Correctness Coverage Evaluation for Medical Multiple-Choice Question Answering Based on the Enhanced Conformal Prediction Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Natural Language Generation Tasks in the Medical Domain
2.2. Uncertainty Quantification in Medical Question Answering Tasks
2.3. Conformal Prediction for Uncertainty Quantification in Medical Question Answering Tasks
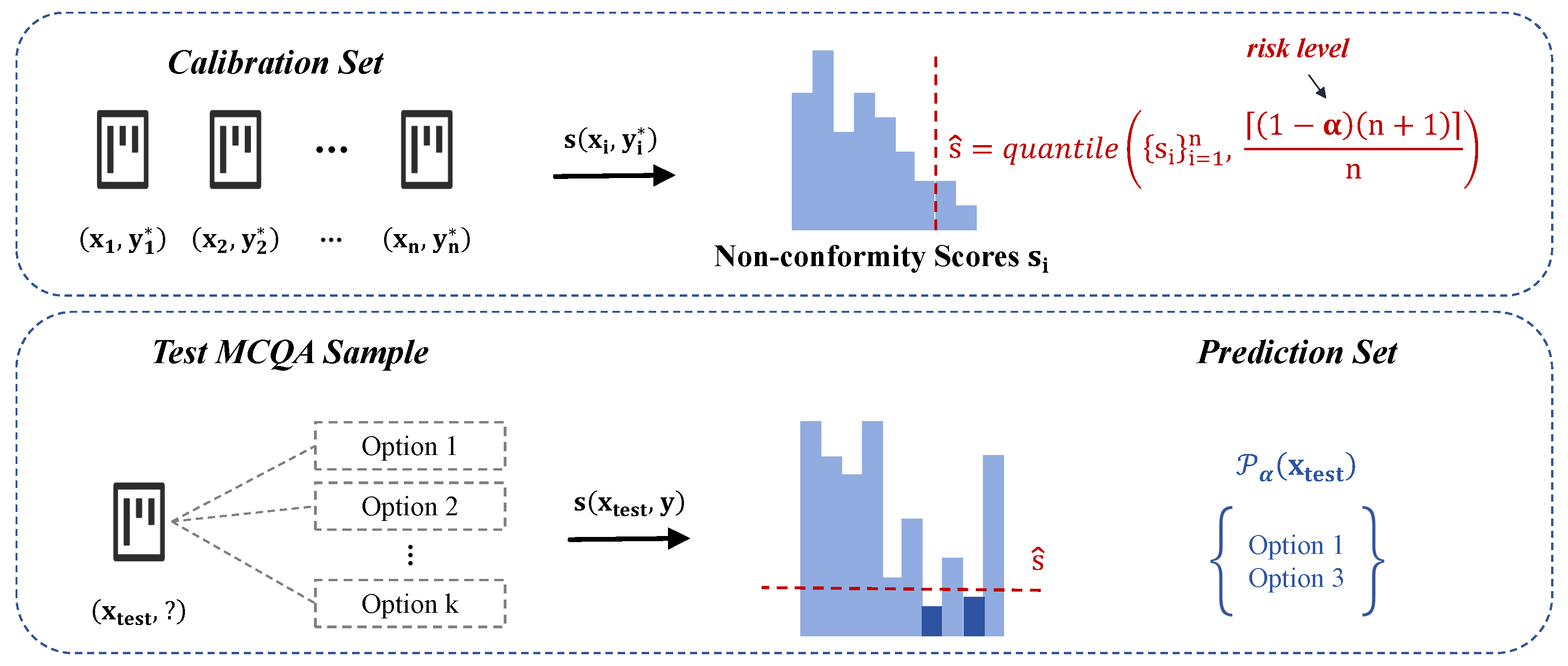
3. Method
3.1. Adaptation of Conformal Prediction to Medical MCQA Tasks
3.2. Guarantee of Task-Specific Metrics
| Algorithm 1: Frequency-based implementation of conformal prediction for medical MCQA |
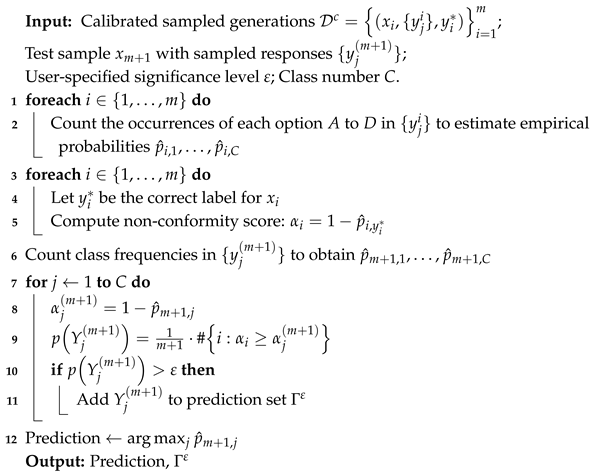 |
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Settings
4.1.1. Datasets
4.1.2. Based LLMs
4.1.3. Hyperparameters
4.1.4. Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Empirical Evaluations
4.2.1. Statistical Guarantees of the EMR Metric
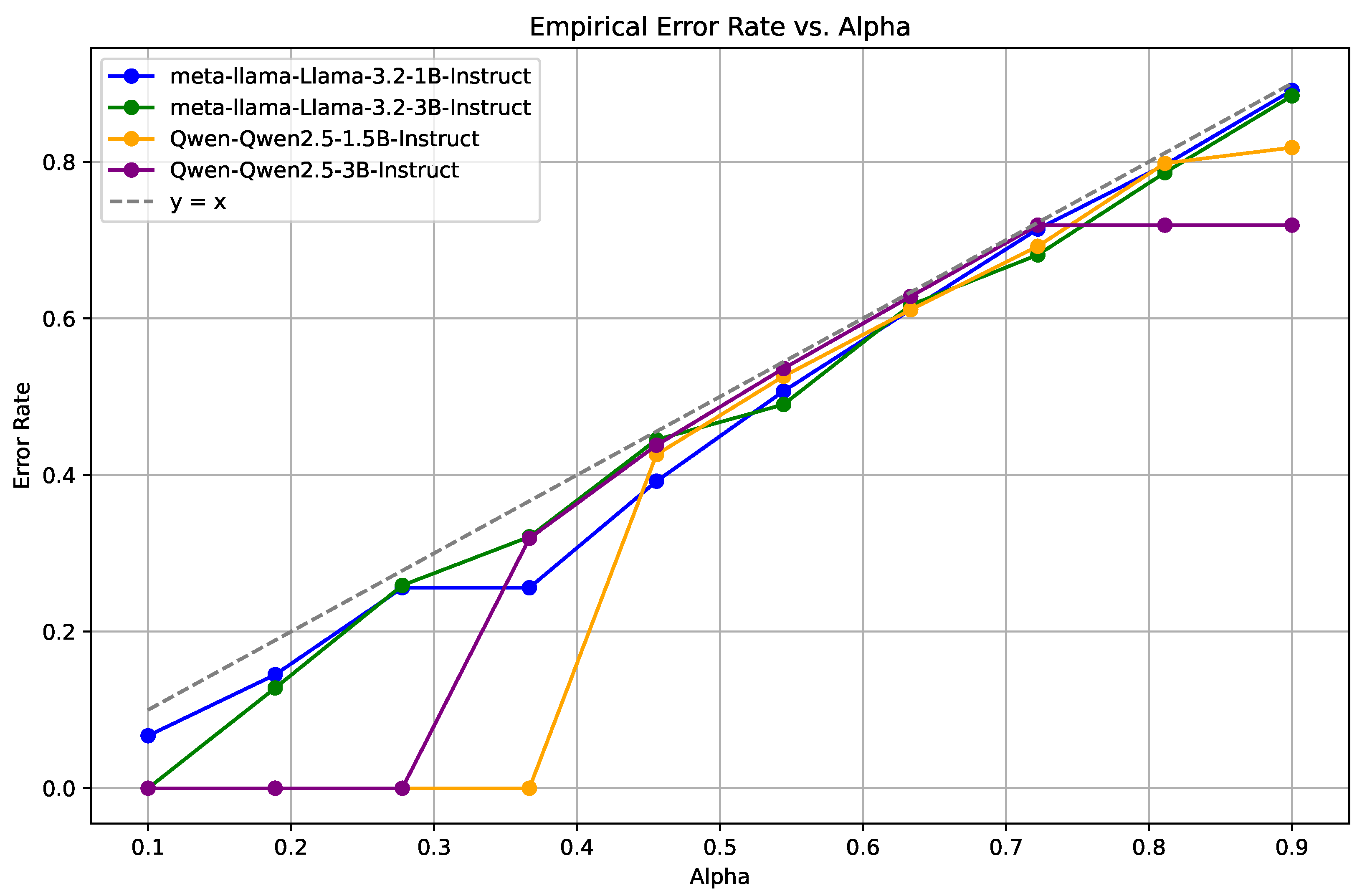
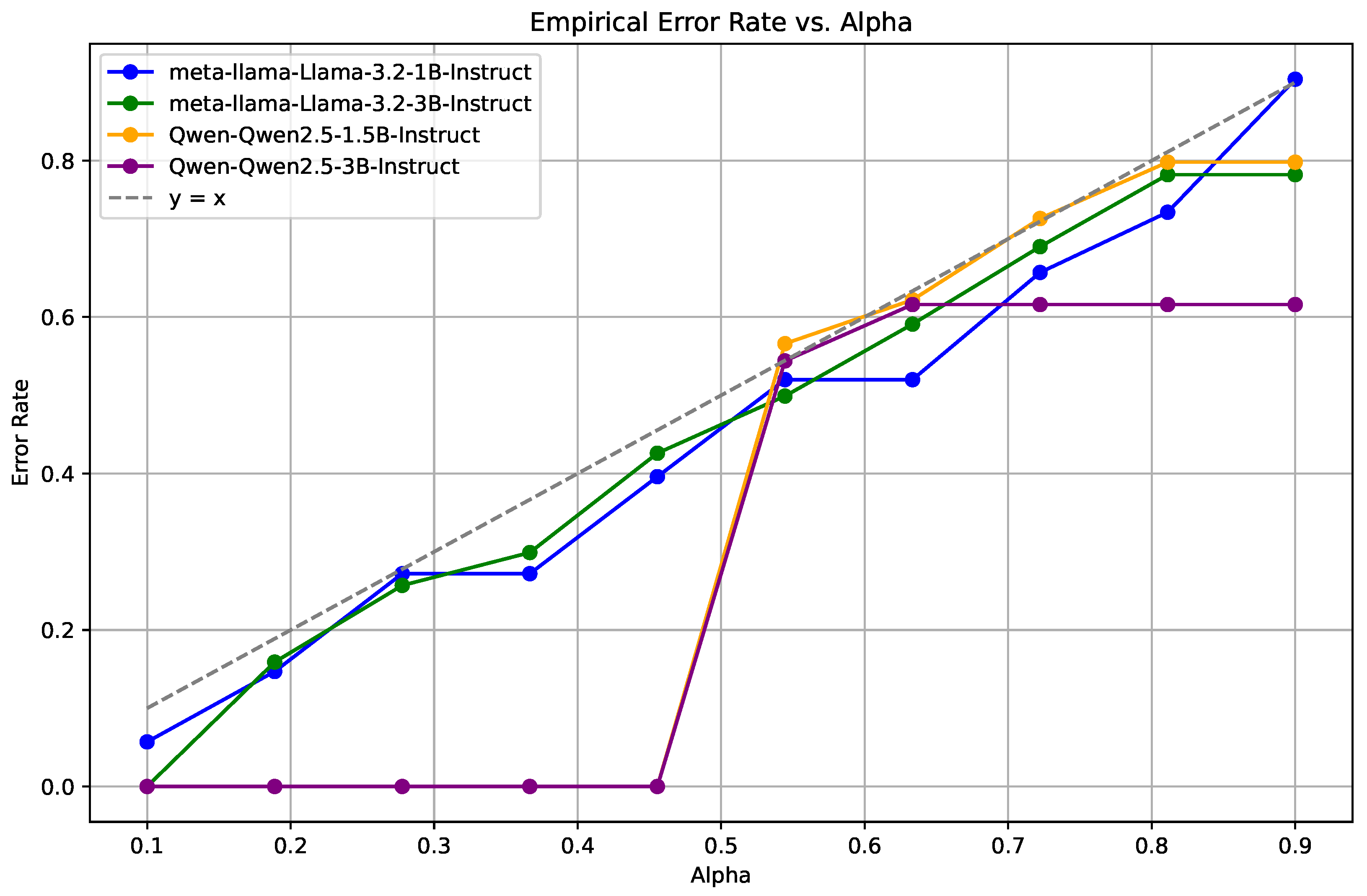
4.2.2. Empirical Coverage Guarantees
4.2.3. Uncertainty Estimation of LLMs
4.3. Sensitivity Analysis
4.3.1. EMR at Various Split Ratios
4.3.2. AUROC Analysis
4.3.3. Reliability Measurement
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| LLMs | Large Language Models |
| QA | Question Answering |
| MCQA | Multiple-Choice Question Answering |
| UQ | Uncertainty Quantification |
| CP | Conformal Prediction |
| EMR | Empirical Miscoverage Rate |
| APSS | Average Prediction Set Size |
| AUROC | Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve |
| NS | Non-Conformity Score |
| MMLU | Massive Multitask Language Understanding |
| MedMCQA | Medical Multiple-Choice Question Answering Dataset |
| MedQA | Medical Question Answering Dataset |
References
- Faria, F.T.J.; Baniata, L.H.; Kang, S. Investigating the predominance of large language models in low-resource Bangla language over transformer models for hate speech detection: A comparative analysis. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, K.; Tu, T.; Gottweis, J.; Sayres, R.; Wulczyn, E.; Amin, M.; Hou, L.; Clark, K.; Pfohl, S.R.; Cole-Lewis, H.; et al. Toward expert-level medical question answering with large language models. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Hager, P.; Jungmann, F.; Holland, R.; Bhagat, K.; Hubrecht, I.; Knauer, M.; Vielhauer, J.; Makowski, M.; Braren, R.; Kaissis, G.; et al. Evaluation and mitigation of the limitations of large language models in clinical decision-making. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2613–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirunavukarasu, A.J.; Ting, D.S.J.; Elangovan, K.; Gutierrez, L.; Tan, T.F.; Ting, D.S.W. Large language models in medicine. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1930–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Mao, R.; Lin, Q.; Ruan, Y.; Lan, X.; Feng, M.; Cambria, E. A survey of large language models for healthcare: From data, technology, and applications to accountability and ethics. Inf. Fusion 2025, 118, 102963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.C.; Amini, M.H.; Wu, Y. Security and privacy challenges of large language models: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2025, 57, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yu, W.; Ma, W.; Zhong, W.; Feng, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, Q.; Peng, W.; Feng, X.; Qin, B.; et al. A survey on hallucination in large language models: Principles, taxonomy, challenges, and open questions. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2025, 43, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Almeida, D.; Wainwright, C.; Mishkin, P.; Zhang, C.; Agarwal, S.; Slama, K.; Ray, A.; et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 27730–27744. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, A.; Gal, Y. What uncertainties do we need in Bayesian deep learning for computer vision? Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Shorinwa, O.; Mei, Z.; Lidard, J.; Ren, A.Z.; Majumdar, A. A survey on uncertainty quantification of large language models: Taxonomy, open research challenges, and future directions. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.05563. [Google Scholar]
- Kadavath, S.; Conerly, T.; Askell, A.; Henighan, T.; Drain, D.; Perez, E.; Schiefer, N.; Hatfield-Dodds, Z.; DasSarma, N.; Tran-Johnson, E.; et al. Language models (mostly) know what they know. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.05221. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, M.; Hu, Z.; Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Fu, J.; He, J.; Hooi, B. Can LLMs express their uncertainty? An empirical evaluation of confidence elicitation in LLMs. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.13063. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Mueller, J. Quantifying uncertainty in answers from any language model and enhancing their trustworthiness. In Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), St. Paul, MN, USA, 8–12 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, L.; Gal, Y.; Farquhar, S. Semantic uncertainty: Linguistic invariances for uncertainty estimation in natural language generation. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Duan, J.; Yuan, C.; Chen, Q.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Shi, X.; Xu, K. Word-sequence entropy: Towards uncertainty estimation in free-form medical question answering applications and beyond. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 139, 109553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Cheng, H.; Wang, S.; Zavalny, A.; Wang, C.; Xu, R.; Kailkhura, B.; Xu, K. Shifting attention to relevance: Towards the predictive uncertainty quantification of free-form large language models. In Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), St. Paul, MN, USA, 8–12 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar, S.; Kossen, J.; Kuhn, L.; Gal, Y. Detecting hallucinations in large language models using semantic entropy. Nature 2024, 630, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Trivedi, S.; Sun, J. Generating with confidence: Uncertainty quantification for black-box large language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2305.19187. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Duan, J.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Shi, X.; Xu, K.; Shen, H.T.; Zhu, X. ConU: Conformal uncertainty in large language models with correctness coverage guarantees. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2024, Online, 6–10 December 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, X.; Miikkulainen, R. Semantic Density: Uncertainty quantification in semantic space for large language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.13845. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Candès, E.J. Selection by prediction with conformal p-values. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2023, 24, 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, M.; Farinhas, A.; Zerva, C.; Figueiredo, M.A.T.; Martins, A.F.T. Conformal prediction for natural language processing: A survey. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2024, 12, 1497–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulos, A.N.; Bates, S. A gentle introduction to conformal prediction and distribution-free uncertainty quantification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.07511. [Google Scholar]
- Angelopoulos, A.N.; Barber, R.F.; Bates, S. Theoretical foundations of conformal prediction. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.11824. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Lala, S.; Jha, N.K. CONFINE: Conformal prediction for interpretable neural networks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.00539. [Google Scholar]
- Angelopoulos, A.N.; Bates, S.; Jordan, M.; Malik, J. Uncertainty sets for image classifiers using conformal prediction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Virtual, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wei, J.; Schuurmans, D.; Le, Q.; Chi, E.; Narang, S.; Chowdhery, A.; Zhou, D. Self-consistency improves chain of thought reasoning in language models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.11171. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, D.; Pan, E.; Oufattole, N.; Weng, W.H.; Fang, H.; Szolovits, P. What disease does this patient have? A large-scale open domain question answering dataset from medical exams. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrycks, D.; Burns, C.; Basart, S.; Zou, A.; Mazeika, M.; Song, D.; Steinhardt, J. Measuring massive multitask language understanding. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Virtual, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Malinin, A.; Gales, M. Uncertainty estimation in autoregressive structured prediction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Virtual, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, Y.; Jin, Y.; Ren, Z. Conformal Alignment: Knowing When to Trust Foundation Models with Guarantees. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.12345. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, F.; Yang, M.; Pang, J.; Wang, L.; Wong, D.; Yilmaz, E.; Shi, S.; Tu, Z. Benchmarking LLMs via Uncertainty Quantification. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 15356–15385. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Geng, T.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T.; Fu, B.; Zheng, F. Sample then Identify: A General Framework for Risk Control and Assessment in Multimodal Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations, Singapore, 24–28 April 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Touvron, H.; Martin, L.; Stone, K.; Albert, P.; Almahairi, A.; Babaei, Y.; Bashlykov, N.; Batra, S.; Bhargava, P.; Bhosale, S.; et al. Llama 2: Open foundation and fine-tuned chat models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.09288. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.; Yang, B.; Zhang, B.; Hui, B.; Zheng, B.; Yu, B.; Li, C.; Liu, D.; Huang, F.; Wei, H.; et al. Qwen2.5 technical report. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.15115. [Google Scholar]
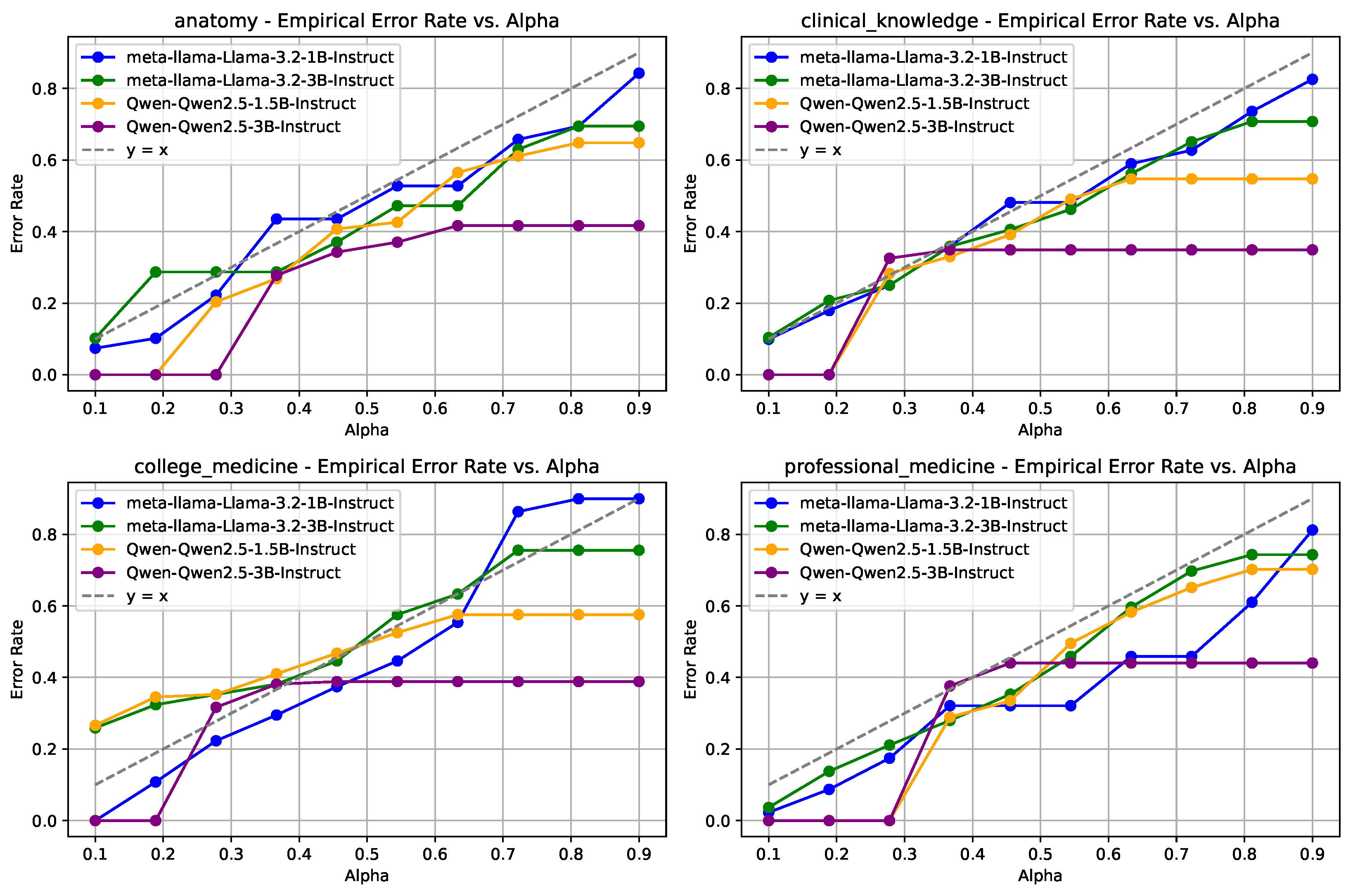
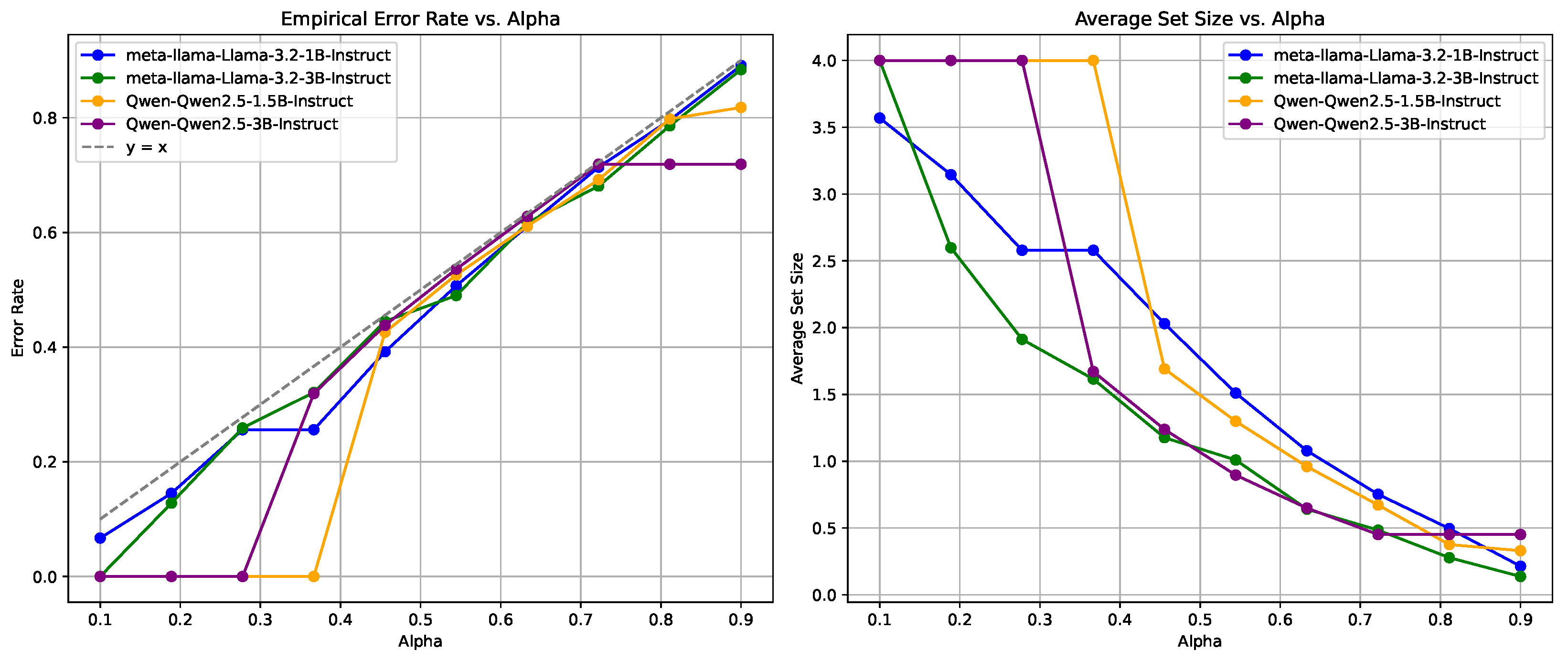
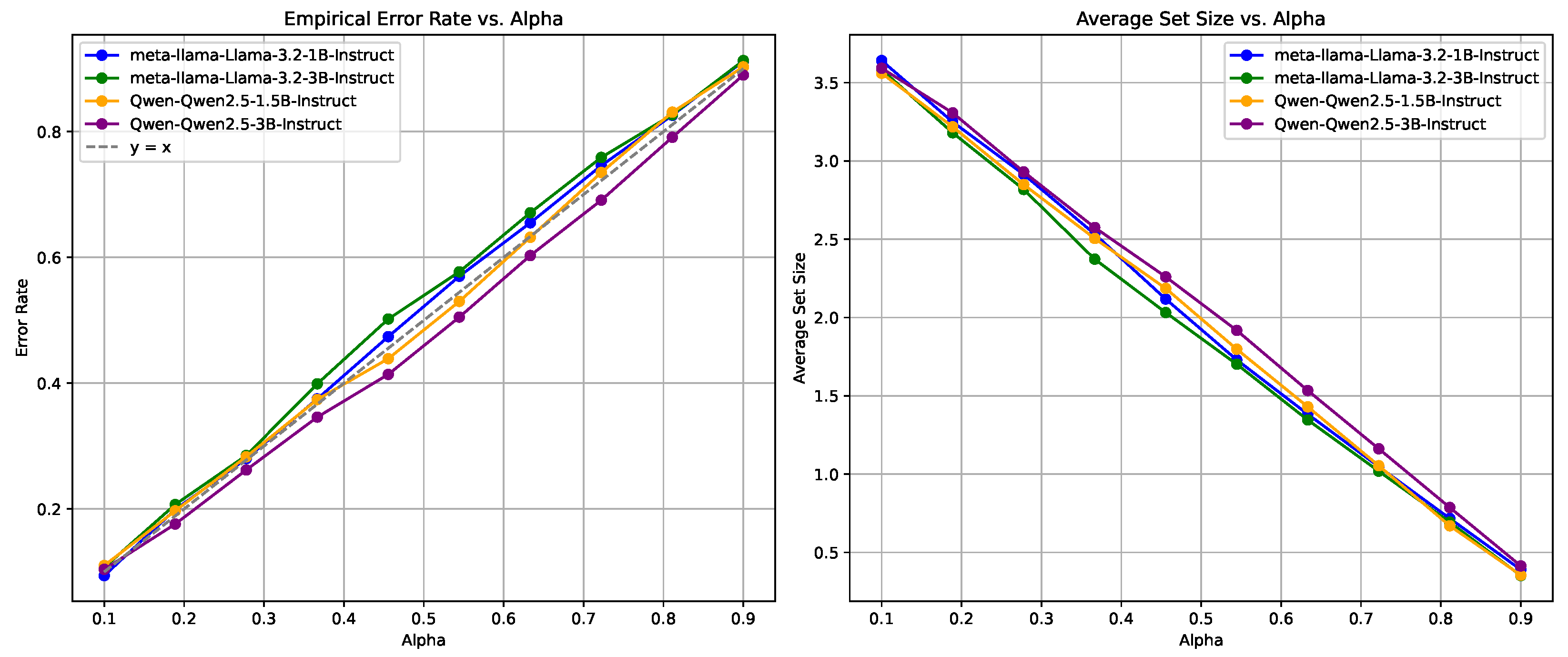
| Datasets | LLMs/ | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MedMCQA | Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct | 3.57 | 3.15 | 2.58 | 2.03 | 1.51 | 1.08 | 1.08 | 0.50 | 0.22 |
| Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct | 4.00 | 2.60 | 1.91 | 1.37 | 1.01 | 0.75 | 0.48 | 0.28 | 0.12 | |
| Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 1.98 | 1.54 | 1.11 | 0.74 | 0.44 | 0.33 | |
| Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 1.45 | 1.17 | 0.75 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | |
| MedQA | Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct | 4.00 | 4.00 | 3.35 | 2.74 | 2.12 | 1.57 | 1.09 | 0.77 | 0.24 |
| Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct | 4.00 | 4.00 | 1.94 | 1.42 | 1.06 | 0.67 | 0.44 | 0.29 | 0.21 | |
| Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 1.30 | 0.83 | 0.47 | 0.38 | |
| Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 0.91 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.64 | |
| MMLU | Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct | 3.89 | 3.32 | 2.83 | 2.14 | 1.53 | 1.04 | 0.68 | 0.21 | 0.03 |
| Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct | 2.43 | 1.66 | 1.24 | 0.92 | 0.65 | 0.49 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | |
| Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct | 4.00 | 4.00 | 1.41 | 1.06 | 0.79 | 0.54 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.43 | |
| Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct | 4.00 | 4.00 | 1.06 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 |
| Datasets | LLMs/ | Split Ratio = 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MedMCQA | Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.20 | 0.20 | |
| Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Datasets | LLMs | Frequency | Logit |
|---|---|---|---|
| MedMCQA | Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct | 0.5872 | 0.6197 |
| Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct | 0.6982 | 0.7005 | |
| Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct | 0.6337 | 0.6517 | |
| Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct | 0.6418 | 0.6930 | |
| MedQA | Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct | 0.5819 | 0.6041 |
| Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct | 0.7375 | 0.7484 | |
| Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct | 0.5752 | 0.6241 | |
| Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct | 0.5693 | 0.6609 | |
| MMLU | Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct | 0.6380 | 0.6358 |
| Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct | 0.7501 | 0.7657 | |
| Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct | 0.7159 | 0.7771 | |
| Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct | 0.6207 | 0.7784 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ke, Y.; Lin, H.; Ruan, Y.; Tang, J.; Li, L. Correctness Coverage Evaluation for Medical Multiple-Choice Question Answering Based on the Enhanced Conformal Prediction Framework. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091538
Ke Y, Lin H, Ruan Y, Tang J, Li L. Correctness Coverage Evaluation for Medical Multiple-Choice Question Answering Based on the Enhanced Conformal Prediction Framework. Mathematics. 2025; 13(9):1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091538
Chicago/Turabian StyleKe, Yusong, Hongru Lin, Yuting Ruan, Junya Tang, and Li Li. 2025. "Correctness Coverage Evaluation for Medical Multiple-Choice Question Answering Based on the Enhanced Conformal Prediction Framework" Mathematics 13, no. 9: 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091538
APA StyleKe, Y., Lin, H., Ruan, Y., Tang, J., & Li, L. (2025). Correctness Coverage Evaluation for Medical Multiple-Choice Question Answering Based on the Enhanced Conformal Prediction Framework. Mathematics, 13(9), 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091538





