EmoBERTa–CNN: Hybrid Deep Learning Approach Capturing Global Semantics and Local Features for Enhanced Emotion Recognition in Conversational Settings
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- This study developed EmoBERTa–CNN, a novel hybrid model integrating pretrained emotion-aware bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (EmoBERTa) with CNN layers to simultaneously capture global contextual semantics and local emotional features. Experimental results demonstrate that this hybrid architecture outperforms single-model approaches in emotion recognition tasks;
- (2)
- This study integrated an attention-pooling layer into the CNN, which dynamically reweights convolutional features according to their relevance. This enables the network to effectively identify and capture critical emotional cues;
- (3)
- Extensive experiments on benchmark ERC datasets demonstrated that EmoBERTa–CNN significantly outperformed existing models in terms of the F1-score.
2. Related Works
2.1. Traditional Methods
2.2. Deep Learning Methods
2.2.1. Traditional Deep Learning Model
2.2.2. Pretrained Language Models—Single Model
2.2.3. Pre-Trained Language Models—Hybrid Model
2.3. Attention Mechanism for NLP
2.4. Summary
3. Methods
3.1. Overview
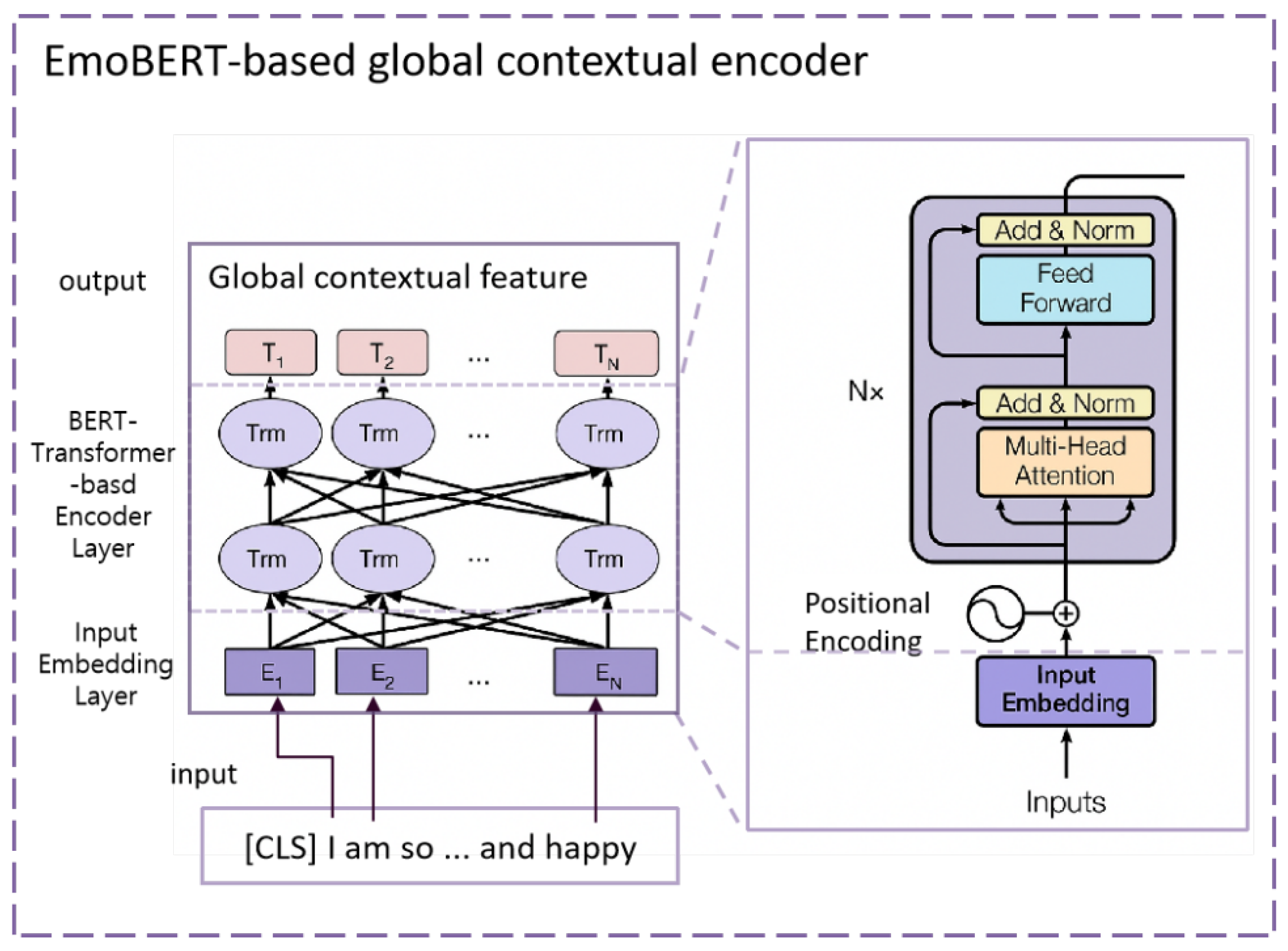
3.2. Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers for Emotion Recognition (EmoBERTa)
3.2.1. Input Representation on EmoBERTa
3.2.2. Encoder Layer
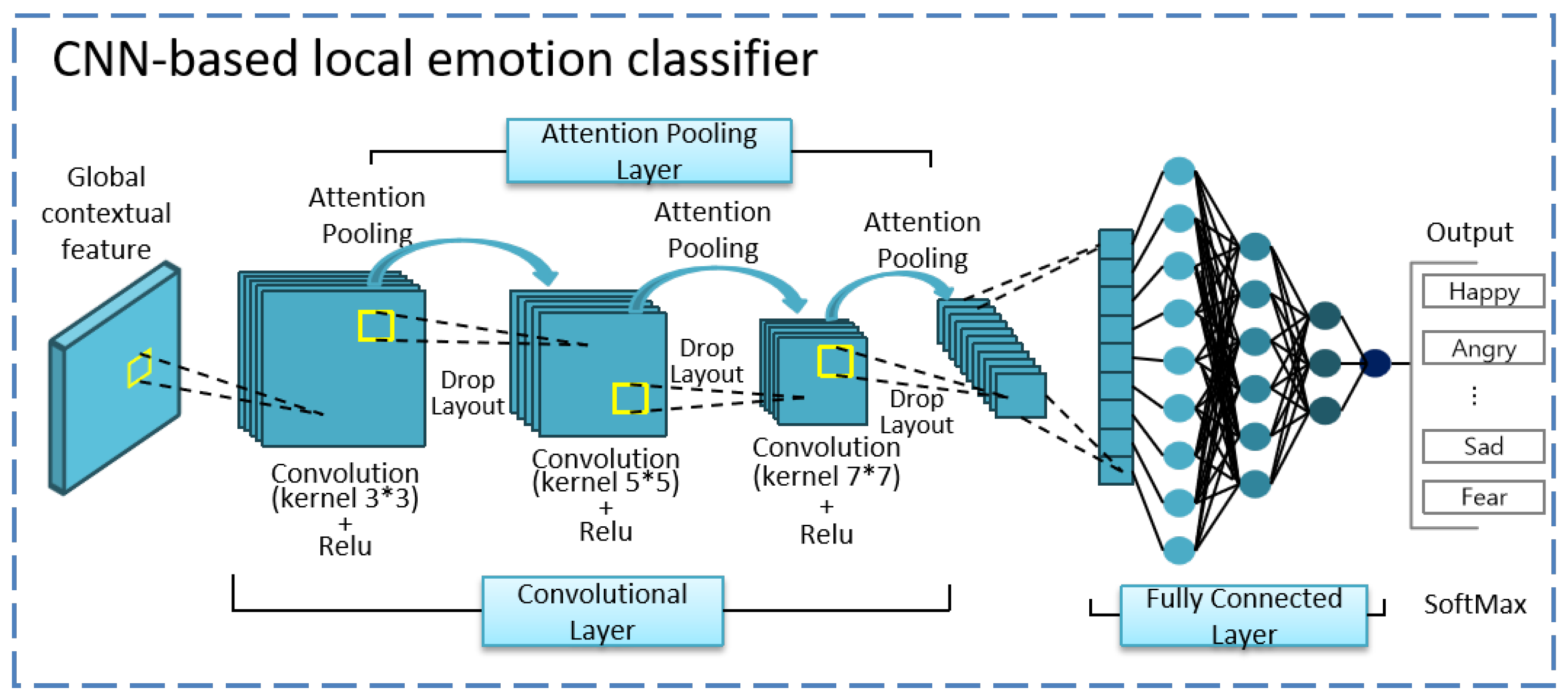
3.3. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) Module
4. Results
4.1. Hyperparameters
4.2. Dataset
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
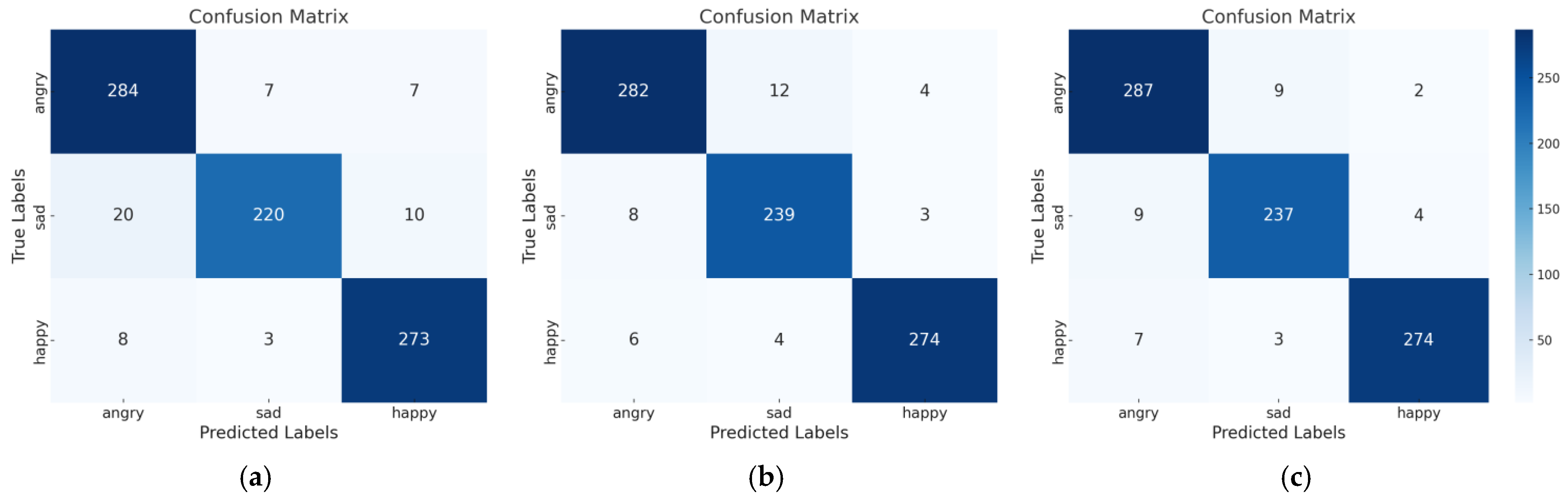
4.4. Analysis of Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MELD | Multimodal EmotionLines Dataset |
| NLP | Natural language processing |
| ERC | Emotion recognition in conversation |
| TER | Textual Emotion Recognition |
| CNNs | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| RNNs | Recurrent Neural Networks |
| PLMs | Pre-trained language models |
| SVM | Support Vector Machines |
| GCNs | Graph Convolutional Networks |
| GRUs | Gated recurrent units |
| LSTMs | Long Short-Term Memory networks |
| GNNs | Graph Neural Networks |
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
| RoBERTa | Robustly Optimized BERT Approach |
| EmoBERTa | Emotion-aware Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
| SOTA | State-of-the-art |
| PTM | Pretrained Transformer Model |
References
- Cowie, R.; Douglas-Cowie, E.; Tsapatsoulis, N.; Votsis, G.; Kollias, S.; Fellenz, W.; Taylor, J. Emotion Recognition in Human-Computer Interaction. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2001, 18, 32–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alva, M.Y.; Nachamai, M.; Paulose, J. A Comprehensive Survey on Features and Methods for Speech Emotion Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Technologies (ICECCT), Tamil Nadu, India, 5–7 March 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Khanna, A.; Gupta, D. Emotion Recognition and Detection Methods: A Comprehensive Survey. J. Artif. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 53–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.; Moniz, H.; Carvalho, J.P. Deep Emotion Recognition in Textual Conversations: A Survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 58, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zheng, W.; Cui, Z.; Zong, Y.; Li, Y. Spatial–Temporal Recurrent Neural Network for Emotion Recognition. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 49, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Gui, X.; Zhang, X. Deep Convolution Neural Networks for Twitter Sentiment Analysis. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 23253–23260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munikar, M.; Shakya, S.; Shrestha, A. Fine-Grained Sentiment Classification Using BERT. In Proceedings of the 2019 Artificial Intelligence for Transforming Business and Society (AITB), Kathmandu, Nepal, 5 November 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the NAACL-HLT, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, M.Z.; Subhan, F.; Imran, M.; Kundi, F.M.; Khan, A.; Shamshirband, S.; Mosavi, A.; Koczy, A.R.V.; Csiba, P. Performance Evaluation of Supervised Machine Learning Techniques for Efficient Detection of Emotions from Online Content. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.01587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaind, B.; Syal, V.; Padgalwar, S. Emotion Detection and Analysis on Social Media. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.08458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, S.K.; Varadhaganapathy, S.; Gupta, R.K.; Shukla, P.K.; Bouye, M.; Hingaa, S.K.; Mahmoud, A.; Kumar, V. Text-Based Emotion Recognition Using Deep Learning Approach. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 2645381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.; Wu, J.; Wen, T. An LSTM-CNN Attention Approach for Aspect-Level Sentiment Classification. J. Comput. Methods Sci. Eng. 2019, 19, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, N.; Poria, S.; Hazarika, D.; Mihalcea, R.; Gelbukh, A.; Cambria, E. DialogueRNN: An Attentive RNN for Emotion Detection in Conversations. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2019, 33, 6818–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, D.; Majumder, N.; Poria, S.; Chhaya, N.; Gelbukh, A. DialogueGCN: A Graph Convolutional Neural Network for Emotion Recognition in Conversation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.11540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Vossen, P. EmoBERTa: Speaker-Aware Emotion Recognition in Conversation with RoBERTa. arXiv 2019, arXiv:2108.12009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Chen, J.; Quan, X.; Xie, Z. DialogXL: All-in-One XLNet for Multi-party Conversation Emotion Recognition. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 13789–13797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Xin, C.; Lai, S.; Wang, A.; Su, J.; Xu, K. CASA: Conversational Aspect Sentiment Analysis for Dialogue Understanding. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2022, 73, 511–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abas, A.R.; Elhenawy, I.; Zidan, M.; Othman, M. BERT-CNN: A Deep Learning Model for Detecting Emotions from Text. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 71, 2943–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Raman, B. A BERT-Based Dual-Channel Explainable Text Emotion Recognition System. Neural Netw. 2022, 150, 392–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, A.; Franco-Salvador, M.; Pawar, N.; Štajner, S.; Rios, M.C.; Benajiba, Y. SymantoResearch at SemEval-2019 Task 3: Combined Neural Models for Emotion Classification in Human-Chatbot Conversations. In Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 6–7 June 2019; pp. 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Feng, C.; Xu, M.; Zheng, T.F.; Hamdulla, A. DialoguePCN: Perception and Cognition Network for Emotion Recognition in Conversations. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 141251–141260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zang, L.; Zhang, R.; Hu, S.; Huang, L. EmotionFlow: Capture the Dialogue Level Emotion Transitions. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 8542–8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarni, F.; Sagheer, A.; Alabbad, A.; Hamdoun, H. Emotion-Aware RoBERTa Enhanced with Emotion-Specific Attention and TF-IDF Gating for Fine-Grained Emotion Recognition. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 17617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Pu, P.; Jiang, L. Emotion-RGC Net: A Novel Approach for Emotion Recognition in Social Media Using RoBERTa and Graph Neural Networks. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0318524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, A.; Varol, O. TurkishBERTweet: Fast and Reliable Large Language Model for Social Media Analysis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 255, 124737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.; Hazarika, D.; Poria, S.; Cambria, E. Recent Trends in Deep Learning Based Natural Language Processing. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2018, 13, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.B.; Yu, C.H.; Wen, Z.; Kong, X. Psychological Assessment Model Based on Text Emotional Characteristics. J. Jilin Univ. 2019, 57, 927–932. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, P.; Hu, X. Combining Context-Relevant Features with Multi-Stage Attention Network for Short Text Classification. Comput. Speech Lang. 2022, 71, 101268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K. Sentiment Classification of Microblog: A Framework Based on BERT and CNN with Attention Mechanism. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 101, 108032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All You Need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Yan, J. Combining Knowledge with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Short Text Classification. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 August 2017; Volume 350, pp. 3172077–3172295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Trabelsi, A.; Zaïane, O. ANA at SemEval-2019 Task 3: Contextual Emotion Detection in Conversations through Hierarchical LSTMs and BERT. In Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 6–7 June 2019; pp. 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poria, S.; Hazarika, D.; Majumder, N.; Naik, G.; Cambria, E.; Mihalcea, R. MELD: A Multimodal Multi-party Dataset for Emotion Recognition in Conversations. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.02508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa Lee, M.C.; Braet, J.; Springael, J. Performance Metrics for Multilabel Emotion Classification: Comparing Micro, Macro, and Weighted F1-scores. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Paper | Dataset | Method | Input Tokens | Emotions | Multi-Turn | Global | Local | Attention |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10] | Six emotional categories | Naive Bayes, SVM | \ | 6 | X | X | O | X |
| [11] | Six emotional categories | Naive Bayes, SMO | \ | 6 | X | X | O | X |
| [12] | Six emotional categories | Bi-GRU+CNN | 128 | 6 | X | X | O | X |
| [13] | Three categories (emotional polarity) | LSTM+CNN | 128 | 3 | X | O | O | O |
| [14] | IEMOCAP | DialogueRNN | 128 | 6 | O | O | X | X |
| [15] | IEMOCAP, MELD | DialogueGCN | 128 | 6, 7 | O | O | O | X |
| [16] | IEMOCAP, MELD | RoBERTa-based | 512 | 6, 7 | O | O | X | X |
| [17] | IEMOCAP, MELD | XLNet-large | 512 | 6, 7 | O | O | X | X |
| [18] | Three categories (emotional polarity) | BERT-based | 256 | 3 | O | O | X | X |
| [19] | ISEAR, SemEval | BERT+CNN | 512 | 6, 3 | X | O | O | X |
| [20] | ISEAR | BERT+LSTM | 128 | 6 | X | O | O | O |
| [21] | SemEval | BERT+GRU | 128 | 3 | O | O | O | X |
| [22] | IEMOCAP, MELD | BERT+GCN | 512 | 6, 7 | O | O | O | X |
| [23] | MELD | BERT+GRU+GNN | 256 | 7 | O | O | O | X |
| [24] | Six emotional categories | RoBERTa+TF-IDF | 512 | 6 | X | O | O | O |
| [25] | Sentiment140, Emotion Dataset | RoBERTa + R-GCN+CRF | 256 | 3, 7 | X | O | O | X |
| [26] | Turkish social media | PTM+CNN | 256 | 3 | X | O | O | X |
| [28] | Text Review | CNN | 128 | 5 | X | O | X | O |
| [29] | Movie Review | TCN | 64 | 2 | X | O | O | O |
| [30] | Three categories (emotional polarity) | BERT+CNN | 128 | 3 | X | O | O | O |
| our | SemEval,MELD | EmoBERTa+CNN | 128 | 3,7 | O | O | O | O |
| Hyper-Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| EmoBERTa learning rate | 1 × 10−6 |
| CNN learning rate | 1 × 10−5 |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Loss function | Categorical cross-entropy |
| Batch size | 16 |
| Dropout | 0.5 |
| Kernel sizes | [3, 5, 7] |
| Epochs | 10 |
| Dataset Split | Total | Happy | Sad | Angry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | 15212 | 4243 | 5463 | 5506 |
| Testing | 832 | 284 | 250 | 298 |
| Dataset Split | Total | Neutral | Joy | Surprise | Anger | Sadness | Disgust | Fear |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | 9989 | 4710 | 1743 | 1205 | 1109 | 683 | 271 | 268 |
| Testing | 2610 | 1256 | 402 | 345 | 281 | 208 | 68 | 50 |
| Model | F1-Score |
| SymantoResearch [21] | 76.8% |
| BERT–CNN [19] | 94.3% |
| EmoBERTa [16] | 93.3% |
| EmoBERTa–CNN (our) | 95.6% |
| EmoBERTa–CNN–Att (our) | 96.0% |
| Emotions Model | Angry | Sad | Happy | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P↑ | R↑ | F1↑ | P↑ | R↑ | F1↑ | P↑ | R↑ | F1↑ | |
| SymantoResearch [21] | 0.73 | 0.79 | 0.76 | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.72 | 0.73 |
| BERT–CNN [19] | 0.91 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.97 |
| EmoBERTa [16] | 0.91 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.88 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.95 |
| EmoBERTa–CNN (our) | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.97 |
| EmoBERTa–CNN–Att (our) | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.97 |
| Model | F1-Score |
|---|---|
| DialogXL [17] | 62.41% |
| Emotionflow [23] | 65.05% |
| EmoBERTa [16] | 66.59% |
| EmoBERTa–CNN (our) | 76.39% |
| EmoBERTa–CNN–Att (our) | 79.45% |
| Emotion Model | Neutral | Joy | Surprise | Anger | Sadness | Disgust | Fear | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P↑ | R↑ | F1↑ | P↑ | R↑ | F1↑ | P↑ | R↑ | F1↑ | P↑ | R↑ | F1↑ | P↑ | R↑ | F1↑ | P↑ | R↑ | F1↑ | P↑ | R↑ | F1↑ | |
| EmoBERTa [16] | 0.75 | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.66 | 0.61 | 0.63 | 0.55 | 0.61 | 0.58 | 0.59 | 0.55 | 0.57 | 0.73 | 0.24 | 0.36 | 0.62 | 0.24 | 0.34 | 0.28 | 0.16 | 0.20 |
| EmoBERTa–CNN (our) | 0.88 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.71 | 0.78 | 0.74 | 0.66 | 0.78 | 0.72 | 0.65 | 0.73 | 0.69 | 0.66 | 0.59 | 0.63 | 0.70 | 0.31 | 0.43 | 0.55 | 0.22 | 0.31 |
| EmoBERTa–CNN–Att (our) | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.64 | 0.80 | 0.71 | 0.75 | 0.72 | 0.73 | 0.78 | 0.59 | 0.67 | 0.63 | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.54 | 0.44 | 0.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Yu, A.; Sheng, X.; Park, J.; Rhee, J.; Cho, K. EmoBERTa–CNN: Hybrid Deep Learning Approach Capturing Global Semantics and Local Features for Enhanced Emotion Recognition in Conversational Settings. Mathematics 2025, 13, 2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13152438
Zhang M, Yu A, Sheng X, Park J, Rhee J, Cho K. EmoBERTa–CNN: Hybrid Deep Learning Approach Capturing Global Semantics and Local Features for Enhanced Emotion Recognition in Conversational Settings. Mathematics. 2025; 13(15):2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13152438
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Mingfeng, Aihe Yu, Xuanyu Sheng, Jisun Park, Jongtae Rhee, and Kyungeun Cho. 2025. "EmoBERTa–CNN: Hybrid Deep Learning Approach Capturing Global Semantics and Local Features for Enhanced Emotion Recognition in Conversational Settings" Mathematics 13, no. 15: 2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13152438
APA StyleZhang, M., Yu, A., Sheng, X., Park, J., Rhee, J., & Cho, K. (2025). EmoBERTa–CNN: Hybrid Deep Learning Approach Capturing Global Semantics and Local Features for Enhanced Emotion Recognition in Conversational Settings. Mathematics, 13(15), 2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13152438





