DAF-UNet: Deformable U-Net with Atrous-Convolution Feature Pyramid for Retinal Vessel Segmentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Adaptive Spatial Feature Extraction: By employing deformable convolution, the network dynamically adjusts its receptive field to capture structurally adaptive spatial information, which significantly enriches feature representation and allows for the precise delineation of complex vascular geometries.
- Enhanced Contextual Information Fusion: The contextual feature-extraction module, based on an advanced ASPP framework, leverages multi-scale atrous convolutions to integrate diverse contextual cues. This design enables the model to robustly detect vessels across varying scales and improve segmentation accuracy in regions with intricate vascular details.
- Robust Hybrid Loss Function: We introduce a novel hybrid loss function that synergistically combines pixel-level and segment-level losses. This formulation not only improves segmentation precision but also enhances the calibration of the model by addressing the challenges posed by the imbalanced distribution of thick and thin vessel pixels.
2. Related Work
2.1. U-Net and Its Improved Structure
2.2. Spatial Pyramid Pooling
3. Method
3.1. Deformable Feature Extractor
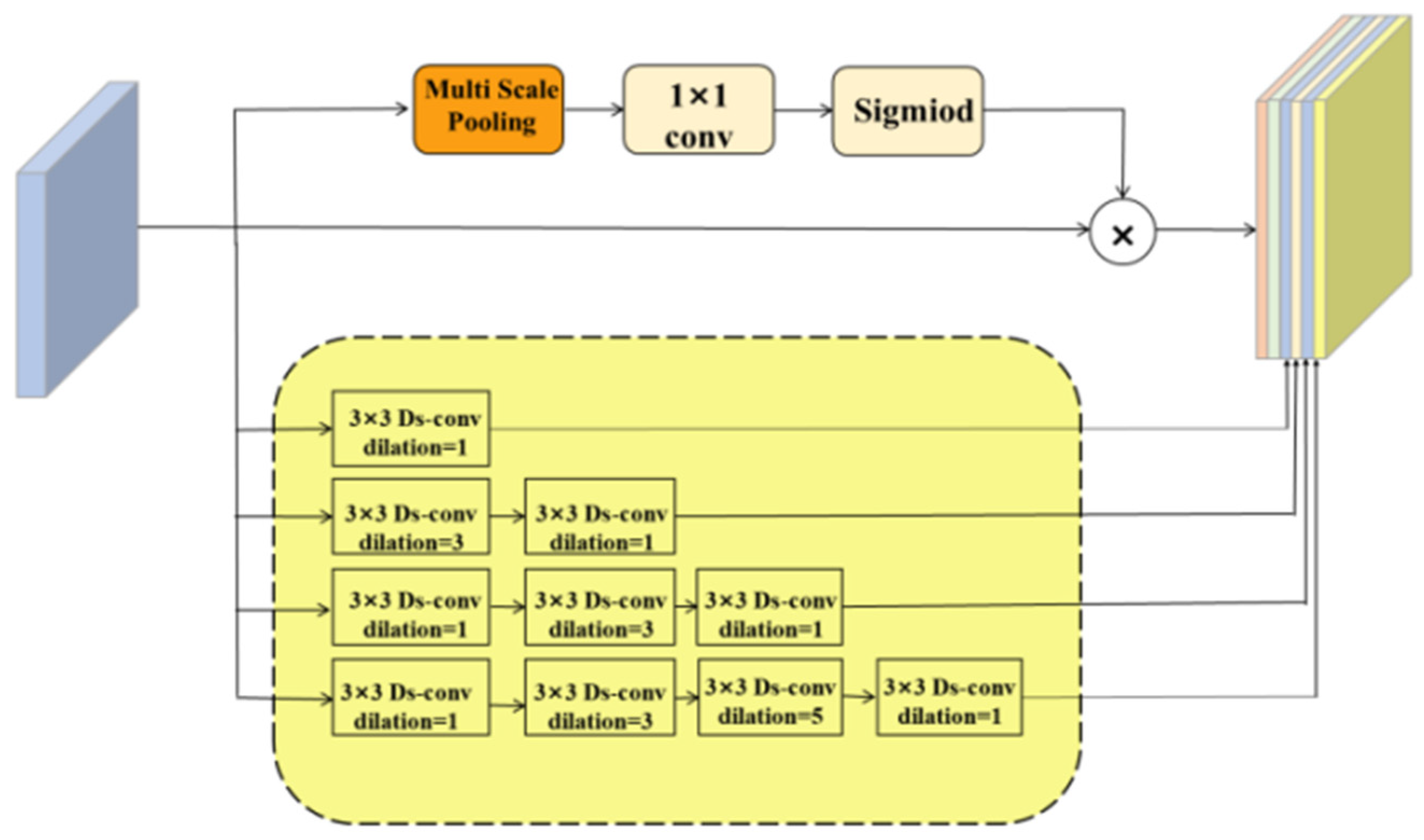
3.2. Adaptive Dilated Fusion Block
3.3. Loss Function
3.3.1. Mixed Loss Function
3.3.2. Hyper-Parameter Selection
4. General Framework
| Algorithm 1: DAF-UNet Workflow for Retinal Vessel Segmentation | |
| Input: Fundus image I | |
| Output: Segmentation mask Ŷ | |
| Step | Description |
| 1 | Preprocess I using CLAHE and gamma correction. |
| 2 | Convert to grayscale and resize to a fixed resolution. |
| 3 | Extract features using the encoder with deformable convolution layers. |
| 4 | Apply adaptive dilated fusion block (ADFB) at the bottleneck. |
| 5 | Fuse multi-scale context using the atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) module. |
| 6 | Decode features via the decoder path with skip connections. |
| 7 | Generate prediction map Ŷ. |
| 8 | Compute hybrid loss: |
| 9 | Backpropagate and update network parameters. |
5. Experiments and Analysis of Their Results
5.1. Datasets
5.2. Evaluation Metrics
5.3. Comparative Experiments
5.4. Ablation Experiments
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, W.L.; Su, X.; Li, X.; Cheung, C.M.; Klein, R.; Cheng, C.Y.; Wong, T.Y. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2014, 2, e106–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, R.N.; Aung, T.; Medeiros, F.A. The pathophysiology and treatment of glaucoma: A review. JAMA 2014, 311, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, K. Computer-aided diagnosis in medical imaging: Historical review, current status and future potential. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2007, 31, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraz, M.M.; Remagnino, P.; Hoppe, A.; Uyyanonvara, B.; Rudnicka, A.R.; Owen, C.G.; Barman, S.A. An ensemble classification-based approach applied to retinal blood vessel segmentation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 2538–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraz, M.M.; Remagnino, P.; Hoppe, A.; Uyyanonvara, B.; Rudnicka, A.R.; Owen, C.G.; Barman, S.A. Blood vessel segmentation methodologies in retinal images—A survey. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2012, 108, 407–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staal, J.; Abramoff, M.D.; Niemeijer, M.; Viergever, M.A.; van Ginneken, B. Ridge-based vessel segmentation in color images of the retina. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2004, 23, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Wu, L.; Guo, J.; Li, M.; Liu, R.; Xu, L.; Lu, Z. Blood vessel segmentation using deep learning and conditional random field. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 30th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Thessaloniki, Greece, 22–24 June 2017; pp. 578–583. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Xiong, W.; An, H.; Wang, S.; Tang, Y. A novel R2U-Net-based method for segmenting retinal vessels. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing (BigComp), Kyoto, Japan, 27 February–2 March 2019; pp. 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, X. LadderNet: Multi-path networks based on U-Net for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.07810. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.; Cheng, J.; Fu, H.; Zhou, K.; Hao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J. CE-Net: Context encoder network for 2D medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 2281–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Raju, K.; Murthy, A.S.D.; Rao, B.C.; Bhargavi, S.; Rao, G.J.; Madhu, K.; Saikumar, K. A Robust And Accurate Video Watermarking System Based On SVD Hybridation For Performance Assessment. Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. 2020, 68, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2–4 May 2016; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 346–361. [Google Scholar]
- Edupuganti, V.G.; Chawla, A.; Kale, A. Automatic Optic Disk and Cup Segmentation of Fundus Images Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Athens, Greece, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 2227–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Chen, P.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, D.; Huang, Z.; Hou, X.; Cottrell, G. Understanding Convolution for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; pp. 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A.A. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Yang, X.; Cheng, K.T. Joint Segment-Level and Pixel-Wise Losses for Deep Learning Based Retinal Vessel Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 1912–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, L.; Fang, H. Study Group Learning: Improving Retinal Vessel Segmentation Trained with Noisy Labels. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2023, 42, 1234–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y. Road extraction by deep residual U-Net. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laouamer, I.; Aiadi, O.; Kherfi, M.L.; Cheddad, A.; Amirat, H.; Laouamer, L.; Drid, K. EnsUNet: Enhancing brain tumor segmentation through fusion of pre-trained models. In International Congress on Information and Communication Technology; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 163–174. [Google Scholar]







| SP | ACC | DSC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | 97.34 | 96.30 | 80.90 |
| CE-net [11] | 98.24 | 95.45 | 82.02 |
| R2-Unet [25] | 98.13 | 95.56 | 81.71 |
| DU-Net | 97.21 | 95.76 | 81.09 |
| Yang, et al. [8] | 98.02 | 95.38 | 81.27 |
| Residual U-Net | 98.01 | 94.83 | 84.34 |
| Recurrent U-Net [24] | 98.16 | 95.56 | 81.55 |
| Laddernet [25] | 98.10 | 95.61 | 82.02 |
| DAF-UNet | 98.21 | 95.92 | 82.98 |
| SP | ACC | DSC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | 96.91 | 96.08 | 80.83 |
| R2-Unet [25] | 98.20 | 96.34 | 79.28 |
| DU-Net | 97.93 | 96.98 | 81.91 |
| Yang, et al. [8] | 98.06 | 96.07 | 79.03 |
| Residual U-Net | 98.20 | 96.23 | 79.11 |
| Recurrent U-Net [24] | 98.36 | 96.22 | 78.10 |
| Laddernet [25] | 98.20 | 96.56 | 79.02 |
| DAF-UNet | 98.71 | 96.32 | 82.27 |
| Δ | |
|---|---|
| U-Net vs. DAF-Unet | +2.08 |
| DU-Net vs. DAF-Unet | +1.89 |
| Residual U-Net vs. DAF-Unet | −1.36 |
| U-Net | DC | ADFB | Loss | MIOU | MPA | ACC | DSC | Param |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| √ | 74.58 | 74.51 | 94.71 | 81.42 | 34.53 | |||
| √ | √ | 74.68 | 81.04 | 94.87 | 81.60 | 30.06 | ||
| √ | √ | 75.33 | 84.62 | 95.29 | 82.96 | 104.89 | ||
| √ | √ | 75.01 | 76.67 | 95.01 | 81.43 | 34.53 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 75.12 | 84.46 | 95.12 | 82.79 | 100.89 | |
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 75.58 | 80.2 | 95.72 | 82.98 | 100.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, Y.; Yang, R.; Zhao, M.; Qi, M.; Peng, S.-L. DAF-UNet: Deformable U-Net with Atrous-Convolution Feature Pyramid for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091454
Duan Y, Yang R, Zhao M, Qi M, Peng S-L. DAF-UNet: Deformable U-Net with Atrous-Convolution Feature Pyramid for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. Mathematics. 2025; 13(9):1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091454
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Yongchao, Rui Yang, Ming Zhao, Mingrui Qi, and Sheng-Lung Peng. 2025. "DAF-UNet: Deformable U-Net with Atrous-Convolution Feature Pyramid for Retinal Vessel Segmentation" Mathematics 13, no. 9: 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091454
APA StyleDuan, Y., Yang, R., Zhao, M., Qi, M., & Peng, S.-L. (2025). DAF-UNet: Deformable U-Net with Atrous-Convolution Feature Pyramid for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. Mathematics, 13(9), 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091454







