Collaborative Optimization of Cloud–Edge–Terminal Distribution Networks Combined with Intelligent Integration Under the New Energy Situation
Abstract
1. Introduction
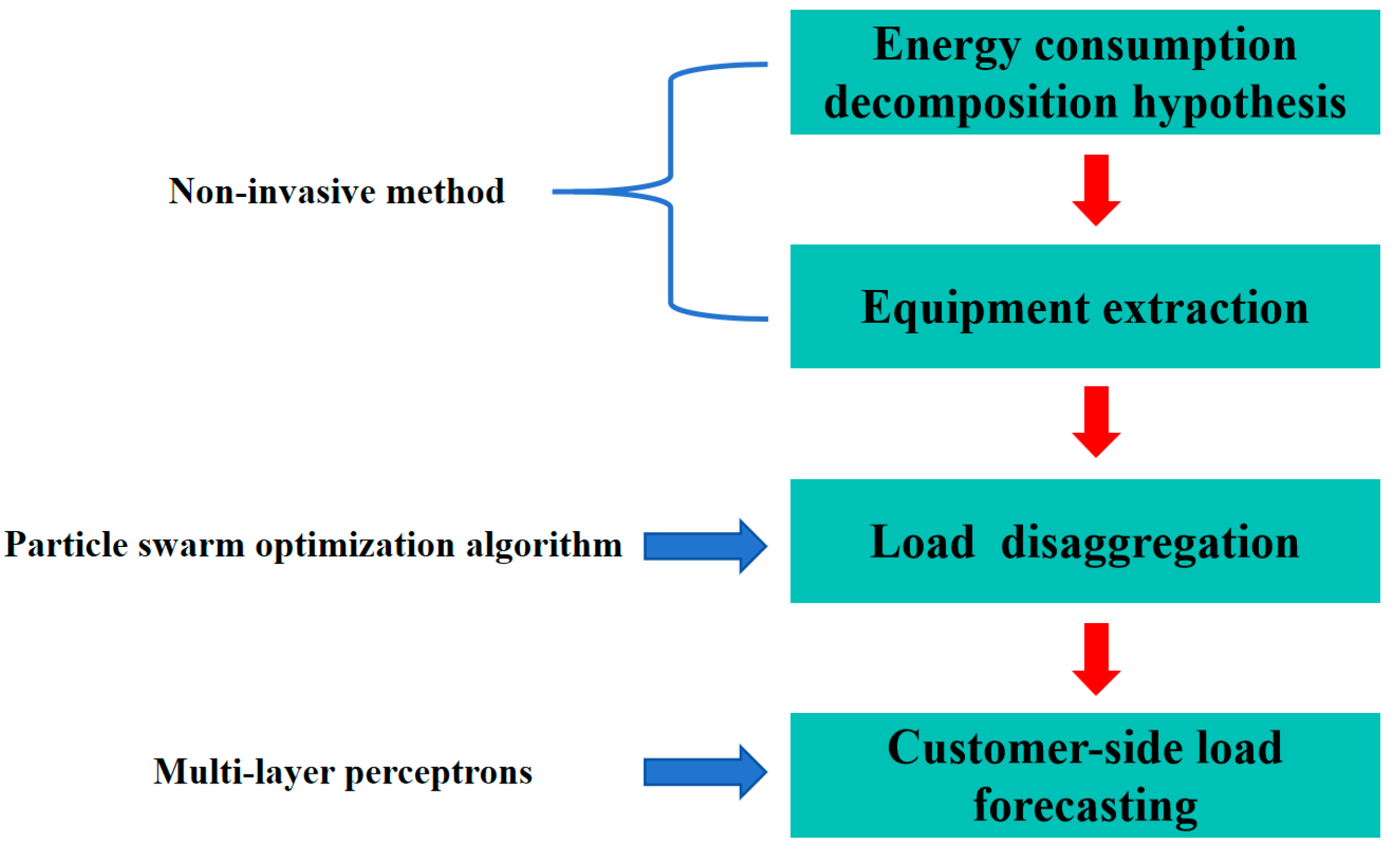
2. Construction of a Distributed Optimization Model for Cloud-Edge-Device Distribution Networks Based on Customer-Side Demands
2.1. Extraction Process of the Equipment
2.2. Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Decomposition Optimization
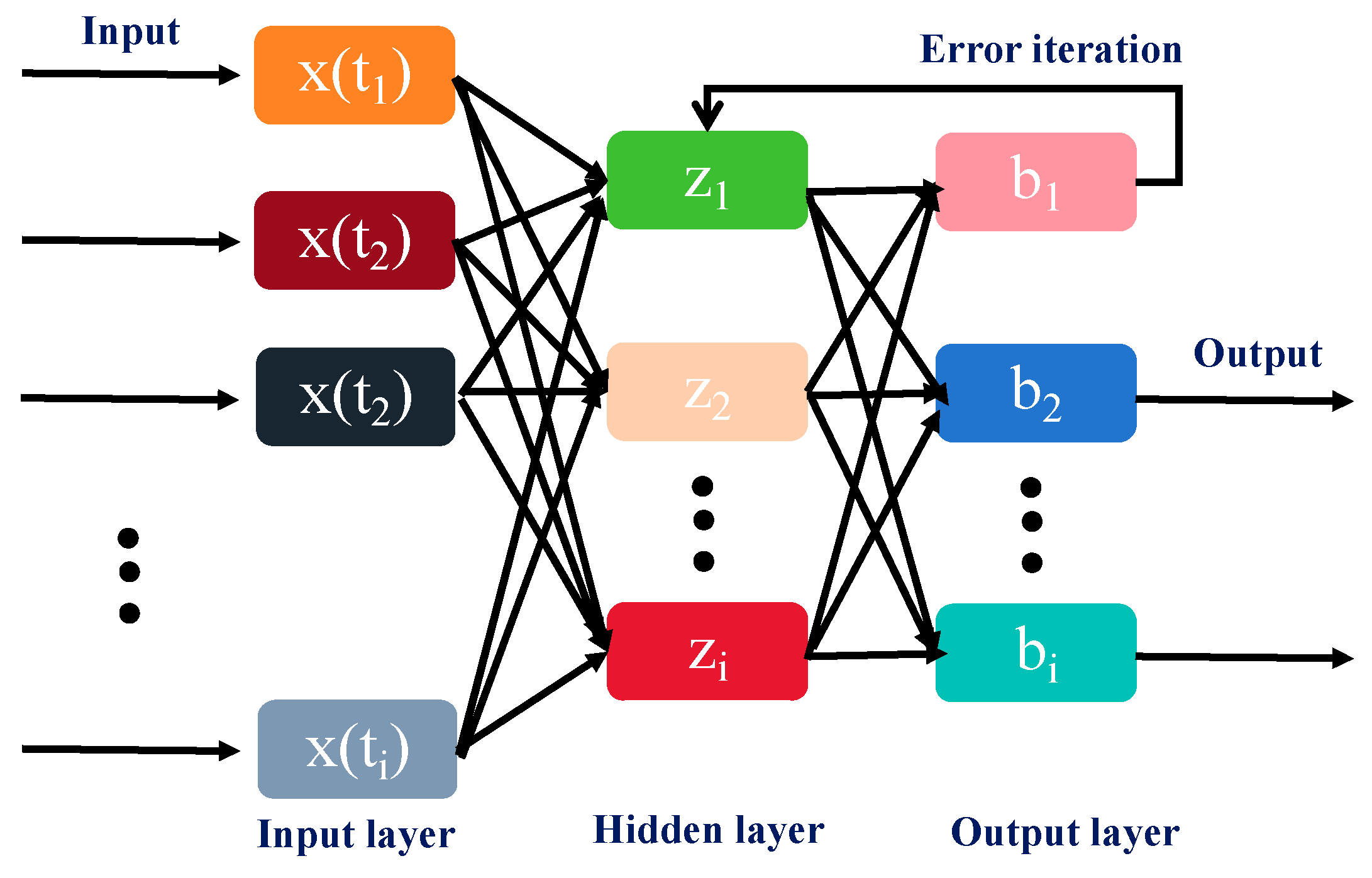
2.3. Power Prediction Algorithm for Customer-Side Electricity Consumption
3. Power Prediction of Renewable Energy Generation Under the Cloud–Edge–Device Framework
3.1. Extraction of Time Information
3.2. Construction of Artificial Neural Network Prediction Model
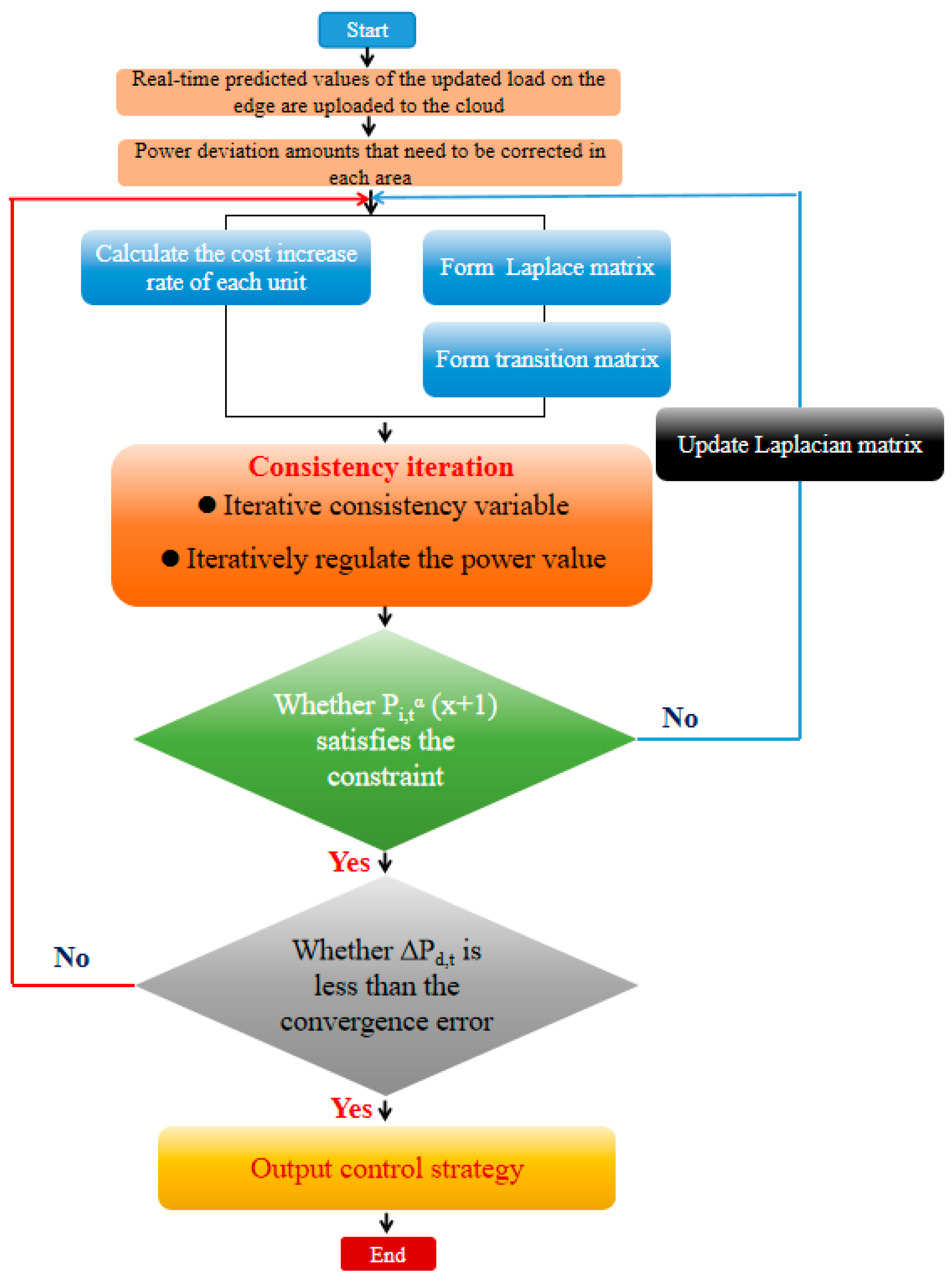
4. Control Strategies for Cloud–Edge–Device Distribution Networks Combined with Artificial Intelligence
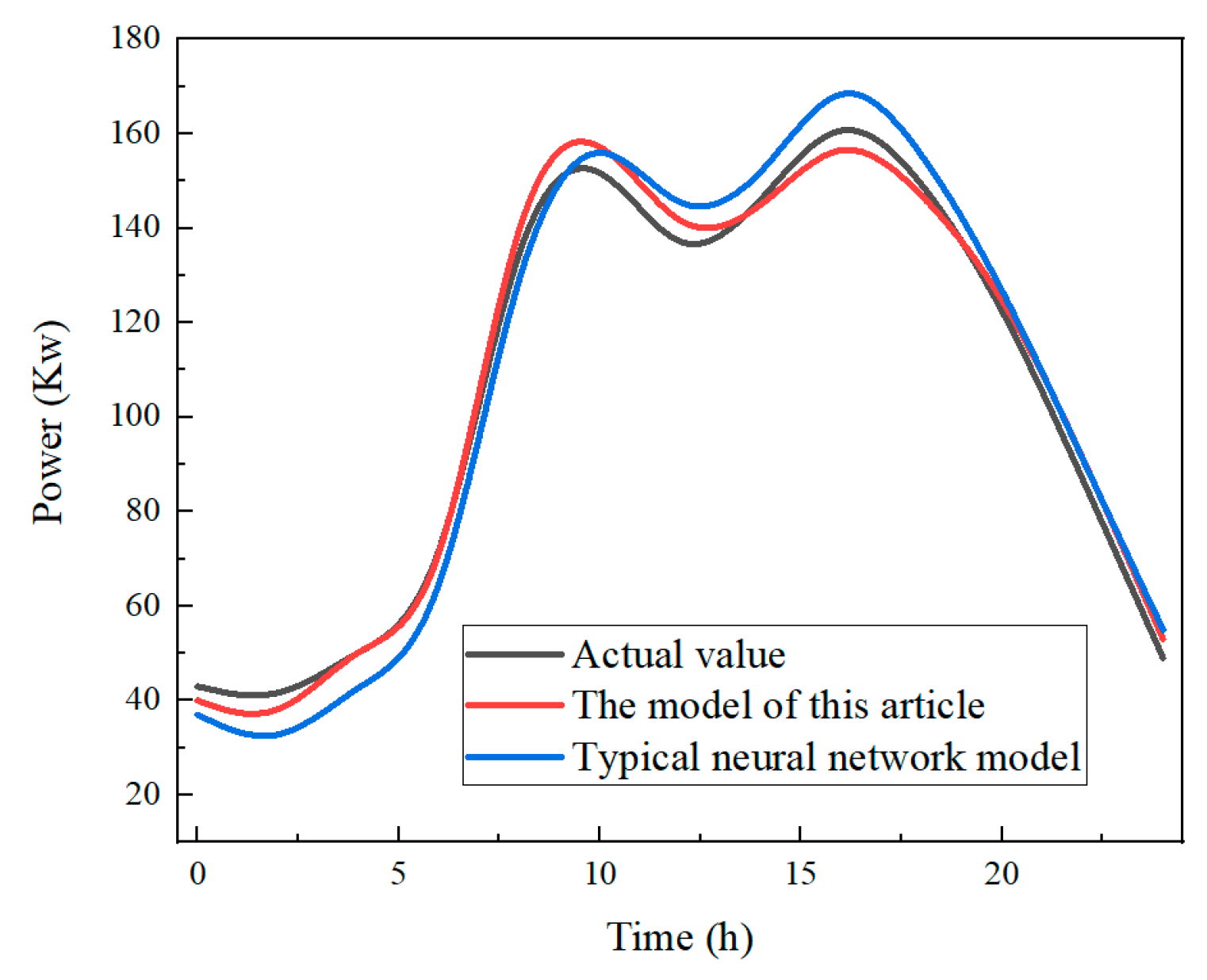
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, Z.T.; Ji, X.S.; Sarker, P.K.; Tang, J.H.; Ge, L.Q.; Xia, M.S.; Xi, Y.Q. A comprehensive review on the applications of coal fly ash. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 141, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.X.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Y.S.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.W.; Romero, C.E. Supercritical CO2 coupled with mechanical force to enhance carbonation of fly ash and heavy metal solidification. Fuel 2022, 315, 123154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.F.; Liang, S.L.; Chen, X.N.; He, T.; Wang, D.D.; Cheng, X. Enhanced wintertime greenhouse effect reinforcing Arctic amplification and initial sea-ice melting. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.X.; Zhang, Y.S.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.W.; Romero, C.E. Mineralization characteristics of coal fly ash in the transition from non-supercritical CO2 to supercritical CO2. Fuel 2022, 318, 123636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.X.; Lu, H.R.; Guo, X.M.; Ma, S.X. Quantitative effects of physical encapsulation during carbonation process based on scaled up simulation of fly ash particles. J. Energy Inst. 2024, 115, 10167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.Y.; Guo, Q.M.; Yu, J.H.; Jahanger, A.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.L. Spatial mismatch of resources in China under the “dual-carbon” goal: A new perspective incorporating energy and environmental factors. Energy 2025, 320, 135297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.Z.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, D.X.; Xue, J.X.; Cao, J.Y.; Zhang, R. Carbon emission reduction responsibility allocation in China’s power generation sector under the “dual carbon” target—Based on a two-stage shared responsibility approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 489, 144699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hodge, B.M.; Lu, S.Y.; Hamann, H.F.; Lehman, B.; Simmons, J.; Campos, E.; Banunarayanan, V.; Black, J.; Tedesco, J. Baseline and target values for regional and point PV power forecasts: Toward improved solar forecasting. Sol. Energy 2015, 122, 804–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zou, R.M.; Liu, F.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, Q.Y. A review of wind speed and wind power forecasting with deep neural networks. Appl. Energy 2021, 304, 117766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, L.; Stang, J.; Ulseth, R. Load prediction method for heat and electricity demand in buildings for the purpose of planning for mixed energy distribution systems. Energy Build. 2008, 40, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, V.T.; Anh, V.T.; Tan, M.P.; Thang, T.N. Minimize the One-Year Energy for Distribution Power Grids With Renewable Energies-Based Distributed Generators, Capacitors, and Soft Open Points. Int. J. Energy Res. 2015, 1, 3457520. [Google Scholar]
- Karthik, N.; Arul, R.; Mohit, B.; Valliappan, R.; Vojtech, B.; Lukas, P. Improved Lyrebird optimization for multi microgrid sectionalizing and cost efficient scheduling of distributed generation. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 17345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amal, K.A.; Mohammed, A.; Rakan, A.; Nazir, A.; Sultan, A.; Othman, A.; Ali, A.; Hassan, A. Mitigating malicious denial of wallet attack using attribute reduction with deep learning approach for serverless computing on next generation applications. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 18720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahra, K.M.; Mehdi, F.; Javad, A.T. An energy-aware virtual machine placement method in cloud data centers based on improved Harris Hawks optimization algorithm. Computing 2025, 107, 136. [Google Scholar]
- Saurabh, V.; Gordhan, J. Elevating manufacturing excellence with multilevel optimization in smart factory cloud computing using hybrid model. Clust. Comput. 2025, 28, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.; Khambadkone, A.M. Energy management for lifetime extension of energy storage system in micro-grid applications. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 4, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucke, K.; Arens, S.; Telle, J.-S.; Steens, T.; Hanke, B.; von Maydell, K.; Agert, C. A non-intrusive load monitoring approach for very short-term power predictions in commercial buildings. Appl. Energy 2021, 292, 116860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucke, K.; Arens, S.; Telle, J.-S.; SunkeSchlüters; Hanke, B.; von Maydell, K.; Agert, C. Particle Swarm Optimization for Energy Disaggregation in Industrial and Commercial Buildings. arXiv 2006, arXiv:2006.12940. [Google Scholar]
- Welikala, S.; Dinesh, C.; Ekanayake, M.P.B.; Godaliyadda, R.I.; Ekanayake, J. Incorporating appliance usage patterns for non-intrusive load monitoring and load forecasting. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 10, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurm, M.; Coroama, V.C. Grid-level short-term load forecasting based on disaggregated smart meter data. Comput. Sci.-Res. Dev. 2018, 33, 265–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopakumar, S.; Sree, R.R.T. Determination of Power Transformer Fault’s Severity Based on Fuzzy Logic Model with GR, Level and DGA Interpretation. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2023, 19, 2527–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, R.R.; Yin, T.; Du, Y.; Huang, R.; Tan, J.; Yu, W.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q.H. Efficient learning of power grid voltage control strategies via model-based deep reinforcement learning. Mach. Learn. 2023, 113, 2675–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.-F.; Peng, L.-L.; Hong, W.-C. Short term load forecasting based on phase space reconstruction algorithmand bi-square kernel regression model. Appl. Energy 2018, 224, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, S.; Zomaya, A. Robust big data analytics for electricity price forecasting in the smart grid. IEEE Trans. Big Data 2017, 5, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.-K.S.; Su, C.-J.; Nien, H.-T.; Tsai, P.-F.; Cheng, C.-Y. Using machine learning and big data approaches to predict travel time based on historical and real-time data from Taiwan electronic toll collection. Soft Comput. 2017, 22, 5707–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.R.; Dou, C.X.; Yue, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhang, Z.Q. Cloud-edge-end collaboration-based joint design of frequency control and transmission communication for virtual power plants. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2025, 166, 110564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, Z.R.; Liu, Y.H.; Luo, J.L.; Yang, K.P. Overall architecture design of power IoT transmission scenario based on cloud-edge-end collaboration. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2025, 2935, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.R.; Li, X.Y.; Yuan, J.; Li, G.Z. Load Balanced Data Transmission Strategy Based on Cloud–Edge–End Collaboration in the Internet of Things. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azgomi, H.; Sohrabi, M.K. MR-MVPP: A map-reduce-based approach for creating MVPP in data warehouses for big data applications. Inf. Sci. 2021, 570, 200–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Chaoran, W.; Yi, L.; Gustaf, O.; Hua, B. Water and related electrical energy use in urban households-Influence of individual attributes in Beijing, China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 130, 190–199. [Google Scholar]
- Muyuan, C. Building molecular model series from heterogeneous CryoEM structures using Gaussian mixture models and deep neural networks. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Cheng, N.; Cai, M.; Cao, C.Z.; Yang, J.W.; Zhang, Z.C. A spatially constrained asymmetric Gaussian mixture model for image segmentation. Inf. Sci. 2021, 575, 41–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, R. Modified Bayesian Information Criterion for Item Response Models in Planned Missingness Test Designs. Analytics 2024, 3, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shota, S.; Shun, S.; Hiroki, S.; Takama, Y. Dynamic Generation of Subordinate Clusters Based on Bayesian Information Criterion for Must-Link Constrained K-Means:Regular Papers. J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform. 2024, 28, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Shinotsuka, H.; Nagata, K.; Yoshikawa, H.; Mototake, Y.; Shouno, H. Development of spectral decomposition based on Bayesian information criterion with estimation of confidence interval. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2020, 21, 402–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, B.E.; Xu, X.L.; Gu, Y.F.; Deng, K.T.; Xu, Y.L.; Zhang, T.Y.; Gao, X.R.; Wang, K.N.; Wei, Q.J. Improved Droop Control Strategy for Islanded Microgrids Based on the Adaptive Weight Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Electronics 2025, 14, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udit, M.; Indra, K.; Ramakrishna, G.; Priyam, G.; Nithesh, N. Artificial intelligence based hybrid solar energy systems with smart materials and adaptive photovoltaics for sustainable power generation. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 17370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginzburg-Ganz, E.; Horodi, E.D.; Shadafny, O.; Savir, U.; Machlev, R.; Levron, Y. Statistical Foundations of Generative AI for Optimal Control Problems in Power Systems: Comprehensive Review and Future Directions. Energies 2025, 18, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, B.; Theodoros, E. Artificial intelligence to support the integration of variable renewable energy sources to the power system. Appl. Energy 2021, 290, 116754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugenia, P.; Lucas, V.; Marius, P. Clear sky solar irradiance models derived through interdependent parameterization. Renew. Energy 2025, 250, 123371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhola, K.R.; Chandramohan, V.P. A numerical study for estimating dynamic performance parameters of 40 × 40 mm2 ultrasonic piezoelectric micro blower and proposing a set of dimensions for optimum performance. Energy 2025, 314, 134198. [Google Scholar]
- Moradzadeh, A.; Zakeri, S.; Shoaran, M.; MohammadiIvatloo, B.; Mohamamdi, F. Short-Term Load Forecasting of Microgrid via Hybrid Support Vector Regression and Long Short-Term Memory Algorithms. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Lu, C.X.; Xie, B.M.; Guo, H.Y.; Zheng, B.Y. Combination of a Rabbit Optimization Algorithm and a Deep-Learning-Based Convolutional Neural Network–Long Short-Term Memory-Attention Model for Arc Sag Prediction of Transmission Lines. Electronics 2024, 13, 4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.W.; Liu, S.M.; Magomedov, R.M.; Davidyants, A.A. Optimization of inflow performance relationship curves for an oil reservoir by genetic algorithm coupled with artificial neural-intelligence networks. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 3116–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, Z.T.; Zhang, J.; Shi, G.Y.; Cao, W.P. Day-ahead and intraday multi-time scale microgrid scheduling based on light robustness and MPC. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 144, 108546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Sun, T.; Fan, M.; You, F.R.; Huang, Y.M. An adaptive power-voltage hierarchical control based on improved consensus algorithm for DC traction power supply system. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2025, 245, 111642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Xi, L. Smart generation system: A decentralized multi-agent control architecture based on improved consensus algorithm for generation command dispatch of sustainable energy systems. Appl. Energy 2024, 365, 123209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushdi, M.A.; Yoshida, S.; Watanabe, K.; Ohya, Y.; Ismaiel, A. Deep Learning Approaches for Power Prediction in Wind-Solar Tower Systems. Energies 2024, 17, 3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fu, W.Y.; Li, C.; Li, B.; Cheng, C.; Gong, Z.H.; Hu, Y.L. Short-Term Wind and Solar Power Prediction Based on Feature Selection and Improved Long- and Short-Term Time-Series Networks. Math. Probl. Eng. 2023, 1, 7745650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




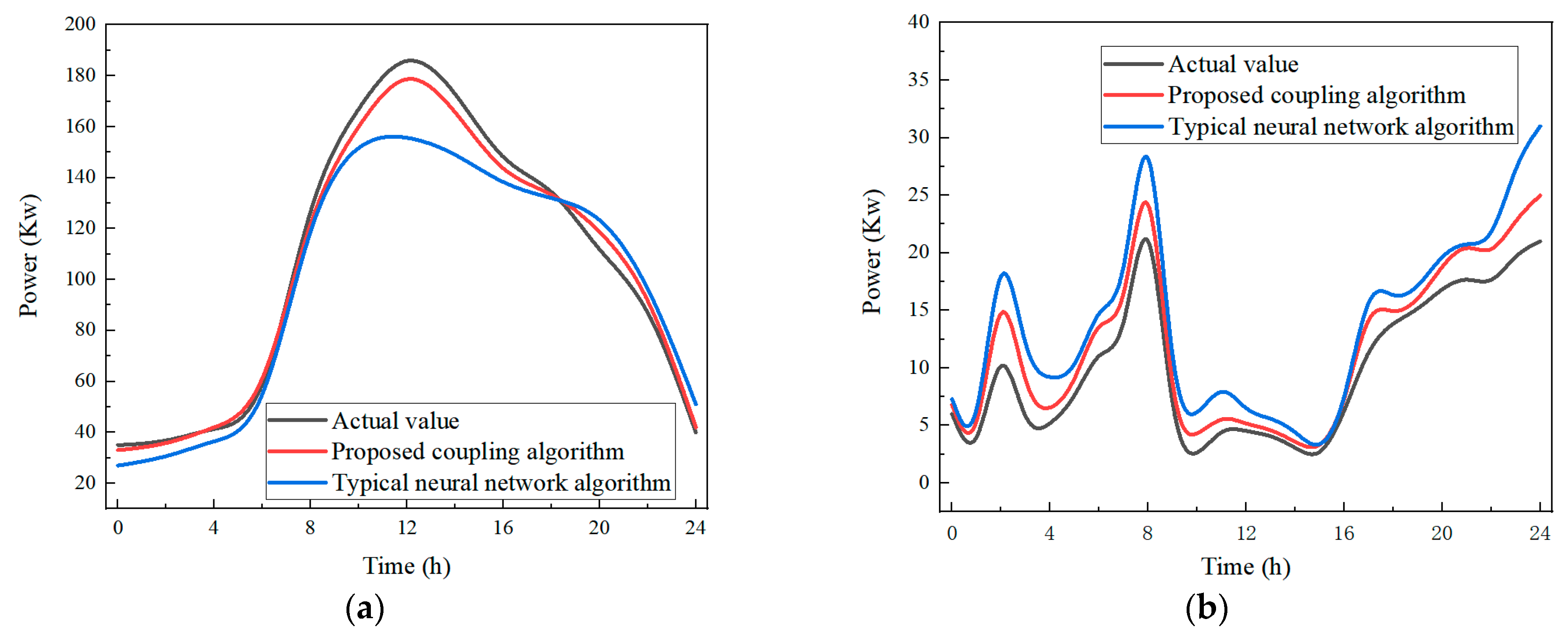
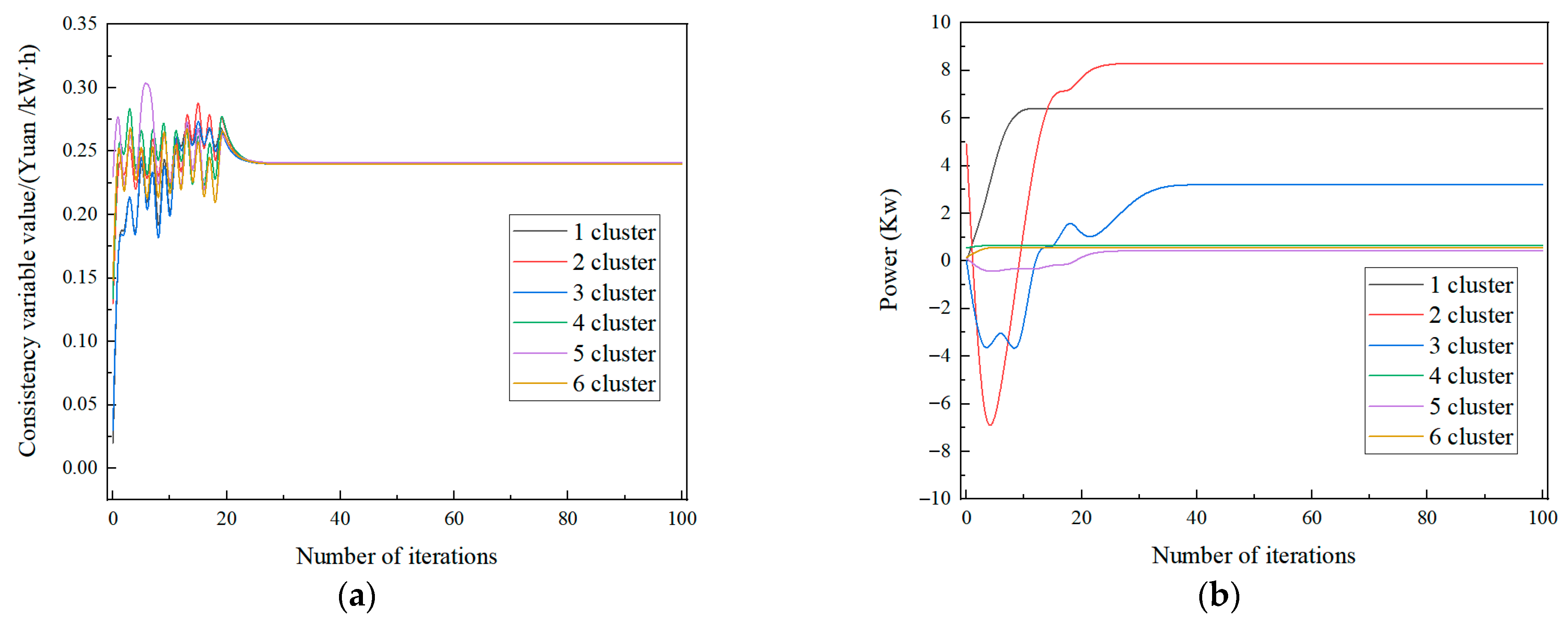
| Name of Hyperparameter | Selected Value |
|---|---|
| The number of neurons | 248 |
| Number of hidden layers | 3 |
| Learning rate | 0.02 |
| Discard rate | 5% |
| Name of Hyperparameter | Selected Value |
|---|---|
| The number of neurons | 226 |
| Number of hidden layers | 3 |
| Learning rate | 0.03 |
| Discard rate | 4% |
| Algorithm | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVR | 1454.8 | 6.07 | 238.5 | 0.968 |
| KM-Reg | 1362.2 | 5.59 | 202.4 | 0.978 |
| GMM-Reg | 1426.1 | 5.73 | 228.1 | 0.981 |
| Neural network algorithm | 1410.1 | 5.64 | 211.2 | 0.986 |
| Proposed coupling algorithm | 1347.2 | 5.36 | 199.4 | 0.991 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, F.; Wu, C.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Tai, Z.; Zhou, H.; Sun, Q. Collaborative Optimization of Cloud–Edge–Terminal Distribution Networks Combined with Intelligent Integration Under the New Energy Situation. Mathematics 2025, 13, 2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13182924
Zhou F, Wu C, Wang Y, Ye Q, Tai Z, Zhou H, Sun Q. Collaborative Optimization of Cloud–Edge–Terminal Distribution Networks Combined with Intelligent Integration Under the New Energy Situation. Mathematics. 2025; 13(18):2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13182924
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Fei, Chunpeng Wu, Yue Wang, Qinghe Ye, Zhenying Tai, Haoyi Zhou, and Qingyun Sun. 2025. "Collaborative Optimization of Cloud–Edge–Terminal Distribution Networks Combined with Intelligent Integration Under the New Energy Situation" Mathematics 13, no. 18: 2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13182924
APA StyleZhou, F., Wu, C., Wang, Y., Ye, Q., Tai, Z., Zhou, H., & Sun, Q. (2025). Collaborative Optimization of Cloud–Edge–Terminal Distribution Networks Combined with Intelligent Integration Under the New Energy Situation. Mathematics, 13(18), 2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13182924






