Influence of Regional PM2.5 Sources on Air Quality: A Network-Based Spatiotemporal Analysis in Northern Thailand
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
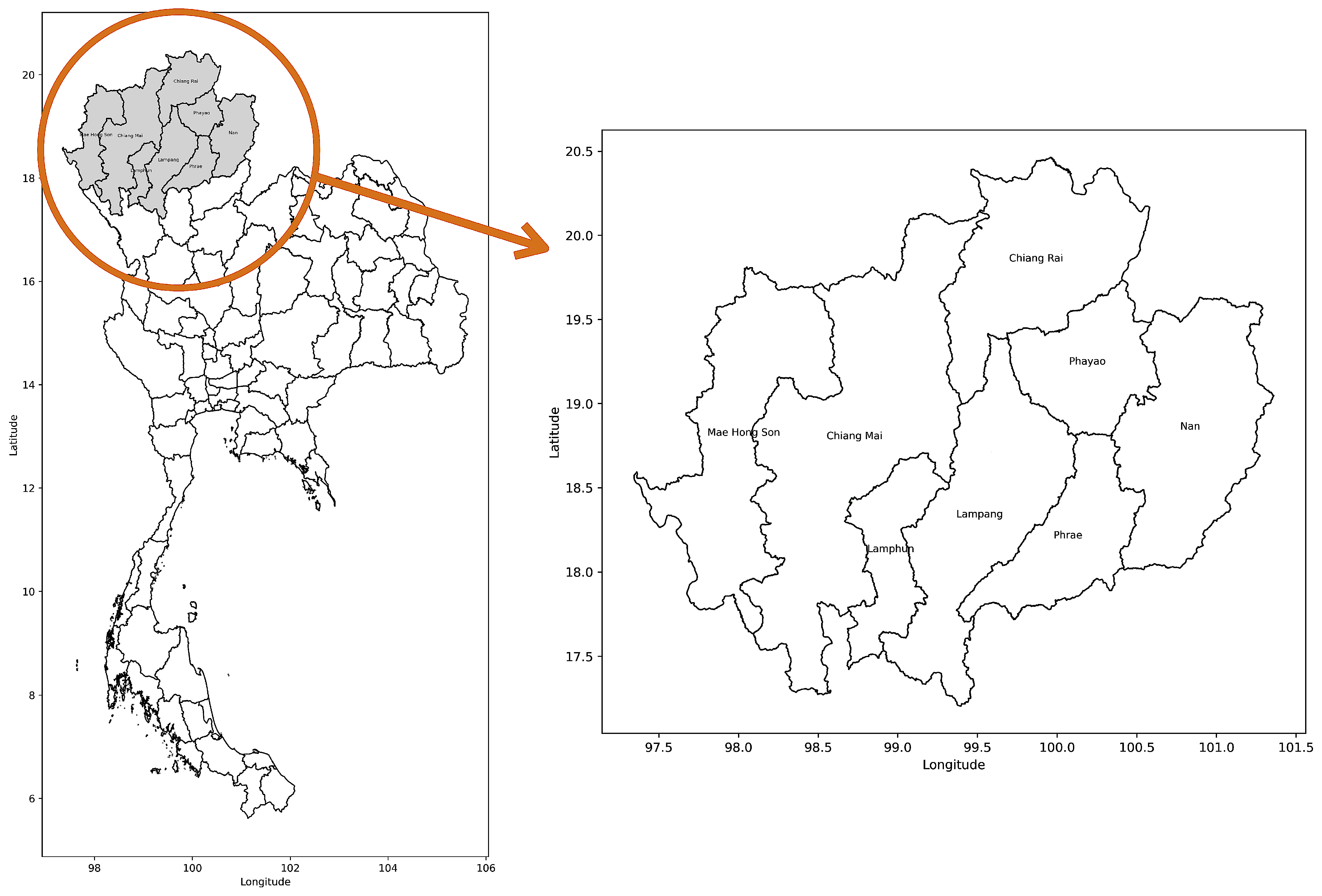
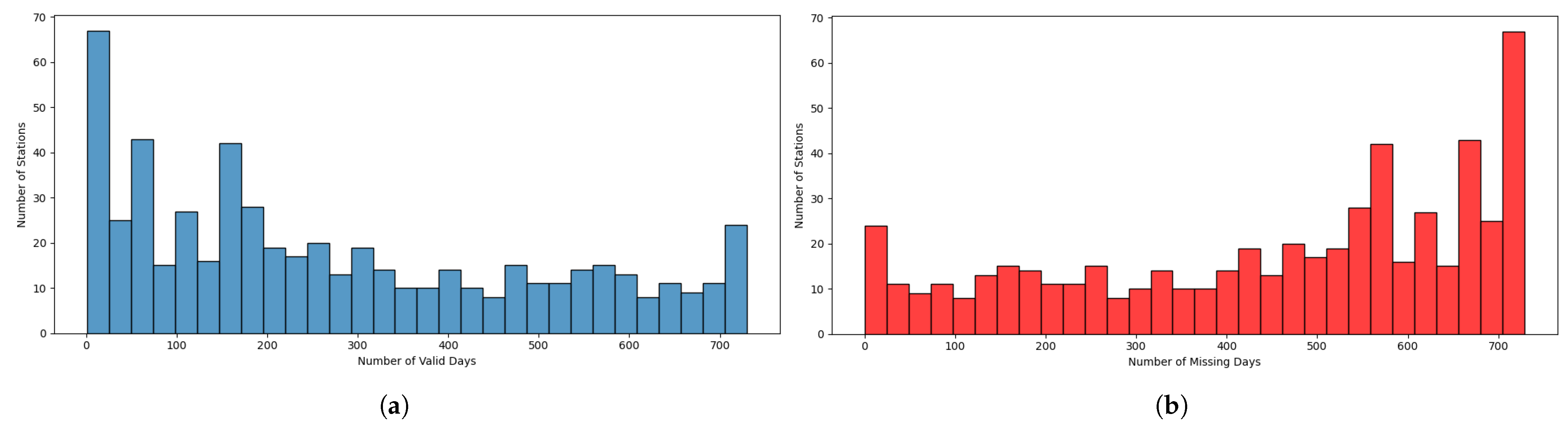
2.1. Study Area, Data Collection, and Preprocessing
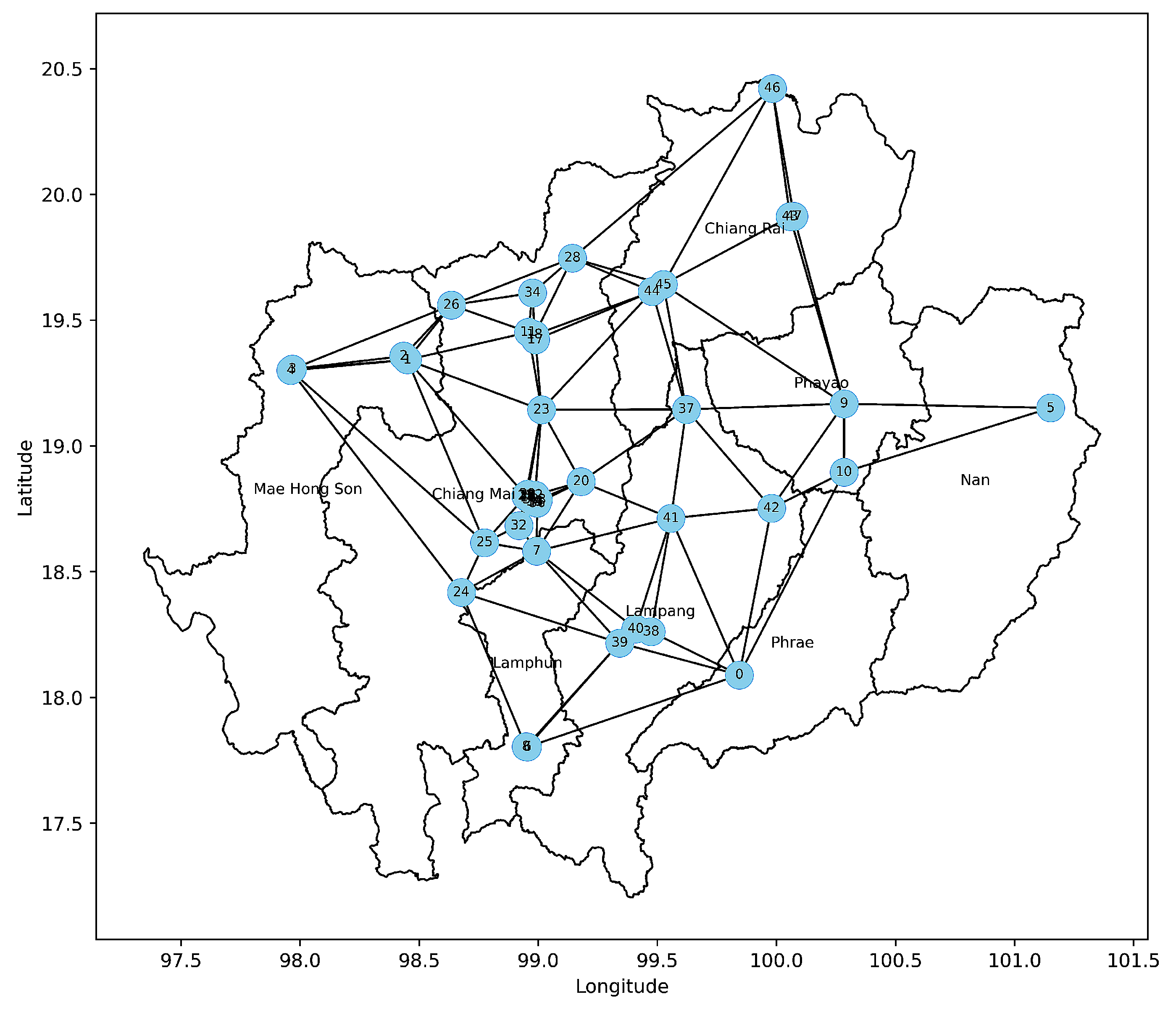
2.2. Spatial Network Construction
2.2.1. Delaunay Triangulation
2.2.2. Regional Shape Analysis
2.3. Temporal Causality and Dependency Analysis
2.3.1. Cross-Correlation
2.3.2. Granger Causality
2.4. Trophic Coherence of the Granger Network
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatial Network Characteristics
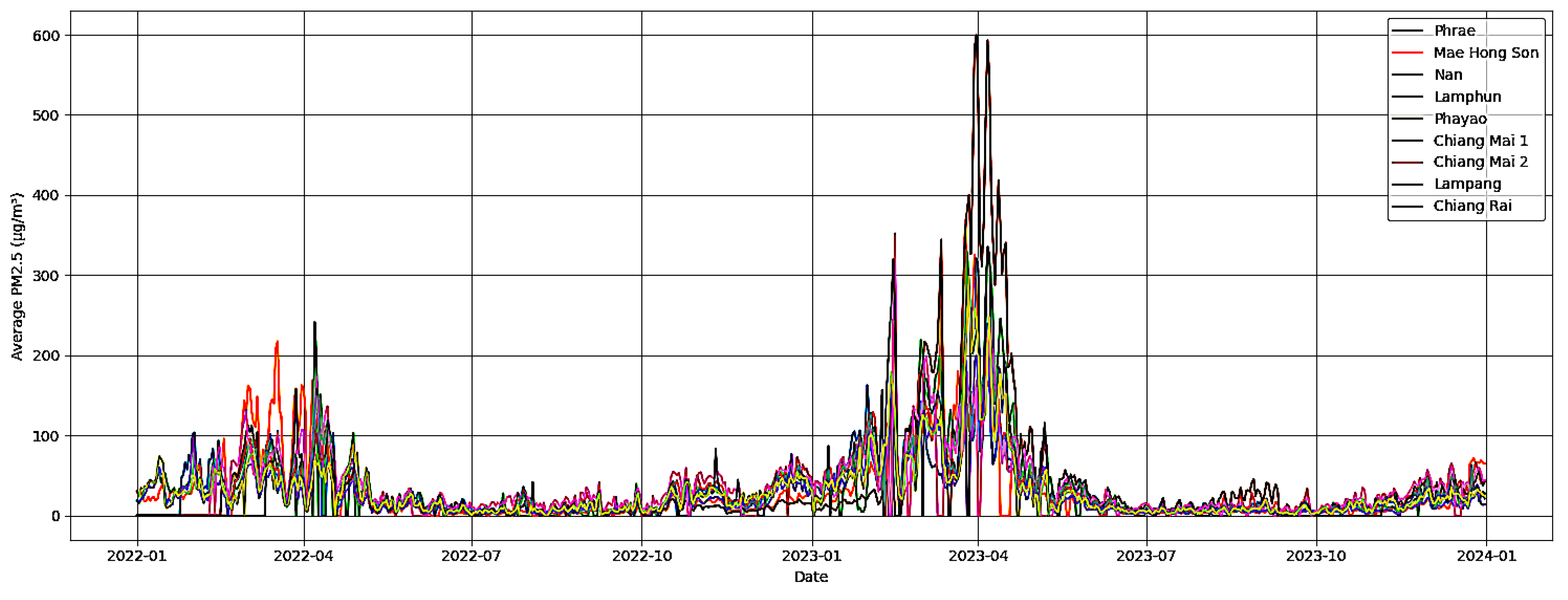
3.2. PM2.5 Trends and Data Overview
3.3. Temporal Dependency and Causality Between Stations
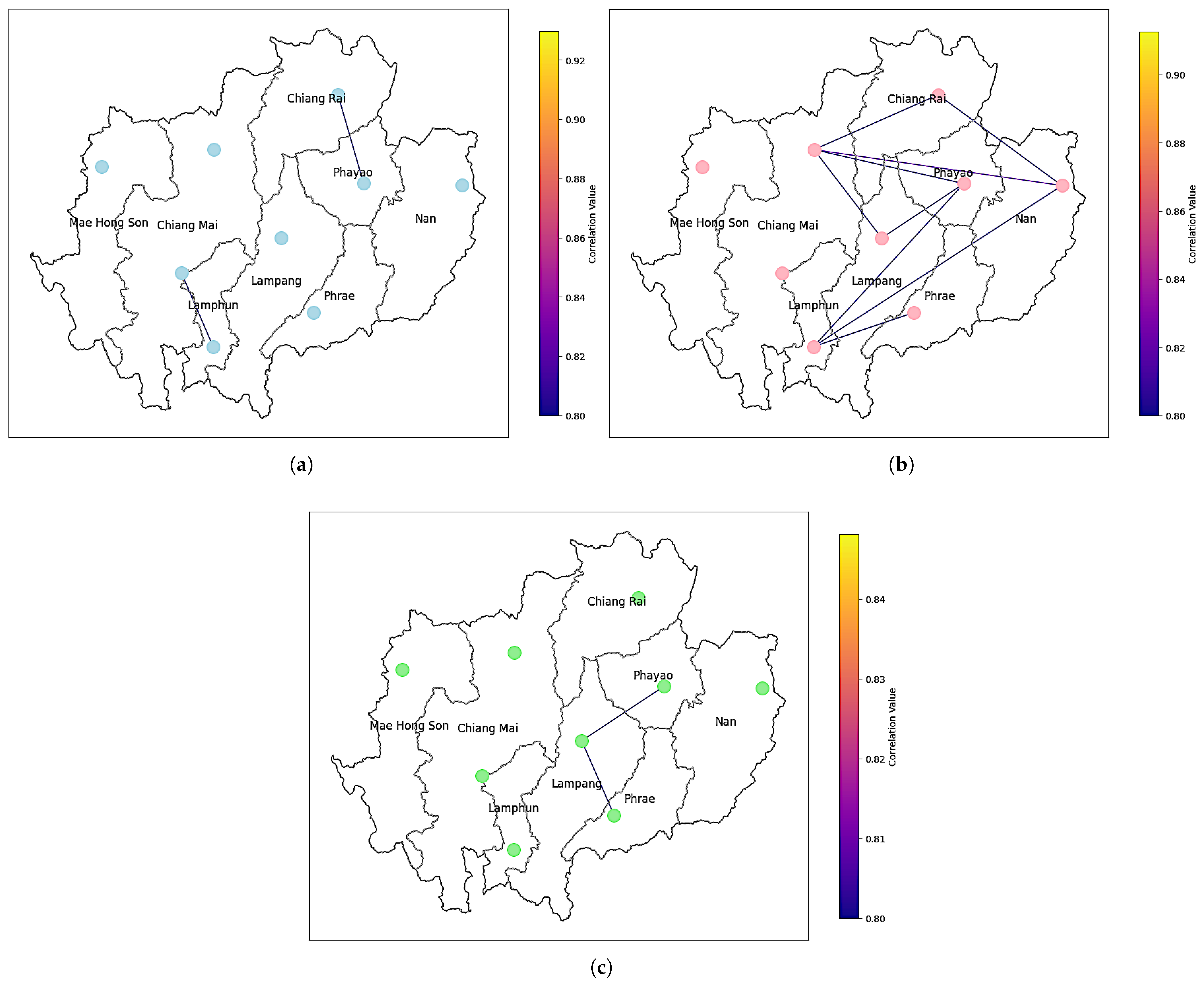
3.3.1. Cross-Correlation Results
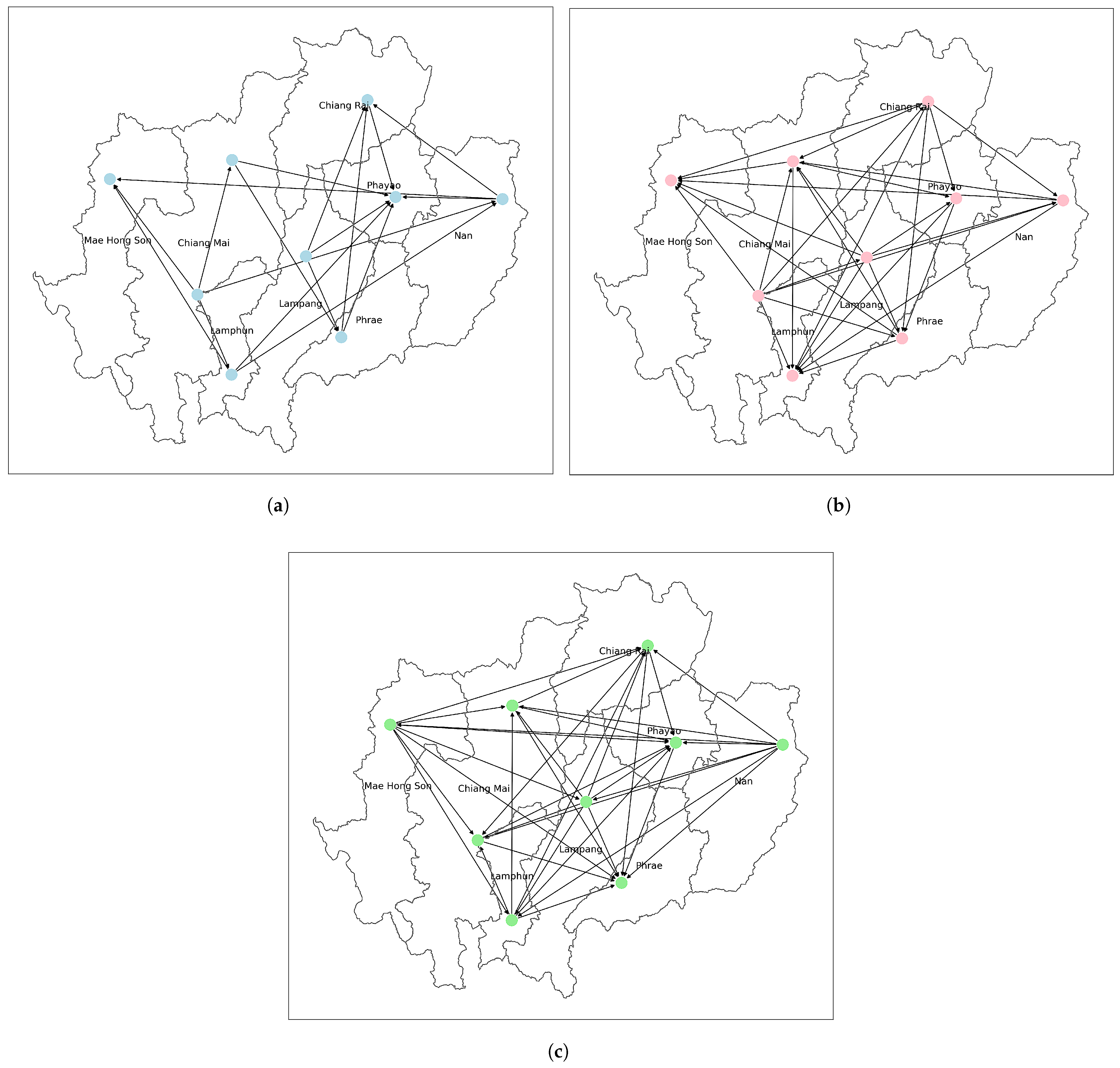
3.3.2. Granger Causality Results
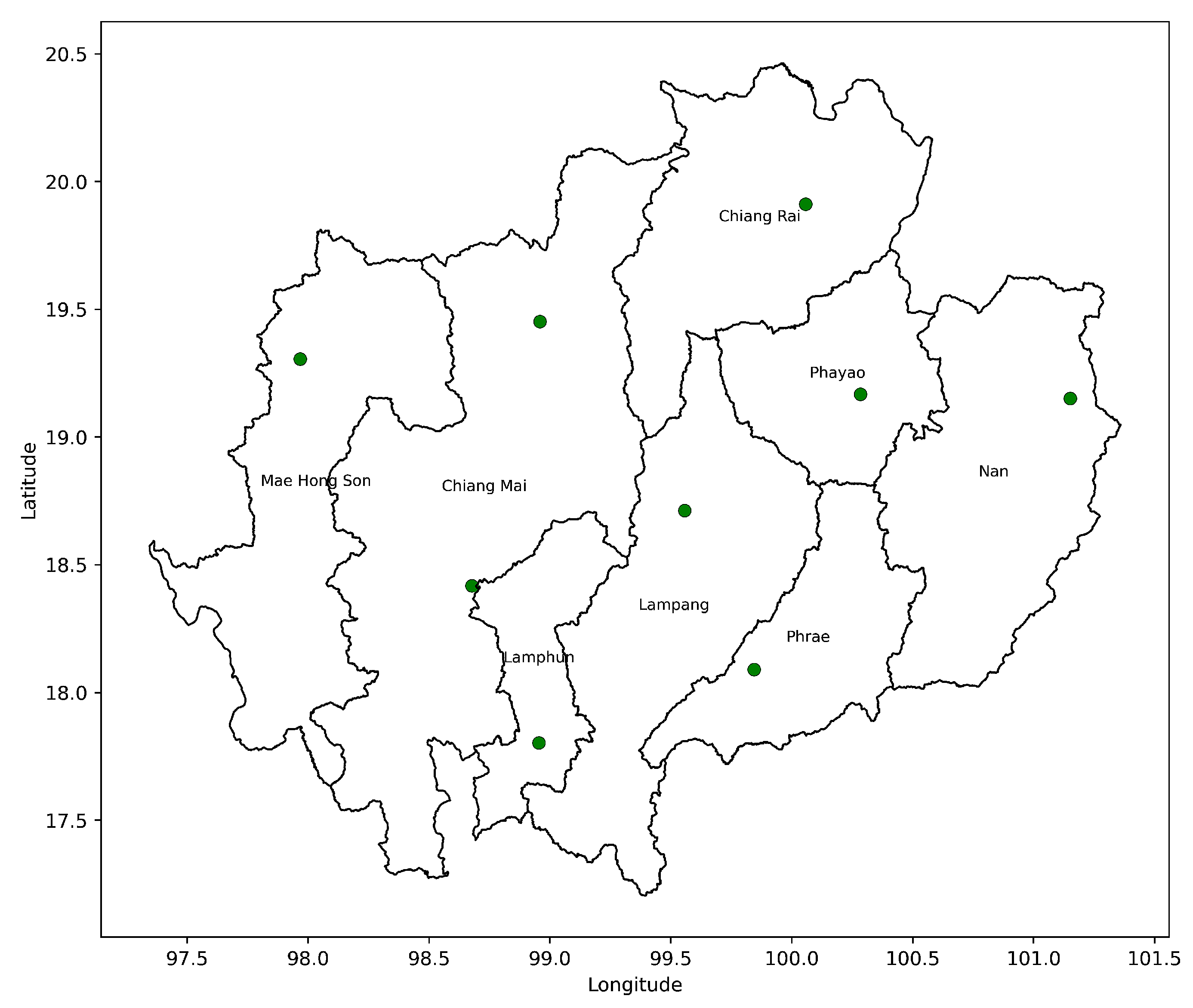
3.4. Trophic Coherence and Network Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Helble, J.J.; DeVito, M.S.; Wu, C.Y.; Smith, F.L.; Marrack, D. Combustion aerosols: Factors governing their size and composition and implications to human health. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2000, 50, 1619–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A., III; Ezzati, M.; Dockery, D.W. Fine-particulate air pollution and life expectancy in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), ozone, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide and carbon monoxide. In WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chansuebsri, S.; Kolar, P.; Kraisitnitikul, P.; Kantarawilawan, N.; Yabueng, W.; Wiriya, W.; Thepnuan, D.; Chantara, S. Chemical composition and origins of PM2.5 in Chiang Mai (Thailand) by integrated source apportionment and potential source areas. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 327, 120517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Su, X.; Zhang, Q.; Peters, G.P.; Liu, Z.; Lei, Y.; He, K. The socioeconomic drivers of China’s primary PM2.5 emissions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 024010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.-F.; Cao, J.-J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.; Lee, C.G.; Ramasamy, B.; Yeung, M. FDI and pollution: A granger causality test using panel data. J. Int. Dev. 2005, 17, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.L.; Yang, Z. The research on air pollution laws in Guanzhong urban agglomeration based on high frequency AQI data. DEStech Trans. Environ. Energy Earth Sci. 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Bai, X.; Tan, H.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Wolters, M.A.; Qin, X.; Zhang, M.; et al. Large-scale transport of PM2.5 in the lower troposphere during winter cold surges in China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, B.; Tan, S.C.; Lee, C.M.; Yao, X.; Yan, H.; Shi, J. A study of air pollution of city clusters. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 3069–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzopoulou, M.; Valois, M.F.; Levy, I.; Mihele, C.; Lu, G.; Bagg, S.; Minet, L.; Brook, J. Robustness of land-use regression models developed from mobile air pollutant measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3938–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashan, N.F.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.R. Dynamics of PM2.5 and network activity during extreme pollution events. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 7, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, K.; Zheng, H.; Ge, L. Digital empowerment to reduce air pollution: The impact of urban network infrastructure construction on PM2.5. J. Asian Econ. 2025, 98, 101930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Suthar, G. Machine learning and deep learning approaches for PM2.5 prediction: A study on urban air quality in Jaipur, India. Earth Sci Inf. 2025, 18, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.W.J. Investigating causal relations by econometric models and cross-spectral methods. Econometrica 1969, 37, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, J.; Petoukhov, V.; Donges, J.F.; Hlinka, J.; Jajcay, N.; Vejmelka, M.; Hartman, D.; Marwan, N.; Palus, M.; Kurths, J. Identifying causal gateways and mediators in complex spatio-temporal systems. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runge, J.; Nowack, P.; Kretschmer, M.; Flaxman, S.; Sejdinovic, D. Detecting and quantifying causal associations in large nonlinear time series datasets. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, W.Y.; Abd Rais, Z.; Ramli, N.; Mohamed Noor, N.; Ul-Saufie, A.Z.; Hamid, H.A.; Mahmad, M.K.N. Granger causality analysis of air pollutants and meteorological parameters. Environ. Earth Sci. Proc. 2025, 33, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Dominguez-Garcia, V.; Donetti, L.; Muñoz, M.A. Trophic coherence determines food-web stability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17923–17928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Jones, N.S. Looplessness in networks is linked to trophic coherence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5618–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boers, N.; Bookhagen, B.; Marwan, N.; Kurths, J.; Marengo, J. Complex networks identify spatial patterns of extreme rainfall events of the South American Monsoon System. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 4386–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boers, N.; Goswami, B.; Rheinwalt, A.; Bookhagen, B.; Hoskins, B.; Kurths, J. Complex networks reveal global pattern of extreme-rainfall teleconnections. Nature 2019, 566, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, W.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y. Visualizing the intercity correlation of PM2.5 time series in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region using ground-based air quality monitoring data. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Fan, J.; Havlin, S.; Chen, X. Correlation and scaling behaviors of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) concentration in China. Europhys. Lett. 2018, 122, 58003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guan, Z.; Li, J.; Su, Z.; Deng, W.; Li, W. Chinese cities’ air quality pattern and correlation. J. Stat. Mech. 2020, 4, 043403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Li, J.; Dong, G.; Tian, L.; Qing, T.; Fang, G.; Dong, Y. Percolation analysis of urban air quality: A case in China. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2020, 541, 123312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, H.; Li, W.W.; Sui, Q.L.; Zhu, Y.H. Dynamic complex network analysis of PM2.5 in Henan province of China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2022, 20, 3033–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhaeuser, K.; Chawla, N.V.; Ganguly, A.R. An exploration of climate data using complex networks. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newslett. 2010, 12, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Meng, J.; Ashkenazy, Y.; Havlin, S.; Schellnhuber, H.J. Network analysis reveals strongly localized impacts of El Niño. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7543–7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Fan, J.; Ashkenazy, Y.; Havlin, S. Percolation framework to describe El Niño conditions. Chaos 2017, 27, 035807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, K.; Gozolchiani, A.; Havlin, S. Climate networks around the globe are significantly affected by El Niño. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 228501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludescher, J.; Gozolchiani, A.; Bogachev, M.I.; Bunde, A.; Havlin, S.; Schellnhuber, H.J. Improved El Niño forecasting by cooperativity detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11742–11745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Cao, Y.; Dong, Y.; Yan, H. A graph neural network and Transformer-based model for PM2.5 prediction through spatiotemporal correlation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2025, 191, 106501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhu, S.; Gao, Y.; Qiu, X.; Chen, L. Long-term PM2.5 concentrations forecasting using CEEMDAN and deep Transformer neural network. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, A.; Boots, B.; Sugihara, K.; Chiu, S.N. Spatial Tessellations: Concepts and Applications of Voronoi Diagrams; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri, D.; Samal, A. A simple method for fitting of bounding rectangle to closed regions. Pattern Recognit. 2007, 40, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, A.; Sugihara, K. Spatial Analysis Along Networks: Statistical and Computational Methods; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pardthaisong, L.; Sin-ampol, P.; Suwanprasit, C.; Charoenpanyanet, A. Haze pollution in Chaing Mai, Thailand: A road to resilience. Procedia Eng. 2018, 212, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Provinces | Out of 48 Stations | Out of 21 Stations |
|---|---|---|
| Chiang Mai | 26 | 7 |
| Chiang Rai | 5 | 3 |
| Lampang | 6 | 4 |
| Lamphun | 3 | 1 |
| Mae Hong Son | 4 | 2 |
| Nan | 1 | 1 |
| Phayao | 2 | 2 |
| Phrae | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaichana, K.; Chaidee, S.; Panma, S.; Sukantamala, N.; Peyrone, N.; Khemphet, A. Influence of Regional PM2.5 Sources on Air Quality: A Network-Based Spatiotemporal Analysis in Northern Thailand. Mathematics 2025, 13, 2468. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13152468
Chaichana K, Chaidee S, Panma S, Sukantamala N, Peyrone N, Khemphet A. Influence of Regional PM2.5 Sources on Air Quality: A Network-Based Spatiotemporal Analysis in Northern Thailand. Mathematics. 2025; 13(15):2468. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13152468
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaichana, Khuanchanok, Supanut Chaidee, Sayan Panma, Nattakorn Sukantamala, Neda Peyrone, and Anchalee Khemphet. 2025. "Influence of Regional PM2.5 Sources on Air Quality: A Network-Based Spatiotemporal Analysis in Northern Thailand" Mathematics 13, no. 15: 2468. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13152468
APA StyleChaichana, K., Chaidee, S., Panma, S., Sukantamala, N., Peyrone, N., & Khemphet, A. (2025). Influence of Regional PM2.5 Sources on Air Quality: A Network-Based Spatiotemporal Analysis in Northern Thailand. Mathematics, 13(15), 2468. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13152468






