Abstract
Knowledge graph completion (KGC) is a critical task for addressing the incompleteness of knowledge graphs and supporting downstream applications. However, it faces significant challenges, including insufficient structured information and uneven entity distribution. Although existing methods have alleviated these issues to some extent, they often rely heavily on extensive training and fine-tuning, which results in low efficiency. To tackle these challenges, we introduce our MLKGC framework, a novel approach that combines large language models (LLMs) with multi-modal modules (MMs). LLMs leverage their advanced language understanding and reasoning abilities to enrich the contextual information for KGC, while MMs integrate multi-modal data, such as audio and images, to bridge knowledge gaps. This integration augments the capability of the model to address long-tail entities, enhances its reasoning processes, and facilitates more robust information integration through the incorporation of diverse inputs. By harnessing the synergy between LLMs and MMs, our approach reduces dependence on traditional text-based training and fine-tuning, providing a more efficient and accurate solution for KGC tasks. It also offers greater flexibility in addressing complex relationships and diverse entities. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark KGC datasets demonstrate that MLKGC effectively leverages the strengths of both LLMs and multi-modal data, achieving superior performance in link-prediction tasks.
MSC:
68-06
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of information technology, knowledge graphs (KGs) have emerged as a pivotal resource across a wide range of applications, including information retrieval [1], intelligent question answering [2], and recommendation systems [3]. KGs are structured repositories of interconnected information, where data are represented in the form of triples, consisting of a head entity, a relation, and a tail entity (e.g., <head entity, relation, tail entity>). A crucial application of KGs is knowledge graph completion (KGC), which aims to predict and fill in missing triples to address the inherent incompleteness of KGs. These missing triples commonly take one of the following forms: , where the tail entity is unknown, or , where the head entity is missing. Here, h, r, and t represent the head entity, the relation, and the tail entity, respectively. However, challenges such as data sparsity during the construction of knowledge graphs have positioned KGC as a significant area of research. KGC methods often face multiple challenges in handling complex real-world scenarios, including an insufficient capability to handle long-tail entities [4], high training costs [5], and limited adaptability of dynamic knowledge graphs [6]. To address these issues, we propose our MLKGC framework, which integrates large language models (LLMs) to optimize processing efficiency for long-tail entities while improving task adaptability. By incorporating multi-modal information integration, MLKGC not only addresses data sparsity but also provides a robust solution for dynamic and heterogeneous KGs environments.
Methods for solving KGC can be broadly categorized into three types: large language model knowledge graph completion (LLMKGC), in-context learning knowledge graph completion (ICLKGC), and multi-modal knowledge graph completion (MMKGC). LLMKGC [7,8,9] leverages vast amounts of unstructured knowledge to enhance KGC by integrating contextual and semantic information from external corpora. This approach improves the reasoning capability for predicting missing links in KGs. ICLKGC [10,11] enables models to infer patterns and predict missing entities or relationships by using only a few examples provided within input prompts. This method is particularly effective for low-resource scenarios and dynamic knowledge graphs. MMKGC [12,13] enhances KGC by incorporating multi-modal data, such as text, images, and audio to provide richer contextual information and improve completion accuracy. While these approaches differ in methodology, each offers a unique advantage for addressing the challenges of KGC, making them complementary solutions in this domain. Large language models, such as GPT-4 [14] and LLAMA [15], boast extensive repositories of internal knowledge derived from their vast pre-trained corpora. This internal knowledge serves as an auxiliary knowledge base, offering a valuable resource to address information scarcity, particularly for long-tail entities in KGs. By leveraging their contextual reasoning and semantic understanding capabilities, LLMs enhance the prediction of missing links and improve the overall robustness of KGC. On the other hand, multi-modal data introduce rich semantic information that structured triples alone cannot fully capture, leaving significant gaps in understanding and representation. The integration of structured triple data with multi-modal inputs, such as text, images, videos, and audio, offers a more comprehensive perspective. Multi-modal data fusion has emerged as a promising technological trend, enabling the synthesis of diverse data types to enhance knowledge representation, improve reasoning capabilities, and fill the gaps left by single-modality approaches. This fusion holds immense potential for advancing the effectiveness and adaptability of KGC.
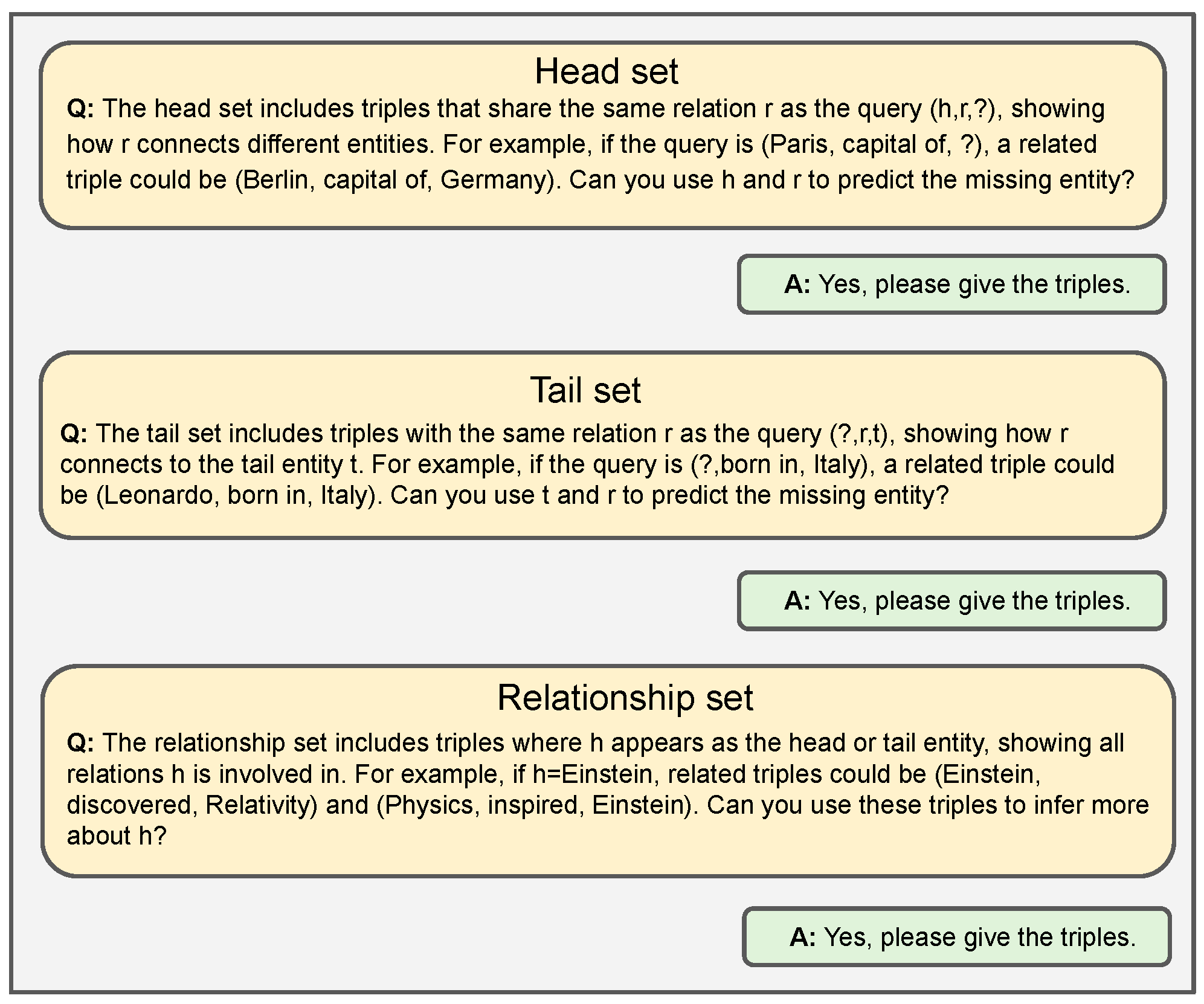
Specifically, we input complete triples into LLMs and use the question-asking mechanism to help the model learn and internalize their patterns in Figure 1. Once LLMs grasp these patterns, we input the two types of incomplete triples— and —into LLMs to construct three corresponding completed triple sets: the head set, the relationship set, andthe tail set. For example, (Einstein, lives in, ?) is completed as (Einstein, lives in, Germany). Specifically, the head set consists of triples sharing the same head entity as , the relationship set contains triples with the same relation as and , and the tail set includes triples with the same tail entity as . Single-modality textual data may overlook important link prediction information, while multi-modal data can complement and enrich each other, providing a more comprehensive understanding. For example, in medical knowledge graph completion [16], imaging data such as X-rays and CT scans are often combined with diagnostic text reports, offering richer contextual information that enhances link prediction accuracy. To address the limitations of single-modality approaches, we introduce multi-modal data, including images and audio, and employ deep learning models such as CNN [17] for image feature extraction and Wav2Vec 2.0 [18] for audio feature extraction. The extracted image and audio features, along with the previously generated candidate sets (head, relationship and tail set), are then input into LLM, which infers the top-k triples according to these sets, which are used as the final output. Our main contributions are as follows.

Figure 1.
The question-answering process of large language models.
- We propose an innovative MLKGC framework, which combines multimodal data and LLMs for KGC tasks. This is the first work to integrate multimodal information with triple-based LLMs methods, offering a novel solution for complex knowledge graph completion tasks.
- We designed three novel supplementary sets: the the head set, the relationship set, and the tail set. By incorporating multi-modal data, such as images and audio, this approach enhances the knowledge representation and reasoning capabilities of the model.
- Empirical results on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of MLKGC, showing that it significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines.
2. Related Work
Triple-based KGC. Most existing KGC methods are triple-based, relying exclusively on triple information to complete knowledge graphs. Early shallow knowledge graph embedding (KGE) methods represent entities and relations as low-dimensional vectors in a continuous embedding space. These approaches can be broadly categorized into translation-based models, such as TransE [19], and semantic matching models, including RESCAL and DistMult [20], depending on their scoring functions. Ref. [21] classified KGE techniques based on the type of information used, ranging from fact-based embeddings to those incorporating additional context. Moreover, Ref. [22] introduced a unified framework for neural embedding models of knowledge bases, leveraging bilinear models for entities and relations prediction and employing effective embedding-based methods to discover combinatorial logic rules. However, these shallow methods are still constrained by their limited expressive power. Recent advancements have integrated more sophisticated network architectures into the KGC task [23], such as GNNs [24], CNNs [25], and Transformers [26]. These models enhance performance by aggregating local structural context into node embeddings. But they remain challenged by the imbalanced structure of knowledge graphs, particularly the scarcity of information for long-tail entities. To address this limitation, meta-learning [27,28] and logical rule-based approaches [29] have been proposed. These methods aim to mitigate the long-tail problem by extracting and summarizing common structural patterns or rules from limited graph data. Alternatively, KICGPT uses a large external knowledge base through LLMs and effectively combines it with the structural information in the knowledge graph to solve the information scarcity problem of long-tail entities. Based on the KICGPT [30] model, we further combine multimodal data as a supplement to the external knowledge base and the structural information in the knowledge graph to better solve the information scarcity problem of long-tail entities.
LLMs for KGs. LLMs mainly apply a large amount of unstructured knowledge in KGC. Unlike traditional KGC methods, which only rely on triple structure information, LLMs can combine contextual and semantic knowledge from external corpora to enhance the reasoning ability of missing links in knowledge graphs. A prominent approach is to fine-tune pre-trained LLMs, such as BERT [31], GPT [32], or T5 [33], to adapt them to the KGC task. For example, KG-BERT [7] adopts a classification-based framework where triples are input as text sequences, enabling the model to predict missing entities or relations by learning contextual representations. Similarly, COMET [8] utilizes a GPT-style generative model to generate reasonable triples based on existing knowledge. In addition, hybrid models that combine LLMs with traditional KGE techniques, such as KGT5, integrate a Transformer-based architecture with triple embeddings to jointly optimize semantic understanding and structural consistency. However, there are still limitations in effectively integrating LLM with structured data. KICGPT [30] uses a unified hint template to align text to ensure the availability of auxiliary text information. Our approach aligns text information converted from different modalities according to the hint template in the KICGPT framework, thereby achieving more accurate knowledge graph completion.
ICL for LLMs. In-Context Learning (ICL) [10] is a feature of large language models (LLMs) such as GPT and T5 and has recently been used for KGC tasks. ICL enables models to infer patterns and predict missing entities or relationships in knowledge graphs using only a few examples provided as part of the input prompts, suitable for low-resource and dynamic knowledge graph scenarios [11]. A notable application of ICL in KGC is its ability to perform zero-shot and few-shot entity or relationship predictions by leveraging textual representations of triples. For example, models like GPT-3 can interpret triple-based examples and generalize to new triples without fine-tuning, as shown in tasks such as entity prediction and relationship prediction. Further improvements include incorporating external knowledge sources and logical reasoning into ICL. For example, an LLM can use an external corpus to enrich the semantic understanding of entities and relationships, thereby improving the prediction accuracy of long-tail entities [34]. In addition, logical patterns or rules (e.g., ) can be used to prompt the model to enhance reasoning capabilities, enabling the extraction and reasoning of complex relationships. Based on previous research, we designed a more effective prompting strategy and combined ICL with the traditional KGC method, which can be used to balance semantic understanding and structural consistency.
Multi-modal KGC. Multi-modal knowledge graph completion (MMKGC) aims to enhance knowledge graph completion by leveraging multimodal data such as text, images, and audio. Traditional knowledge graph completion methods mainly rely on structural information (e.g., triples) to infer missing entities or relations. However, they have difficulty capturing the rich semantic and contextual information embedded in multimodal content. Recent research has introduced methods to integrate multimodal data into the knowledge graph embedding process. For example, models such as IKRL [35] incorporate visual information to improve entity and relation representations [12]. Similarly, text-aware models leverage text descriptions related to entities and relations to enhance embeddings, as shown in models such as LiteralE and ConMask [13]. Another line of work explores fusing multiple modalities through advanced neural architectures. For example, Transformer-based models such as MTransE [36] use a cross-modal attention mechanism to align multimodal embeddings. However, effectively fusiing heterogeneous modalities, addressing data sparsity, and ensuring scalability for large-scale knowledge graphs remain major challenges. Based on the KICGPT [30] framework, we use pre-trained models to convert various modal data such as image and audio into a unified text form and input it into the large language model as supplementary information. Ultimately, the large language model provides more accurate result vectors, which can integrate heterogeneous modalities, solve the problem of data sparsity, and more comprehensively improve the effect of knowledge graph completion.
3. Methodology
A knowledge graph consists of facts about the world, represented as triples , where are the head entity and tail entity, and represents the relation between the head and tail entity. The relations in the world are numerous, and the entities h and t and the relation r are mapped to continuous low-dimensional vector space , and . We define the scoring function as to estimate the plausibility of any given fact . We illustrate the notation and corresponding meaning in Table 1.

Table 1.
Notations.
3.1. Problem Formulation
Incomplete triples such as and in knowledge graphs create challenges for entity prediction. Our goal is to identify plausible candidates to fill these gaps by analyzing known relationships, determining likely tail entities for and deducing possible head entities for . In knowledge graph embedding technology, entities are treated as vectors, with relations acting as operations in a vector space to calculate relationships between them. Initially, entities and relations are mapped into a continuous low-dimensional vector space. A scoring function is then defined to assess the reliability of each triple, where a higher score indicates a greater likelihood of truth. Finally, a loss function optimizes the overall reliability of all triples in the knowledge graph. For evaluation, it is common to track the ranks of correct answers in ordered lists to verify whether they precede incorrect ones. Common evaluation metrics include the mean reciprocal rank and Hits@n, which measures the proportion of ranks exceeding a threshold n.
3.2. Overall Method
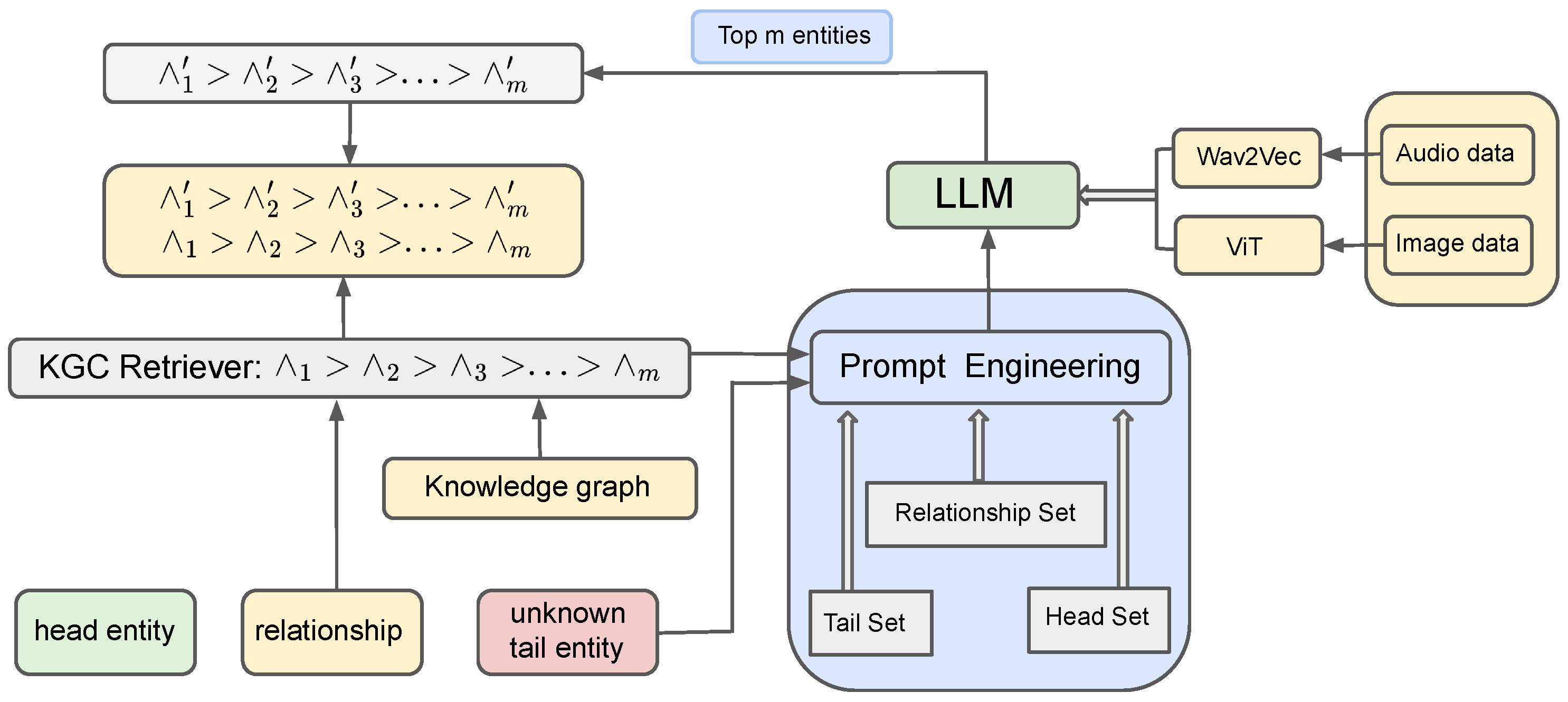
We construct head, tail, and relationship sets through sampling and semantic relevance ranking using pre-trained embedding models in Figure 2. During inference, dynamically generated and ranked example sets guide large language models to generate candidate answers with explanations. Additionally, we incorporate multimodal data, such as images and audio, to enhance the representation of entities and relationships in the knowledge graph.
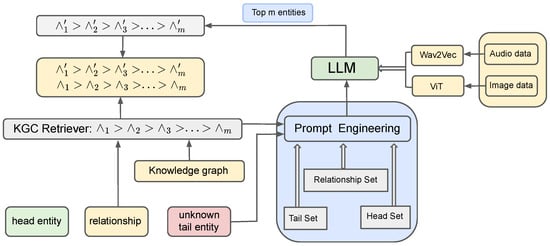
Figure 2.
GreenIllustration of our MLKGC framework.
3.2.1. Information Set
We construct three sets of triples: a head set , a tail set , and a relationship set S.
- Head Set: The head set consists of triples designed to enhance the understanding of query semantics through the analogy of the LLMs. The training KG triples and validation KG triples are sampled from different distributions and respectively. Formally, , where includes triples that share the same head entity as the query .
- Tail Set: Similar to the head set, the training and validation triples are sampled from distinct distributions. Formally, , where includes triples that share the same tail entity as the query .
- Relationship Set: The relationship set S comprises triples that offer more information about the query’s entity g. Specifically, S includes all triples, where g appears as either the head or the tail entity in the training and validation datasets. Formally, .
Take the head set as an example; to ensure diversity in the head set , we employ an entity-coverage-based strategy aimed at maximizing the inclusion of diverse entities during the construction of the set. Initially, an empty set is defined to track entities that have been included in the selected triples. At each iteration, a triple from is selected to maximize the inclusion of entities not yet present in . The entities of the selected triple are then added to , and the process continues until all triples in are selected. If all entities are already covered, the remaining triples are selected randomly to maintain balance. This iterative approach ensures that the set incorporates a diverse set of triples, thereby helping the model generalize its understanding of the relation across different examples. By prioritizing diversity, this construction method enhances the ability to effectively leverage analogies of the model.
To rank the relationship set S by relevance to the query, we adopt a semantic similarity-based approach using pre-trained embedding models (e.g., BERT [31]). First, both the query and each triple in S are embedded into a shared high-dimensional vector space, capturing their semantic representations. Next, the cosine similarity between the query’s embedding and each triple’s embedding is computed to evaluate their relevance. The triples are then ranked in descending order of similarity scores, forming an ordered list S that prioritizes the most relevant triples for supplementation. This ranking ensures that the selected triples provide contextually meaningful information about the query’s head entity h, enabling the model to enrich its understanding of the query context. During inference, both the head set and the relationship set are dynamically constructed based on the query. The head set includes triples that share the same relation as the query, , ensuring that the demonstration examples are directly comparable to the query. The relationship set S, on the other hand, contains triples where the query’s head entity h appears either as the head or the tail entity, providing supplementary context. This dynamic construction of and S ensures flexibility and relevance for each query, allowing the model to leverage the ordered lists and S effectively during its reasoning process.
3.2.2. Prompt Engineering with Large Language Models
Prompts play a crucial role in guiding LLMs to generate useful and relevant outputs. High-quality prompts help steer the model toward producing more accurate and valuable results, unlocking the full potential of LLMs. During the inference phase, we dynamically generate the relevant head set, tail set, and relationship set based on the query and use these sets as input examples for LLMs. To evaluate the relevance of these examples to the query, we leverage pre-trained embedding models (e.g., BERT [31]) to encode both the query and the examples into a shared high-dimensional semantic space. In this space, cosine similarity is calculated between the query and each example to rank them by semantic relevance. The ranked examples emphasize the information most aligned with the query, providing LLMs with precise contextual guidance to enhance the quality of generated candidate answers.
Next, LLMs utilize the ranked example sets to perform reasoning and generate a set of candidate answers, each accompanied by explanatory information, such as the rationale or references supporting the prediction. To make optimal use of the input token limit, the model dynamically adjusts the number and diversity of input examples, ensuring comprehensive semantic context coverage. Finally, the candidate answers are ranked by confidence scores and presented for human review. By combining efficient ranking, enhanced contextual understanding, and human oversight, this approach ensures the accuracy and reliability of knowledge graph completion results.
3.2.3. Multimodal Information Supplement
Given the remarkable success of the CLIP [37] model in the multimodal domain, it has become a cornerstone for advancing the integration of vision and language tasks. CLIP accomplishes this by jointly learning representations for both images and text in a shared embedding space through contrastive learning. Inspired by CLIP’s ability to bridge modalities, we propose extending its principles to the domain of knowledge graph completion. In this context, knowledge graph entities and relations can be represented as multimodal embeddings by incorporating textual descriptions, visual representations, or other contextual modalities. For instance, entities in a knowledge graph (e.g., “Eiffel Tower”) could be associated with both textual descriptions (“A famous monument in Paris”) and visual representations (images of the Eiffel Tower). By aligning these diverse representations in a shared space, a multimodal knowledge graph model could learn richer and more robust embeddings. This multimodal approach not only enhances the model’s ability to generalize across various types of queries (e.g., completing triples with missing visual context) but also opens up opportunities to leverage external multimodal resources, such as linking images and texts from the web, to enrich and validate graph data.
Specifically, we introduce image and audio data into the traditional KGC framework, enabling the model to better understand and complete missing triples. By constructing the head set, tail set, and relationship set, we can incorporate image and audio information as supplementary modalities, enhancing the representation of entities and relationships. For example, suppose we have a missing triple , where h represents , r represents , and ? is the missing entity. In traditional KGC methods, we would retrieve triples related to from the head set, such as or , and infer the missing entity based on these text-based clues. To deepen the model’s understanding, we can also introduce image and audio data to further enrich the context of the entity . For instance, we could provide an image of an apple and an audio description like . By combining these image and audio modalities with text, we can construct a multimodal head set that encompasses more dimensions of descriptive information, helping the model gain a more comprehensive understanding of the entity and its related relationship.
Similarly, for the relationship set, we can integrate image or audio information related to the relationship r. For example, the relationship can be illustrated through images of various fruits or described audibly, highlighting their similarities. By incorporating multimodal information, the model can not only extract insights about entities and relationships from text but also enhance its understanding and reasoning capabilities through visual and auditory cues.
4. Experiment
4.1. Setup
Datasets. We evaluate the proposed methods on three widely used benchmarks for link prediction: FB15k-237 [38], WN18RR [25], and CN15K [39]. FB15k-237 is a subset of the Freebase knowledge graph, encompassing commonsense knowledge on topics such as movies, sports, awards, and travel. WN18RR is derived from WordNet [40] and contains knowledge about English morphology. Both FB15k-237 and WN18RR have been processed to remove redundant inverse relations to mitigate information leakage. Compared to FB15k-237, the knowledge graph in WN18RR is significantly sparser. CN15K is a subgraph of ConceptNet that includes 15,000 entities and 241,158 uncertain relational facts in English. The dataset statistics are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Statistics of datasets.
Baselines. To evaluate the performance of our proposed MLKGC, we compare it against a range of triple-based, text-based and LLM-based baselines. The triple-based models include RESCAL [41], TransE [19], DistMult [20], ComplEx [42], and RotatE [43]. Text-based baselines include Pretrain-KGE. For LLM-based baselines, we extend the zero-shot and one-shot link prediction capabilities of ChatGPT-4o to the entire dataset, reporting updated results as and . Among pre-trained language models (PLMs), KG-BERT [7] was the first to integrate PLMs into the KGC task. CSPromKG, on the other hand, combines PLMs with traditional knowledge graph embedding models, achieving a balance between computational efficiency and predictive performance.
Evaluation metrics and settings. To evaluate the performance of link prediction models, we report the Mean Reciprocal Rank (MRR), as well as Hits@1, Hits@3, and Hits@10 metrics under the “filtered” setting. This standard evaluation practice removes valid entities, excluding the ground truth target entities, from the ranked list. This ensures that the evaluation metrics accurately reflect the model’s ability to prioritize the correct entity, without penalizing it for predicting other valid alternatives. All our experiments were conducted on a single GPU (A800, CUDA version 12.6) to ensure efficiency and reproducibility. In the experiments, we used ChatGPT as the large language model.
4.2. Experimental Results
Table 3 presents the experimental results of our MLKGC model on three benchmark datasets: WN18RR, FB15k-237N, and CN15K. The results demonstrate that our approach consistently delivers strong performance across various metrics, including MRR, H@1, H@3 and H@10. Focusing on the WN18RR dataset as an example, although our method slightly lags behind the baseline in the H@1 metric, it shows substantial improvements in the other metrics, with a 2.3% increase in MRR, a 10.3% increase in H@3, and a 9.2% increase in H@10. These improvements suggest that our approach excels in identifying and ranking relevant entities further down the ranked list, even if it performs slightly worse in identifying the top-ranked entity in certain cases. The consistent gains across all datasets and most metrics emphasize the robustness and broad applicability of our MLKGC model. These results confirm the effectiveness of our method in capturing complex relational patterns and leveraging contextual information for knowledge graph completion tasks.

Table 3.
Comparison between the proposed methods and baseline methods. The best result for each metric is shown in bold. For the MRR, H@1, H@3, and H@10 metrics, a higher value indicates better performance.
In addition, both KGBERT and CSProm-KG utilize entity descriptions to improve entity embedding representations, thereby enhancing the model’s understanding and representation of entities. However, it is important to note that our MLKGC method achieves significant improvements of 4.7% and 29.6% in MRR compared to the two aforementioned methods. This result not only highlights the advantages of MLKGC in handling entity relationships and text self-alignment tasks but also demonstrates its superior ability to integrate and leverage multimodal information. The proposed method outperforms baseline triple-based methods, showcasing the potential of the LLM’s internal knowledge base and the effectiveness of multimodal models in extending and applying knowledge across diverse domains. This advantage not only emphasizes the model’s ability to better capture relational semantics but also underscores its enhanced capacity for integrating multi-source information and performing knowledge reasoning.
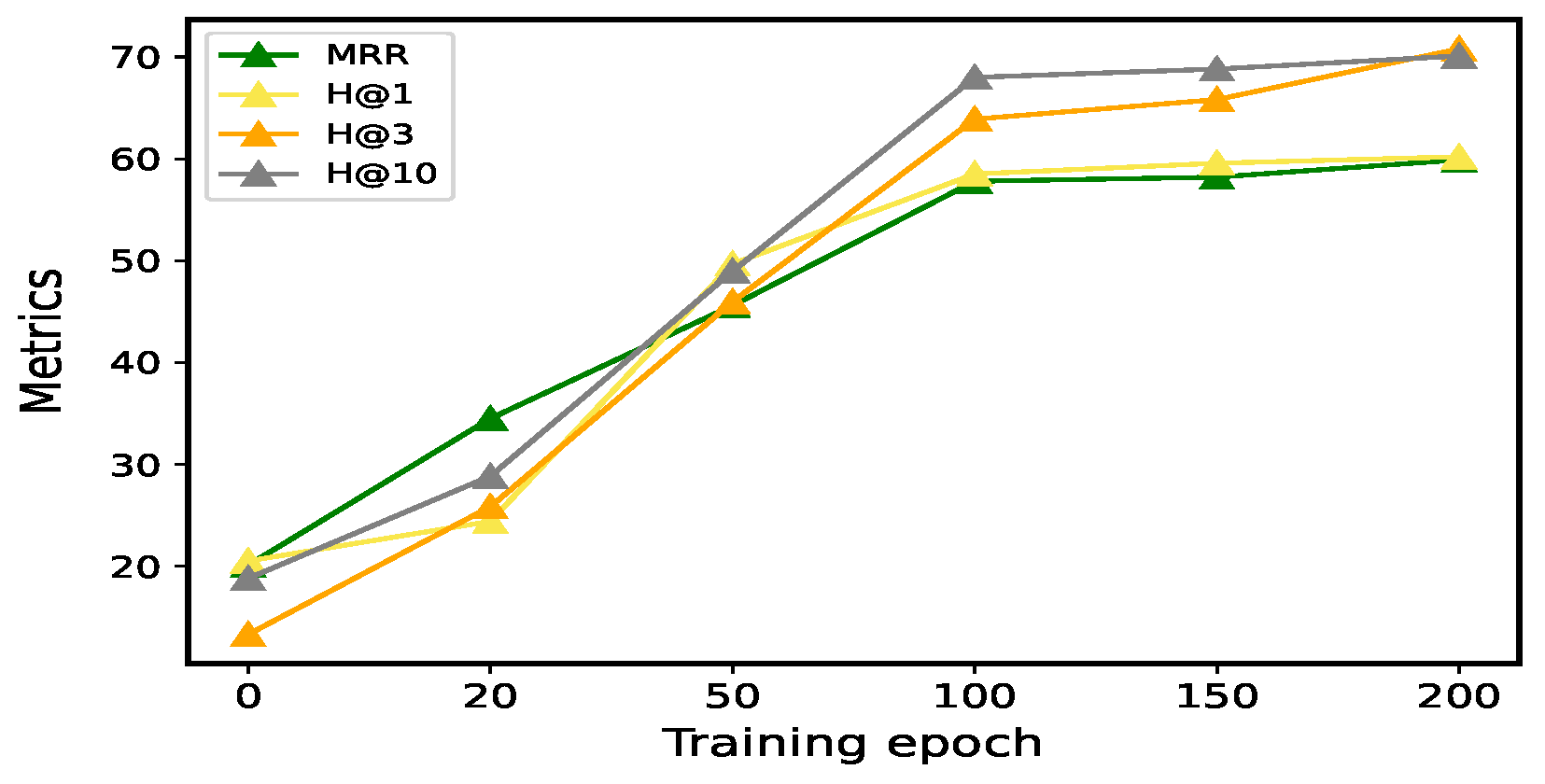
Additionally, we conducted experiments with epoch = 0, 20, 50, 100, 150, and 200 on three benchmark datasets to evaluate the effect of training epochs on model performance. We aim to observe how performance evolves as the number of training epochs increases and to identify the point at which further training provides diminishing returns. As shown in Figure 3, the performance on the validation set begins to stabilize and converge when the epoch reaches 100, indicating that the model has learned the majority of the relevant patterns and relationships in the data. Beyond this point, further increasing the number of epochs has a negligible impact on performance, suggesting that additional training could lead to over-fitting or simply be unnecessary. Based on these observations, we selected 100 epochs as the optimal training duration for our experiment.
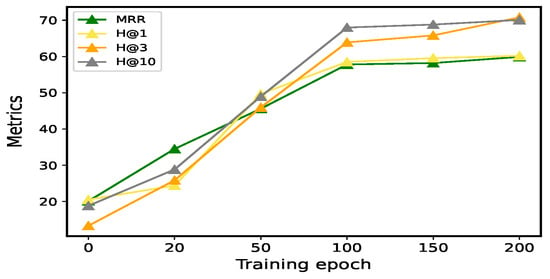
Figure 3.
MRR, H@1, H@3, and H@10 scores on the validation set on the WN18RR dataset. We set the epochs to 0, 20, 50, 100, 150, and 200, respectively.
4.3. Ablation Study
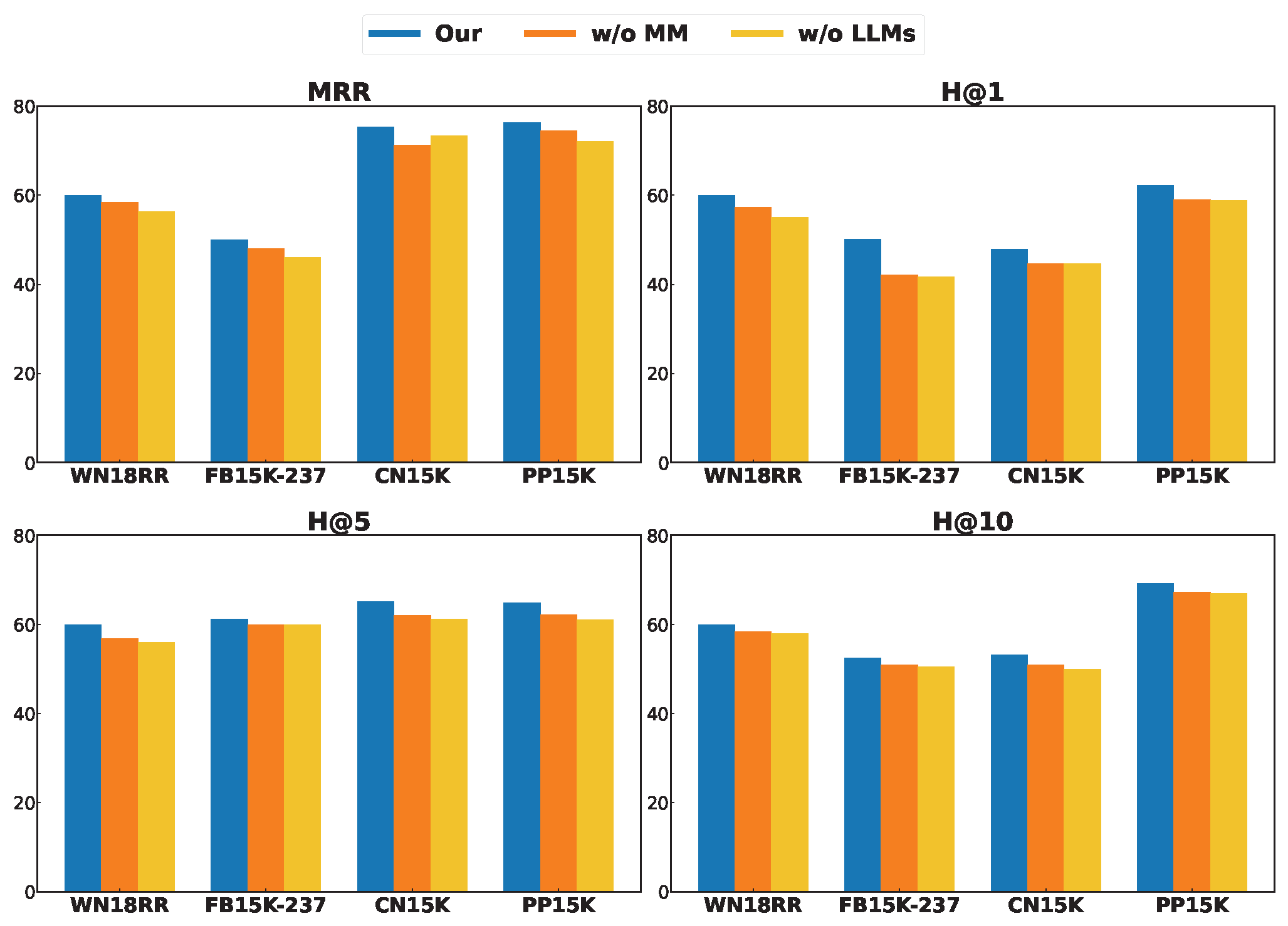
To verify the effectiveness of the LLM internal knowledge base and multimodal models in extending and applying knowledge across different domains, we conducted an ablation study on the MMKICGPT model. Specifically, we set up w/o LLM and w/o MM, which represent the removal of the LLM module and the multimodal (Multi-Modal) module from the model, respectively. The experimental results show that w/o LLM outperforms w/o MM in terms of MRR, H@1, H@3, and H@10, as illustrated in Figure 4. This indicates the critical role of the multimodal module in the integration and improvement strategy. This result not only validates the significant contribution of the multimodal module in integrating multi-source information, enriching relational expressions and enhancing the model’s robustness, but also further highlights the core role of the LLM module in capturing semantic depth and knowledge reasoning. Taken together, the organic combination of these two components enables MMKICGPT to achieve outstanding performance in knowledge graph completion tasks, offering new insights and directions for model optimization and multimodal integration.
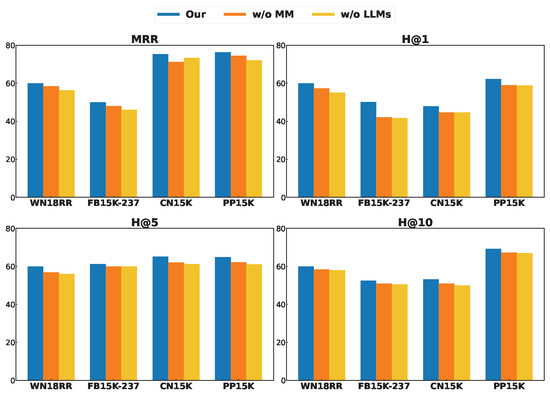
Figure 4.
Ablation results on three datasets.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we propose a GPT-based multimodal knowledge graph completion (MLKGC) framework aimed at addressing the limitations of existing link prediction tasks in KGC caused by missing triples. By guiding LLMs to learn and infer missing triples, our approach enhances the completeness and accuracy of KGC tasks. To further expand the expressive capacity of knowledge graphs, we innovatively introduce audio and image modalities to supplement and enrich knowledge from diverse domains, thereby strengthening the model’s ability to understand and reason with multimodal information. We conducted comprehensive experiments on several mainstream KGC benchmark datasets. The results demonstrate that the MLKGC method effectively leverages the language understanding capabilities of LLMs and the complementary information provided by multimodal data, exhibiting superior performance and broad applicability in link prediction tasks. Moreover, the method shows significant advantages in handling long-tail entities and complex relational expressions.
6. Future Work
In future work, we plan to further improve the MLKGC method in the following respects. First, we will explore the integration of domain adaptation techniques to enhance the LLMs’ ability to learn domain-specific knowledge, thereby addressing its knowledge gaps. Second, we will optimize the multimodal data alignment strategy to ensure more effective complementarity between different modalities, thereby improving overall task performance. Finally, we will further evaluate the applicability of our MLKGC method across a wider range of real-world applications and optimize its computational efficiency to meet practical deployment requirements.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.T.; Methodology, P.Y.; Validation, W.L.; Formal analysis, B.Y.; Data curation, W.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, C.; Yu, H.; Wan, F. Information retrieval technology based on knowledge graph. In Proceedings of the 2018 3rd International Conference on Advances in Materials, Mechatronics and Civil Engineering (ICAMMCE 2018), Hangzhou, China, 13–15 April 2018; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gan, J.; Li, H.; Lei, N. Design and research of intelligent question-answering (q&a) system based on high school course knowledge graph. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2021, 26, 1884–1890. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Zhuang, F.; Qin, C.; Zhu, H.; Xie, X.; Xiong, H.; He, Q. A survey on knowledge graph-based recommender systems. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2020, 34, 3549–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, E.; Wang, D.; Huang, J.; Hu, W. Open knowledge enrichment for long-tail entities. In Proceedings of the Web Conference 2020, WWW ’20, Taipei, Taiwan, 20–24 April 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 384–394. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, D.; Song, X.; Ma, C.; Tan, Z.; Ye, Z.; Dong, J.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, Z.; Karypis, G. Dgl-ke: Training knowledge graph embeddings at scale. In Proceedings of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Virtual Event, China, 25–30 July 2020; pp. 739–748. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Lyu, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.-H.; Zheng, P. Exploiting knowledge graphs in industrial products and services: A survey of key aspects, challenges, and future perspectives. Comput. Ind. 2021, 129, 103449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Mao, C.; Luo, Y. Kg-bert: Bert for knowledge graph completion. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.03193. [Google Scholar]
- Bosselut, A.; Rashkin, H.; Sap, M.; Malaviya, C.; Celikyilmaz, A.; Choi, Y. Comet: Commonsense transformers for automatic knowledge graph construction. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.05317. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Vashishth, S.; Sanyal, S.; Talukdar, P.; Yang, Y. A re-evaluation of knowledge graph completion methods. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 5516–5522. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Rae, J.W.; Borgeaud, S.; Cai, T.; Millican, K.; Hoffmann, J.; Song, F.; Aslanides, J.; Henderson, S.; Ring, R.; Young, S.; et al. Scaling language models: Methods, analysis & insights from training gopher. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.11446. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, L.; Deng, S.; Tan, C.; Xu, C.; Huang, F.; Si, L.; Chen, H. Hybrid transformer with multi-level fusion for multimodal knowledge graph completion. In Proceedings of the 45th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Madrid, Spain, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 904–915. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B.; Weninger, T. Open-world knowledge graph completion. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; Anadkat, S.; et al. Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08774. [Google Scholar]
- Touvron, H.; Lavril, T.; Izacard, G.; Martinet, X.; Lachaux, M.-A.; Lacroix, T.; Rozi, B.; Goyal, N.; Hambro, E.; Azhar, F.; et al. Llama: Open and efficient foundation language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.13971. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Y.; He, S.; Liu, K.; Zeng, X.; Liu, S.; Zhao, J. Path-based knowledge reasoning with textual semantic information for medical knowledge graph completion. BMC Med. Informatics Decis. Mak. 2021, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagvaral, B.; Lee, W.-K.; Roh, J.-S.; Kim, M.-S.; Park, Y.-T. Path-based reasoning approach for knowledge graph completion using cnn-bilstm with attention mechanism. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 142, 112960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baevski, A.; Zhou, Y.; Mohamed, A.; Auli, M. wav2vec 2.0: A framework for self-supervised learning of speech representations. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 12449–12460. [Google Scholar]
- Bordes, A.; Usunier, N.; Garcia-Duran, A.; Weston, J.; Yakhnenko, O. Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Nickel, M.; Murphy, K.; Tresp, V.; Gabrilovich, E. A review of relational machine learning for knowledge graphs. Proc. IEEE 2015, 104, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Mao, Z.; Wang, B.; Guo, L. Knowledge graph embedding: A survey of approaches and applications. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2017, 29, 2724–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yih, W.-T.; He, X.; Gao, J.; Deng, L. Embedding entities and relations for learning and inference in knowledge bases. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6575. [Google Scholar]
- Targ, S.; Almeida, D.; Lyman, K. Resnet in resnet: Generalizing residual architectures. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.08029. [Google Scholar]
- Schlichtkrull, M.; Kipf, T.N.; Bloem, P.; Van Den Berg, R.; Titov, I.; Welling, M. Modeling relational data with graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the Semantic Web: 15th International Conference, ESWC 2018, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 3–7 June 2018; Proceedings 15. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 593–607. [Google Scholar]
- Dettmers, T.; Minervini, P.; Stenetorp, P.; Riedel, S. Convolutional 2d knowledge graph embeddings. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Gao, J.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, R.; Ji, Y. Hitter: Hierarchical transformers for knowledge graph embeddings. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.12813. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, W.; Yu, M.; Chang, S.; Guo, X.; Wang, W.Y. One-shot relational learning for knowledge graphs. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.09040. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Q.; Chen, H. Meta relational learning for few-shot link prediction in knowledge graphs. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.01515. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghian, A.; Armandpour, M.; Ding, P.; Wang, D.Z. DRUM: End-To-End Differentiable Rule Mining on Knowledge Graphs; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Huang, Q.; Kwok, J.T.; Zhang, Y. KICGPT: Large language model with knowledge in context for knowledge graph completion. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2023; Association for Computational Linguistics: Singapore, 2023; pp. 8667–8683. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ju, Q.; Deng, H.; Wang, P. K-bert: Enabling language representation with knowledge graph. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 2901–2908. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Peng, J.; Mao, C.; Luo, Y. Exploring large language models for knowledge graph completion. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.13916. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, A.; Kochsiek, A.; Gemulla, R. Sequence-to-sequence knowledge graph completion and question answering. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.10321. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Q.; Li, L.; Dai, D.; Zheng, C.; Ma, J.; Li, R.; Xia, H.; Xu, J.; Wu, Z.; Liu, T.; et al. A survey on in-context learning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2301.00234. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Guo, L.; Xu, Y.; Hu, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, H. Native: Multi-modal knowledge graph completion in the wild. In SIGIR; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Tian, Y.; Yang, M.; Zaniolo, C. Multilingual knowledge graph embeddings for cross-lingual knowledge alignment. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.03954. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2021), Online, 18–24 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Toutanova, K.; Chen, D.; Pantel, P.; Poon, H.; Choudhury, P.; Gamon, M. Representing text for joint embedding of text and knowledge bases. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–21 September 2015; pp. 1499–1509. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Chen, M.; Shi, W.; Sun, Y.; Zaniolo, C. Embedding Uncertain Knowledge Graphs; ser. AAAI’19/IAAI’19/EAAI’19; AAAI Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- AlMousa, M.; Benlamri, R.; Khoury, R. A novel word sense disambiguation approach using wordnet knowledge graph. Comput. Speech Lang. 2022, 74, 101337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, M.; Tresp, V.; Kriegel, H.-P. A three-way model for collective learning on multi-relational data. ICML 2011, 11, 3104482–3104584. [Google Scholar]
- Trouillon, T.; Welbl, J.; Riedel, S.; Gaussier, É.; Bouchard, G. Complex embeddings for simple link prediction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Deng, Z.-H.; Nie, J.-Y.; Tang, J. Rotate: Knowledge graph embedding by relational rotation in complex space. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.10197. [Google Scholar]
- Vashishth, S.; Sanyal, S.; Nitin, V.; Talukdar, P. Composition-based multi-relational graph convolutional networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1911.03082. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Shen, T.; Long, G.; Zhou, T.; Wang, Y.; Chang, Y. Structure-augmented text representation learning for efficient knowledge graph completion. In Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021, WWW’21, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 12–23 April 2021; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1737–1748. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, Z.; Deng, S.; Chen, H.; Xiong, F.; Chen, M.; Chen, H. From discrimination to generation: Knowledge graph completion with generative transformer. In Proceedings of the Web Conference 2022, WWW’22; Lyon, France, 25–29 April 2022, Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 162–165. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Lam, K.-Y. Knowledge is flat: A seq2seq generative framework for various knowledge graph completion. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.07299. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, A.; Li, B.; Lam, K.-Y. Dipping plms sauce: Bridging structure and text for effective knowledge graph completion via conditional soft prompting. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.01709. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Qiao, S.; Ou, Y.; Yao, Y.; Deng, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, N. Llms for knowledge graph construction and reasoning: Recent capabilities and future opportunities. World Wide Web 2024, 27, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).