An Algorithm for Finding Approximate Symbolic Pole/Zero Expressions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Algorithm
- Starting from a SPICE–like netlist [7], the symbolic state matrix, which contains all parameters as symbols, is written. The numerical values of the poles are then calculated as eigenvalues of the state matrix, where the entries are replaced with their respective parameter values.
- The symbolic parameters , …, , are selected in order of decreasing relative differential sensitivities of the modulus with respect to :their number M is set by the user. For a complex pole, the sensitivity of the phase, defined similarly, is also used. Any other choice of the set of symbolic parameters may be adopted, depending on the specific design problem.
- Attempts to simplify the circuit equations by replacing a circuit element with parameter by an open circuit are made; these attempts are performed for all non-symbolic parameters, in the increasing order of the moduli. An attempt is validated if , where is computed with (3), being the value with the above simplification, and is user-defined. The new form of the symbolic state matrix is generated after each successful attempt.
- Attempts to simplify circuit equations, replacing a circuit element with parameter by a short circuit are made; these attempts are performed for all non-symbolic parameters, in the increasing order of the moduli. An attempt is validated if , where is computed with (3), being the value with the above simplification, and is user-defined. The new form of the symbolic state matrix is generated after each successful attempt.
- Attempts to cut an as-large-as-possible group of the same index rows and columns are made, the remaining matrix having as an eigenvalue. Each attempt is validated if , where is computed with (3), being the value with the above simplification, and is user-defined. A reduced-order symbolic state matrix is generated after each successful attempt. If this matrix has order 1 or 2, the expression can be found straightforwardly.
- The symbolic LR iterations are performed using a simplified matrix from steps three to five. These iterations stop if , where is calculated using (3), is the numerical value of the symbolic expression of the modulus obtained after that iteration, and is user-defined. For complex eigenvalues, a similar phase error is used along with the modulus error. The user-defined simplification error during the LR iterations is . Attempts to cut groups of the same index rows and columns, as in step 5, are made after each LR iteration.
| Algorithm 1. Symbolic Pole/Zero Extraction for a pole |
| Read the SPICE–like netlist Generate the symbolic and the numeric state matrix A Calculate the numerical values of the poles as eigenvalues of A Select symbolic parameters , …, in the decreasing order of The circuit equations are simplified: for , by open-circuit if validate simplification else reject simplification end if end for for , by short-circuit if validate simplification else reject simplification end if end for for , cut row and column of the same index if validate cut try another cut else reject cut try another cut end if end for The symbolic pole is obtained: if = else if and are else symbolic LR iterations are performed end if |
3. Application Cases
3.1. Wide-Band Amplifier
3.2. Band-Stop Filter
4. Discussion
- -
- The elimination of all terms containing a circuit parameter in is more or less equivalent to the replacement of the corresponding circuit element by an open circuit or by a short circuit.
- -
- The controlled cutting of some row–column pairs and the convergent LR iterations performed on moderate-complexity matrices are efficient procedures, having no correspondence in the Analog Insydes algorithm, which simplifies the symbolic expression “hoping that it will become” a first- or second-order polynomial in s [2].
- -
- The numerical value of the targeted p/z modified by a simplification attempt is computed by a fast iterative method in the Analog Insydes algorithm. At the same time, a more time-consuming standard procedure for eigenvalue computation is employed in the proposed algorithm for this purpose.
- -
- -
- The computation of two poles, followed by the short-circuit replacement of two capacitors, etc. [1], is a technique that can be used for some exceptional cases only, similar to the pole splitting, unlike the LR iterations and the associated techniques in our algorithm.
- -
- While in [1] a capacitor can be replaced by a short circuit only, our algorithm may replace any circuit element by a short circuit or an open circuit (which, in general, leads to less significant modifications of the p/z values—see the computation of p6 in our example).
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| p/z | pole/zero |
| SAG | simplification after generation |
| PR | proposed algorithm |
| AI | Analog Insydes |
| OA | operational amplifier |
| MNA | modified nodal analysis |
| ACO | ant colony optimization |
| PSR | power supply rejection |
| LDO | low-dropout regulator |
| SoC | system-on-chip |
References
- Guerra, O.; Rodriguez-Garcia, J.D.; Fernandez, F.V.; Rodriguez-Vazquez, A. A symbolic pole/zero extraction methodology based on analysis of circuit time-constants. Analog. Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2002, 31, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, E. Symbolic Approximation and Modeling Techniques for Analysis and Design of Analog Circuits. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Kaiserslautern, Kaiserslautern, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, F.V.; Sánchez-López, C.; Castro-López, R.; Roca-Moreno, E. Symbolic Pole/Zero Analysis. In Design of Analog Circuits through Symbolic Analysis; Fakhfakh, M., Tlelo-Cuautle, E., Fernández, F.V., Eds.; Bentham Books: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2012; pp. 287–304. [Google Scholar]
- Nebel, G.; Kleine, U.; Pfleiderer, H. Symbolic pole/zero calculation using SANTAFE. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1995, 30, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analog Insydes. Available online: https://www.itwm.fraunhofer.de/en/departments/sys/products-and-services/analog-insydes.html (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Constantinescu, F.; Nițescu, M.; Marin, C.V. Computation of approximate symbolic pole/zero expressions. Analog. Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2004, 40, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghe, A.G.; Constantinescu, F. Pole/zero computation for linear circuits. In Proceedings of the 6th European Symposium on Computer Modeling and Simulation, Valletta, Malta, 14–16 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sanberg, I.W.; So, H.C. A two-sets-of-eigenvalues approach to the computer analysis of linear systems. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 1969, 16, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, E.J. On the calculation of zeros of a linear constant system. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 1971, 18, 183–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghe, A.G.; Constantinescu, F.; Nițescu, M. Improved LR Algorithm for Computation of the Approximate Symbolic Pole/Zero Expressions. In Proceedings of the AFRICON 2013, Pointe aux Piments, Mauritius, 9–12 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cristea, P.D.; Tuduce, R. State equations of circuits with excess elements—Revisited. Rev. Roum. Sci. Techn. Electrotechn. Et Energ. 2011, 56, 219–228. [Google Scholar]
- Marin, M.E.; Staicu, C.S.; Gheorghe, A.G.; Constantinescu, F. Generation of State Equations for Circuits with Excess Elements. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Symposium on Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering (ISFEE), Bucharest, Romania, 5–7 November 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Gheorghe, A.G.; Marin, M.E.; Bortosu, C.G. Approximate Symbolic Pole/Zero Expressions of a Band-stop Filter. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Scientific Conference Electronics (ET), Sozopol, Bulgaria, 13–15 September 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shokouhifar, M.; Jalali, A. Automatic symbolic simplification of analog circuits in MATLAB using ant colony optimization. In Proceedings of the 22nd Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE 2014), Tehran, Iran, 20–22 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Behmanesh-Fard, N.; Yazdanjouei, H.; Shokouhifar, M.; Werner, F. Mathematical Circuit Root Simplification Using an Ensemble Heuristic–Metaheuristic Algorithm. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Sommer, R. Modeling of Low-dropout Regulator to Optimize Power Supply Rejection in System-on-Chip Applications. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Synthesis, Modeling, Analysis and Simulation Methods and Applications to Circuit Design (SMACD), Lausanne, Switzerland, 15–18 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gatermann, C.; Sommer, R. Teaching the MOSFET: A Circuit Designer’s View. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Synthesis, Modeling, Analysis and Simulation Methods and Applications to Circuit Design (SMACD), Villasimius Sardinia, Italy, 12–15 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gheorghe, A.G.; Constantinescu, F.; Marin, M.E. Symbolic Formulas for Settling Time and Phase Margin of Op-Amp with Arbitrary Number of Poles and Zeros. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Scientific Conference Electronics (ET), Sozopol, Bulgaria, 13–15 September 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gheorghe, A.G.; Marin, M.E.; Bortosu, C.G. Symbolic Expression of Damping Factor and Damping Resistance of Passive High-Pass LCL Filters. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Symposium ELMAR, Zadar, Croatia, 16–18 September 2024; pp. 277–281. [Google Scholar]



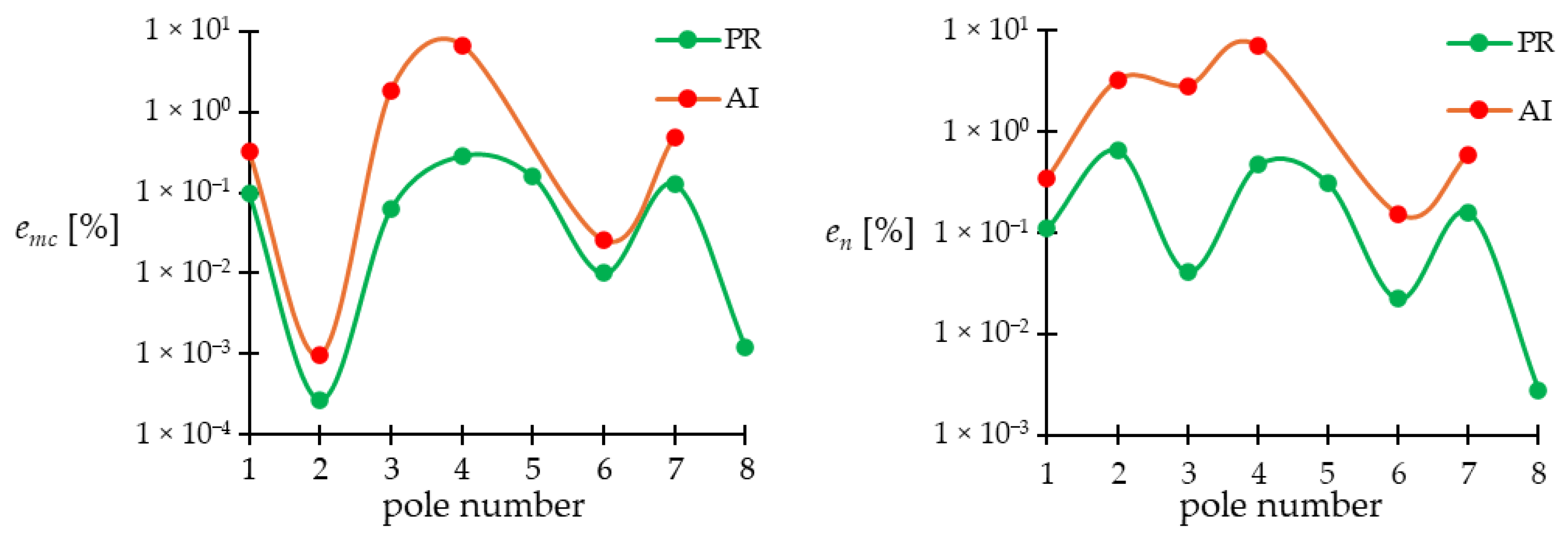






| Pole | Parameters/ Sensitivities | Alg. | emc [%] | en [%] | eMc [%] | eac [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p1 | C1, R1, R6/ 1.00, 0.85, 0.15 | PR | 1.0 × 10−1 | 1.1 × 10−1 | 1.2 × 10−1 | 1.1 × 10−1 |
| AI | 3.2 × 10−1 | 3.4 × 10−1 | 3.7 × 10−1 | 3.4 × 10−1 | ||
| p2 | C2, Rbe3, F2, R5, R3, R4, R2, F3, R6, R1, RE3/ 1.03, 0.83, 0.72, 0.72, 0.72, 0.66, 0.65, 0.52, 0.37, 0.35, 0.20 | PR | 2.7 × 10−4 | 6.6 × 10−1 | 5.5 | 1.34 |
| AI | 9.9 × 10−4 | 3.2 | 9.5 | 2.92 | ||
| p3 | Cbe2, Rbe2/ 1.04, 1.03 | PR | 6.3 × 10−2 | 4.1 × 10−2 | 2.0 × 10−1 | 1.3 × 10−1 |
| AI | 1.81 | 2.81 | 4.21 | 2.86 | ||
| p4 | Cbe1, Rbe1, F1, R5, R1/ 0.98, 0.98, 0.92, 0.38, 0.30 | PR | 0.29 | 0.47 | 0.78 | 0.51 |
| AI | 6.69 | 6.94 | 7.34 | 6.99 | ||
| p5 | Cbe3, RE3, Rbe3, F3/ 0.98, 0.80, 0.20, 0.19 | PR | 0.16 | 0.31 | 0.44 | 0.28 |
| AI | - | - | - | - | ||
| p6 | Cbc1, R5, Rce1, R2, R1, R6/ 0.98, 0.29, 0.28, 0.14, 0.13, 0.13 | PR | 1.0 × 10−2 | 2.2 × 10−2 | 3.7 × 10−2 | 2.1 × 10−2 |
| AI | 2.6 × 10−2 | 1.5 × 10−1 | 4.5 | 1.66 | ||
| p7 | Cbc2, R3, Rce2/ 0.99, 0.97, 0.01 | PR | 1.3 × 10−1 | 1.6 × 10−1 | 1.8 × 10−1 | 1.6 × 10−1 |
| AI | 4.9 × 10−1 | 5.9 × 10−1 | 6.8 × 10−1 | 5.8 × 10−1 | ||
| p8 | Cbc3, RE2/ 1.00, 0.99 | PR | 1.2 × 10−3 | 2.8 × 10−3 | 4.8 × 10−3 | 2.6 × 10−3 |
| AI | - | - | - | - |
| Zero | Parameters/ Sensitivities | Alg. | emc [%] | en [%] | eMc [%] | eac [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z2 | R6, F2/ 0.57, 0.57 | PR | 8.6 × 10−1 | 8.1 × 10−1 | 2.48 | 1.44 |
| AI | - | - | - | - | ||
| z3 | Cbe2, Rbe2, F2, R6, C2, R5, R2, R4, Rbe3, F3/ 0.62, 0.62, 0.44, 0.44, 0.43, 0.42, 0.39, 0.39, 0.35, 0.35 | PR | 3.09 | 4.95 | 8.79 | 5.32 |
| AI | - | - | - | - | ||
| z4 | Cbe1, Rbe1, F1/ 1.01, 1.01, 0.99 | PR | 4.0 × 10−2 | 6.9 × 10−1 | 5.6 × 10−1 | 3.6 × 10−1 |
| AI | 1.8 × 10−1 | 9.0 × 10−1 | 1.22 | 8.3 × 10−1 | ||
| z5 | Cbe3, RE3, Rbe3, F3/ 0.98, 0.80, 0.20, 0.19 | PR | 1.17 | 1.54 | 1.88 | 1.53 |
| AI | - | - | - | - | ||
| z6 | Cbc1, R2/ 1.00, 0.84 | PR | 4.7 × 10−6 | 7.6 × 10−6 | 1.2 × 10−5 | 8.0 × 10−6 |
| AI | 4.7 × 10−6 | 7.6 × 10−6 | 1.2 × 10−5 | 8.0 × 10−6 | ||
| z7 | RE2, Cbc2, Cbc3/ 1.00, 0.50, 0.50 | PR | 4.9 × 10−3 | 7.4 × 10−3 | 1.0 × 10−2 | 7.4 × 10−3 |
| AI | 9.5 × 10−3 | 1.4 × 10−2 | 1.9 × 10−2 | 1.4 × 10−2 |
| Pole | Alg. | Symbolic Expression | ens [%] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p1 | PR | 0.1 | |||
| AI | 0.3 | ||||
| p2 | PR | or | 1.0 | ||
| AI | 3.2 | ||||
| p3 | PR | 2.8 | |||
| AI | 2.8 | ||||
| p4 | PR | or | 0.87 | ||
| AI | 8.87 | ||||
| p5 | PR | 1.54 | |||
| AI | - | - | |||
| p6 | PR | 0.74 | |||
| AI | 10 | ||||
| p7 | PR | or | 1.8 1.2 | ||
| AI | or | 1.8 0.6 | |||
| p8 | PR | 0.3 | |||
| AI | - | - | |||
| Zero | Alg. | Symbolic Expression | ens [%] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z2 | PR | 3.03 | |||
| AI | - | - | |||
| z3 | PR | 6.5 | |||
| AI | - | - | |||
| z4 | PR | 0.07 | |||
| AI | 0.9 | ||||
| z5 | PR | or | 1.5 | ||
| AI | - | - | |||
| z6 | PR | 0.7 | |||
| AI | 0.7 | ||||
| z7 | PR | 7 × 10−3 | |||
| AI | 1 × 10−2 | ||||
| Pole | Parameters/Sensitivities | Alg. | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p2, p3 | R5, C2, F2, Cbe2, Rbe2, R3, R4, R2, RE3, R1, R6, Rbe3, F3/ 0.58, 0.58, 0.57, 0.57, 0.57, 0.56, 0.53, 0.53, 0.38, 0.29, 0.29, 0.20, 0.20 | PR | 1.34 | 1.75 | 2.35 | 1.79 |
| Pole | Parameters/Sensitivities | Alg. | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p2, p3 | R5, C2, F2, Cbe2, Rbe2, R3, R4, R2, RE3, R1, R6, Rbe3, F3/ 0.58, 0.58, 0.57, 0.57, 0.57, 0.56, 0.53, 0.53, 0.38, 0.29, 0.29, 0.20, 0.20 | PR | 9.79 × 10−5 | 0.127 | 0.497 | 0.157 |
| Pole | Alg. | Symbolic Expression | [%] | [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p2, p3 | PR | 1.61 | 0.127 |
| Pole | Parameters/Sensitivities | Alg. | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p2 | F2, F3, F1, Rbe1/ 1.68, 0.99, 2.91 × 10−2, 1.23 × 10−2 | PR | 3.48 | 4.01 | 5.12 | 4.08 |
| p3 | F2, F3, Rbe1, F1/ 0.75, 0.45, 1.28 × 10−2, 5.65 × 10−3 | PR | 0.08 | 0.23 | 1.27 | 0.44 |
| Pole | Alg. | Symbolic Expression | ens [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| p2 p3 | PR | 4.054 0.248 |
| Pole | Parameters/Sensitivities | Alg. | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p2, p3 | F2, F3, F1, Rbe1/ 2.52, 1.42, 2.78 × 10−2, 2.73 × 10−2 | PR | 1.18 | 3.48 | 2.84 | 1.87 |
| Pole | Parameters/Sensitivities | Alg. | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p2, p3 | F2, F3, F1, Rbe1/ 2.52, 1.42, 2.78 × 10−2, 2.73 × 10−2 | PR | 0.000 | 0.997 | 1.958 | 0.718 |
| Pole | Alg. | Symbolic Expression | [%] | [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p2 p3 | PR | 3.51 | 0.99 |
| Pole | PR [ω] | HSPICE [ω] |
|---|---|---|
| p1 | −3.138 × 103 + 5.446 × 103 I | −3.138 × 103 + 5.446 × 103 I |
| p2 | −3.138 × 103 − 5.446 × 103 I | −3.138 × 103 − 5.446 × 103 I |
| p3 | −6.295 × 103 + 0.000 I | −6.295 × 103 + 0.000 I |
| p4 | −6.270 × 106 + 0.000 I | −6.270 × 106 + 0.000 I |
| p5 | −3.135 × 106 + 5.441 × 106 I | −3.135 × 106 + 5.441 × 106 I |
| p6 | −3.135 × 106 − 5.441 × 106 I | −3.135 × 106 − 5.441 × 106 I |
| Zero | PR [ω] | HSPICE [ω] |
|---|---|---|
| z1, z3, z5 | 0.000 + 1.987 × 105 I | 1.818 × 101 + 1.986 × 105 I |
| z2, z4, z6 | 0.000 − 1.987 × 105 I | 1.818 × 101 − 1.986 × 105 I |
| Pole | Symbolic Expressions |
|---|---|
| p1 | |
| p2 | |
| p3 | |
| p4 | |
| p5 | |
| p6 |
| Zero | Symbolic Expressions |
|---|---|
| z1, z3, z5 | |
| z2, z4, z6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gheorghe, A.G.; Constantinescu, F. An Algorithm for Finding Approximate Symbolic Pole/Zero Expressions. Mathematics 2025, 13, 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13203314
Gheorghe AG, Constantinescu F. An Algorithm for Finding Approximate Symbolic Pole/Zero Expressions. Mathematics. 2025; 13(20):3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13203314
Chicago/Turabian StyleGheorghe, Alexandru Gabriel, and Florin Constantinescu. 2025. "An Algorithm for Finding Approximate Symbolic Pole/Zero Expressions" Mathematics 13, no. 20: 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13203314
APA StyleGheorghe, A. G., & Constantinescu, F. (2025). An Algorithm for Finding Approximate Symbolic Pole/Zero Expressions. Mathematics, 13(20), 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13203314





