Context-Aware Dynamic Integration for Scene Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
Highlights of the Proposed Study
- Dynamic Multimodal Integration: Introduces a dynamic switch network that adaptively fuses image features with extensive text-based object descriptors from the Recognize-Anything Model (RAM), enabling context-aware weighting for improved scene recognition accuracy.
- Enhanced Semantic Understanding: Leverages RAM’s rich and diverse object tagging (over 4500 categories) combined with the CLIP text encoder to capture comprehensive semantic relationships, surpassing traditional approaches limited by smaller category sets.
- Versatility and Robust Performance: Demonstrates consistent and superior accuracy across multiple challenging benchmarks (MIT Indoor 67, Places365, SUN397) with both CNN-based and Vision Transformer-based backbones, validating the method’s adaptability and effectiveness.
2. Related Works
2.1. Semantic-Aware Scene Recognition (SASceneNet)
2.2. Fusion of Object and Scene Network (FOSNet)
2.3. Multiple Representation Network (MRNet)
2.4. Recognize-Anything Model (RAM)
2.5. Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP)
2.6. Dynamic Switch Networks
2.7. Recent Surveys and Comprehensive Approaches
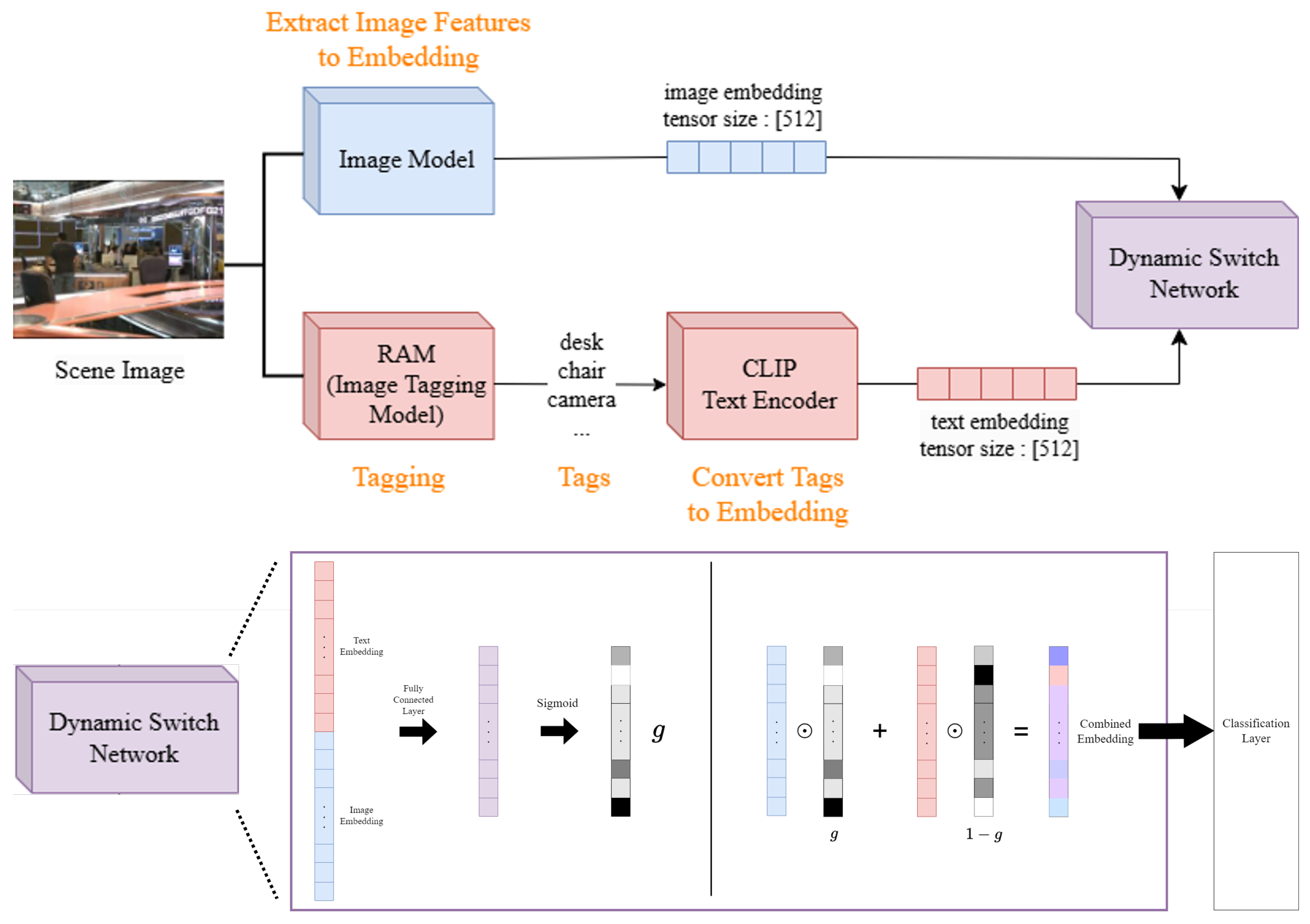
3. Methods
3.1. Overall Architecture
3.2. Dataset
3.2.1. MIT Indoor 67
3.2.2. Places365
3.2.3. SUN397
4. Results
4.1. Performance Evaluation
4.2. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
4.3. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thapa, A.; Horanont, T.; Neupane, B.; Aryal, J. Deep learning for remote sensing image scene classification: A review and meta-analysis. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Liao, M.; Tavakolian, M.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, B.; Hu, D.; Pietikäinen, M.; Liu, L. Deep learning for scene classification: A survey. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.10531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matei, A.; Glavan, A.; Talavera, E. Deep learning for scene recognition from visual data: A survey. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Hybrid Artificial Intelligence Systems, Gijón, Spain, 11–13 November 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 763–773. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Lee, F.; Xie, L.; Cai, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, Q. Scene recognition using multiple representation network. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 118, 108530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, W.; Baek, S.; Baek, J.; Shin, W.; Gwak, M.; Park, P.; Lee, S. Reinforced Intelligence Through Active Interaction in Real World: A Survey on Embodied AI. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2025, 23, 1597–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Mei, X.; Li, W.; Hong, L.; Sun, B.; Li, H. Scene complexity: A new perspective on understanding the scene semantics of remote sensing and designing image-adaptive convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattoni, A.; Torralba, A. Recognizing indoor scenes. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2019; pp. 413–420. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, D.; Zhou, B.; Khosla, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Network dissection: Quantifying interpretability of deep visual representations. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6541–6549. [Google Scholar]
- López-Cifuentes, A.; Escudero-Viñolo, M.; Bescós, J.; García-Martín, A. Semantic-aware scene recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 102, 107256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, H.; Hyun, J.; Kim, E. FOSNet: An end-to-end trainable deep neural network for scene recognition. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 82066–82077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herranz, L.; Jiang, S.; Li, X. Scene recognition with cnns: Objects, scales and dataset bias. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las VEgas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 571–579. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Lu, J.; Feng, J.; Yuan, B.; Zhou, J. Scene recognition with objectness. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 74, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, L.; Wu, X.; Tian, Z.; Peng, B.; Zhao, H.; Jia, J. GroupContrast: Semantic-aware Self-supervised Representation Learning for 3D Understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Naseer, A.; Alnusayri, M.; Alhasson, H.F.; Alatiyyah, M.; AlHammadi, D.A.; Jalal, A.; Park, J. Multimodal scene recognition using semantic segmentation and deep learning integration. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2025, 11, e2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Yan, G.W.; Jiang, J.W.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Song, B. Construction of a multiscale feature fusion model for indoor scene recognition. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deevi, P.K.; Lee, C.; Gan, L.; Nagesh, S.; Pandey, G.; Chung, S.J. RGB-X Object Detection via Scene-Specific Fusion Modules. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Alazeb, A.; Chughtai, B.R.; Al Mudawi, N.; AlQahtani, Y.; Alonazi, M.; Aljuaid, H.; Jalal, A.; Liu, H. Remote intelligent perception system for multi-object detection and scene recognition. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1398703. [Google Scholar]
- Rafique, A.A.; Ghadi, Y.Y.; Alsuhibany, S.A.; Chelloug, S.A.; Jalal, A.; Park, J. CNN Based Multi-Object Segmentation and Feature Fusion for Scene Classification. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2022, 73, 4657–4675. [Google Scholar]
- Du, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhao, K.; Wu, G. Translate-to-Recognize Networks for RGB-D Scene Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Jo, Y.; Hong, I.; Park, S. MRNet: Multifaceted Resilient Networks for Medical Image-Text Retrieval. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.03039. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Luo, Z.; Xie, Y.; Qin, Y.; Luo, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2024 Workshop, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024.
- Zhang, Y. Recognize-Anything: Open-Source and Strong Foundation Model for Image Tagging. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/xinyu1205/recognize-anything (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Pan, X.; Ye, T.; Han, D.; Song, S.; Huang, G. Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training with Knowledge Graphs. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.08901. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, S.; Hebbar, R.; Somandepalli, K.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Y.; Cole-McLaughlin, K.; Wang, H.; Narayanan, S. MovieCLIP: Visual Scene Recognition in Movies. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Elhenawy, M.; Ashqar, H.I.; Rakotonirainy, A.; Alhadidi, T.I.; Jaber, A.; Tami, M.A. Vision-Language Models for Autonomous Driving: CLIP-Based Dynamic Scene Understanding. Electronics 2025, 14, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Y. CLIP4STR: A Simple Baseline for Scene Text Recognition with Pre-trained Vision-Language Model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.14014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Qi, L.; Geng, X. CILP-FGDI: Exploiting Vision-Language Model for Fine-Grained Domain Identification. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.16065. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, W.; Yu, Y.; Li, L. Towards making the most of bert in neural machine translation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 9378–9385. [Google Scholar]
- Cenk Eser, M.; Medeiros, E.S.; Riza, M.; Engel, M. Dynamic link switching induces stable synchronized states in sparse networks. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.08007. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, S.; Lv, Z.; Zaydi, N.H.; Ibrar, M.; Hu, X. DSMLB: Dynamic switch-migration based load balancing for multicontroller SDN in IoT. Comput. Netw. 2022, 214, 109145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Kenett, Y.N.; Cui, Z.; Takeuchi, H.; Fink, A.; Benedek, M.; Zeitlen, D.C.; Zhuang, K.; Lloyd-Cox, J.; Kawashima, R.; et al. Dynamic switching between brain networks predicts cognitive performance. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Lee, F.; Liu, L.; Kotani, K.; Chen, Q. Scene recognition: A comprehensive survey. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 102, 107205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Meng, G.; Pan, C. Scene text detection and recognition with advances in deep learning: A survey. Int. J. Doc. Anal. Recognit. 2019, 22, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumathi, K.; Kumar, P.; Mahadevaswamy, H.R.; Ujwala, B.S. Optimizing multimodal scene recognition through relevant feature fusion and transfer learning. MethodsX 2025, 14, 103226. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Lapedriza, A.; Khosla, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Places: A 10 million image database for scene recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Hays, J.; Ehinger, K.A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Sun database: Large-scale scene recognition from abbey to zoo. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 3485–3492. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Ramanan, D. Multi-scale recognition with DAG-CNNs. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1215–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Chen, G.; Song, X.; Liu, L. Deep patch representations with shared codebook for scene classification. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. (TOMM) 2019, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.S.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yan, S.; Liu, C.L. Hybrid CNN and dictionary-based models for scene recognition and domain adaptation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2015, 27, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Huang, W.; Wang, L.; Qiao, Y. Locally supervised deep hybrid model for scene recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 26, 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Chen, W.; Wassell, I. Dictionary learning inspired deep network for scene recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Qiao, Y. Weakly supervised patchnets: Describing and aggregating local patches for scene recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 2028–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Tang, H.; An, S. Coordinate CNNs and LSTMs to categorize scene images with multi-views and multi-levels of abstraction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 120, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Larson, M. From volcano to toyshop: Adaptive discriminative region discovery for scene recognition. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 1760–1768. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Xia, Y.; Shen, D. Foreground fisher vector: Encoding class-relevant foreground to improve image classification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 4716–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, M.; Li, Y.; Vasconcelos, N. Semantic fisher scores for task transfer: Using objects to classify scenes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 42, 3102–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | Backbone | MIT Indoor 67 Top 1 Accuracy (%) | SUN397 Top 1 Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DAG-CNN [39] | VGG | 77.50 | 56.20 |
| Mix-CNN [40] | VGG | 79.63 | 57.47 |
| Hybrid CNNs [41] | VGG | 82.24 | 64.53 |
| LS-DHM [42] | VGG | 83.75 | 67.56 |
| Multiscale CNNs [12] | VGG | 86.04 | 70.17 |
| Dual CNN-DL [43] | VGG | 86.43 | 70.13 |
| VSAD [44] | VGG | 86.20 | 73.00 |
| SDO [13] | VGG | 86.76 | 73.41 |
| MVML-LSTM [45] | VGG | 80.52 | 63.02 |
| Adi-Red [46] | ResNet 50 | - | 73.59 |
| fgFV [47] | ResNet 50 | 85.35 | - |
| MFAFSNet [48] | ResNet 50 | 88.06 | 73.35 |
| SASceneNet [10] | ResNet 50 | 87.10 | 74.04 |
| MRNet [4] | ResNet 50 | 88.08 | 73.98 |
| Ours | ResNet 50 | 89.28 | 75.18 |
| Swin-Tiny Accuracy (%) | Swin-Tiny + Ours Accuracy (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| MIT Indoor 67 | 80.66 | 85.98 |
| Places365 | 54.81 | 57.39 |
| SUN397 | 63.14 | 66.15 |
| Module | MIT Indoor 67 Top 1 Accuracy (%) | SUN397 Top 1 Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Image Model | 84.40 | 70.87 |
| Text Model | 79.54 | 61.26 |
| Proposed Method (Image + Text) | 89.28 | 75.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, C.H.; Ahn, S. Context-Aware Dynamic Integration for Scene Recognition. Mathematics 2025, 13, 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13193102
Bae CH, Ahn S. Context-Aware Dynamic Integration for Scene Recognition. Mathematics. 2025; 13(19):3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13193102
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Chan Ho, and Sangtae Ahn. 2025. "Context-Aware Dynamic Integration for Scene Recognition" Mathematics 13, no. 19: 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13193102
APA StyleBae, C. H., & Ahn, S. (2025). Context-Aware Dynamic Integration for Scene Recognition. Mathematics, 13(19), 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13193102





