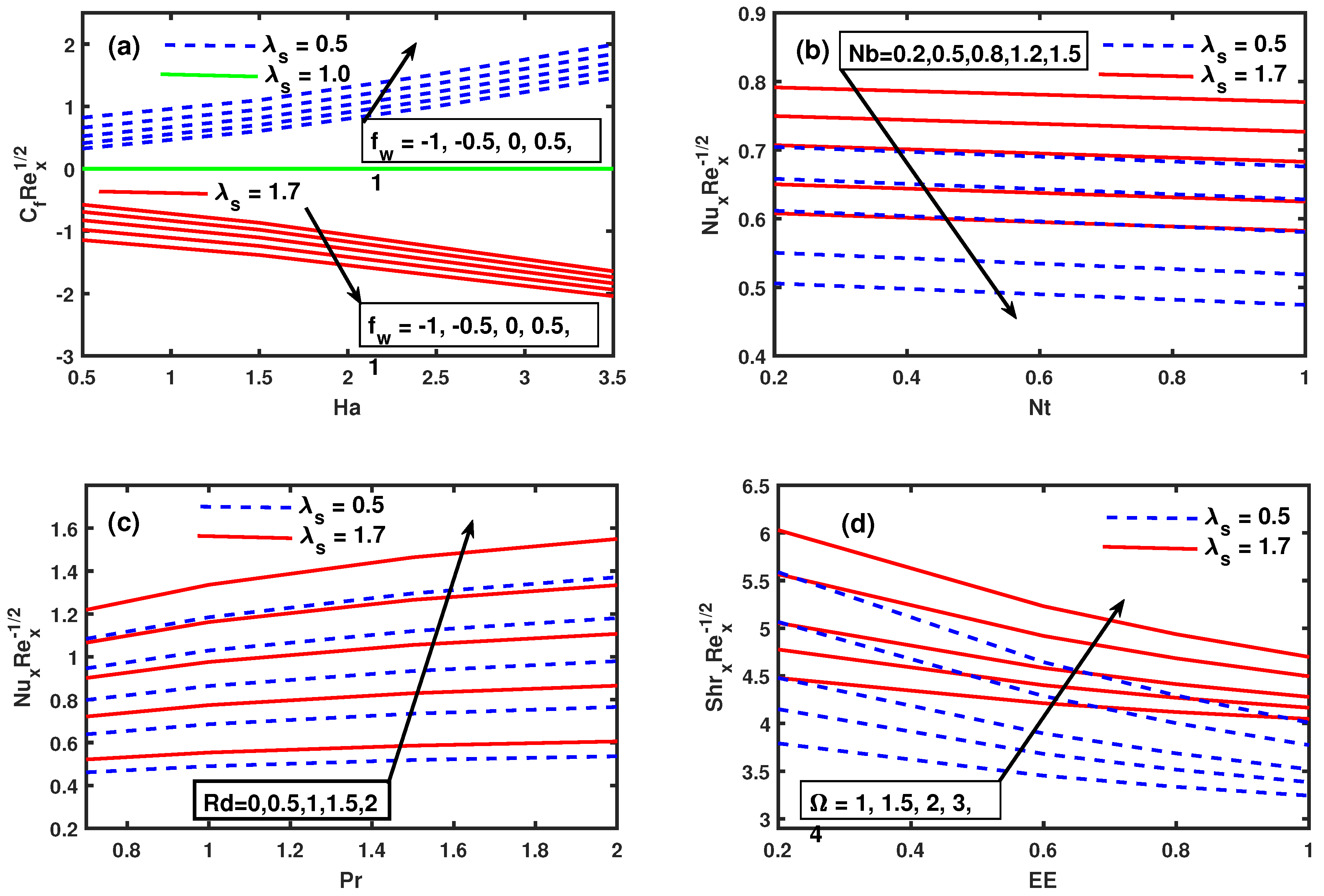
- The exceeding values of Hartman number , suction/injection material law index , aligned magnetic field parameter and unsteadiness parameter recede the velocity when whereas enhance when . An opposite trend is observed for Weissenberg number .
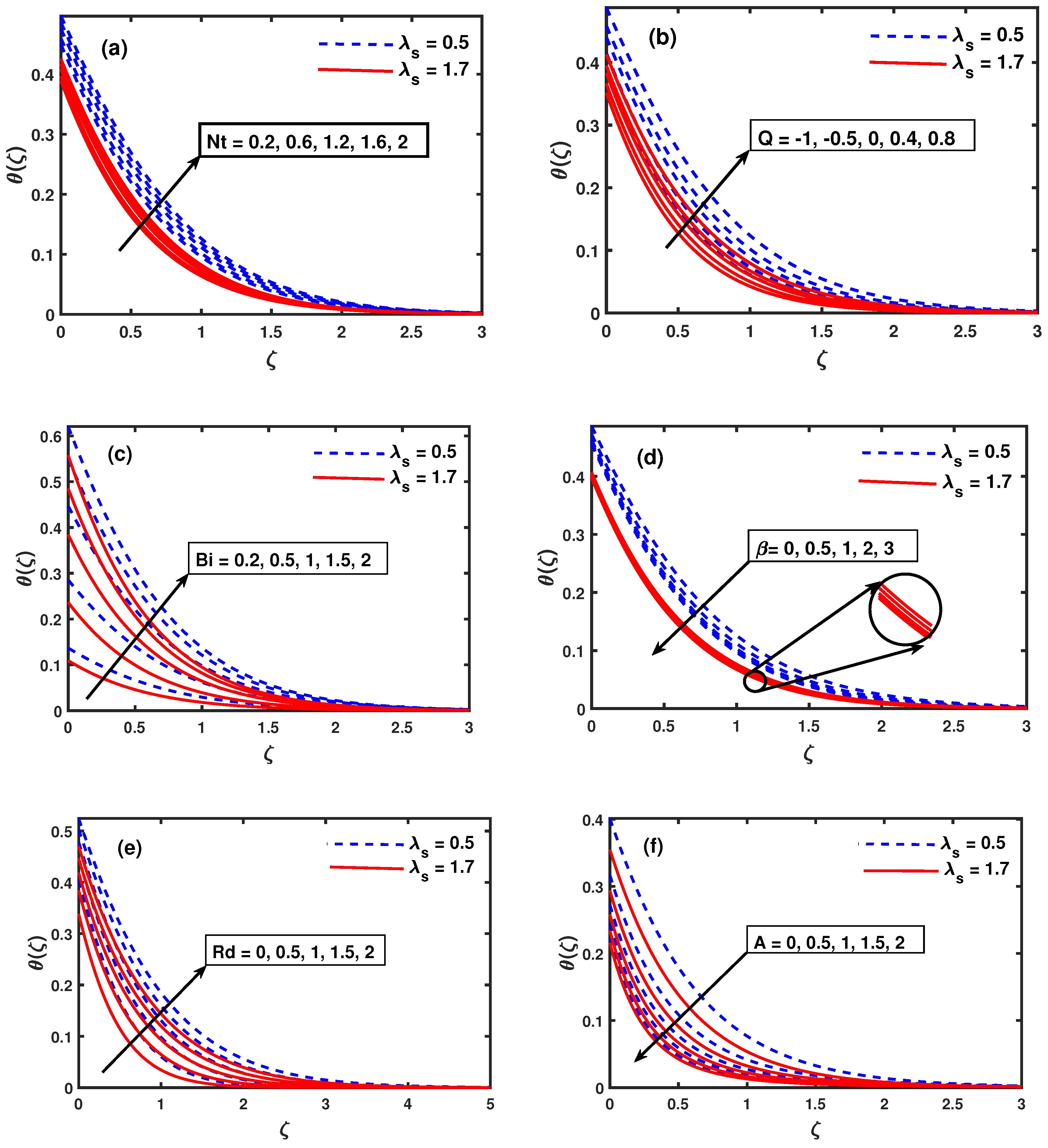
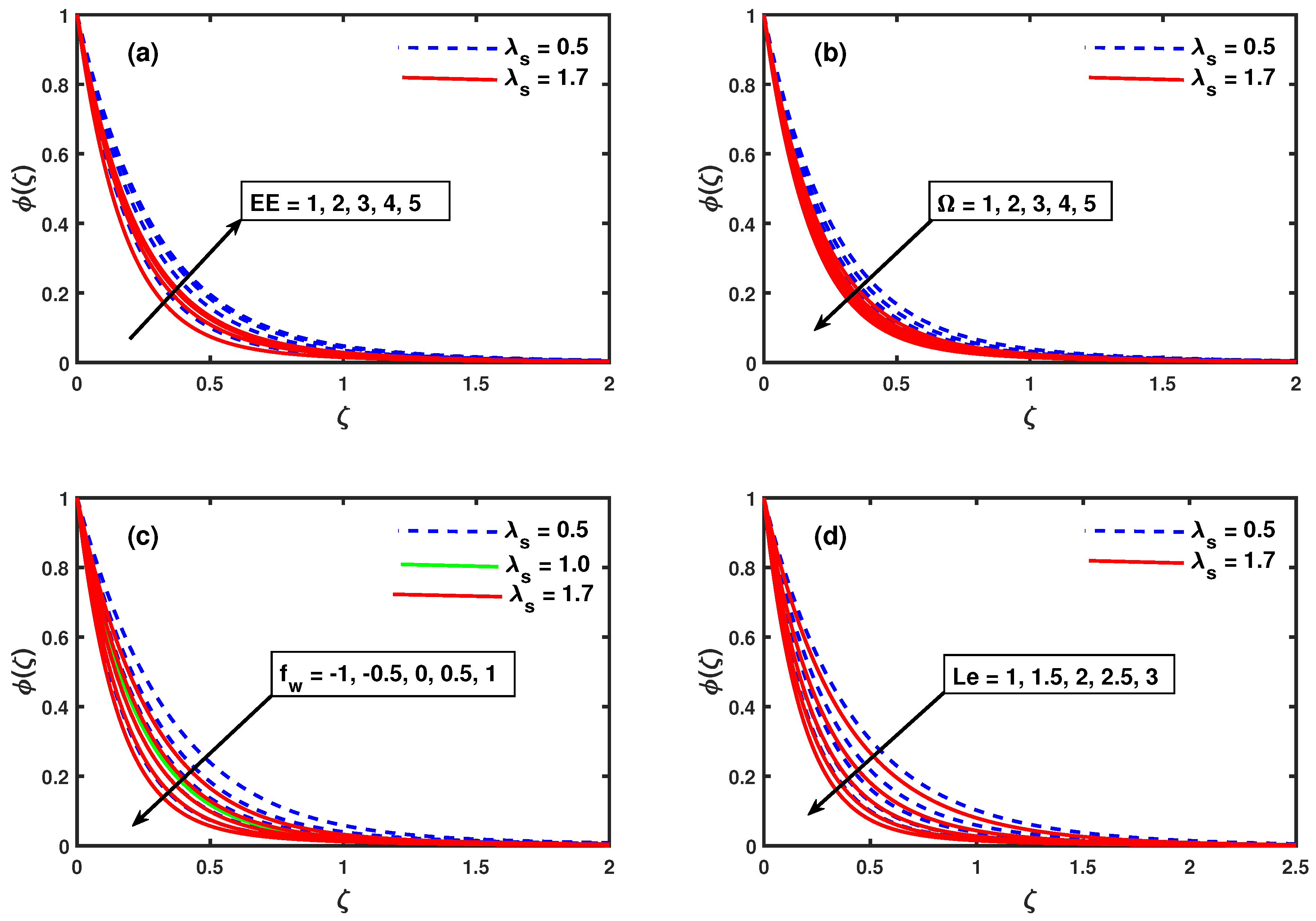
- The greater values of , , , Q and results in increased temperature distribution whereas the , , and unsteadiness causes it to decline in both cases ().
- The greater values of and results in increased temperature distribution when but a decline is observed for .
- The volume fraction of nanoparticles is upsurged with increment in but it diminishes against , and in both cases ().
- Skin friction grows larger with increment in values of when there is slow stretching , but the opposite pattern is observed for fast stretching .
- Nusselt number declines against progressive values of thermophoresis and Brownian motion parameters , .
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Non-dimensional temperature | |
| Temperature at surface | |
| Non-dimensional nanoparticles concentration | |
| Concentration at surface | |
| Temperature away from the surface | |
| Positive constants | |
| Concentration away from the surface | |
| E | Activation energy |
| Motile organisms away from the surface | |
| Velocity components | |
| Velocity of stretching/shrinking wedge | |
| Free stream velocity | |
| Thermal expansion coefficient | |
| Kinematic viscosity | |
| Density of fluid | |
| Prandtl number | |
| Thermophoretic diffusion coefficient | |
| Brownian diffusion coefficient | |
| m | Falkner-Skan power law |
| Uniform magnetic field | |
| Electrical conductivity | |
| Lewis number | |
| Wedge angle parameter | |
| Weissenberg number | |
| Base fluid heat capacity | |
| Heat generation/absorption | |
| E | Activation energy |
| Boltzmann constant | |
| n | Fitted rate constant |
| Stefan-Boltzmann number | |
| Mean assimilation coefficient | |
| Stream function | |
| Power law index | |
| Williamson parameter | |
| Brownian motion | |
| Thermophoresis | |
| chemical reaction rate | |
| Biot number | |
| Hartmann number | |
| Local Renolds number |
References
- Choi, S.U.; Eastman, J.A. Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticles; Argonne National Lab.: Lemont, IL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Buongiorno, J. Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 2006, 128, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, W.; Gamachu, D. Nonlinear convection flow of Williamson nanofluid past a radially stretching surface. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 085026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Nie, Y.; Ali, B. Multiple slip effects on MHD unsteady viscoelastic nano-fluid flow over a permeable stretching sheet with radiation using the finite element method. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manh, T.D.; Nam, N.D.; Abdulrahman, G.K.; Moradi, R.; Babazadeh, H. Impact of MHD on hybrid nanomaterial free convective flow within a permeable region. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 140, 2865–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Khan, W.; Sun, H.; Ali, M.; Irfan, M.; Shahzed, M.; Sultan, F. Mathematical modeling and analysis of Cross nanofluid flow subjected to entropy generation. Appl. Nanosci. 2019, 10, 3149–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, S.M.H.; Mehryan, S.; Sheremet, M.A.; Izadi, M.; Ghodrat, M. Numerical study of mixed bio-convection associated with a micropolar fluid. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2020, 18, 100539. [Google Scholar]
- Hiemenz, K. Die Grenzschicht an einem in den gleichformigen Flussigkeitsstrom eingetauchten geraden Kreiszylinder. Dinglers Polytech. J. 1911, 326, 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Awaludin, I.; Weidman, P.; Ishak, A. Stability analysis of stagnation-point flow over a stretching/shrinking sheet. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 045308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkin, J.H.; Pop, I. Stagnation point flow past a stretching/shrinking sheet driven by Arrhenius kinetics. Appl. Math. Comput. 2018, 337, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M.M.; Abbas, M.A.; Rashidi, M.M. A robust numerical method for solving stagnation point flow over a permeable shrinking sheet under the influence of MHD. Appl. Math. Comput. 2018, 316, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Z.; Kumam, P.; Deebani, W. Radiative MHD Casson Nanofluid Flow with Activation energy and chemical reaction over past nonlinearly stretching surface through Entropy generation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatunmbi, E.; Adeniyan, A. MHD stagnation point-flow of micropolar fluids past a permeable stretching plate in porous media with thermal radiation, chemical reaction and viscous dissipation. J. Adv. Math. Comput. Sci. 2018, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, L.G. Advanced Transport Phenomena: Fluid Mechanics and Convective Transport Processes; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Falkneb, V.; Skan, S.W. LXXXV. Solutions of the boundary-layer equations. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1931, 12, 865–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Hussain, S.; Nie, Y.; Rehman, A.U.; Khalid, M. Buoyancy Effetcs On FalknerSkan Flow of a Maxwell Nanofluid Fluid with Activation Energy past a wedge: Finite Element Approach. Chin. J. Phys. 2020, 68, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T. Thermal boundary layers over a wedge with uniform suction or injection in forced flow. Acta Mech. 1990, 83, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, A.; Nazar, R.; Pop, I. MHD boundary-layer flow past a moving wedge. Magnetohydrodynamics 2009, 45, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, B.; Hussain, S.; Nie, Y.; Khan, S.A.; Naqvi, S.I.R. Finite element simulation of bioconvection Falkner–Skan flow of a Maxwell nanofluid fluid along with activation energy over a wedge. Phys. Scr. 2020, 95, 095214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.; Rida, S.; Arafa, A.; Mubarak, M. Heat and Mass Transfer in an Unsteady Magnetohydrodynamics Al2O3—Water Nanofluid Squeezed Between Two Parallel Radiating Plates Embedded in Porous Media With Chemical Reaction. J. Heat Transf. 2020, 142, 012401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Rasool, G.; Hussain, S.; Baleanu, D.; Bano, S. Finite Element Study of Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) and Activation Energy in Darcy–Forchheimer Rotating Flow of Casson Carreau Nanofluid. Processes 2020, 8, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, T.; Waqas, H.; Khan, S.A.; Ellahi, R.; Sait, S.M. Significance of nonlinear thermal radiation in 3D Eyring–Powell nanofluid flow with Arrhenius activation energy. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaivanan, R.; Ganesh, N.V.; Al-Mdallal, Q.M. An investigation on Arrhenius activation energy of second grade nanofluid flow with active and passive control of nanomaterials. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2020, 22, 100774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, M.; Ali, M.; Sultan, F.; Khan, W.A.; Hussain, Z. Computational investigation of magneto-cross fluid flow with multiple slip along wedge and chemically reactive species. Results Phys. 2020, 16, 102972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Waqas, M.; Alsaedi, A.; Bashir, G.; Alzahrani, F. Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) stretched flow of tangent hyperbolic nanoliquid with variable thickness. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 229, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdy, A.; Hoshoudy, G. EMHD time-dependant tangent hyperbolic nanofluid flow by a convective heated Riga plate with chemical reaction. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process. Mech. Eng. 2019, 233, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaib, A.; Haq, R.U.; Sheikholeslami, M.; Chamkha, A.J.; Rashidi, M.M. Impact of non-darcy medium on mixed convective flow towards a plate containing micropolar water-based tio 2 nanomaterial with entropy generation. J. Porous Media 2020, 23, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraz, F.; Imran, S.M.; Ali, B.; Haider, S. Thermo-diffusion and multi-slip effect on an axisymmetric Casson flow over a unsteady radially stretching sheet in the presence of chemical reaction. Processes 2019, 7, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.A.; Bhatti, M.M.; Sheikholeslami, M. Peristaltic propulsion of Jeffrey nanofluid with thermal radiation and chemical reaction effects. Inventions 2019, 4, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, L.; Xiaomin, L.; Ali, B.; Majeed, S.; Abdal, S. The Impact of Nanoparticles Due to Applied Magnetic Dipole in Micropolar Fluid Flow Using the Finite Element Method. Symmetry 2020, 12, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, M.; Gul, H.; Sheikholeslami, M. Effect of second order slip condition on the flow of tangent hyperbolic fluid—A novel perception of Cattaneo–Christov heat flux. Phys. Scr. 2019, 94, 115707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, L.; Xiaomin, L.; Ali, B.; Majeed, S.; Abdal, S.; Ali, S.K. Analysis of Magnetic Properties of Nano-Particles Due to a Magnetic Dipole in Micropolar Fluid Flow over a Stretching Sheet. Coatings 2020, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Hussain, S.; Nie, Y.; Hussein, A.K.; Habib, D. Finite element investigation of Dufour and Soret impacts on MHD rotating flow of Oldroyd-B nanofluid over a stretching sheet with double diffusion Cattaneo Christov heat flux model. Powder Technol. 2021, 377, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, L.; Liu, X.; Ali, B.; Mujeed, S.; Abdal, S. Finite Element Analysis of Thermo-Diffusion and Multi-Slip Effects on MHD Unsteady Flow of Casson Nano-Fluid over a Shrinking/Stretching Sheet with Radiation and Heat Source. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Nie, Y.; Hussain, S.; Manan, A.; Sadiq, M.T. Unsteady magneto-hydrodynamic transport of rotating Maxwell nanofluid flow on a stretching sheet with Cattaneo–Christov double diffusion and activation energy. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2020, 20, 100720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Naqvi, R.A.; Hussain, D.; Aldossary, O.M.; Hussain, S. Magnetic Rotating Flow of a Hybrid Nano-Materials Ag-MoS2 and Go-MoS2 in C2H6O2-H2O Hybrid Base Fluid over an Extending Surface Involving Activation Energy: FE Simulation. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A.; Ali, R.; Hussain, M.; Kamran, M. Unsteady axisymmetric flow and heat transfer over time-dependent radially stretching sheet. Alex. Eng. J. 2017, 56, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, F.M. Viscous Fluid Flow; Magraw-Hill Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, B.; Naqvi, R.A.; Nie, Y.; Khan, S.A.; Sadiq, M.T.; Rehman, A.U.; Abdal, S. Variable Viscosity Effects on Unsteady MHD an Axisymmetric Nanofluid Flow over a Stretching Surface with Thermo-Diffusion: FEM Approach. Symmetry 2020, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Yu, X.; Sadiq, M.T.; Rehman, A.U.; Ali, L. A Finite Element Simulation of the Active and Passive Controls of the MHD Effect on an Axisymmetric Nanofluid Flow with Thermo-Diffusion over a Radially Stretched Sheet. Processes 2020, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, N.S.; Nadeem, S.; Haq, R.U.; Khan, Z. Numerical solutions of Magnetohydrodynamic boundary layer flow of tangent hyperbolic fluid towards a stretching sheet. Indian J. Phys. 2013, 87, 1121–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilias, M.R.; Rawi, N.A.; Zaki, N.H.M.; Shafie, S. Aligned MHD Magnetic Nanofluid Flow Past a Static Wedge. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdal, S.; Ali, B.; Younas, S.; Ali, L.; Mariam, A. Thermo-Diffusion and Multislip Effects on MHD Mixed Convection Unsteady Flow of Micropolar Nanofluid over a Shrinking/Stretching Sheet with Radiation in the Presence of Heat Source. Symmetry 2020, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, C.; Hoque, M.M.; Sivasankar, T. Radiative flow of Casson fluid over a moving wedge filled with gyrotactic microorganisms. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Shafie, S.; Khan, I. MHD heat transfer flow of Casson fluid past a stretching wedge subject to suction and injection. Malays. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2017, 13, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.J.; Raju, R.S.; Rao, J.A. Influence of viscous dissipation on unsteady MHD natural convective flow of Casson fluid over an oscillating vertical plate via FEM. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2018, 9, 1907–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, K.; Reddy, P.S.; Reddy, M.S. Carreau nanofluid heat and mass transfer flow through wedge with slip conditions and nonlinear thermal radiation. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2019, 41, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, J.N. Solutions Manual for an Introduction to the Finite Element Method; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1993; p. 41. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, W.; Gadisa, G. Finite element solution of nonlinear convective flow of Oldroyd-B fluid with Cattaneo-Christov heat flux model over nonlinear stretching sheet with heat generation or absorption. Propuls. Power Res. 2020, 55, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Hussain, S.; Abdal, S.; Mehdi, M.M. Impact of Stefan blowing on thermal radiation and Cattaneo–Christov characteristics for nanofluid flow containing microorganisms with ablation/accretion of leading edge: FEM approach. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2020, 135, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Nie, Y.; Khan, S.A.; Sadiq, M.T.; Tariq, M. Finite Element Simulation of Multiple Slip Effects on MHD Unsteady Maxwell Nanofluid Flow over a Permeable Stretching Sheet with Radiation and Thermo-Diffusion in the Presence of Chemical Reaction. Processes 2019, 7, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Nie, Y.; Ali, B. Multiple Slip Effects on Magnetohydrodynamic Axisymmetric Buoyant Nanofluid Flow above a Stretching Sheet with Radiation and Chemical Reaction. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Rana, P.; Bég, O.A.; Ismail, A.M. Finite element simulation of magnetohydrodynamic convective nanofluid slip flow in porous media with nonlinear radiation. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 1305–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, W.; Gadisa, G. Finite Element Method Solution of Boundary Layer Flow of Powell-Eyring Nanofluid over a Nonlinear Stretching Surface. J. Appl. Math. 2019, 2019, 3472518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariel, P. Hiemenz flow in hydromagnetics. Acta Mech. 1994, 103, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, A.; Nazar, R.; Pop, I. Falkner-Skan equation for flow past a moving wedge with suction or injection. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 2007, 25, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Khan, W.A. Effect of viscous dissipation and internal heat generation/absorption on heat transfer flow over a moving wedge with convective boundary condition. Heat Transf. Res. 2013, 42, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yih, K. MHD forced convection flow adjacent to a non-isothermal wedge. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 1999, 26, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Shafie, S.; Khan, I. Heat generation and absorption in MHD flow of Casson fluid past a stretching wedge with viscous dissipation and newtonian heating. J. Teknol. 2018, 80, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Postelnicu, A.; Pop, I. Falkner–Skan boundary layer flow of a power-law fluid past a stretching wedge. Appl. Math. Comput. 2011, 217, 4359–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Number of Elements | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 | 1.068133 | 0.914246 | 0.148457 | 0.054075 |
| 100 | 1.067776 | 0.914217 | 0.148492 | 0.054118 |
| 180 | 1.067636 | 0.914206 | 0.148507 | 0.054136 |
| 360 | 1.067585 | 0.914202 | 0.148512 | 0.054142 |
| 500 | 1.067582 | 0.914202 | 0.148513 | 0.054143 |
| 700 | 1.067578 | 0.914201 | 0.148513 | 0.054144 |
| 1000 | 1.067575 | 0.914201 | 0.148513 | 0.054144 |
| Ariel [55] | Current Results | % Error | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perturbation Solution | Approximate Solution | (a) Exact Solution | (b) | ||
| 0.0 | 1.232588 | 1.224745 | 1.232588 | 1.232589 | 0.000081 |
| 0.4 | 1.295290 | 1.288410 | 1.295368 | 1.295369 | 0.000077 |
| 0.8 | 1.463725 | 1.462874 | 1.467976 | 1.467977 | 0.000068 |
| 1.0 | 1.570687 | 1.581139 | 1.585331 | 1.585332 | 0.000063 |
| 1.4 | 1.774774 | 1.840810 | 1.862848 | 1.862849 | 0.000161 |
| 1.6 | 1.842391 | 2.005172 | 2.017154 | 2.017155 | 0.000050 |
| 3.0 | - | 3.240355 | 3.240950 | 3.240952 | 0.000062 |
| 5.0 | - | 5.147815 | 5.147965 | 5.147968 | 0.000058 |
| 10.0 | - | 10.074740 | 10.074741 | 10.074748 | 0.000069 |
| Ishak [56] | Ahmadand Khan [57] | Yin [58] | Imran Ullaha [59] | Postelnicu and Pop [60] | FEM Current Results | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1.0 | 0.7566 | 0.75655 | 0.75658 | 0.7566 | 0.75657 | 0.756576 |
| −0.5 | 0.9692 | 0.96922 | 0.96923 | 0.9692 | 0.96923 | 0.969232 |
| 0.0 | 1.2326 | 1.23258 | 1.23259 | 1.2326 | 1.23259 | 1.232591 |
| 0.5 | 1.5418 | 1.54175 | 1.54175 | 1.5418 | 1.54175 | 1.541756 |
| 1.0 | 1.8893 | 1.88931 | 1.88931 | 1.8893 | 1.88931 | 1.889321 |
| Pr | White [38] | FEM (Current Results) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.1980 | 0.2090 | 0.198129 | 0.209153 |
| 0.3 | 0.3037 | 0.3278 | 0.303719 | 0.327831 |
| 0.6 | 0.3916 | 0.4289 | 0.391677 | 0.428928 |
| 0.7 | 0.4178 | 0.4592 | 0.418094 | 0.459555 |
| 1.0 | 0.4696 | 0.5195 | 0.469604 | 0.519524 |
| 2.0 | 0.5972 | 0.6690 | 0.597241 | 0.669056 |
| 6.0 | 0.8672 | 0.9872 | 0.867297 | 0.987299 |
| 10.0 | 1.0297 | 1.1791 | 1.029779 | 1.179182 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, B.; Naqvi, R.A.; Mariam, A.; Ali, L.; Aldossary, O.M. Finite Element Study for Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) Tangent Hyperbolic Nanofluid Flow over a Faster/Slower Stretching Wedge with Activation Energy. Mathematics 2021, 9, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9010025
Ali B, Naqvi RA, Mariam A, Ali L, Aldossary OM. Finite Element Study for Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) Tangent Hyperbolic Nanofluid Flow over a Faster/Slower Stretching Wedge with Activation Energy. Mathematics. 2021; 9(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Bagh, Rizwan Ali Naqvi, Amna Mariam, Liaqat Ali, and Omar M. Aldossary. 2021. "Finite Element Study for Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) Tangent Hyperbolic Nanofluid Flow over a Faster/Slower Stretching Wedge with Activation Energy" Mathematics 9, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9010025
APA StyleAli, B., Naqvi, R. A., Mariam, A., Ali, L., & Aldossary, O. M. (2021). Finite Element Study for Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) Tangent Hyperbolic Nanofluid Flow over a Faster/Slower Stretching Wedge with Activation Energy. Mathematics, 9(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9010025








