Abstract
Person re-identification (Re-ID) has attracted considerable attention in the field of computer vision, primarily due to its critical role in video surveillance and public security applications. However, most existing Re-ID approaches rely on image-level erasing techniques, which may inadvertently remove fine-grained visual cues that are essential for accurate identification. To mitigate this limitation, we propose an effective feature erasing-based data augmentation framework that aims to explore discriminative information within individual samples and improve overall recognition performance. Specifically, we first introduce a diagonal swapping augmentation strategy to increase the diversity of the training samples. Secondly, we design a feature erasing-driven method applied to the extracted pedestrian feature to capture identity-relevant information at the feature level. Finally, extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves competitive performance compared to many representative approaches.
Keywords:
person re-identification; diagonal swapping augmentation strategy; image feature-level erasing; data augmentation; computer vision MSC:
68T10
1. Introduction
Person re-identification (Re-ID) [1,2] aims to recognize instances of the same individual across a network of cameras, and it holds significant practical value. In fields such as intelligent surveillance [3], public security [4], and smart cities [5], Re-ID technology facilitates the automatic identification and tracking of specific individuals, thereby enhancing system efficiency and intelligence. Although existing person Re-ID approaches have achieved significant progress, the removal of fine-grained visual cues remains a challenging issue, particularly for image-level erasing techniques. To address this limitation, it is important to propose a feature erasing-based algorithm capable of learning fine-grained discriminative features that contribute to improved identity recognition accuracy.
Most traditional person Re-ID methods depend on hand-crafted features, such as Speeded-Up Robust Features (SURFs) [6], Histograms of Oriented Gradients (HOGs) [7], and Scale Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) [8] features, to facilitate identity matching and improve recognition accuracy. While these features capture certain low-level visual cues, they are often limited in their ability to represent complex semantic information and exhibit sensitivity to variations in pose, illumination, and background. Moreover, the process of designing and extracting these features typically demands substantial human expertise and computational resources, making it both time-consuming and less adaptable to large-scale or real-world scenarios. The advent of deep learning-based methods [9,10,11,12] has brought transformative changes to the field. These approaches have not only automated the feature extraction process but have also significantly enhanced recognition performance. In particular, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) [13] have demonstrated remarkable effectiveness in learning hierarchical and discriminative representations directly from raw image data. By capturing both low-level textures and high-level semantic features, CNN-based methods are better suited to handle the intra-class variations and inter-class similarities inherent in person Re-ID tasks. As a result, deep learning has become the dominant paradigm in contemporary Re-ID research.
Nevertheless, most existing person Re-ID approaches adopt image erasing-based techniques, such as random occlusion [14,15] or region masking [16,17], as a form of data augmentation or attention regulation. While these methods are effective in enhancing model robustness by forcing the network to focus on diverse and complementary regions, they may inadvertently remove discriminative local features that are critical for distinguishing visually similar individuals. This loss of fine-grained visual information, including subtle cues such as clothing textures, accessories, or body part details, can severely impair the model’s ability to perform accurate identity recognition, especially in challenging scenarios with high inter-class similarity and low intra-class variability. Therefore, there is a pressing need to explore more refined erasing strategies that preserve identity-relevant information while still promoting generalization.
To address the aforementioned challenge, we develop an effective feature erasing-based data augmentation framework, which seeks to enhance identity discrimination and boost recognition accuracy. Rather than operating directly on image pixels, our approach strategically modifies the learned feature representations to suppress redundant or overly dominant cues, thereby encouraging the model to attend to complementary and informative patterns. Additionally, we incorporate a targeted augmentation strategy that diversifies the training data and promotes robustness against appearance variations. Comprehensive experimental evaluations on multiple benchmark datasets confirm the effectiveness of our method, which consistently delivers competitive performance relative to many existing techniques.
To summarize, the primary contributions of this paper are as follows:
- (1)
- An effective feature erasing-based data augmentation framework is proposed to explore discriminative information within individual samples;
- (2)
- A feature erasing-driven method applied to the extracted pedestrian feature is introduced to capture identity-relevant information at the feature level;
- (3)
- A diagonal swapping augmentation strategy is reported to increase the diversity of the input training samples;
- (4)
- Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves competitive performance compared to many representative approaches.
2. Related Work
2.1. Person Re-Identification
Person Re-ID remains a highly challenging problem in the field of computer vision, largely attributed to the significant variations in human pose, camera viewpoints, illumination, and background clutter. Early research in this domain predominantly relied on manually engineered features to represent pedestrian appearances [18,19,20,21,22]. While these handcrafted descriptors offered initial insights, they often struggled with generalization across complex real-world scenarios. In contrast, recent advances in deep learning have led to a paradigm shift, with learning-based methods now dominating major Re-ID benchmarks [23,24,25,26], owing to their superior ability to extract robust and discriminative features from raw image data. To explore robust features within individual body areas, Song et al. [27,28] propose the Mask-Guided Contrastive Attention Model (MGCAM), which is the first approach to leverage binary masks for the person Re-ID task. To simultaneously explore both local and global discriminative features at the same time, Cai et al. [29] introduce MMGA, a multi-scale body-part mask-guided attention network, which further guides the attention learning process. Ghorbel et al. [16] propose a feature-dropping branch aimed at discovering complementary and informative features from individual samples. Most of these binary mask-based approaches usually rely on predefined body-part segmentation or external pose estimation models, which may introduce noise or limit their generalization capability. Specifically, inaccuracies in pose estimation or segmentation boundaries can lead to suboptimal attention guidance, thereby degrading the overall feature representation and recognition performance, especially under complex backgrounds or occlusions.
With the widespread adoption of visual attention mechanisms in computer vision, attention-based person Re-ID approaches have emerged as a promising direction, aiming to improve feature representation by focusing on discriminative regions of the human body. To better capture both spatial and semantic details, Li et al. [30] propose an innovative harmonious attention network, which simultaneously integrates hard regional attention for discriminative part localization and soft pixel-level attention for detailed feature enhancement, achieving a balanced and complementary attention mechanism. Chen et al. [31] introduce a hierarchical attention mechanism that prioritizes salient foreground information while progressively refining focus toward fine-grained visual attributes, such as clothing color. This approach draws inspiration from the selective and staged nature of human visual perception, which first distinguishes primary subjects from cluttered backgrounds and then shifts attention to detailed appearance cues. The effectiveness of the method relies heavily on accurately distinguishing the foreground person from complex backgrounds. Inaccurate foreground extraction may mislead the attention mechanism and degrade performance.
These studies in person Re-ID can be broadly grouped into three thematic directions. First, methods addressing challenging scenarios target issues such as occlusion [32], clothes changes [33], crowded scenes [34], illumination variations [2], and extreme viewpoints [35]. Second, feature enhancement approaches leverage attention mechanisms [36], salient part erasing [34], and foreground enrichment to capture more discriminative and robust representations [25]. Third, model optimization strategies encompass hybrid discriminative–generative learning [37], ranking representation refinement [23], distribution alignment via camera-aware normalization [10], and lightweight spatial rescaling for efficiency [38]. Together, these lines of research illustrate both the diversity of real-world challenges and the methodological breadth driving progress in person Re-ID. Unlike existing image-level erasing or attention-based augmentation methods that may discard fine-grained visual cues, our framework performs erasing at the feature level, preserving detailed appearance information while enhancing discriminative capacity. In addition, the proposed diagonal swapping augmentation increases sample diversity in a structured manner, further improving recognition performance without relying on scene-specific priors or complex network modifications.
2.2. Image-Level Erasing Technique
With the rapid advancement of deep learning, image erasing techniques [39,40] have been widely adopted in various computer vision tasks, such as object detection, object tracking, and person Re-ID. By intentionally masking out salient regions of input images during training, these methods encourage models to explore complementary or less discriminative cues, thereby improving feature robustness and generalization. In the context of person Re-ID, image erasing serves as an effective regularization strategy to mitigate overfitting to dominant body parts and enhance recognition performance under occlusion or viewpoint variations. Luo et al. [9] adopt a random erasing strategy to alleviate the occlusion issue and enhance the generalization capability of person Re-ID models. To enrich the diversity of training data, Zang et al. [41] introduce a data augmentation framework that combines random erasing with a novel random scaling mechanism, enabling the generation of image samples with controllable visual variability. Aiming to improve robustness against variations in occlusion, pose, and illumination, Ding et al. [42] integrate non-local attention modules and random erasing technique into their model, effectively enhancing feature discrimination and global context awareness. The random erasing strategy introduces local perturbations during training, encouraging the model to focus on diverse and complementary features beyond the most salient regions. Chen et al. [43] propose the Knowledge Transfer with Simulated Inter-Image Erasing (KTSE), a novel augmentation paradigm designed to mitigate the challenges of determining optimal erasure boundaries. By simulating occlusions across different image instances, KTSE avoids the common pitfalls of under-utilized supervision and over-suppressed representations, facilitating more balanced and transferable feature learning. In an effort to mitigate the model’s dependence on clothing-related features, Yin et al. [44] incorporate a random erasing mechanism that compels the network to attend more closely to identity-consistent cues, such as body shape or posture, thereby enhancing its robustness to variations in apparel.
While image erasing techniques have been widely adopted to enhance model robustness by introducing occlusion-like augmentations at the pixel level, they inherently suffer from several limitations. First, these methods often rely on randomly removing rectangular regions from the input images, which may unintentionally discard discriminative visual cues or introduce excessive semantic distortion. Second, due to their image-level operation, they lack fine-grained semantic awareness and cannot precisely target redundant or over-represented features in the feature space. In contrast, feature erasing operates directly on high-level representations, allowing for more targeted and interpretable suppression of dominant activations, thereby better encouraging the model to explore complementary identity-discriminative cues. Moreover, feature-level operations are less sensitive to low-level noise and are more aligned with the model’s learned abstraction, making them inherently more stable and effective in promoting generalization.
2.3. Data Augmentation
Data augmentation [45] serves as a crucial auxiliary strategy for enhancing the generalization capability of deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) by artificially increasing the diversity of training samples. Existing augmentation techniques can be broadly categorized into five major paradigms based on their underlying transformation principles:
- (1)
- Geometric-based augmentations, such as horizontal and vertical flipping, alter spatial configurations without affecting semantic content;
- (2)
- Sample-mixing strategies, such as CutMix [46] and Mixup [47], generate novel training instances by combining content from multiple images to improve data efficiency and regularization;
- (3)
- Search-driven augmentations, exemplified by RandAug [48] and AutoAug [49], rely on algorithmic search to identify optimal augmentation policies;
- (4)
- Photometric-based augmentations, including operations like Gaussian blurring and color jittering, simulate variations in lighting and appearance;
- (5)
- Information-dropping methods, such as Cutout [50] and Random Erasing [39,40], deliberately occlude regions to encourage spatial robustness.
Despite their effectiveness, most existing data augmentation techniques operate predominantly at the image level, focusing on perturbations within the pixel space. However, for complex multi-vision tasks that involve structured or cross-modal representations, it is increasingly important to explore augmentation strategies beyond the raw image domain. These strategies should aim to manipulate data at the feature, semantic, or relational levels, where more task-relevant and discriminative patterns can be captured. This motivates a shift towards non-image-level augmentation paradigms that can adaptively enrich the diversity of internal representations while preserving semantic consistency across multiple visual perspectives.
3. Methodology
3.1. Overview
In this work, we propose a feature-level augmentation paradigm that enhances person Re-ID performance by selectively suppressing dominant activations in the representation space. Unlike conventional augmentation techniques that manipulate raw pixel data, our method operates directly on deep features, enabling the model to uncover diverse identity-discriminative cues by mitigating over-reliance on redundant patterns. To further improve generalization, we design an adaptive augmentation scheme that introduces controlled feature perturbations aligned with semantic consistency, thereby increasing robustness to appearance variations. The overall framework is shown in Figure 1, which consists of two main components: diagonal swapping augmentation strategy and image feature-level erasing. The augmented and original samples are input into our feature-erasing-driven stream, where Gaussian blur erasing is performed. These modules interact to enrich training diversity while preserving discriminative features, thereby enhancing the model’s performance.
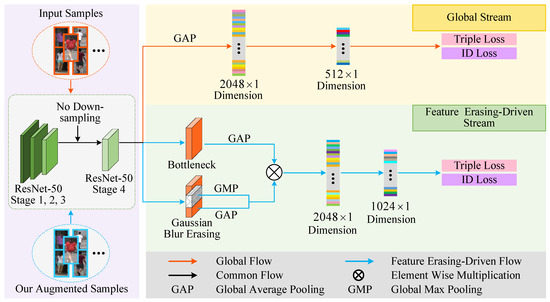
Figure 1.
Overall framework of our proposed feature erasing-based data augmentation approach designed for the person Re-ID task.
3.2. Diagonal Swapping Augmentation Strategy
In person Re-ID and other fine-grained visual recognition tasks, deep learning models are prone to overfitting spatially fixed visual cues, particularly when trained on datasets with limited diversity in pose, viewpoint, background, or occlusion. These models often rely on consistent positional patterns, such as the typical location of clothing features or background textures, which undermines their ability to generalize across unconstrained environments. Such over-dependence on spatial regularities can lead to poor performance when the test distribution deviates from the training conditions. To alleviate this issue, conventional data augmentation techniques such as horizontal flipping, random cropping, and rotation have been widely adopted. While effective to a degree, these axis-aligned transformations primarily preserve the internal spatial relationships within local regions and do not fully eliminate position-dependent feature reliance. Moreover, they are insufficient in disrupting long-range spatial correlations that are frequently exploited by deep convolutional networks, often leading to shortcut learning.
To diversify spatial configurations beyond conventional augmentations, we introduce a novel diagonal swapping strategy designed to induce structured yet semantically consistent variations. The complete processing pipeline of the proposed diagonal swapping augmentation strategy is illustrated in Figure 2, which demonstrates how global structural diversity can be introduced in a supervised learning setting without altering ground-truth identity information. The original input sample is first divided into four patches, each of which may optionally undergo localized augmentation operations to enrich intra-region variability. Subsequently, diagonally opposing patches are swapped. Specifically, the top left is exchanged with the bottom right, and the top right is exchanged with the bottom left, resulting in a reconfigured image that deviates from axis-aligned patterns. This rearrangement introduces spatial perturbations that challenge the model to extract robust and position-invariant identity features, ultimately mitigating overfitting to fixed positional cues and enhancing generalization across diverse person Re-ID scenarios.
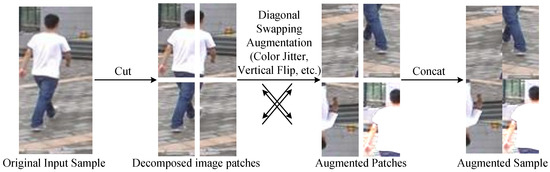
Figure 2.
The pipeline of the proposed diagonal swapping augmentation strategy designed for the person Re-ID task. The original input is divided into four patches, optionally augmented to enrich intra-region variability, and then diagonally swapped to produce a reconfigured image that breaks axis-aligned patterns.
Consider a labeled training set denoted as , where each sample corresponds to an identity label , . Here, C, H, and W refer to the number of channels, height, and width of the image, respectively, while M indicates the total number of labeled samples.
Our augmentation strategy initiates by partitioning each sample into four non-overlapping subregions through simultaneous division along the vertical (height) and horizontal (width) axes, which can be formulated as follows:
where , , , and denote the resulting top-left, top-right, bottom-left, and bottom-right patches, respectively, and represents the partitioning operation along the vertical and horizontal dimensions.
Then, we perform a diagonal swapping operation on the partitioned sample to obtain a new rearranged image , which can be expressed as follows:
where denotes the diagonal swapping operator, which interchanges diagonally opposite patches of the input sample. This transformation introduces structured perturbation at the spatial layout level, thereby enhancing the model’s ability to learn spatially invariant features.
Subsequently, independent augmentation operations are applied to each subregion, and the resulting four modified patches are concatenated to form a new composite sample , which can be formally defined as follows:
where corresponds to the final augmented image. , , , and represent instance-specific augmentation transformation (e.g., color jitter, vertical flip) applied to each corresponding patch. Although the four patch-wise augmentations stem from the same augmentation pool, their stochastic behavior introduces diversity at both the local patch and holistic image level. The function performs vertical and horizontal concatenation to reconstruct a full-resolution image with enriched structural variance across the input image dataset.
This augmentation strategy encourages the model to generalize better by increasing intra-sample variability without altering semantic identity. It serves to mitigate overfitting, particularly in semi-supervised scenarios where unlabeled data is leveraged for representation learning.
By significantly perturbing the global layout without modifying the content itself, the proposed strategy encourages the model to shift its focus from rigid spatial locations to more transferable visual patterns such as texture, contour, and chromatic features. This promotes the learning of location-invariant representations and improves generalization under challenging scenarios such as misalignment, occlusion, or background variation. Furthermore, the augmentation is lightweight, label-preserving, and easily integrable into mainstream training pipelines.
3.3. Image Feature-Level Erasing
Image feature-level erasing refers to the deliberate suppression of salient activations within intermediate feature representations of a deep neural network. Unlike traditional erasing methods that randomly mask raw input image pixels, this technique directly manipulates the model’s internal response to a given input. The primary objective is to mitigate over-reliance on discriminative but spatially fixed patterns, thereby encouraging the network to discover alternative and complementary cues. This technique is particularly beneficial in recognition tasks where visual distinctions are subtle and localized, such as person Re-ID. In these scenarios, convolutional neural networks tend to focus on a few dominant features like clothing color or accessories. When such features are consistently highlighted, the model may fail to generalize to unseen variations. Feature-level erasing addresses this issue by removing or suppressing high-response regions in the activation maps, forcing the model to attend to secondary attributes such as texture, structure, or pose-specific details.
Among erasure-based strategies, the technique of random erasing [40] has become a widely adopted regularization method across various computer vision applications, including image retrieval, object detection, semantic segmentation, and classification. However, hard erasure techniques often lead to excessive information loss, particularly when applied to already abstracted feature representations. To address this issue, we propose the image feature erasing-driven approach (as illustrated in Figure 3), which aims to mitigate the missing discriminative representations induced by hard erasure. Rather than fully occluding regions of feature maps, our method applies controlled attenuation to the erased regions, thus reducing information loss while still introducing perturbation for regularization.
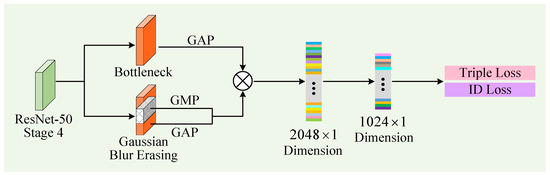
Figure 3.
The processing workflow of the image feature erasing–driven strategy designed for the person Re-ID task.
Concretely, let the erased regions be denoted by , where each corresponds to a spatial region within the n-th channel of the feature map, , and N denotes the total number of channels. We apply Gaussian filtering to these regions to reduce the abruptness of the erasure, thereby preserving a softened version of the feature content. The smoothing kernel can be expressed as follows:
where and are the horizontal and vertical standard deviations, respectively. In our implementation, we set and , a choice that is validated in the hyperparameter sensitivity study presented in Section 4.4.3.
This design ensures that the erased regions are not completely nullified but instead softly attenuated through blurring, thereby allowing the network to retain low-intensity yet potentially informative signals. Crucially, since the manipulation is conducted in the feature space rather than directly on the raw input, the semantic integrity of the original image remains largely unaffected. This approach preserves global identity-relevant information while modulating local activations, which promotes more balanced feature utilization and reduces over-reliance on spatially fixed discriminative cues. Consequently, it encourages the learning of more robust and generalizable feature representations by minimizing redundancy and fostering diversity in the embedding space.
In conclusion, image feature-level erasing serves as a targeted and adaptive regularization strategy. By explicitly suppressing dominant feature activations without sacrificing semantic coherence, it guides the model toward capturing identity-consistent yet spatially diverse patterns. This, in turn, enhances generalization performance, particularly in fine-grained and open-world recognition scenarios where robustness to spatial variation is critical.
3.4. Loss Function
In this study, we employ both triplet loss and identity loss as complementary supervisory signals to enhance discriminative and robust feature learning. The identity loss, formulated as standard softmax cross-entropy over identity labels, promotes inter-class separability by enforcing distinct classification boundaries. This objective drives the network to maximize identity prediction accuracy and effectively capture global identity-level semantics, which can be defined as follows:
Subsequently, the triplet loss is employed to refine intra-class compactness and inter-class dispersion in the learned embedding space. This relational supervision helps encode finer-grained local details that are often overlooked by purely classification-based approaches. The loss function can be formulated as follows:
Therefore, the total loss function of person Re-ID can be expressed as follows:
where is the hyperparameter that balances between the and . The detailed choice of this hyperparameter is provided in Section 4.4.4. By jointly optimizing both objectives, our framework simultaneously leverages absolute identity discrimination and relative similarity structure, resulting in feature embeddings that are not only identity-discriminative but also well-structured in Euclidean space.
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset and Evaluation Metrics
4.1.1. Datasets
We selected the Market-1501 [21], DukeMTMC-reID [51], and MSMT17 [52] datasets to comprehensively evaluate the generalization and robustness of the proposed method across diverse Re-ID scenarios. These three datasets are widely adopted benchmarks in the person Re-ID community, and they differ significantly in terms of scale, scene diversity, and challenge level, making them complementary for evaluation purposes.
Market-1501 comprises a total of 36,036 pedestrian images spanning 1501 unique identities, acquired from 6 distinct surveillance cameras. The dataset is partitioned into a training set of 12,936 images from 751 individuals, a gallery set of 19,732 images from the remaining 750 individuals, and a query set containing 3368 images. It is a medium-sized dataset that provides a relatively clean setting with moderate background variation.
DukeMTMC-reID consists of 36,411 images corresponding to 1812 person identities, captured across 8 non-overlapping camera views. The data is split into a training subset of 16,522 images from 702 identities, a gallery subset with 17,661 images (covering 1100 identities, including 408 distractor identities), and a query subset with 2228 images representing 702 individuals. It introduces increased complexity, as it includes more significant viewpoint and illumination variations, as well as more occlusion and background clutter.
MSMT17 is a large-scale dataset with 126,411 annotated person images distributed across 4101 identities and collected from 15 diverse camera viewpoints. Specifically, it contains 32,621 training images of 1041 labeled identities, 82,161 testing images from 3060 identities, and 11,659 images used for querying. It is one of the largest and most challenging person Re-ID datasets, covering both indoor and outdoor scenes and a higher degree of variation in lighting, background, and scale.
By evaluating our method on all three datasets, we aim to demonstrate its effectiveness under varying degrees of difficulty and environmental diversity. This ensures that the conclusions drawn from our experiments are not biased toward a specific dataset or scenario.
To facilitate a clearer understanding of the dataset structure, we provide a detailed breakdown of the training, gallery, and query set distributions across all three datasets, as presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
The distribution of the training, gallery, and query sets across all three datasets.
4.1.2. Evaluation Metrics
To measure retrieval performance, we adopt the standard Cumulative Matching Characteristic (CMC) at Rank-1, Rank-5, and Rank-10, along with mean average precision (mAP). The CMC metric reports the probability of the correct match appearing within the top-k retrieved results, while mAP captures both precision and recall by averaging over all queries. This evaluation scheme provides a balanced and robust assessment of both identification accuracy and ranking quality. The can be formulated as follows:
where N is the total number of query samples and .
The mAP can be formulated as follows:
where represents the Average Precision (AP) corresponding to the query sample N.
4.2. Implementation Details
Implementation Details
The proposed model is trained on a single NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 GPU (24 GB VRAM) with a total batch size of 64. Each mini-batch is constructed by sampling 4 instances per identity, resulting in 16 unique identities per batch to facilitate effective metric learning. The feature extraction backbone employs the ResNet-50 [53] architecture, which is initialized using weights pre-trained on the ImageNet dataset [54]. We employ the Batch DropBlock (BDB) Network [55] as our baseline framework.
We optimize our network using the Adam algorithm, configured with a weight decay coefficient of 5 × 10−4 to prevent overfitting. The momentum terms are set to and , ensuring stable and adaptive updates throughout training. The learning rate is initialized at 0.00035 and progressively adjusted using a cosine annealing schedule, which gradually decreases the learning rate in a smooth, non-linear manner to facilitate convergence and mitigate the risk of premature stagnation. The entire training process spans 160 epochs. For the Gaussian smoothing hyperparameters in Equation (4), we set and ; further justification is provided in Section 4.4.3. The loss-balancing coefficient in Equation (7) is set to ; see Section 4.4.4 for an analysis of this choice.
4.3. Comparison with Representative Methods
4.3.1. Evaluation on Market-1501 Dataset
We conduct an extensive comparative evaluation against 11 leading-person Re-ID approaches on the Market-1501 benchmark. As presented in Table 2, our approach consistently achieves superior performance across multiple evaluation metrics. Specifically, it attains the highest Rank-1 accuracy, outperforming the closest competitor AE-Net. In terms of mAP, our model matches the performance of the AE-Net, indicating its capability to balance both retrieval precision and recall. These results collectively highlight the robustness and generalizability of the proposed framework. The consistent improvements across Rank-1 accuracy and mAP suggest that our method not only enhances identity-level discrimination but also effectively captures diverse visual cues under varying viewpoints and background clutter. To evaluate the computational requirements of the proposed framework during the inference phase, we report the inference time per image, as shown in Table 2. Our method achieves the lowest inference latency, matching that of the CAL and BV methods, which further demonstrates the efficiency of the proposed approach.

Table 2.
Performance comparison with representative methods on Market-1501, DukeMTMC-reID, and MSMT17. The evaluation includes both Rank-1 accuracy and mAP. Bold and Underline denote the top two results. A dash (-) indicates that the corresponding result was not reported in the original reference.
4.3.2. Evaluation on DukeMTMC-reID Dataset
We benchmark our proposed method against 10 cutting-edge person Re-ID techniques on the DukeMTMC-reID dataset. As summarized in Table 2, our framework yields superior performance, achieving a 0.6% gain in Rank-1 accuracy over the next-best method, AE-Net. These findings highlight the efficacy of our feature erasure-guided augmentation strategy in uncovering salient identity-specific cues at the sample level, thereby enhancing the overall discriminative capability of the learned representations. In addition, the improvement demonstrates the model’s capacity to capture fine-grained visual distinctions. This makes our approach particularly suitable for practical scenarios where subtle appearance variations must be reliably recognized.
4.3.3. Evaluation on MSMT17 Dataset
Table 2 presents a comparative assessment of our proposed method against six representative person Re-ID models on the MSMT17 benchmark. Our approach attains the highest accuracy, surpassing the second-best method, AE-Net, by margins of 0.6% in Rank-1 and 0.2% in mAP. Beyond this, our framework consistently outperforms all competing methods across key evaluation metrics. These outcomes strongly substantiate the efficacy of the proposed feature erasure-driven augmentation approach in enhancing the model’s ability to extract robust and identity-discriminative representations under challenging, large-scale conditions.
Overall, these results demonstrate that our feature-level erasing combined with diagonal swapping effectively preserves fine-grained identity cues and enhances model generalization, leading to competitive performance. This confirms that feature-level augmentation mitigates information loss common in image-level methods, while structured sample diversity improves robustness across varied conditions.
4.4. Ablation Analysis
4.4.1. Effectiveness of the Diagonal Swapping Augmentation Strategy
To assess the contribution of the diagonal swapping augmentation mechanism, we conduct ablation studies on both the Market-1501 and DukeMTMC-reID datasets. The results, summarized in Table 3, reveal that removing this component leads to a noticeable decline in performance. Specifically, the exclusion of diagonal swapping results in drops of 0.8% and 1.4% in Rank-1 and mAP on Market-1501, and 1.4% and 1.3% on DukeMTMC-reID, respectively. These performance degradations highlight the role of the proposed augmentation scheme in enriching intra-sample structural variability, which facilitates more effective learning of discriminative features and contributes to the superior performance observed in the complete model.

Table 3.
Ablation analysis of the proposed diagonal swapping augmentation strategy on the Market-1501 and DukeMTMC-reID datasets. w/o denotes the model without the diagonal swapping augmentation strategy. Rank-1 and mAP are listed.
4.4.2. Effectiveness of the Image Feature-Level Erasing
In order to evaluate the specific impact of the image feature-level erasing mechanism, we perform targeted ablation experiments on the Market-1501 and DukeMTMC-reID datasets. As reported in Table 4, removing this module from the full model leads to a measurable reduction in recognition accuracy. On Market-1501, the absence of this technique causes Rank-1 and mAP to drop by 0.6% and 1.6%, respectively, while on DukeMTMC-reID, performance declines by 1.0% in Rank-1 and 0.8% in mAP. These results underscore the effectiveness of feature-space erasing in suppressing overly dominant activations and encouraging the network to exploit complementary identity-specific cues. By promoting a more balanced and spatially diverse representation, this component significantly enhances the model’s overall discriminative capacity.

Table 4.
Ablation analysis of the proposed image feature-level erasing on the Market-1501 and DukeMTMC-reID datasets. w/o denotes the model without the image feature-level erasing. Rank-1 and mAP are listed.
4.4.3. Analysis of the Hyperparameters and
To investigate the influence of the Gaussian smoothing parameters and defined in Equation (4), we perform a series of controlled experiments on the Market-1501 dataset. The search space spans values from 1 to 5 for both parameters, incremented by 1. As illustrated in Figure 4, the best performance is achieved when and , yielding the highest Rank-1 accuracy and mAP. This combination achieves an optimal balance between suppressing high-frequency noise and preserving subtle identity-relevant features. Larger values lead to stronger smoothing but risk detail loss, whereas smaller values retain details but may amplify noise. These findings not only demonstrate the sensitivity of the model to appropriate smoothing configurations, but also underscore the pivotal role of the image feature-level erasing mechanism in enhancing the network’s capacity to learn robust and discriminative representations.
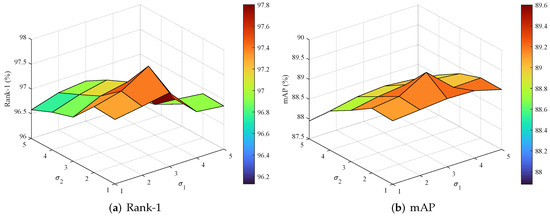
Figure 4.
Parameter sensitivity analysis on Market-1501: 3D surface plots reveal how variations in and influence Rank-1 and mAP.
4.4.4. Analysis of the Hyperparameter
Figure 5 presents a detailed investigation into the impact of the hyperparameter in Equation (7), which modulates the trade-off between the constituent loss terms in the overall optimization objective. Empirical evaluations across a range of values reveal that model performance, measured in terms of both Rank-1 accuracy and mAP, improves consistently as increases from 0.2 to 1.1. When exceeds this threshold and lies within the interval from 1.1 to 2.5, a gradual decline in performance is observed. These experimental findings suggest that an excessively large disrupts the equilibrium between loss components and negatively affects the learning process. The best performance is achieved when is set to 1.1, indicating that this value strikes an effective balance among the supervisory signals and contributes to stable and discriminative feature learning. Furthermore, this indicates that small values make the classification loss dominant, enhancing inter-class separability, while large values emphasize similarity learning, strengthening the feature space structure. The optimal is obtained when these objectives are balanced.
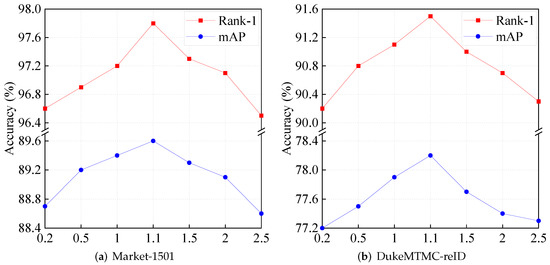
Figure 5.
Ablation analysis of the hyperparameter on the Market-1501 and DukeMTMC-reID datasets. Rank-1 and mAP are listed.
5. Conclusions and Future Works
This study proposes a feature erasing-based data augmentation framework that leverages semantic erasing in the representation space to uncover and emphasize informative identity attributes within individual samples. First, we introduce a diagonal swapping augmentation mechanism that rearranges local image regions to enhance spatial diversity without disrupting global semantic consistency. Second, we apply a feature erasure module directly on the learned embeddings, enabling the model to attend to complementary identity-relevant cues by perturbing over-represented activations. This dual augmentation pipeline fosters more robust and discriminative feature learning. Comprehensive experimental evaluations conducted on multiple large-scale Re-ID benchmarks confirm the superiority of our method over a range of representative approaches, validating its effectiveness in promoting generalization and fine-grained identity understanding.
While our feature erasing-based augmentation and diagonal swapping strategies demonstrate comparative performance, certain limitations remain. The diagonal swapping operation may introduce unintended artifacts in images with heavy occlusion or pronounced spatial asymmetry, potentially affecting identity feature consistency. Additionally, the effectiveness of feature-level erasing can be influenced by the underlying network architecture, suggesting a degree of sensitivity that warrants further investigation.
In future research, we plan to extend our framework to video-based person Re-ID and multi-modal scenarios. Such extensions will require incorporating temporal dynamics to capture motion cues effectively and developing modality alignment mechanisms to handle heterogeneous data sources. These adaptations represent promising directions for future research to further enhance robustness and generalizability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Z.; methodology, S.Z.; software, H.Z.; validation, S.Z.; formal analysis, H.Z.; investigation, H.Z.; resources, S.Z.; data curation, S.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, S.Z.; writing—review and editing, S.Z.; visualization, H.Z.; supervision, S.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Scientific Research Startup Fund of Hangzhou Dianzi University under Grant KYS085624260.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ye, M.; Shen, J.; Lin, G.; Xiang, T.; Shao, L.; Hoi, S.C.H. Deep Learning for Person Re-Identification: A Survey and Outlook. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 2872–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Luo, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, W. Illumination Unification for Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 6766–6777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.; Peng, Y.X.; Sun, X.; Zheng, W.S. Distilling consistent relations for multi-source domain adaptive person re-identification. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 157, 110821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gao, X.; Wu, M.; Lam, S.K.; He, S.; Tiwari, P. Looking Clearer With Text: A Hierarchical Context Blending Network for Occluded Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2025, 20, 4296–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, N.K.S.; Sa, P.K.; Bakshi, S. Person re-identification for smart cities: State-of-the-art and the path ahead. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 138, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, H.; Ess, A.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. Speeded-up robust features (SURF). Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2008, 110, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Gu, Y.; Liao, X.; Lai, S.; Jiang, W. Bag of Tricks and a Strong Baseline for Deep Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 1487–1495. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Z.; Wei, L.; Xie, L.; Ai, H.; Tian, Q. Camera-Based Batch Normalization: An Effective Distribution Alignment Method for Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Zhang, L.; Yan, S.; Tang, H.; Tang, J. Erasing, transforming, and noising defense network for occluded person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 34, 4458–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Liu, X.; Kong, J. Text-Guided Prototype Generation for Occluded Person Re-Identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2024, 31, 2350–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; Volume 25, pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, R.; Ma, B.; Chang, H.; Gu, X.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. Feature Completion for Occluded Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 4894–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Qu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Tu, Y.; Bai, X. Content-Adaptive Auto-Occlusion Network for Occluded Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 4223–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbel, M.; Ammar, S.; Kessentini, Y.; Jmaiel, M. Masking for better discovery: Weakly supervised complementary body regions mining for person re-identification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 197, 116636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Dong, X.; Bao, J.; Chen, D.; Yuan, L.; Chen, D.; Li, H. PersonMAE: Person Re-Identification Pre-Training With Masked AutoEncoders. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 10029–10040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, X. Person Re-identification by Salience Matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 2528–2535. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.S.; Li, X.; Xiang, T.; Liao, S.; Lai, J.; Gong, S. Partial Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 4678–4686. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Hospedales, T.M.; Xiang, T. Transferring a Semantic Representation for Person Re-Identification and Search. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4184–4193. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Shen, L.; Tian, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Tian, Q. Scalable Person Re-Identification: A Benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1116–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, S.; Hong, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Tian, Q. Deep Representation Learning With Part Loss for Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 2860–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Zhu, X.; Gong, S. Learning hybrid ranking representation for person re-identification. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 121, 108239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Budhwant, P.; Zheng, Z.; Nevatia, R. Seas: Shape-aligned supervision for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 164–174. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Coleman, S.; Kerr, D. AE-Net: Appearance-Enriched Neural Network with Foreground Enhancement for Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Liu, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Lu, H. CLIMB-ReID: A Hybrid CLIP-Mamba Framework for Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 25 February–4 March 2025; Volume 39, pp. 9589–9597. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Huang, Y.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, L. Mask-guided contrastive attention model for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 1179–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Shan, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L. Mask-guided contrastive attention and two-stream metric co-learning for person re-identification. Neurocomputing 2021, 465, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, J. Multi-Scale Body-Part Mask Guided Attention for Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 1555–1564. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhu, X.; Gong, S. Harmonious Attention Network for Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 2285–2294. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Gu, T.; Lu, J.; Bao, J.A.; Zhou, J. Person Re-Identification via Attention Pyramid. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 7663–7676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Lai, S.; Qian, X. Occlusion-Sensitive Person Re-Identification via Attribute-Based Shift Attention. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 2170–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Chang, H.; Ma, B.; Bai, S.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. Clothes-Changing Person Re-Identification With RGB Modality Only. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1060–1069. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Liu, W. Guided saliency feature learning for person re-identification in crowded scenes. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 357–373. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.; Pang, G.; Wang, L.; Jiao, J.; Feng, X.; Shen, C.; Li, J. BV-Person: A Large-Scale Dataset for Bird-View Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10943–10952. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, D.; Zhao, S.; Hu, J.; Feng, H.; Cai, D.; He, X. ES-Net: Erasing Salient Parts to Learn More in Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 1676–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Yang, X.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Kautz, J. Joint discriminative and generative learning for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2138–2147. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Jiao, L.; Yang, S.; Li, L.; Wang, Z. Simple and Effective: Spatial Rescaling for Person Reidentification. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, Z.; Li, S.; Yang, Y. Camstyle: A novel data augmentation method for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Zheng, L.; Kang, G.; Li, S.; Yang, Y. Random erasing data augmentation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 13001–13008. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, X.; Li, G.; Gao, W.; Shu, X. Learning to disentangle scenes for person re-identification. Image Vis. Comput. 2021, 116, 104330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Linze, L.; Rongchang, L.; Cong, W.; Tianyang, X.; Wu, X.J. Robust Person Re-Identification Approach with Deep Learning and Optimized Feature Extraction. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo Workshops, Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 15–19 July 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Jiang, X.; Pei, G.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y. Knowledge transfer with simulated inter-image erasing for weakly supervised semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; pp. 441–458. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Q.; Ding, G.; Zhang, T.; Gong, Y. Robust Fine-Grained Learning for Cloth-Changing Person Re-Identification. Mathematics 2025, 13, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y. GW-net: An efficient grad-CAM consistency neural network with weakening of random erasing features for semi-supervised person re-identification. Image Vis. Comput. 2023, 137, 104790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Han, D.; Oh, S.J.; Chun, S.; Choe, J.; Yoo, Y. Cutmix: Regularization strategy to train strong classifiers with localizable features. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October 2019–2 November 2019; pp. 6023–6032. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Cisse, M.; Dauphin, Y.N.; Lopez-Paz, D. mixup: Beyond Empirical Risk Minimization. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cubuk, E.D.; Zoph, B.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Randaugment: Practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 702–703. [Google Scholar]
- Cubuk, E.D.; Zoph, B.; Mane, D.; Vasudevan, V.; Le, Q.V. Autoaugment: Learning augmentation policies from data. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.09501. [Google Scholar]
- DeVries, T.; Taylor, G.W. Improved Regularization of Convolutional Neural Networks with Cutout. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.04552. [Google Scholar]
- Gou, M.; Karanam, S.; Liu, W.; Camps, O.; Radke, R.J. DukeMTMC4ReID: A Large-Scale Multi-camera Person Re-identification Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1425–1434. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, S.; Gao, W.; Tian, Q. Person Transfer GAN to Bridge Domain Gap for Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.; Chen, M.; Gu, X.; Zhu, S.; Tan, P. Batch DropBlock Network for Person Re-Identification and Beyond. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3690–3700. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).