Financing Newsvendor with Trade Credit and Bank Credit Portfolio
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
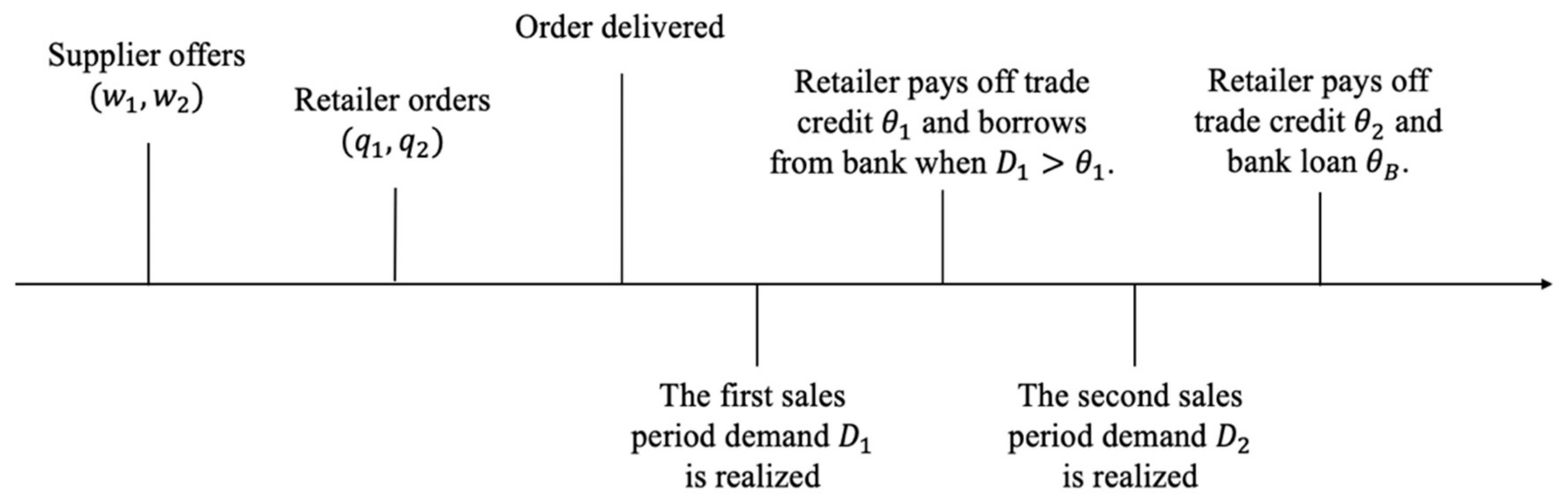
3. Model
4. Financing with Trade Credit Portfolio
4.1. Single-TC1 Problem
4.2. Single-TC2 Problem
4.3. TCP Problem
4.4. Numerical Analysis
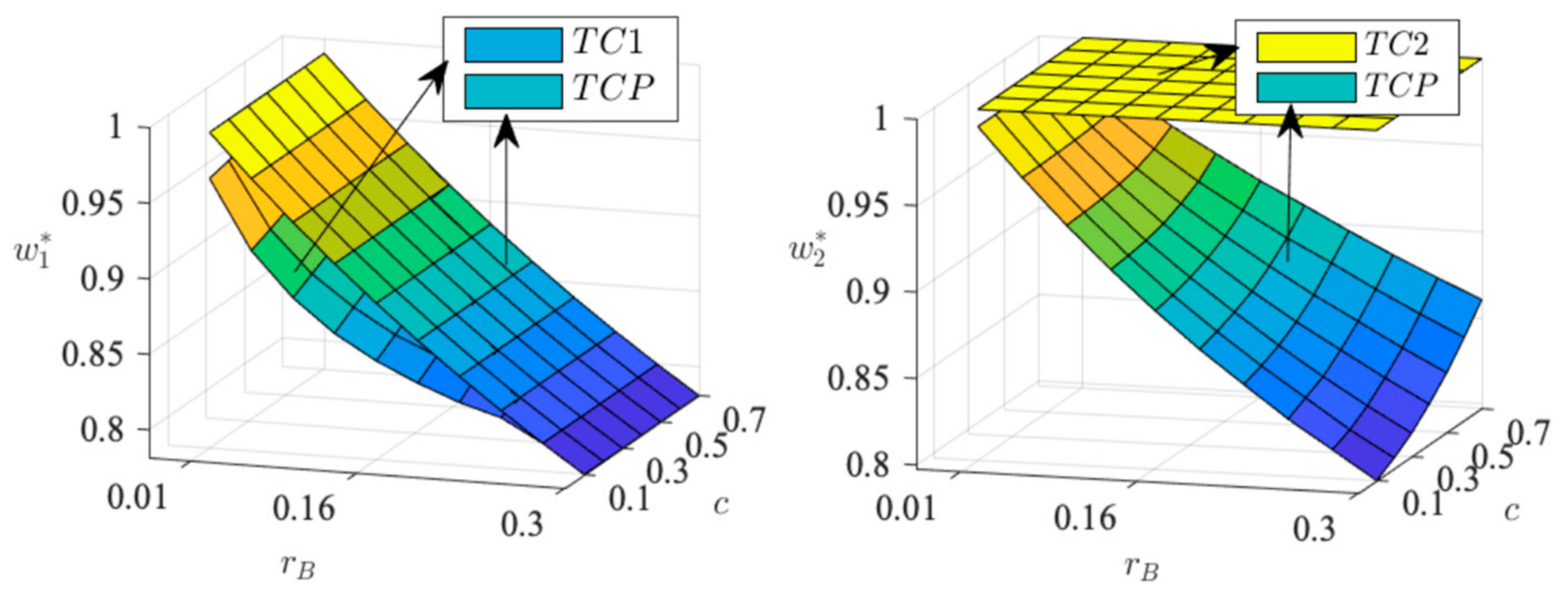
4.4.1. The Supplier’s Price and the Retailer’s Order Quantity
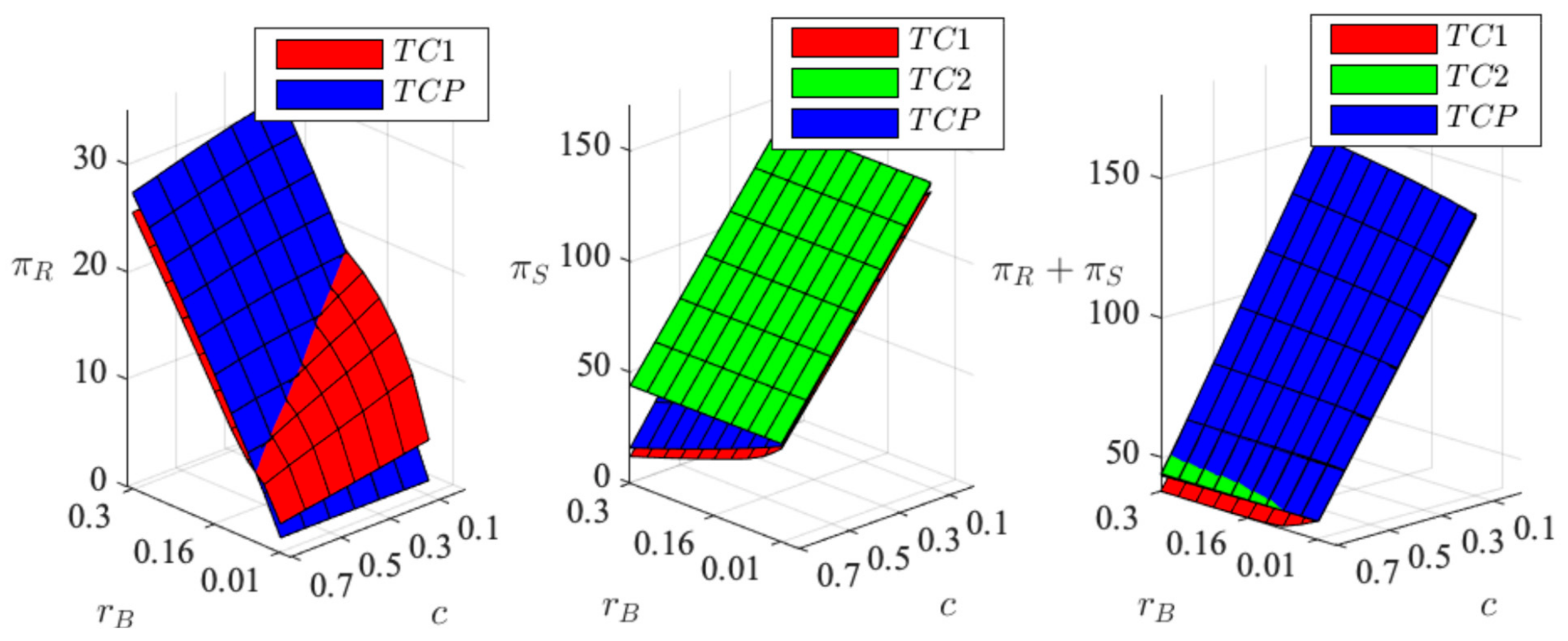
4.4.2. Comparison of the Parties’ Profit
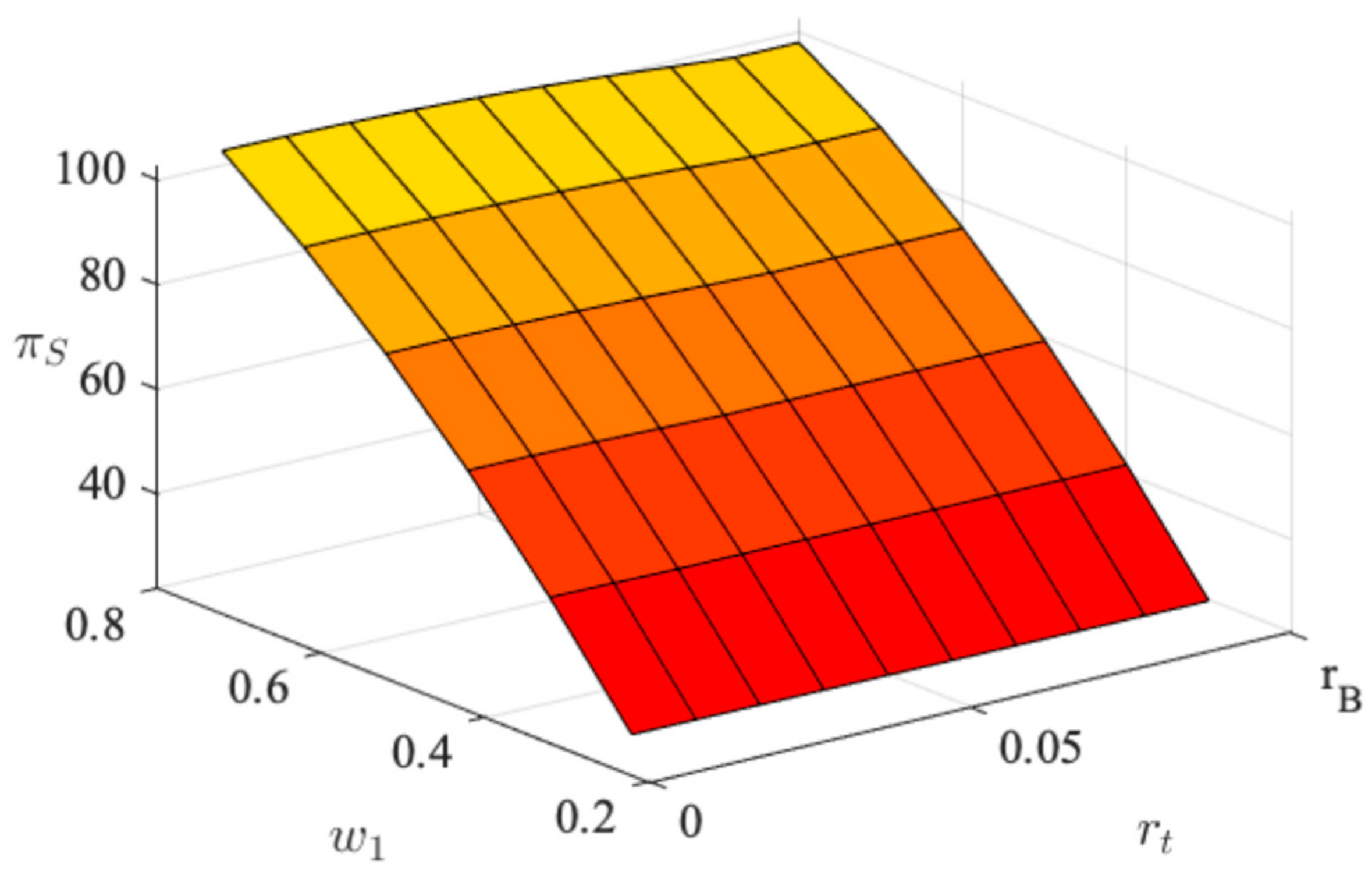
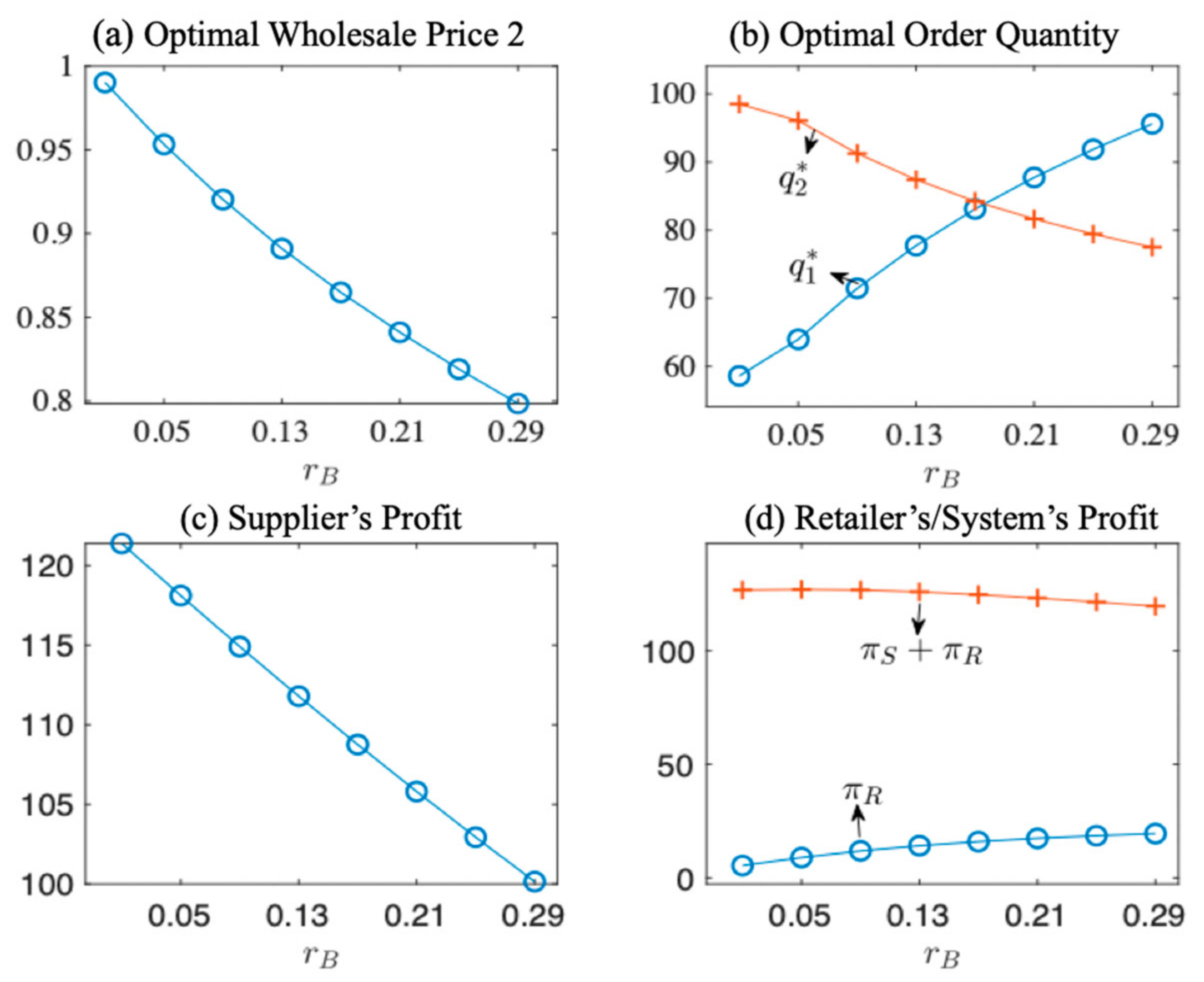
4.4.3. Impact of the Bank Interest Rate
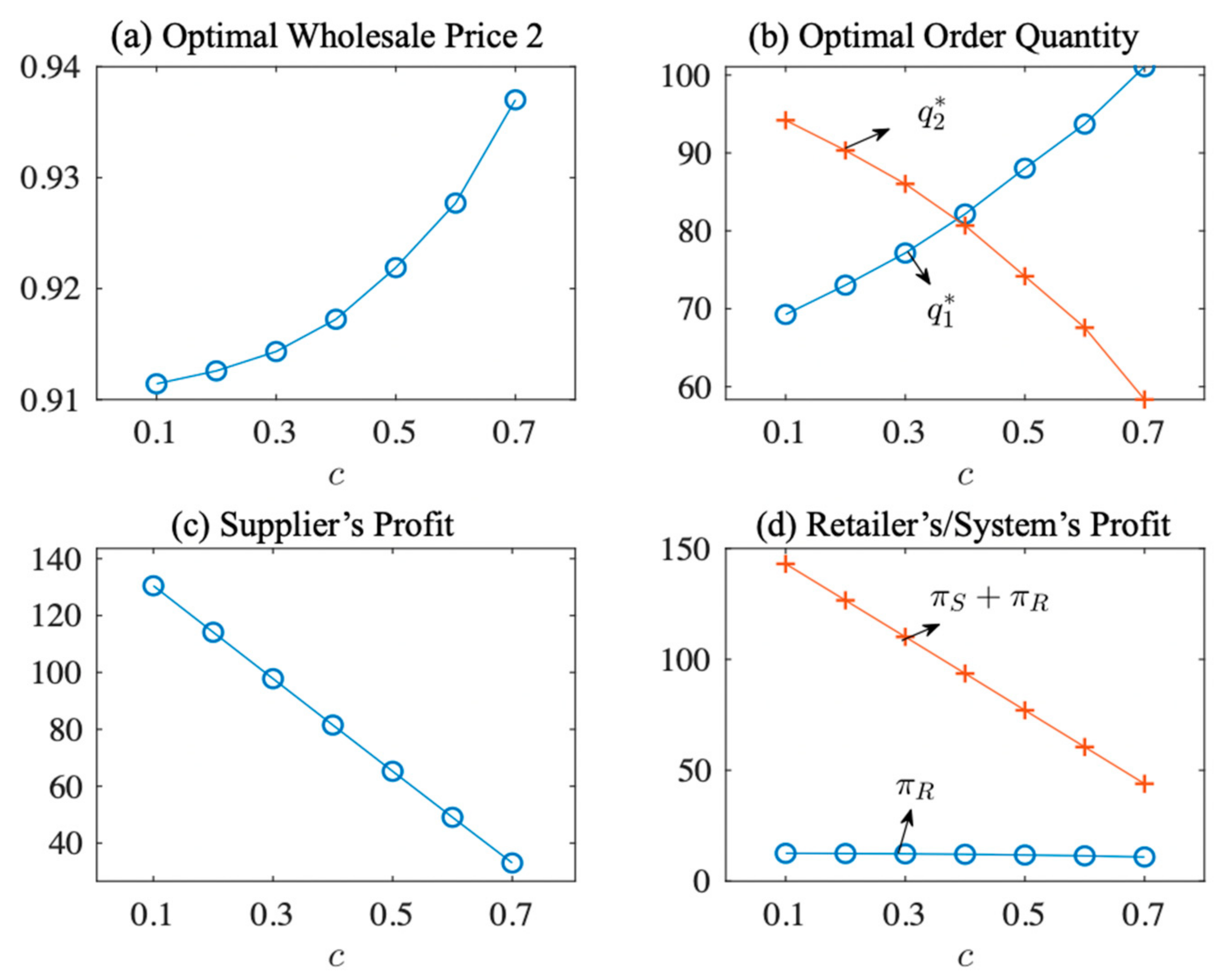
4.4.4. Impact of the Manufacturing Cost
4.5. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- (1)
- When , the marginal costs of two trade credit are
- (2)
- When hen , the marginal costs of two trade credits are
- (3)
- When , the above conditions are not met, thus the optimal order quantity satisfies . □
References
- Yang, S.A.; Birge, J.R. Trade credit, risk sharing, and inventory financing portfolios. Manag. Sci. 2018, 64, 3667–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunat, V. Trade credit: Suppliers as debt collectors and insurance providers. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2007, 20, 491–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Wang, L.A. Stochastic inventory model with trade credit. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2009, 11, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvelis, P.; Zhao, W. Financing the newsvendor: Supplier vs. bank, and the structure of optimal trade credit contracts. Oper. Res. 2012, 60, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, V.; Tang, C.S. Managing opportunistic supplier product adulteration: Deferred payments, inspection, and combined mechanisms. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2012, 14, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, H.; Lai, G. Sourcing with deferred payment and inspection under supplier product adulteration risk. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2015, 24, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Qian, Q.; Yang, S.A. Financial Pooling in a Supply Chain; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chod, J.; Lyandres, E.; Yang, S.A. Trade credit and supplier competition. J. Financ. Econ. 2019, 131, 484–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, B.; Chen, X.; Cai, G. Equilibrium financing in a distribution channel with capital constraint. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2012, 21, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beranek, W. Financial implications of lot–size inventory models. Manag. Sci. 1967, 13, B401–B408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archibald, T.W.; Thomas, L.C.; Betts, J.M.; Johnston, R.B. Should start-up companies be cautious? Inventory policies which maximize survival probabilities. Manag. Sci. 2002, 48, 1161–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shubik, M.; Sobel, M.J. Control of dividends, capital subscriptions, and physical inventories. Manag. Sci. 2013, 59, 1107–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, G.; Debo, L.G.; Sycara, K. Sharing inventory risk in supply chain: The implication of financial constraint. Omega 2009, 37, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Shang, K. Joint inventory and cash management for multidivisional supply chains. Oper. Res. 2015, 63, 1098–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzacott, J.A.; Zhang, R.Q. Inventory management with asset-based financing. Manag. Sci. 2004, 50, 1274–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Birge, J.R. Equity valuation, production, and financial planning: A stochastic programming approach. Nav. Res. Logist. 2006, 53, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, V.; Seshadri, S. Hedging inventory risk through market instruments. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2005, 7, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldentey, R.; Haugh, M. Optimal control and hedging of operations in the presence of financial markets. Math. Oper. Res. 2006, 31, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alan, Y.; Gaur, V. Operational investment and capital structure under asset-based lending. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2018, 20, 601–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, V.; Kouvelis, P. Introduction to the Special Issue on Research at the Interface of Finance, Operations, and Risk Management (iFORM): Recent Contributions and Future Directions. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2018, 20, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silaghi, F.; Moraux, F. Trade credit contracts: Design and regulation. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2022, 296, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, C.W.; Higgins, R.C. Inventory policy and trade credit financing. Manag. Sci. 1973, 20, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Li, B.; Song, D.; Chen, X. Green credit financing versus trade credit financing in a supply chain with carbon emission limits. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 292, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J. Strategic trade credit in a supply chain with buyer competition. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2022, 24, 2183–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esenduran, G.; Gray, J.V.; Tan, B. A dynamic analysis of supply chain risk management and extended payment terms. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2022, 31, 1394–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Ho Yoo, S. Government intervention in environmental performance considering working capital issues: Control the supplier or the buyer? Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 163, 107790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Xu, C.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, J. Research on financing strategy under the integration of green supply chain and blockchain technology. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 184, 109598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, N.; Yan, Y.; Qin, Z. Analysis of financing strategy in coopetition supply chain with opportunity cost. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2023, 305, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.N.; He, X.L. Optimal trade credit with deferred payment and multiple decision attributes in supply chain finance. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 147, 106627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, J.; Chen, N.J.; Yang, S.A. The impact of trade credit provision on retail inventory: An empirical investigation using synthetic controls. Manag. Sci. 2022, 69, 4591–4608. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Li, X.; Zhao, R. Suppliers’ trade credit strategies with transparent credit ratings: Null, exclusive, and nonchalant provision. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2022, 297, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, V.; Aydin, G.; Brunet, P.Y. Risk, financing and the optimal number of suppliers. In Supply Chain Disruptions; Springer: London, UK, 2012; pp. 195–240. [Google Scholar]
- Reindorp, M.; Tanrisever, F.; Lange, A. Purchase order financing: Credit, commitment, and supply chain consequences. Oper. Res. 2018, 66, 1287–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachon, G.P. The allocation of inventory risk in a supply chain: Push, pull, and advance-purchase discount contracts. Manag. Sci. 2004, 50, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chod, J. Inventory, risk shifting, and trade credit. Manag. Sci. 2017, 63, 3147–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Qi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. A trade-credit-based incentive mechanism for a risk-averse retailer with private information. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 154, 107101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhuo, W.; Shao, L.; Talluri, S. Mean-variance analysis of wholesale price contracts with a capital-constrained retailer: Trade credit financing vs. bank credit financing. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 294, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, B. Impact of Capital Position and Financing Strategies on Encroachment in Supply Chain Dynamics. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, R.A. An economic model of trade credit. J. Financ. Quant. Anal. 1974, 9, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peura, H.; Yang, S.A.; Lai, G. Trade credit in competition: A horizontal benefit. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2017, 19, 263–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| the demand realization of the sales period; PDF , CDF | |
| the price of the shorter-term trade credit () or of the longer-term trade credit () | |
| trade credit early discount; | |
| retailer’s order quantity of the shorter-term trade credit () or of the longer-term trade credit () | |
| retailer’s total order quantity | |
| well-funded retailer’s order quantity | |
| bank interest rate | |
| debt of the shorter-term trade credit () or of the longer-term trade credit () | |
| bank loan | |
| unit manufacturing cost | |
| the retailer’s profit; is the retailer’s profit under single-TCi mode | |
| the supplier’s profit; is the supplier’s profit under single-TCi mode; is the supplier ’s profit | |
| the retailer’s marginal income | |
| the retailer’s marginal cost of the shorter-term trade credit () or of the longer-term trade credit () | |
| hazard rate | |
| general failure rate |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, R. Financing Newsvendor with Trade Credit and Bank Credit Portfolio. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091464
Zhang Y, Zhang B, Chen R. Financing Newsvendor with Trade Credit and Bank Credit Portfolio. Mathematics. 2025; 13(9):1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091464
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yue, Bin Zhang, and Rongguang Chen. 2025. "Financing Newsvendor with Trade Credit and Bank Credit Portfolio" Mathematics 13, no. 9: 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091464
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhang, B., & Chen, R. (2025). Financing Newsvendor with Trade Credit and Bank Credit Portfolio. Mathematics, 13(9), 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091464






