Aggregating Image Segmentation Predictions with Probabilistic Risk Control Guarantees
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We provide finite-sample risk control guarantees for ensembles using distribution-free uncertainty quantification, leveraging health information exchanges between medical agents to address the practical considerations in healthcare: shared patients between medical institutions, as well as data privacy restrictions.
- Our approach provides statistical guarantees even when the distribution of the private dataset of each agent is different from that of the target population for the ensemble.
- To our knowledge, this is the first work to use the Learn then Test (LTT) calibration framework to merge prediction sets in medical AI.
2. Related Work
3. Calibrating Deep Ensembles with Statistical Guarantees
3.1. Setup
3.2. The Learn Then Test Framework
| Algorithm 1 Fixed Sequence Algorithm |
Inputs: a collection of ordered null hypotheses to test, the corresponding valid p-values of the nulls. a level to control the FWER. Output: set of rejected null hypotheses.
|
3.3. Local Calibration with Global Statistical Guarantees
4. Experimental Setting
4.1. Polyp Segmentation Dataset
4.2. Brain Tumor Segmentation Dataset
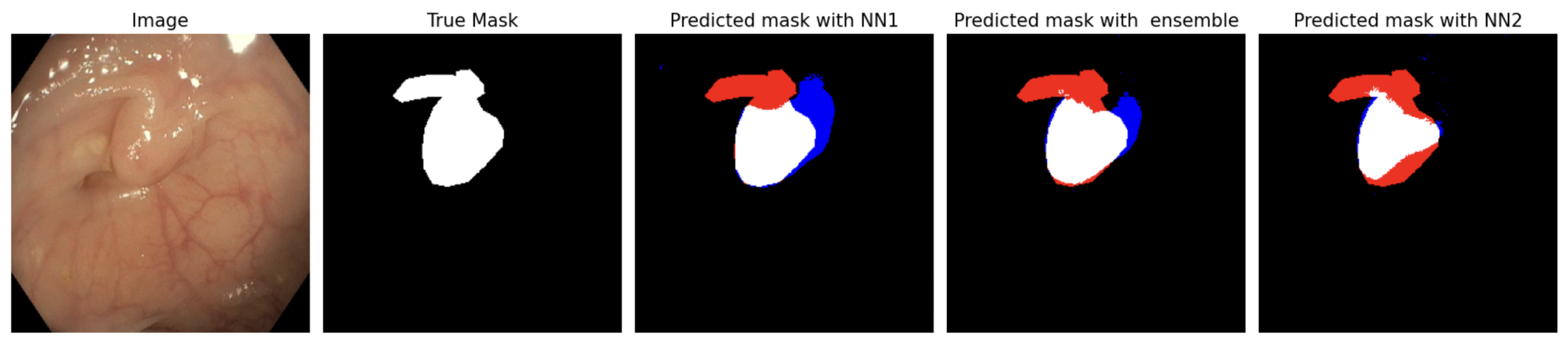
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Polyp Segmentation
5.2. Brain Tumor Segmentation
6. Conclusions
Main Takeaway from This Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Fixed Sequence Testing and Valid p-Values
| Algorithm A1 Fixed Sequence Algorithm adapted to our framework |
Inputs: our calibration dataset, a partition of the discretized hyperparameter space, a level to control the FWER, our desired risk control threshold. Output: family of subsets of containing pairs satisfying the local and global statistical guarantees of (14).
|
References
- Zhang, F.; Kreuter, D.; Chen, Y.; Dittmer, S.; Tull, S.; Shadbahr, T.; Schut, M.; Asselbergs, F.; Kar, S.; Sivapalaratnam, S.; et al. Recent methodological advances in federated learning for healthcare. Patterns 2024, 5, 101006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, C.J.; Karthikesalingam, A.; Suleyman, M.; Corrado, G.C.; King, D. Key challenges for delivering clinical impact with artificial intelligence. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieke, N.; Hancox, J.; Li, W.; Milletari, F.; Roth, H.R.; Albarqouni, S.; Bakas, S.; Galtier, M.N.; Landman, B.A.; Maier-Hein, K.; et al. The future of digital health with federated learning. npj Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menachemi, N.; Rahurkar, S.; Harle, C.A.; Vest, J.R. The benefits of health information exchange: An updated systematic review. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2018, 25, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everson, J.; Adler-Milstein, J. Gaps in health information exchange between hospitals that treat many shared patients. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2018, 25, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M.; Inoue, R.; Miyata, S.; Shimizu, H. Health information exchange between specialists and general practitioners benefits rural patients. Appl. Clin. Inform. 2021, 12, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, B.; Agarwal, S.; Coombs, L.P.; Dreyer, K.; Wald, C. 2020 ACR Data Science Institute Artificial Intelligence Survey. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. JACR 2021, 18, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelopoulos, A.N.; Pomerantz, S.; Do, S.; Bates, S.; Bridge, C.P.; Elton, D.C.; Lev, M.H.; González, R.G.; Jordan, M.I.; Malik, J. Conformal Triage for Medical Imaging AI Deployment. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, J.; Facelli, J.C. Conformal prediction in clinical medical sciences. J. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2022, 6, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Angelopoulos, A.N.; Pomerantz, S. Improving Trustworthiness of AI Disease Severity Rating in Medical Imaging with Ordinal Conformal Prediction Sets. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2022, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022; Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 545–554. [Google Scholar]
- Olsson, H.; Kartasalo, K.; Mulliqi, N.; Capuccini, M.; Ruusuvuori, P.; Samaratunga, H.; Delahunt, B.; Lindskog, C.; Janssen, E.A.; Blilie, A.; et al. Estimating diagnostic uncertainty in artificial intelligence assisted pathology using conformal prediction. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geirhos, R.; Zimmermann, R.S.; Bilodeau, B.; Brendel, W.; Kim, B. Don’t trust your eyes: On the (un)reliability of feature visualizations. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2306.04719. [Google Scholar]
- Angelopoulos, A.N.; Bates, S.; Candès, E.J.; Jordan, M.I.; Lei, L. Learn then Test: Calibrating Predictive Algorithms to Achieve Risk Control. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2110.01052. [Google Scholar]
- Angelopoulos, A.N.; Bates, S.; Fisch, A.; Lei, L.; Schuster, T. Conformal Risk Control. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2208.02814. [Google Scholar]
- Zecchin, M.; Simeone, O. Localized Adaptive Risk Control. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.07976. [Google Scholar]
- Blot, V.; Angelopoulos, A.N.; Jordan, M.I.; Brunel, N.J.B. Automatically Adaptive Conformal Risk Control. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.17819. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, S.; Angelopoulos, A.; Lei, L.; Malik, J.; Jordan, M. Distribution-free, risk-controlling prediction sets. J. ACM (JACM) 2021, 68, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, R.; Thiery, A.H. Uncertainty Quantification and Deep Ensembles. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2007.08792. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, A.; Kora, R. A comprehensive review on ensemble deep learning: Opportunities and challenges. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2023, 35, 757–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, E.K.; Pleiss, G.; Cunningham, J.P. The Effects of Ensembling on Long-Tailed Data. In Proceedings of the NeurIPS 2023 Workshop Heavy Tails in Machine Learning, New Orleans, LA, USA, 15 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bousselham, W.; Thibault, G.; Pagano, L.; Machireddy, A.; Gray, J.; Chang, Y.H.; Song, X. Efficient Self-Ensemble for Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2111.13280. [Google Scholar]
- Gasparin, M.; Ramdas, A. Merging uncertainty sets via majority vote. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.09379. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Jha, D.; Ghatwary, N.; Realdon, S.; Cannizzaro, R.; Salem, O.E.; Lamarque, D.; Daul, C.; Riegler, M.A.; Anonsen, K.V.; et al. A multi-centre polyp detection and segmentation dataset for generalisability assessment. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J. Brain Tumor Dataset. 2017. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/brain_tumor_dataset/1512427/5 (accessed on 26 July 2024).
- Georgescu, M.I.; Ionescu, R.T.; Miron, A.I. Diversity-Promoting Ensemble for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.12388. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.04597. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Fan, K.; Mo, W.; Cao, X.; Jiao, K. Dual ensemble system for polyp segmentation with submodels adaptive selection ensemble. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanni, L.; Cuza, D.; Lumini, A.; Loreggia, A.; Brahman, S. Polyp Segmentation with Deep Ensembles and Data Augmentation. In Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Healthcare: Vol. 1: Image and Data Analytics; Lim, C.P., Vaidya, A., Chen, Y.W., Jain, T., Jain, L.C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 133–153. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, T.T.T.; Thanh, N.C.; Long, T.Q. Polyp segmentation in colonoscopy images using ensembles of U-Nets with EfficientNet and asymmetric similarity loss function. In Proceedings of the 2020 RIVF International Conference on Computing and Communication Technologies (RIVF), Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam, 14–15 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Welikala, R.; Fraz, M.; Williamson, T.; Barman, S. The automated detection of proliferative diabetic retinopathy using dual ensemble classification. Int. J. Diagn. Imaging 2015, 2, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y. Learn to Threshold: ThresholdNet with Confidence-Guided Manifold Mixup for Polyp Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 1134–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Milletarì, F.; Xu, D.; Rieke, N.; Hancox, J.; Zhu, W.; Baust, M.; Cheng, Y.; Ourselin, S.; Cardoso, M.J.; et al. Privacy-preserving Federated Brain Tumour Segmentation. In Proceedings of the MLMI@MICCAI, Shenzhen, China, 13 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sheller, M.J.; Reina, G.A.; Edwards, B.; Martin, J.; Bakas, S. Multi-institutional deep learning modeling without sharing patient data: A feasibility study on brain tumor segmentation. In Proceedings of the Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries: 4th International Workshop, BrainLes 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, 16 September 2018; Revised Selected Papers, Part I 4. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 92–104. [Google Scholar]
- Mendler-Dünner, C.; Guo, W.; Bates, S.; Jordan, M. Test-time collective prediction. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 13719–13731. [Google Scholar]
- Cherubin, G. Majority vote ensembles of conformal predictors. Mach. Learn. 2019, 108, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauraha, N.; Spjuth, O. Synergy conformal prediction. In Proceedings of the Tenth Symposium on Conformal and Probabilistic Prediction and Applications, Virtual, 8–10 September 2021; Carlsson, L., Luo, Z., Cherubin, G., An Nguyen, K., Eds.; Proceedings of Machine Learning Research (PMLR): New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 152, pp. 91–110. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Pathak, R.; Angelopoulos, A.N.; Bates, S.; Jordan, M.I. Data-Adaptive Tradeoffs among Multiple Risks in Distribution-Free Prediction. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.19605. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, J. A distribution-free valid p-value for finite samples of bounded random variables. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.08975. [Google Scholar]
- Bretz, F.; Posch, M.; Glimm, E.; Klinglmueller, F.; Maurer, W.; Rohmeyer, K. Graphical approaches for multiple comparison procedures using weighted Bonferroni, Simes, or parametric tests. Biom. J. Biom. Z. 2011, 53, 894–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlTahhan, F.E.; Khouqeer, G.A.; Saadi, S.; Elgarayhi, A.; Sallah, M. Refined Automatic Brain Tumor Classification Using Hybrid Convolutional Neural Networks for MRI Scans. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badža, M.M.; Barjaktarović, M.Č. Classification of Brain Tumors from MRI Images Using a Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Medical Center | Number of Images in the Dataset |
|---|---|
| Ambroise Paré Hôpital, Paris, France | 256 |
| Istituto Oncologico Veneto, Padova, Italy | 301 |
| Centro Riferimento Oncologico, IRCCS, Italy | 457 |
| Oslo University Hospital, Oslo, Norway | 227 |
| John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, UK | 208 |
| University of Alexandria, Alexandria, Egypt | 88 |
| (H-B) | FPR (H-B) | (PRW) | FPR (PRW) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.970 | 0.4696 | 0.970 | 0.4696 |
| 0.25 | 0.970 | 0.2206 | 0.970 | 0.2206 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.970 | 0.1770 | 0.970 | 0.1770 | ||
| 0.75 | 0.975 | 0.2495 | 0.975 | 0.2495 | ||
| 1.00 | 0.980 | 0.3637 | 0.980 | 0.3637 | ||
| 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.970 | 0.4696 | 0.970 | 0.4696 |
| 0.25 | 0.970 | 0.2206 | 0.970 | 0.2206 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.970 | 0.1770 | 0.970 | 0.1770 | ||
| 0.75 | 0.975 | 0.2495 | 0.975 | 0.2495 | ||
| 1.00 | 0.980 | 0.3637 | 0.980 | 0.3637 | ||
| 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.970 | 0.4696 | 0.970 | 0.4696 |
| 0.25 | 0.970 | 0.2206 | 0.970 | 0.2206 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.970 | 0.1770 | 0.970 | 0.1770 | ||
| 0.75 | 0.975 | 0.2495 | 0.975 | 0.2495 | ||
| 1.00 | 0.980 | 0.3637 | 0.980 | 0.3637 | ||
| 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.960 | 0.2126 | 0.960 | 0.2126 |
| 0.25 | 0.960 | 0.1205 | 0.960 | 0.1205 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.960 | 0.0929 | 0.960 | 0.0929 | ||
| 0.75 | 0.965 | 0.1030 | 0.965 | 0.1030 | ||
| 1.00 | 0.975 | 0.1960 | 0.975 | 0.1960 | ||
| 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.960 | 0.2126 | 0.960 | 0.2126 |
| 0.25 | 0.960 | 0.1205 | 0.960 | 0.1205 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.960 | 0.0929 | 0.960 | 0.0929 | ||
| 0.75 | 0.965 | 0.1030 | 0.965 | 0.1030 | ||
| 1.00 | 0.975 | 0.1960 | 0.975 | 0.1960 | ||
| 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.960 | 0.2126 | 0.960 | 0.2126 |
| 0.25 | 0.955 | 0.0831 | 0.960 | 0.1205 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.960 | 0.0929 | 0.960 | 0.0929 | ||
| 0.75 | 0.965 | 0.1030 | 0.965 | 0.1030 | ||
| 1.00 | 0.975 | 0.1960 | 0.975 | 0.1960 | ||
| 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.945 | 0.1114 | 0.945 | 0.1114 |
| 0.25 | 0.935 | 0.0086 | 0.935 | 0.0086 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.935 | 0.0067 | 0.935 | 0.0067 | ||
| 0.75 | 0.940 | 0.0091 | 0.945 | 0.0128 | ||
| 1.00 | 0.960 | 0.0352 | 0.960 | 0.0352 | ||
| 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.940 | 0.0970 | 0.945 | 0.1114 |
| 0.25 | 0.930 | 0.0057 | 0.935 | 0.0086 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.935 | 0.0067 | 0.935 | 0.0067 | ||
| 0.75 | 0.940 | 0.0091 | 0.940 | 0.0091 | ||
| 1.00 | 0.955 | 0.0238 | 0.955 | 0.0238 | ||
| 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.940 | 0.0970 | 0.940 | 0.0970 |
| 0.25 | 0.930 | 0.0057 | 0.930 | 0.0057 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.930 | 0.0050 | 0.935 | 0.0067 | ||
| 0.75 | 0.935 | 0.0066 | 0.940 | 0.0091 | ||
| 1.00 | 0.955 | 0.0238 | 0.955 | 0.0238 |
| FPR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.10 | 0.05 | 1/5 | 0.98 | 0.0219 |
| 2/5 | 0.99 | 0.0276 | ||
| 3/5 | 0.99 | 0.0231 | ||
| 4/5 | – | – | ||
| 0.10 | 1/5 | 0.98 | 0.0219 | |
| 2/5 | 0.99 | 0.0276 | ||
| 3/5 | 0.99 | 0.0231 | ||
| 4/5 | – | – | ||
| 0.20 | 1/5 | 0.98 | 0.0219 | |
| 2/5 | 0.99 | 0.0276 | ||
| 3/5 | 0.99 | 0.0231 | ||
| 4/5 | – | – | ||
| 0.15 | 0.05 | 1/5 | 0.93 | 0.0123 |
| 2/5 | 0.95 | 0.0127 | ||
| 3/5 | 0.97 | 0.0134 | ||
| 4/5 | – | – | ||
| 0.10 | 1/5 | 0.93 | 0.0123 | |
| 2/5 | 0.94 | 0.0117 | ||
| 3/5 | 0.96 | 0.0117 | ||
| 4/5 | 0.99 | 0.0145 | ||
| 0.20 | 1/5 | 0.92 | 0.0116 | |
| 2/5 | 0.94 | 0.0117 | ||
| 3/5 | 0.96 | 0.0117 | ||
| 4/5 | 0.99 | 0.0145 | ||
| 0.20 | 0.05 | 1/5 | 0.82 | 0.0074 |
| 2/5 | 0.86 | 0.0072 | ||
| 3/5 | 0.91 | 0.0074 | ||
| 4/5 | 0.98 | 0.0100 | ||
| 0.10 | 1/5 | 0.82 | 0.0074 | |
| 2/5 | 0.86 | 0.0072 | ||
| 3/5 | 0.91 | 0.0074 | ||
| 4/5 | 0.98 | 0.0100 | ||
| 0.20 | 1/5 | 0.80 | 0.0068 | |
| 2/5 | 0.86 | 0.0072 | ||
| 3/5 | 0.90 | 0.0069 | ||
| 4/5 | 0.98 | 0.0100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alvarez, J.; Roman-Rangel, E. Aggregating Image Segmentation Predictions with Probabilistic Risk Control Guarantees. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111711
Alvarez J, Roman-Rangel E. Aggregating Image Segmentation Predictions with Probabilistic Risk Control Guarantees. Mathematics. 2025; 13(11):1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111711
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlvarez, Joaquin, and Edgar Roman-Rangel. 2025. "Aggregating Image Segmentation Predictions with Probabilistic Risk Control Guarantees" Mathematics 13, no. 11: 1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111711
APA StyleAlvarez, J., & Roman-Rangel, E. (2025). Aggregating Image Segmentation Predictions with Probabilistic Risk Control Guarantees. Mathematics, 13(11), 1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111711







