Variable-Step Semi-Implicit Solver with Adjustable Symmetry and Its Application for Chaos-Based Communication
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a new formulation of the symmetry parameter for the CD method, which is expressed in such a way that does not depend on a particular value of the integration step. This expression makes it straightforward to combine the CD method with any variable-step controller, e.g., that presented in [36]. We investigate the proposed method using two chaotic systems and show that the chaotic regimes depend mainly on the symmetry coefficient but not on the step size, except at large step size values at the edge of stability.
- We propose a novel symmetry coefficient modulation approach to chaotic communication by implementing modulation through a variable-step-size controller parameter, namely tolerance (tol). We illustrate the developed approach with the CSS based on the Sprott Case S chaotic oscillator.
- We analyze the parameters of the developed communication system by using a quantified return map analysis (QRMA) to measure the confidentiality and bit error rate (BER) to measure noise immunity. A comparative analysis is presented which shows that the modulation technique developed has a higher performance compared to that of alternative modulation approaches in both systems estimated at lower signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) levels.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Composite Diagonal Methods with a Fixed Integration Step
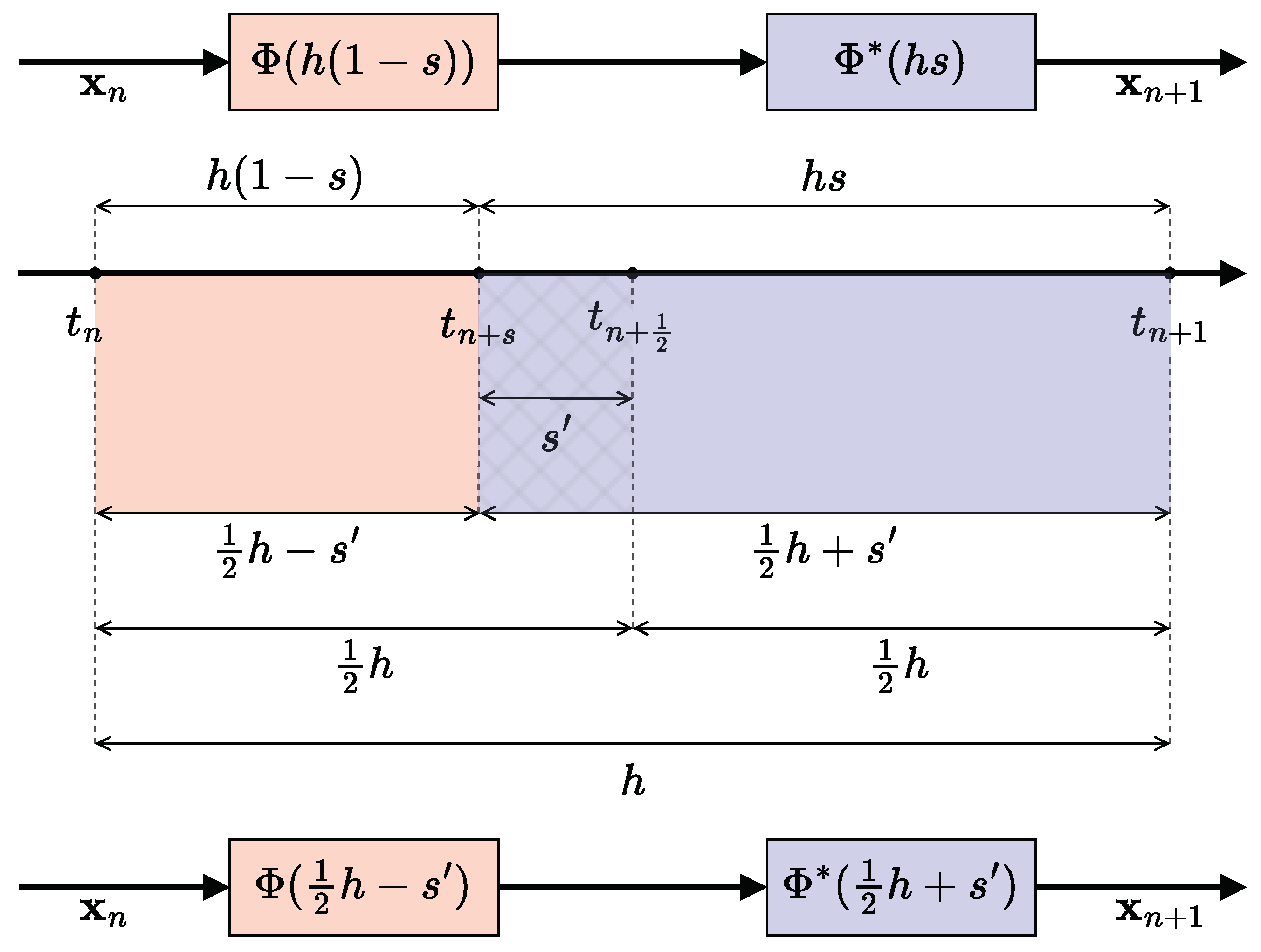
2.2. A Novel Expression of the Symmetry Coefficient
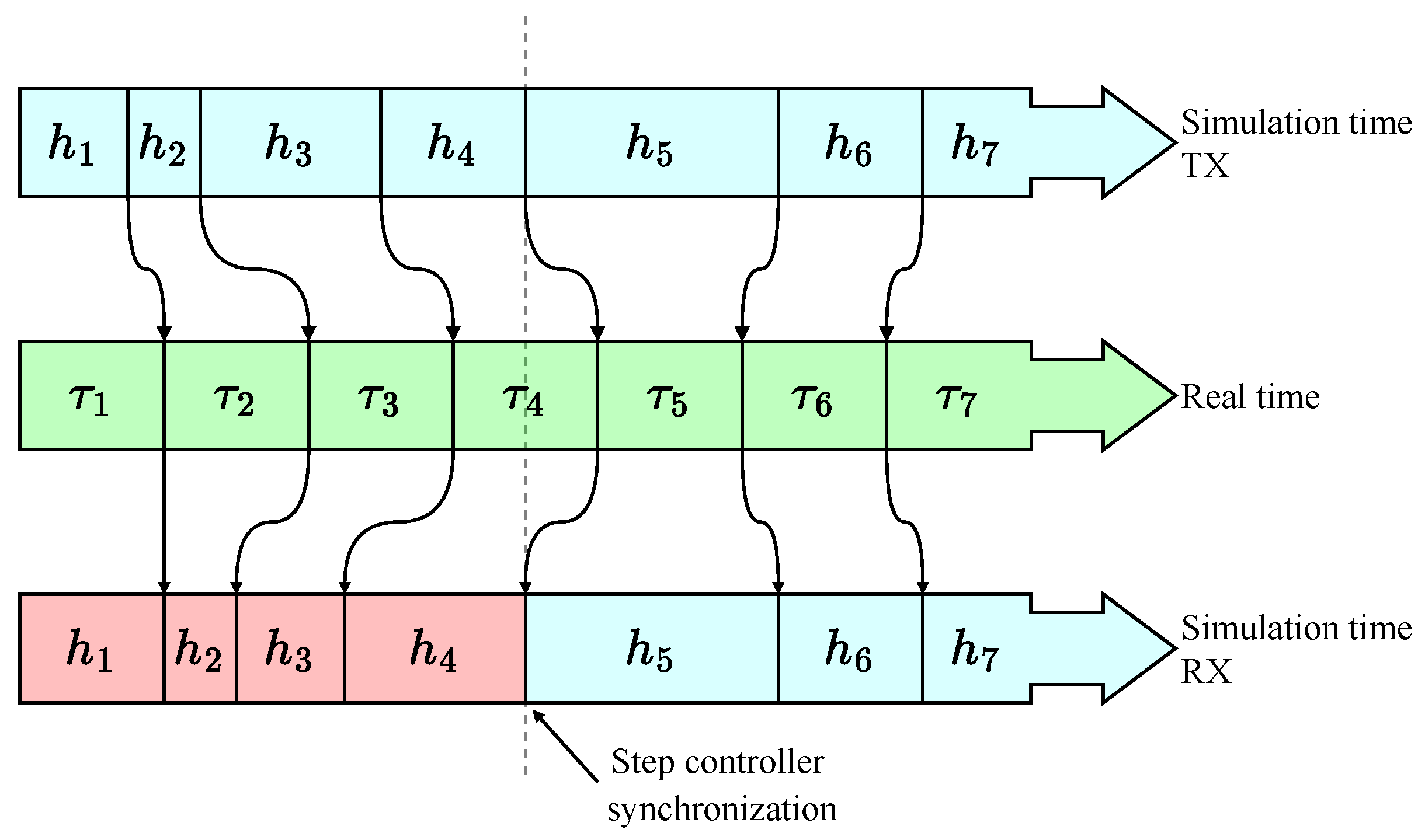
2.3. CD Methods with Variable Integration Steps
2.4. Chaotic Oscillators Under Consideration
2.4.1. Sprott Case S System
2.4.2. The Chen System
2.5. A Chaotic Communication System with Variable-Step Modulation
2.6. The Quantified Return Map Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Simulation Setup
3.2. The Influence of the Symmetry Distortion Coefficient on the ODE Dynamics
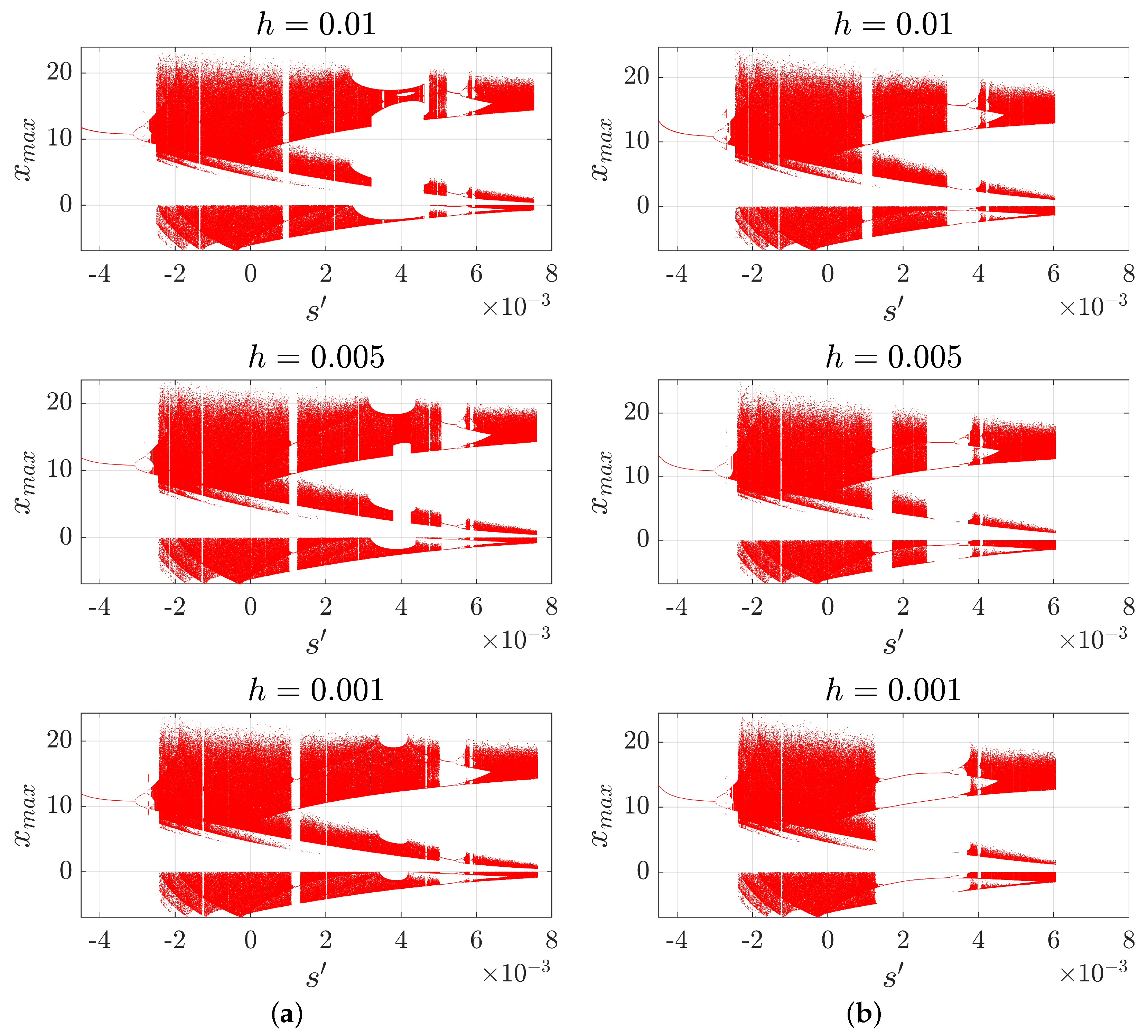
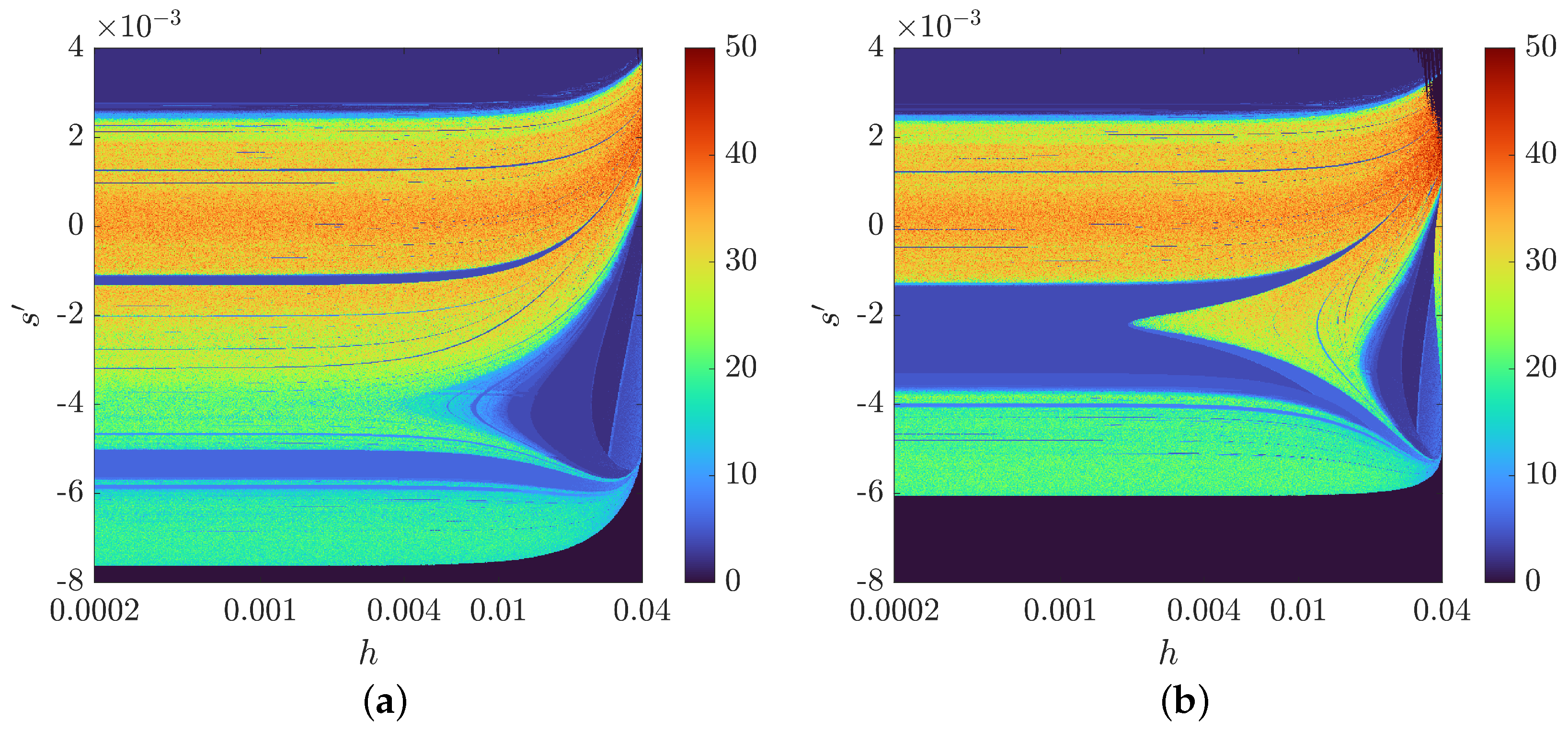
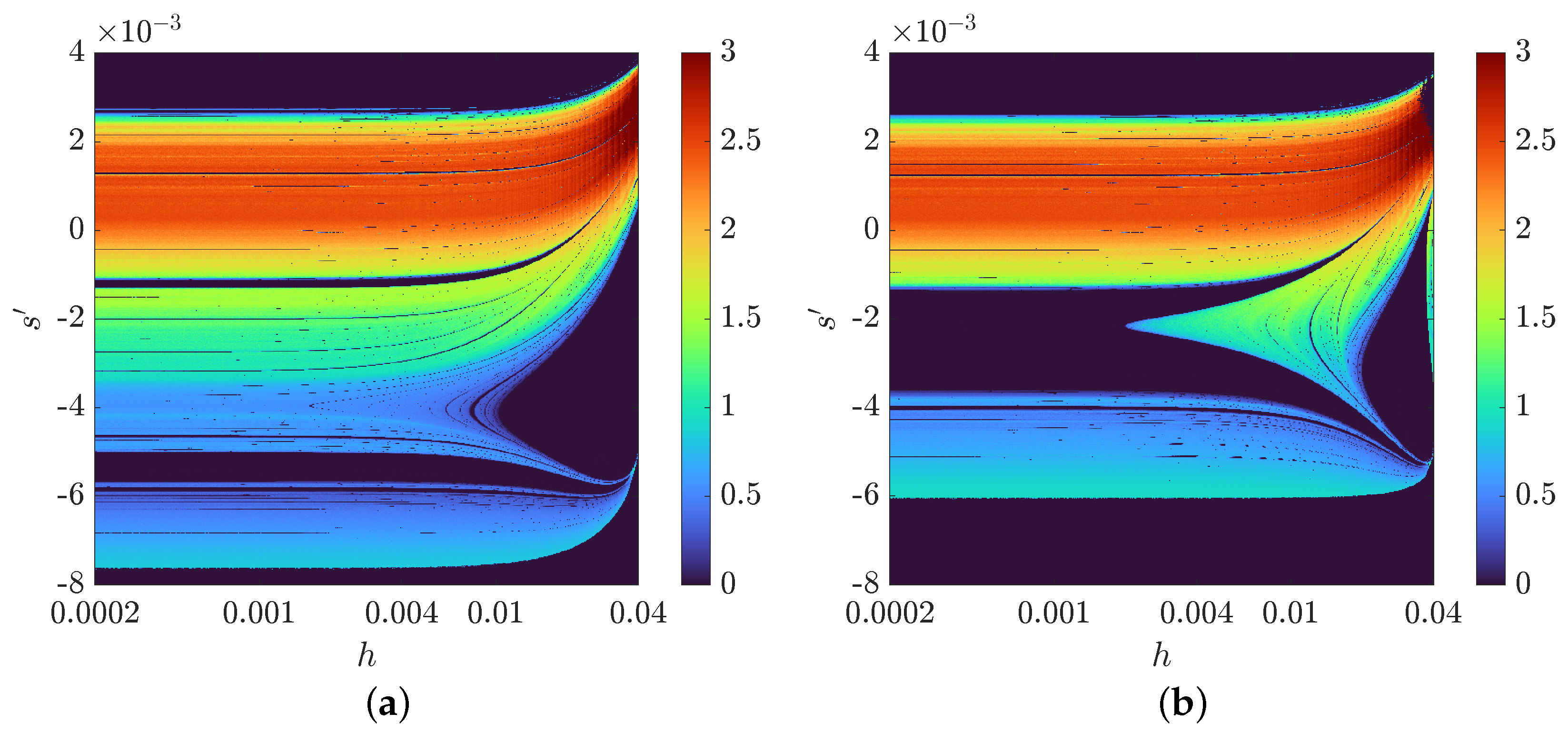
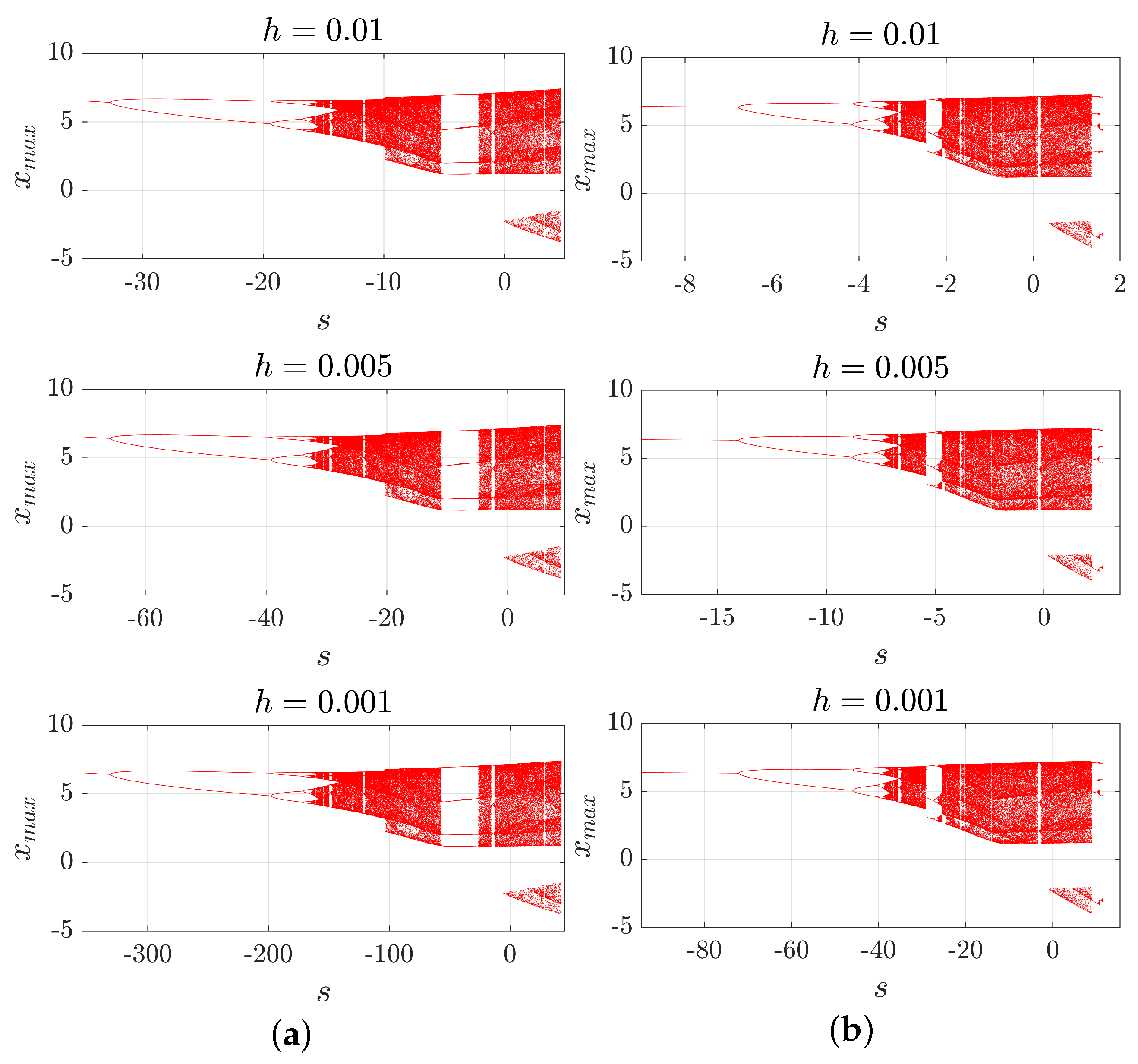
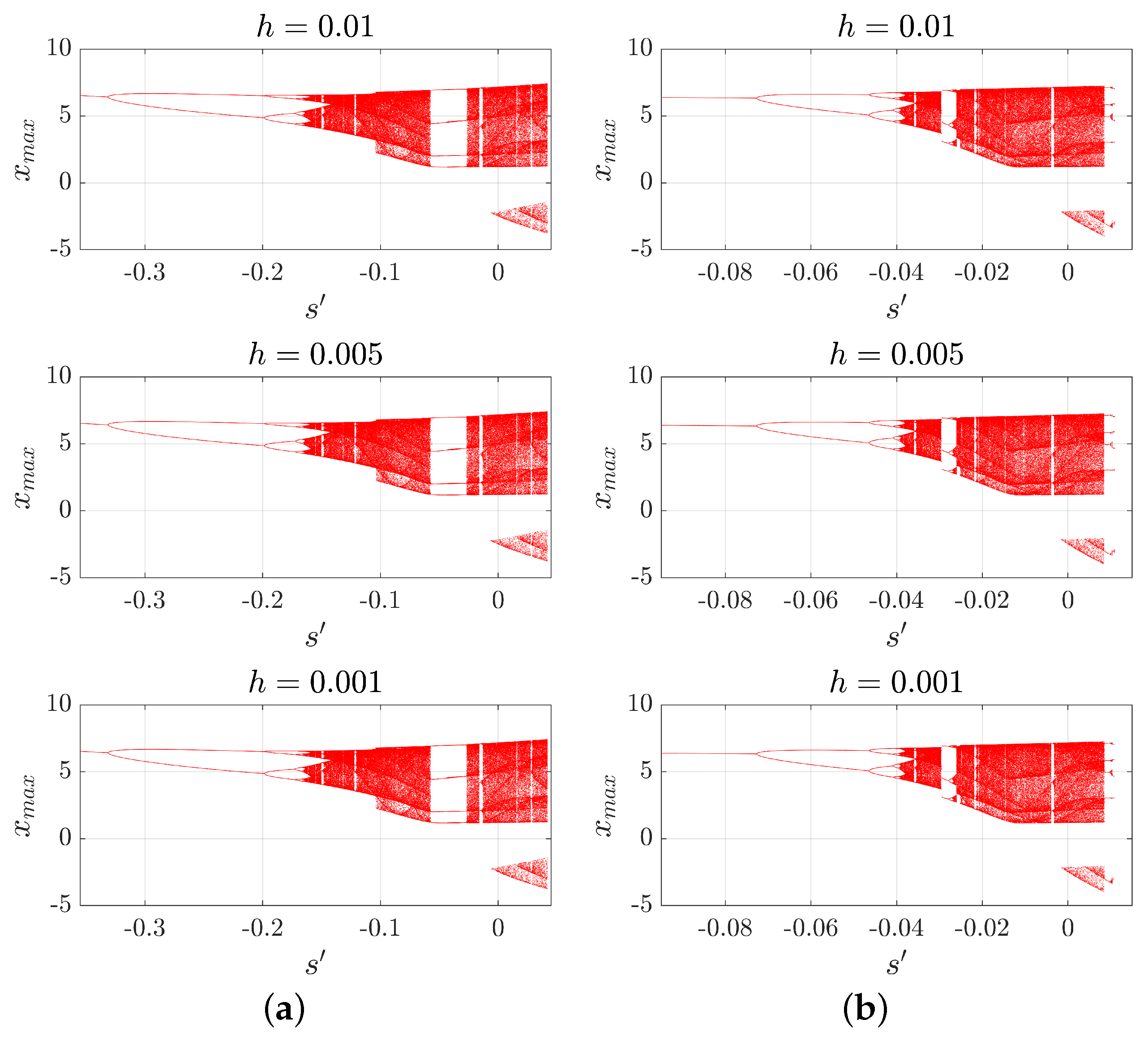
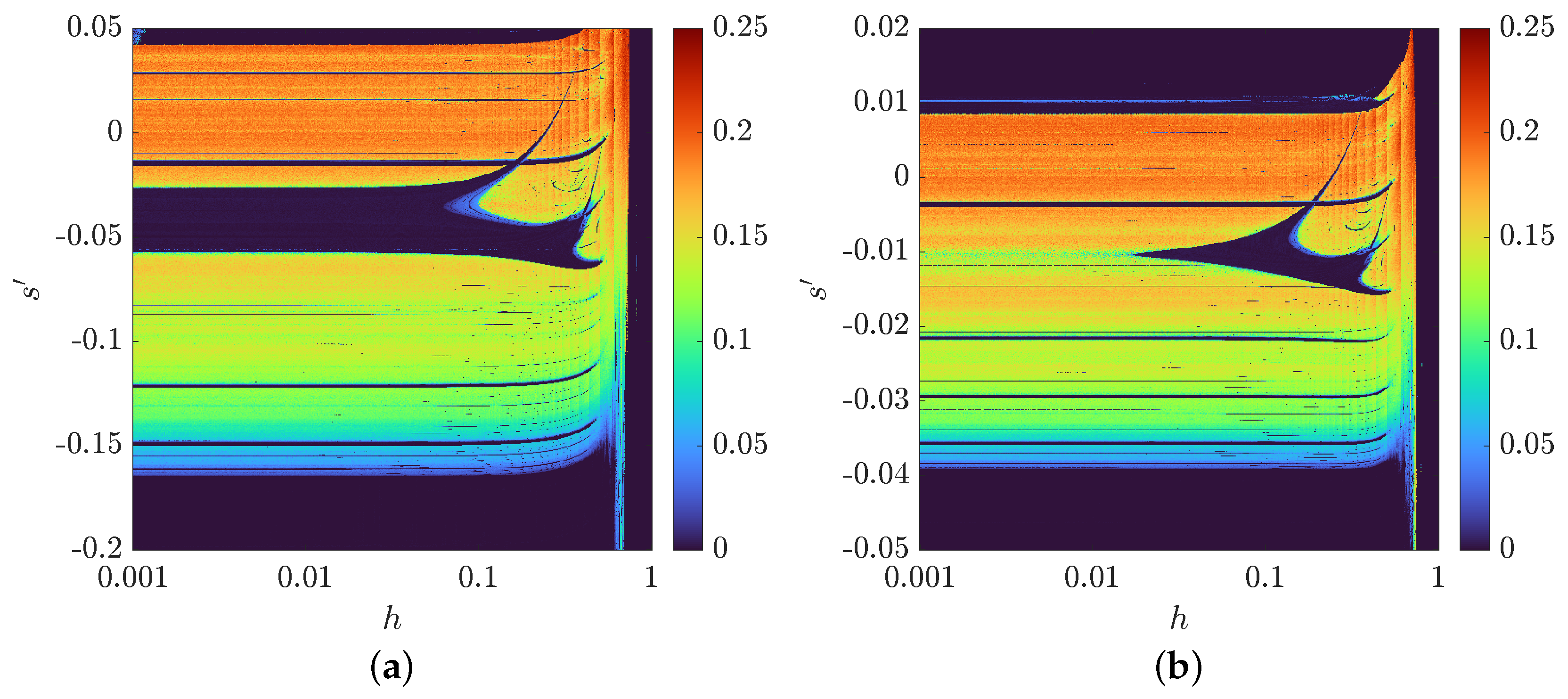
3.3. The Bifurcation Diagrams and s-h Diagrams
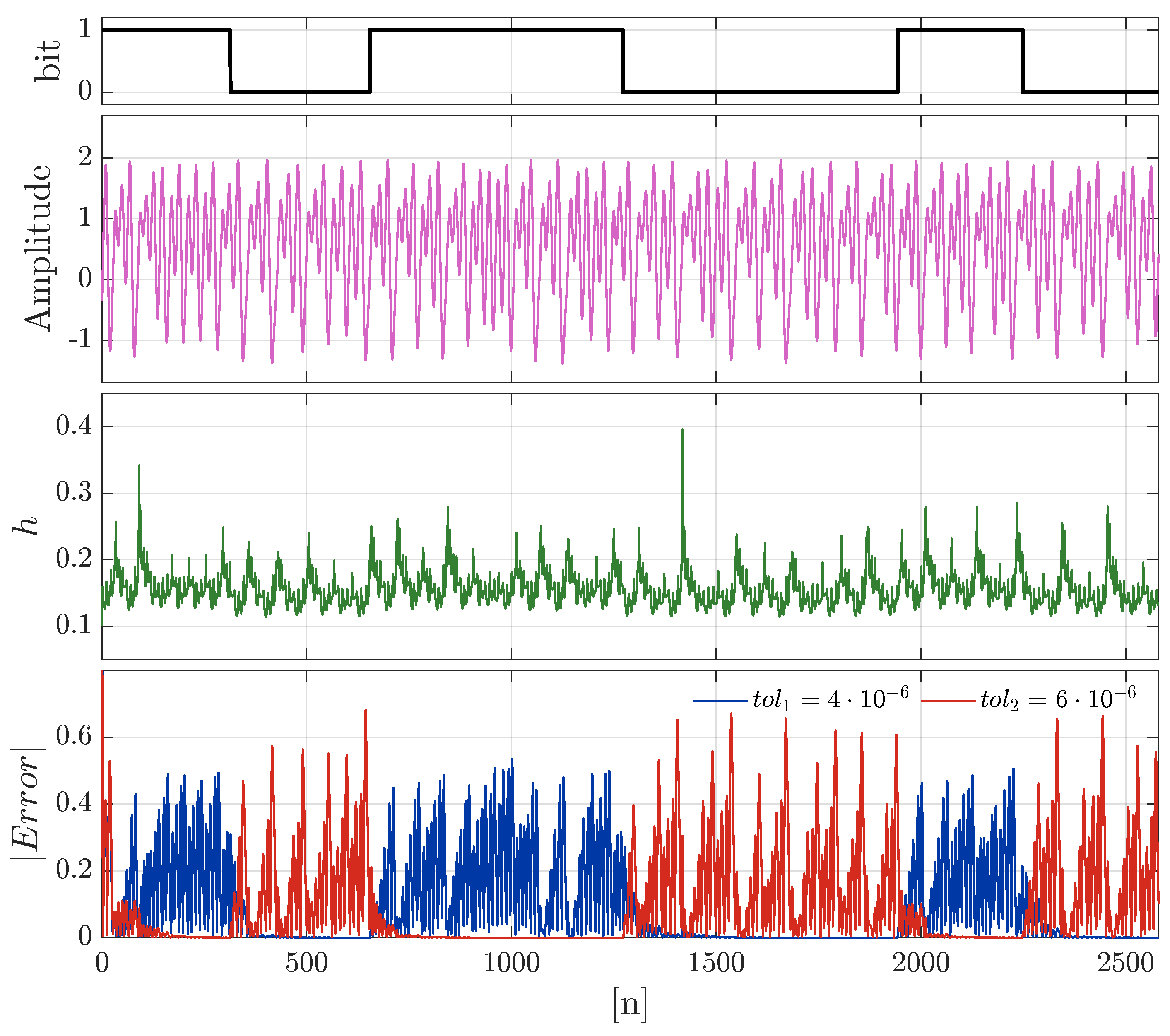
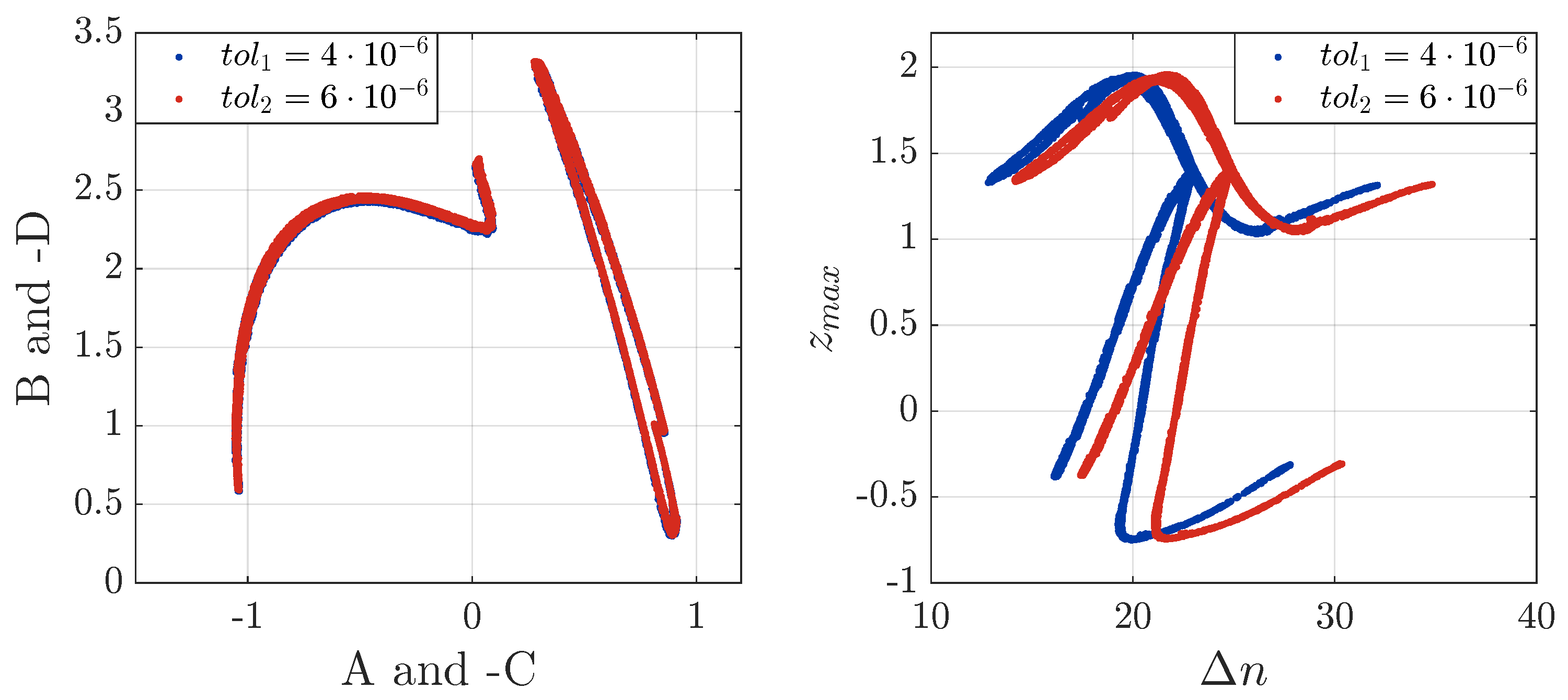
3.4. A Variable-Time-Step Approach to Coherent Chaotic Communication
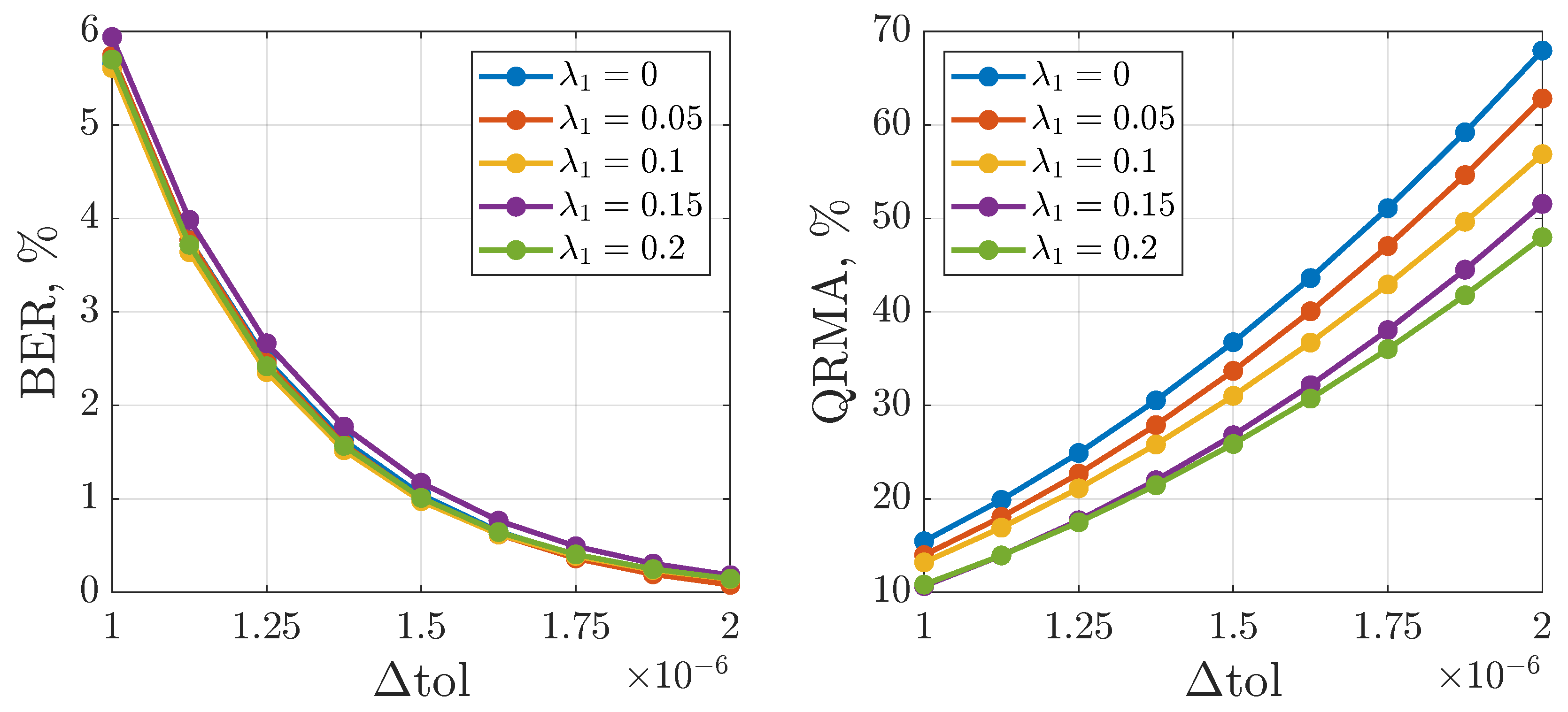
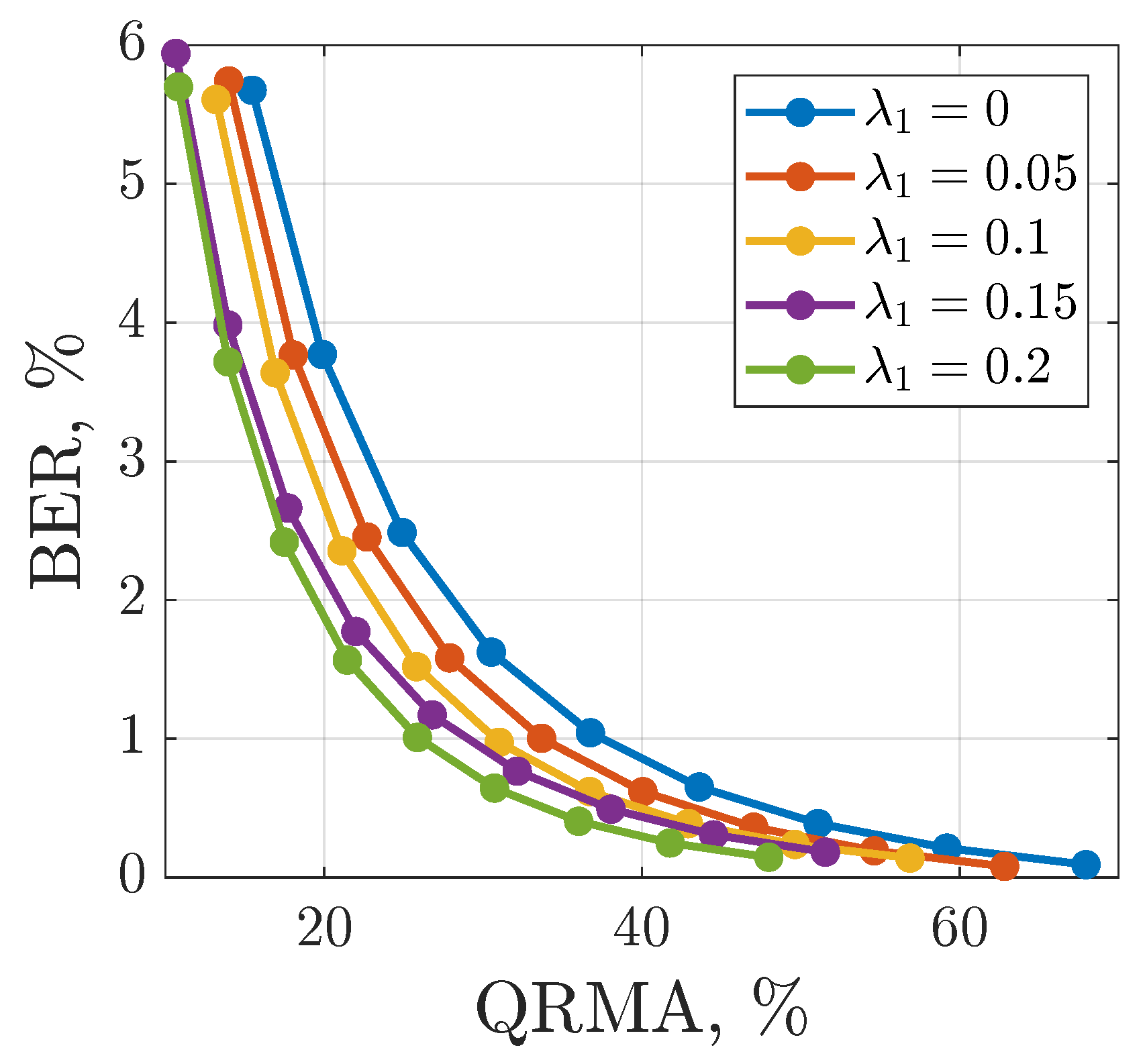
3.5. Privacy and Noise Tolerance Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BER | Bit error rate |
| CD | Composite diagonal (method) |
| CCS | Chaotic communication system |
| CSK | Chaotic shift keying |
| DCCS | Direct chaotic communication system |
| DOF | Degree of freedom |
| FDS | Finite-difference scheme |
| LLE | Largest Lyapunov exponent |
| ODE | Ordinary differential equation |
| PM | Parameter modulation |
| SCM | Symmetry coefficient modulation |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
| VMPM | Variable-step parameter modulation |
| VS-MCD | Variable-step modified composite diagonal (method) |
| QRMA | Quantified return map analysis |
Appendix A. A Study on the Dynamics of the Chen System Implemented Using the VS-MCD Method
References
- Timberlake, T.; Hasbun, J.E. Computation in classical mechanics. Am. J. Phys. 2008, 76, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hairer, E.; Lubich, C. Long-term analysis of the Störmer–Verlet method for Hamiltonian systems with a solution-dependent high frequency. Numer. Math. 2016, 134, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, Z.; Tian, H.; Liu, J. Symplectic dynamics and simultaneous resonance analysis of memristor circuit based on its van der Pol oscillator. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørsett, S.P. Semi-Explicit Runge-Kutta Methods; Department of Mathematics, University of Trondheim: Trondheim, Norway, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, R. Diagonally implicit Runge–Kutta methods for stiff ODE’s. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 1977, 14, 1006–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qian, X.; Song, S. Novel high-order energy-preserving diagonally implicit Runge–Kutta schemes for nonlinear Hamiltonian ODEs. Appl. Math. Lett. 2020, 102, 106091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diele, F.; Marangi, C. Explicit symplectic partitioned Runge–Kutta–Nyström methods for non-autonomous dynamics. Appl. Numer. Math. 2011, 61, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolke, R.; Knoth, O. Implicit–explicit Runge–Kutta methods applied to atmospheric chemistry-transport modelling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2000, 15, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, G.; Kapral, R. Asynchronous algorithm for integration of reaction–diffusion equations for inhomogeneous excitable media. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2000, 10, 812–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Green, W.H.; Wong, H.W.; Oluwole, O.O. Accelerating multi-dimensional combustion simulations using GPU and hybrid explicit/implicit ODE integration. Combust. Flame 2012, 159, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunc, H.; Sari, M. A new implicit-explicit local method to capture stiff behavior with covid-19 outbreak application. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.05817. [Google Scholar]
- Butusov, D.N.; Ostrovskii, V.Y.; Karimov, A.I.; Andreev, V.S. Semi-explicit composition methods in memcapacitor circuit simulation. Int. J. Embed. Real-Time Commun. Syst. (IJERTCS) 2019, 10, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butusov, D.; Tutueva, A.; Fedoseev, P.; Terentev, A.; Karimov, A. Semi-implicit multistep extrapolation ODE solvers. Mathematics 2020, 8, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burden, R.L.; Faires, J.D. 2.2 fixed-point iteration. In Numerical Analysis, 3rd ed.; PWS Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1985; p. 64. [Google Scholar]
- Holder, T.; Leimkuhler, B.; Reich, S. Explicit variable step-size and time-reversible integration. Appl. Numer. Math. 2001, 39, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butusov, D.; Rybin, V.; Karimov, A. Fast time-reversible synchronization of chaotic systems. Phys. Rev. E 2025, 111, 014213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutueva, A.; Butusov, D. Avoiding dynamical degradation in computer simulation of chaotic systems using semi-explicit integration: Rössler oscillator case. Fractal Fract. 2021, 5, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Fan, S.; Xing, W.; Sun, J. Study of weak vibrating signal detection based on chaotic oscillator in MEMS resonant beam sensor. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 50, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiderer, L.J.; Braun, D. Quantum metrology with quantum-chaotic sensors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimov, T.; Druzhina, O.; Karimov, A.; Tutueva, A.; Ostrovskii, V.; Rybin, V.; Butusov, D. Single-coil metal detector based on spiking chaotic oscillator. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 107, 1295–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estudillo-Valdez, M.A.; Adeyemi, V.A.; Tlelo-Cuautle, E.; Sandoval-Ibarra, Y.; Nuñez-Perez, J.C. FPGA realization of four chaotic interference cases in a terrestrial trajectory model and application in image transmission. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, B.; Koshiba, T. Chaotic image encryption: State-of-the-art, ecosystem, and future roadmap. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2022, 5, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Cui, Y. Signal denoising based on Duffing oscillators system. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 86554–86563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, L.; Ghanes, M.; Plestan, F.; Aoustin, Y.; Barbot, J.P. A noise less-sensing semi-implicit discretization of a homogeneous differentiator: Principle and application. In Proceedings of the 2021 European Control Conference (ECC), Delft, The Netherlands, 29 June–2 July 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; 2021; pp. 2340–2345. [Google Scholar]
- Eisencraft, M.; Fanganiello, R.; Grzybowski, J.; Soriano, D.; Attux, R.; Batista, A.; Macau, E.; Monteiro, L.H.A.; Romano, J.; Suyama, R.; et al. Chaos-based communication systems in non-ideal channels. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2012, 17, 4707–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaddoum, G. Wireless chaos-based communication systems: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 2621–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuningsih, S.H.; Supian, S.; Sukono, S.; Subiyanto, S. Wireless chaos-based communication system: Literature Review. Int. J. Quant. Res. Model. 2021, 2, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarchik, A.N.; Jaimes-Reátegui, R.; Rodríguez-Flores, C.; García-López, J.; Huerta-Cuéllar, G.; Martín-Pasquín, F.J. Secure chaotic communication based on extreme multistability. J. Frankl. Inst. 2021, 358, 2561–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkin, I.; Kuznetsova, O. An approach to generating extremely multistable chaotic systems. J. Math. Sci. 2022, 262, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capligins, F.; Babajans, R.; Cirjulina, D.; Kolosovs, D.; Litvinenko, A. Frequency-modulated antipodal Chaos Shift Keying Chaotic Communication on Field Program Gate Array: Prototype Design and Performance Insights. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirjulina, D.; Babajans, R.; Kolosovs, D. Experimental Study on Quadrature Chaos Shift Keying Communication System. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Workshop on Microwave Theory and Technology in Wireless Communications (MTTW), Riga, Latvia, 2–4 October 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; 2024; pp. 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Cirjulina, D.; Babajans, R.; Capligins, F.; Litvinenko, A. Experimental Study on Colpitts Chaotic Oscillator-Based Communication System Application for the Internet of Things. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirjulina, D.; Babajans, R.; Kolosovs, D. Design particularities of quadrature chaos shift keying communication system with enhanced noise immunity for IoT applications. Entropy 2025, 27, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybin, V.; Karimov, T.; Bayazitov, O.; Kvitko, D.; Babkin, I.; Shirnin, K.; Kolev, G.; Butusov, D. Prototyping the symmetry-based chaotic communication system using microcontroller unit. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecora, L.M.; Carroll, T.L. Synchronization in chaotic systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1990, 64, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hairer, E.; Norsett, S.; Wanner, G. Solving Ordinary Differential Equations I: Nonstiff Problems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; Volume 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, K.M.; Oppenheim, A.V. Chaotic signals and systems for communications. In Proceedings of the 1993 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 27–30 April 1993; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; 1993; Volume 3, pp. 137–140. [Google Scholar]
- Karimov, T.; Rybin, V.; Kolev, G.; Rodionova, E.; Butusov, D. Chaotic communication system with symmetry-based modulation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babkin, I.; Rybin, V.; Andreev, V.; Karimov, T.; Butusov, D. Coherent Chaotic Communication Using Generalized Runge–Kutta Method. Mathematics 2024, 12, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hairer, E.; Lubich, C.; Wanner, G. Geometric numerical integration illustrated by the Störmer–Verlet method. Acta Numer. 2003, 12, 399–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprott, J.C. Some simple chaotic flows. Phys. Rev. E 1994, 50, R647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Ueta, T. Yet another chaotic attractor. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 1999, 9, 1465–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybin, V.; Butusov, D.; Rodionova, E.; Karimov, T.; Ostrovskii, V.; Tutueva, A. Discovering chaos-based communications by recurrence quantification and quantified return map analyses. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2022, 32, 2250136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, G.; Cerdeira, H.A. Extracting messages masked by chaos. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 74, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, G.; Alvarez, G. Return-map cryptanalysis revisited. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2006, 16, 1557–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Wang, J.; Fan, Y. Wind power forecasting method of large-scale wind turbine clusters based on DBSCAN clustering and an enhanced hunter-prey optimization algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 307, 118341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybin, V.; Butusov, D.; Babkin, I.; Pesterev, D.; Arlyapov, V. Some properties of a discrete Lorenz system obtained by variable midpoint method and its application to chaotic signal modulation. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2024, 34, 2450009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang-Feng, X.; Le-Quan, M.; Guan-Rong, C. A Chaotic Communication Scheme Based on Generalized Synchronization and Hash Functions. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2004, 21, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoudi, S.; Azzaz, M.S.; Djeddou, M.; Benssalah, M. An FPGA real-time implementation of the Chen’s chaotic system for securing chaotic communications. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2009, 7, 467–474. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, N.M.; Jamal, R.K. A novel secure communication system using Chen’s chaotic model. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2022, 54, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, G. Chaos in the fractional order Chen system and its control. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2004, 22, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, Q.; Wang, C. Impulsive control and synchronization of unified chaotic system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2004, 20, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rybin, V.; Babkin, I.; Bobrova, Y.; Galchenko, M.; Mikhailov, A.; Karimov, T. Variable-Step Semi-Implicit Solver with Adjustable Symmetry and Its Application for Chaos-Based Communication. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13081229
Rybin V, Babkin I, Bobrova Y, Galchenko M, Mikhailov A, Karimov T. Variable-Step Semi-Implicit Solver with Adjustable Symmetry and Its Application for Chaos-Based Communication. Mathematics. 2025; 13(8):1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13081229
Chicago/Turabian StyleRybin, Vyacheslav, Ivan Babkin, Yulia Bobrova, Maksim Galchenko, Alexander Mikhailov, and Timur Karimov. 2025. "Variable-Step Semi-Implicit Solver with Adjustable Symmetry and Its Application for Chaos-Based Communication" Mathematics 13, no. 8: 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13081229
APA StyleRybin, V., Babkin, I., Bobrova, Y., Galchenko, M., Mikhailov, A., & Karimov, T. (2025). Variable-Step Semi-Implicit Solver with Adjustable Symmetry and Its Application for Chaos-Based Communication. Mathematics, 13(8), 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13081229






