A Literature Review of Stochastic Modeling for Phylogenetic Comparative Analysis in Trait Evolution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Stochastic Frameworks in PCMs
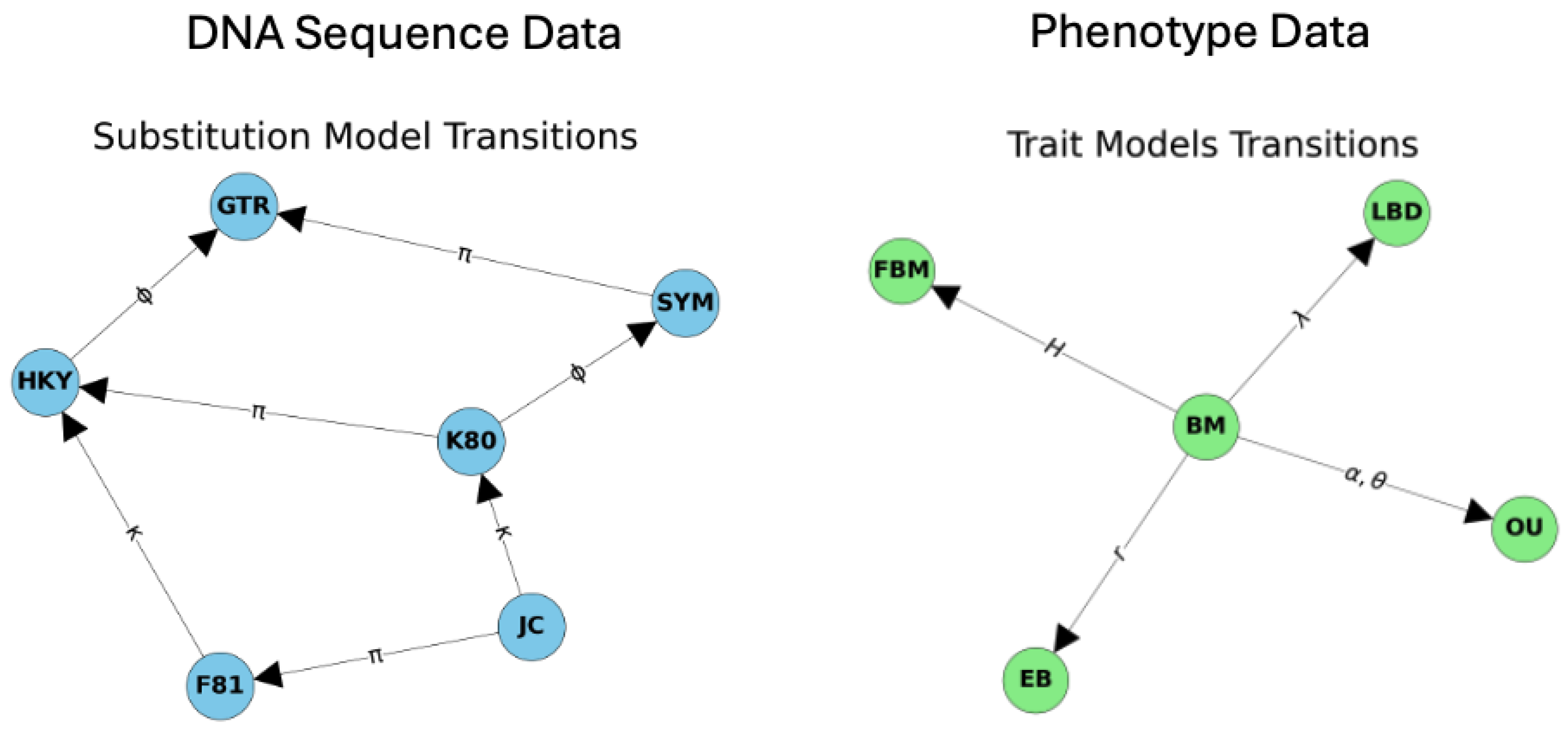
2.1. The Stochastic Model for Trait Evolution
2.2. Modeling Adaptation to Random Environment
2.3. Multivariate Normal Models
2.4. Non-Gaussian Processes
2.4.1. Non-Negative Trait Model
2.4.2. Bounded Trait Model
2.5. Phylogenetic Adaptive Regression and Rate of Evolution Model
2.5.1. Optimal Regression Model
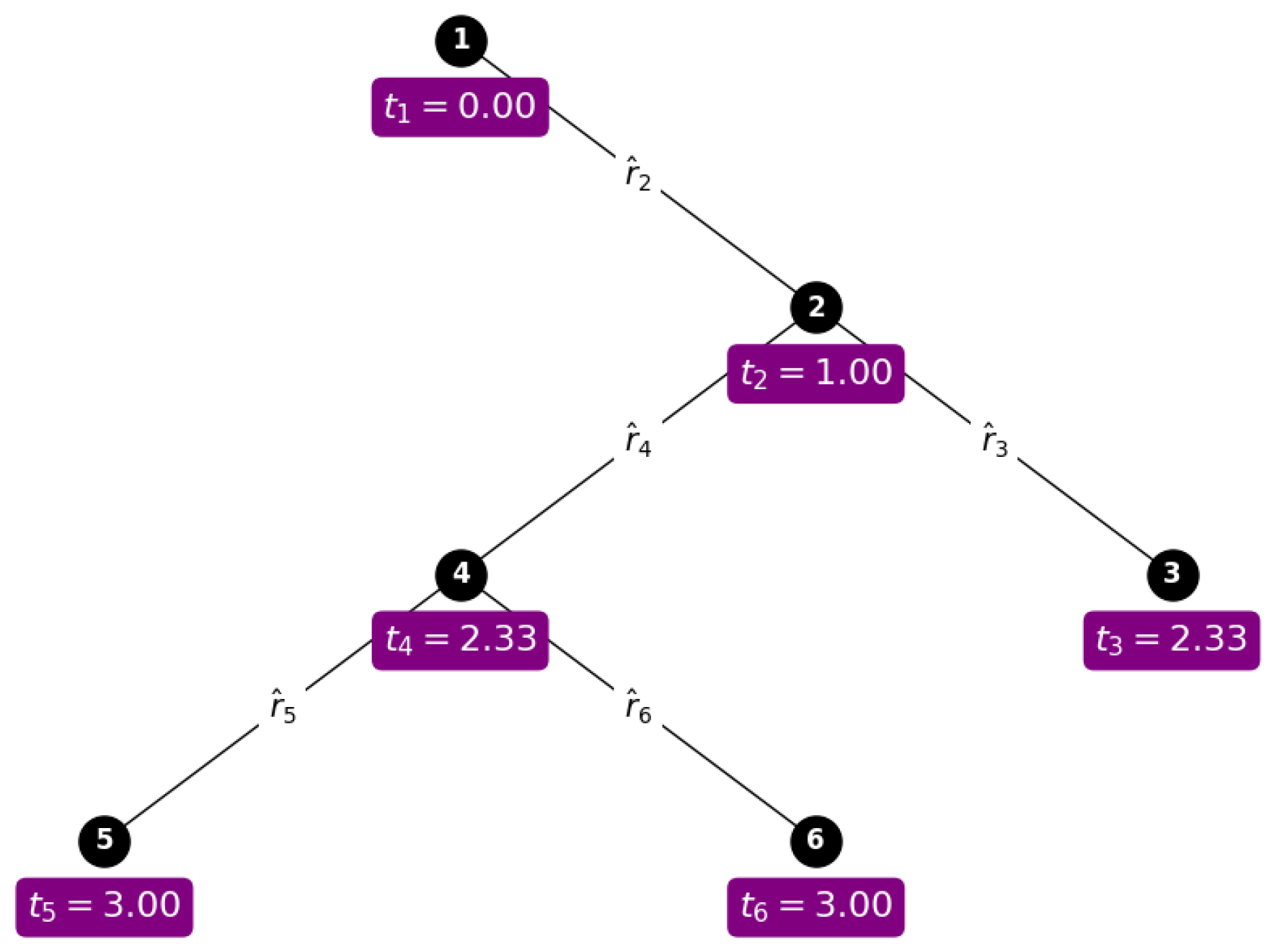
2.5.2. Rate of Trait Evolution
2.6. Joint Modeling Trait Evolution with DNA Data
2.7. Count-Based Trait Data
2.8. Phylogenetic Networks
3. Software
4. Prospective Research and Future Applications
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Meara, B.C. Evolutionary inferences from phylogenies: A review of methods. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.C.; Berns, C.M.; Kozak, K.H.; Wiens, J.J. Are rates of species diversification correlated with rates of morphological evolution? Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 2729–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassler, G.; Tolkoff, M.R.; Allen, W.L.; Ho, L.S.T.; Lemey, P.; Suchard, M.A. Inferring phenotypic trait evolution on large trees with many incomplete measurements. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2022, 117, 678–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwery, O.; Freyman, W.; Goldberg, E.E. adequaSSE: Model Adequacy Testing for Trait-Dependent Diversification Models. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lartillot, N.; Poujol, R. A phylogenetic model for investigating correlated evolution of substitution rates and continuous phenotypic characters. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 729–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Housworth, E.A.; Martins, E.P.; Lynch, M. The phylogenetic mixed model. Am. Nat. 2004, 163, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, J.M.; Jhwueng, D.C.; Boettiger, C.; O’Meara, B.C. Modeling stabilizing selection: Expanding the Ornstein–Uhlenbeck model of adaptive evolution. Evolution 2012, 66, 2369–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.F.; Pienaar, J.; Orzack, S.H. A comparative method for studying adaptation to a randomly evolving environment. Evolution 2008, 62, 1965–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polly, P.D. Paleontology and the Comparative Method: Ancestral Node Reconstructions versus Observed Node Values. Am. Nat. 2001, 157, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagel, M. Inferring the historical patterns of biological evolution. Nature 1999, 401, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.C. A generalized K statistic for estimating phylogenetic signal from shape and other high-dimensional multivariate data. Syst. Biol. 2014, 63, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.C.; Collyer, M.L. Extending phylogenetic regression models for comparing within-species patterns across the tree of life. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2024, 15, 2234–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomberg, S.P.; Muniz, M.; Bui, M.N.; Janke, C. Multivariate Trait Evolution: Models for the Evolution of the Quantitative Genetic G-Matrix on Phylogenies. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.S.T.; Dinh, V. When can we reconstruct the ancestral state? A unified theory. Theor. Popul. Biol. 2022, 148, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Phylogenies and the comparative method. Am. Nat. 1985, 125, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.F. Stabilizing selection and the comparative analysis of adaptation. Evolution 1997, 51, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, L.J.; Losos, J.B.; Jonathan Davies, T.; Gillespie, R.G.; Gittleman, J.L.; Bryan Jennings, W.; Kozak, K.H.; McPeek, M.A.; Moreno-Roark, F.; Near, T.J.; et al. Early bursts of body size and shape evolution are rare in comparative data. Evolution 2010, 64, 2385–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Meara, B.C.; Ané, C.; Sanderson, M.J.; Wainwright, P.C. Testing for different rates of continuous trait evolution using likelihood. Evolution 2006, 60, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martins, E.P.; Hansen, T.F. Phylogenies and the comparative method: A general approach to incorporating phylogenetic information into the analysis of interspecific data. Am. Nat. 1997, 149, 646–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, E.P.; Diniz-Filho, J.A.F.; Housworth, E.A. Adaptive constraints and the phylogenetic comparative method: A computer simulation test. Evolution 2002, 56, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, M.A.; King, A.A. Phylogenetic comparative analysis: A modeling approach for adaptive evolution. Am. Nat. 2004, 164, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Inferring Phylogenies; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyeda, J.C.; Harmon, L.J. A novel Bayesian method for inferring and interpreting the dynamics of adaptive landscapes from phylogenetic comparative data. Syst. Biol. 2014, 63, 902–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhwueng, D.C.; Wang, C.P. Phylogenetic Curved Optimal Regression for Adaptive Trait Evolution. Entropy 2021, 23, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhwueng, D.C. Stochastic Modeling of Morphological Rate Evolution: Phylogenetic Regression with Approximate Bayesian Computation. 2024; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont, M.A. Approximate bayesian computation. Annu. Rev. Stat. Its Appl. 2019, 6, 379–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoszek, K.; Liò, P. Modelling trait dependent speciation with approximate Bayesian computation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.03715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressler, C.E.; Butler, M.A.; King, A.A. Detecting adaptive evolution in phylogenetic comparative analysis using the Ornstein–Uhlenbeck model. Syst. Biol. 2015, 64, 953–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoszek, K.; Pienaar, J.; Mostad, P.; Andersson, S.; Hansen, T.F. A phylogenetic comparative method for studying multivariate adaptation. J. Theor. Biol. 2012, 314, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoszek, K.; Tredgett Clarke, J.; Fuentes-González, J.; Mitov, V.; Pienaar, J.; Piwczyński, M.; Puchałka, R.; Spalik, K.; Voje, K.L. Fast mvSLOUCH: Multivariate Ornstein–Uhlenbeck-based models of trait evolution on large phylogenies. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2024, 15, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, E.P. Phylogenies and the Comparative Method in Animal Behavior; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, D.C.; Otárola-Castillo, E. geomorph: An R package for the collection and analysis of geometric morphometric shape data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2013, 4, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.C.; Collyer, M.L. Phylogenetic comparative methods and the evolution of multivariate phenotypes. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2019, 50, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caumul, R.; Polly, P.D. Phylogenetic and environmental components of morphological variation: Skull, mandible, and molar shape in marmots (Marmota, Rodentia). Evolution 2005, 59, 2460–2472. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, A.; Polly, P.D. Methods for studying morphological integration and modularity. Quant. Methods Paleobiol. 2010, 16, 213–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomberg, S.P.; Rathnayake, S.I.; Moreau, C.M. Beyond Brownian motion and the Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process: Stochastic diffusion models for the evolution of quantitative characters. Am. Nat. 2020, 195, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhwueng, D.C. Modeling rate of adaptive trait evolution using Cox–Ingersoll–Ross Process: An approximate Bayesian computation approach. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2020, 145, 106924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, F.C.; Démery, V. Inferring bounded evolution in phenotypic characters from phylogenetic comparative data. Syst. Biol. 2016, 65, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.F. Three modes of evolution? Remarks on rates of evolution and time scaling. J. Evol. Biol. 2024, 37, 1523–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhwueng, D.C.; Lin, M.H. On the Fractional Brownian Motion for Modeling and Simulating Phylogenetic Trait Evolution. 2024; in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Bastide, P.; Didier, G. The Cauchy process on phylogenies: A tractable model for pulsed evolution. Syst. Biol. 2023, 72, 1296–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhwueng, D.C.; Maroulas, V. Phylogenetic ornstein–uhlenbeck regression curves. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2014, 89, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jhwueng, D.C.; Chang, C.H. Stochastic Modeling of Adaptive Trait Evolution in Phylogenetics: A Polynomial Regression and Approximate Bayesian Computation Approach. Mathematics 2025, 13, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.F.; Bolstad, G.H.; Tsuboi, M. Analyzing disparity and rates of morphological evolution with model-based phylogenetic comparative methods. Syst. Biol. 2022, 71, 1054–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latrille, T.; Lartillot, N. An improved codon modeling approach for accurate estimation of the mutation bias. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2022, 39, msac005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirarab, S.; Nguyen, N.; Guo, S.; Wang, L.S.; Kim, J.; Warnow, T. PASTA: Ultra-large multiple sequence alignment for nucleotide and amino-acid sequences. J. Comput. Biol. 2015, 22, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Raghavan, S.; Nelesen, S.; Linder, C.R.; Warnow, T. Rapid and accurate large-scale coestimation of sequence alignments and phylogenetic trees. Science 2009, 324, 1561–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirarab, S.; Reaz, R.; Bayzid, M.S.; Zimmermann, T.; Swenson, M.S.; Warnow, T. ASTRAL: Genome-scale coalescent-based species tree estimation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, i541–i548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L. BEST: Bayesian estimation of species trees under the coalescent model. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2542–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yu, L.; Edwards, S.V. A maximum pseudo-likelihood approach for estimating species trees under the coalescent model. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yu, L.; Pearl, D.K.; Edwards, S.V. Estimating species phylogenies using coalescence times among sequences. Syst. Biol. 2009, 58, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitner, B.S.; Pearse, W.; Roehrdanz, P.; Enquist, B.J.; Sanderson, M.J. APPENDIX C. Re-scaling phylogenetic branches to reflect trait evolution. Univ. Ariz. Grad. Coll. 2020, 1001, 86. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z. Computational Molecular Evolution; OUP Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jhwueng, D.C. Estimating Absolute Rates of Molecular Evolution and Divergence Times Using an Autoregressive Conditional Heteroskedasticity Framework. 2024; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Jhwueng, D.C. Modeling the Phylogenetic Rates of Continuous Trait Evolution: An Autoregressive–Moving-Average Model Approach. Mathematics 2025, 13, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhwueng, D.C. Statistical Modeling and Analysis of Phylogenetic Trait Evolution Variability in Species Using Heteroskedasticity Models. 2024; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Ives, A.R.; Garland Jr, T. Phylogenetic logistic regression for binary dependent variables. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradis, E.; Claude, J. Analysis of comparative data using generalized estimating equations. J. Theor. Biol. 2002, 218, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhwueng, D.C.; Wu, C.Y. A Novel Phylogenetic Negative Binomial Regression Model for Count-Dependent Variables. Biology 2023, 12, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhwueng, D.C.; O’Meara, B.C. Trait evolution on phylogenetic networks. BioRxiv 2015, 023986. [Google Scholar]
- Solís-Lemus, C.; Bastide, P.; Ané, C. PhyloNetworks: A package for phylogenetic networks. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3292–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastide, P.; Ané, C.; Robin, S.; Mariadassou, M. Inference of adaptive shifts for multivariate correlated traits. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 662–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastide, P.; Solís-Lemus, C.; Kriebel, R.; Sparks, K.W.; Ané, C. Phylogenetic comparative methods on phylogenetic networks with reticulations. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 800–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, B.; Rose, J.; Bastide, P.; Ané, C. Accounting for Within-Species Variation in Continuous Trait Evolution on a Phylogenetic Network. Bull. Soc. Syst. Biol. 2023, 2, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ané, C. Identifiability of local and global features of phylogenetic networks from average distances. J. Math. Biol. 2023, 86, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, J.A.; Banos, H.; Xu, J.; Ané, C. Identifying circular orders for blobs in phylogenetic networks. Adv. Appl. Math. 2025, 163, 102804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revell, L.J. phytools: An R package for phylogenetic comparative biology (and other things). Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, D.L.; Revell, L.J.; Glor, R.E.; Losos, J.B. Ecological opportunity and the rate of morphological evolution in the diversification of Greater Antillean anoles. Evolution 2010, 64, 2731–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitov, M.V. Package PCMBase: Simulation and Likelihood Calculation of Phylogenetic Comparative Models Version 1.2.14 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=PCMBase (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Mitov, V.; Bartoszek, K.; Asimomitis, G.; Stadler, T. Fast likelihood calculation for multivariate Gaussian phylogenetic models with shifts. Theor. Popul. Biol. 2020, 131, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoszek, K.; Fuentes-Gonz’alez, J.; Mitov, V.; Pienaar, J.; Piwczy’nski, M.; Puchalka, R.; Spalik, K.; Voje, K.L. Model Selection Performance in Phylogenetic Comparative Methods Under Multivariate Ornstein–Uhlenbeck Models of Trait Evolution. Syst. Biol. 2023, 72, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, M. Blouch: Bayesian Linear Ornstein-Uhlenbeck Models for Comparative Hypotheses. Syst. Biol. 2024, 73, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhwueng, D.C. Building an adaptive trait simulator package to infer parametric diffusion model along phylogenetic tree. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.C.; Collyer, M.L. Phylogenetic ANOVA: Group-clade aggregation, biological challenges, and a refined permutation procedure. Evolution 2018, 72, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package), Version 3.698; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Borstein, S.R.; O’Meara, B.C. AnnotationBustR: An R package to extract subsequences from GenBank annotations. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borstein, S.R.; Hammer, M.P.; O’Meara, B.C.; McGee, M.D. The macroevolutionary dynamics of pharyngognathy in fishes fail to support the key innovation hypothesis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhleh, L.; Ringe, D.; Warnow, T. Perfect phylogenetic networks: A new methodology for reconstructing the evolutionary history of natural languages. Language 2005, 81, 382–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gearty, W.; O’Meara, B.; Berv, J.; Ballen, G.A.; Ferreira, D.; Lapp, H.; Schmitz, L.; Smith, M.R.; Upham, N.S.; Nations, J.A. CRAN Task View: Phylogenetics. 2024. Available online: https://mirror.truenetwork.ru/CRAN/web/views/Phylogenetics.html (accessed on 22 December 2024).
- Card, D.C.; Jennings, W.B.; Edwards, S.V. Genome evolution and the future of phylogenomics of non-avian reptiles. Animals 2023, 13, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Chavez, C.; Brauer, F.; Feng, Z. Mathematical Models in Epidemiology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, L.J. An Introduction to Stochastic Processes with Applications to Biology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Britton, T.; Pardoux, E.; Ball, F.; Laredo, C.; Sirl, D.; Tran, V.C. Stochastic Epidemic Models with Inference; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 2255. [Google Scholar]
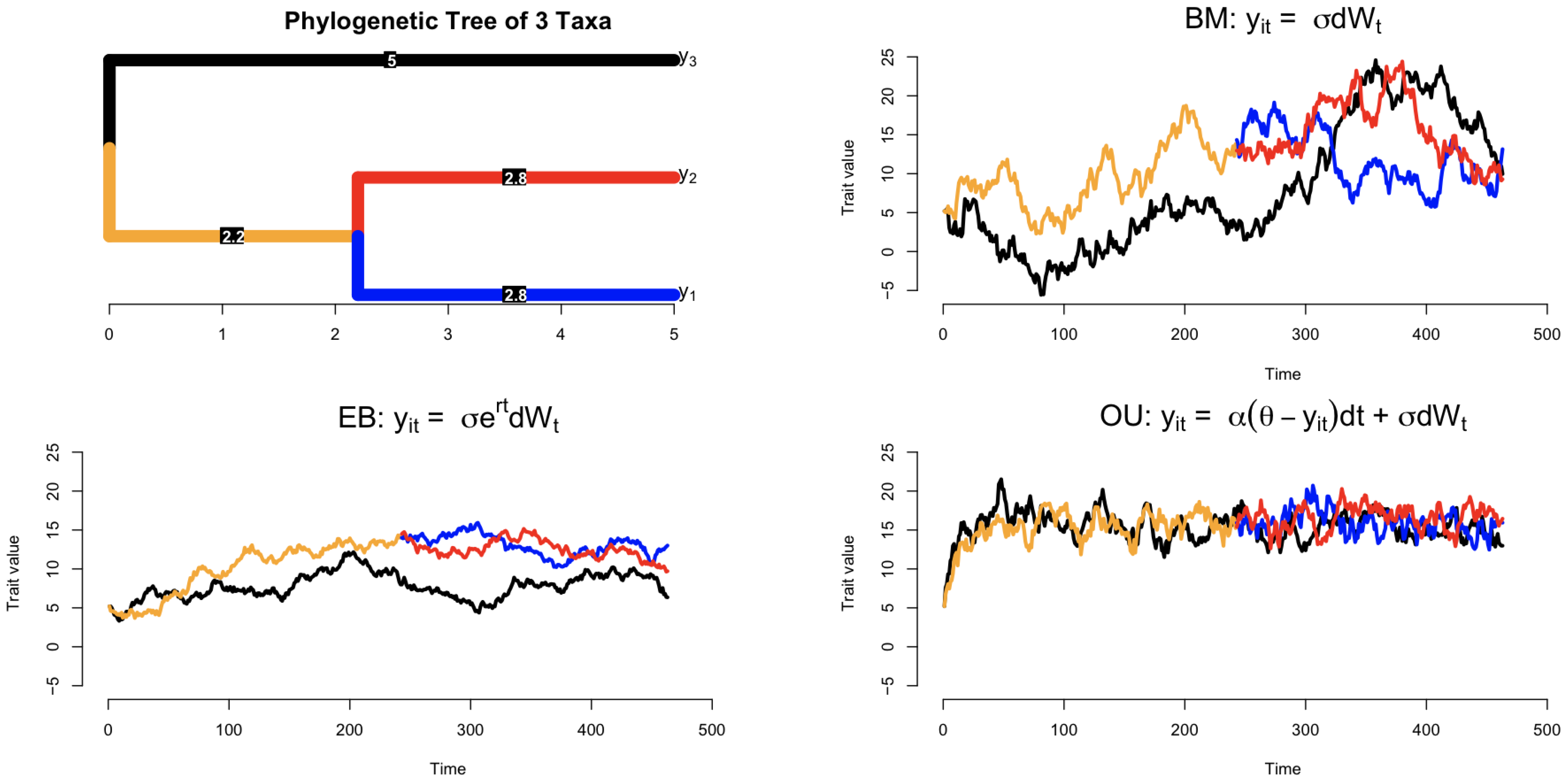




| Model | Model Equation | Phenemenon | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brownian motion (BM) [15,18] | (0;) | Natural selection | |
| Ornstein–Uhlenbeck (OU) [19,20,21] | () | Stabilizing selection | |
| Early burst (EB) [17] | Adaptive radiation |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxon 1 | A | C | T | G | A | T | C | G | A | T |
| Taxon 2 | G | T | A | C | G | A | T | T | G | C |
| Taxon 3 | T | A | C | G | T | T | A | G | C | A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jhwueng, D.-C. A Literature Review of Stochastic Modeling for Phylogenetic Comparative Analysis in Trait Evolution. Mathematics 2025, 13, 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13030361
Jhwueng D-C. A Literature Review of Stochastic Modeling for Phylogenetic Comparative Analysis in Trait Evolution. Mathematics. 2025; 13(3):361. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13030361
Chicago/Turabian StyleJhwueng, Dwueng-Chwuan. 2025. "A Literature Review of Stochastic Modeling for Phylogenetic Comparative Analysis in Trait Evolution" Mathematics 13, no. 3: 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13030361
APA StyleJhwueng, D.-C. (2025). A Literature Review of Stochastic Modeling for Phylogenetic Comparative Analysis in Trait Evolution. Mathematics, 13(3), 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13030361






