A Double Inertial Mann-Type Method for Two Nonexpansive Mappings with Application to Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
- Then, the following conditions are satisfied:
- (i)
- There exists such that
- (ii)
- (i)
- Every weak sequential cluster point of belongs to .
- (ii)
- For every , the sequence converges.
- Then, weakly converges to a point in .
3. Main Results
Algorithm 1: Double Inertial Mann-Type Method. |
Initialization. Select , and . Step 1. Compute Step 2. Compute Step 3. Compute Replace k by and return to Step 1. |
Algorithm 2: Double Inertial Mann-Type Method for Split-Equilibrium Problem. |
Initialization. Select , and . Step 1. Compute Step 2. Compute Step 3. Compute Replace k by and return to Step 1. |
Algorithm 3: Double Inertial Mann-Type Method for Projective Split-Equilibrium Problem I. |
Initialization. Select, and. Step 1. Compute Step 2. Compute Step 3. Compute Replace k by and return to Step 1. |
Algorithm 4: Double Inertial Mann-Type Method for Projective Split-Equilibrium Problem II |
Initialization. Select , and . Step 1. Compute Step 2. Compute Step 3. Compute Replace k by and return to Step 1. |
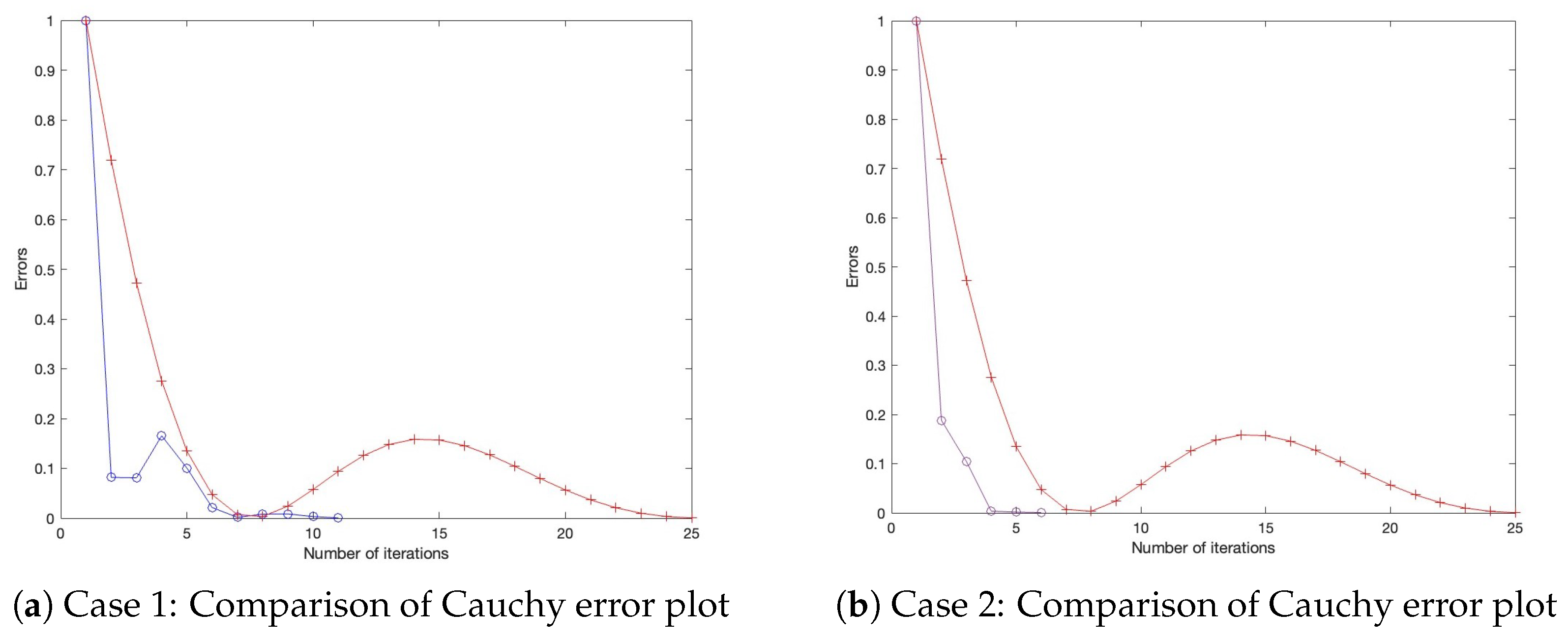
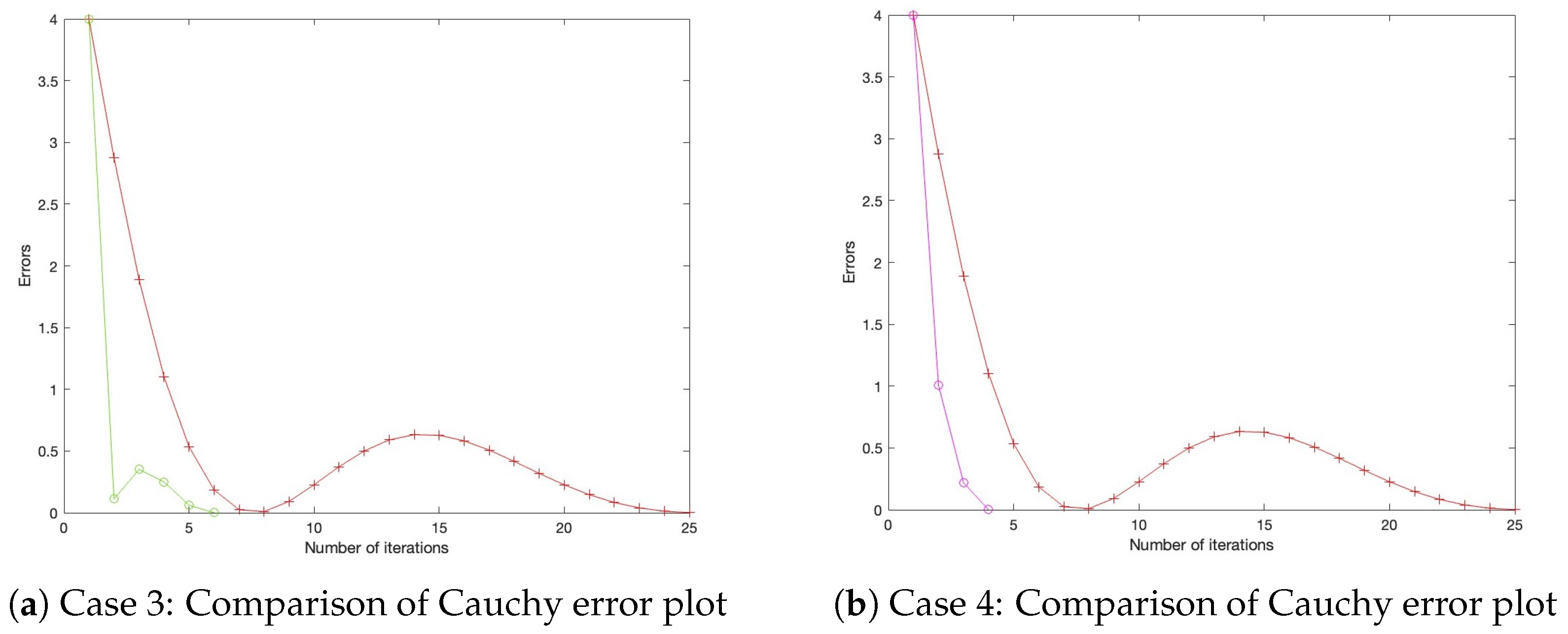
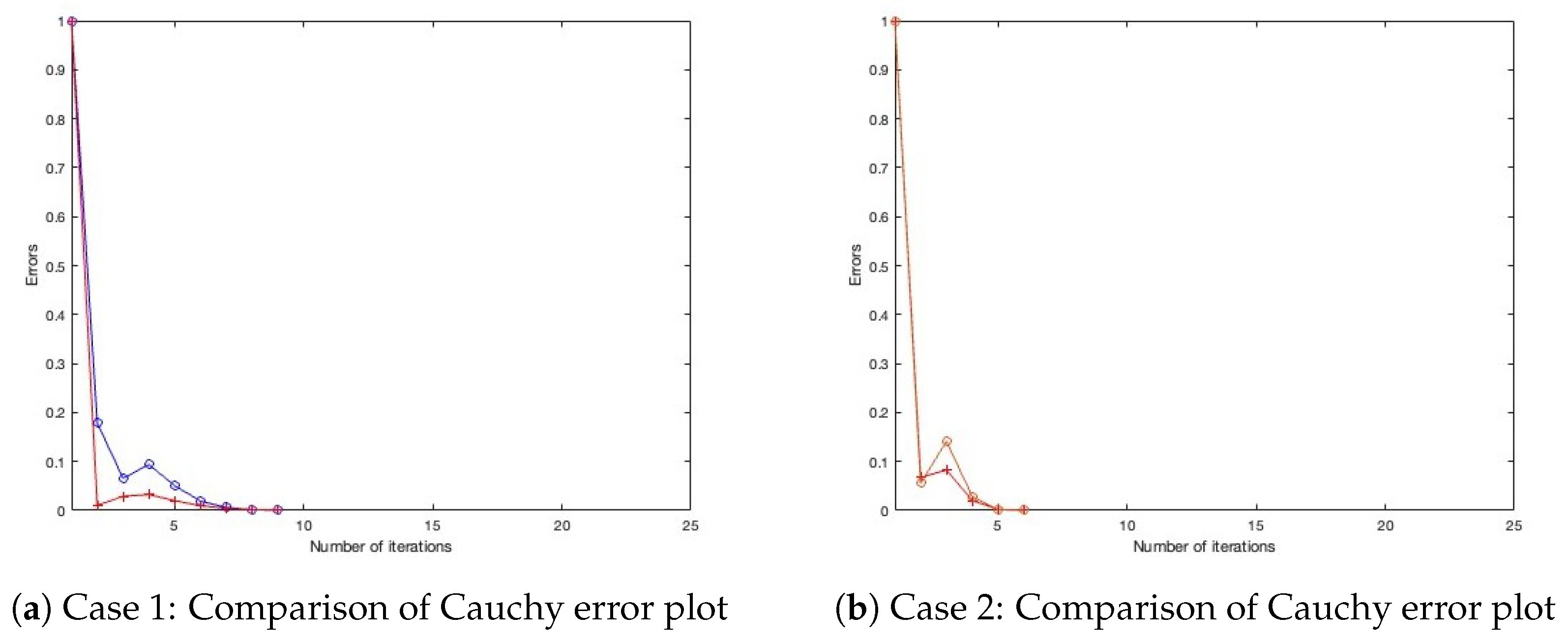
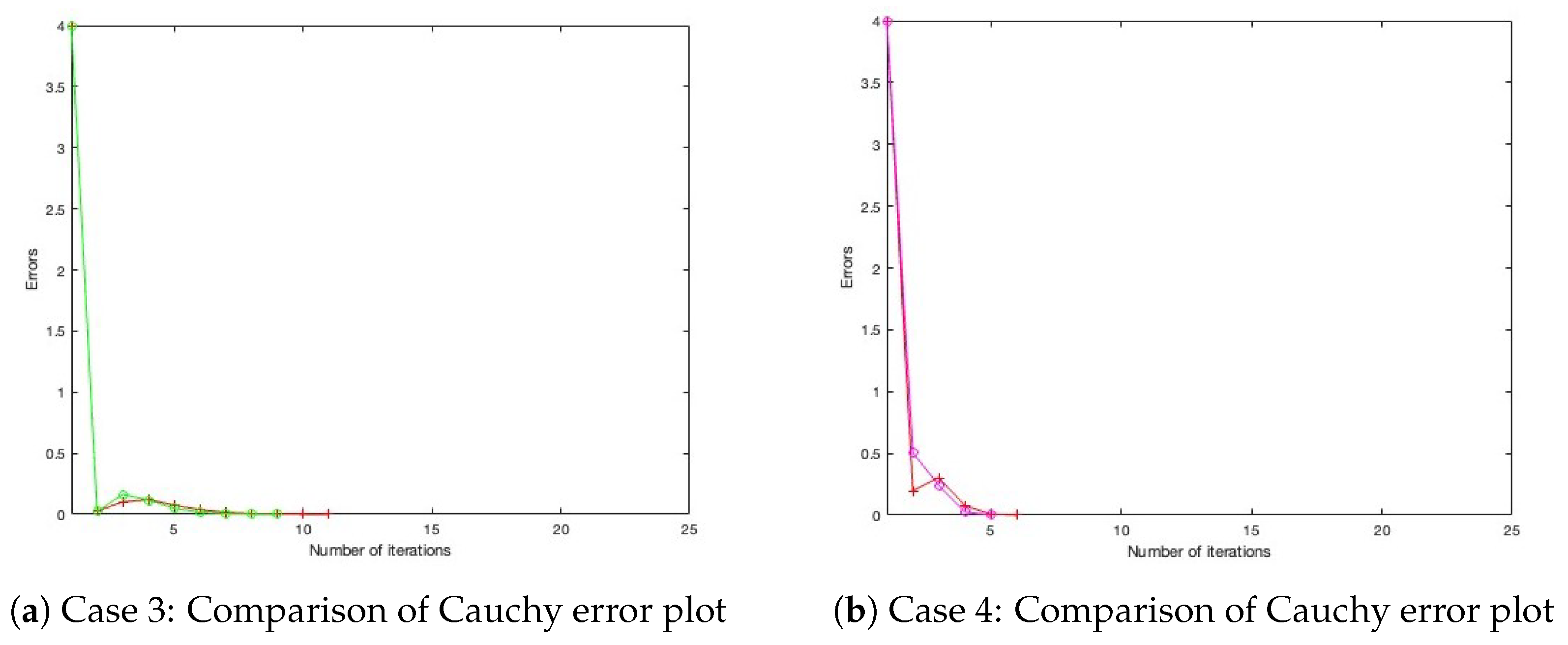
- Case 1: Define , with initial settings and .
- Case 2: Define , with initial settings and .
- Case 3: Define , with initial settings and .
- Case 4: Define , with initial settings and . All parameters for Algorithm 1, as well as those for the benchmark algorithm from the literature, are configured under three distinct settings, as presented in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3, with their corresponding Cauchy plot comparisons shown in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6.
4. Application to Data Classification Problem
- Least squares model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdou, A.A.N. Fixed Point Theorems: Exploring Applications in Fractional Differential Equations for Economic Growth. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiha, I.; Aoua, L.; Oussaeif, T.; Ouannas, A.; lshorman, S.; Jebril, I.; Momani, S. Common fixed point theorem in non-Archimedean Menger PM-spaces using CLR property with application to functional equations. IAENG Int. J. Appl. Math. 2023, 53, 360–368. [Google Scholar]
- Chouhan, S.; Desai, B. Fixed-Point Theory and Its Some Real-Life Applications. In Research Highlights in Mathematics and Computer Science; Book Publisher International: Versailles, France, 2022; Volume 1, pp. 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patriche, M. Bayesian abstract fuzzy economies, random quasi-variational inequalities with random fuzzy mappings and random fixed point theorems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2014, 245, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarf, H. Fixed-point theorems and economic analysis. Am. Sci. 1983, 71, 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, W.R. Mean value methods in iteration. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 1953, 4, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, S. Weak convergence theorems for nonexpansive mappings in Banach spaces. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 1979, 67, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyak, B.T. Some methods of speeding up the convergence of iteration methods. USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 1964, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maingé, P.E. Convergence theorems for inertial KM-type algorithms. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2008, 219, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyiola, O.S.; Shehu, Y. Convergence results of two-step inertial proximal point algorithm. Appl. Numer. Math. 2022, 182, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Iyiola, O.S.; Shehu, Y. Subgradient extragradient method with double inertial steps for variational inequalities. J. Sci. Comput. 2022, 90, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajai, W.; Kankam, K.; Yao, J.C.; Cholamjiak, W. A double inertial embedded modified S-iteration algorithm for nonexpansive mappings: A classification approach for lung cancer detection. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2025, 150, 108978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudafi, A. Split monotone variational inclusions. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2011, 150, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witthayarat, U.; Abdou, A.; Cho, Y. Shrinking projection methods for solving split equilibrium problems and fixed point problems for asymptotically nonexpansive mappings in Hilbert spaces. Fixed Point Theory Appl. 2015, 2015, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrie, A.; Wangkeeree, R. Hybrid projected subgradient-proximal algorithms for solving split equilibrium problems and split common fixed point problems of nonexpansive mappings in Hilbert spaces. Fixed Point Theory Appl. 2018, 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suantai, S.; Cholamjiak, P.; Cho, Y.J.; Cholamjiak, W. On solving split equilibrium problems and fixed point problems of nonspreading multi-valued mappings in Hilbert spaces. Fixed Point Theory Appl. 2016, 2016, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. On solving split equilibrium problems and fixed point problems of α-nonexpansive multi-valued mappings in Hilbert spaces. Fixed Point Theory 2023, 24, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Bnouhachem, A. Strong convergence algorithm for split equilibrium problems and hierarchical fixed point problems. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 390956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangtunyakarn, A. Hybrid algorithm for finding common elements of the set of generalized equilibrium problems and the set of fixed point problems of strictly pseudo-contractive mapping. Fixed Point Theory Appl. 2011, 2011, 274820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, K.R.; Rizvi, S.H. Iterative approximation of a common solution of a split equilibrium problem, a variational inequality problem and a fixed point problem. J. Egypt. Math. Soc. 2013, 21, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alansari, M.; Kazmi, K.R.; Ali, R. Hybrid iterative scheme for solving split equilibrium and hierarchical fixed point problems. Optim. Lett. 2020, 14, 2379–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harisa, S.A.; Khan, M.A.A.; Mumtaz, F. Shrinking Cesàro means method for the split equilibrium and fixed point problems in Hilbert spaces. Adv. Difference Equ. 2020, 2020, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inthakon, W.; Niyamosot, N. The split equilibrium problem and common fixed points of two relatively quasi-nonexpansive mappings in Banach spaces. J. Nonlinear Convex Anal. 2019, 20, 685–702. [Google Scholar]
- Jolaoso, L.O.; Karahan, I. A general alternative regularization method with line search technique for solving split equilibrium and fixed point problems in Hilbert spaces. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2020, 391, 105150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrot, N.; Rabbani, M.; Khonchaliew, M.; Dadashi, V. A new extragradient algorithm for split equilibrium problems and fixed point problems. J. Inequal. Appl. 2019, 2019, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajai, W.; Nabheerong, P.; Cholamjiak, W. A double inertial Mann algorithm for split equilibrium problems application to breast cancer screening. J. Nonlinear Convex Anal. 2024, 25, 1697–1716. [Google Scholar]
- Blum, E.; Oettli, W. From optimization and variational inequalities to equilibrium problems. Math. Stud. 1994, 63, 123–145. [Google Scholar]
- Combettes, P.L.; Hirstoaga, S.A. Equilibrium programming in Hilbert spaces. J. Nonlinear Convex Anal. 2005, 6, 117–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ofoedu, E.U. Strong convergence theorem for uniformly L-Lipschitzian asymptotically pseudocontractive mapping in real Banach space. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2006, 321, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, K.; Kirk, W.A. Topics in Metric Fixed Point Theory; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Opial, Z. Weak convergence of the sequence of successive approximations for nonexpansive mappings. Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 1967, 73, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combettes, P.L. The convex feasibility problem in image recovery. Adv. Imaging Electron Phys. 1996, 95, 155–270. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, C.; Censor, Y.; Gibali, A.; Reich, S. The split common null point problem. J. Nonlinear Convex Anal. 2012, 13, 759–775. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.B.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Siew, C.K. Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing 2006, 70, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censor, Y.; Elfving, T. A multiprojection algorithm using Bregman projections in a product space. Numer. Algorithms 1994, 8, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.; Pradhan, N.; Dhaka, V.S. Comparative analysis to predict breast cancer using machine learning algorithms: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), Pune, India, 26–28 February 2020; pp. 192–196. [Google Scholar]





| Algorithm 1 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.01 |
| Algorithm of Mainge [9] | 0.9 | - | 0.9 | - |
| Algorithm 1 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.05 |
| Algorithm of Mainge [9] | 0.6 | - | 0.6 | - |
| Algorithm 1 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.005 |
| Algorithm of Mainge [9] | 0.3 | - | 0.3 | - |
| Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Median | Mode | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTI Type | 0 | 2 | 1.3886 | 2 | 2 | 0.7712 |
| Urinalysis Nitrite | 0 | 1 | 0.1536 | 0 | 0 | 0.3611 |
| Urinalysis Leukocyte Esterase | 0 | 6 | 2.5663 | 3 | 3 | 1.0820 |
| Age | 1 | 98 | 55.8223 | 66 | 21 | 25.9832 |
| Weight | 8.5 | 90 | 51.9077 | 53 | 45 | 13.2993 |
| BMI | 13.2810 | 33.2700 | 21.7309 | 21.8750 | 15.6210 | 4.1219 |
| Serum Vit D level | 4.9600 | 62.4000 | 24.8455 | 23.6000 | 20.5000 | 8.4848 |
| CBC hct | 21 | 51 | 36.7169 | 37 | 36 | 5.1781 |
| Height | 69 | 185 | 153.7289 | 155 | 150 | 13.1780 |
| Wbc | 1 | 5 | 3.5904 | 4 | 3 | 1.0433 |
| eGFR | 0 | 281 | 139.4970 | 140.5000 | 66 | 82.2671 |
| DM | 0 | 1 | 0.3494 | 0 | 0 | 0.4775 |
| L | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithm 2—case 1 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.01 | 0.9 | |
| Algorithm 2—case 2 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.005 | 0.9 | |
| Algorithm 2—case 3 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.005 | 0.9 | |
| Algorithm of Suantai [16] | 0.9 | - | - | - | |
| Algorithm of Yajai [12] | 0.9 | 0.5 |
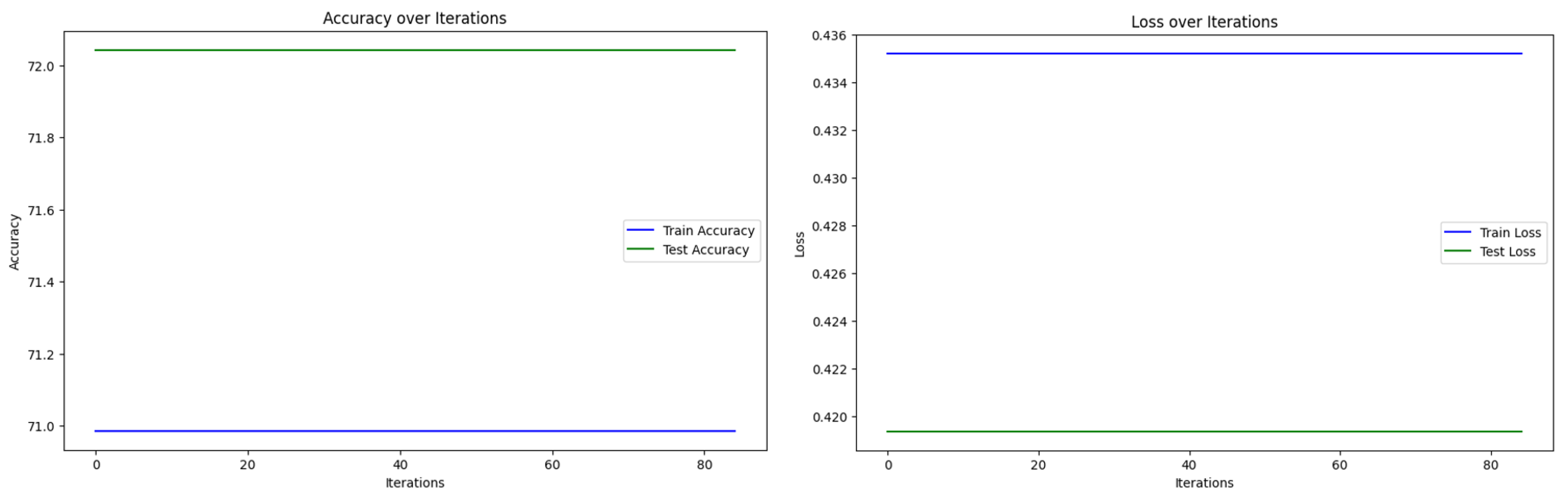
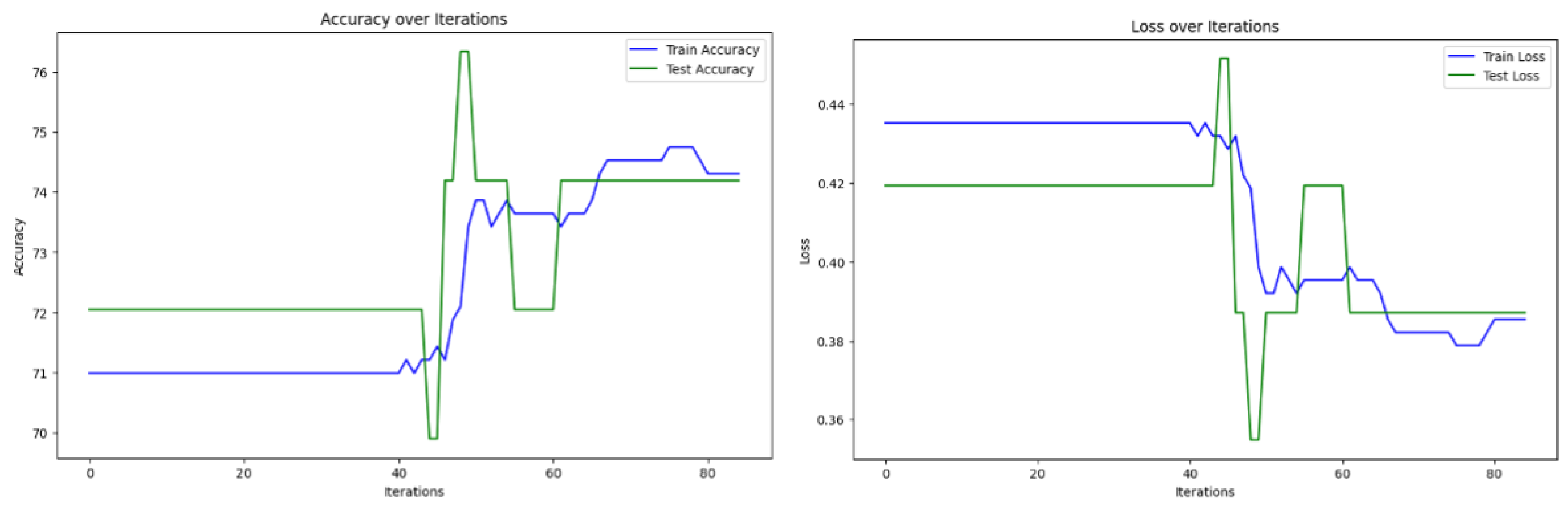
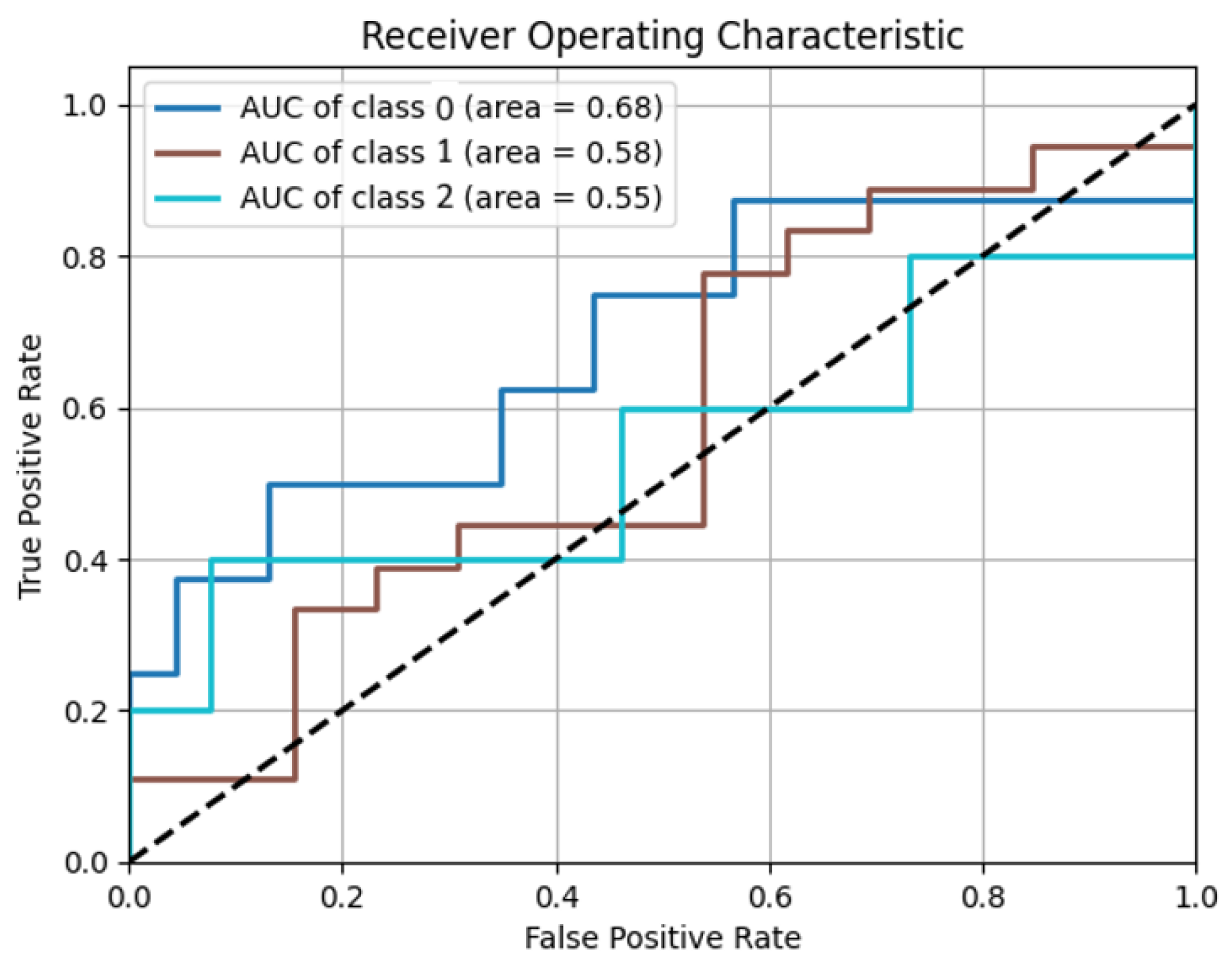
| Iterations | Computation Time (s) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | Accuracy (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithm 2—case 1 | 85 | 13.4534 | 81.6667 | 77.7035 | 78.3688 | 78.4946 |
| Algorithm 2—case 2 | 85 | 19.2733 | 79.6052 | 77.5362 | 78.1291 | 76.3441 |
| Algorithm 2—case 3 | 85 | 20.4867 | 81.6667 | 77.7035 | 78.3688 | 78.4946 |
| Algorithm of Suantai [16] | 85 | 11.2421 | 52.6882 | 66.6667 | 58.8044 | 72.0430 |
| Algorithm of Yajai [12] | 85 | 46.9684 | 76.3266 | 73.6901 | 73.8186 | 74.1935 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naravejsakul, K.; Sukson, P.; Waratamrongpatai, W.; Udomluck, P.; Khwanmuang, M.; Cholamjiak, W.; Yajai, W. A Double Inertial Mann-Type Method for Two Nonexpansive Mappings with Application to Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosis. Mathematics 2025, 13, 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13152352
Naravejsakul K, Sukson P, Waratamrongpatai W, Udomluck P, Khwanmuang M, Cholamjiak W, Yajai W. A Double Inertial Mann-Type Method for Two Nonexpansive Mappings with Application to Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosis. Mathematics. 2025; 13(15):2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13152352
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaravejsakul, Krittin, Pasa Sukson, Waragunt Waratamrongpatai, Phatcharapon Udomluck, Mallika Khwanmuang, Watcharaporn Cholamjiak, and Watcharapon Yajai. 2025. "A Double Inertial Mann-Type Method for Two Nonexpansive Mappings with Application to Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosis" Mathematics 13, no. 15: 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13152352
APA StyleNaravejsakul, K., Sukson, P., Waratamrongpatai, W., Udomluck, P., Khwanmuang, M., Cholamjiak, W., & Yajai, W. (2025). A Double Inertial Mann-Type Method for Two Nonexpansive Mappings with Application to Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosis. Mathematics, 13(15), 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13152352





