Composite Test Functions for Benchmarking Nonlinear Optimization Software
Abstract
1. Nonlinear Optimization: A Generic Model
- (1)
- Minimize f(x) subject to x ∈ D.
- (2)
- D: = {l ≤ x ≤ u, g(x) ≤ 0}.
2. Convex vs. Nonconvex Models
- (3)
- min f(x1, x2), −3 ≤ x1 ≤ 3, −3 ≤ x2 ≤ 3, where the objective function f is defined by
3. Benchmarking Nonlinear Optimization Software
4. Selecting Test Problems
5. Composite Test Functions
6. Test Environment Options
6.1. Compiler-Based Development
6.2. Modeling Environments for Optimization
6.3. Excel
6.4. Integrated Computing Environments
7. Illustrative Models and Results
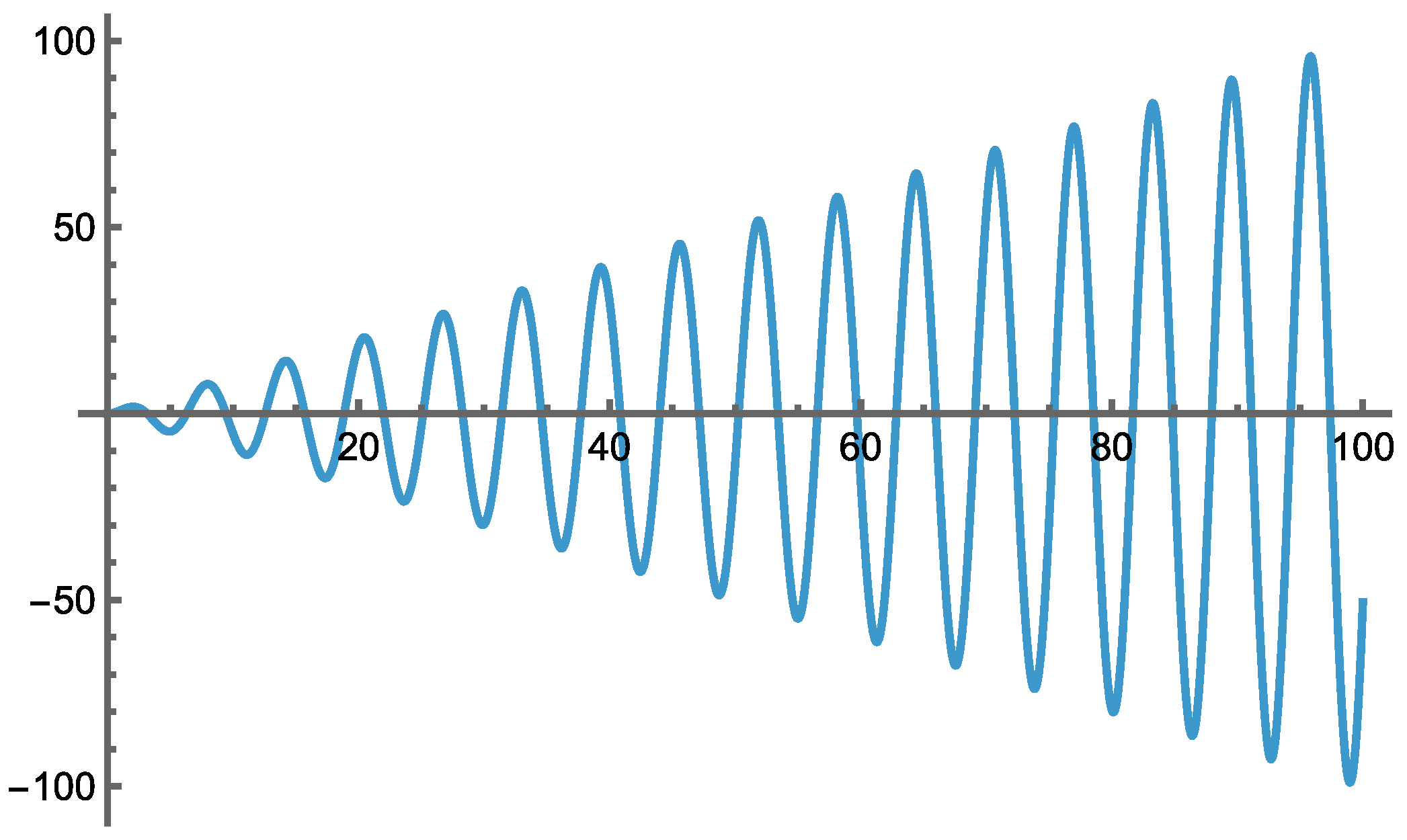
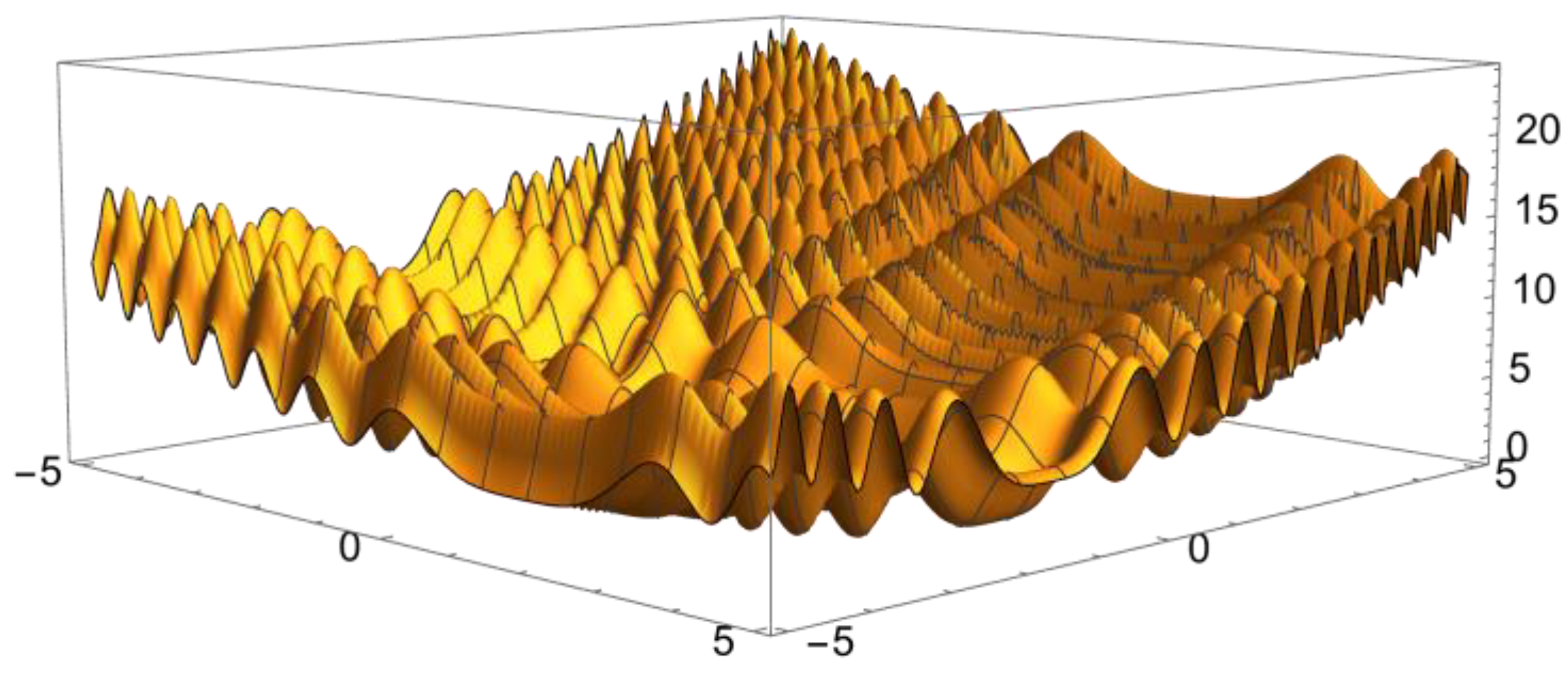
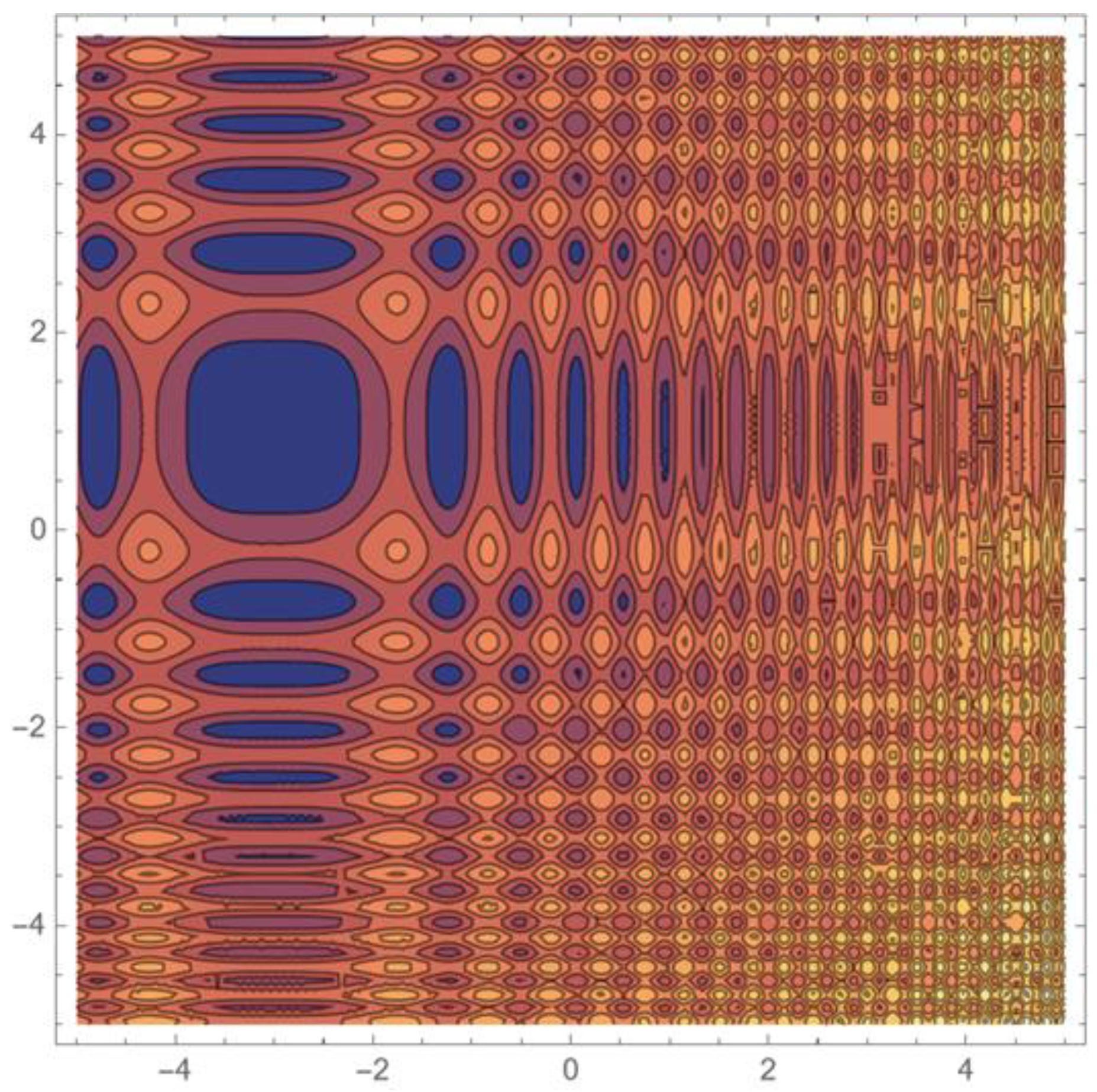
7.1. A Composite Model Function Class
- (4)
- f(x) = s∑i=1,n (xi –xi*)2 + ∑k=1,kmax ak sin2[bk Pk(x − x*)].
- (5)
- f = s(x–xopt)2 + a(sin(b(x–xopt)2))2.
7.2. Test Environment
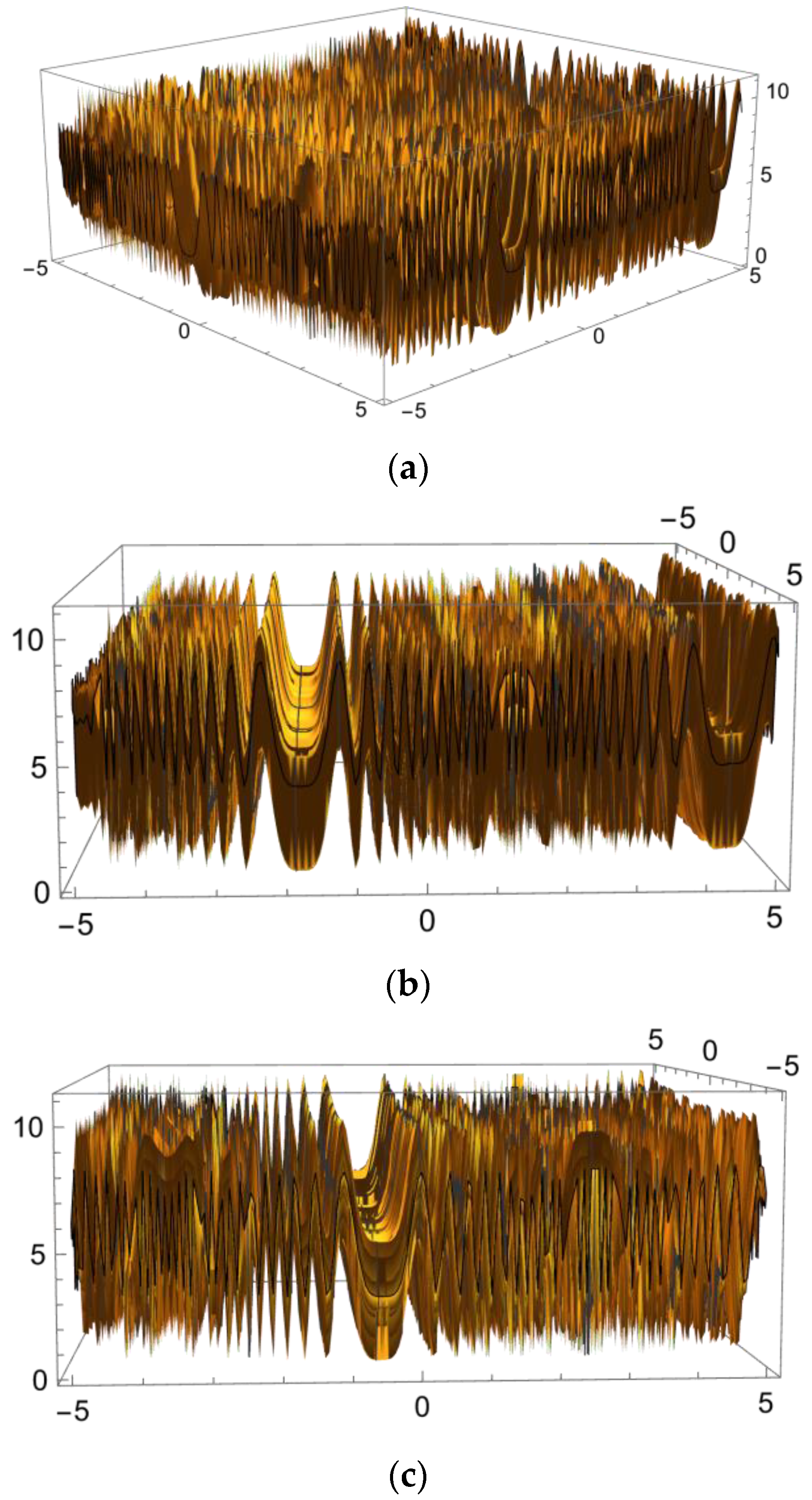
7.3. Two-Variable Model Examples
Illustrative Test Results
| Test run | Local solver success rate * | Global solver success rate * |
| 1 | 0.180 (i.e., 180 out of 1000) | 0.512 (i.e., 512 out of 1000) |
| 2 | 0.158 | 0.558 |
| 3 | 0.175 | 0.534 |
| 4 | 0.160 | 0.515 |
| 5 | 0.178 | 0.562 |
| * Successful solution is reported if the numerical optimum value returned is less than eps = 10−8. | ||
7.4. Three-Variable Model Examples
Illustrative Test Results
| Test run | Local solver success rate * | Global solver success rate * |
| 1 | 0.00 (i.e., 0 out of 100) | 0.28 (i.e., 28 out of 100) |
| 2 | 0.00 | 0.33 |
| 3 | 0.00 | 0.32 |
| 4 | 0.00 | 0.37 |
| 5 | 0.00 | 0.35 |
| * Successful solution is reported if the numerical optimum value returned is less than eps = 10−8. | ||
7.5. Five-Variable Model Examples
Illustrative Test Results
| Test run | Local solver success rate * | Global solver success rate * |
| 1 | 0.00 (i.e., 0 out of 100) | 0.06 (i.e., 6 out of 100) |
| 2 | 0.00 | 0.06 |
| 3 | 0.00 | 0.07 |
| 4 | 0.00 | 0.05 |
| 5 | 0.00 | 0.02 |
| * Successful solution is reported if the numerical optimum value returned is less than eps = 10−8. | ||
8. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rockafellar, R.T. Lagrange multipliers and optimality. SIAM Rev. 1993, 35, 183–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfram Research. Mathematica (Release 14.2); Wolfram Research: Champaign, IL, USA, 2025; Available online: https://www.wolfram.com/mathematica/ (accessed on 28 October 2025).
- Galewski, M. Basics of Nonlinear Optimization—Around the Weierstrass Theorem; Birkhäuser, Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rowland, T.; Weisstein, E.W. Bolzano-Weierstrass Theorem. From MathWorld—A Wolfram Web Resource. 2025. Available online: https://mathworld.wolfram.com/Bolzano-WeierstrassTheorem.html (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Nocedal, J.; Wright, S.J. Numerical Optimization, 2nd ed.; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Horst, R.; Pardalos, P.M.; Thoai, N.V. Introduction to Global Optimization; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Horst, R.; Pardalos, P.M. (Eds.) Handbook of Global Optimization; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Pintér, J.D. Global Optimization in Action; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kearfott, R.B. Rigorous Global Search: Continuous Problems; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Floudas, C.A. Deterministic Global Optimization; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Strongin, R.G.; Sergeyev, Y.D. Global Optimization with Non-Convex Constraints: Sequential and Parallel Algorithms; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pintér, J.D. Global optimization: Software, test problems, and applications. In Handbook of Global Optimization, Volume 2; Pardalos, P.M., Romeijn, H.E., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 515–569. [Google Scholar]
- Tawarmalani, M.; Sahinidis, N. Convexification and Global Optimization in Continuous and Mixed-Integer Nonlinear Programming; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zabinsky, Z.B. Stochastic Adaptive Search for Global Optimization; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Neumaier, A. Complete search in continuous global optimization and constraint satisfaction. In Acta Numerica 2004; Iserles, A., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004; pp. 271–369, preprint; Available online: https://arnold-neumaier.at/papers.html#glopt03 (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Liberti, L.; Maculan, N. (Eds.) Global Optimization—From Theory to Implementation; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhigljavsky, A.; Žilinskas, A. Stochastic Global Optimization; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix, E.M.T.; G-Tóth, B. Introduction to Nonlinear and Global Optimization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Weise, T. Global Optimization Algorithms—Theory and Application. Published by the Author. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/200622167_Global_Optimization_Algorithm_Theory_and_Application (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Schäffler, S. Global Optimization—A Stochastic Approach; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Locatelli, M.; Schoen, F. Global Optimization: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sergeyev, Y.D.; Strongin, R.G.; Lera, D. Introduction to Global Optimization Exploiting Space-Filling Curves; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Paulavičius, R.; Žilinskas, J. Simplicial Global Optimization; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sergeyev, Y.D.; Kvasov, D.E. Deterministic Global Optimization—An Introduction to the Diagonal Approach; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Stripinis, L.; Paulavičius, R. Derivative-Free DIRECT-Type Global Optimization—Applications and Software; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, O. Basic Concepts of Global Optimization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, I.; Kampas, F.J.; Pintér, J.D. Solving circle packing problems by global optimization: Numerical results and industrial applications. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 191, 786–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, E. Packomania. 2025. Available online: http://www.packomania.com/ (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Kampas, F.J.; Pintér, J.D.; Castillo, I. Model development and solver demonstrations in class using randomized test problems. Oper. Res. Forum 2023, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankratov, A.; Romanova, T.; Litvinchev, I. Packing oblique 3D objects. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duriagina, Z.; Pankratov, A.; Romanova, T.; Litvinchev, I.; Bennell, J.; Lemishka, I.; Maximov, S. Optimized packing titanium alloy powder particles. Computation 2023, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, I.; Pintér, J.D.; Kampas, F.J. The boundary-to-boundary p-dispersion configuration problem with oval objects. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2024, 75, 2327–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyan, Y.; Yaskov, G.; Romanova, T.; Litvinchev, I.; Velarde Cantú, J.M.; Acosta, M.L. Packing spheres into a minimum-height parabolic container. Axioms 2024, 13, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, G. Solving Non-Standard Packing Problems by Global Optimization and Heuristics; Springer Briefs in Optimization; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fasano, G.; Pintér, J.D. (Eds.) Optimized Packings with Applications; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hochbaum, D. Complexity and algorithms for nonlinear optimization problems. Ann. Oper. Res. 2007, 153, 257–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiena, S.S. The Algorithm Design Manual, 2nd ed.; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, S.; Barak, B. Computational Complexity: A Modern Approach; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Heineman, G.T.; Pollice, G.; Selkow, S. Algorithms in a Nutshell, 2nd ed.; O’Reilly Media: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pardalos, P.M.; Du, D.-Z.; Graham, R.L. (Eds.) Handbook of Combinatorial Optimization, 2nd ed.; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Martí, R.; Pardalos, P.M.; Resende, M.G.C. (Eds.) Handbook of Heuristics; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mittelmann, H.D. Decision Tree for Optimization Software. 2025. Available online: https://plato.asu.edu/guide.html (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Mittelmann, H.D. Benchmarking optimization software—A (hi)story. Oper. Res. Forum 2020, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, L.C.W.; Szegö, G.P. (Eds.) Towards Global Optimisation; Elsevier North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1975; Volumes 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Hock, W.; Schittkowski, K. Test Examples for Nonlinear Programming Codes; Lecture Notes in Economics and Mathematical Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; Volume 187. [Google Scholar]
- Schittkowski, K. More Test Examples for Nonlinear Programming; Lecture Notes in Economics and Mathematical Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987; Volume 182. [Google Scholar]
- Schittkowski, K. An Updated Set of 306 Test Problems for Nonlinear Programming with Validated Optimal Solutions—User’s Guide; Research Report; Department of Computer Science, University of Bayreuth: Bayreuth, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, P.; Jaumard, B.; Lu, S.-H. Global optimization of univariate Lipschitz functions: II. New algorithms and computational comparison. Math. Program. 1992, 55, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floudas, C.A.; Pardalos, P.M.; Adjiman, C.S.; Esposito, W.R.; Gümüş, Z.H.; Harding, S.T.; Klepeis, J.L.; Meyer, C.A.; Schweiger, C.A. Handbook of Test Problems in Local and Global Optimization; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Casado, L.G.; Martínez, J.A.; García, I.; Sergeyev, Y.D. New interval analysis support functions using gradient information in a global minimization algorithm. J. Glob. Optim. 2003, 25, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Khompatraporn, C.; Zabinsky, Z.B. A numerical evaluation of several stochastic algorithms on selected continuous global optimization test problems. J. Glob. Optim. 2005, 31, 635–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumaier, A.; Shcherbina, O.; Huyer, W.; Vinkó, T. A comparison of complete global optimization solvers. Math. Program. Ser. B 2005, 103, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Yang, X.S. A literature survey of benchmark functions for global optimisation problems. Int. J. Math. Model. Numer. Optim. 2013, 4, 150–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, L.M.; Sahinidis, N.V. Derivative-free optimization: A review of algorithms and comparison of software implementations. J. Glob. Optim. 2013, 56, 1247–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, N.I.M.; Orban, D.; Toint, P.L. CUTEst: A constrained and unconstrained testing environment with safe threads for mathematical optimization. Comput. Optim. Appl. 2015, 60, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audet, C.; Hare, W. Derivative-Free and Blackbox Optimization; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Beiranvand, V.; Hare, W.; Lucet, Y. Best practices for comparing optimization algorithms. Optim. Eng. 2017, 18, 815–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoen, F. A wide class of test functions for global optimization. J. Glob. Optim. 1993, 3, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathar, R.; Žilinskas, A. A class of test functions for global optimization. J. Glob. Optim. 1994, 5, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaviano, M.; Kvasov, D.E.; Lera, D.; Sergeyev, Y.D. Software for generation of classes of test functions with known local and global minima for global optimization. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 2003, 29, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, B.; Locatelli, M. A new class of test functions for global optimization. J. Glob. Optim. 2007, 38, 479–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.J.; Qu, B.Y.; Suganthan, P.N.; Hernández-Díaz, A.G. Problem Definitions and Evaluation Criteria for the CEC 2013 Special Session on Real-Parameter Optimization; Technical Report 201212.34; Computational Intelligence Laboratory, Zhengzhou University: Zhengzhou, China; Nanyang Technological University: Singapore, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Free Software Foundation (1988–2025). GCC, the GNU Compiler Collection. © Free Software Foundation, Inc. Available online: https://gcc.gnu.org/ (accessed on 28 October 2025).
- Fourer, R.; Gay, D.M.; Kernighan, B.W. AMPL—A Modeling Language for Mathematical Programming, 2nd ed.; Duxbury-Thomson: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 2003; Available online: https://ampl.com/resources/books/ampl-book/ (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- AMPL Optimization AMPL. 2025. Available online: https://ampl.com (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Brooke, A.; Kendrick, D.; Meeraus, A. GAMS: A User’s Guide; The Scientific Press: Redwood City, CA, USA, 1988; Available online: www.gams.com (accessed on 28 October 2025).
- GAMS Development Corporation. GAMS (The General Algebraic Modeling Language). 2025. Available online: https://www.gams.com/products/gams/gams-language/ (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Schrage, L. Optimization Modeling with LINGO. 2002. Available online: https://www.lindo.com/downloads/Lingo_Textbook_5thEdition.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- LINDO Systems. LINGO—Optimization Modeling Software for Linear, Nonlinear, and Integer Programming. 2025. Available online: https://www.lindo.com/index.php/products/lingo-and-optimization-modeling (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Vanderbei, R.J. Benchmarks for Nonlinear Optimization. 2025. Available online: https://vanderbei.princeton.edu/bench.html (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Frontline Systems. Premium Solver Platform. 2025. Available online: https://www.solver.com/premium-solver-platform (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Neumann, J. The mathematician. In Works of the Mind; Heywood, R.B., Ed.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1947; pp. 180–196. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pintér, J.D. Composite Test Functions for Benchmarking Nonlinear Optimization Software. Mathematics 2025, 13, 3524. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13213524
Pintér JD. Composite Test Functions for Benchmarking Nonlinear Optimization Software. Mathematics. 2025; 13(21):3524. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13213524
Chicago/Turabian StylePintér, János D. 2025. "Composite Test Functions for Benchmarking Nonlinear Optimization Software" Mathematics 13, no. 21: 3524. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13213524
APA StylePintér, J. D. (2025). Composite Test Functions for Benchmarking Nonlinear Optimization Software. Mathematics, 13(21), 3524. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13213524








