Information Perception Adaptive Filtering Algorithm Sensitive to Signal Statistics: Theory and Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- By combining an asymmetric loss function with an information perception strategy, we propose a novel AF algorithm, termed the IPAF algorithm.
- (2)
- We provide a detailed performance analysis of the IPAF algorithm, including convergence analysis, mean square deviation analysis, and computational complexity analysis.
- (3)
- We validate the effectiveness of the proposed information perception strategy. The IPAF algorithm is compared with other robust algorithms under four different environments—Gaussian inputs, non-Gaussian inputs with symmetric noise, and asymmetric noise—demonstrating its superior performance.
- (4)
- We further validate the performance of the proposed algorithm on real datasets.
| (·)T α β |·| E[·] λmax I R ||·|| Tr(·) | Transpose operator Skewness mapping parameters Kernel mapping parameters Absolute value operator Mathematical expectation operator Largest eigenvalue of a matrix Identity matrix Autocorrelation matrix Euclidean norm of a vector Trace of a matrix |
2. Algorithm Design
| Algorithm 1. Algorithm summary |
| Initialization: for i = 1,2 … |
| Parameter update: |
| end |
3. Algorithm Performance Analysis
3.1. Convergence Analysis
3.2. Mean Squared Deviation Analysis
3.3. Computational Complexity
4. Simulation Results
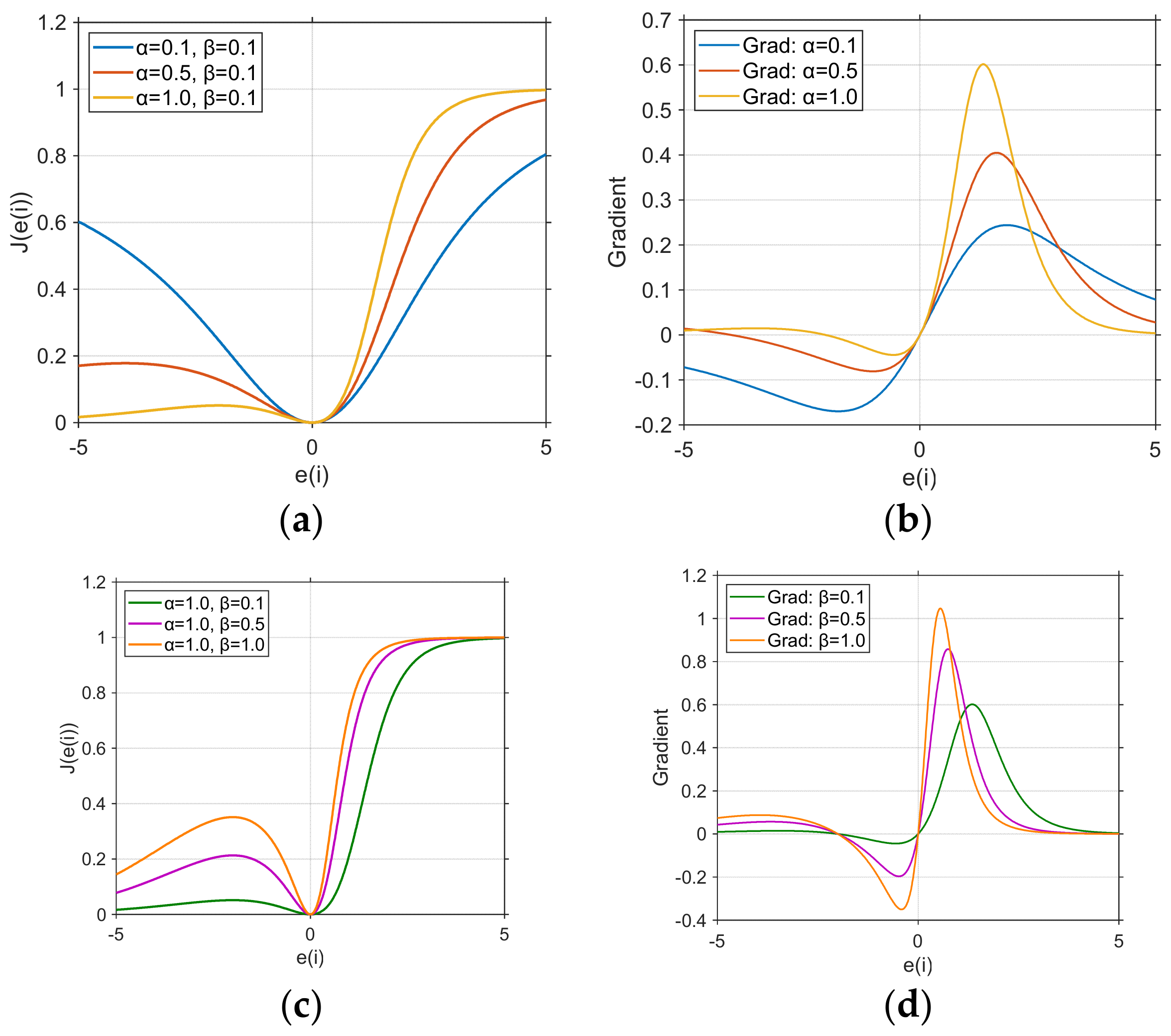
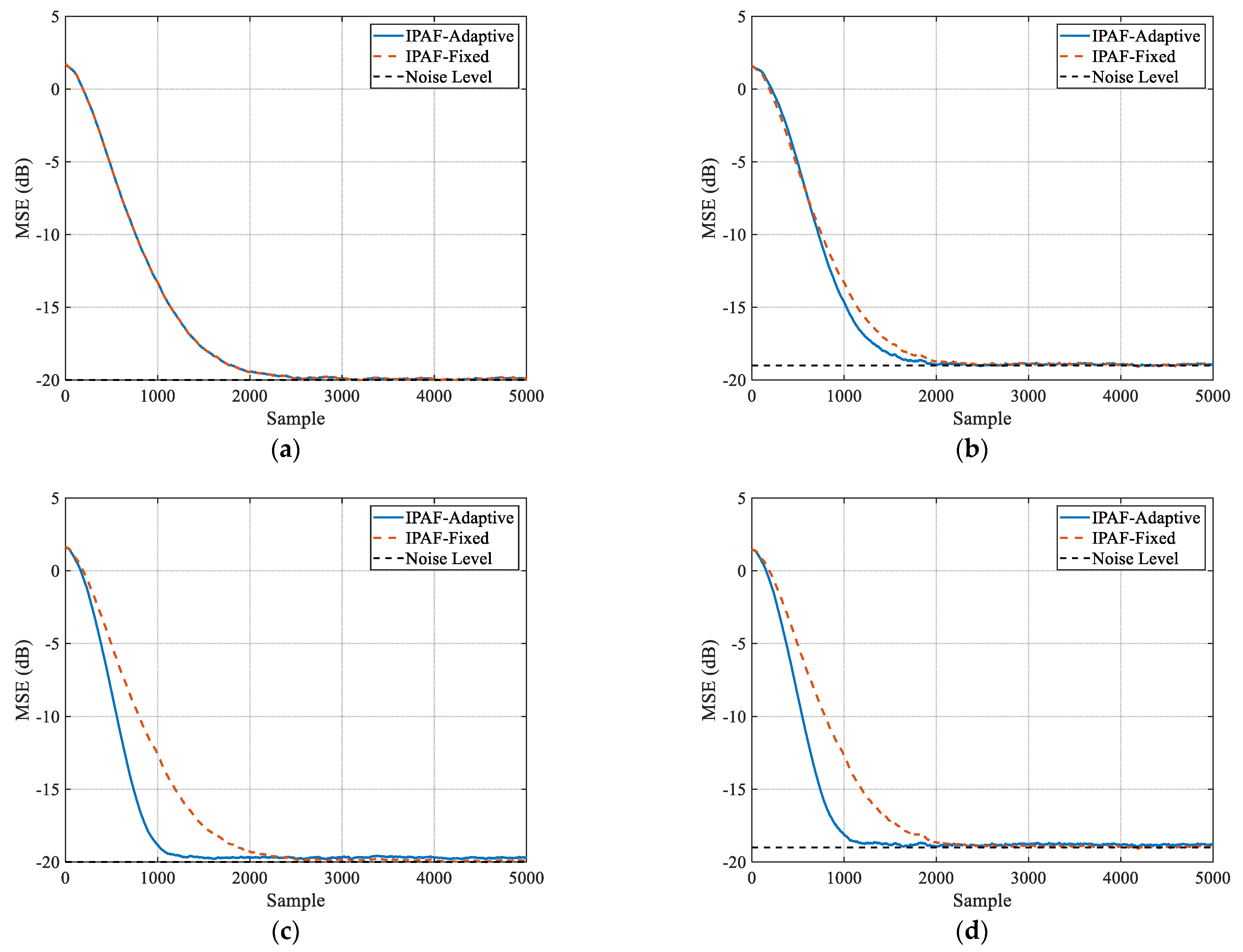
4.1. Impact of Information-Perception Strategy
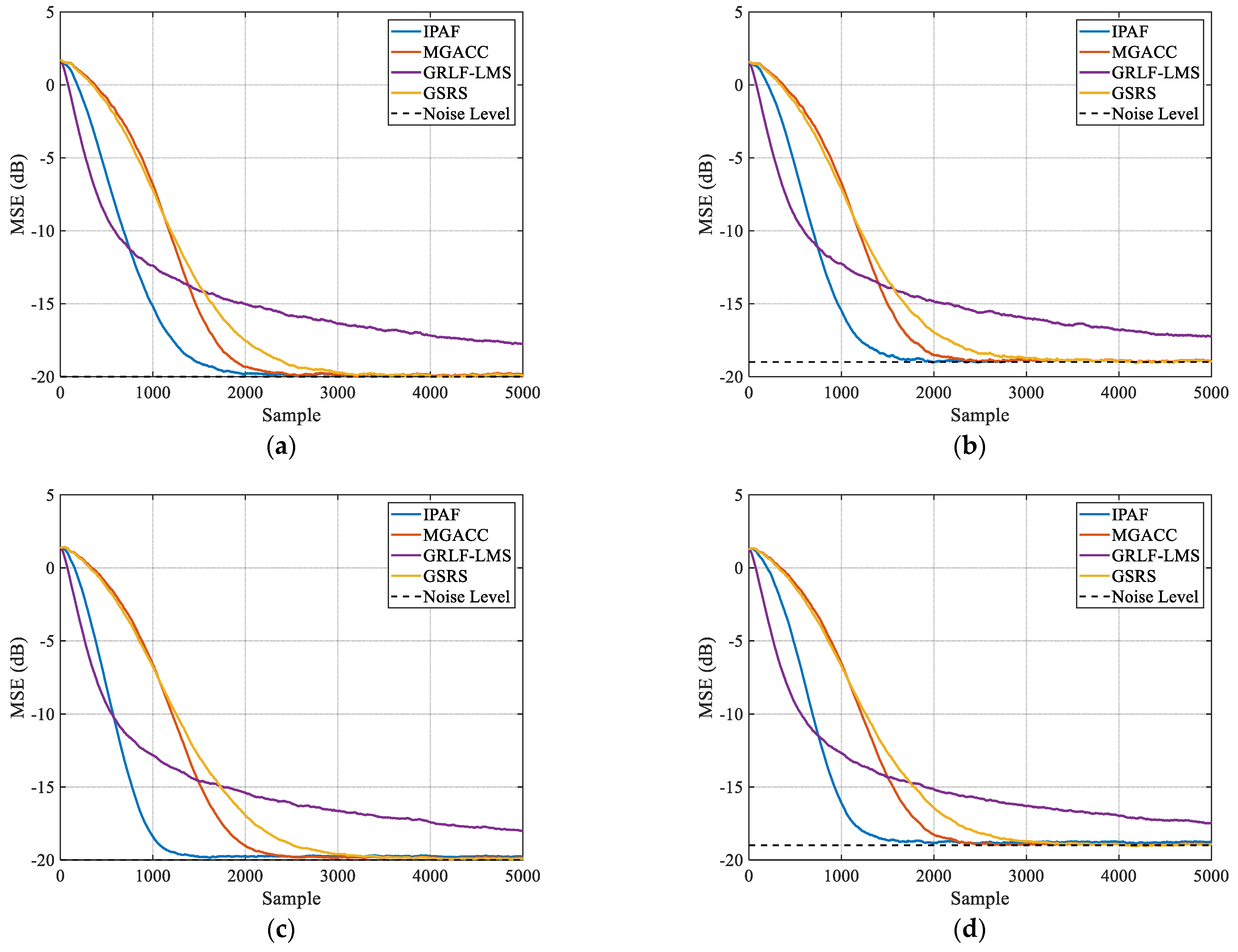
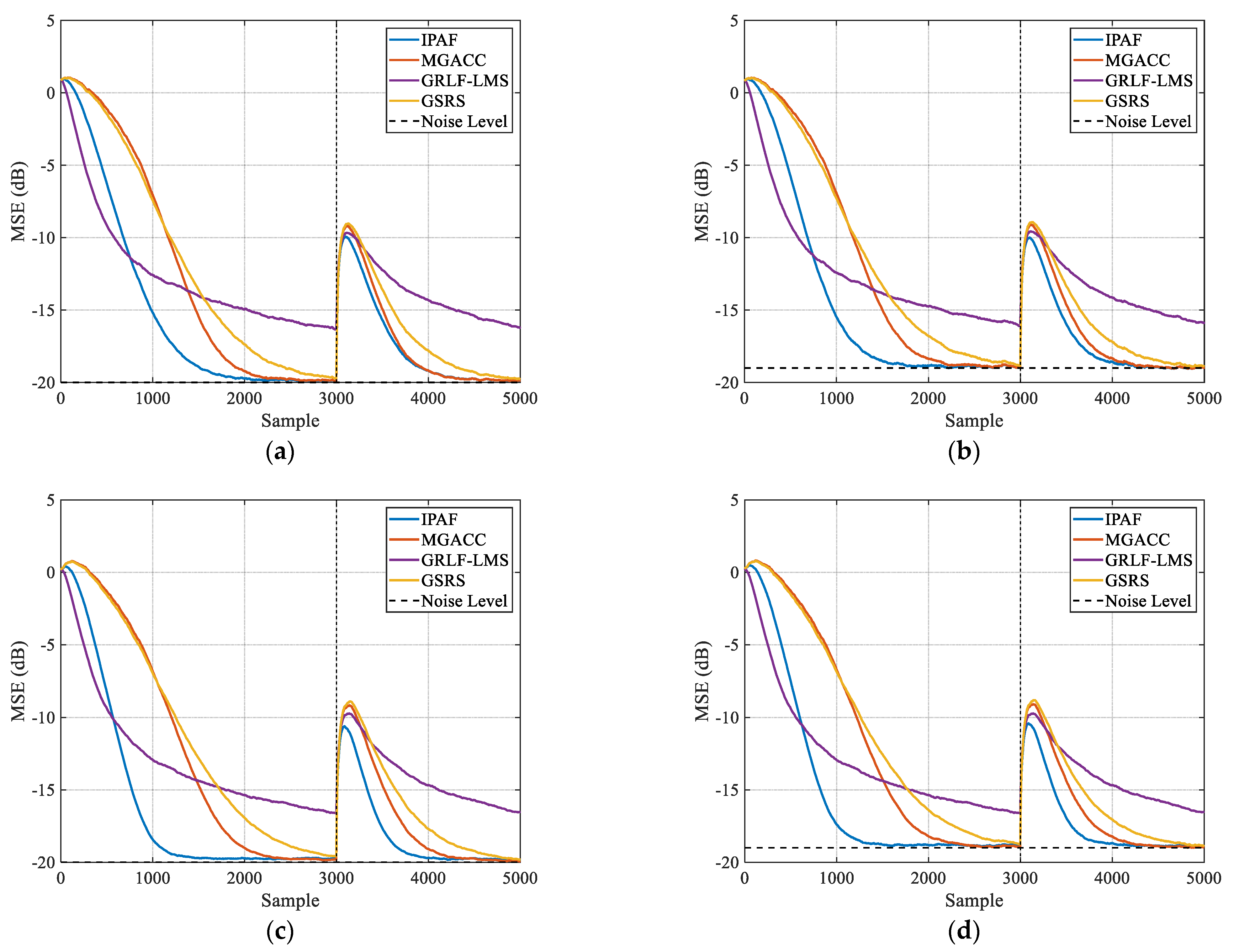
4.2. Algorithm Performance Comparison
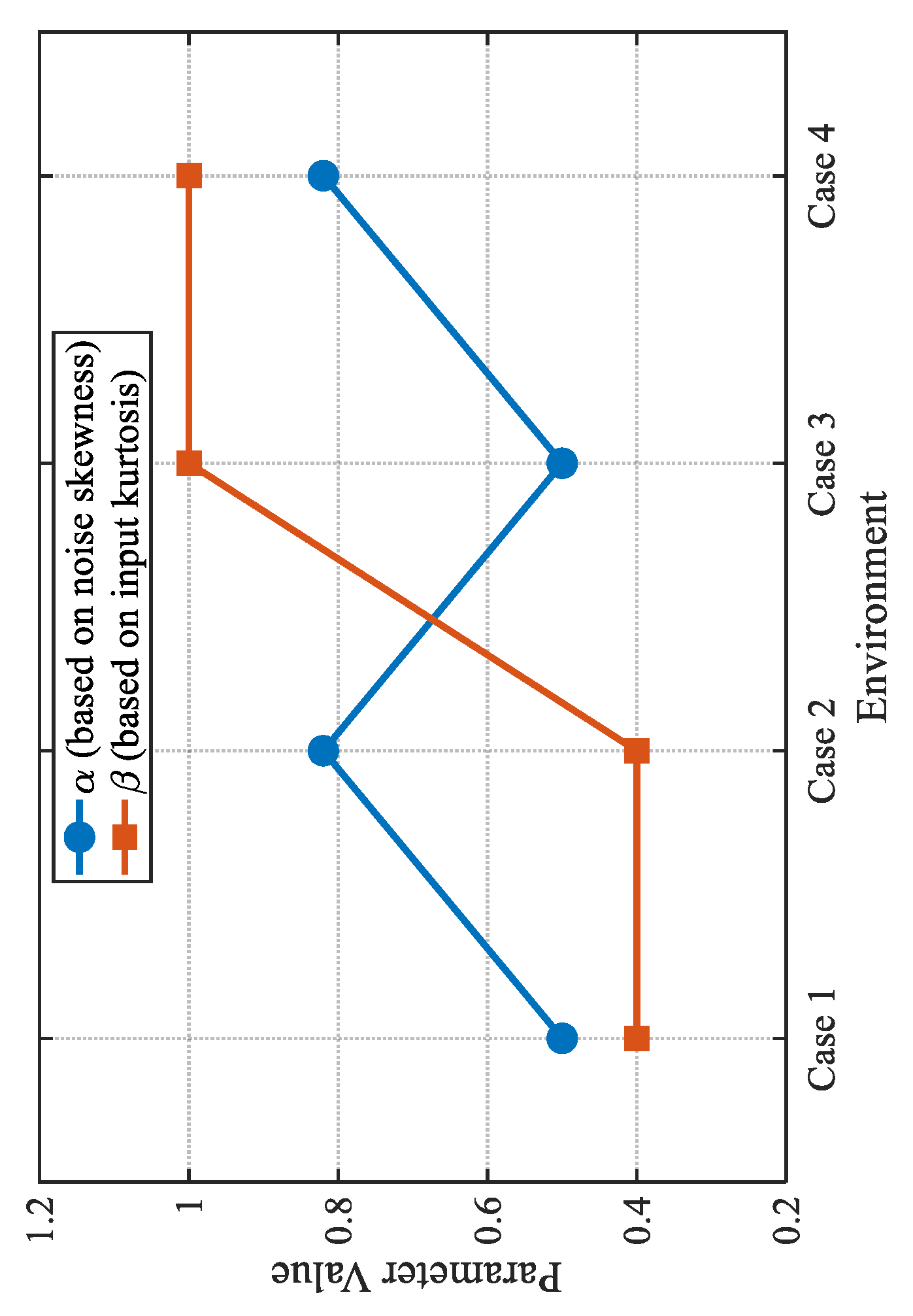
4.2.1. Case 1
4.2.2. Case 2
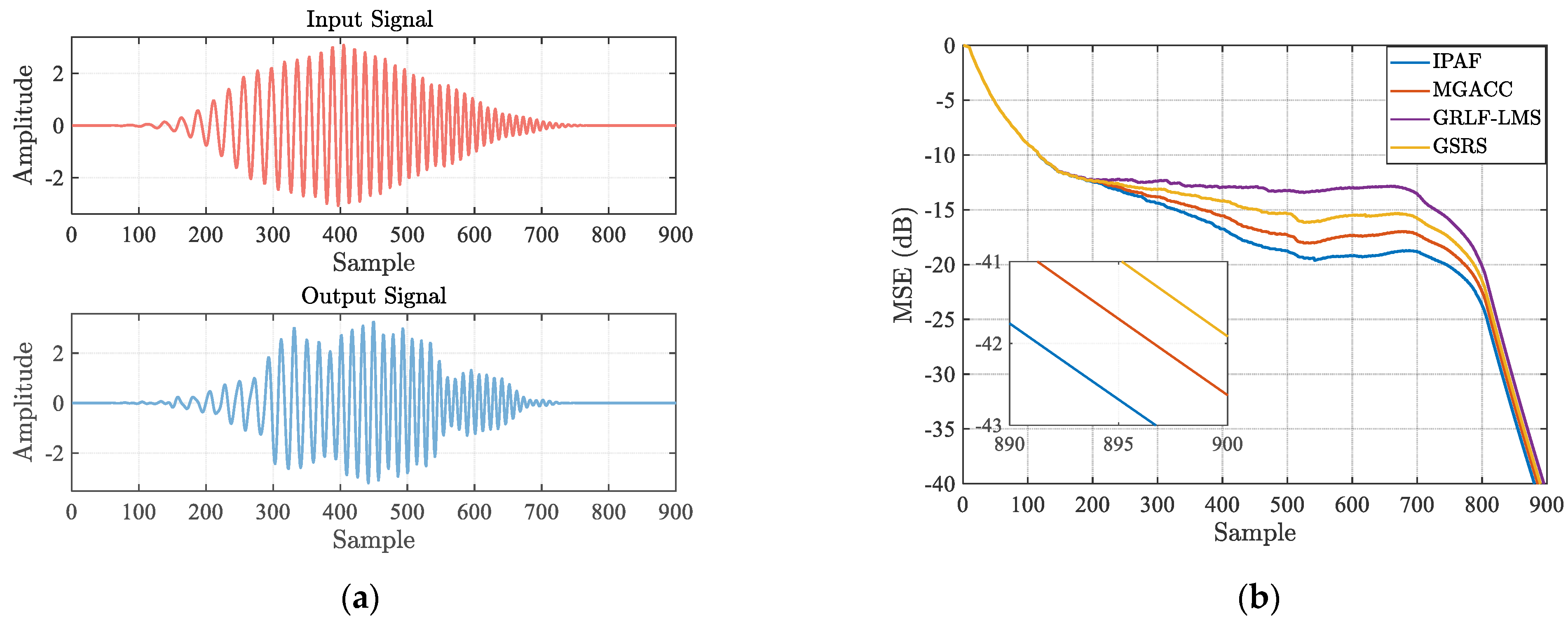
4.3. Daisy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balassa, B.E.; Nagy, N.G.; Gyurian, N. Perception and social acceptance of 5G technology for sustainability development. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 467, 142964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonci, A.; Cen Cheng, P.D.; Indri, M.; Nabissi, G.; Sibona, F. Human-robot perception in industrial environments: A survey. Sensors 2021, 21, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lu, W.; Yi, F.; Liu, M. Passive sensing using multiple types of communication signal waveforms for Internet of Everything. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 29295–29307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Zeng, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Qiu, W. Research on the construction of information perception technology methods and models for global strategic mineral resources. China Min. Mag. 2025, 34, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Peng, B. Maximum total generalized correntropy adaptive filtering for parameter estimation. Signal Process. 2023, 203, 108787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-D. Modern Signal Processing; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG: Berlin, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ding, F. Adaptive parameter estimation for a general dynamical system with unknown states. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2020, 30, 1351–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, X. Iterative identification methods for a class of bilinear systems by using the particle filtering technique. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2021, 35, 2056–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ding, F. Optimal adaptive filtering algorithm by using the fractional-order derivative. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2021, 29, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, V.M. Learning Management System (LMS) use with online instruction. Int. J. Technol. Educ. 2021, 4, 68–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, N.S. The impact of AI and LMS integration on the future of higher education: Opportunities, challenges, and strategies for transformation. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H. Robust hybrid affine projection filtering algorithm under α-stable environment. Signal Process. 2023, 208, 108981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J. Affine projection algorithms based on sigmoid cost function. Signal Process. 2024, 219, 109397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleologu, C.; Benesty, J.; Ciochină, S. Data-reuse recursive least-squares algorithms. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Chen, J.; Richard, C. Theoretical analysis of the performance of the data-reuse RLS algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2023, 71, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Q.; Ikbal, M.A.; Kumar, P. Optimized LMS algorithm for system identification and noise cancellation. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 30, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, A.; Aljojo, N.; Zainol, A.; Alshutayri, A.; Alharbi, B.; Aldhahri, E.; Khairullah, E.F.; Almandeel, S. Identification of critical factors affecting the students’ acceptance of Learning Management System (LMS) in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Innov. 2021, 9, 353–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerguine, A.; Ahmad, J.; Moinuddin, M.; Al-Saggaf, U.M.; Zoubir, A.M. An efficient normalized LMS algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 110, 3561–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, X. Variable step-size LMS algorithm based on hyperbolic tangent function. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 42, 4415–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Biswal, B. Spline adaptive filtering algorithm based on different iterative gradients: Performance analysis and comparison. J. Autom. Intell. 2023, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.C. Hierarchical learning-based cascaded adaptive filtering for nonlinear system identification. Digit. Signal Process. 2025, 160, 105031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhao, C.; Gao, Z.; Yan, D. Low-Complexity Constrained Recursive Kernel Risk-Sensitive Loss Algorithm. Symmetry 2022, 14, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Wang, B.; Zhu, B.; Zhu, Y. An improved proportional normalization least mean p-power algorithm for adaptive filtering. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 42, 6951–6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, J. Affine projection algorithm based on least mean fourth algorithm for system identification. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 11930–11938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Xiong, K.; Iu, H.H.; Tse, C.K. Logarithmic hyperbolic cosine adaptive filter and its performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 51, 2512–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Li, Y.; Zakharov, Y.V.; Xue, W.; Qi, J. Constrained least lncosh adaptive filtering algorithm. Signal Process. 2021, 183, 108044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Cheng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Biswal, B. Diffusion adaptive filtering algorithm based on the Fair cost function. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Pandey, R.; Bora, S.S.; George, N.V. A robust family of algorithms for adaptive filtering based on the arctangent framework. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 69, 1967–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S. A family of robust adaptive filtering algorithms based on sigmoid cost. Signal Process. 2018, 149, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrhman, O.M.; Sen, L. Robust adaptive filtering algorithms based on the half–quadratic criterion. Signal Process. 2023, 202, 108775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrhman, O.M.; Dou, Y.; Li, S. A generalized robust logarithmic family-based adaptive filtering algorithms. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2023, 70, 3199–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Bhattacharjee, S.S.; Christensen, M.G. Generalized soft-root-sign based robust sparsity-aware adaptive filters. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2023, 30, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Hou, Z.; Fu, S.; Tian, Y. Robust two-stage instance-level cost-sensitive learning method for class imbalance problem. Knowl. Based Syst. 2024, 300, 112143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, X. Geometric algebra correntropy: Definition and application to robust adaptive filtering. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2019, 67, 1164–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoukens, M.; Noël, J.P. Wiener-Hammerstein Process Noise System. Available online: https://www.nonlinearbenchmark.org/benchmarks/wiener-hammerstein-process-noise (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Database for the Identification of Systems. Available online: http://homes.esat.kuleuven.be/~smc/daisy/ (accessed on 12 October 2025).

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yun, S.; Guan, S.; Zhao, Y.; Xiang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Biswal, B. Information Perception Adaptive Filtering Algorithm Sensitive to Signal Statistics: Theory and Design. Mathematics 2025, 13, 3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13203294
Yun S, Guan S, Zhao Y, Xiang Q, Zhang C, Biswal B. Information Perception Adaptive Filtering Algorithm Sensitive to Signal Statistics: Theory and Design. Mathematics. 2025; 13(20):3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13203294
Chicago/Turabian StyleYun, Shiwei, Sihai Guan, Yong Zhao, Qiang Xiang, Chuanwu Zhang, and Bharat Biswal. 2025. "Information Perception Adaptive Filtering Algorithm Sensitive to Signal Statistics: Theory and Design" Mathematics 13, no. 20: 3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13203294
APA StyleYun, S., Guan, S., Zhao, Y., Xiang, Q., Zhang, C., & Biswal, B. (2025). Information Perception Adaptive Filtering Algorithm Sensitive to Signal Statistics: Theory and Design. Mathematics, 13(20), 3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13203294






