Abstract
The automotive suspension must perform competently to support comfort and safety when driving. Traditionally, car suspension control tuning is performed through trial and error or with classical techniques that cannot guarantee optimal performance under varying road conditions. The study aims at designing a Linear Quadratic Regulator-based Bacterial Memetic Algorithm (LQR-BMA) for suspension systems of automobiles. BMA combines the bacterial foraging optimization algorithm (BFOA) and the memetic algorithm (MA) to enhance the effectiveness of its search process. An LQR control system adjusts the suspension’s behavior by determining the optimal feedback gains using BMA. The control objective is to significantly reduce the random vibration and oscillation of both the vehicle and the suspension system while driving, thereby making the ride smoother and enhancing road handling. The BMA adopts control parameters that support biological attraction, reproduction, and elimination-dispersal processes to accelerate the search and enhance the program’s stability. By using an algorithm, it explores several parts of space and improves its value to determine the optimal setting for the control gains. MATLAB 2024b software is used to run simulations with a randomly generated road profile that has a power spectral density (PSD) value obtained using the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) method. The results of the LQR-BMA are compared with those of the optimized LQR based on the genetic algorithm (LQR-GA) and the Virus Evolutionary Genetic Algorithm (LQR-VEGA) to substantiate the potency of the proposed model. The outcomes reveal that the LQR-BMA effectuates efficient and highly stable control system performance compared to the LQR-GA and LQR-VEGA methods. From the results, the BMA-optimized model achieves reductions of 77.78%, 60.96%, 70.37%, and 73.81% in the sprung mass displacement, unsprung mass displacement, sprung mass velocity, and unsprung mass velocity responses, respectively, compared to the GA-optimized model. Moreover, the BMA-optimized model achieved a −59.57%, 38.76%, 94.67%, and 95.49% reduction in the sprung mass displacement, unsprung mass displacement, sprung mass velocity, and unsprung mass velocity responses, respectively, compared to the VEGA-optimized model.
Keywords:
quarter-car suspension; full-state feedback control; bacterial memetic algorithm; optimization; vehicle dynamics; active suspension system MSC:
93C10
1. Introduction
With effective suspension, the driver experiences comfort, enhanced vehicle stability, and improved control. Its primary purpose is to keep the car body and all its wheels stable and steady in uneven road conditions and establish very close contact between the vehicle and the road. With most passive systems, the set spring and damper rates can make it difficult to trade off a comfortable ride for good handling. The optimal usefulness of systems like active and semi-active suspension is their ability to react instantly to uneven roads and unstable driving conditions. Such a system has been improved using control strategies such as full-state feedback control. Using optimal control settings, full-state feedback control, or an LQR controller enables direct control over the vertical oscillations and vertical velocity of the vehicle body and the suspension system. LQR is a linear control strategy [1], which requires a precise model of the system, and there is difficulty in tuning its weighting matrices [2]. Thus, its performance needs to be enhanced to achieve an optimal solution. Choosing the right feedback gains can be daunting due to the nonlinearity nature of vehicle and road dynamics. This research proposes the Bacterial Memetic Algorithm (BMA) to find the best solution for the full-state feedback control system of a quarter-car suspension. BMA is an algorithm that combines the global search strategy of the Bacterial Foraging Optimization Algorithm (BFOA) with the local search ability provided by the Memetic Algorithms (MA). The method ensures that the solution space is checked in detail as efforts are made to fine-tune the control parameters. The study’s goal is to minimize the shifting and bouncing of the sprung mass, thereby making the car ride more comfortable and steering better on the road. To confirm that the BMA-optimized LQR controller performs better, its performance will be compared with that of the GA-optimized and VEGA-optimized LQR controllers.
Recent research studies have proposed different and various vehicle suspensions and optimization techniques to enhance suspension stability, passenger comfort, and improve road handling. For instance, in [3] various types of vehicle suspension systems were reviewed, including passive, semi-active, active, hydraulic, pneumatic, and electromagnetic active suspension systems. The study concluded by postulating electromagnetic suspension as a future trend that could be implemented in vehicle suspension designs due to its efficiency, improved ride quality, and simplified structural design. Abdolvahab et al. [4] employed a quarter-car model and derived a mathematical model for passive and active suspension systems. An LQR controller was implemented in the design, and comparisons were made for the passive and active suspension systems. The results revealed the optimum functionality of the LQR controller, ensuring minimal suspension displacement and vibration isolation across various road profiles. Li et al. [5] designed a 7-DOF suspension model and a road preview-based Explicit Model Predictive Control (EMPC) for magnetorheological semi-active suspensions in all-terrain vehicles. Under both preview and non-preview states, comparative analyses with Skyhook controllers validate that EMPC provides notable improvements in road holding and vehicle stability, reinforcing the superiority of EMPC damping effects. Ro et al. studied the application of fuzzy logic control on an active suspension system [6]. A quarter car was modeled mathematically using Newton equations, with the vehicle’s displacement, velocity, and acceleration tested to prove the effectiveness of the fuzzy algorithm implemented. Nitish and Sanjay [7] proposed a GA-PID optimized controller for a quarter-car suspension model. The research work focused on integrating the suspension system’s efficiency and highlighted the cogency of GAs to enhance traditional suspension systems. The proposed model demonstrated better performance compared to the traditional PID controller. Amit et al. [8] conducted a study on three controller variants (fuzzy logic, PID, and GA-PID genetic algorithm) for active suspension systems and had a comparative analysis among them. The fuzzy and GA PID controllers indicated higher-level performance compared to the PID controller, exhibiting commendable improvements in reducing vertical oscillations and vibrations. Moreover, Abroon et al. [9] proposed a fuzzy logic controller for semi-active suspension systems optimized using the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm. On one hand, the controller demonstrated good performance, while on the other hand, its practicality was compromised by constraints associated with the mathematical model as well as the nonlinear characteristic of the system. Ahmed et al. [10] designed a PID controller for a passive suspension system. Although the controller performed well for passive suspension systems under various input conditions, further tuning is still necessary to achieve optimal results. Du and Zhang conducted a thorough study on a fuzzy state feedback control strategy for electrohydraulic active suspensions, addressing nonlinear actuator dynamics, sprung mass variation, and control input constraints [11]. Rashid et al. studied PID, fuzzy logic, and hybrid controllers for controlling vehicle suspension vibrations. The quarter-car mathematical model used was derived using Newton’s laws of motion [12]. Biglarbegian et al. studied a neuro-fuzzy control strategy for a quarter car with a semi-active suspension system [13]. Fuzzy state feedback was also implemented to increase the system’s performance. Furthermore, Diao et al. [14] proposed a custom hierarchical control strategy to manage parameter uncertainties and external disturbances in the electro-hydraulic control active suspension systems. An advanced constraint-adaptive backstepping controller was employed for synthesizing the target force in body vertical motion tracking. From the simulation results, a significant decrease in the sprung mass acceleration resulting from rough road profiles was achieved, with improved ride comfort accentuated. In [15], an adaptive finite-time fuzzy control strategy was proposed to enhance the adaptive capability of active suspension systems under complex and nonlinear road conditions. Y. Shen et al. presented an optimal design of a vehicle inerter-spring-damper (ISD) suspension based on the fractional-order skyhook-groundhook hybrid (SH-GH) control principle [16]. In [17], the constrained H∞ optimal control problem associated with nonlinear active suspensions was addressed by utilizing the data-driven reinforcement learning algorithm.
In the case of the BMA, its applications have extended across a wide range of optimization problems. For instance, in [18], the BMA was employed for offline path planning of mobile robots. The algorithm was implemented to discover the shortest and crash-free route for mobile robots. Two different robots—an omnidirectional and a Bioloid mobile robot—were investigated with the algorithm to test its effectiveness. Due to the promising accuracy of the BMA, it has been adopted as a selection tool for the surface electromyography (SEMG)-based hand recognition problem [19]. The research utilized SEMG signals to test and analyze the feasibility of the proposed algorithm. The Colonial Bacterial Memetic Algorithm was applied to [20] a dart-playing robot [21], demonstrated a 100% success rate in real-world robotic applications, and outperformed other methods when comparisons were made. The research extensively demonstrated the constructiveness of the model through a real-life example, while achieving reliable and consistent results. Furthermore, the BMA was also applied to the asymmetric capacitated vehicle routing problem [22]. In the research work, a comparative analysis was conducted between the BMA and other heuristic methods. From the results presented, the proposed algorithm demonstrated better performance than its counterparts on all data levels, with at least 30% improvement. The BMA was also adopted as a search method in a trained fuzzy system-based model of single-weld bead geometry [20]. Precise models were developed to express the weld bead geometry (WBG) in terms of welding process variables (WPVs). On the other hand, the BMA has failed to achieve better results compared to the GA when it was implemented on the Storage Location Assignment Problem (SLAP) [20], although the unsatisfactory results were attributed to parameter settings. The results were unable to prove the superiority of the BMA over the GA concerning the SLAP, despite previous works revealing the opposite in other problem domains [22].
In this article, the optimal design of an LQR controller for a quarter-car suspension system based on the BMA is proposed. BMA is a modern search technique that has emerged recently [23]. The method interpolates bacterial mutation and gene transfer operations using the Levenberg–Marquardt Algorithm (LMA)—a technique employed to solve nonlinear least squares minimization problems—to achieve accurate and optimal solutions to optimization problems. This coalescence of evolutionary and gradient-based (global and local search) algorithms is successfully employed in global optimization approaches, particularly for optimizing parameter values and enhancing function approximation performance [24]. The fundamental part of the BMA with Modified Operator Execution Order contains the bacterium that transfers a replica of a gene from a host cell to an infected cell. The algorithm consists of the following steps: initialization, local search, gene transfer, and bacterial mutation operations on each individual, including some LMA operations [25]. This study analyzed the vertical displacements and velocities of the vehicle body and the suspension under an uneven road profile. The results of the BMA-LQR model were compared with those of two other built models—the GA-LQR and the VEGA-LQR models—to assess the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed model. The primary contribution of this paper can be summarized as follows:
- This paper proposes an LQR-BMA control technique that significantly minimizes the vertical displacement and velocity of the vehicle body and suspension, thereby enhancing the ride comfort and stability of the vehicle.
- This article presents a comprehensive and comparative study of the proposed model alongside other heuristic methods, offering insights into the role of evolutionary algorithms in enhancing the performance of car suspension systems.
- This research demonstrates that LQR-BMA is a reliable, robust control strategy suitable for vehicle suspension systems.
The other sections of this study are organized as follows: Section 2 presents the mathematical model of the quarter-car suspension system, the optimization algorithms implemented, and the LQR controller. Section 3 highlights the simulation results obtained from the three models, i.e., BMA-LQR, GA-LQR, and VEGA-LQR. In Section 4, the results were discussed extensively and comparatively. Section 5 concludes the study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mathematical Modeling
In this paper, a model of a two-spring, two-mass suspension is adopted. The mathematical equations were derived using Newton’s second law of motion. The MATLAB environment was utilized for the simulation and analysis of the designed model. The state-space approach, due to its simplicity, is considered a tool for analyzing the dynamics of the overall system. Table 1 contains the data parameters of the designed model.
Figure 1 illustrates the prototype of a quarter-car active suspension system. In the model, mc [Kg] and mk [Kg] represent the sprung and unsprung masses, respectively; yc [m] and yk [m] are the displacements of the corresponding masses; u [m] is the road displacement; kr [N/m] and Kk [N/m] are the spring constants of the suspension springs of the vehicle body and the tire; br [N.s/m] is the damper coefficient, and Fa (t) [N] denotes the actuating force controlled by the algorithm-based (i.e., BMA_LQR, GA_LQR, and VEGA_LQR) controllers.
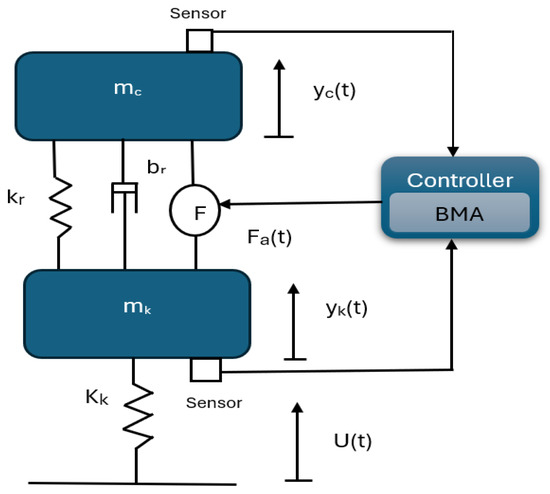
Figure 1.
Model of a quarter-car active suspension adapted from [26].
2.1.1. Equations of Motion
The dynamic mathematical equations of the quarter car suspension system (i.e., Equations (1)–(10)) are hereby deduced according to Newton’s law of motion as expressed in [27].
Equations (1) and (2) represent the equations of motion for the sprung and unsprung masses, respectively. Where , , and represent the dynamic forces of the suspension spring, vehicle body spring, and damper, respectively. The following Equations (3)–(6) are derived by further simplifying the Equations:
where is the sprung mass velocity; is the unsprung mass velocity is the sprung mass acceleration, is the unsprung mass acceleration.
In the state space representation, the state variables—X1, X2, X3, and X4—are used. X1 = − is the suspension displacement; X2 = ; X3 = u − is the tire displacement; X4 = ; Z = u.
Therefore, the state and output vectors are stated as follows:
2.1.2. The State Space Equations Have the General Form

Table 1.
Model parameters of the quarter car suspension system [28].
Table 1.
Model parameters of the quarter car suspension system [28].
| Parameters | Mean Value | Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| kr | N/m | 0 N/m |
| br | 1450 Ns/m | −550 + 450 Ns/m |
| kk | N/m | N/m |
| mc | 395.3 Kg | −42.77 + 75.38 Kg |
| mk | 48.3 Kg | 0 Kg |
2.2. Bacterial Memetic Algorithm
Modern optimization algorithms, completely inspired by natural selection, have become the most effective methods for finding optimal and accurate solutions to problems associated with nonlinear systems, high-dimensional systems, discontinuous systems, and multimodal systems. One of these optimization techniques is the bacterial evolutionary algorithm (BEA). The BEA consists of two bacterial operators—the bacterial mutation and the gene transfer operation. In the bacterial mutation phase, individuals in the population are optimized one by one through the inheritance of the best individuals from the parent generation by their offspring. During the gene transfer operation, information is transferred between different individuals. Memetic Algorithms (MAs) are search heuristic techniques that blend both evolutionary and local search methods to find optimal solutions to optimization problems. The Bacterial Memetic Algorithm (BMA) [23] is a hybrid optimization method that amalgamates bacterial foraging techniques with MAs. It employs the bacterial technique instead of the classical genetic algorithm, at the same time using the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm (LMA) [29,30] as the local search method. The BMA is a hybrid optimization technique that combines the bacterial evolutionary algorithm with a local search operation [18]. It is inspired by the natural behavior of bacteria, particularly their foraging and reproductive processes, while incorporating local search techniques to refine the solution. Memetic algorithms have been applied in various fields, ranging from offline path planning of mobile robots [18], fuzzy rule-based optimization [31], asymmetric capacitated vehicle routing [22], a darts-playing robot [21], surface electromyography [19], and the Storage Location Assignment Problem (SLAP) [32].
BMA, as a modern evolutionary algorithm [18], incorporates biological attraction into its local search process [33], in the sense that the natural behavior of a bacterium, which involves moving towards nutrient-rich areas and transferring and conveying beneficial traits via chemotaxis, is imitated. In the case of the BMA, biological attraction refers to the viability of a candidate solution to move within the search space towards the fittest solutions. This postulation plays a vital role in the optimization process by enhancing and encouraging the transfer of the fittest gene from parents to offspring, as well as creating a balance between exploitation and exploration [33].
BMA, as a modern evolutionary algorithm, employs three primary operations during its optimization process, as shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3: local search, gene transfer, and bacterial mutation [25]. The fitness function serves as a gauge for assessing the robustness of each solution within the context of the optimization problem and thereby refining the solutions within the population.
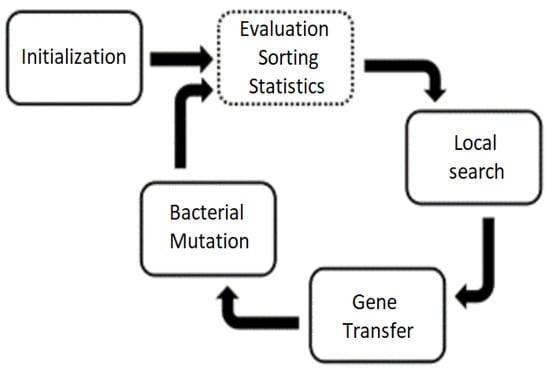
Figure 2.
Bacterial Memetic Algorithm (BMA) flow chart [22]. In the dotted-lined box, the fitness function of the optimization problem is used to check the fitness of each solution. The fittest solutions are sorted from the population and used for the next iteration.
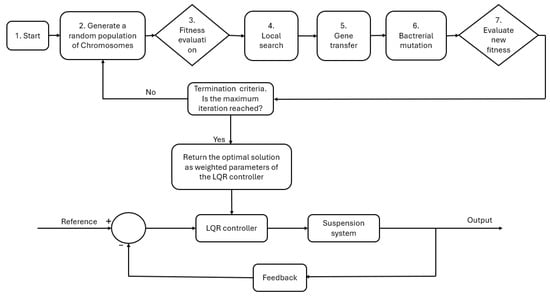
Figure 3.
BMA-LQR tuning process.
Initially, a population of candidate solutions is generated randomly, with each set of population in an iteration referred to as a generation. Each candidate is evaluated for fitness in every generation, with the fittest solutions used in the next iteration to form subsequent generations. Thus, better solutions are created in further iterations. The probability that an individual is selected for the next iteration is given by the Roulette wheel selection. With as the fitness of individual i, M as the population size, as the selection probability for the candidate solution i, the Roulette wheel selection equation is given in Equation (11) as expressed in [34]
During the bacterial mutation, offspring (clones) of each solution are produced. The clones inherit the genome of their parents [22]. Hence, not only is a large set of candidates generated, but optimal solutions are also achieved by exploring a broader range of possible solutions and avoiding premature convergence. To ensure the convergence of the fittest solutions produced in the bacterial mutation phase, the Levenberg–Marquardt Algorithm (LMA)—an iterative optimization algorithm for solving nonlinear least squares problems—is employed to conduct a local search operation [23]. Also, the mutation rate should be taken into consideration, as a too-high mutation rate can derange effective solutions, while a too-low mutation rate can prevent or reduce the exploration of untapped areas of the search space. In the gene transfer phase, the parent solutions within the population of every generation transfer genetic behaviors to their offspring. This improves the overall performance of the algorithm as it focuses its search on regions of solutions with better fitness. The fitness function serves as a gauge for assessing the robustness of each bacterium based on the criteria defined in the optimization problem. Table 2 presents the BMA parameters utilized in the simulation to effectively tune the LQR controller and achieve optimal weight coefficients for matrices Q and R.

Table 2.
BMA simulation parameters.
2.3. Genetic Algorithm (GA)
Genetic algorithms are computational models inspired by natural selection, which are often employed to obtain optimal solutions to optimization problems. These algorithms represent a latent solution to the defined optimization problem using a simple chromosome-like data structure and apply recombination operators to these structures to preserve vital information [35]. Developed by John Holland in the 1970s as a method inspired by the principles of natural selection, GA emulates natural evolution and adaptation principles, such as inheritance, mutation, selection, and crossover, to generate solutions to optimization problems, as shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5. GA begins by developing a population of candidate solutions—often represented as chromosomes in an iterative process, with each number of individuals present in a single iteration called a generation. Based on their fitness, individuals are selected to produce offspring through crossover and mutation operations, creating a new generation of solutions that ideally inherit beneficial traits from their predecessors. One of the key strengths of GA is its ability to traverse a wide search space and avoid or reduce the likelihood of getting trapped in local optima, allowing it to be applied to problems that are nonlinear, multimodal, or lack gradient information. GAs are seldom regarded as a function optimizer, although the scope of the issues to which genetic algorithms have been applied is quite broad [35]. It has been successfully applied across various engineering, scientific, and economic fields, including control system tuning, machine learning, scheduling, and structural design. In energy management [36], GA was employed as an optimization tool to achieve optimal solar energy, wind energy, and storage capacity in a hybrid system. In the parameter optimization of a 7DOF robotic manipulator [22,37], GA was utilized to find the best parameter estimate for the developed nonlinear model, leading to a high-performance system. Table 3 shows the GA parameters applied in the simulation to effectively tune the LQR controller and achieve optimal weight coefficients for matrices Q and R.
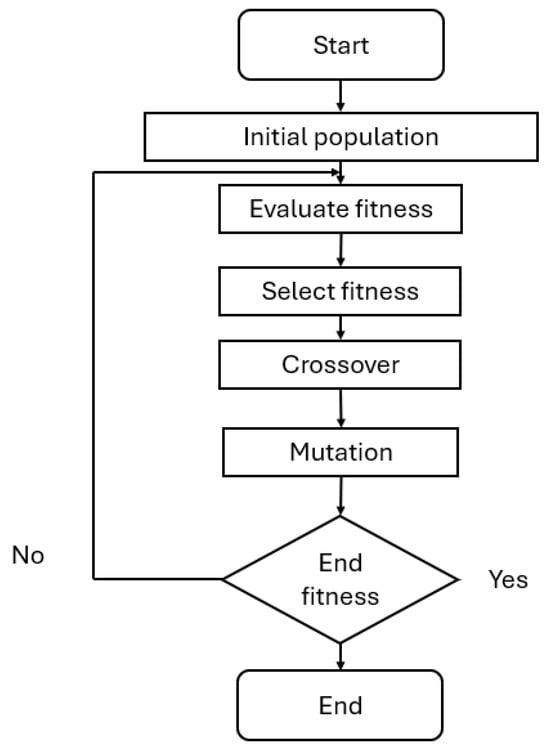
Figure 4.
Genetic algorithm flowchart [38].
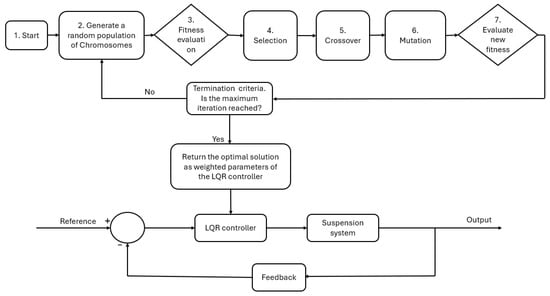
Figure 5.
GA-LQR tuning process.

Table 3.
GA simulation parameters.
2.4. Virus Evolutionary Genetic Algorithm (VEGA)
The evolutionary theory in biology assumes that the gene of a virus or transposon from another individual is incorporated into the chromosome of the individual by the virus and bacteria, and sometimes, this leads to peaceful and rapid horizontal evolution over a short period [39]. The VEGA draws on principles from the virus theory of evolution to achieve optimal solutions, particularly in nonlinear systems. The VEGA comprises two populations: a host population and a virus population [40]. The process adopted by VEGA in its search for optimal solutions is illustrated in Figure 6. It begins by generating a population of candidate solutions (hosts) and simultaneously initializing a set of viruses. While each individual represents a potential solution to the optimization problem, each virus is a solution that attempts to infect and improve host individuals. The fitness function of the optimization problem evaluates both the hosts and the viruses. Aside from the natural operations of traditional GAs, which employ selection, crossover, and mutation as the only genetic operators to advance a population of potential solutions, VEGA integrates the process with a virus–host interaction. During this phase, the hosts are infected by viruses, which alter their genetic structures and give birth to mutant offspring. The infected hosts are referred to as clones. Based on the fitness evaluation, the original hosts are replaced by the clones with better fitness.
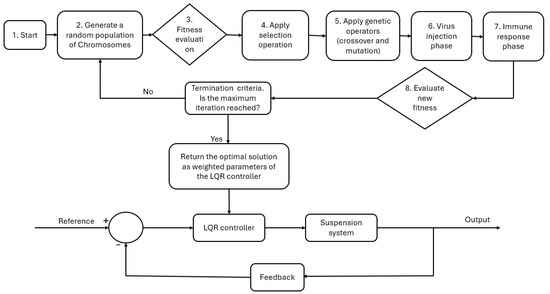
Figure 6.
VEGA-LQR tuning process.
VEGA utilizes infection as a key process in achieving optimal solutions to optimization problems without compromising the overall solution quality. By integrating evolutionary algorithms with the virus adaptation method, the chances of getting trapped in local optima can be minimized. Additionally, VEGA operates effectively with static, dynamic, nonlinear, multimodal, and high-dimensional optimization problems. In static and linear models, changes are repeated in each generation, but in dynamic, nonlinear, and multimodal system models, both viruses and hosts change together as the search progresses. Because of this, the algorithm can adjust its search method to suit the specific needs and conditions of each problem. Table 4 presents the VEGA parameters used in the simulation to effectively tune the LQR controller and achieve optimal weight coefficients for matrices Q and R.

Table 4.
VEGA simulation parameters.
2.5. Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR)
The LQR is an effective feedback controller employed to regulate the behavior of dynamic systems. Optimal control is achieved when the cost function of the dynamic system is at its minimum. Linear differential equations are used to define the system dynamics owing to the compatibility of the LQR with Linear Time-Invariant (LTI) systems. This makes the design of the controller simple, rugged, and easily implemented in a wide range of control problems. In the case of a car suspension system, the mathematical model is given in state-space form, where all state variables are utilized to determine the optimal feedback gain that minimizes the cost function, thereby stabilizing the state error and reducing the control effort. Figure 7 shows the block diagram of the LQR controller based on the state-space model. Equations (12)–(24) represent the mathematical derivations of the feedback gain of the LQR controller as expressed in [27].
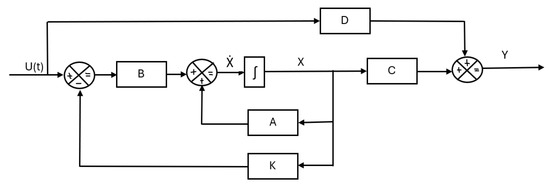
Figure 7.
Block diagram of the model with a feedback gain. Where A, B, C, and D are the system, input, output, and feedforward matrices, respectively. X is the state variable, and U and Y represent the input and output of the system, respectively. K is the feedback gain and ∫ is the integrator.
Using the output equation stated in Equation (7), the objective function is given as follows:
where , , , and correspond to the weight coefficients in the LQR cost function relating to the extent to which certain control parameters of the system are attenuated. Regarding the defined state outputs, , , , and are set to mitigate body acceleration, body displacement, suspension deflection, and the control variable, respectively.
Rewriting the equation yields
where Q = diag [ , R = [] represent the weighted matrices of the LQR controller, U is the control law of the LQR, and Y is the output of the suspension system.
Substituting Y = −CX + DF into Equation (12), we obtain
where
Equation (18) represents the control Equation of the LQR.
K represents the gain matrix of the LQR and can be calculated as follows:
The P matrix can be estimated from the Algebraic Riccati Equation (ARE):
Let
where , , , and are coefficients of the control load Equation.
From Equations (8) and (9), the state space equations for the LQR controller are deduced as follows:
where
3. Results
In this section, the simulated results for the LQR-optimized controller, as performed in MATLAB, are presented based on the derived mathematical model. The three algorithms used—BMA, GA, and VEGA—were all implemented and simulated under a randomly generated road geometry using power spectral density (PSD)—a technique for simulating road surfaces with varying degrees of roughness, as shown in Figure 6. Comparisons were made in the results to analyze the performance of the LQR controller optimized using different algorithms. The objective is to achieve minimum displacement, velocity, and acceleration of the vehicle body, thereby ensuring passenger comfort and safety.
Figure 8 illustrates a road profile for simulating the proposed model generated using power spectral density (PSD) in the MATLAB environment. Since vertical displacements occur due to uneven roads encountered by a vehicle, the randomly generated road profile helps create a similar scenario that the vehicle might encounter in real-life situations. Generating the road profile using the PSD enables the simulation and analysis to be carried out under varying road roughness conditions. The number of samples determines both the length and detail of the computed PSD; many samples produce smoother PSD curves. The PSD settings are given as follows: N (number of samples) = 1000; The random road profile with the frequency (f) range of 0 to pi is characterized in Equation (25) as expressed in [4].
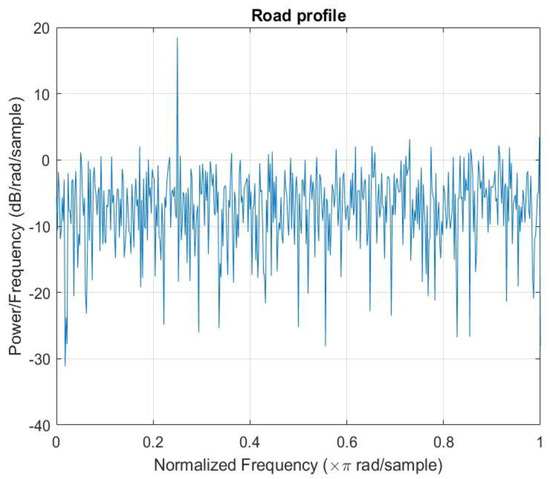
Figure 8.
Randomly generated road profile using PSD.
Figure 9 and Figure 10 show the vibration and deflection reactions of both the unsprung (suspension) and sprung (body) masses, respectively, under the influence of the road profile. The proposed model has shown a better performance than its counterparts. The vertical displacement has been significantly reduced by 10% compared to the other algorithms (i.e., GA and VEGA).
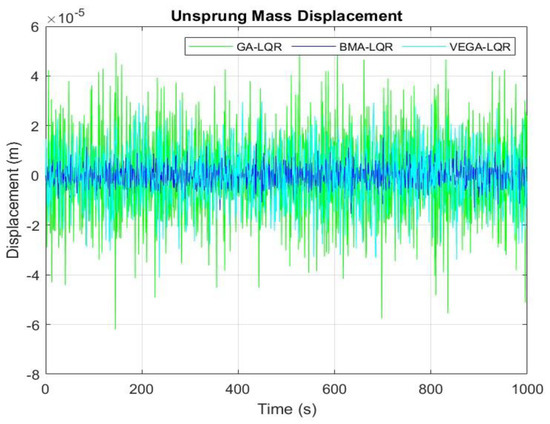
Figure 9.
Displacement response of unsprung mass.
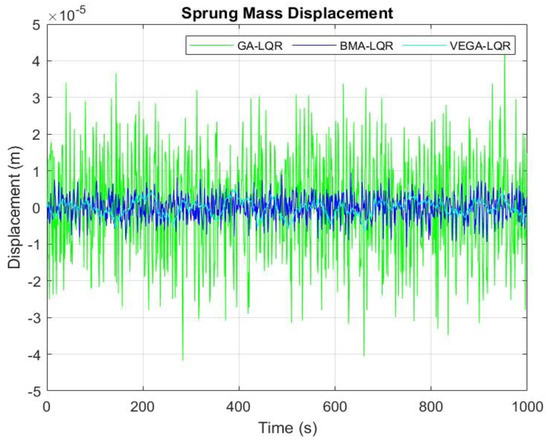
Figure 10.
Displacement response of sprung mass.
Figure 11 and Figure 12 present the results of the vertical velocity of the suspension and body systems, respectively. Similarly to the case of vertical displacement, the BMA has outperformed the GA and VEGA, resulting in a reduced vertical velocity. Here, the vertical velocity of the BMA-optimized model is approximately one-fifth that of the GA- and VEGA-optimized models, thereby enhancing ride comfort performance.
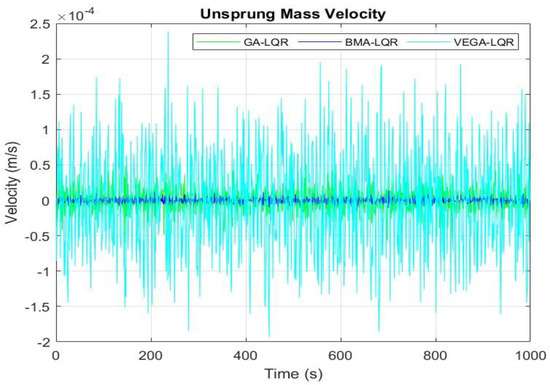
Figure 11.
Velocity response of unsprung mass.
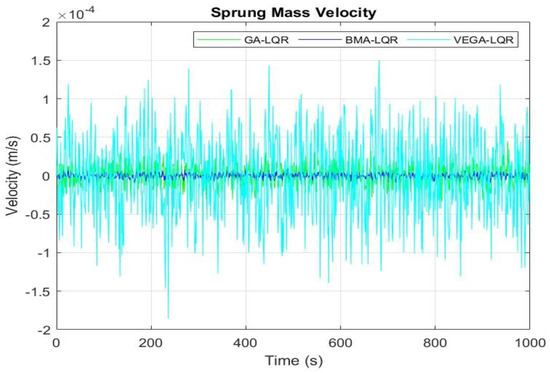
Figure 12.
Velocity response of sprung mass.
Table 5 presents a comparison table of the algorithm-based optimized models for the sprung mass displacement, unsprung mass displacement, sprung mass velocity, and unsprung mass velocity of the active quarter-car suspension system. The LQR-VEGA has demonstrated minimum displacement for the sprung mass ( m), compared to the LQR-BMA ( m) and the LQR-GA ( m). In contrast, the LQR-BMA has demonstrated the minimum displacement for the unsprung mass m) compared to LQR-GA (m) and LQR-VEGA (m), thereby depicting an increase not only in the stability of the vehicle but also in the ride comfort of the passengers. Conjunctively, better results were achieved by the LQR-BMA in response to the velocities of the sprung ( m/s) and unsprung masses ( m/s) compared to LQR-GA ( m/s and m/s) and LQR-VEGA ( m/s and m/s), highlighting its effective role in improving road handling performance.

Table 5.
Comparison of the optimized models.
4. Discussion
The proposed model aimed to improve the stability, ride comfort, and road handling performance of the vehicle in road profiles with varying roughness by optimizing the tuning of an LQR controller using BMA. From the simulation results (Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12), the BMA-optimized model has demonstrated a better performance than the other metaheuristic-optimized models, such as the GA and VEGA, because the BMA includes a memetic (local search) phase that refines each solution, improving accuracy, convergence precision, and easy search for optimum weighting parameters of the LQR controller. Moreover, because the BMA has a better convergence speed than the GA and VEGA, optimal solutions are attained more quickly, resulting in a smoother and significantly reduced vertical displacement of both the vehicle and the suspension system, as shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10. With Figure 9 and Figure 10 representing the displacement responses of the unsprung and sprung masses, an optimal result (a significantly reduced displacement of the suspension) has been achieved by the BMA-LQR optimized model, thereby resulting in increased comfort and safety of passengers.
In the other two models, the GA-LQR-optimized model has shown better performance than the VEGA-LQR-optimized model. Additionally, because the BMA combines the Bacterial Foraging Algorithm (BFA) and memetic algorithms for its exploration, a more robust search over the solution space is achieved via bacterial foraging. This contributed to the reduced vertical velocity of the vehicle and suspension system compared to other optimization methods, as shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10, respectively. Figure 9 and Figure 10 show the velocity responses of the sprung and unsprung masses. Similarly to the case of the displacement response, the BMA-LQR-optimized model outperforms its counterparts, demonstrating it to be a promising and effective solution. Moreover, while the GA and VEGA traded off minimizing suspension displacement at the expense of balancing multiple and complex optimization objectives, the BMA demonstrated a better trade-off between comfort and road handling, contributed by the optimal damping and stiffness behavior of the tuned LQR controller.
From Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12, the proposed model demonstrates its robustness to noise and variation across random road profiles, a critical feature for real-world suspension systems, thereby maintaining consistent and optimal performance. Additionally, Table 5 presents the responses of the optimized model regarding the vertical displacement and velocity of the sprung and unsprung masses in the quarter-car suspension model. The data in the table highlight the efficiency and efficacy of the proposed model. From the results achieved, the BMA-optimized model has shown a 77.78%, 60.96%, 70.37%, and 73.81% reduction in the sprung mass displacement, unsprung mass displacement, sprung mass velocity, and unsprung mass velocity responses, respectively, compared to the GA-optimized model. On the other hand, the BMA-optimized model has shown a −59.57%, 38.76%, 94.67%, and 95.49% reduction in the sprung mass displacement, unsprung mass displacement, sprung mass velocity, and unsprung mass velocity responses, respectively, compared to the VEGA-optimized model. Here, the BMA has indicated a high level of compatibility with active suspension systems (a challenge faced by other optimization methods), which shows that it can also perform effectively with both passive and semi-active suspension systems. During the bacterial mutation, the mutation rate is a critical factor that determines how optimal the solutions can be. Too high a mutation rate can disrupt good solutions, while a too-low mutation rate may prevent exploration of new regions of the search space. Therefore, a suitable value must be chosen carefully and precisely for better tuning. Furthermore, the fact that the BMA can balance between exploration and exploitation (i.e., combining global search with local refinement)—reducing the chances of getting trapped in local minima leading to premature convergences—has significantly contributed to the fewer oscillations and lower vibration levels achieved by the BMA-LQR-optimized model under the uneven road disturbance. The self-adaptive parameterization—a feature that allows the BMA to quickly and automatically adjust its behavior based on the defined problem—further improves and integrates its ability to balance exploration and exploitation. Although the LQR is designed for linear time-invariant systems, whereas the vehicle suspension dynamics are often nonlinear, the BMA has shown its effectiveness in precisely tuning the weighting parameters to achieve optimal feedback gain of the LQR controller.
5. Conclusions
This research demonstrates the effective role that evolutionary algorithms can play in the optimization of a car suspension system. By employing modern computational methods, particularly BMA, high-performance systems with minimal vertical displacement and velocity can be easily achieved. The BMA, with its robust processes of natural selection, bacterial mutation, and gene transfer, has proven to be a versatile and effective tool for addressing a wide range of optimization problems.
The traditional LQR control method has long been inconsistent and imperfect in achieving an optimal level of control in active suspension systems. Therefore, to overcome these limitations, an improved optimization technique that combines and utilizes the Bacterial Foraging Algorithm (BFA) and memetic algorithms to effectively determine the weight coefficients of matrices Q and R of the LQR is presented in this paper. First, a quarter-car active suspension system is adopted for the study. The mathematical and state-space models were developed according to Newton’s second law of motion. Then, the three algorithms (BMA, GA, and VEGA) were developed and implemented within the MATLAB environment on the model. Finally, a comparative analysis was conducted on the simulation results to evaluate the performance of each algorithm. The results, as shown in Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12, highlight the distinction between BMA and other algorithms in the optimization of car suspension systems. From Figure 9 and Figure 10, the BMA-based controller has demonstrated better performance than the GA and VEGA (though the LQR-VEGA model has shown the least body displacement) under the road profile by significantly reducing the rate of random vibration of the vehicle body and suspension system with about 77.78% and −59.57% and 60.96% and 38.76%, respectively, resulting in improved ride comfort and road holding stability. Moreover, in the proposed model, the vertical velocities of the sprung and unsprung masses have improved by about 70.37% and 94.67% and 73.81% and 95.49%, compared to GA and VEGA, as shown in Figure 11 and Figure 12.
By incorporating BMA in future models and designs of car suspension systems, more efficient and sustainable systems could be built. However, further research can be conducted to explore the effectiveness and robustness of the BMA, using this research as a foundation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.T.S. and A.B.; methodology, A.B. and P.T.S.; software, B.A.M. and A.B.K.; validation, B.A.M., A.B., and P.T.S.; formal analysis, B.A.M.; investigation, B.A.M. and A.B.; resources, A.B.K.; data curation, A.B. and A.B.K.; writing—original draft preparation, B.A.M.; writing—review and editing, B.A.M. and A.B.; visualization, A.B.K.; supervision, A.B., P.T.S., and A.B.K.; project administration, P.T.S. and A.B.K.; funding acquisition, P.T.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Supported by the University of Debrecen Program for Scientific Publication.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the University of Debrecen for supporting this research, which is supported by the University of Debrecen Program for Scientific Publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Maaruf, M.; Hamanah, W.M.; Abido, M.A. Hybrid Backstepping Control of a Quadrotor Using a Radial Basis Function Neural Network. Mathematics 2023, 11, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaya, M.S.; Bature, A.; Yusuf, L.A.; Madugu, I.S.; Abubakar, U.; Abubakar, S.A. Comparison of Control Strategies Applied to Nonlinear Quarterly Car Passive Suspension System. Int. Rev. Autom. Control 2015, 8, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiregna, I.; Sirata, G. A review of the vehicle suspension system. J. Mech. Energy Eng. 2020, 4, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolvahab, A.; Shfiei, S.G.; Armin, B. Simulation and analysis of passive and active suspension system using quarter car model for different road profile. Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. 2012, 3, 636–644. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Liang, H.; Xia, D.; Fu, J.; Yu, M. Explicit model predictive control of magnetorheological suspension for all-terrain vehicles with road preview. Smart Mater. Struct. 2024, 33, 035037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ro, P.L.; Kim, C.; Kim, H. An Active Suspension System using Fuzzy Logic Control. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–4 June 1993; pp. 2252–2253. [Google Scholar]
- Katal, N.; Singh, S.K. Optimization of PID controller for quarter-car suspension system using genetic algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Eng. Technol. 2012, 1, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Amit, B.P.; Jagrut, G.J.; Nikunj, V.; Nirav, G.M. Development of active suspension system for car using fuzzy logic controller, PID and genetically optimize PID controller. J. Inf. Knowl. Res. Electr. Eng. 2013, 2, 347–351. [Google Scholar]
- Abroon, J.Q.; Umar, A.F.; Afzal, K.; Tahir, M.K.; Farrukh, M.; Ali, F. Optimization of semi-active suspension system using particle swarm optimization algorithm. AASRI Conf. Intell. Syst. Control 2013, 4, 160–166. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Ali, A.S.; Ghazaly, N.M.; Abdel-Jaber, G. PID controller of active suspension system for a quarter car model. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 2015, 8, 890–909. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Zhang, N. Fuzzy Control for Nonlinear Uncertain Electrohydraulic Active Suspensions With Input Constraint. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2009, 17, 343–356. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, M.M.; Rahim, N.A.; Hussain, M.A.; Mohamed, F. Development and Testing of Hybrid Fuzzy Logic Controller for Car Suspension System Using Magneto-Rheological Damper. In Proceedings of the Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 5–9 October 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Biglarbegian, M.; Melek, W.; Golnaraghi, F. Intelligent Control of Vehicle Semi-Active Suspension Systems for improved Ride Comfort and Road Handling. In Proceedings of the Fuzzy Information on the North American Annual Meeting, Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–6 June 2006; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, D.; Dong, Z.; Qin, Y. Active suspension hierarchical control with parameter uncertainty and external disturbance of electro-hydraulic actuators. Appl. Math. Model. 2024, 134, 50–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Huang, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, X. Adaptive finite-time fuzzy prescribed performance fault-tolerant control for uncertain active suspensions with actuator nonlinear characteristics. J. Sound Vib. 2025, 618, 119232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, R.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Li, M. Vibration control of vehicle ISD suspension based on the fractional-order SH-GH stragety. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 234, 112880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Deng, J.; Duan, D.; Zhou, T.; Liu, S. Constrained H∞ optimal control for nonlinear active suspensions via data-driven reinforcement learning algorithm. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 2025, 20, 071007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botzheim, J.; Toda, Y.; Kubota, N. Bacterial memetic algorithm for offline path planning. Memetic Comp. 2012, 4, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Fang, Y.; Botzheim, J.; Kubota, N.; Liu, H. Bacterial memetic algorithm based feature selection for surface EMG based hand motion recognition in long-term use. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Athens, Greece, 6–9 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Horváth, C.M.; Botzheim, J.; Thomessen, T.; Korondi, P. Bacterial memetic algorithm trained fuzzy system-based model of single weld bead geometry. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 164864–164881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, S.; Budai, C.; Botzheim, J. Colonial bacterial memetic algorithm and its application on a darts playing robot. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holló-Szabó, Á.; Botzheim, J. Bacterial memetic algorithm for asymmetric capacitated vehicle-routing problem. Electronics 2022, 11, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botzheim, J.; Cabrita, C.; Kóczy, L.T.; Ruano, A.E. Fuzzy rule extraction by bacterial memetic algorithms. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2009, 24, 312–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gál, L.; Kóczy, L.T.; Lovassy, R. Function Approximation Performance of Fuzzy Neural Networks Based on Frequently Used Fuzzy Operations and a Pair of New Trigonometric Norms. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 18–23 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gál, L.; Kóczy, L.T.; Lovassy, R. Three Step Bacterial Memetic Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Intelligent Engineering Systems, Las Palmas of Gran Canaria, Spain, 5–7 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.S.; Jaber, G.A.; Ghazaly, N.M. H∞ Control of Active Suspension System for a Quarter Car Model. Int. J. Veh. Struct. Syst. 2016, 8, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liang, G. Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization Genetic LQR Controller for Active Suspension. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Sande, T.P.J.; Gysen, B.L.J.; Besselink, I.J.M.; Paulides, J.J.H.; Lomonova, E.A.; Nijmeijer, H. Robust control of an electromagnetic active suspension system: Simulations and Measurements. Mechatronics 2013, 23, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenberg, K. A method for the solution of certain non-linear problems. Q. Appl. Math. 1994, 2, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, D.W. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 1963, 11, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrita, C.; Botzheim, J.; Gedeon, T.D.; Ruano, A.E.; Koczy, L.T.; Fonseca, C. Bacterial Memetic Algorithm for Fuzzy Rule Base Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2006 World Automation Congress, Budapest, Hungary, 24–26 July 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Udvardy, K.; Görbe, P.; Bódis, T.; Botzheim, J. Conceptual Framework for Adaptive Bacterial Memetic Algorithm Parameterization in Storage Location Assignment Problem. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscato, P. On evolution, search, optimization, genetic algorithms and martial arts: Towards memetic algorithms. Caltech Concurr. Comput. Program C3P Rep. 1989, 826, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Blickle, T.; Thiele, L. A comparison of selection schemes used in evolutionary algorithms. Evol. Comput. 1996, 4, 361–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, T.V. Genetic Algorithm; IIT Bombay: Mumbai, India, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Arabali, A.; Ghofrani, M.; Etezadi-Amoli, M.; Fadali, M.S.; Baghzouz, Y. Genetic-algorithm-based optimization approach for energy management. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2012, 28, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, C.; Montazeri, A.; Monk, S.D.; Taylor, C.J. A genetic algorithm approach for parameter optimization of a 7DOF robotic manipulator. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 1261–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sime, T.L.; Aluvada, P.; Habtamu, S.; Tolosa, Z. Modeling of genetic algorithm tuned adaptive fuzzy fractional order PID speed control of permanent magnet synchronous motor for electric vehicle. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2024, 6, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S. A genetic algorithm by use of virus evolutionary theory for scheduling problem. In Proceedings of the Korea Society for Simulation Conference, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 24–26 October 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kubota, N.; Fukuda, T.; Shimojima, K. Trajectory planning of cellular manipulator system using virus-evolutionary genetic algorithm. Robot. Auton. Syst. 1996, 19, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).