Role of Bi-Directional Migration in Two Similar Types of Ecosystems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. General Model Formulation and Stability Analysis
- , , , , , , , ,
- , , , , , , ,
- , , and
- with , ,
- ,
- , ,
- and .
3. Applications
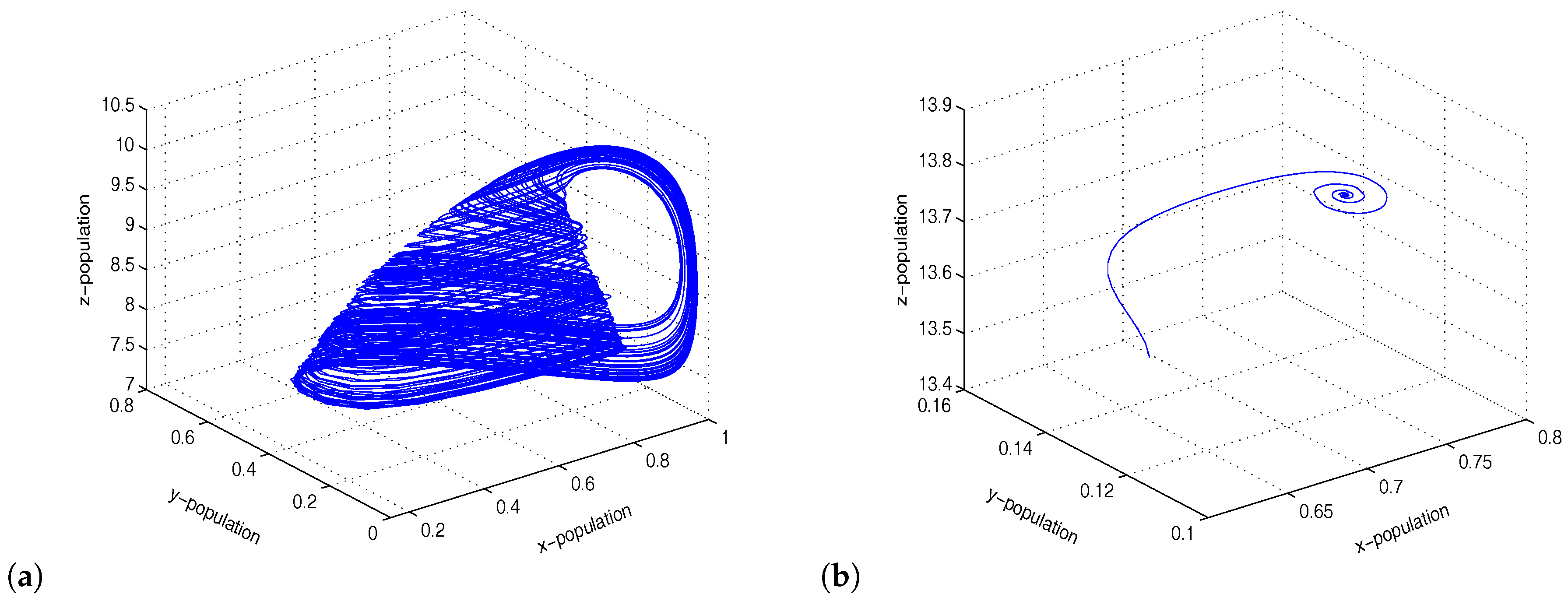
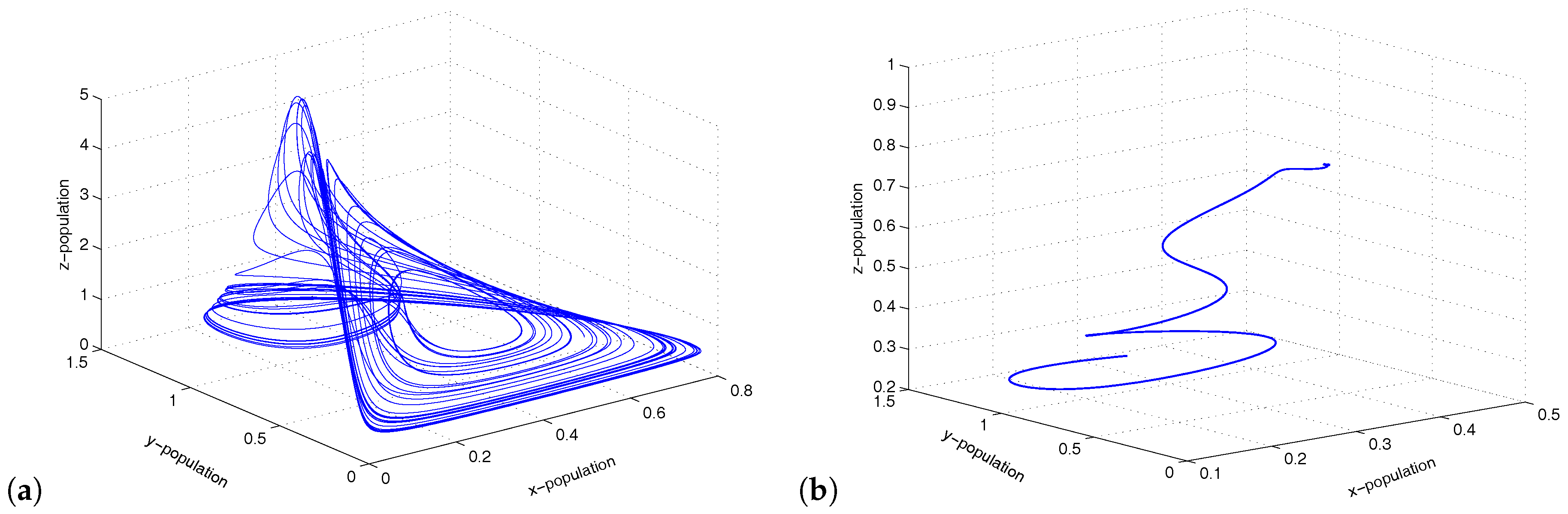
3.1. Hastings–Powell Model
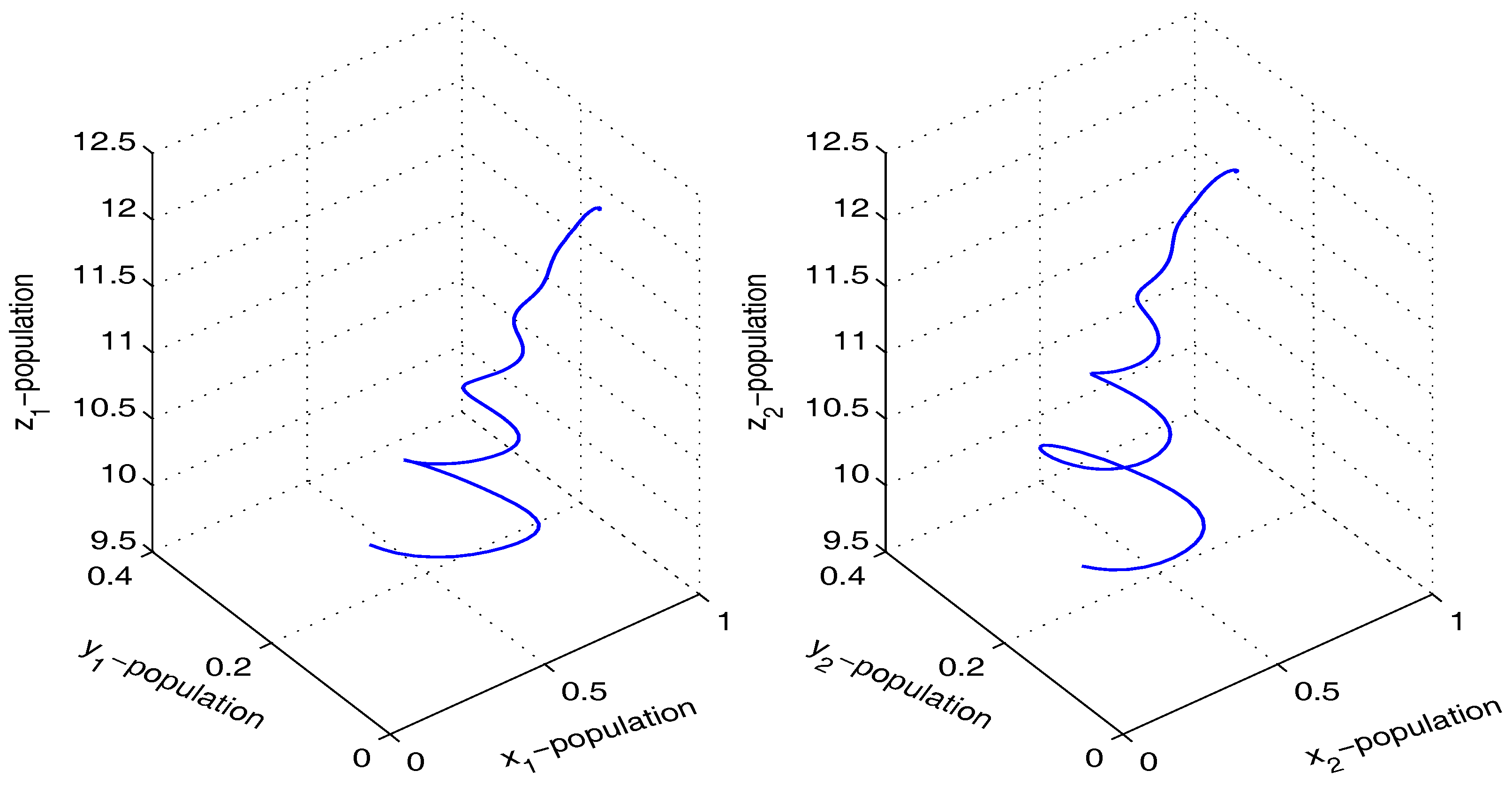
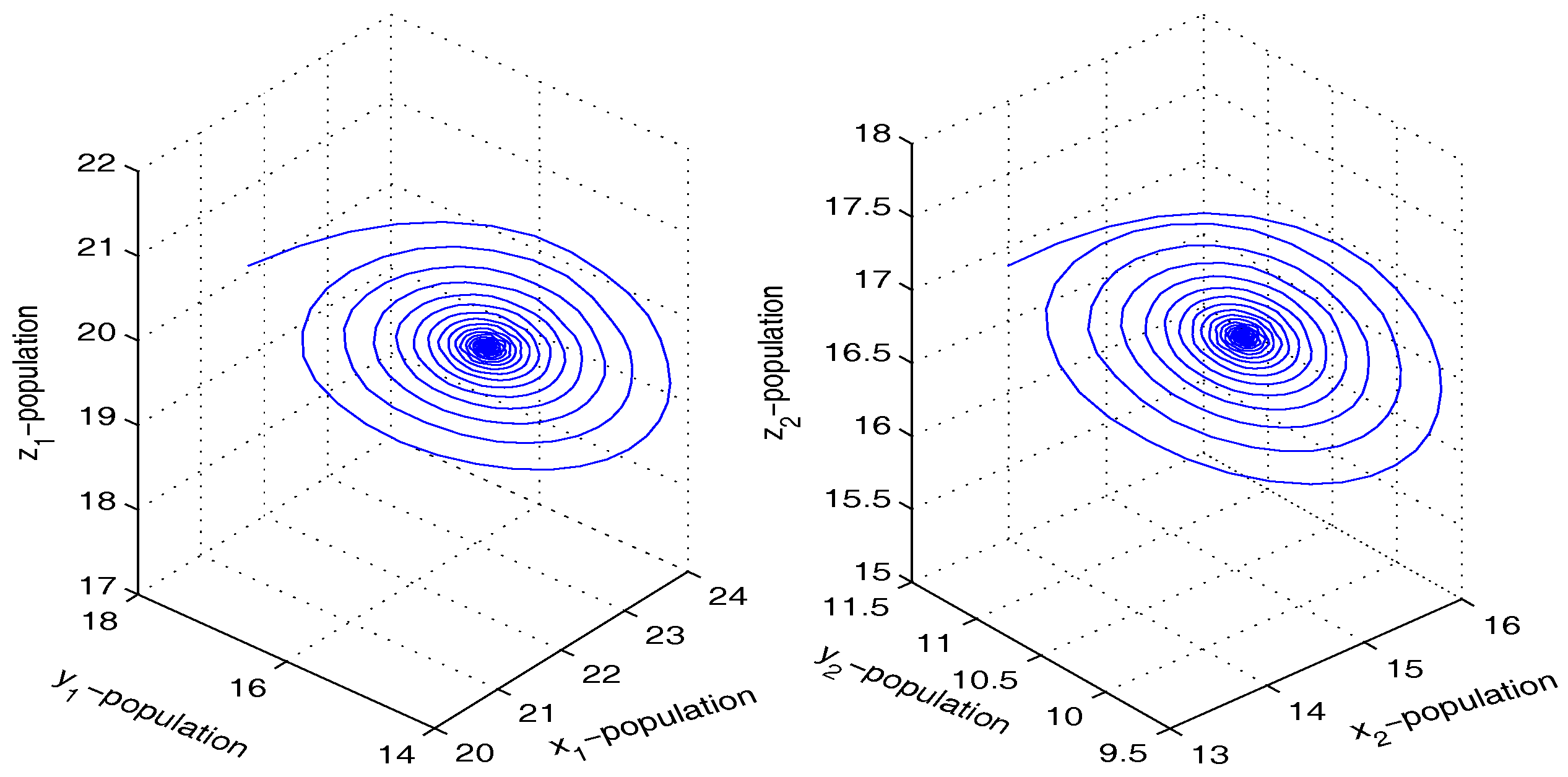
Coupling between Chaotic HP Model and Stable HP Model
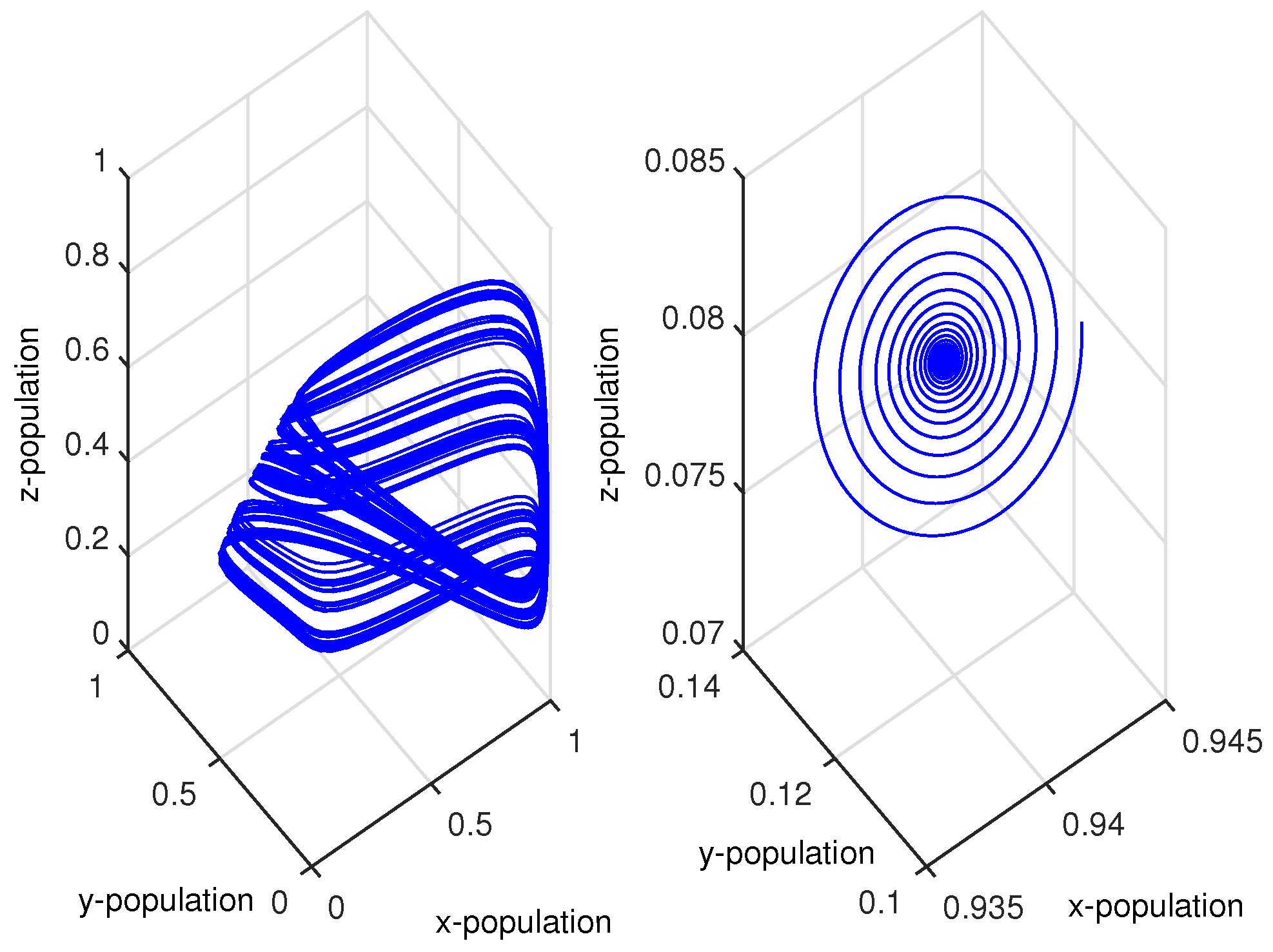
3.2. Upadhyay–Rai Model
Coupling between Chaotic UR Model and Stable UR Model
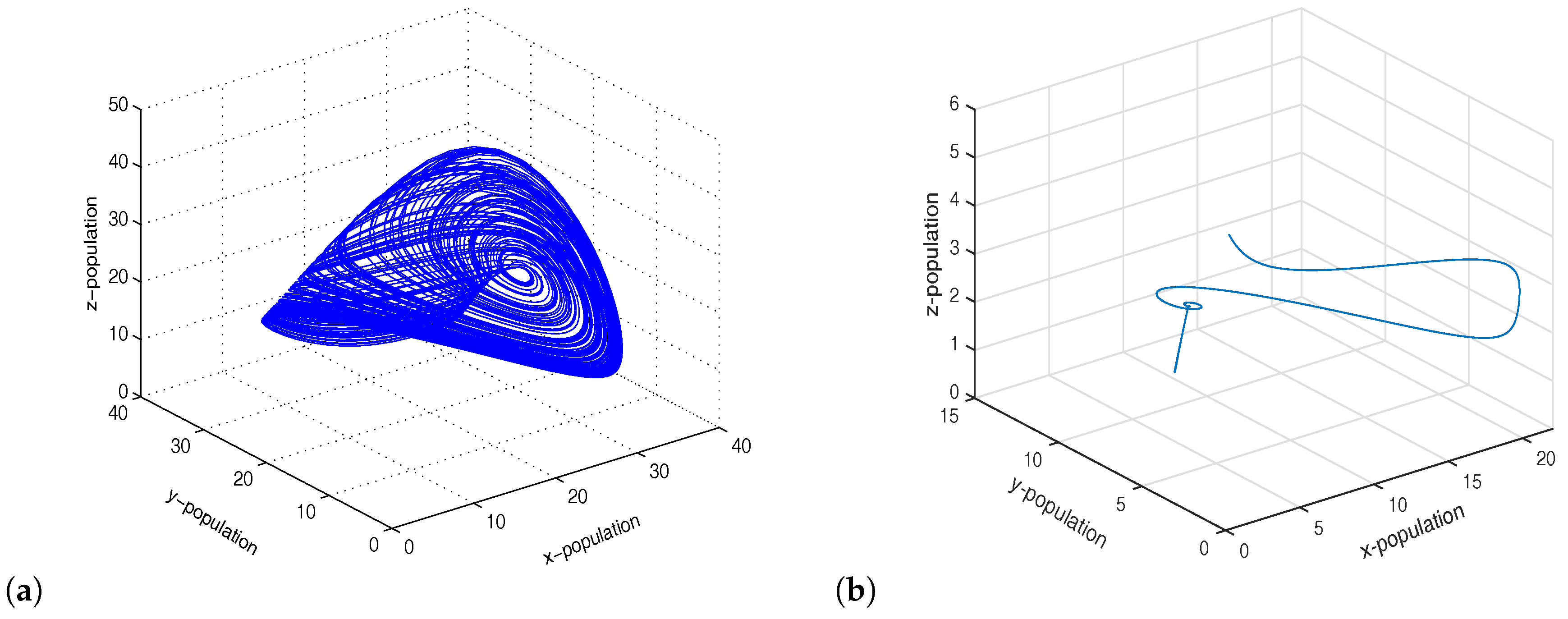
3.3. Priyadarshi–Gakkhar Model
Coupling between Chaotic PG Model and Stable PG Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malthus, T.R. An Essay on the Principle of Population; Joseph Johnson: London, UK, 1798. [Google Scholar]
- Verhulst, P.F. Notice sur la loi que la population suit dans son accroissement. Correspondance Mathmatique et Physique Publie par A. Quetelet 1838, 10, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Volterra, V. Fluctuations in the abundance of a species considered mathematically. Nature 1926, 118, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotka, A.J. Elements of Physical Biology; Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1925. [Google Scholar]
- Gilpin, M.E. Spiral chaos in a predator-prey model. Am. Nat. 1979, 113, 306–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, A.; Powell, T. Chaos in three-species food chain. Ecology 1991, 72, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R.K.; Rai, V. Why chaos is rarely observed in natural populations. Chaos Solitons Fractals 1997, 8, 1933–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, K.; Namba, T. Omnivory creates chaos in simple food web models. Ecology 2005, 86, 3411–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, A.; Gakkhar, S. Dynamics of Leslie-Gower type generalist predator in a tri-trophic food web system. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2013, 18, 3202–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, K.; Hastings, A. Re-evaluating the omnivory-stability relationship in food webs. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1997, 264, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhayay, J.; Sarkar, R. Chaos to order: Preliminary experiments with a population dynamics models of three tropic levels. Ecol. Model. 2003, 163, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Samanta, S.; Chattopadhyay, J. Revisited Hastings and Powell model with omnivory and predator switching. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2014, 66, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levins, R. Some demographic and genetic consequences of environmental heterogeneity for biological control. Bull. Entomol.Soc. Am. 1969, 15, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilpin, M. (Ed.) Metapopulation Dynamics: Empirical and Theoretical Investigations; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Hanski, I.; Thomas, C.D. Metapopulation dynamics and conservation: A spatially explicit model applied to butterflies. Biol. Conserv. 1994, 68, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanski, I. Metapopulation Ecology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Dingle, H. Migration strategies of insects. Science 1972, 175, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, A.F.G.; Horth, S.; Kindlmann, P. Migration in insects: Cost and strategies. J. Anim. Ecol. 1993, 62, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthiopoulos, J.; Harwood, J.; Thomas, L.E.N. Metapopulation consequences of site fidelity for colonially breeding mammals and birds. J. Anim. Ecol. 2005, 74, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyllenberg, M.; Soderbacka, G.; Ericsson, S. Does migration stabilize local population dynamics? Analysis of a discrete metapopulation model. Mat. Biosci. 1993, 118, 25–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, H.I. Effects of immigration on chaotic population dynamics. J. Theor. Biol. 1992, 154, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, L.; Hart, D. Effects of Immigration on the Dynamics of Simple Population Models. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1999, 55, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, R.D. Population dynamics in two-patch environments: Some anomalous consequences of an optimal habitat distribution. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1985, 28, 181–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.L.J.; De Castro, L.M.; Justo, A.M.D. Synchronism in a metapopulation model. Bull. Math. Biol. 2000, 62, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeve, J.D. Environmental variability, migration, and persistence in host-parasitoid systems. Am. Nat. 1988, 132, 810–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeve, J.D. Stability, variability, and persistence in host-parasitoid systems. Ecology 1990, 71, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.D. Large-scale spatial structure and population dynamics in arthropod predator-prey systems. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 1988, 25, 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ruxton, G.D. Low levels of immigration between chaotic populations can reduce system extinctions by inducing asynchronous regular cycles. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1994, 256, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Samanta, S.; Chattopadhyay, J. The impact of diffusive migration on ecosystem stability. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2015, 78, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieme, R. Mathematics in Population Biology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Birkhoff, G.; Rota, G. Ordinary Differential Equation; John Wiley and Sons: Boston, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- McCann, K.; Yodzis, P. Biological Conditions for Chaos in a Three-Species Food Chain. Ecology 1994, 75, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R.K.; Rai, V. Complex dynamics and synchronization in two non-identical chaotic ecological systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 40, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parshad, R.D.; Kumari, N.; Kouachi, S. A remark on “Study of a Leslie–Gower-type tritrophic population model” [Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 14 (2002) 1275–1293]. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2015, 71, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Straughan, B. Explosive Instabilities in Mechanics; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Quittner, P.; Souplet, P. Superlinear Parabolic Problems: Blow-Up, Global Existence and Steady States; Birkhauser Verlag: Basel, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Parshad, R.D.; Quansah, E.; Black, K.; Beauregard, M. Biological control via “ecological” damping: An approach that attenuates non-target effects. Math. Biosci. 2016, 273, 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parshad, R.D.; Upadhyay, R.K.; Mishra, S.; Tiwari, S.K.; Sharma, S. On the explosive instability in a three-species food chain model with modified Holling type IV functional response. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2016, 40, 5707–5726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parshad, R.D.; Quansah, E.; Beauregard, M.; Kouachi, S. On “small” data blow-up in a three species food chain model. Comput. Math. Appl. 2017, 73, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parshad, R.D.; Basheer, A.; Jana, D.; Tripathi, J.P. Do prey handling predators really matter: Subtle effects of a Crowley-Martin functional response. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2017, 103, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassell, M.P. The Dynamics of Arthropod Predator-Prey Systems; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, V.A.; Nicholson, A.J.; Williams, E.J. Interaction between hosts and parasites when some host individuals are more difficult to find than others. J. Theor. Biol. 1962, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chewning, W.C. Migratory effects in predator-prey models. Math. Biosci. 1975, 23, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pal, N.; Samanta, S.; Martcheva, M.; Chattopadhyay, J. Role of Bi-Directional Migration in Two Similar Types of Ecosystems. Mathematics 2018, 6, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/math6030036
Pal N, Samanta S, Martcheva M, Chattopadhyay J. Role of Bi-Directional Migration in Two Similar Types of Ecosystems. Mathematics. 2018; 6(3):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/math6030036
Chicago/Turabian StylePal, Nikhil, Sudip Samanta, Maia Martcheva, and Joydev Chattopadhyay. 2018. "Role of Bi-Directional Migration in Two Similar Types of Ecosystems" Mathematics 6, no. 3: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/math6030036
APA StylePal, N., Samanta, S., Martcheva, M., & Chattopadhyay, J. (2018). Role of Bi-Directional Migration in Two Similar Types of Ecosystems. Mathematics, 6(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/math6030036





