Abstract
Generative adversarial networks (GANs)-based image deep learning methods are useful to improve object visibility in nighttime driving environments, but they often fail to preserve critical road information like traffic light colors and vehicle lighting. This paper proposes a method to address this by utilizing both unpaired and four-channel paired training modules. The unpaired module performs the primary night-to-day conversion, while the paired module, enhanced with a fourth channel, focuses on preserving road details. Our key contribution is an inverse road light attention (RLA) map, which acts as this fourth channel to explicitly guide the network’s learning. This map also facilitates a final cross-blending process, synthesizing the results from both modules to maximize their respective advantages. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach more accurately preserves lane markings and traffic light colors. Furthermore, quantitative analysis confirms that our method achieves superior performance across eight no-reference image quality metrics compared to existing techniques.
Keywords:
cycle-consistent generative adversarial network (CycleGAN); four-channel paired training; L-channel; road light attention mask MSC:
68T45
1. Introduction
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) have gained significant attention in the field of computer vision for generating new data and have been widely applied across diverse industries [1]. Among these GAN-based models, pix2pix, a conditional GAN, uses paired datasets comprising input and target images to learn image-to-image translation [2]. This model can be employed for various tasks, such as image synthesis or grayscale-to-color conversion of photos to color images [3]. However, pix2pix requires paired datasets, limiting the data collection process.
Thus, cycle-consistent GAN (CycleGAN), which employs unpaired datasets, has been proposed to address this problem [4]. Due to its advantages, CycleGAN has been widely used in diverse fields [5], including medical image enhancement, photograph style transfer, and nighttime image conversion. The vision system in autonomous driving plays a crucial role in recognizing road information to enhance driving safety. Recent studies have employed CycleGAN to detect road object information in nighttime driving settings [6]. However, the visibility of essential visual elements (e.g., traffic lights and road noise), which are critical in nighttime driving, remains challenging to improve.
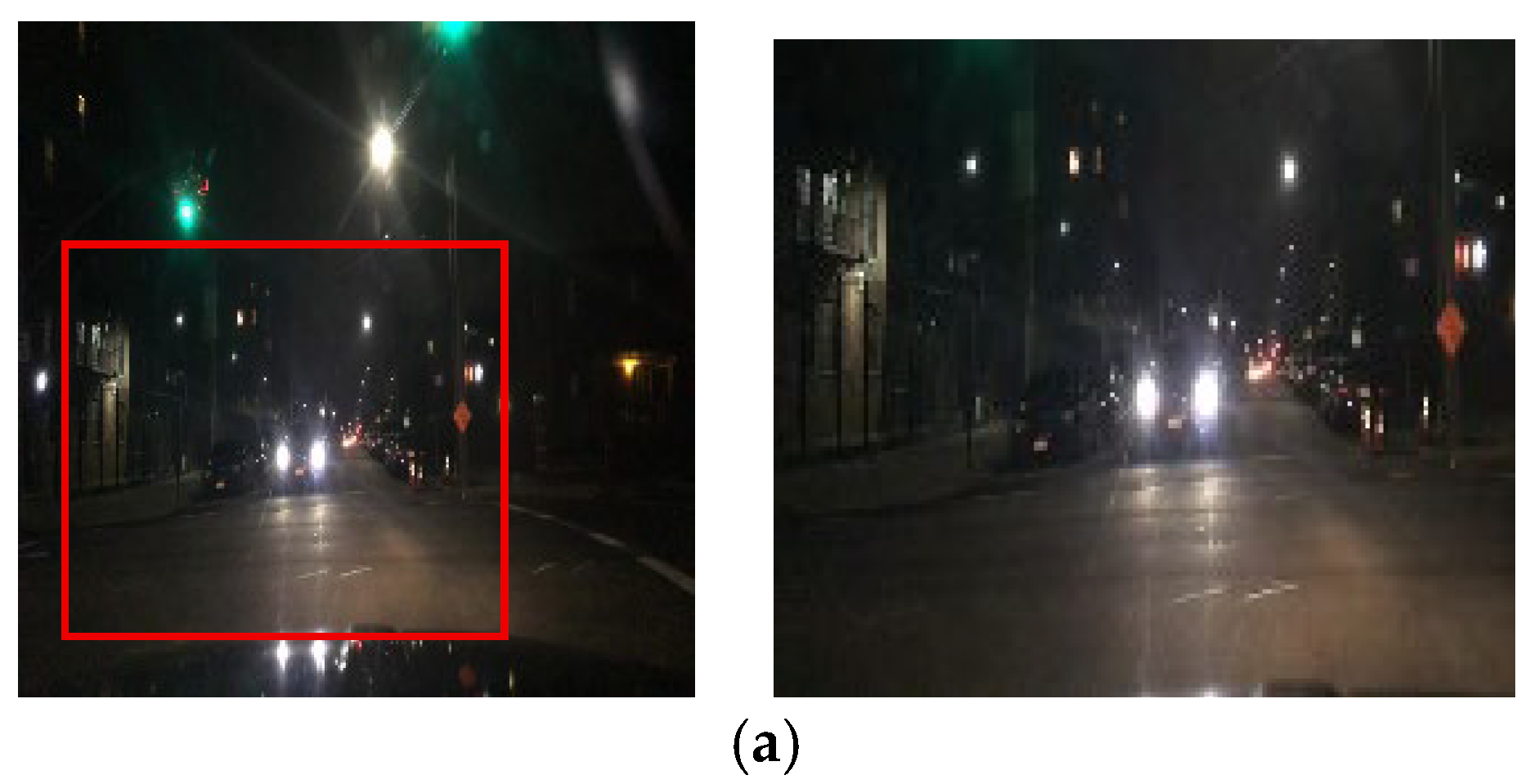
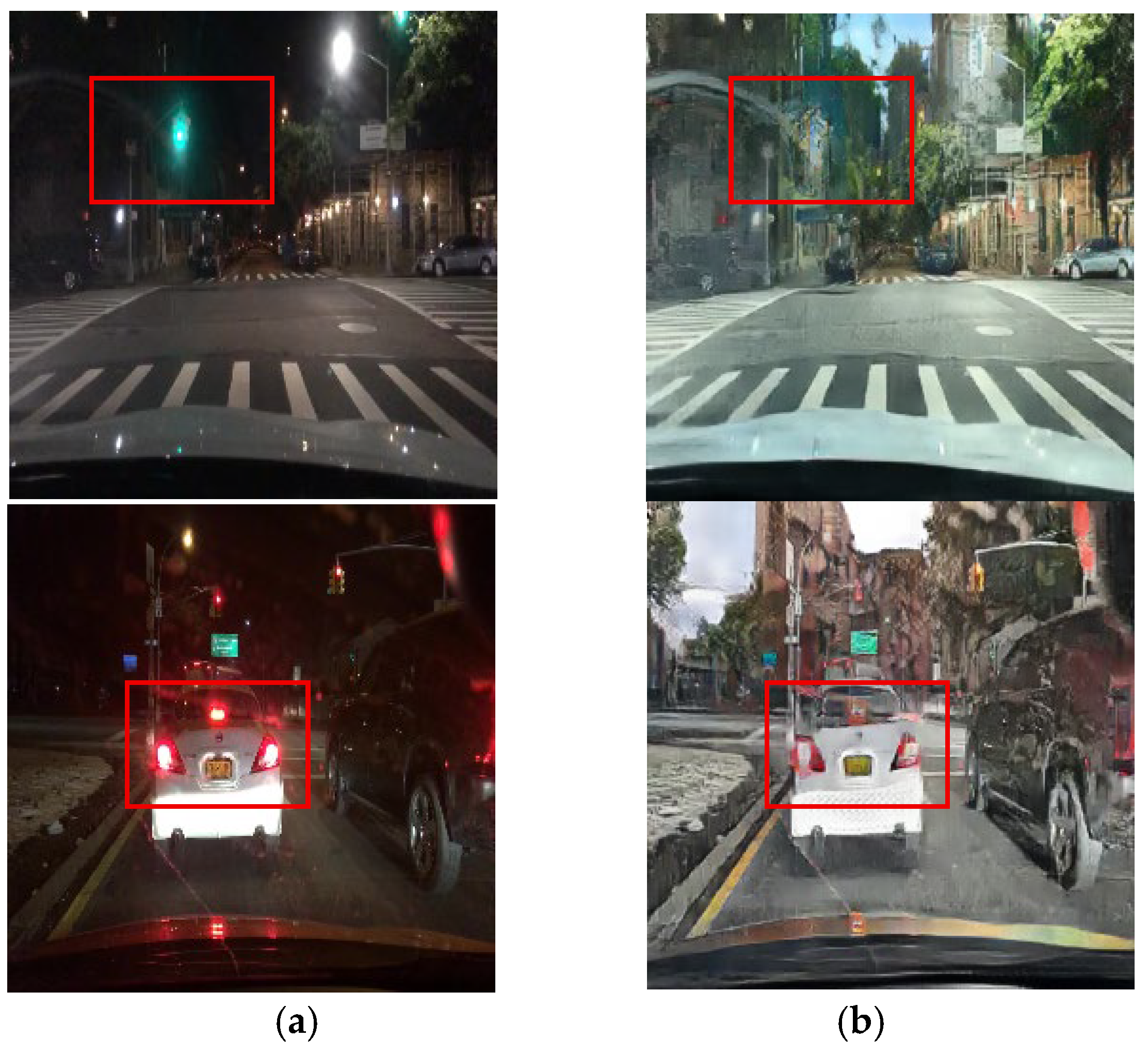
As CycleGAN learns nighttime-to-daytime image conversion using unpaired datasets, it acquires data more easily than models that employ paired datasets. However, by training on unpaired datasets, CycleGAN can convert nighttime images to daytime images but loses critical object information that a driver must recognize during driving. Figure 1 illustrates how an unpaired training module loses traffic light colors and vehicle taillight information. During image conversion, dark areas are selectively enhanced, removing light information (e.g., traffic signal lights or vehicle illumination) due to the learning process. This limitation arises because unpaired datasets are employed for training, making it difficult to specify and convert certain features, limiting the effectiveness of nighttime-to-daytime conversion. The proposed method applies the unpaired training module and supplements it with a paired training module to address this problem.
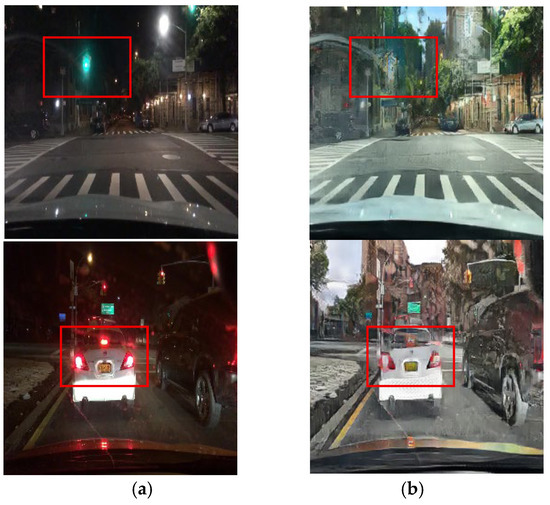
Figure 1.
Input (night images) and resulting images using the unpaired training module: (a) input images and (b) unpaired training module images.
A sufficient dataset is required to effectively train the paired learning module. Otherwise, the learning module may overfit the results to the characteristics of the limited data, leading to poor conversion performance on general images [7]. However, collecting perfectly aligned night–day image pairs in real-world conditions is challenging.
In this paper, daytime images are first processed through the unpaired module to generate synthetic nighttime counterparts, which are then paired with their original daytime images to construct a paired dataset. Additionally, a four-channel learning approach with light-road information is introduced to enhance the learning performance of the paired learning module. This paper complementarily employs the unpaired learning module and four-channel paired learning module to preserve or enhance traffic light colors, vehicle lighting, and road information when converting images from nighttime to daytime. A road light attention (RLA) map is applied to the images generated by each module to maximize their advantages, and a cross-blending technique is proposed to combine the results from the two modules.
In summary, this study makes the following contributions.
- A dual-module framework integrating an unpaired training module for global, stylistic conversion and a four-channel paired module for preserving fine details.
- An inverse road light attention (RLA) map utilized as a fourth input channel to explicitly guide the network in preserving critical luminous features like traffic lights.
- An RLA-map-based cross-blending technique to seamlessly fuse the outputs, combining natural backgrounds from the unpaired module with the detailed foregrounds from the paired module.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2 reviews studies related to image enhancement methods and image-to-image translation using learning techniques. Next, Section 3 explains the proposed method, including the CycleGAN training strategy, the application of the RLA map, and the cross-blending approach. Then, Section 4 presents the experimental results and comparative analysis. Finally, Section 5 concludes the paper and suggests directions for future research.
2. Related Work
2.1. Low-Light Surrounding Image Enhancement
Low luminance image enhancement is a technique that improves the visual quality of images, aiming to produce sharper, more natural images by adjusting the contrast and reducing color distortion in footage taken in low-light environments. High dynamic range (HDR) enhancement and tone mapping techniques are crucial methods for effectively preserving details in images where dark and bright areas coexist. The HDR enhancement processes images with a wide range of contrasts, preserving details in dark areas and preventing overexposure in bright areas. The multiexposure fusion technique is a representative method that combines several images captured with various exposure values to achieve an optimal contrast balance [8].
Additionally, the Retinex-based HDR processing technique separates lighting and reflection components to ensure color constancy while adjusting the image brightness and contrast. Approaches based on the Retinex theory reduce color distortion and enhance details, even in low-light images [9,10]. Along with HDR enhancement, tone mapping techniques are critical in converting HDR images to a range that can be represented on a typical display [11,12].
Global tone mapping adjusts the brightness range by applying the same transformation function to the entire image, offering the advantage of simplicity and low computational cost. However, tone mapping can result in excessive contrast reduction in some image regions, and local tone mapping is applied when more sophisticated adjustments are needed. Local tone mapping adjusts the local contrast of the image, allowing for more detailed control of brightness, but this can increase the computational cost due to the calculation complexity.
In addition, histogram-based methods are also widely used as image enhancement techniques [13]. For example, histogram equalization adjusts the luminance distribution of the image to improve overall contrast uniformly [14]. However, the HE technique can result in unnatural artifacts due to excessive contrast enhancement, leading to the development of contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization [15], which performs histogram equalization on localized regions of the image and applies a contrast limitation to prevent excessive contrast adjustment. Although these traditional methods have been widely used for image enhancement tasks, they have limitations in handling complex image characteristics or adapting to various image types. Learning-based approaches to overcome these limitations have recently gained attention, with ongoing research on image-to-image translation [1,2,3,4].
2.2. Image-to-Image Translation
Image-to-image translation transforms an input image into a different domain while retaining essential structural content and adapting to the target domain’s characteristics [3,4,16]. Image-to-image translation is widely employed in diverse tasks, including style transfer, image synthesis, and image segmentation [17,18]. Learning the mapping between various image domains is essential to enable image-to-image translation, and generative models are crucial for performing this task [19,20].
Generative models learn the distribution of given data and can generate new data. Representative examples of such models include GANs and variational autoencoders (VAEs) [1,2,20,21]. Further, GANs operate via a competitive learning process between two networks: the generator and discriminator. The generator creates data, whereas the discriminator determines whether the generated data are real or fake. This process enables the generation of increasingly realistic data. For example, GANs can transform a horse into a zebra or change a summer landscape into a winter landscape. In addition, VAEs approximate data distributions and can generate new data by learning the latent space of the data. For instance, VAEs can generate new images of digits by learning the MNIST dataset of handwritten numbers or produce new facial images using the CelebA dataset of faces [22].
The generative model employed in this paper, CycleGAN, learns to transform images using two domain datasets without paired images. In addition, CycleGAN comprises two generators (G and F) and two discriminators (DX and DY) to mitigate the problem of mode collapse, where the generator does not consider the input features, and all inputs are crowded into one mode [23]. The first generator (G) performs the forward transformation, converting the input image into an output image. The second generator (F) performs the reverse transformation, converting the output image back into the input image. The forward and reverse transformations apply the standard adversarial loss, represented as follows:
where denotes the generator responsible for transforming domain into domain , and represents the discriminator that distinguishes whether an image from domain is real or fake. Moreover, represents the original domain before transformation, and samples from this domain are denoted by . Similarly, indicates the target domain after transformation, and samples from this domain are denoted by . In addition, represents the expectation. The first term encourages discriminator to recognize images belonging to the real domain as real. In contrast, the second term forces discriminator to recognize the fake image , generated by from an image belonging to domain , as fake.
After passing through the generators and , the image returns to its original form, and this process is referred to as cycle consistency, which can be achieved by introducing the adversarial loss described earlier and the cycle-consistency loss. The cycle-consistency loss calculates the difference between the original image and transformed image when the generated image is converted back into the input image, using this difference as the loss value. Equation (2) represents the cycle-consistency loss:
where the first term represents the expectation of the absolute difference between the original image from domain and the result of applying the forward mapping followed by the reverse mapping . Similarly, the second term represents the expectation of the absolute difference between the original image from domain and the outcome of applying reverse mapping followed by forward mapping .
In addition, to preserve the color composition of the image, an identity loss () is used. This loss encourages the generator to be identity mapping when a real image from the target domain is provided as input. It is defined as follows:
where the first term calculates the expectation of the L1 difference between a target domain image and the output of the generator This encourages to be identity mapping when real images from its target domain are provided as input. Similarly, the second term measures the difference between an original domain image and the output , encouraging generator to also preserve the attributes of inputs from domain . This loss is particularly effective at preserving the color composition of the original image.
Equation (4) represents the final loss, combining the adversarial loss, cycle-consistency loss, and identity loss described earlier:
where denotes the combined adversarial loss, cycle-consistency loss, and identity loss of the two domains. The and are hyper-parameters that control the relative importance of the cycle-consistency and identity losses.
The main task of this study can be performed using CycleGAN. Recent research on CycleGAN has applied it to address the problem of nighttime vehicle detection [6]. A method has been proposed where a synthetic nighttime image is generated using daytime images to reduce the domain gap between daytime and nighttime environments, and this synthetic nighttime image is applied to train a nighttime vehicle detection model. This approach enables learning without nighttime data annotations, but due to the transformation limitations of CycleGAN, unrealistic lighting effects may occur, making it challenging to replicate nighttime environments perfectly. Generating synthetic nighttime images is relatively more straightforward than generating fake daytime images, but this process causes the loss of object information.
Additionally, night-to-day image translation enables improved object and location estimation in nighttime environments [24]. To this end, methods like ToDayGAN and ComboGAN have been proposed to enhance the original CycleGAN framework [25]. However, as these methods still struggle with the inherent trade-off between stylistic conversion and content preservation, the fine details of critical objects are often not adequately preserved.
Addressing this challenge of detail preservation has become a primary research direction with several key strategies emerging. One strategy focuses on enhancing the feature representation within the GAN itself using data-driven attention. For instance, the Self-Attention GAN (SAGAN) incorporates self-attention layers to capture long-range spatial dependencies, improving global coherence [26]. Another strategy involves creating hybrid models that combine generative approaches with other image enhancement theories. Recent studies have explored this by integrating principles from physical models like dehazing [27] or by using Retinex-based methods with fuzzy logic to more faithfully restore color and illumination [28]. A third direction aims to improve real-world generalization and reduce artifacts, which is crucial when training on synthetic data. To this end, recent work in related fields like image deblurring has employed meta-tuning strategies to help networks adapt to new types of real-world degradation, thereby enhancing robustness [29].
In contrast to these approaches that rely on dynamically learned attention, hybrid theories, or advanced training strategies, the method proposed in this paper introduces an explicit guidance strategy. This involves providing a pre-computed RLA map, based on domain-specific knowledge (e.g., nighttime road lighting), as an additional guidance channel to the network. The goal is to supply a strong, deterministic prior to the translation process, thereby ensuring the preservation of critical object details.
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Overview of the Proposed Method
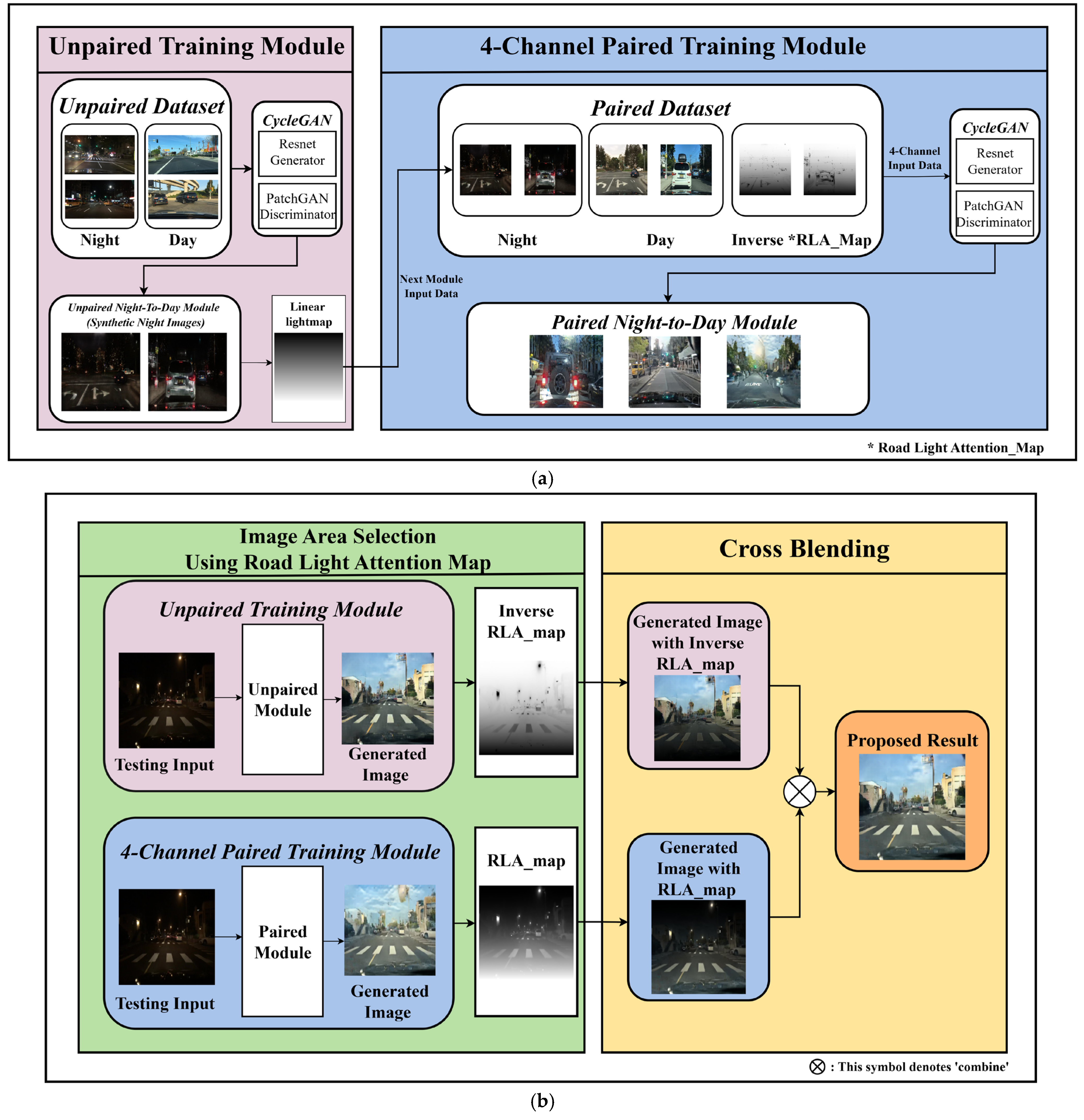
Figure 2a illustrates the training stage, which comprises an unpaired training module and a four-channel paired training module. In contrast, Figure 2b shows the image synthesis stage, where a cross-blending technique is applied to combine the results from both modules, maximizing their respective advantages to produce the final output.
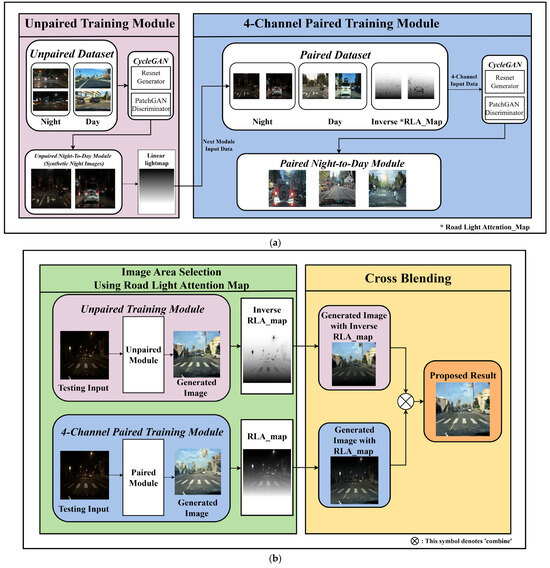
Figure 2.
Overview of the flow chart: (a) a training stage where an unpaired module generates synthetic data for a four-channel paired module and (b) an image synthesis stage where the outputs are fused using RLA-map-based cross-blending to produce the final image.
The first CycleGAN module focuses on unpaired training to generate daytime images, which effectively support night-to-day translation. However, the detailed object information that must be recognized in real driving scenarios may be lost. An additional paired training CycleGAN module, based on four-channel input, is designed to address this problem. This module was created by augmenting data and adding a light information channel. The upper area of the daytime images (generated by the unpaired training module) and the lower area of the daytime images (converted via the paired training module) were selectively blended using the RLA map to preserve road details while effectively performing nighttime-to-daytime image translation. Section 3.2 and Section 3.3 provide further details on the night-to-day image conversion training process and the image area selection and cross-blending process, respectively.
3.2. Night-to-Day Image Conversion Training Process
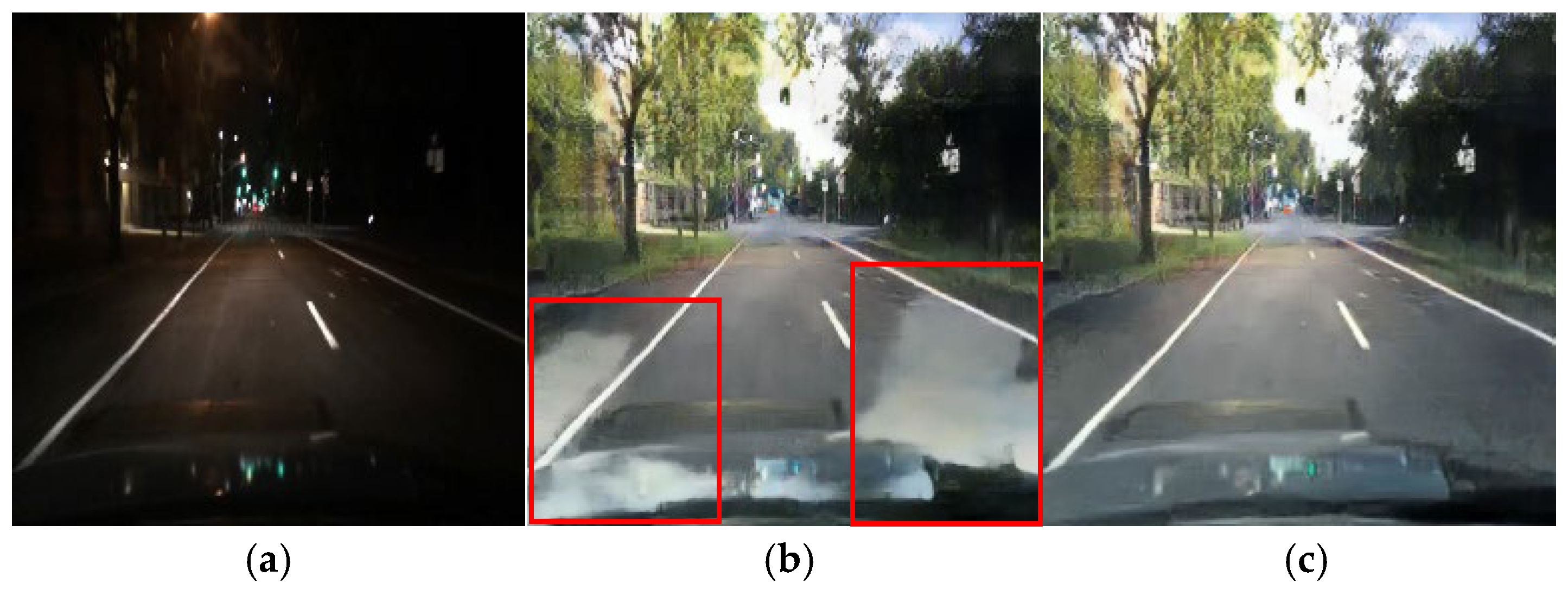
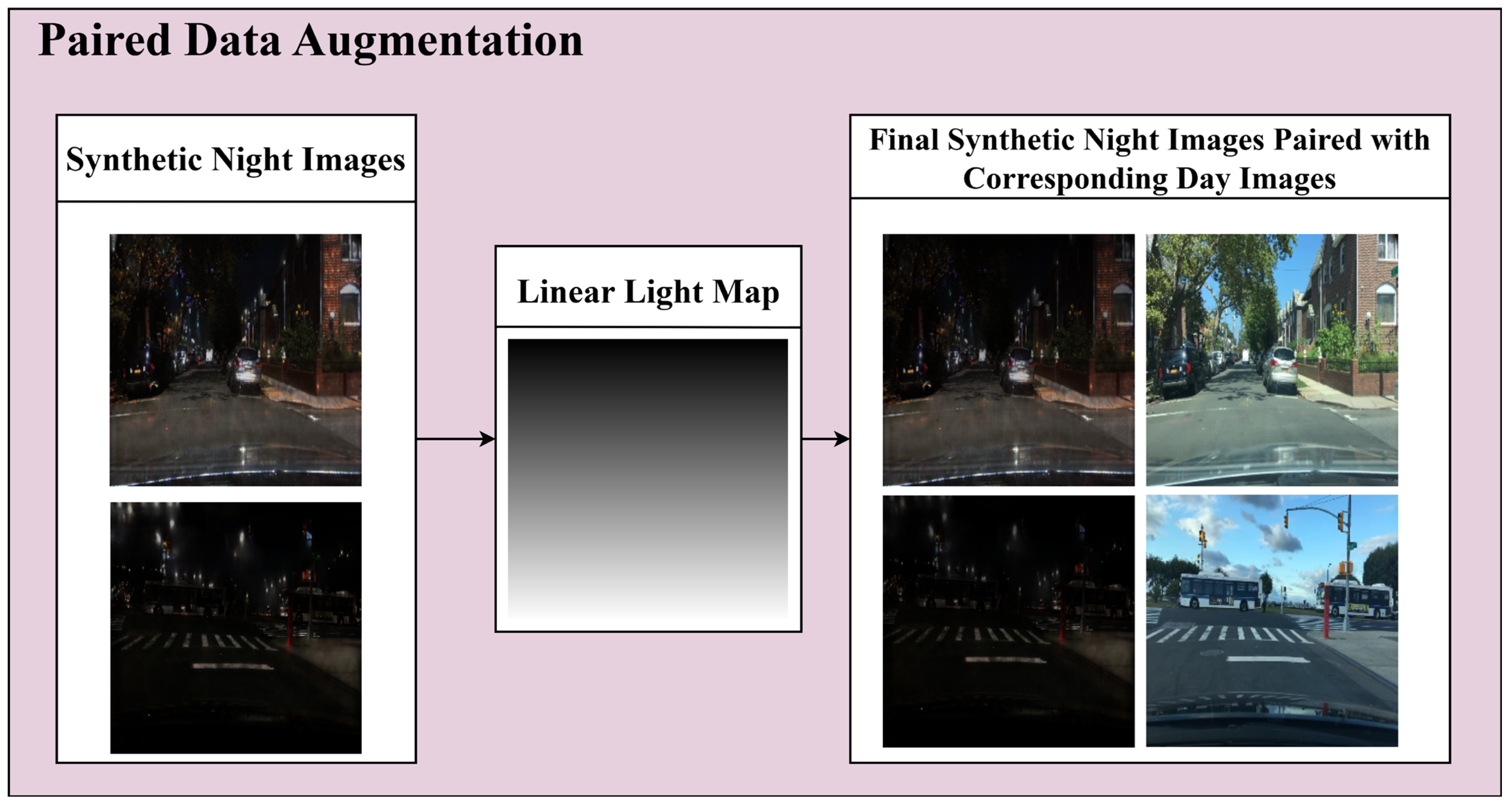
The first CycleGAN module, the unpaired module, focuses on nighttime-to-daytime image translation across the entire image and is employed for data augmentation with limited paired day and night images. The nighttime images generated by the first module are paired with daytime images of the same background to form the dataset for the second CycleGAN module, the four-channel paired training module. During this process, artifacts are often observed in the upper region of the generated nighttime images, which can be resolved by applying a linear light map to the image. Figure 3 presents the results of applying a linear light map to the nighttime images generated by the unpaired training module.
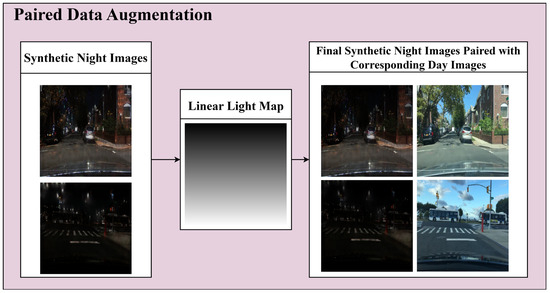
Figure 3.
Data augmentation using an unpaired training module.
Equation (5) defines the linear light map that is applied to mitigate this noise and enhance the quality of the image:
where denotes the linear light map function, represents the vertical coordinate in the image, and denotes the total height of the image. As increases from 0 to , increases linearly from the average intensity value () of the image to 255. After applying the function to ensure that the value does not exceed 255, the value is normalized by dividing it by 255, resulting in a value between 0 and 1. Algorithm 1 illustrates the data augmentation process, including creating the TodayGAN light map in the unpaired training module.
| Algorithm 1 Unpaired Training Module |
| Require: Unpaired input images: 1: Let be the output of the unpaired training module 2: = UnpairedTrainingModule() 3: Compute the linear light map follows: 4: 5: where and denotes the mean intensity of the image 6: Compute the final using the linear light map: 7: 8: Return |
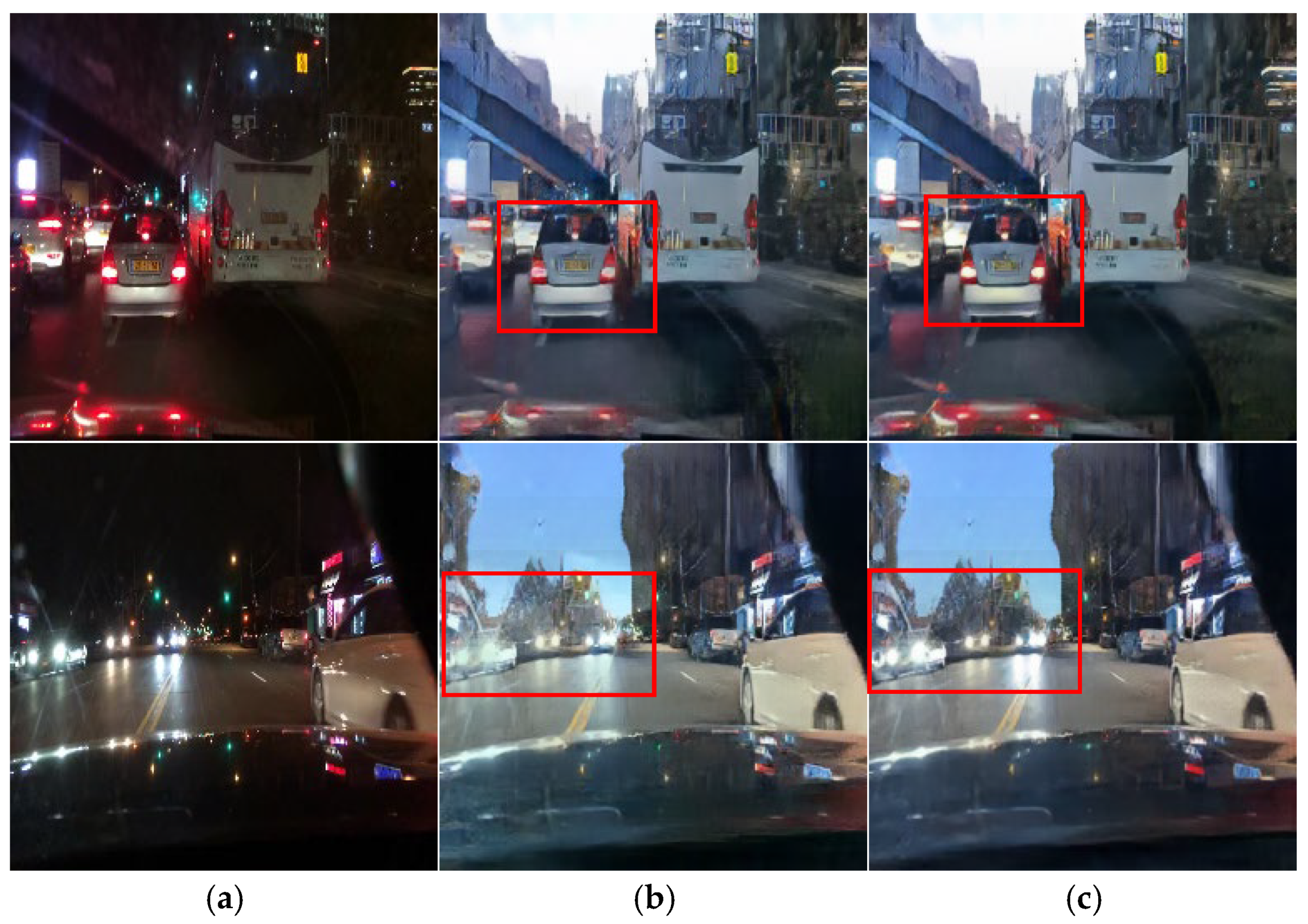
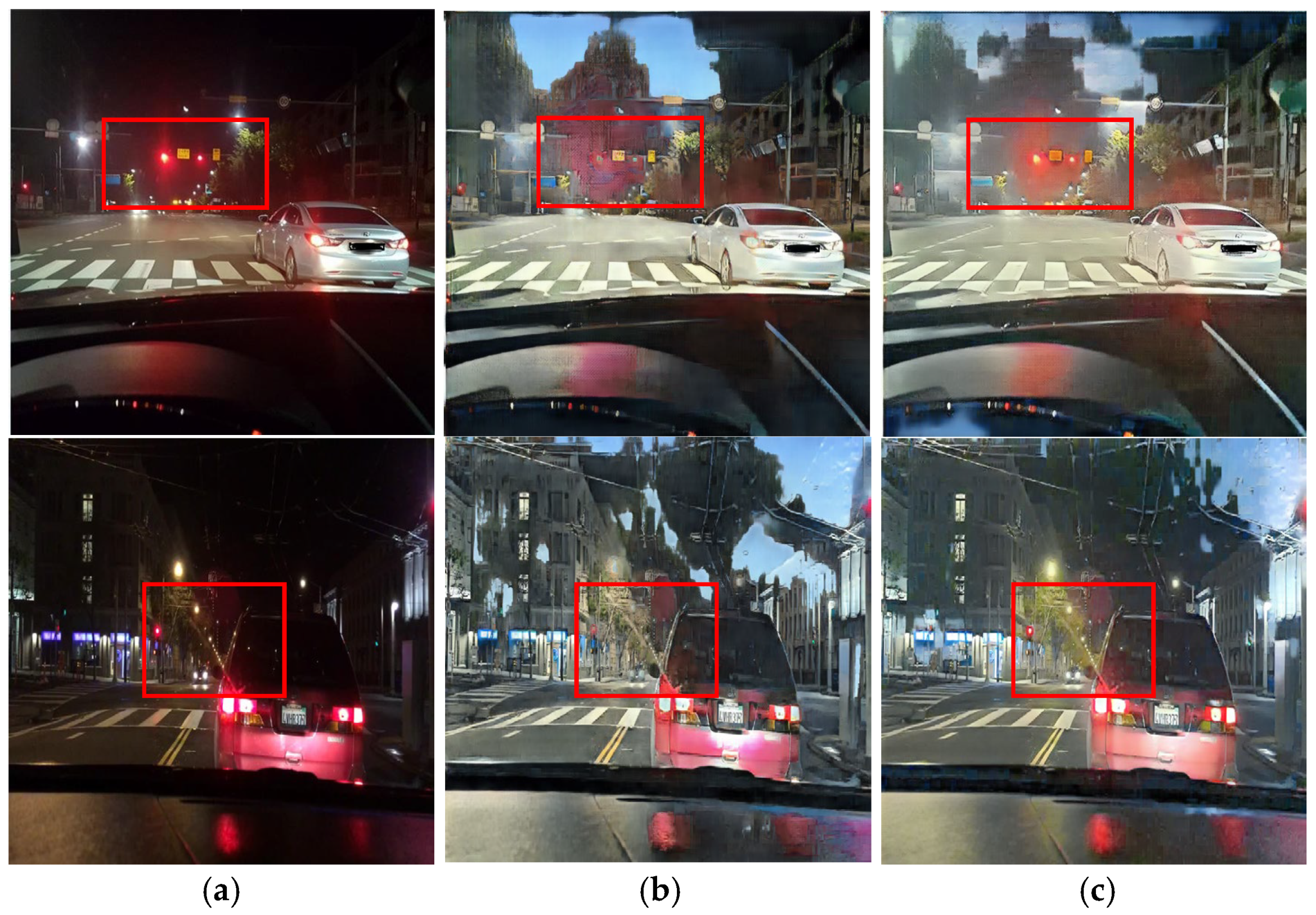
The CycleGAN method was initially designed for unpaired image translation. However, this study employs a paired training strategy to preserve local lighting details during night-to-day translation, as unpaired training often fails to maintain critical object information essential for driving environments. Figure 4 depicts the daytime images converted via the unpaired and paired CycleGANs, respectively. Figure 4b presents the result of training with the unpaired CycleGAN, highlighting artifacts such as distortions in traffic light and vehicle taillight colors. In contrast, the daytime images converted using the paired training module display better transformation of the traffic lights and preserve vital road information, demonstrating that the paired training module outperforms the unpaired training module in terms of traffic light representation. In this paper, the paired CycleGAN module is applied complementarily to the unpaired CycleGAN module to preserve the object details in the input images.
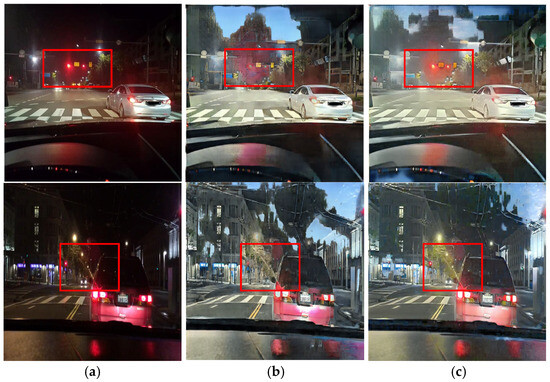
Figure 4.
Image comparison of the unpaired and paired training modules: (a) input images, (b) unpaired resulting images, and (c) paired resulting images.
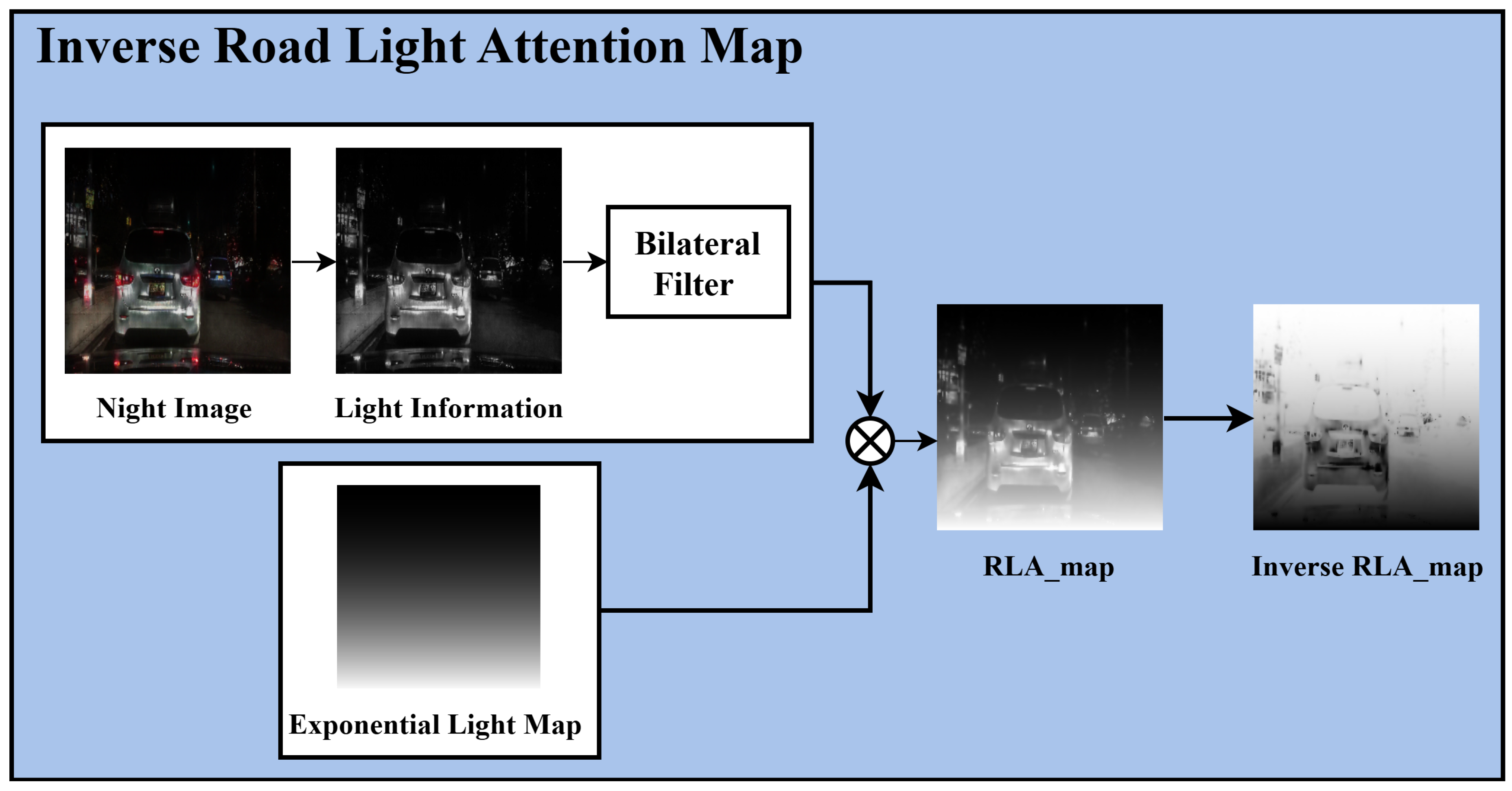
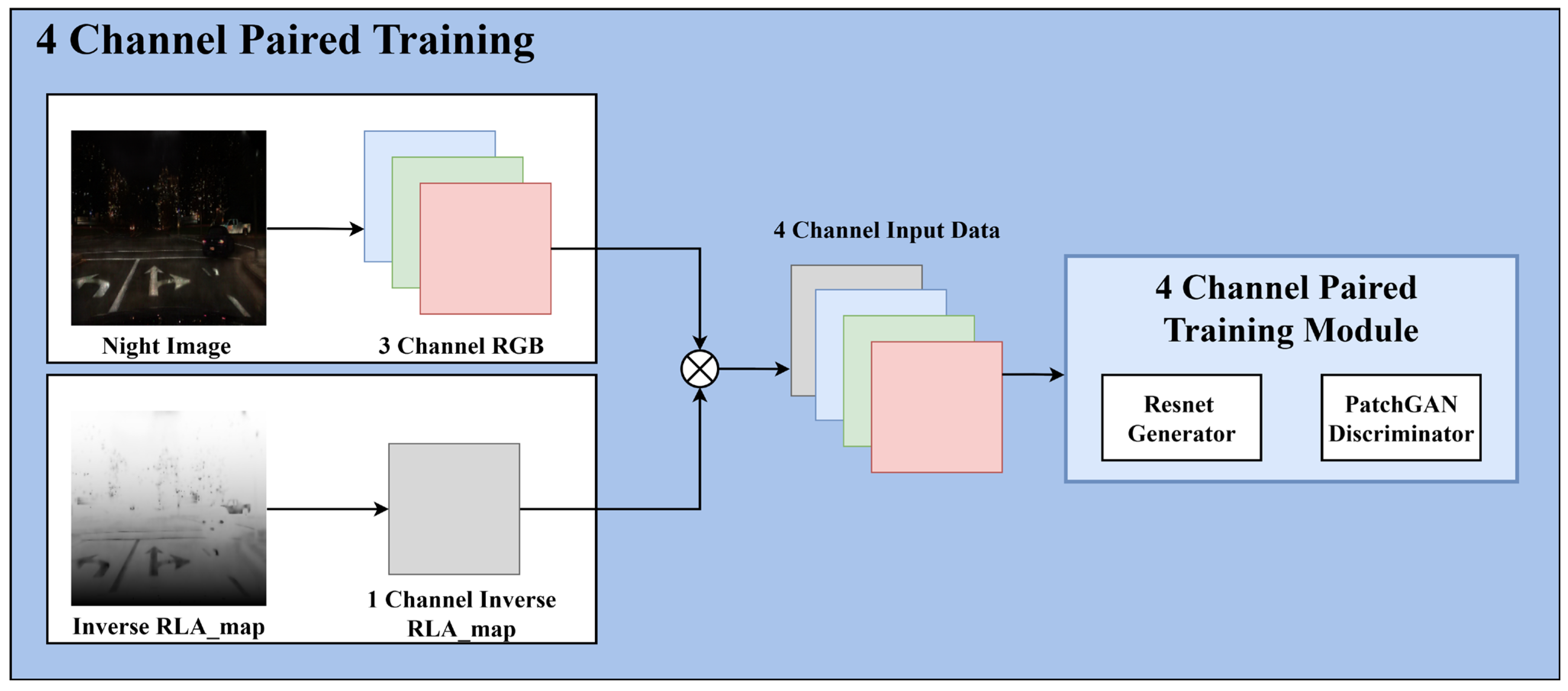
As mentioned, using the paired training module to convert input nighttime images to daytime images preserves traffic light and vehicle taillight color information. A four-channel paired training module is introduced to maximize the advantages of this paired training, including additional light information in the input compared to the conventional red, green, and blue (RGB) three-channel approach. This expansion increases the channel dimension of the input tensor from three to four, and the filter size in the first convolutional layer of the generator and discriminator changes from to . The key to four-channel paired training is to prevent artifacts by slowing the learning of bright light-source regions, which are physically prone to saturation, and to achieve natural results by strengthening the learning of the perceptually more important surrounding background regions. To achieve this, an inverse RLA map is introduced and learned in the fourth dimension. Figure 5 illustrates the process of generating the inverse RLA map.
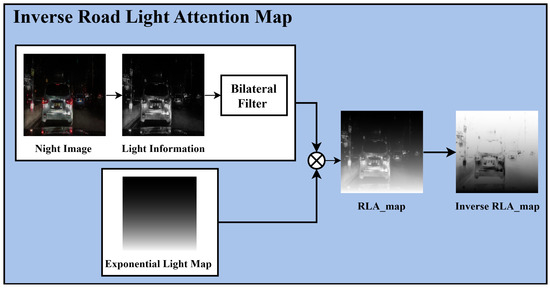
Figure 5.
Inverse road light attention map process.
The proposed inverse RLA map can be generated by processing the light information extracted from the input nighttime image using a bilateral filter, followed by applying an exponential light map. Unlike the linear light map in the unpaired training module, the exponential function enables the construction of a steep gradient map. By applying the exponential function, the paired training module can select critical areas to focus on via four-channel training. In addition, applying the inverse to the generated RLA map and darkening the traffic light and taillight areas enhance the training of these regions. Equation (6) mathematically represents the process of generating the inverse RLA map:
where the input is the brightness information of the nighttime image , and a bilateral filter preserves the edges while generating a natural lighting distribution. Then, an exponential light map is generated by applying an exponential coefficient to the normalized vertical coordinate , where denotes the vertical coordinate in the image and indicates the total image height. This light map, combined with the bilateral filter, smoothly extracts the influence of bright lighting areas in the nighttime image and generates an RLA map that increases the relative weight of the lower road areas. Finally, the inverse RLA map is obtained by applying an inversion operation to the generated RLA map. In this study, is set to 2, which results in a brightness weight that gradually increases from the top and sharply increases toward the bottom. Algorithm 2 details the process of generating the inverse RLA map.
| Algorithm 2 Inverse Road Light Attention (RLA) Map Generation |
| Require: Input: 1: Convert the RGB images to the LAB color space: 2: Extract the L-channel: 3: Apply the bilateral filter: BilateralFilter() 4: Compute the exponential light map: 5. Generate the RLA map: 6: Invert the attention map: 7: Return |
By incorporating the generated inverse RLA map into the existing RGB three-channel input method during training, a four-channel paired training module is created, which performs nighttime-to-daytime image conversion and detail enhancement. Figure 6 illustrates the four-channel paired training process.
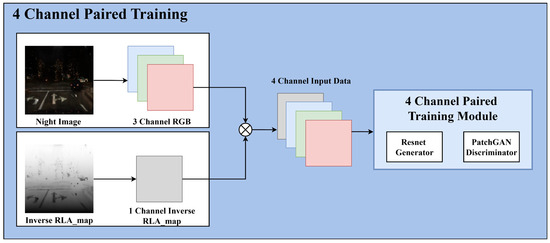
Figure 6.
Four-channel paired training process.
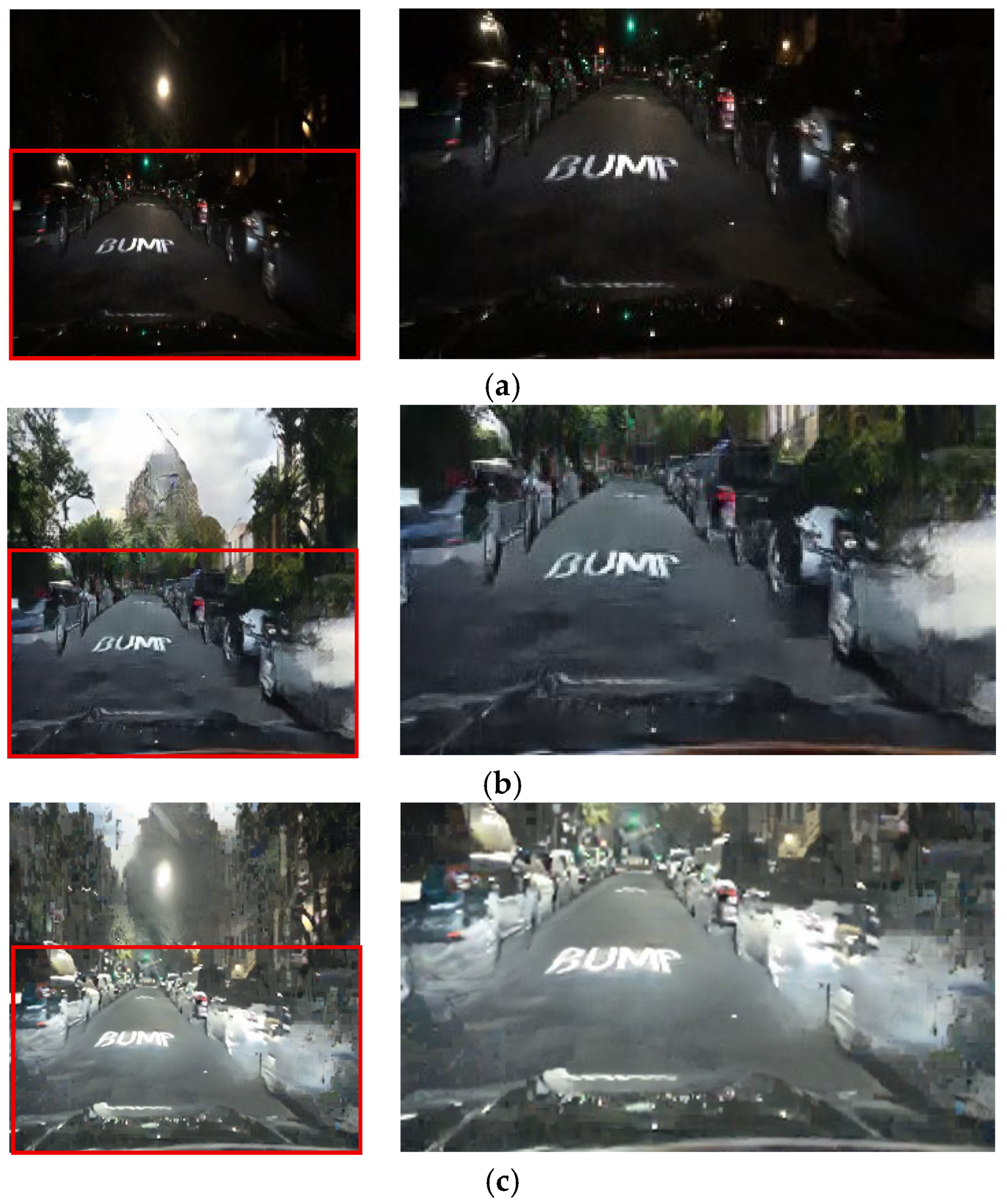
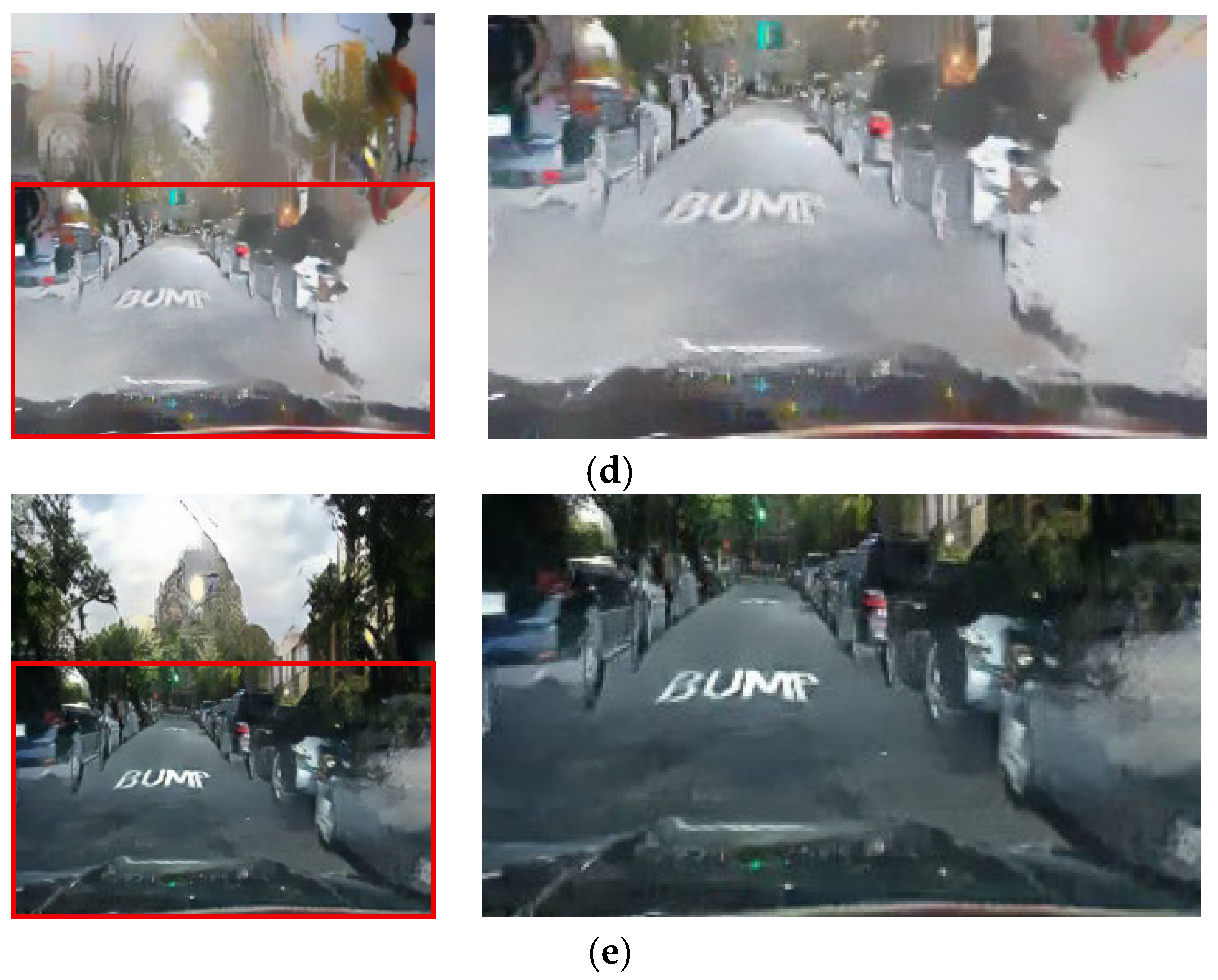
This paired training approach preserves critical road features, such as traffic lights and vehicle lighting, and ensures stable transformation of road areas. This four-channel paired training module maximizes the advantages of paired training in maintaining critical road information. Figure 7 and Figure 8 demonstrate the benefits of this four-channel paired training module.

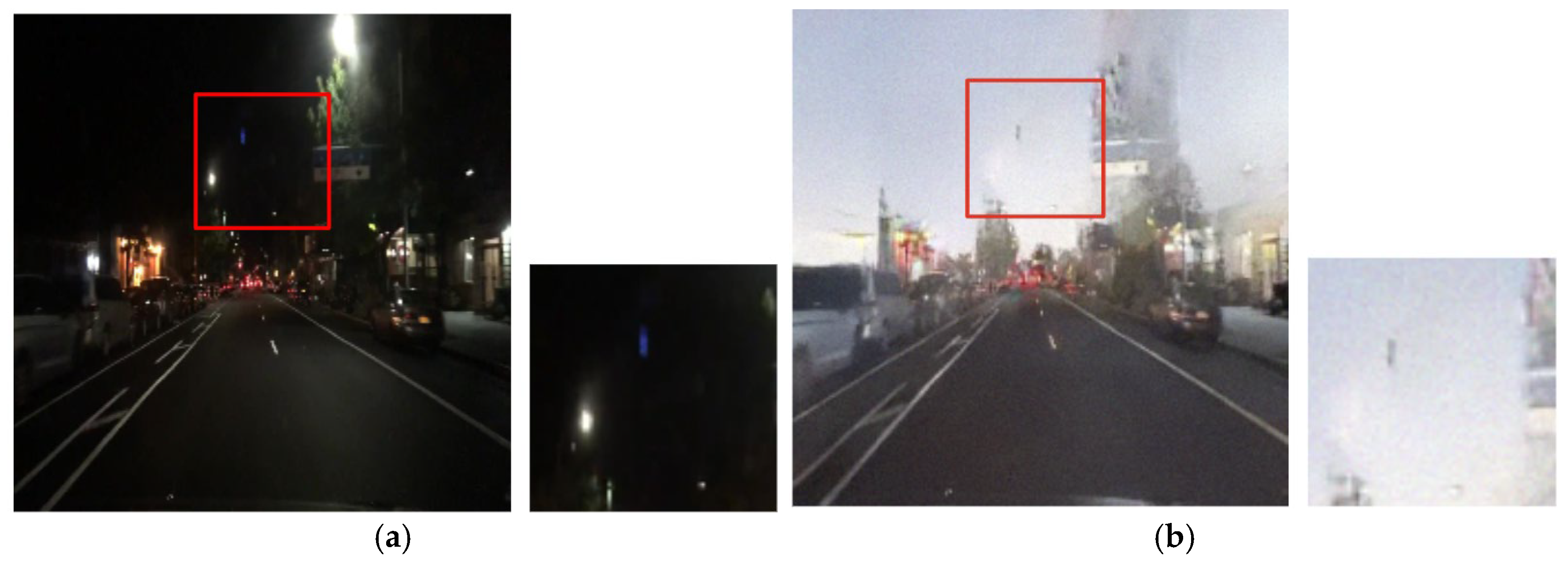
Figure 7.
Input (night images) and resulting images highlighting light conversion errors: (a) input images, (b) three-channel paired training images, and (c) four-channel paired training images.

Figure 8.
Input (night images) and resulting images highlighting light clarity: (a) input images, (b) three-channel paired training images, and (c) four-channel paired training images.
Figure 7 reveals that the four-channel paired training module produces daytime images with more stable transformation of road areas than the three-channel paired training module. In the four-channel training, the incorrect light transformation effects observed in the lower regions in the three-channel training are considerably reduced, resulting in a clearer and more natural preservation of essential visual road information, such as lane markings and surrounding objects.
The proposed method addresses problems that could not be resolved by the conventional three-channel training approach, such as the reduced clarity of vehicle lights and excessive light diffusion. In nighttime scenes, bright light sources near vehicle lights often excessively diffuse during the image conversion process, leaving abnormal light bleeding in the converted daytime image.
In contrast, the results from the proposed method in Figure 8 demonstrate that the saturation of vehicle lights is enhanced, and the light spreading effect is minimized. The first row in Figure 8 indicates that the traffic light colors are preserved, and the saturation of the vehicle stop light increased in the four-channel paired training. The spreading and blurring of light around the vehicle lights is significantly reduced in the second row.
In summary, Section 3.2 introduces two CycleGAN modules to perform nighttime-to-daytime image translation while preserving critical visual information relevant to road environments. The first module learns the transformation from nighttime to daytime images using an unpaired approach and is also applied for data augmentation to expand the limited paired image dataset. The second module focuses on preserving and enhancing details based on paired data and reflects the road lighting and reflection information via a four-channel input. Adding a light information channel to the input images allows for brightness weighting adjustment during training, enhancing the representation of critical objects, such as traffic lights and vehicle taillights.
3.3. Image Area Selection and Blending
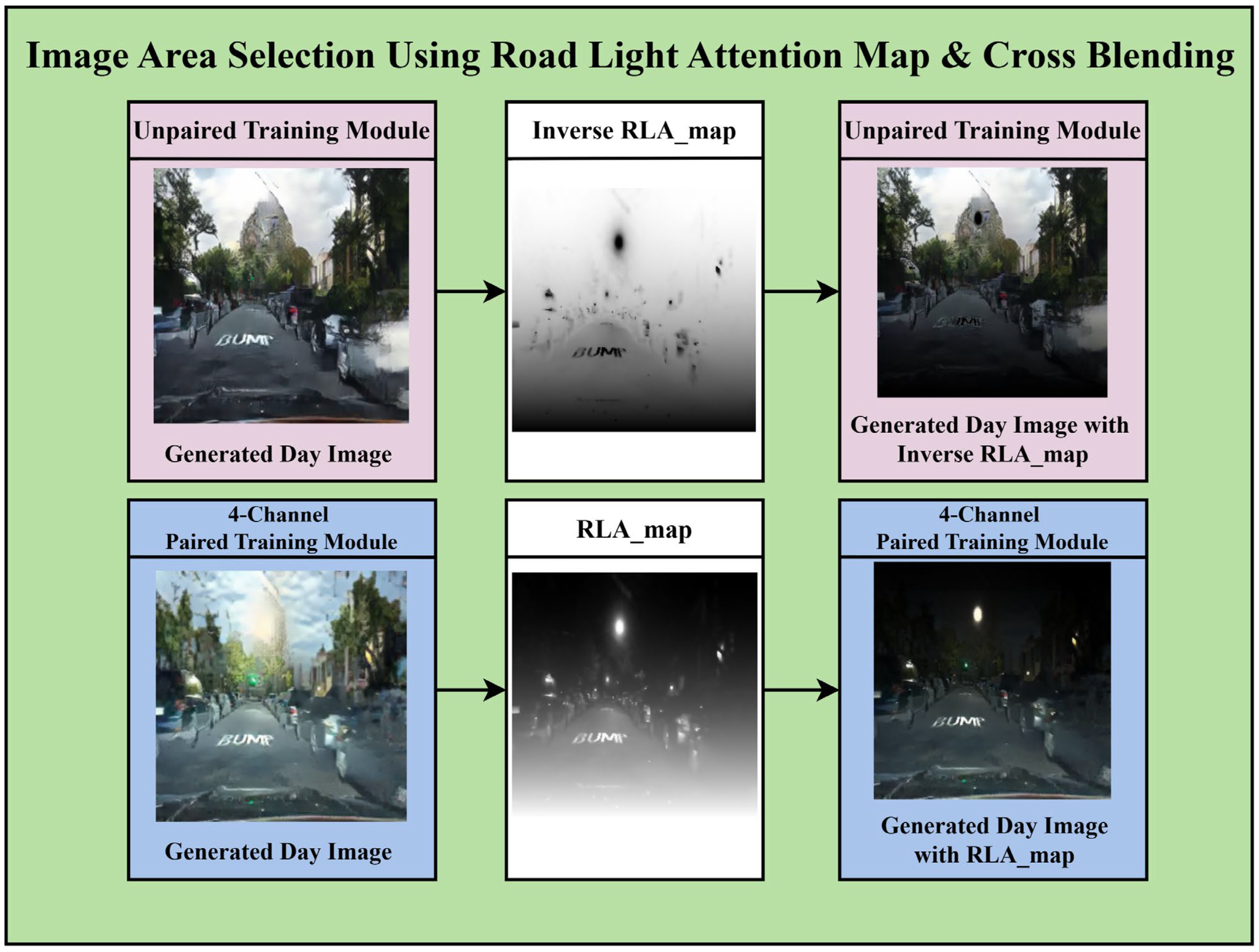
Applying the input nighttime images to the unpaired and paired training modules revealed that although the unpaired training performs intuitive nighttime-to-daytime conversion across the entire image (global), the paired training module excels at enhancing detailed information in the near-field areas. This proposed method employs the RLA map applied in the four-channel paired training module to perform both tasks simultaneously. For the unpaired training module, which transforms the sky area during the nighttime-to-daytime conversion, the inverse RLA map is applied to select the upper part of the image. For the paired training module, which preserves road details, the RLA map is applied to select the light information and lower part of the image. Figure 9 illustrates how the regions of the converted daytime images from each module are selected via the RLA map.
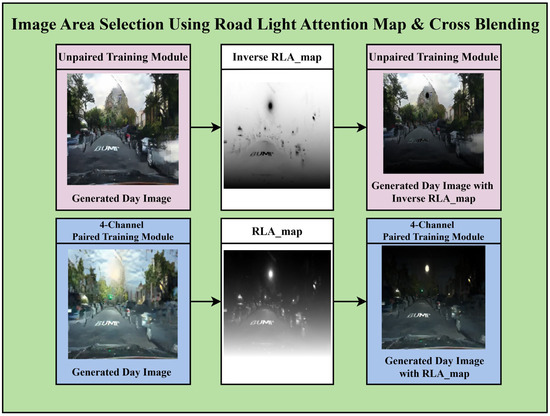
Figure 9.
Image area selection using the road light attention (RLA) map.
Based on the RLA map, the unpaired training module performs well in transforming the upper region, and the paired training module excels in the lower region. Applying these complementary characteristics, a cross-blending process is performed to integrate the results of the two modules into a single image. In this process, the RLA map and its inverse are employed as maps to select specific regions from the two daytime image results. In the daytime image generated by unpaired training, the inverse of the attention map is applied to extract the upper region, whereas in the paired training result, the attention map is applied as-is to select the lower region. The selected portions from both images are fused based on the maps. Cross-blending is an effective approach that simultaneously reflects the advantages of both CycleGAN modules via simple masking and selective merging, without the need for complex operations. The overall visual quality of the resulting image can be significantly enhanced by integrating the natural colors of the sky and distant backgrounds provided by the unpaired module with the precise details of roads, vehicles, and traffic lights preserved by the paired module.
In summary, Section 3.3 proposes an image selection and merging process to achieve optimal region-specific transformation performance using the complementary characteristics of unpaired and paired training. The RLA map distinguishes important regions of the image based on road brightness information. Through this information, regions located at the top (e.g., the sky or distant backgrounds) employ the unpaired training results, whereas regions at the bottom containing critical near-field objects (e.g., roads, vehicles, and traffic lights) are selected from the paired training results. The two results are combined via attention map-based cross-blending, resulting in the final daytime image that achieves detail preservation and style transformation performance. Algorithm 3 details the entire process.
| Algorithm 3 Image Area Selection and Cross-Blending Process |
| Require: 1. Definition: denotes the generator trained in the unpaired module 2. Definition: denotes the generator trained in the four-channel paired module 3. Unpaired translation: 4. Paired translation: 5: Weight-unpaired result: 6: Weight-paired result: 7: Cross-blending: 8: Return |
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Simulation Settings
We conducted the training and experiments on a Windows 10 Education (64-bit) system with an Intel i5-6500 central processing unit (Intel, Santa Clara, CA, USA) at 3.2 GHz and 16.0 GB of RAM, along with a TITAN RTX graphics processing unit (Nvidia, Santa Clara, CA, USA). For the training parameters, we set the image crop size to 256 × 256 and the batch size to 1, initialized the learning rate to 0.0002 with linear decay every 50 epochs, and trained for a total of 400 epochs.
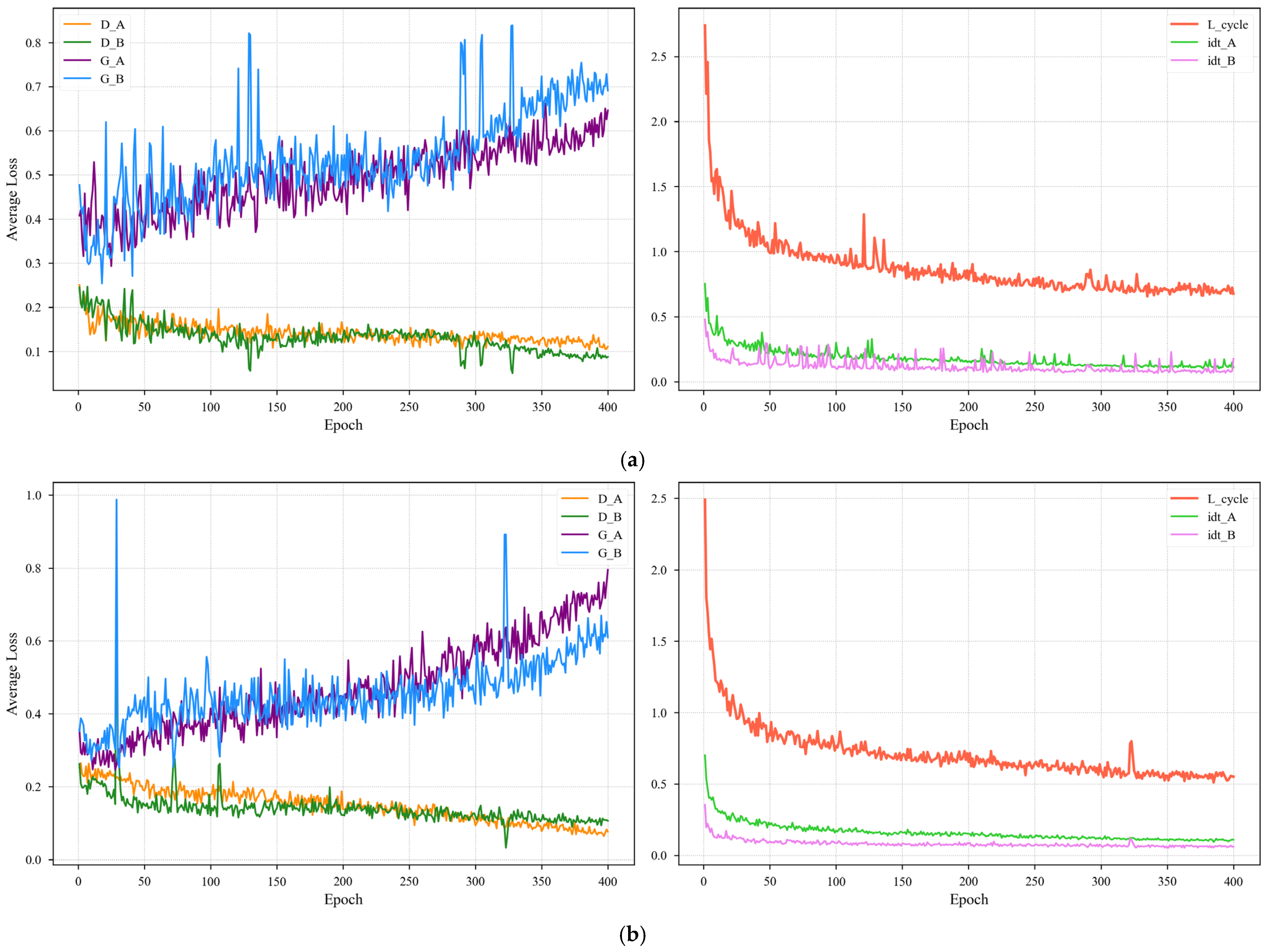
Figure 10 plots the training loss curves, which confirm the stable convergence of both our modules. For each module, the content preservation losses (cycle-consistency and identity) steadily decrease and then stabilize, proving that the generators learned to maintain the image’s core structure and color. At the same time, the adversarial losses reached a stable equilibrium, indicating a healthy training dynamic free from mode collapse.
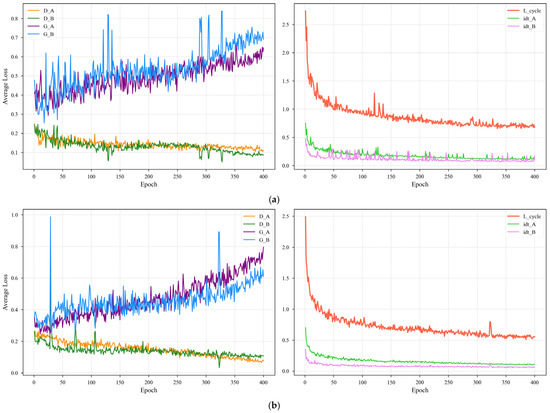
Figure 10.
Training loss curves demonstrating the stable convergence of (a) the unpaired training module and (b) the four-channel paired training module. For each module, the left plot shows the adversarial losses (G for generator, D for discriminator) reaching a stable equilibrium. The right plot shows the content preservation losses (L_cycle for cycle-consistency, idt for identity) successfully converging. Subscript “A” denotes the day-to-night direction, and “B” denotes the night-to-day direction.
The training objective was guided by the standard CycleGAN loss function, composed of an adversarial loss, a cycle-consistency loss, and an identity loss. These coefficients were determined experimentally, and the corresponding weights for the cycle-consistency loss () and identity loss ( were set to 10.0 and 0.5, respectively [4].
The training dataset for the unpaired training module comprises 2800 images from the BDD73k dataset. To create the paired dataset, we then used an additional 3000 daytime images, which were not employed in training, to generate synthetic night images via the unpaired training module. The paired training module combined 3000 pairs of daytime images, their corresponding synthetic night images generated by the unpaired training module, and the corresponding inverse RLA map as the training data.
4.2. Ablation Experiments
We performed an ablation study to evaluate the contribution of each module. As detailed in Table 1, this involved systematically removing components from our proposed four-stage method to analyze their individual impact.

Table 1.
Configurations for each case in the ablation study.
- Case 1: Employs Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPMs) to serve as a comparative benchmark against our CycleGAN-based approach.
- Case 2: Serves as the baseline, consisting of our paired module with a standard three-channel (RGB) input.
- Case 3: Adds the inverse RLA map as a fourth input channel to Case 2 to assess the map’s contribution.
- Case 4: Represents the full model, which blends the paired and unpaired modules, but uses a suboptimal blending parameter (γ = 0.5) to validate our choice of γ.
- Case 5: Our final model, which combines the four-channel paired module with the unpaired module using the optimal parameter (γ = 2).
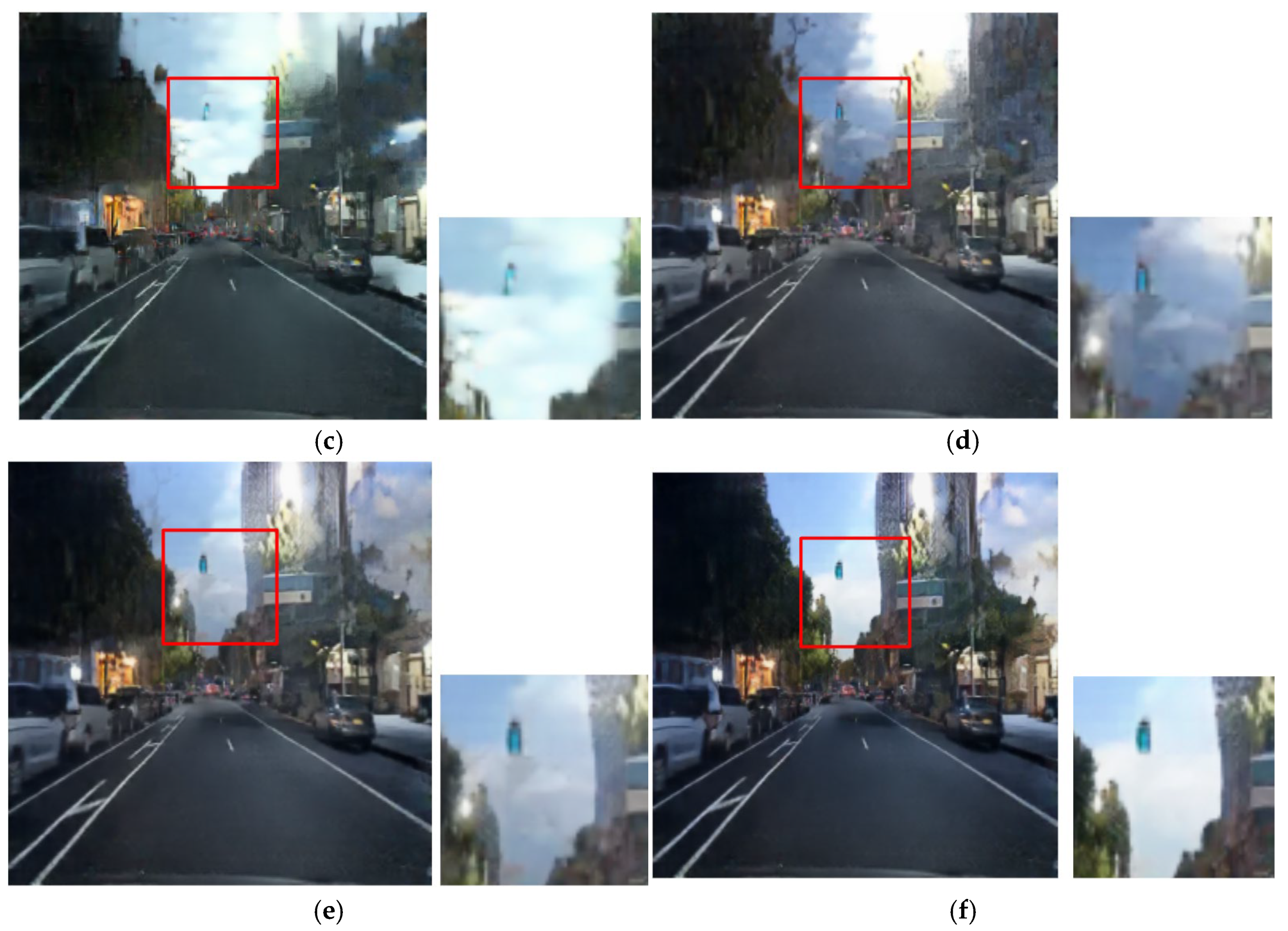
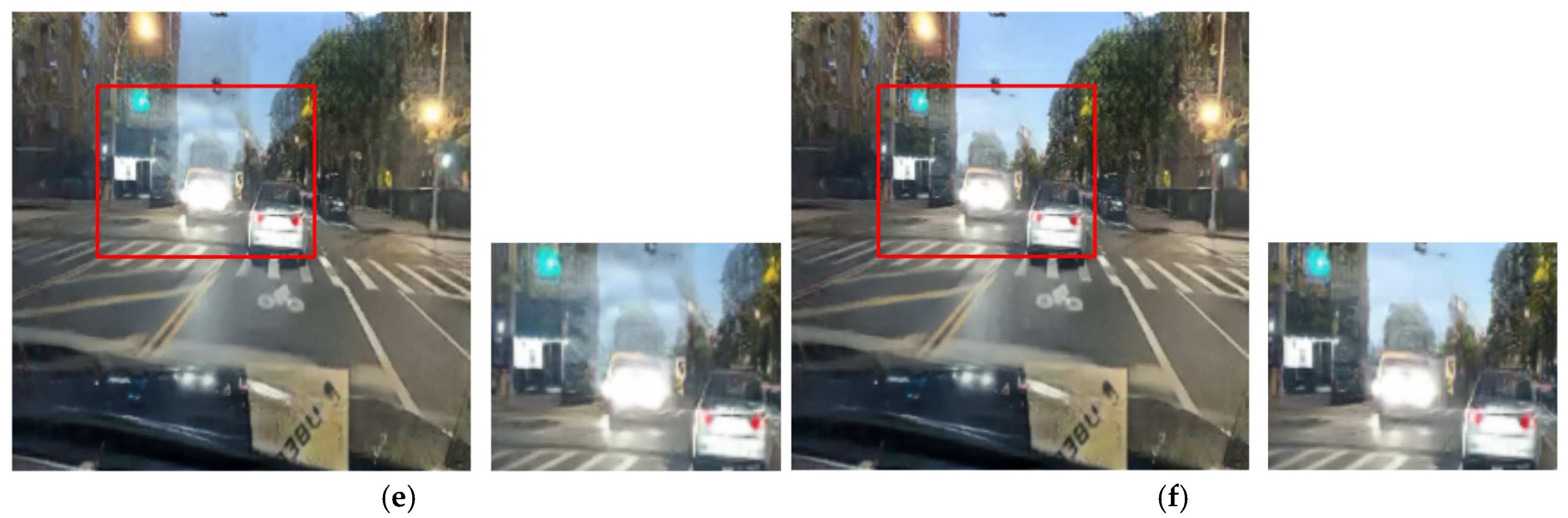
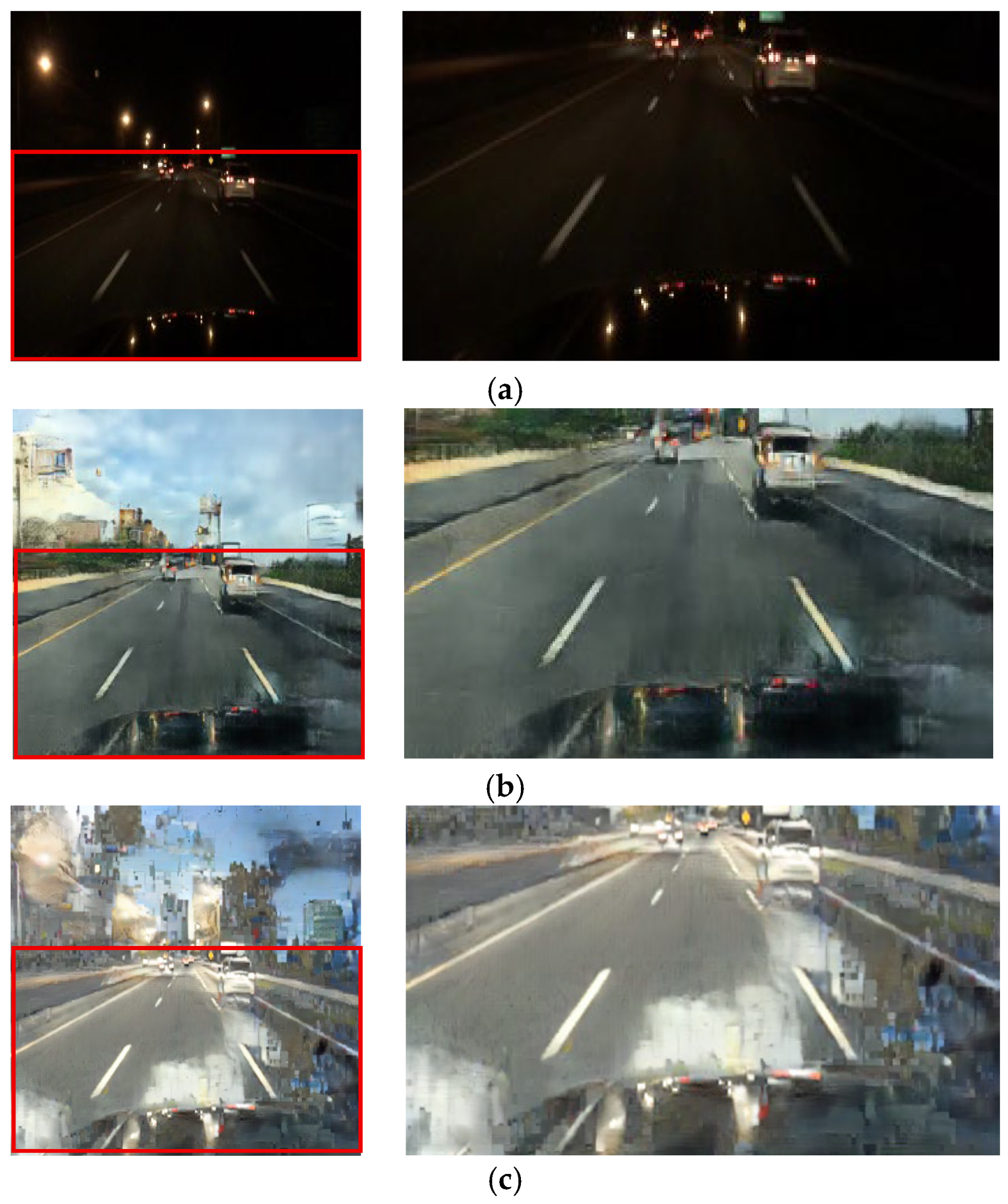
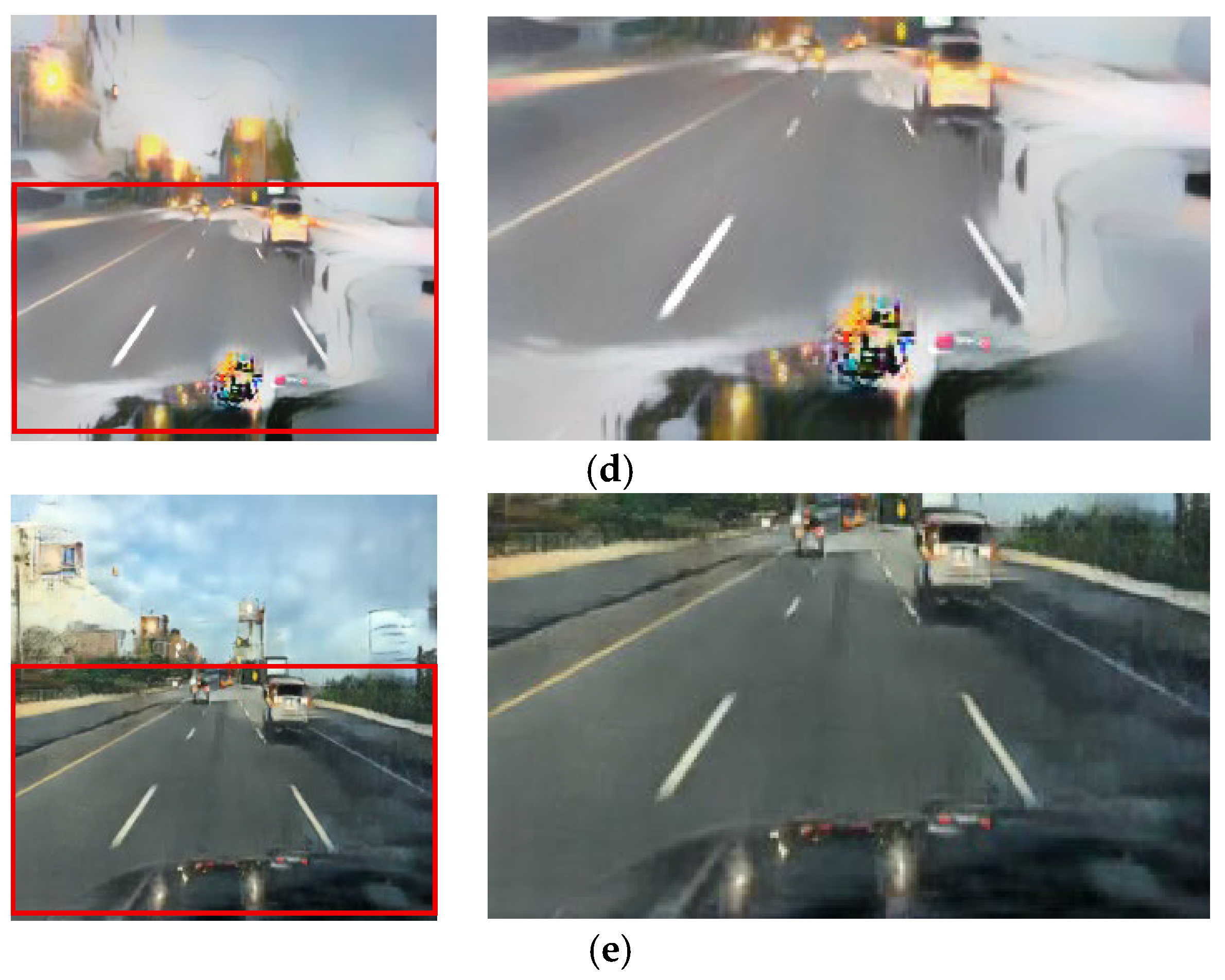
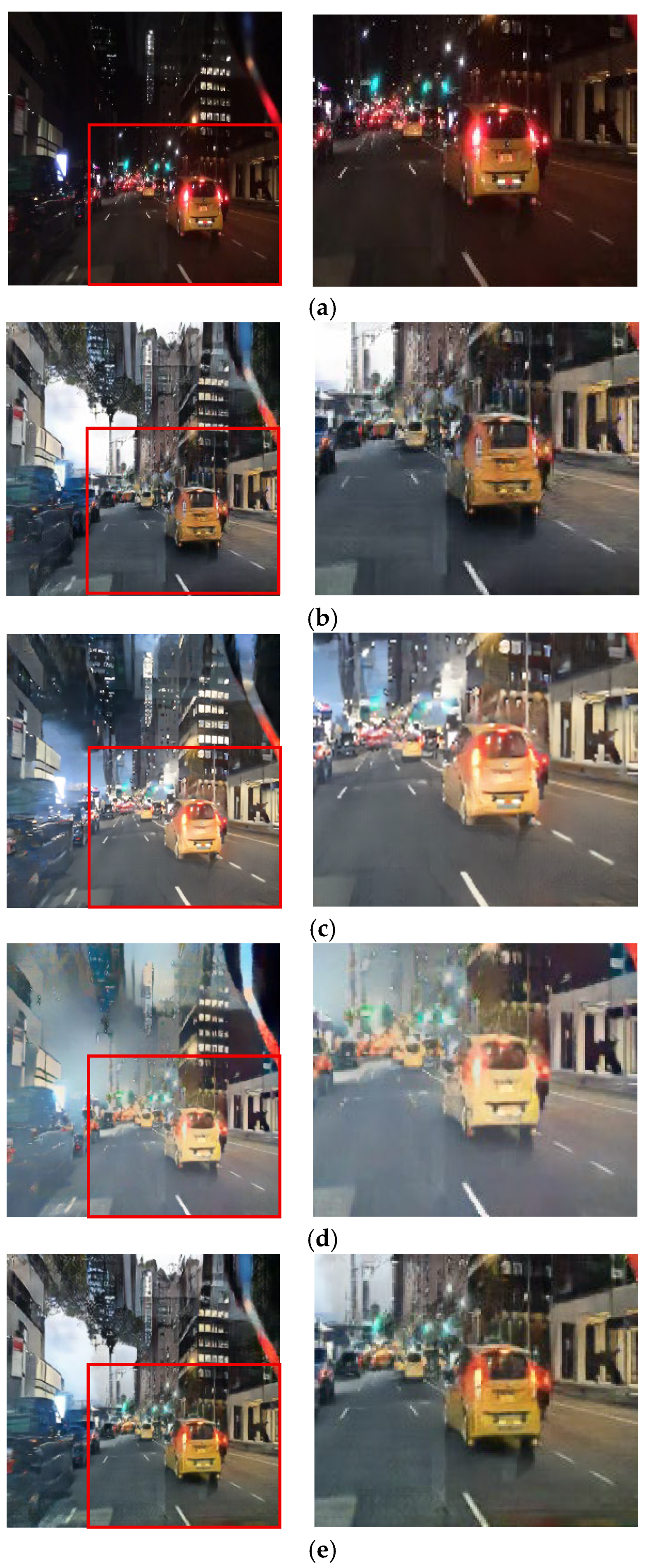
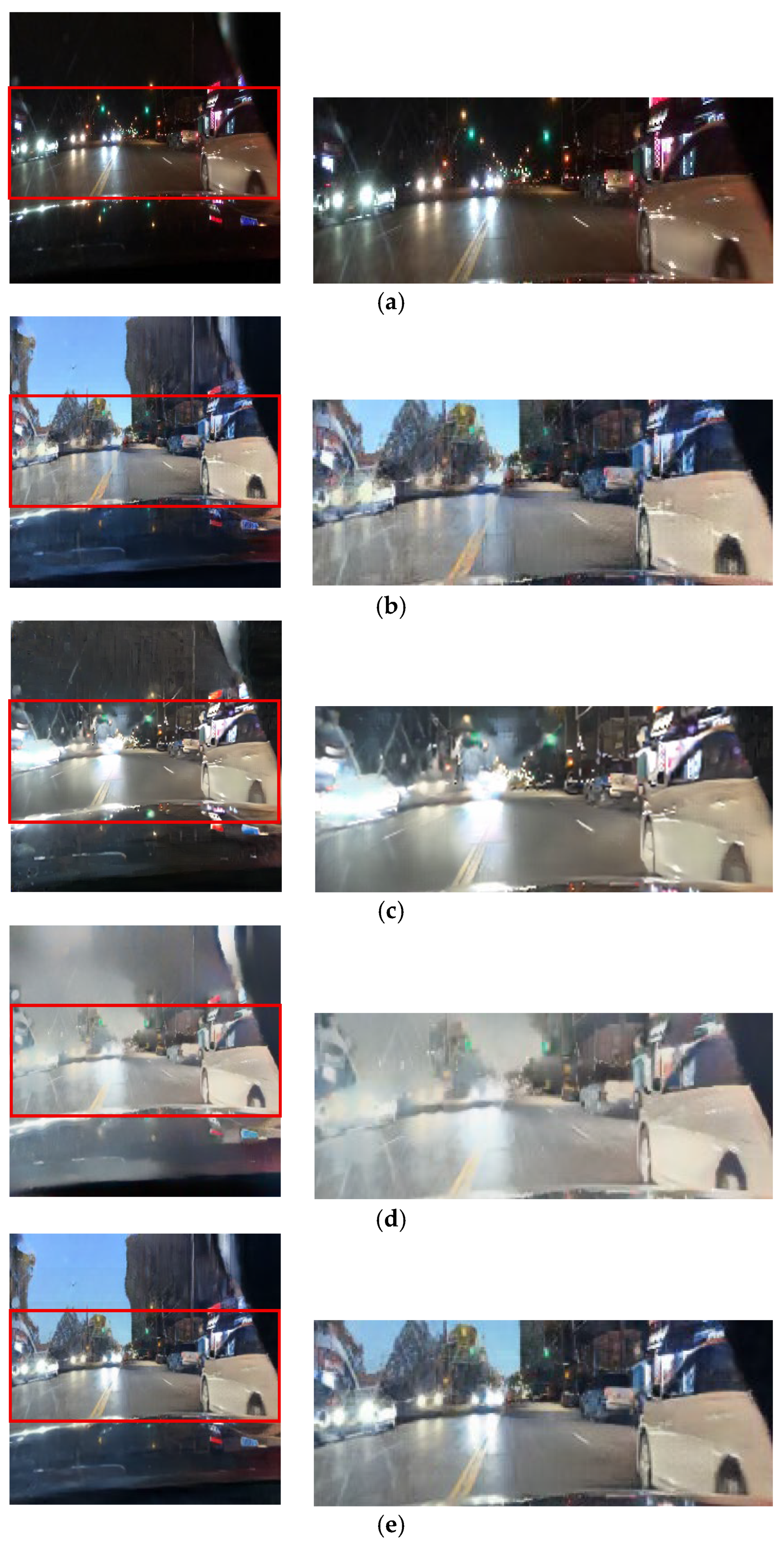
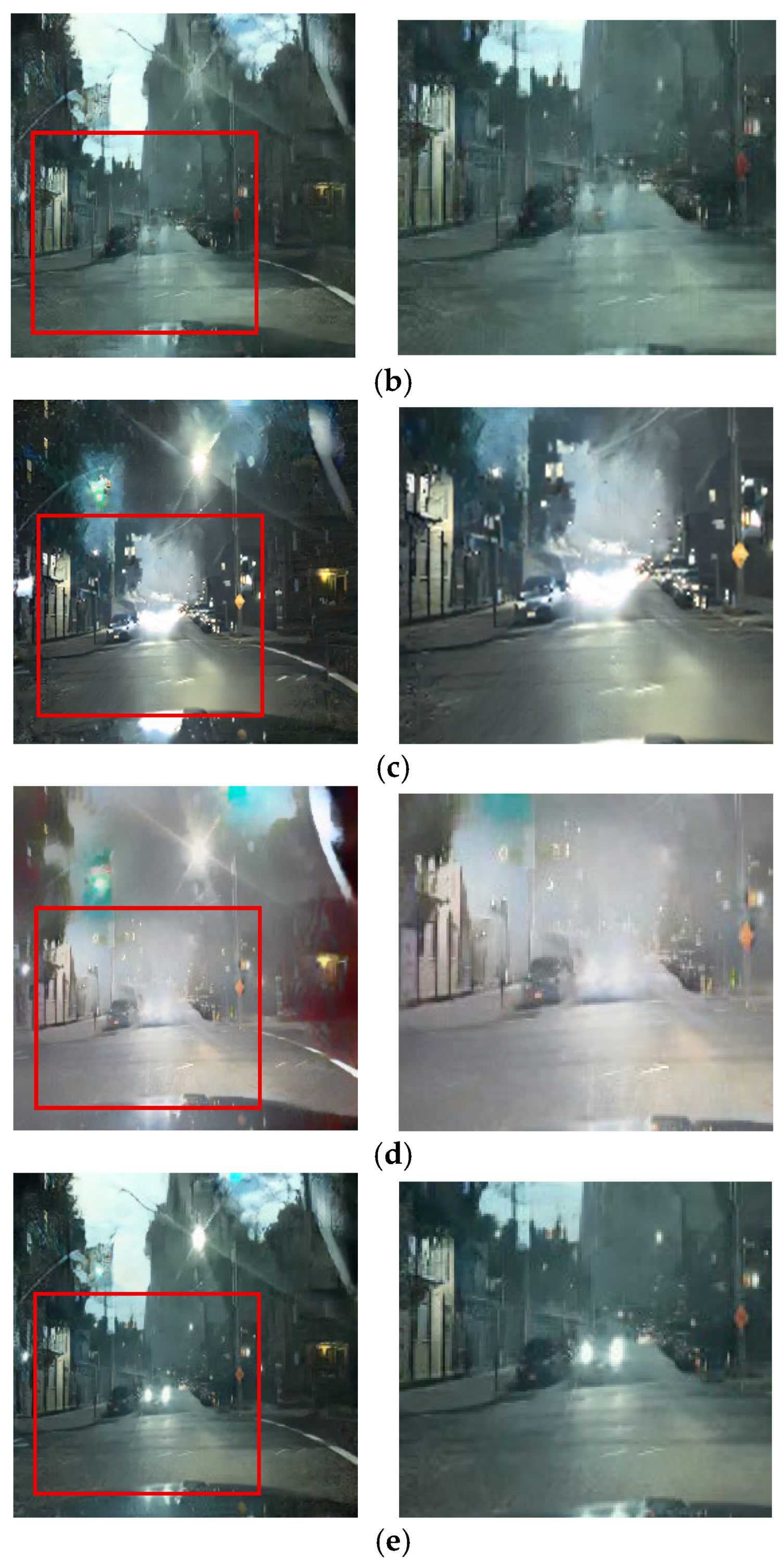
The qualitative results from the ablation study first validate our selection of the CycleGAN framework over alternatives such as DDPMs [30]. As shown in Figure 11b and Figure 12b, the output from Case 1 fails to preserve the structural and color integrity of critical light sources. In contrast, our CycleGAN-based approach in Case 2 provides a more effective baseline (Figure 11c and Figure 12c). While it shows initial signs of restoring the traffic signal, the preservation is minor. Furthermore, this process introduces prominent artifacts into the sky region. This trade-off is addressed by the subsequent components. In Case 3, the addition of the inverse RLA map renders the colors of luminous objects significantly more vivid (Figure 11d and Figure 12d), but this enhanced focus concurrently exacerbates the noise in the sky. The cross-blending mechanism was designed specifically to resolve this issue. Case 4 (Figure 11e and Figure 12e), which employs a suboptimal parameter of γ = 0.5, demonstrates a substantial reduction in this sky noise. Finally, Case 5 (Figure 11f and Figure 12f) uses the optimal parameter of γ = 2 to eliminate artifacts while achieving the highest clarity and color fidelity for traffic signals and vehicle lights.


Figure 11.
Qualitative comparison in ablation experiments: (a) input, (b) case 1, (c) case 2, (d) case 3, (e) case 4, and (f) case 5.
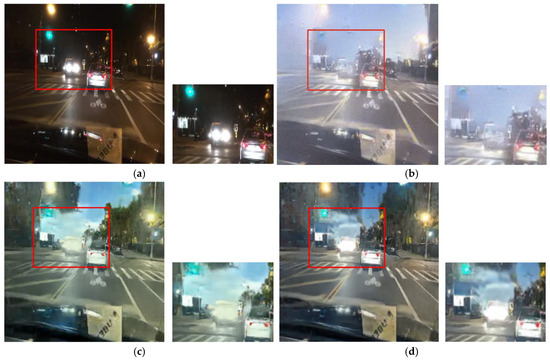

Figure 12.
Qualitative comparison in ablation experiments: (a) input, (b) case 1, (c) case 2, (d) case 3, (e) case 4, and (f) case 5.
4.3. Comparative Experiments
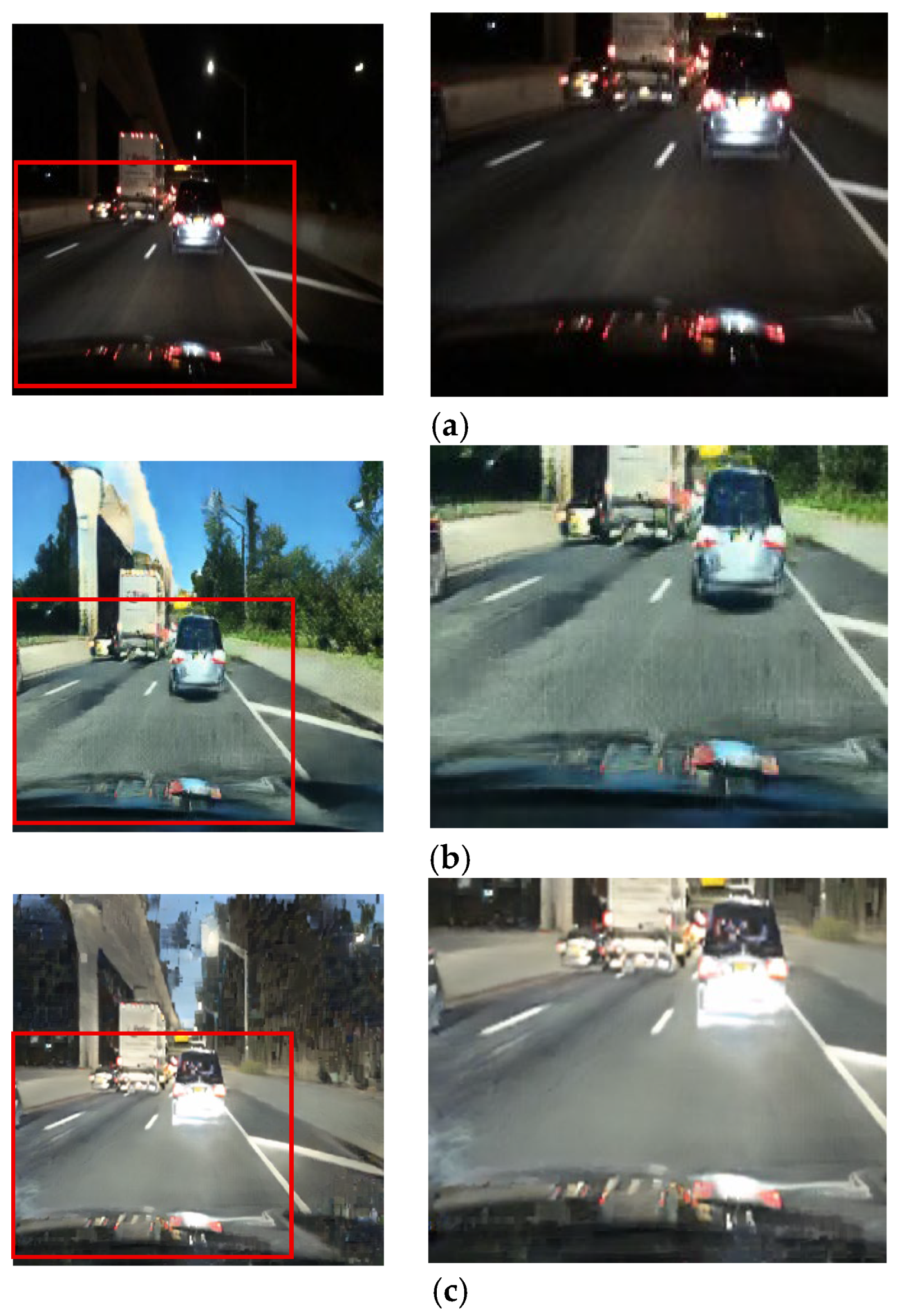
To evaluate the performance of our night-to-day image conversion, we conducted comparative experiments with several baseline methods: a paired-data CycleGAN, ToDayGAN, and the SLAT DayConv technique [31]. The input images for this evaluation consist of nighttime driving scenes where fundamental information, such as lane markings and vehicle lights, remains perceivable. The results are presented in Figure 13, Figure 14, Figure 15, Figure 16, Figure 17, Figure 18 and Figure 19. While achieving perfect photorealism remains a challenging goal for all methods, the following comparisons demonstrate our proposed framework’s superior ability to maintain vital road information where other methods struggle.
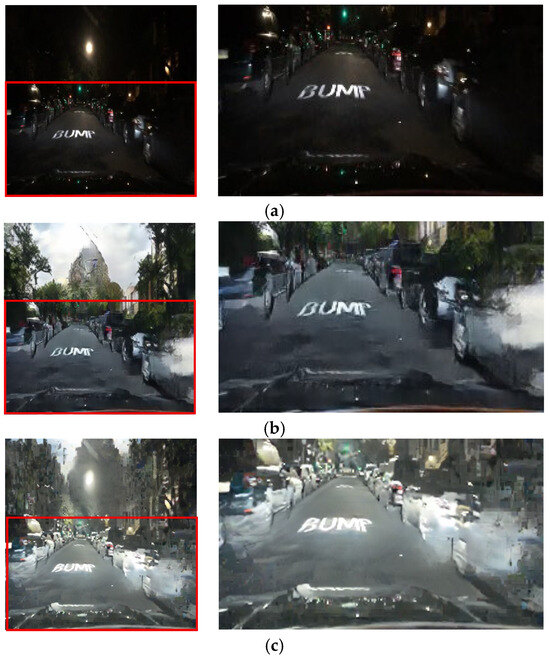
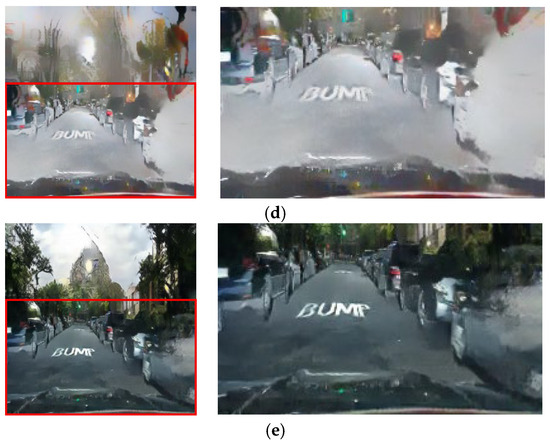


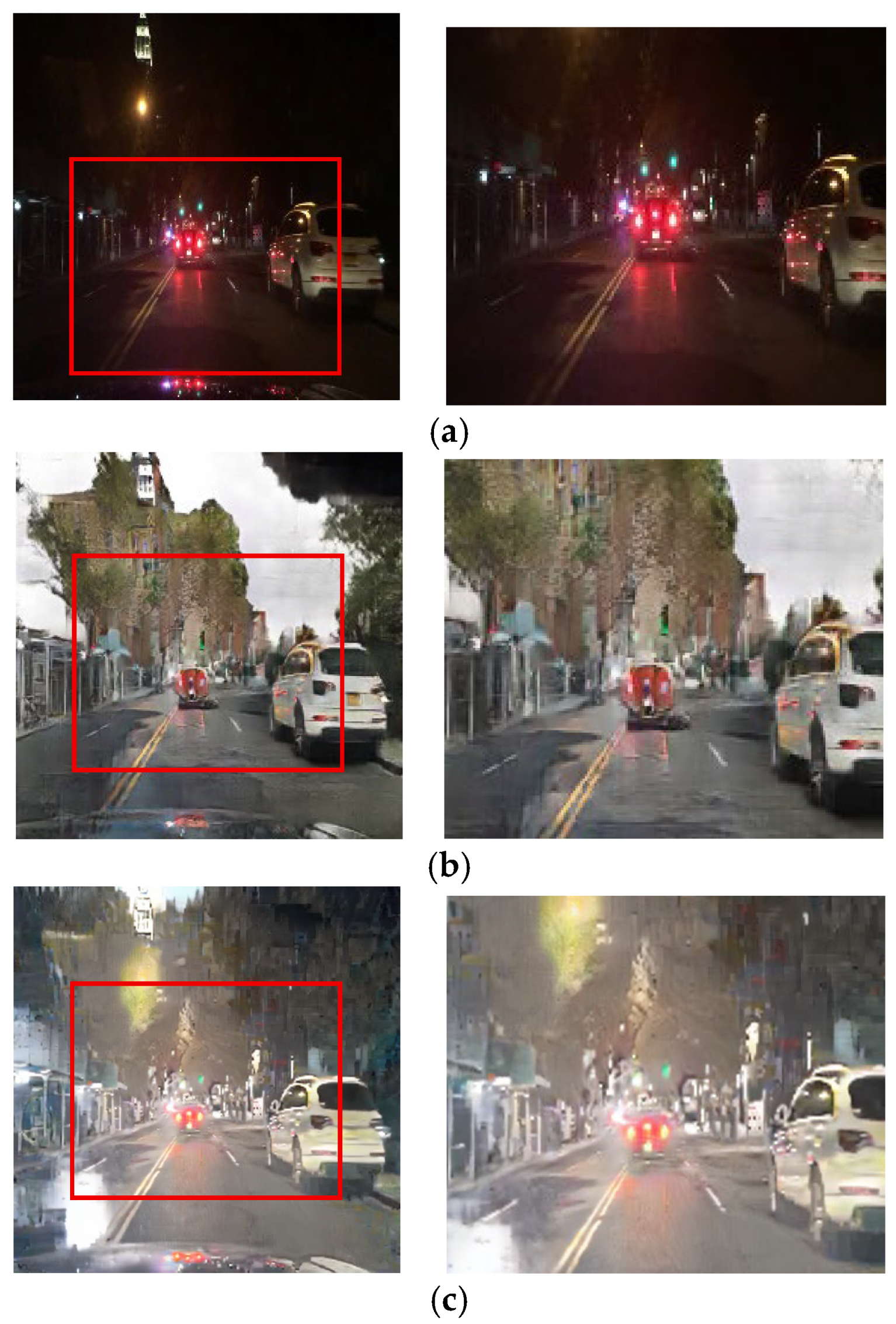
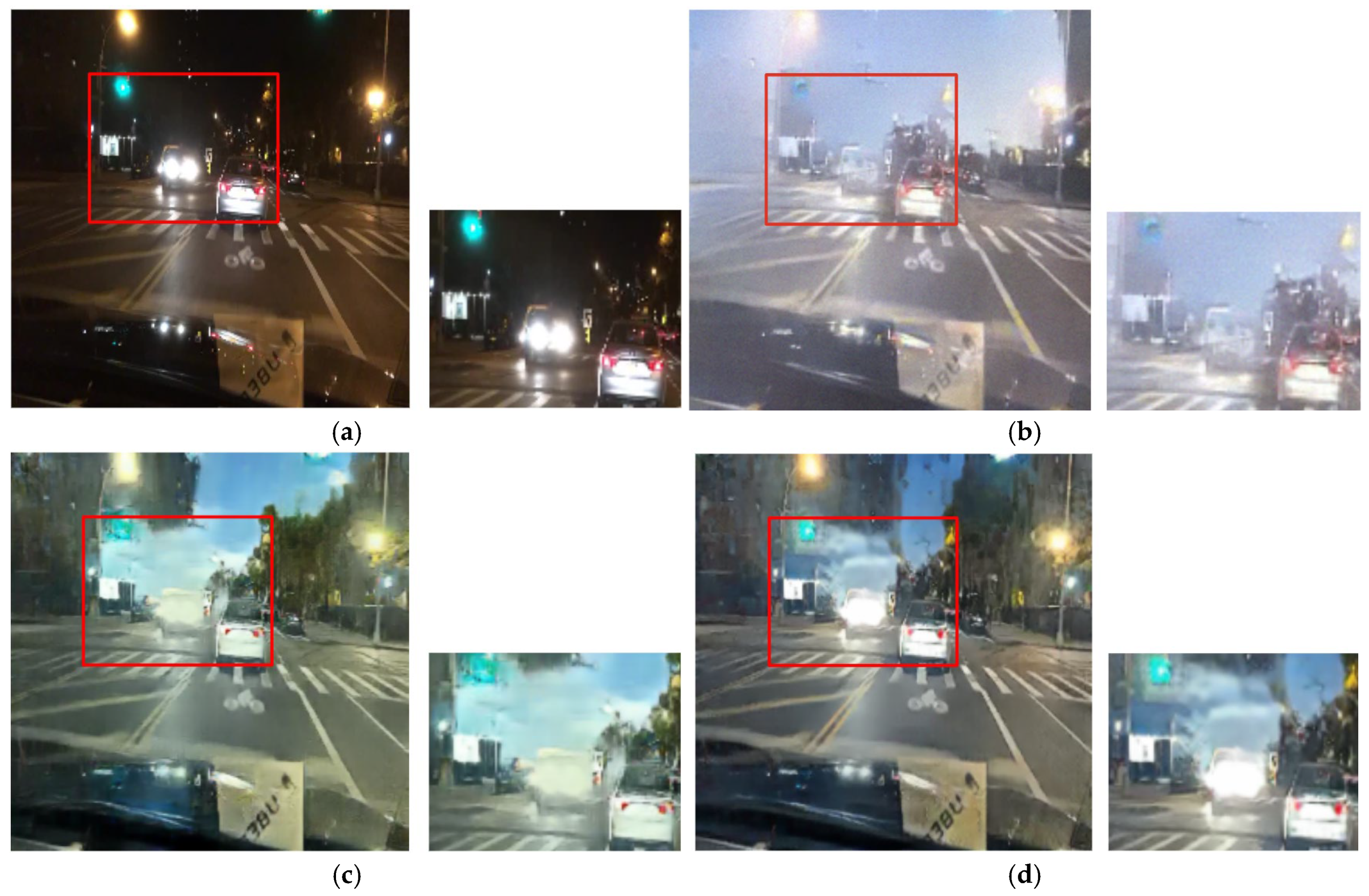
Figure 13.
Input and resulting images: (a) input image, (b) paired CycleGAN, (c) ToDayGAN, (d) SLAT DayConv [31], and (e) proposed method.
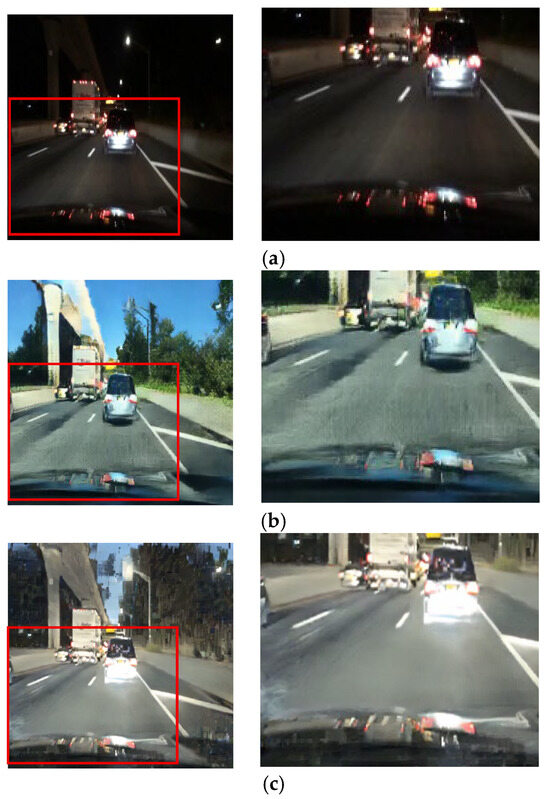

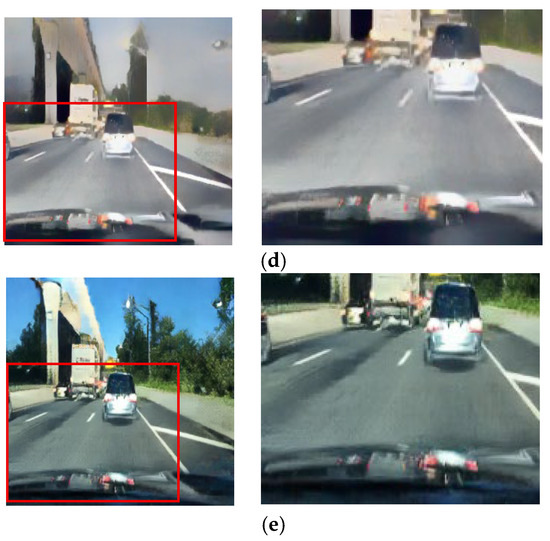
Figure 14.
Input and resulting images: (a) input image, (b) paired CycleGAN, (c) ToDayGAN, (d) SLAT DayConv [31], and (e) proposed method.
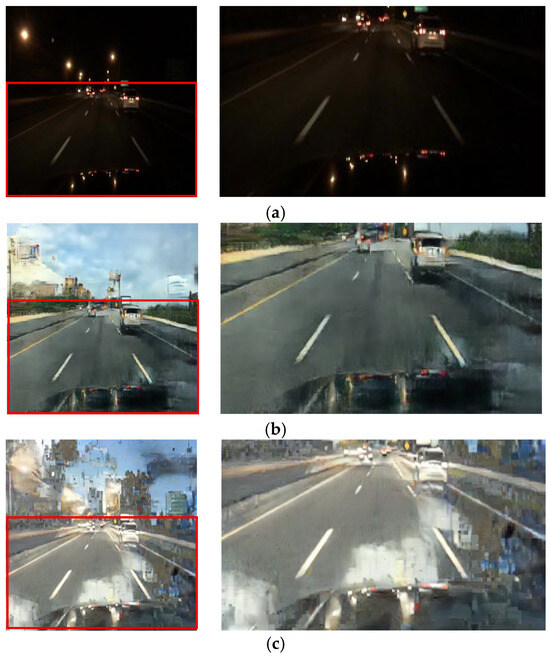
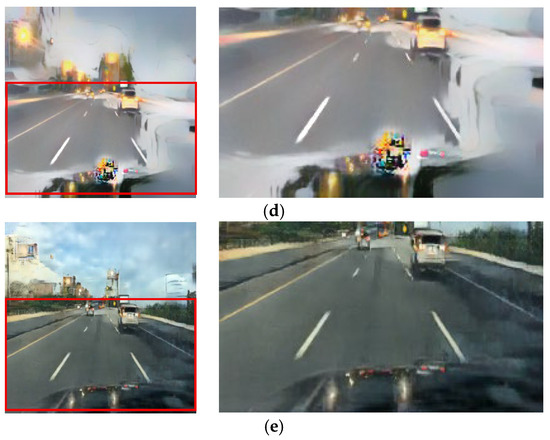


Figure 15.
Input and resulting images: (a) input image, (b) paired CycleGAN, (c) ToDayGAN, (d) SLAT DayConv [31], and (e) proposed method.
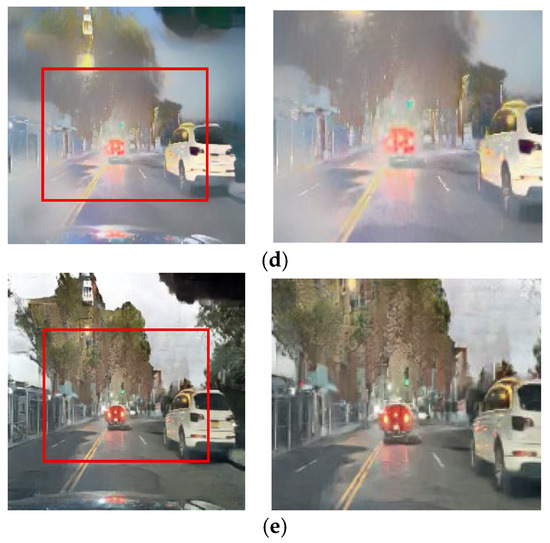


Figure 16.
Input and resulting images: (a) input image, (b) paired CycleGAN, (c) ToDayGAN, (d) SLAT DayConv [31], and (e) proposed method.

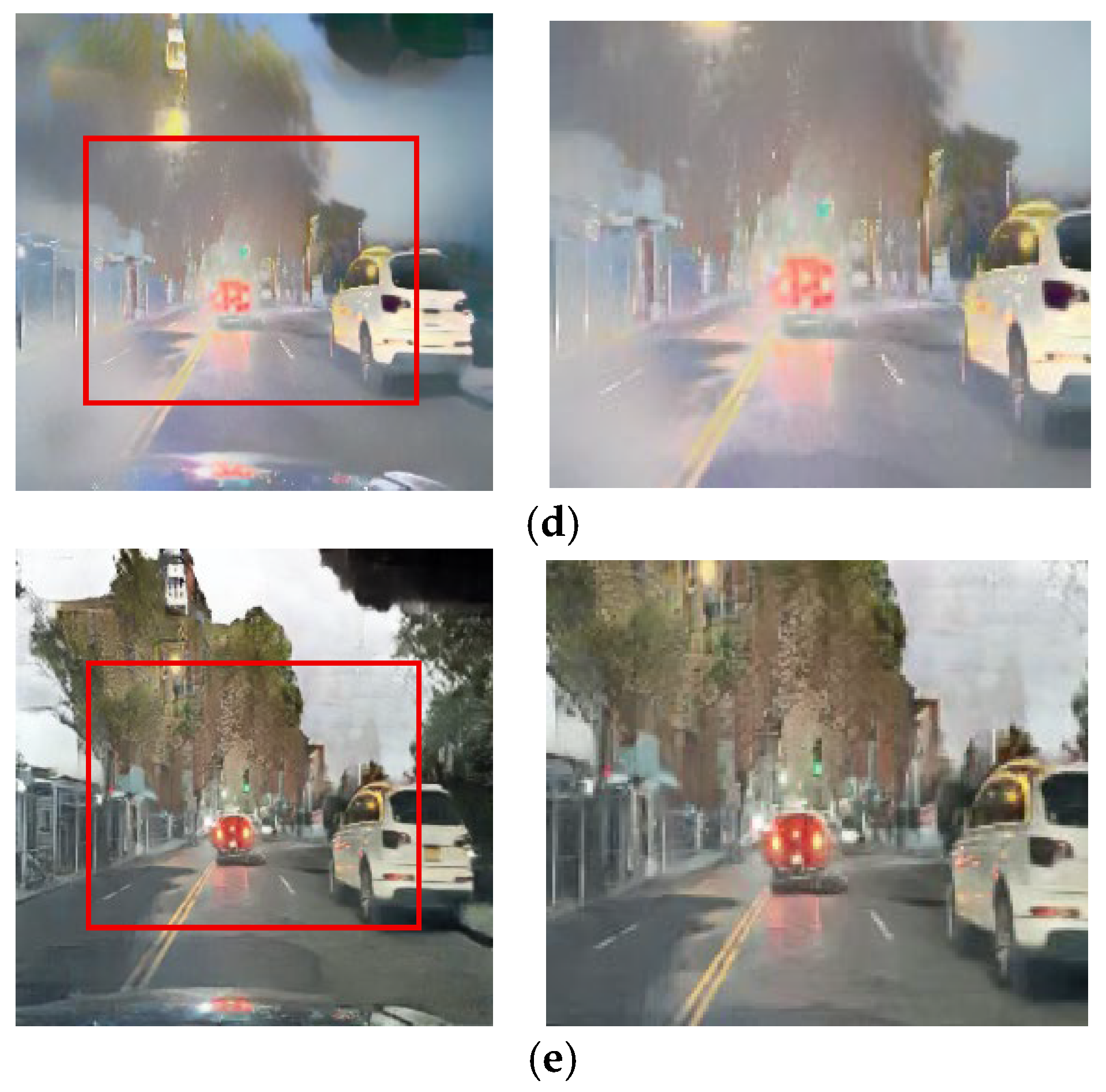
Figure 17.
Input and resulting images: (a) input image, (b) paired CycleGAN, (c) ToDayGAN, (d) SLAT DayConv [31], and (e) proposed method.
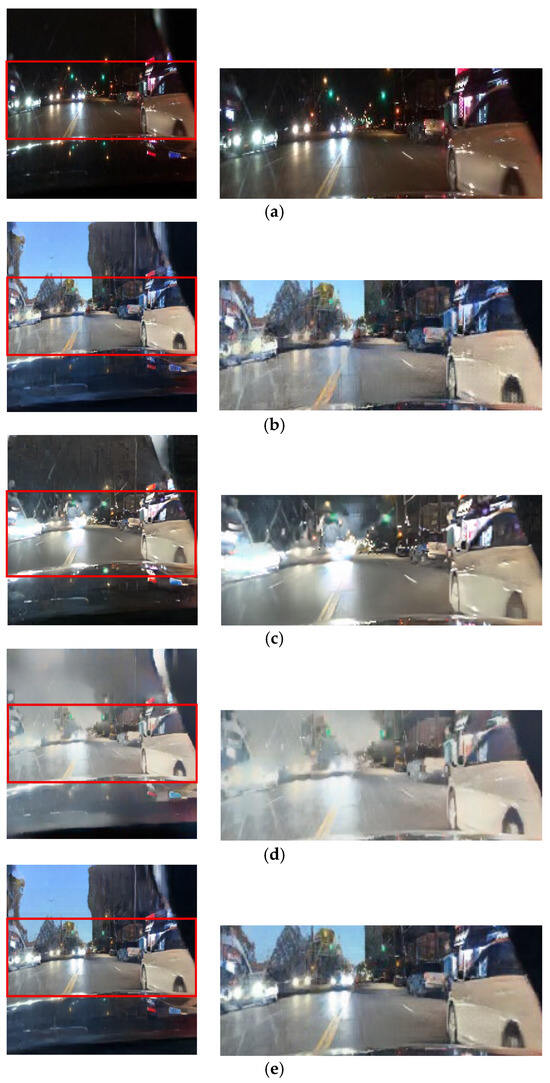

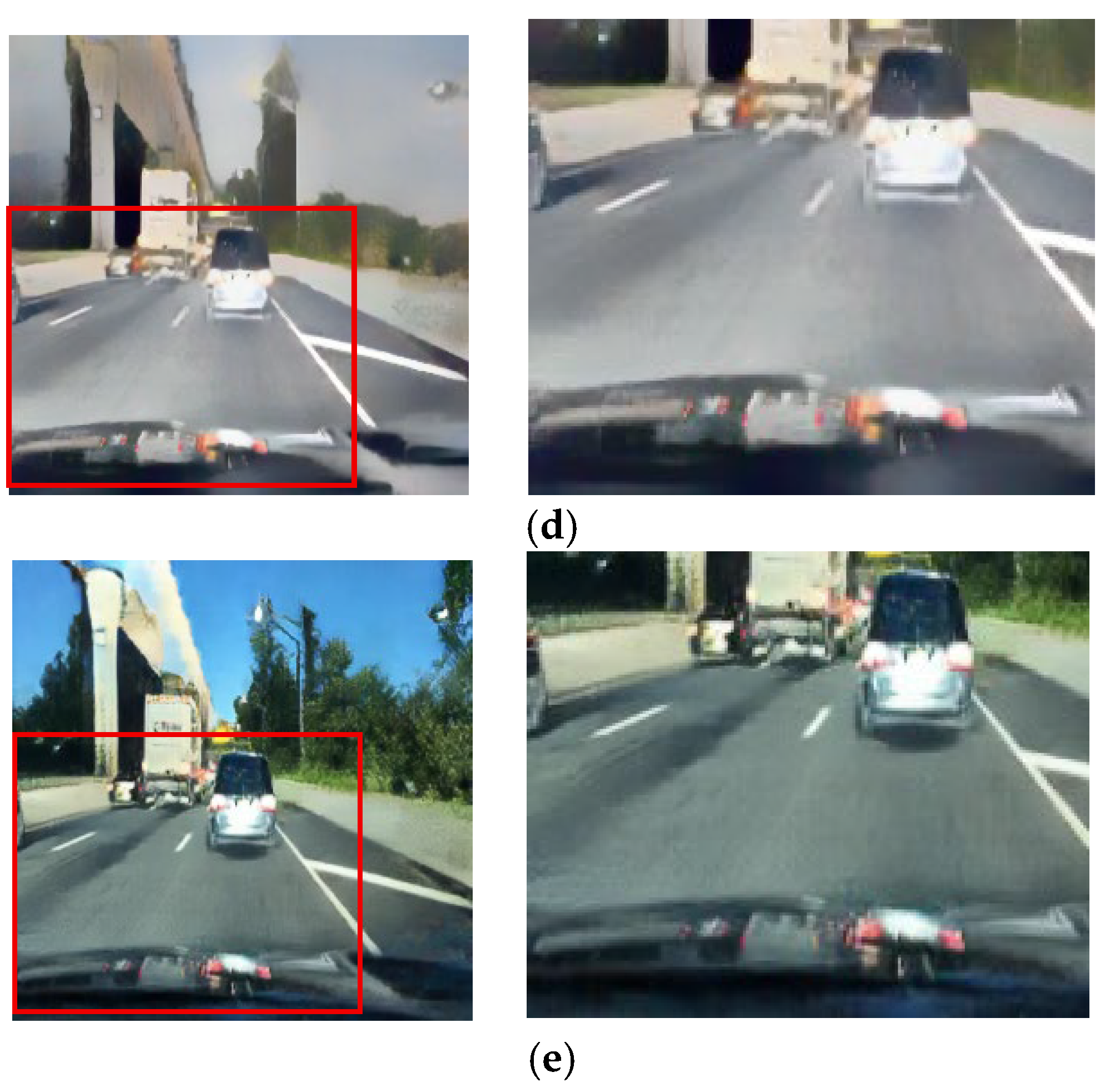
Figure 18.
Input and resulting images: (a) input image, (b) paired CycleGAN, (c) ToDayGAN, (d) SLAT DayConv [31], and (e) proposed method.

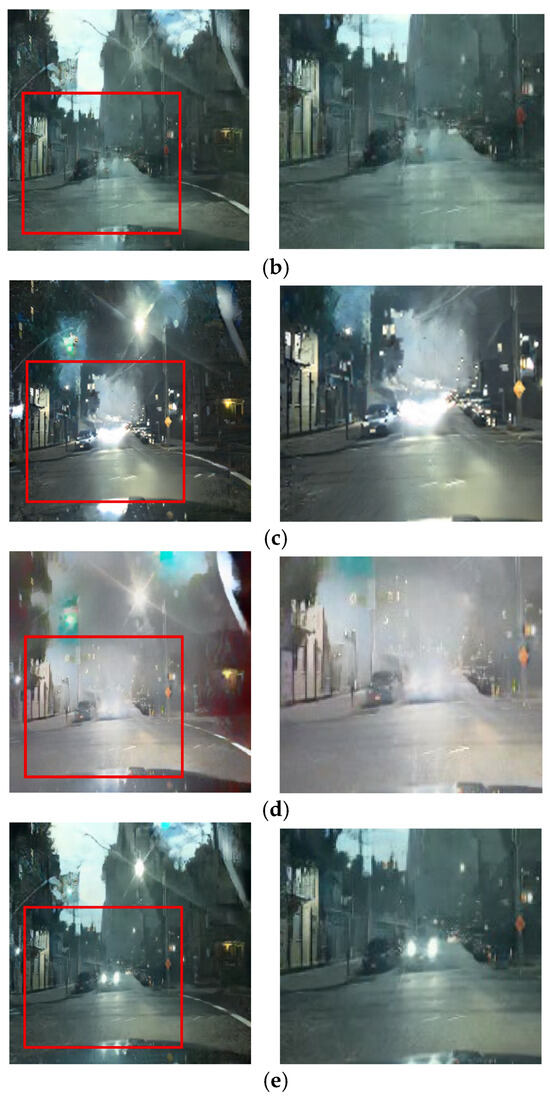
Figure 19.
Input and resulting images: (a) input image, (b) paired CycleGAN, (c) ToDayGAN, (d) SLAT DayConv [31], and (e) proposed method.
Figure 13, Figure 14 and Figure 15 showcase general driving scenes. Here, conventional methods often introduce significant visual artifacts and unnatural light distortions around light sources. In contrast, our method (e) produces a more stable and coherent translation. While some background textures may exhibit artifacts—a limitation discussed further in Section 5—our approach successfully maintains the sharpness of crucial elements like lane markings and road signs, avoiding the noticeable degradation seen in other results.
This challenge is most critical in preserving colored lights, a key focus of our work. As shown in Figure 16 and Figure 17, competing methods consistently fail in this regard, causing the red color of vehicle stop lights to either wash out, spread unnaturally, or disappear entirely. This failure to preserve the signal’s color represents a critical loss of semantic information for safety-related applications. Our method, however, robustly preserves the distinct red color of these lights. This is a direct result of the RLA map guiding the paired module to prioritize learning in these specific luminous regions, proving its effectiveness in maintaining semantic color integrity.
Similarly, preserving the structure of headlights is vital for recognizing the presence of other vehicles. Figure 18 and Figure 19 depict scenarios where competing methods cause headlights to blur excessively or blend into the background. Our framework, again, ensures that headlights are preserved with clear boundaries. By maintaining the integrity of these essential visual cues, our approach directly contributes to the goal of enhancing driver perception and safety in low-light environments.
4.4. Quantitative Evaluations
We quantitatively evaluated the performance of the proposed method using image quality metrics. The blind/referenceless image spatial quality evaluator (BRISQUE) is a no-reference assessment metric that evaluates image quality without a reference image. This model analyzes the statistical image features to detect and quantify distortions by modeling the visual perception of sharpness. The BRISQUE method evaluates the degree to which an image preserves naturalness and details, with lower scores indicating better quality.
The perception-based image quality evaluation (PIQE) is another no-reference assessment metric that detects and quantifies perceptual distortions in images. This method is based on the human visual system and does not employ subjective training data. Instead, this method detects distortions at the block level based on local characteristics, generating block-level quality maps to assess the image quality more precisely [32].
The spatial and spectral entropy-based quality (SSEQ) is a no-reference metric that evaluates the image quality based on its spatial and spectral entropy. The SSEQ metric precisely detects image distortions by comprehensively analyzing spatial and spectral characteristics to compute the quality score. This metric performs well across diverse distortion types and demonstrates a high correlation with human subjective quality assessments.
The cumulative probability of blur detection (CPBD) is a no-reference metric for detecting image blur. This method applies a probabilistic model based on human sensitivity to blur recognition to estimate the probability of detecting blur at each edge, and this method accumulates these probabilities to generate the final quality score. This metric quantifies the blur in an image, with higher values indicating a sharper image [33].
The JPEG_2000 metric evaluates the image quality of the JPEG 2000 format by analyzing the spatial characteristics and artifacts. This method quantifies the visual quality degradation caused by compression [34].
The spatial-spectral sharpness (S3) metric measures image sharpness, calculated by combining the spectral gradient and spatial changes of the image. This approach allows for the identification of sharp regions in the image and is employed for blur estimation and no-reference quality assessment [35].
The convolutional neural network (CNN)-based image quality assessment (CNNIQA) is another no-reference assessment model that uses a dual-channel CNN to predict the quality of an image. This method evaluates the image objectively based on the Visual Information Fidelity framework and extracts rich features by combining max and average pooling [36].
The multimedia assessment and inference of quality with attention (MANIQA) is a model for no-reference image quality assessment. This method employs a transformer-based attention mechanism to enhance global and local interactions in the image, demonstrating superior performance on GAN-based distorted images [37].
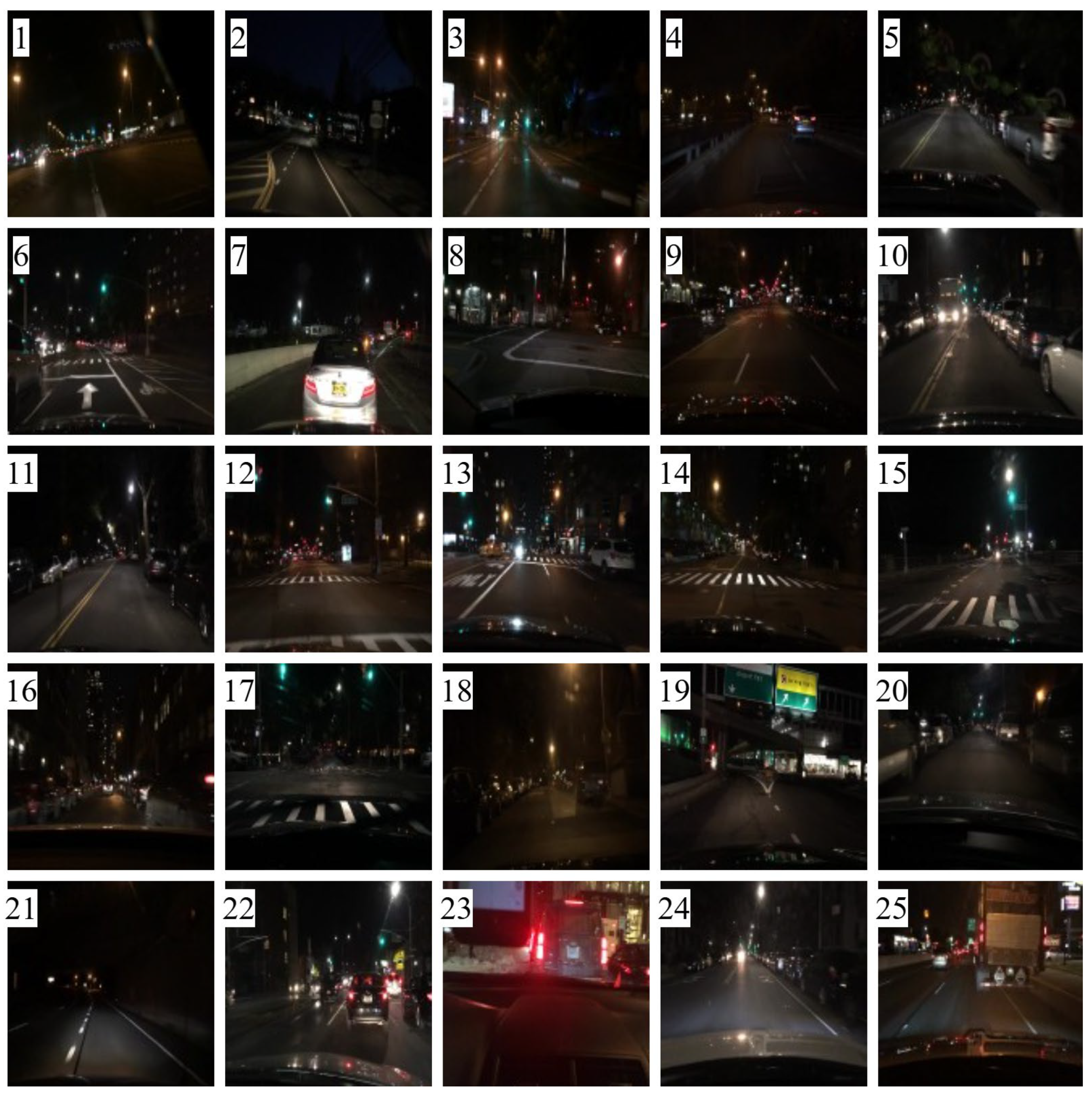
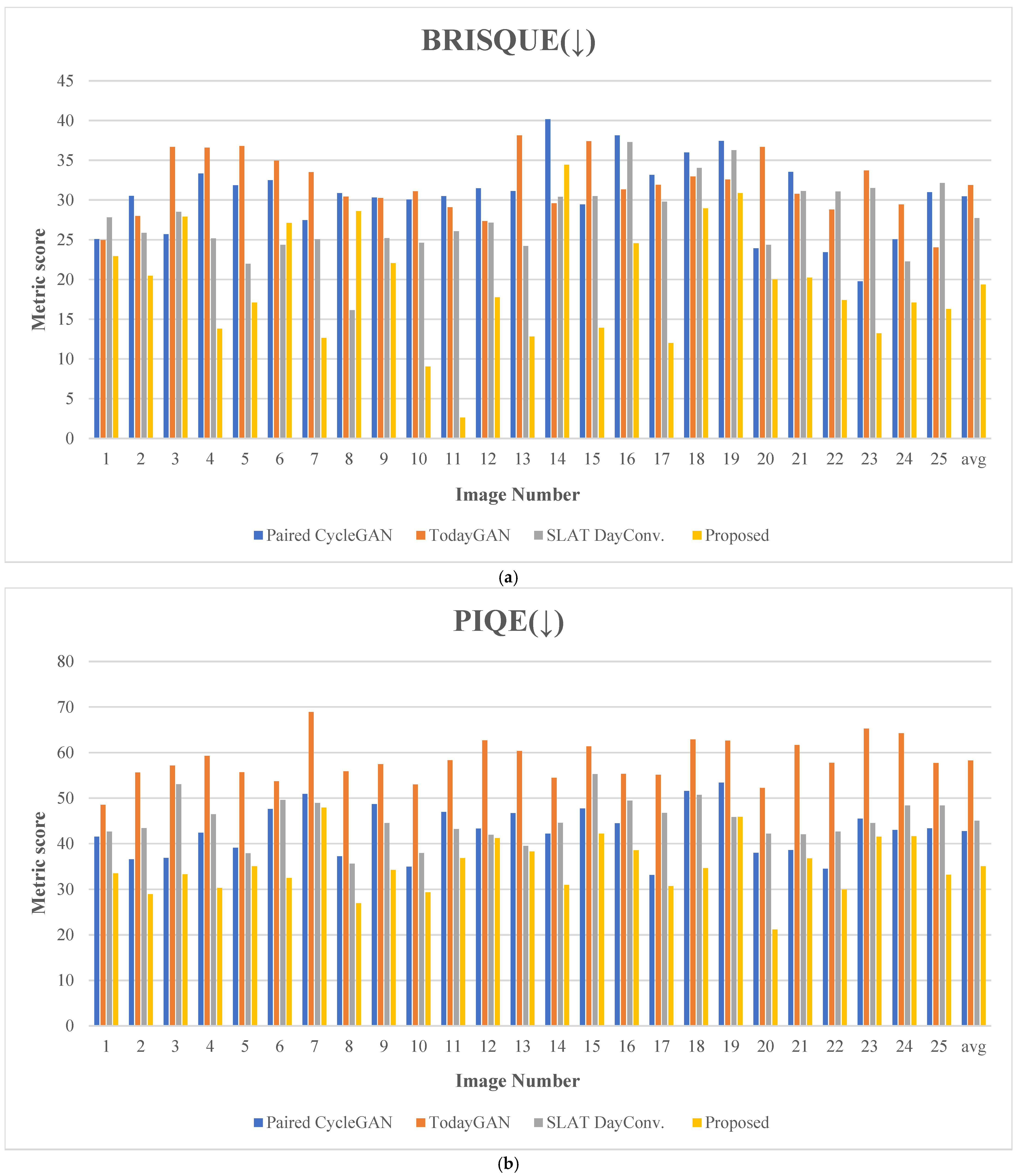
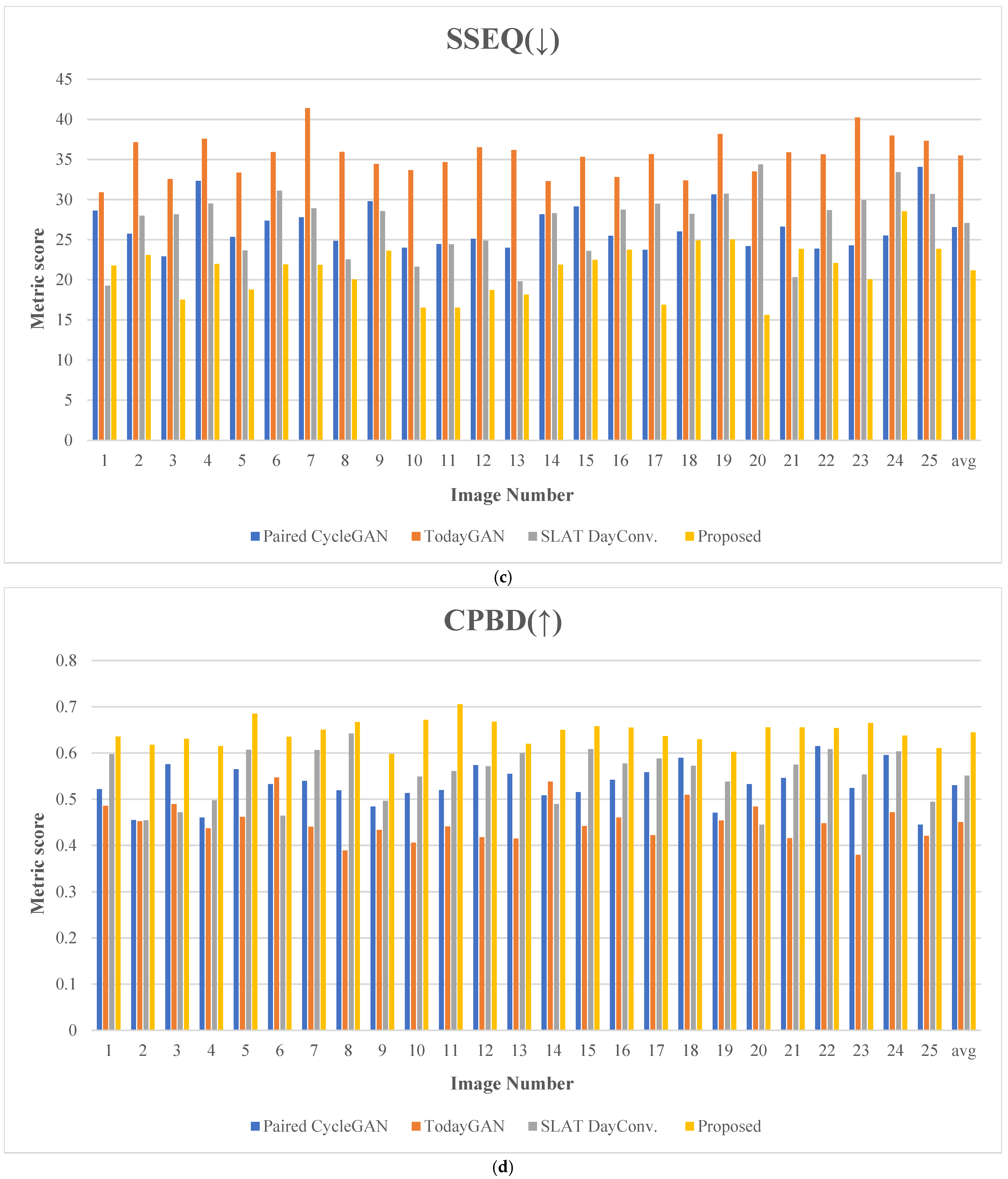
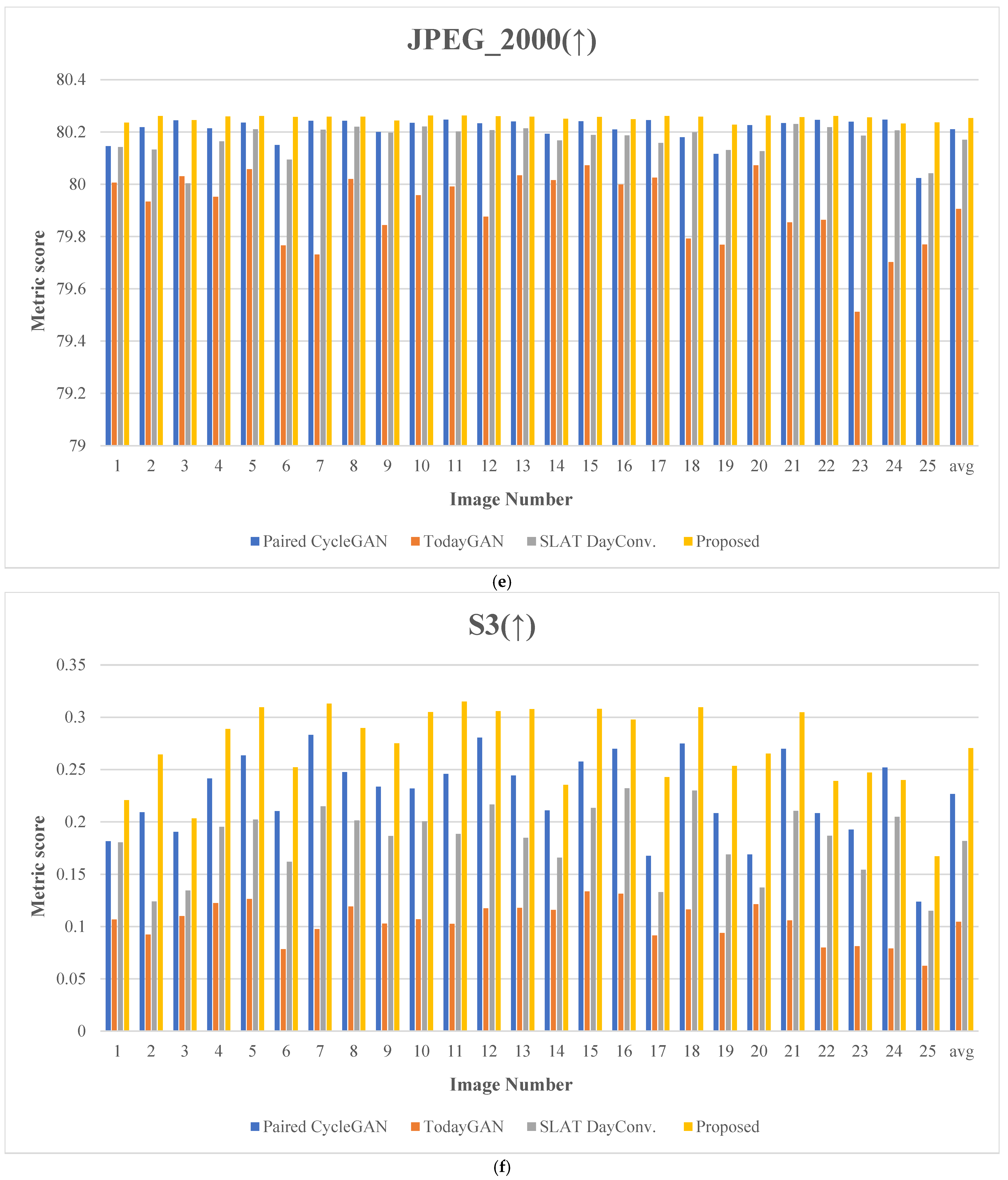
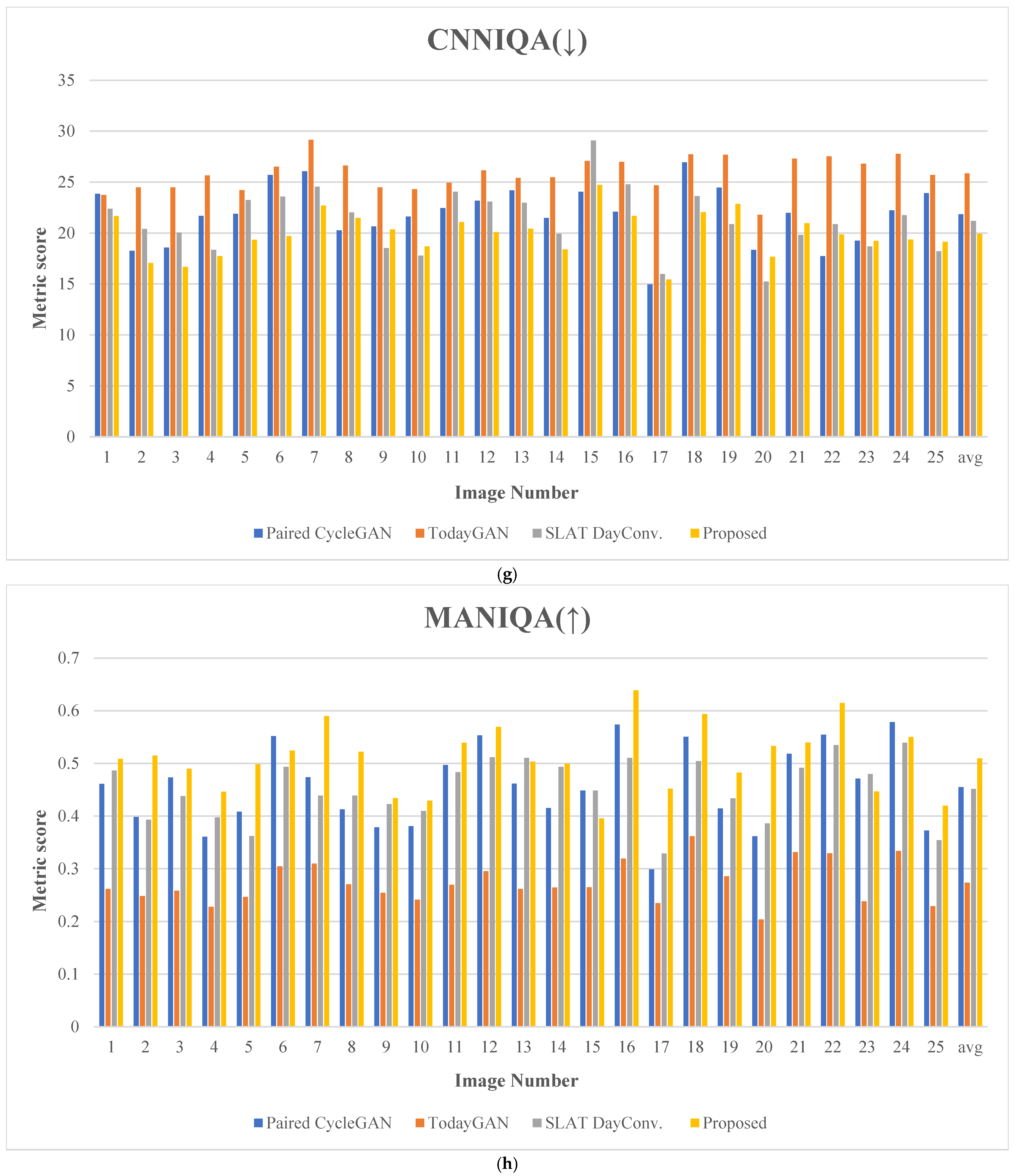
Figure 20 presents the evaluation results for 25 comparative images. Figure 21 depicts the test images used for score measurement. These images consist of nighttime driving environments where fundamental information, such as well-defined lane markings and vehicle lights, remains perceivable. The proposed method consistently ranks highly across several quality assessment metrics, demonstrating excellent robustness and minimal performance variation.
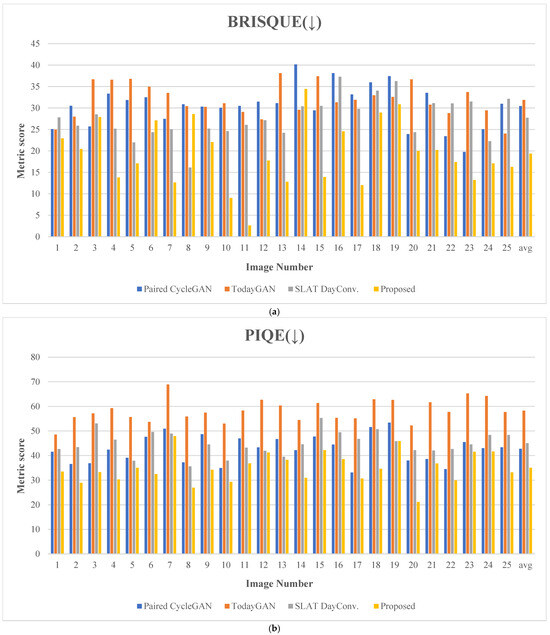
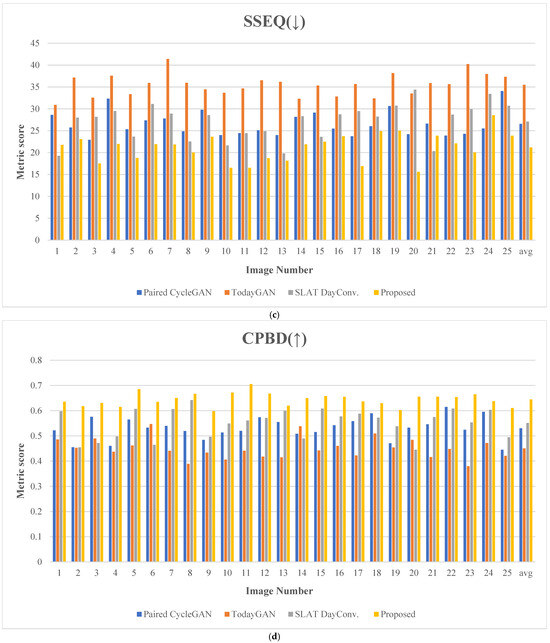
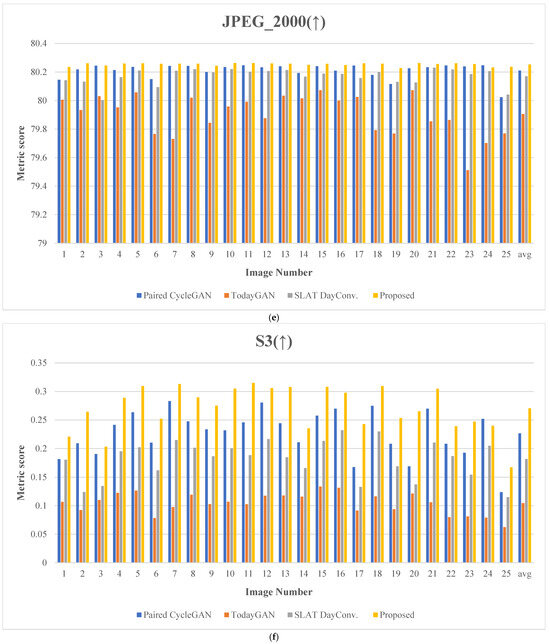
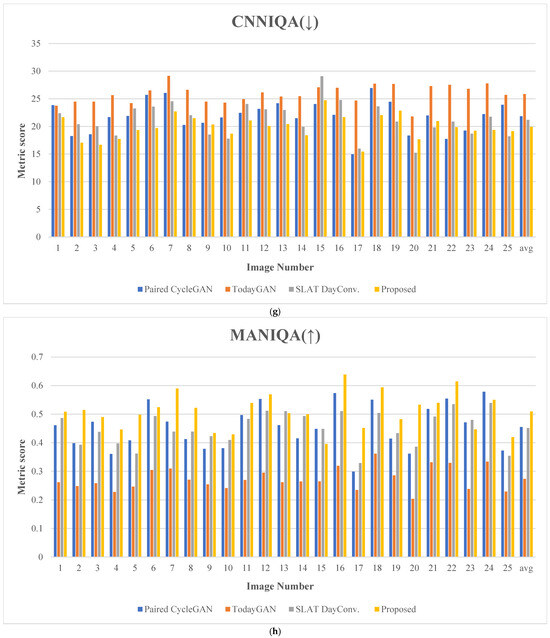
Figure 20.
Metric scores: (a) blind/reference less image spatial quality evaluator (BRISQUE), (b) perception-based image quality evaluation (PIQE), (c) spatial and spectral entropy-based quality (SSEQ), (d) cumulative probability of blur detection (CPBD), (e) JPEG_2000 score, (f) spatial-spectral sharpness (S3) score, (g) convolutional neural networks for no-reference image quality assessment (CNNIQA) score, and (h) multidimension attention network for no-reference image quality assessment (MANIQA). (The y-axis represents the metric score; the x-axis indicates the image number; The arrows in the titles indicate whether a higher score (↑) or a lower score (↓) is better.)
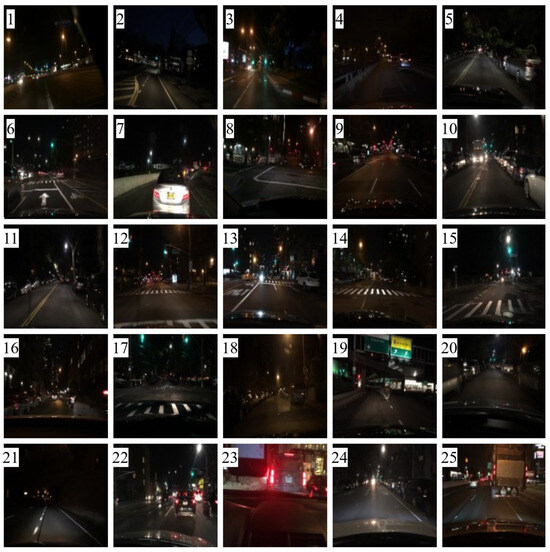

Figure 21.
Test images (the numbers in figures are the image numbers in Figure 20).
Additionally, Table 2 compares the average values for the 25 experimental images among the proposed method and existing methods, including the paired CycleGAN, ToDayGAN, and SLAT DayConv techniques [31].

Table 2.
Comparison of metric scores. (↑) Higher scores are preferable, and (↓) lower scores are preferable. Bold font highlights the best results in each corresponding metric.
The proposed method achieves the highest ranking across eight quality assessment metrics, demonstrating superior performance. In the BRISQUE evaluation, which quantifies visual distortions, the proposed method recorded the lowest score of 19.350, indicating excellent performance. This result is approximately 30.18% lower than the second-lowest score of 27.713, indicating that the proposed method produces images with minimal visual distortion.
Regarding the PIQE metric, the proposed method achieves the best performance with a score of 34.999. This result is about 18.04% lower than the second-lowest score of 42.705, indicating that the proposed method minimizes visual distortions, noise, and other degradations well while maintaining a natural image quality.
For the SSEQ metric, the proposed method achieved the best score of 21.183, which is about 20.26% lower than the second-best score of 26.565. This result demonstrates that the proposed method preserves structural quality well, maintaining a clear structure without compromising details.
With the CPBD metric, the proposed method demonstrates the best performance with a score of 0.644 in terms of the image detail representation and contrast. This measure is 16.88% higher than the second-lowest score of 0.551.
Concerning the JPEG_2000 metric, the proposed method achieved an excellent score of 80.253, exceeding the second-highest score of 80.210 by about 0.05%. This outcome demonstrates that the proposed method performs well by maintaining a high compression ratio while preserving the details of the original image.
Regarding the S3 metric, the proposed method achieved a score of 0.270, which is about 18.94% higher than the second-highest score of 0.227. This result demonstrates that the proposed method performs well in evaluating structural similarity, which quantifies quality by measuring the structural differences between images.
For the CNNIQA metric, the proposed method achieved the best score of 19.935, which is approximately 5.94% lower than the second-best score of 21.195. This outcome demonstrates that the proposed method excels in deep learning-based image quality assessment, preserving image details and perceptual quality.
Finally, concerning the MANIQA metric, the proposed method achieved a score of 0.509, exceeding the second-highest score of 0.455 by nearly 11.87%. This measure demonstrates the outstanding performance of the proposed method on attention-based image quality assessment.
We also benchmarked the computational performance of our framework against the same baselines, with results summarized in Table 3. On an NVIDIA TITAN RTX GPU with a 256 × 256 input, our method (10.21 s) achieved a highly competitive inference time, outperforming major models like SLAT DayConv and Paired CycleGAN. While our model’s GFLOPs are higher than ToDayGAN’s, this complexity is a direct trade-off for the dual-module architecture, which was intentionally designed for the superior visual quality demonstrated in Table 2. These results highlight our framework’s excellent balance between high-fidelity translation and practical efficiency.

Table 3.
Comparison of computational complexity (GFLOPs) and inference time (seconds): Lower values are preferable for both metrics.
However, as it prioritizes accuracy, the proposed method faces limitations in real-time applications due to its sequential, dual-module processing. Future research will therefore focus on optimizing the framework. A promising direction is to develop a unified, lightweight network that incorporates our guided generation principle or to apply model compression techniques like knowledge distillation for deployment in real-world systems.
5. Discussion
In this study, we introduced a dual-module framework designed to preserve critical road information, such as traffic light colors, during night-to-day image translation. The core of our approach is a pre-defined RLA map used as a fourth conditional channel, which guides the network to focus on luminous objects. The effectiveness of this guided approach is confirmed by our quantitative results in Table 2, where our method consistently outperformed prior techniques across eight no-reference image quality metrics. Higher scores in metrics like MANIQA and CPBD suggest that our method successfully preserves the fine-scale details of road markings and vehicle contours, which is crucial for driver safety.
Despite these promising results, we acknowledge several limitations that offer clear avenues for future work. A primary consideration is the computational complexity of the dual-module architecture, which presents a challenge for real-time applications. Future work could address this by developing a more efficient, unified network architecture that incorporates the guided attention mechanism or by applying model optimization techniques such as knowledge distillation. Another limitation is the framework’s reliance on synthetic data, which can create a domain gap, leading to qualitative artifacts. To improve generalization and reduce these artifacts, a promising direction is to incorporate advanced training strategies, such as the meta-tuning approaches used in recent studies [29]. Finally, to fully validate our method’s utility, the evaluation could be extended beyond perceptual metrics. A critical next step is to quantify the impact on downstream tasks, such as measuring object detection performance on the translated images. Such an analysis would provide direct evidence of the benefits for autonomous systems.
6. Conclusions
This paper addresses the critical challenge of preserving road information, such as traffic light colors, during night-to-day image translation. We proposed a novel framework that integrates an unpaired training module for global style conversion and a four-channel paired training module for fine-detail preservation. The core of our method is the introduction of an inverse RLA map. This map serves as a conditional fourth channel to guide the paired module’s training and also facilitates a final cross-blending stage that synthesizes the outputs from both modules.
Experimental results demonstrated that our approach is highly effective in enhancing road details and ensuring accurate color reproduction compared to existing techniques. By successfully preserving this vital information, our method can significantly aid driver perception in low-light environments and is expected to contribute to accident prevention.
Our future work aims to build on these results by broadening the framework’s applicability. We plan to test its robustness and generalization on more diverse datasets, particularly under adverse weather conditions like rain and fog. Successfully validating our approach in these challenging scenarios would reinforce the broader principle of this study: that combining the generative power of deep learning with explicit, domain-specific guidance leads to more robust and trustworthy outcomes in high-stakes applications. We believe this principle of “guided generation” holds significant potential in other fields where information integrity is critical, such as medical imaging and satellite analysis, paving the way for more controllable generative models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.-H.L. (Sung-Hak Lee); methodology, Y.-J.L. and S.-H.L. (Sung-Hak Lee); software, Y.-J.L.; validation, Y.-J.L., Y.-H.G., S.-H.L. (Seung-Hwan Lee), D.-M.S., and S.-H.L. (Sung-Hak Lee); formal analysis, Y.-J.L. and S.-H.L. (Sung-Hak Lee); investigation, Y.-J.L. and S.-H.L. (Sung-Hak Lee); resources, Y.-J.L. and S.-H.L. (Sung-Hak Lee); data curation, Y.-J.L., Y.-H.G., S.-H.L. (Seung-Hwan Lee), D.-M.S. and S.-H.L. (Sung-Hak Lee); writing—original draft preparation, Y.-J.L.; writing—review and editing, S.-H.L. (Sung-Hak Lee); visualization, Y.-J.L.; supervision, S.-H.L. (Sung-Hak Lee); project administration, S.-H.L. (Sung-Hak Lee); funding acquisition, S.-H.L. (Sung-Hak Lee). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by a Korea Creative Content Agency (KOCCA) grant funded by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism (MCST) in 2024 (Project Name: Development of optical technology and sharing platform technology to acquire digital cultural heritage for high quality restoration of composite materials cultural heritage, Project Number: RS-2024-00442410, Contribution Rate: 50%) and the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP)-Innovative Human Resource Development for Local Intellectualization program grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (IITP-2025-RS-2022-00156389, 50%).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available at https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/kareem00ali/night-to-day (accessed on 24 March 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Networks. Sci. Robot. 2014, 3, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional Generative Adversarial Nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmid, M.; Alam, M.S.; Rao, N.; Ashrafi, K.M.A. Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 9th International Women in Engineering (WIE) Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, WIECON-ECE 2016, Thiruvananthapuram, India, 25–26 November 2023; pp. 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2242–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Fan, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, M. Application of Improved CycleGAN in Laser-Visible Face Image Translation. Sensors 2022, 22, 4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruda, V.F.; Paixão, T.M.; Berriel, R.F.; De Souza, A.F.; Badue, C.; Sebe, N. Cross-Domain Car Detection Using Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation: From Day to Night. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Budapest, Hungary, 14–19 July 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decuyper, M.; Stockhoff, M.; Vandenberghe, S.; Ying, X. An Overview of Overfitting and its Solutions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1168, 022022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayar, S.K.; Mitsunaga, T. High dynamic range imaging: Spatially varying pixel exposures. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Hilton Head, SC, USA, 15 June 2000; Volume 1, pp. 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, S.; Singh, K. A study on Retinex based method for image enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Inventive Systems and Control, ICISC 2018, Coimbatore, India, 19–20 January 2018; pp. 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Sun, L.; Liang, Z.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, L. Joint HDR Denoising and Fusion: A Real-World Mobile HDR Image Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 13966–13975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhard, E. Parameter Estimation for Photographic Tone Reproduction. J. Graph. Tools 2002, 7, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farbman, Z.; Fattal, R.; Lischinski, D.; Szeliski, R. Edge-preserving decompositions for multi-scale tone and detail manipulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 2008, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Rahardja, S.; Khan, M.M.; Movania, M.M.; Abed, F. A Tone-Mapping Technique Based on Histogram Using a Sensitivity Model of the Human Visual System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 3469–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E. Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zuiderveld, K. Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization. In Graphics Gems; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1994; pp. 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyez, H.; Schockaert, C.; Rambach, J.; Mirbach, B.; Stricker, D. Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation: A Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Cha, M.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, J. Learning to Discover Cross-Domain Relations with Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; Volume 4, pp. 2941–2949. [Google Scholar]
- Minaee, S.; Boykov, Y.; Porikli, F.; Plaza, A.; Kehtarnavaz, N.; Terzopoulos, D. Image Segmentation Using Deep Learning: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 3523–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oussidi and Elhassouny, A. Deep generative models: Survey. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Computer Vision, ISCV 2018, Fez, Morocco, 2–4 April 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2014—Conference Track Proceedings, Banff, AB, Canada, 14–16 April 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, D.J.; Mohamed, S.; Wierstra, D. Stochastic Backpropagation and Approximate Inference in Deep Generative Models. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2014, Beijing, China, 21–26 June 2014; Volume 4, pp. 3057–3070. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, H.W.L.; Han, R.; Yin, H.H.F. Application of Variational AutoEncoder (VAE) Model and Image Processing Approaches in Game Design. Sensors 2023, 23, 3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Valkov, L.; Russell, C.; Gutmann, M.U.; Sutton, C. VEEGAN: Reducing Mode Collapse in GANs using Implicit Variational Learning. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 3309–3319. [Google Scholar]
- Anoosheh, A.; Sattler, T.; Timofte, R.; Pollefeys, M.; Van Gool, L. Night-to-Day Image Translation for Retrieval-based Localization. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 5958–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anoosheh, A.; Agustsson, E.; Timofte, R.; Van Gool, L. ComboGAN: Unrestrained Scalability for Image Domain Translation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Goodfellow, I.; Metaxas, D.; Odena, A. Self-Attention Generative Adversarial Networks. CEUR Workshop Proc. 2018, 3885, 69–78. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1805.08318 (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Wang, W.; Yin, B.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Liu, H. A Low Light Image Enhancement Method Based on Dehazing Physical Model. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2025, 143, 1595–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragavendirane, M.S.; Dhanasekar, S. Low-Light Image Enhancement via New Intuitionistic Fuzzy Generator-Based Retinex Approach. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 38454–38469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Q.T.; Duong, M.T.; Lee, S.; Hong, M.C. Adaptive Image Deblurring Convolutional Neural Network with Meta-Tuning. Sensors 2025, 25, 5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saharia, C.; Chan, W.; Chang, H.; Lee, C.; Ho, J.; Salimans, T.; Fleet, D.; Norouzi, M. Palette: Image-to-Image Diffusion Models. In Proceedings of the SIGGRAPH ’22: ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–11 August 2022; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.; Kwon, H.J.; Lee, S.H. Enhanced Night-to-Day Image Conversion Using CycleGAN-Based Base-Detail Paired Training. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatanath, N.; Praneeth, D.; Chandrasekhar Bh, M.; Channappayya, S.S.; Medasani, S.S. Blind image quality evaluation using perception based features. In Proceedings of the 2015 Twenty First National Conference on Communications (NCC), Mumbai, India, 27 February–1 March 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narvekar, N.D.; Karam, L.J. A No-Reference Image Blur Metric Based on the Cumulative Probability of Blur Detection (CPBD). IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 2678–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sazzad, Z.M.P.; Kawayoke, Y.; Horita, Y. No reference image quality assessment for JPEG2000 based on spatial features. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2008, 23, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.; Chandler, D.M. S3: A Spectral and Spatial Sharpness Measure. In Proceedings of the 2009 First International Conference on Advances in Multimedia, Colmar, France, 20–25 July 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Ye, P.; Li, Y.; Doermann, D. Convolutional Neural Networks for No-Reference Image Quality Assessment. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wu, T.; Shi, S.; Lao, S.; Gong, Y.; Cao, M.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y. MANIQA: Multi-Dimension Attention Network for No-Reference Image Quality Assessment. Available online: https://github.com/IIGROUP/MANIQA (accessed on 15 July 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).