Abstract
Large-scale Visual-Language Models have demonstrated powerful adaptability in video recognition tasks. However, existing methods typically rely on fine-tuning or text prompt tuning. In this paper, we propose a visual-only prompting method that employs watermark and trademark prompts to bridge the distribution gap of spatial-temporal video data with Visual-Language Models. Our watermark prompts, designed by a trainable prompt generator, are customized for each video clip. Unlike conventional visual prompts that often exhibit noise signals, watermark prompts are intentionally designed to be imperceptible, ensuring they are not misinterpreted as an adversarial attack. The trademark prompts, bespoke for each video domain, establish the identity of specific video types. Integrating watermark prompts into video frames and prepending trademark prompts to per-frame embeddings significantly boosts the capability of the Visual-Language Model to understand video. Notably, our approach improves the adaptability of the CLIP model to various video action recognition datasets, achieving performance gains of 16.8%, 18.4%, and 13.8% on HMDB-51, UCF-101, and the egocentric dataset EPIC-Kitchen-100, respectively. Additionally, our visual-only prompting method demonstrates competitive performance compared with existing fine-tuning and adaptation methods while requiring fewer learnable parameters. Moreover, through extensive ablation studies, we find the optimal balance between imperceptibility and adaptability. Code will be made available.
MSC:
68T05
1. Introduction
Visual-Language Models (VLMs), such as Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP) [1] and A Large-scale ImaGe and Noisy-text embedding (ALIGN) [2], have revolutionized the paradigm of visual representation learning. Instead of using a linear classifier to predict a fixed set of one-hot encoding labels, VLMs learn separate unimodal encoders for images and texts to predict the correct image–text pairings in the joint embedding space. Leveraging the rich information embedded in natural language supervision, these models exhibit significant potential in learning visual representations. This capability facilitates transfer across a wide spectrum of downstream tasks, including Optical Character Recognition (OCR) [3], video action recognition [4,5], image segmentation [6], and various forms of fine-grained object classification [1]. To bridge the distribution gap between source and target domains, VLMs incorporate text prompts preceding the actual labels. For instance, in a specific task such as video action recognition, CLIP utilizes the hard prompt template “A photo of a person {label}.”, signifying the human action (Figure 1a). However, such prompt engineering does not generalize well across diverse video domains, including movies and egocentric videos. This limitation highlights the need for a parameter- and data-efficient video adaptation method capable of operating with minimal training samples, ensuring broader applicability across diverse video scenarios.
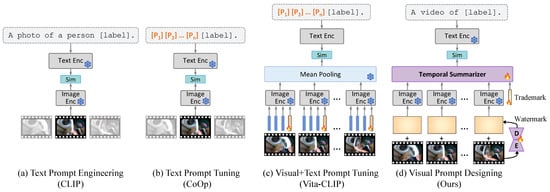
Figure 1.
Comparative overview of video adaption methods in Visual-Language Models: (a) CLIP, (b) CoOp, (c) Vita-CLIP, and our (d) watermark and trademark prompts.
Recently, there have been efforts to automatically tune the text prompt for optimal performance. The notable methods in this regard are CoOp [7] and CoCoOp [8], which introduce learnable text prompts that precede the actual label, aiming to discover the most effective task-specific text prompt (Figure 1b). However, the learned soft prompts lack interpretability. They only tune the target-specific head while leaving the visual representations of the backbone model unchanged. Moreover, when adapting to video datasets such as UCF101 [9], CLIP and CoOp typically use only a single center frame from each video clip as the input image, thereby transforming the task into image classification. Yet, this approach encounters substantial challenges in classifying actions that are fundamentally opposed, such as “close” versus “open” or “put” versus “take”, especially when relying solely on a single frame. The lack of temporal context in this approach makes it difficult to distinguish between actions that are visually similar but contextually distinct.
To tackle these problems, there are several works that focus on transferring the knowledge of the CLIP model to the video domain, such as video retrieval [10,11] and action classification [4,5]. ActionCLIP [5] and ViFi-CLIP [4] adapt the CLIP model to video datasets by fine-tuning the entire CLIP encoders in a fully supervised manner. Considering that video data include an additional temporal axis compared with image data, these methods are less efficient, requiring increased computational resources and longer training times. Vita-CLIP [12] employs the prompting strategy on both the vision and text sides, leaving the weights of the pre-trained CLIP frozen (Figure 1c). While this method has improved the performance in zero-shot video transfer tasks, it also requires pre-training on the large-scale video dataset, i.e., Kinetics [13], which reduces its data efficiency. Moreover, the token-level prompts need to unpack the pre-trained image encoder into patch embedding and visual encoding components to insert the prompt tokens. This approach inherently depends on transformer-based architectures, limiting its adaptability across different model types. Furthermore, when vision-language models are accessed via APIs provided by third parties, modifying internal layers becomes infeasible—further restricting the applicability of this prompting strategy. Prompting, also known as adversarial reprogramming [14], is a kind of adversarial attack where the modification of input data readapts a model to perform a task specified by the adversary [15]. This explicit intervention in the model’s input processing pipeline can raise security or usage concerns. Model owners might perceive this prompt-based approach as an attack, potentially leading to account restrictions or disablement. Thus, there is an urgent need to handle the visual prompts that are efficient and non-aggressive to the pre-trained models.
Therefore, we propose a novel prompt-based method, watermark prompts and trademark prompts, for efficient adaptation to the video action recognition task (Figure 1d). Unlike conventional watermarks, our watermark prompts are customized to be imperceptible while maintaining adaptability within the pre-trained VLM. On the other hand, trademark prompts are designed to identify classes of video domain, facilitating the distinction of video types. Considering that an action in a video consists of both spatial (where) and temporal (when) information, we systematically address these dimensions by employing watermark prompts and trademark prompts, respectively. To handle the spatial aspect, we employ a prompt generator for designing the watermark prompt. The prompt generator ensures that the watermark prompt is input-dependent, allowing efficient generalization across diverse distributions of video, such as different backgrounds or varying levels of brightness. The prompt encoder can be either a simple, trainable module or a pre-trained, frozen video feature extractor. The prompt decoder comprises a spatial prompt decoder and a mask decoder, which help to control the impact of the watermark prompt. Note that the prompt generator is sensitive to parameter initialization. We initially set the weights of the prompt generator to small values, aiming to gradually influence the video with the generated prompt. For the temporal aspect, we introduce a trademark prompt token alongside per-frame representation. The trademark prompt is dataset-dependent, enabling adaptation to a wide range of dataset collections, such as egocentric videos and movie action videos. The final video representation, adapted to the source domain, is summarized by an attention mechanism to effectively merge temporal context. The prompt generator, trademark prompt, and temporal summarizer are parameter efficient and jointly optimized while training. By carefully prompting the input data from the target video to the source domain, we eliminate the need for text prompt tuning. Instead, we employ a straightforward and interpretable prompt, “A video of label”.
To evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of the proposed watermark and trademark prompts, we test our model in a few-shot manner across a broad spectrum of video datasets, including both third-person datasets such as HMDB-51 [16] and UCF-101 [9] and egocentric dataset EPIC-Kitchen-100 [17]. Our method significantly improved the video action classification accuracy of the CLIP model by 16.8%, 18.4%, and 13.8% on these datasets, respectively. When compared with the latest state-of-the-art video adaptation methods, our model outperforms all zero-shot transfer approaches, requiring less training time and lower computational costs. In addition, our visual-only prompting method can be competitive with existing few-shot text and visual prompting methods while using a smaller number of learnable parameters. These results indicate the potential of the proposed watermark and trademark prompts, making it particularly suitable for use in resource-constrained environments. Moreover, we conduct a series of ablation studies to find the optimal design of each component. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that the proposed visual prompt-based method (1) is data-efficient to train, (2) preserves the original video quality and is non-aggressive to the VLM, (3) enables the use of either Transformer or Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) visual encoders, and (4) allows the VLM to adapt to various downstream video datasets with efficient parameters and effective performance.
2. Related Work
2.1. Generalizability, Transferability, and Adaptability
Typically, to access generalizability, the CLIP model is trained on large-scale datasets and then tested on downstream datasets in a zero-shot manner [1,4,5,11,18]. However, it is more challenging to collect large-scale video data compared with images. For example, the most widely used video dataset, Kinetics-400 [13], consists of 300 K video clips, whereas CLIP is trained on 400 M image–text pairs. Additionally, video action recognition datasets [9,16,17] only provide human action categories without informative captions. These labels constrain the text space by the number of action categories, limiting the potential for natural language supervision. Thus, the video representation is easy to overfit to the trained labels and scenes, which restricts the generalizability of Visual Language Models. Lin et al. [19] demonstrate that the Kinetics pre-trained CLIP model shows limited zero-shot performance when recognizing unseen actions.
On the other hand, fully supervised learning methods [13,20,21] can evaluate the transferability of the model by training on the entire downstream training set. These methods often show higher accuracy than zero-shot methods in specific tasks. However, they require extensive labeled data, and training on these data is time-consuming, which is proportional to the number of labeled videos.
Accordingly, to find the trade-off between model accuracy and training time, we train the model in a few-shot manner to enhance adaptability. Few-shot learning significantly reduces the amount of labeled data required for training, allowing the model to adapt to new categories and scenes efficiently. Moreover, our model employs an external adaptation strategy that can be integrated with VLMs, regardless of whether the encoder is a CNN or Transformer.
2.2. Video Adaptation in VLMs
Many studies have focused on adapting video data to VLMs. These methods can be categorized based on the location of the tuned parameters: backbone, head, adapter, text prompt, and visual prompt.
The most straightforward approach is to fine-tune the entire backbone of CLIP encoders [4,5,11,19,22,23] in a fully supervised manner. However, optimizing all parameters is time-consuming, and they only achieve high accuracy when trained on large-scale datasets, which diminishes both efficiency and effectiveness. An alternative approach is to tune only a subset of the parameters, such as target-specific heads [5,11,18,22,23,24,25,26,27]. Since CLIP can only process a single frame at a time, the head is designed to learn temporal information of multiple frame sequences while leaving the frame-level visual representations of the backbone model unchanged. On the other hand, adapters insert extra lightweight modules within the encoders to slightly modify the visual representations [5,23,24,25,26]. Although they improve the adaptability in a few-shot setting, adapters are typically designed to work with specific architectures, limiting their flexibility and requiring modifications to be applied to a wide range of models.
Conversely, the prompting approach, which originated from the Natural Language Processing (NLP) domain, aims to generate task-specific inputs to adapt pre-trained models for performing desired functions [11,12,18]. Unlike other methods, the prompting strategy transfers knowledge in the data space and keeps the parameters of pretrained backbone models frozen. Given that the CLIP model receives multi-modalities, the prompt can be added to either the text side or the visual side. For the text prompt, a simple approach is to incorporate manually designed hard prompts [1] or learned soft prompts [7,8]. Similar to head tuning, the text prompt only changes the text representations of candidate actions, resulting in limited performance in videos with different views or scenes. Additionally, tuning the text prompt along with other methods often causes label inconsistencies, making it difficult to optimize the tuned parameters.
In contrast, we focus on visual-only prompting to bridge the distribution gap between VLMs and various video domains. Our method incorporates only a small number of parameters to generate visual prompts while supporting various backbone encoders. The details of the model are described in the next section.
3. Methodology
Our approach efficiently adapts the CLIP model to video domain data by introducing lightweight watermark and trademark prompts that operate along the spatial and temporal axes, respectively. For spatial representation, watermark prompts are generated via a prompt generator designed as an autoencoder. For temporal modeling, a trademark prompt is appended to each frame-level feature, and the final video representation is obtained through the transformer’s attention mechanism. The overall designs are illustrated in Figure 2 and Figure 3c, with architectural details of the watermark prompt generator summarized in Table 1. Notably, the original CLIP image encoder and text encoder remain unchanged and are kept frozen throughout.
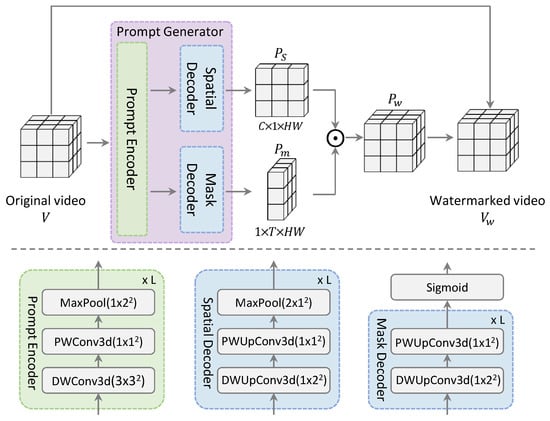
Figure 2.
Framework of watermark prompts generator. The generator comprises a prompt encoder and two decoders (spatial and mask), jointly working to generate watermark prompts for each input video.
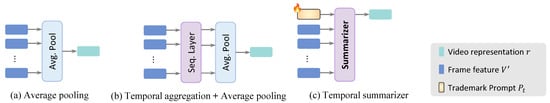
Figure 3.
Comparative overview of temporal feature aggregation methods. (a) Average pooling, (b) a two-step process—temporal aggregation followed by average pooling, and (c) temporal summarizer.

Table 1.
Architecture details of watermark prompts generator.
3.1. Watermark Prompts Generation
3.1.1. Prompt Encoder: Mapping Latent Features
The main objective of the prompt encoder within our prompt generator is to extract latent representations from video data. Accordingly, the prompt encoder, denoted as , can either be a trainable lightweight network or a pre-trained deep visual backbone.
Consider an input video, represented as , where C represents the channels of input video frames, T denotes the temporal dimensions, and are the spatial dimensions. In the case of a trainable encoder, we simply stack 3D convolutional layers and 3D max pooling layers to extract visual representation (Figure 2). To enhance parameter efficiency, we decompose a 3D convolutional layer into a depth-wise and a point-wise convolutional layer [28]. The trainable encoder is designed to output a size comparable to conventional visual backbones, which involves increasing the number of channels while reducing the spatial dimensions. Formally, the resulting latent embedding can be represented as follows:
which is then fed to the decoders of the prompt generator.
3.1.2. Prompt Decoder: Designing Watermark Prompts
Our decoders consist of two components: a spatial prompt decoder and a mask decoder .
The spatial prompt decoder transforms the latent representation into a single prompt map. Symmetric to the encoding process, the transposed convolutional layers are used to increase the spatial dimension while decreasing the number of channels, ensuring the output matches the same size as the input video. Unlike the encoder, the spatial prompt decoder compresses the temporal dimension to one, aiming to generate a consistent watermark for each video frame. The spatial prompts are consistent across all frames of the video. This design choice is made to ensure that the watermark is not easily perceptible to viewers. Consequently, the size of the spatial prompt is
The mask decoder is structured to stack transposed convolutional layers to generate per-pixel weights. It increases both the spatial and temporal dimensions to match those of the input video. In contrast, it compresses the channel dimension to one, focusing on extracting pixel-wise features. The extracted mask features are passed through a sigmoid layer, effectively normalizing the output values within a range of 0 to 1. Both decoders also adopt the strategy of decomposing the convolutional layers to enhance the parameter efficiency. Accordingly, the output dimension of the mask decoder is
To effectively merge the spatial prompt with the mask, we expand the time axis of the spatial prompt and the channel axis of the mask to equalize their dimensions. These expanded outputs are element-wise multiplied, which helps to regulate the scale of the spatial prompt to generate the watermark prompt. The watermark prompt is then directly added to the original video, allowing for a smooth transition of target data to the source domain. To preserve the imperceptibility of the watermarked video frames, pixel-wise clipping is employed, ensuring they remain within the valid Red, Green, Blue (RGB) scale. Formally, the process of watermark prompt generation is as follows:
Here, represents the watermarked video consisting of T video frames. Each frame is processed through the CLIP image encoder to extract the corresponding per-frame feature:
Given that the watermark prompt is conditioned upon the original video input and decoded through locally connected networks, it can adapt to target inputs in a few-shot manner. It is important to note that the prompt is sensitive to the parameter initialization. To guarantee the imperceptibility of watermark prompts, we set the initial parameters to small values so that the generated prompts have a gradual impact on the input video.
We have also tested using the various families of visual backbones as the image encoder , including Vision Transformer (ViT) and ResNet [29]. These individual frame features are then aggregated with the trademark prompt to extract a comprehensive representation of the entire video, as described next.
3.2. Trademark Prompts Summarization
To efficiently adapt an image model to video data, it is necessary to summarize the temporal context inherent in video content. The simplest way to integrate the sequence of frame features is to calculate the average of all features (Figure 3a). This straightforward approach treats all video frames equally and does not involve any additional parameters. Other studies [5,11] employ a temporal processing network, such as transformers or Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), to initially extract the temporally processed feature, followed by average pooling (Figure 3b). In contrast, our method simplifies this process into a single step (Figure 3c). We introduce a learnable trademark prompt token, , which precedes the frame features and is then processed through the transformer encoder. The encoder automatically calculates the weights of each frame by self-attention. The final embedding of the trademark prompt token is then utilized to represent the overall video representation r:
3.3. Natural Language Supervision
The prompt generator, the trademark prompt, and the temporal summarizer are trained under the supervision of natural language. Recent works [12,18] heavily rely on learnable text prompts for adapting video to VLMs. In contrast, we avoid the use of the non-interpretable text prompt tuning method. We only focus on transferring the visual representation to the source domain. As we process the video action recognition task, we employ a straightforward text prompt: “A video of {label}”. The text prompt is fed into the pre-trained text encoder to extract textual features. Using the same contrastive objectives as in CLIP, the model is trained to map the video representation in the embedding space of language.
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.1. Datasets
Existing works have mainly focused on the third-person view video action recognition datasets such as HMDB-51 [16] and UCF-101 [9]. To fully evaluate the adaptability of our model, we additionally employ an egocentric video dataset, EPIC-Kitchen-100 (EK-100) [17]. This dataset offers a unique visual perspective, capturing activities from a first-person point of view. We observe that the three datasets exhibit negligible overlap in their data collections, which cover diverse video domains of movies, YouTube, and native kitchen environments, respectively. The HMDB-51 dataset has 51 action categories, and the UCF-101 contains 101 classes. The EK-100 is labeled with verbs and nouns, and our model is trained to recognize 97 verb classes. We measure the top-1 and top-5 classification accuracy of our models on the respective validation sets.
4.1.2. Implementation Details
We adopt the pre-trained CLIP (ViT-B/16) as the VLM for encoding the video frames and text. The representation of each video frame is obtained from the outputs of the class token in the image encoder. The parameters of image and text encoders remain frozen, and we only train the prompt generator, trademark prompts, and the temporal summarizer. In the prompt generator, we set the default dimension of latent features to d = 128. The input videos are recorded at 30 frames per second (fps), from which 8 frames are sampled with a temporal gap of 4 frames. During the training phase, each frame is resized to using bicubic interpolation, followed by a random crop to for data augmentation. We apply normalization using the standard ImageNet mean and standard deviation to each frame. At inference time, we employ multi-view inference with 3 spatial crops and 1 temporal view. To test the efficiency of our model, all experiments are conducted in a few-shot (k = 8) setting, which can be performed on a single NVIDIA A100 GPU (80 GB memory, NVIDIA Corporation, Santa Clara, CA, USA) with a batch size of 64.
4.2. Quantitative Results
4.2.1. Main Results
First, to investigate the effectiveness of the proposed watermark prompts and trademark prompts, we progressively add each module to the CLIP model (Table 2). The CLIP model, which uses only a single frame from the middle of the video clip, exhibits limited contextual information and shows low accuracies in action recognition tasks. Therefore, we sample 8 frames from each video clip and aggregate per-frame features by average pooling, which has no additional parameters to train. This simple expansion of the input from single to multiple frames helps to enhance performance. Note that the EK-100 is an egocentric video dataset, which has a large domain gap with the source domain, resulting in relatively lower accuracy compared with the other datasets. Nevertheless, the integration of the watermark and the trademark prompts significantly boosts the adaptability of the CLIP model to various video datasets. Compared with the multi-frame CLIP model, the watermark prompts increase the top-1 accuracy by 3.4%, 3.5%, and 2.9% on HMDB-51, UCF-101, and EK-100, respectively, requiring only 0.04 M trainable parameters. More importantly, the trademark prompts, along with the temporal summarizer, significantly boost performance. Given the imperceptibility constraint and the limited number of parameters in our watermark prompts, the trademark prompts contribute more to performance improvement. As each prompt alters the video at different levels (pixel and frame), their synergy led to further performance improvement when both prompts were combined with CLIP. The qualitative analysis of watermark prompts is conducted in Section 4.4.

Table 2.
The main results of action recognition on HMDB-51, UCF-101, and EK-100 datasets. We report the top-1 and top-5 accuracies on 8-shot, 8-frame settings.
4.2.2. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
We conduct a comparative analysis of our model with state-of-the-art CLIP-based video adaptation methods on the HMDB-51 and UCF-101 datasets. As shown in Table 3, the baseline models are categorized based on whether they are tested in a zero-shot or few-shot manner. ActionCLIP [5], X-CLIP [11], and ViFi-CLIP [4] simply fine-tune the pre-trained CLIP encoders with target data but face high computational costs and extended training time. On the other hand, A5 [18] adopts the text prompt tuning method with temporal modeling to transfer the knowledge of video data to the CLIP model. Vita-CLIP [12] uses learnable prompt tokens on both the visual and text sides while keeping the pre-trained CLIP model frozen. In contrast, our approach focuses solely on visual prompting, significantly reducing trainable parameters compared with existing methods. Unlike learnable prompt tokens, which are limited to transformer-based visual backbones, our watermark prompting method is adaptable to various visual architectures. This flexibility allows for backbone selection tailored to each dataset, enhancing adaptability across diverse video scenarios.

Table 3.
Comparison with the CLIP-based video adaptation methods on HMDB-51 and UCF-101 in zero-shot and few-shot () settings. All models employ the ViT-B/16 as the image encoder. We also specify the number of frames, views, trainable parameters, and whether the models fine-tune the CLIP model or adopt text/visual-prompt tuning strategy.
In the zero-shot setting, models are pre-trained on a large-scale video dataset, such as Kinetics-400 [13], and then tested on the target validation data, which needs a substantial amount of computational resources, especially for fine-tuning methods. For the few-shot scenario, all methods use an 8-shot setting for a fair comparison. We report results using 16 frames of input only in the comparison. The performance of our few-shot model surpasses all the zero-shot models by a large margin while requiring less training time and computational costs. Moreover, our model shows competitive results to few-shot models, even with fewer frames, views, and trainable parameters. Notably, our model outperforms the fine-tuned ActionCLIP model on the UCF-101 dataset, demonstrating the efficacy of our proposed method.
To assess the effectiveness of visual and text prompts, we incorporate the text prompt tuning method into our model, similar to the approach used in CoOp [7]. As shown in Table 4, the text-only prompt tuning method shows lower performance compared with the visual-only prompting method on the UCF-101 dataset. Interestingly, the accuracies of action recognition even decreased when both visual and text prompts were tuned together. It is important to note that the text prompts serve as supervision for the video data. Training the text prompts results in unstable convergence of the carefully designed visual prompts, leading to performance degradation.

Table 4.
Performance comparison of visual prompt tuning (watermark and trademark) and text prompt tuning (CoOp).
4.3. Ablation Studies
In this section, we ablate different components of the proposed model. All experiments are conducted in 8-shot, 8-frame settings on the UCF-101 dataset.
4.3.1. Prompt Encoder Design
Our prompt encoder can be flexibly designed to generate watermark prompts. Table 5 presents the accuracies of our self-designed CNN-based encoder and Transformer-based encoder, Omnivore [30]. Omnivore is a vision model that operates across multiple modalities, including images, depth maps, and videos. Due to the Transformer’s limited generalizability in data-hungry scenarios, the Omnivore model is kept frozen and only used for extracting latent features from video clips. Both the CNN- and Transformer-based encoders are effective at generating watermark prompts and show robust performance in action classification. We adopt CNN-based encoder with d = 128 by default, as it performs well and requires fewer parameters.

Table 5.
Ablations for prompt encoder in the prompt generator. We tested both CNN-based and Transformer-based models.
4.3.2. Prompt Decoder Design
The prompt decoder, a core component in generating watermark prompts, consists of a spatial prompt decoder and a mask decoder. Table 6 investigates the impact of each decoder. We first remove the prompt generator and directly add learnable noisy visual prompts to the input video, which have the same dimension as the watermark prompts. Such a design of input-independent visual prompts results in lower accuracy and requires double trainable parameters. By employing both spatial prompt decoder and mask decoder, we achieve a win–win scenario: improved performance in action classification along with a reduction in the number of parameters. Although the mask decoder is used to ensure the imperceptibility of watermarks, it does not degrade performance, resulting in a non-aggressive model while maintaining effectiveness.

Table 6.
Ablation experiments with different prompt decoders in prompt generator.
4.3.3. Temporal Aggregation Design
As a video is composed of a sequence of image frames, incorporating a temporal aggregation module is crucial for adapting the CLIP model to video data. Table 7 shows the influence of three different temporal aggregation methods illustrated in Figure 3. We also report the throughput, measured on a single A100 GPU. The simplest method, average pooling, achieves relatively low accuracy. Nevertheless, it offers the advantage of low computational cost, providing a high throughput of 190 video clips per second. Placing a transformer encoder prior to the average pooling layer can significantly enhance the performance of action classification at the cost of reduced throughput. Our temporal summarizer, coupled with the trademark prompts, eliminates the need for using average pooling. Furthermore, this module enables our model to achieve the highest accuracy compared with other methods. Most notably, it attains the best trade-off between accuracy and computational cost, demonstrating the efficiency and effectiveness of our model.

Table 7.
Ablations for temporal aggregation methods. We report the throughput, measured as the number of video clips processed per second on a single 80 GB A100 GPU.
4.3.4. CLIP Image Encoder
The proposed visual prompting method can be used in various families of image encoders within the CLIP model, including ViT and ResNet. As shown in Table 8, the ViT shows better adaptability compared with CNNs. We choose the ViT-B/16 model by default due to GPU memory constraints.

Table 8.
Ablations for different families of image encoder in CLIP model.
4.4. Qualitative Results
To show the imperceptibility of the proposed watermark prompts, we visualize the original video frames alongside the watermarked frames on HMDB-51 (top), UCF-101 (middle), and EK-100 (bottom). As shown in Figure 4, within each frame, the left side displays the original video frame, while the right side shows the watermarked frame. The generated watermarks, directly added onto the frame pixels, remain invisible to the human eye. Accordingly, these kinds of visual prompts do not compromise the quality of video clips. Moreover, they are difficult to remove using simple editing techniques. As a result, our model finds the right balance between imperceptibility and adaptability in video adaptation.

Figure 4.
Comparative visualization of original video frames (left) and the watermarked frames (right) on HMDB-51 (top), UCF-101 (middle), and EK-100 (bottom).
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we propose a novel visual-only prompting method, watermark and trademark prompts, to adapt the pre-trained CLIP model for video action recognition tasks. The input-dependent watermark prompts are designed by the prompt generator, and the dataset-dependent trademark prompts are customized for each video domain. In addition, the temporal summarizer is proposed to aggregate the contextual information. Our model is trained in a data-efficient way and can be quickly adapted to various downstream video action recognition datasets, which boosts the potential of the CLIP model for understanding videos. For future work, we intend to extend our method to improve the generalizability of VLMs across various video domains.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.J.; methodology, L.J. and H.J.; validation, L.J., H.J. and H.J.J.; resources, E.Y.K.; writing—original draft preparation, L.J.; writing—review and editing, L.J. and E.Y.K.; visualization, H.J. and H.J.J.; supervision, E.Y.K.; project administration, L.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data available in a publicly accessible repository.
Acknowledgments
Following are results of a study on the “Convergence and Open Sharing System” Project, supported by the Ministry of Education and National Research Foundation of Korea.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| VLMs | Visual-Language Models |
| ViT | Vision Transformer |
| CLIP | Contrastive Language–Image Pre-training |
| ALIGN | A Large-scale ImaGe and Noisy-text embedding |
| OCR | Optical Character Recognition |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| RGB | Red, Green, Blue (color channels) |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
References
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning Transferable Visual Models from Natural Language Supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 18–24 July 2021; Meila, M., Zhang, T., Eds.; PMLR: Birmingham, UK, 2021; Volume 139, pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, C.; Yang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Parekh, Z.; Pham, H.; Le, Q.V.; Sung, Y.; Li, Z.; Duerig, T. Scaling Up Visual and Vision-Language Representation Learning with Noisy Text Supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 18–24 July 2021; Meila, M., Zhang, T., Eds.; PMLR: Birmingham, UK, 2021; Volume 139, pp. 4904–4916. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, G.; Sun, Y.; Nian, F.; Zhu, M.; Tang, W.; Hu, Z. COME: Clip-OCR and Master ObjEct for text image captioning. Image Vis. Comput. 2023, 136, 104751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, H.; Khattak, M.U.; Maaz, M.; Khan, S.; Khan, F.S. Fine-tuned CLIP Models are Efficient Video Learners. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 6545–6554. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Xing, J.; Liu, Y. ActionCLIP: A New Paradigm for Video Action Recognition. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.08472. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, B.; Lei, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y. ZegCLIP: Towards Adapting CLIP for Zero-shot Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 11175–11185. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, J.; Loy, C.C.; Liu, Z. Learning to Prompt for Vision-Language Models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 2337–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, J.; Loy, C.C.; Liu, Z. Conditional Prompt Learning for Vision-Language Models. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 16816–16825. [Google Scholar]
- Soomro, K.; Zamir, A.R.; Shah, M. UCF101: A Dataset of 101 Human Actions Classes from Videos in the Wild. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1212.0402. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Ji, L.; Zhong, M.; Chen, Y.; Lei, W.; Duan, N.; Li, T. CLIP4Clip: An empirical study of CLIP for end to end video clip retrieval and captioning. Neurocomputing 2022, 508, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.; Peng, H.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S.; Meng, G.; Fu, J.; Xiang, S.; Ling, H. Expanding Language-Image Pretrained Models for General Video Recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2022, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wasim, S.T.; Naseer, M.; Khan, S.; Khan, F.S.; Shah, M. Vita-CLIP: Video and text adaptive CLIP via Multimodal Prompting. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 23034–23044. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira, J.; Zisserman, A. Quo Vadis, Action Recognition? A New Model and the Kinetics Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6299–6308. [Google Scholar]
- Elsayed, G.F.; Goodfellow, I.; Sohl-Dickstein, J. Adversarial Reprogramming of Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bahng, H.; Jahanian, A.; Sankaranarayanan, S.; Isola, P. Exploring Visual Prompts for Adapting Large-Scale Models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.17274. [Google Scholar]
- Kuehne, H.; Jhuang, H.; Garrote, E.; Poggio, T.; Serre, T. HMDB: A large video database for human motion recognition. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 2556–2563. [Google Scholar]
- Damen, D.; Doughty, H.; Farinella, G.M.; Furnari, A.; Kazakos, E.; Ma, J.; Moltisanti, D.; Munro, J.; Perrett, T.; Price, W.; et al. Rescaling Egocentric Vision: Collection, Pipeline and Challenges for EPIC-KITCHENS-100. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 33–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, C.; Han, T.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, W. Prompting Visual-Language Models for Efficient Video Understanding. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2022, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 105–124. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, K.Y.; Ding, H.; Zhou, J.; Peng, Y.X.; Zhao, Z.; Loy, C.C.; Zheng, W.S. Rethinking CLIP-based Video Learners in Cross-Domain Open-Vocabulary Action Recognition. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.01560. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. Learning Spatiotemporal Features with 3D Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 4489–4497. [Google Scholar]
- Feichtenhofer, C.; Fan, H.; Malik, J.; He, K. A Closer Look at Spatiotemporal Convolutions for Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6450–6459. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, A.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, Y.G. Open-VCLIP: Transforming CLIP to an Open-Vocabulary Video Model via Interpolated Weight Optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; pp. 36978–36989. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Huang, J.; Li, G.; Feng, J.; Wu, X.; Li, T.H. Revisiting Temporal Modeling for CLIP-based Image-to-Video Knowledge Transferring. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 6555–6564. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Geng, S.; Zhang, R.; Gao, P.; de Melo, G.; Wang, X.; Dai, J.; Qiao, Y.; Li, H. Frozen CLIP Models are Efficient Video Learners. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Lin, Z.; Zhu, X.; Shao, J.; Li, H. ST-Adapter: Parameter-efficient Image-to-Video Transfer Learning. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022; pp. 26462–26477. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Lee, J.; Sohn, K. Dual-Path Adaptation from Image to Video Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 2203–2213. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Sun, Z.; Ouyang, W. Revisiting Classifier: Transferring Vision-Language Models for Video Recognition. In Proceedings of the 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; pp. 2847–2855. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Girdhar, R.; Singh, M.; Ravi, N.; van der Maaten, L.; Joulin, A.; Misra, I. Omnivore: A Single Model for Many Visual Modalities. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 16102–16112. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).