Abstract
Infrared and visible image fusion plays a critical role in multimodal perception systems, particularly under challenging conditions such as low illumination, occlusion, or complex backgrounds. However, existing approaches often struggle with global feature modelling, cross-modal dependency learning, and preserving structural details in the fused images. In this paper, we propose a novel adversarial fusion framework driven by a state-space modelling paradigm to address these limitations. In the feature extraction phase, a computationally efficient state-space model is utilized to capture global semantic context from both infrared and visible inputs. A cross-modality state-space architecture is then introduced in the fusion phase to model long-range dependencies between heterogeneous features effectively. Finally, a multi-class discriminator, trained under an adversarial learning scheme, enhances the structural fidelity and detail consistency of the fused output. Extensive experiments conducted on publicly available infrared–visible fusion datasets demonstrate that the proposed method achieves superior performance in terms of information retention, contrast enhancement, and visual realism. The results confirm the robustness and generalizability of our framework for complex scene understanding and downstream tasks such as object detection under adverse conditions.
MSC:
68T07; 54H30; 68T01
1. Introduction
Single-modality sensors often exhibit inherent limitations in capturing complete and comprehensive scene information. In recent years, the challenge of acquiring and effectively integrating data from multiple modalities has attracted significant research interest [1,2]. Among various multimodal data fusion tasks, infrared and visible image fusion has emerged as a critical and active research area [3,4]. Infrared images can capture the thermal radiation emitted by objects, offering unique advantages in target detection and tracking tasks under low-illumination or nighttime conditions [5,6]. However, infrared images typically suffer from low contrast and blurry details [7,8]. In contrast, visible images provide rich color and texture information, delivering superior visual quality under well-lit or daytime environments [9,10]. Nevertheless, their performance may degrade significantly in the presence of severe illumination variations or occlusions [11,12]. Infrared and visible image fusion aims to integrate the complementary information of both modalities to achieve more comprehensive and accurate scene perception than either modality alone. This fusion strategy has shown great potential in various applications, including scene surveillance, military reconnaissance, and target tracking [13,14].
Existing infrared and visible image fusion methods can be broadly categorized into traditional statistical model-based approaches and deep learning-based approaches [15,16]. Statistical methods typically employ multi-scale decomposition strategies to separate the source images into multiple layers containing different structural information, followed by layer-wise fusion and reconstruction based on predefined rules [17,18]. However, these methods are limited in terms of feature representation capability and cross-scene adaptability [19,20]. In recent years, deep neural network-based fusion approaches have gained increasing attention due to their superior modeling capacity. These methods can be roughly divided into three categories: convolutional neural network (CNN)-based methods [21,22], autoencoder-based methods [23,24], and generative adversarial network (GAN)-based methods [25,26]. CNN-based fusion approaches often rely heavily on the design of loss functions, which may restrict their generalization capability across diverse tasks. Autoencoder-based methods are constrained by the representational capacity of the training data and often struggle to selectively integrate the complementary advantages of infrared and visible images. In contrast, adversarial learning-based fusion methods establish a game-theoretic framework that enables adaptive optimization of the fused image quality, and thus have garnered significant attention in recent studies.
Deep learning-based fusion models typically consist of three stages: feature extraction, feature fusion, and image reconstruction. The feature extraction module is responsible for capturing high-level representations from both infrared and visible images, while the fusion module integrates the multimodal features effectively. The reconstruction module then generates the final fused image. Common feature extraction strategies include convolutional-based and Transformer-based architectures. Convolutional structures offer high computational efficiency but are limited in their ability to model long-range dependencies. In contrast, Transformer architectures provide strong global modeling capabilities, yet they often incur substantial computational overhead.
To address the aforementioned challenges, this paper proposes a novel generative adversarial network based on a state-space model for infrared and visible image fusion. First, to overcome the limitations of CNNs in feature representation and the high computational cost of Transformer architectures, we design a state-space-based feature extraction module. This module enables global feature perception with linear computational complexity, thereby improving the fusion performance without significantly increasing the computational burden. Second, we extend the computational formulation of the state-space model and develop a cross state-space-based feature fusion module, which achieves efficient integration of multimodal features. Finally, to adaptively optimize the quality of the fused images, we introduce a multi-class discriminator structure that iteratively refines the network parameters through adversarial training, leading to enhanced visual fidelity of the fusion results. Specifically, the main contributions of this work are as follows:
- (1)
- A state-space-based feature extraction module is proposed, which enables global feature perception of infrared and visible images while maintaining low computational complexity. This design effectively mitigates the limitations of traditional CNNs in feature representation and the high computational cost associated with Transformer-based architectures.
- (2)
- A cross state-space-based multimodal feature fusion module is constructed, which introduces a state-space modeling mechanism to capture long-range dependencies between different modalities. This design enables efficient and complementary integration of infrared and visible information, thereby enhancing the structural consistency and detail preservation of the fused images.
- (3)
- A multi-class discriminator-based adversarial learning mechanism is designed to guide the fusion network toward more refined visual optimization during the multimodal image generation process. By constructing a more discriminative multi-class discriminator, the proposed approach significantly improves both the subjective visual quality and objective evaluation metrics of the fused images.
2. Related Work
In this subsection, we provide a review of existing image fusion methods, including traditional approaches and deep learning-based techniques.
2.1. Image Fusion Based on Traditional Methods
The fundamental idea of traditional image fusion methods typically involves three stages: feature extraction, fusion, and reconstruction. These methods include multi-scale decomposition-based approaches [27], sparse representation-based approaches [28], and saliency-based approaches [29]. In the following, we provide a detailed description of the key characteristics of these methods. Multi-scale decomposition techniques are commonly implemented in the transform domain, such as fusion algorithms based on discrete wavelet transform (DWT) [30], shearlet transform [31], curvelet transform [32], and nonsubsampled contourlet transform (NSCT) [33]. In addition, certain decomposition algorithms in the spatial domain can also be categorized as multi-scale methods, including those based on guided filtering [34] and bilateral filtering [35]. A typical example of transform-domain fusion is the use of discrete wavelet transform (DWT) to fuse infrared and visible images. DWT performs signal decomposition through scale (dilation) and shift (translation) operations, enabling it to represent both temporal (spatial) and frequency information. In two-dimensional image processing, the discrete wavelet transform is typically implemented using a row-column separable scheme. A one-dimensional wavelet transform is first applied along the image rows and then along the columns, yielding four sub-bands: LL (low–low), LH (low–high), HL (high–low), and HH (high–high) [36]. The LL sub-band captures the coarse structure and dominant contours of the image, while the other three sub-bands preserve horizontal, vertical, and diagonal details, respectively [37]. This decomposition can be applied recursively to the LL sub-band to obtain finer-grained multiscale representations. During the fusion stage, sub-bands from the source images are typically combined using rules such as weighted averaging, max-selection, or energy-based strategies, followed by inverse DWT to reconstruct the fused image [38].
In the spatial domain, filtering-based methods such as guided filtering and bilateral filtering have been widely used to decompose the input images into base and detail layers. The base layers primarily represent global illumination and background structure, while the detail layers preserve local textures and edges. Fusion is performed separately on each layer: base layers are commonly combined via weighted averaging to maintain global consistency, whereas detail layers are fused using max-selection strategies to enhance salient features such as thermal targets and edge contrast [39]. Sparse representation-based methods encode image patches as sparse coefficient vectors using learned overcomplete dictionaries. The fusion process is carried out in the sparse domain, where coefficients are combined based on activity-level measures such as the norm or local energy. The fused sparse representation is then reconstructed to obtain the final image. This approach has shown strong performance in retaining structural details and edges, though its effectiveness is highly dependent on the quality and adaptability of the learned dictionaries [40]. Recently, saliency-guided fusion has emerged as a promising extension of traditional methods. Unlike earlier approaches that relied solely on saliency for image decomposition, these techniques employ saliency maps to dynamically modulate fusion weights. Typically, source images are first decomposed using a multiscale transform, and saliency maps are generated for each layer. These maps are then normalized and used to construct weight maps that guide the fusion of corresponding layers across modalities [41].
Despite their contributions, traditional fusion techniques face several fundamental limitations. First, they are heavily reliant on manually crafted fusion rules, which lack adaptability to diverse and dynamic scenes. Second, traditional methods often struggle to capture high-level semantic relationships between structures in the source images, making it difficult to preserve fine-grained detail or context-aware correspondence. These shortcomings have led to a growing interest in deep learning-based fusion methods, which enable end-to-end optimization and cross-modal representation learning to address these challenges more effectively [42].
2.2. Deep Learning-Based Methods
In the early stages of infrared and visible image fusion research, the lack of large-scale, paired infrared–visible datasets posed a significant challenge for training deep neural networks. As a result, researchers commonly relied on large-scale generic image datasets to pretrain neural networks, which were then transferred to the image fusion task. Within this basic framework, various extensions have been proposed. For instance, DenseFuse [24] employed DenseNet [43] to construct an autoencoder architecture. The feature extraction and reconstruction capabilities of the encoder were trained on the COCO [44] dataset, and a norm-based fusion strategy was subsequently applied to combine the features and reconstruct the fused image. Although this approach features a relatively simple structure, it still relies on manually designed fusion rules, which limits its adaptability. NestFuse [23] introduced a dual-encoder architecture, where two identical encoders were used to extract features separately from infrared and visible images. These features were then fused using an attention-based strategy, and a decoder was used to reconstruct the final fused image. This method achieved promising results. However, autoencoder-based fusion methods generally rely on pretrained encoders and decoders, which are not specifically optimized for infrared feature extraction or fused image reconstruction due to the absence of large-scale infrared or fused image datasets. This mismatch undoubtedly restricts the performance and further development of autoencoder-based methods in this field.
As research in this area continued to mature, researchers began to employ neural networks to learn the entire image fusion process end-to-end, minimizing manual intervention or subjective rule design. These approaches are commonly classified as CNN-based methods. RFN-Nest [45] proposed a multi-level feature extractor to simultaneously extract features from both visible and infrared images. A lightweight fusion network was then constructed to integrate multimodal features across multiple scales. Finally, a reconstruction network was used to generate the fused image from the aggregated multi-scale features. This fully data-driven pipeline—comprising feature extraction, fusion, and reconstruction—demonstrated superior performance compared to traditional rule-based strategies. Similarly, PIAFusion [22] utilized a dual-branch CNN backbone to extract features from infrared and visible images, respectively. A progressive fusion module, inspired by differential amplifier circuits, was designed to enable effective interaction between modalities during the feature extraction process. The final fused image was generated using a single-stream reconstruction network trained with a combination of gradient loss and pixel-wise loss, yielding high-quality fusion results.
Structural improvements to network architectures have yielded only limited gains in fusion quality. To further enhance CNN-based fusion methods, some researchers have introduced high-level vision tasks to guide and optimize the fusion process. SeAFusion [46] incorporates an additional image segmentation network into the fusion framework. The segmentation network performs instance segmentation on the fused image generated by the fusion network, and the accuracy of the segmentation output is used as a constraint to ensure that the fused image contains richer semantic information. Similarly, STDFusion [47] adopts a related strategy by manually annotating salient regions in infrared images and enforcing a loss constraint that encourages the salient regions in the fused image to closely resemble those in the infrared input. This approach leads to improved retention of critical thermal information in the fusion results. In addition to segmentation and saliency detection, other studies have explored the integration of object detection tasks to promote better fusion. DetFusion [48] utilizes two detection heads to simultaneously supervise the visible and infrared backbones. The network is guided by object detection labels to perform adaptive feature fusion, achieving strong performance in both image fusion and object detection tasks.
Some researchers have also considered the impact of illumination conditions on the quality of fused images. During the fusion process, it is common for brightness degradation to occur, resulting in fused images that exhibit lower overall brightness than either of the input images. This degradation negatively affects the visual quality and interpretability of the fused output. To address this issue, MLFFusion [49] introduces a regional illumination-aware loss, which constrains the brightness levels in different regions of the fused image to mitigate the effects of brightness degradation during fusion. However, in extremely low-light environments, the input images themselves may lack sufficient illumination information. In such cases, even though brightness degradation may be avoided during fusion, the resulting images still fail to exhibit satisfactory visual clarity or scene illumination. To solve this problem, DIVFusion [50] proposes a multi-task collaborative fusion network that couples image fusion with brightness enhancement within a unified framework, enabling effective fusion in extremely dark conditions. This approach, however, introduces a new challenge: overexposure may occur in well-lit scenes, as the enhancement module unnecessarily boosts brightness. To improve adaptability across different illumination conditions, IAIFNet [51] designs a dynamic weighting mechanism that adjusts the balance between tasks based on the input scene. Specifically, the network emphasizes the fusion task under normal lighting conditions, while activating the joint brightness enhancement and fusion pipeline only when dark scenes are detected. This strategy effectively suppresses overexposure in non-dark environments and improves the overall robustness of the fusion model.
Unlike end-to-end training strategies, some researchers have developed adversarial iterative approaches for training image fusion models. In the generative adversarial network (GAN) framework, a generator is employed to produce high-quality fused images, while a discriminator is tasked with distinguishing whether the generated fused image is “fake”. The generator and discriminator are trained alternately in an adversarial manner until the discriminator can no longer distinguish the generated images from real ones, signaling convergence. Under this general framework, FusionGAN [25] designs a discriminator that estimates the likelihood of the fused image belonging to either the visible or infrared domain, with training progressing until both probabilities converge toward zero. GAN-FM [26] employs a full-resolution generator with skip connections and two independent Markovian discriminators, each dedicated to assessing the fusion quality of one input modality. GANMcC [52] simultaneously estimates the distributions of both the visible and infrared domains. Through multi-class adversarial training, the fused results are encouraged to maintain a balanced representation of both modalities. TarDAL [53] proposes a lightweight, object-aware dual-adversarial learning network, which uses a two-stage optimization scheme for detection-oriented fusion. AT-GAN [54] introduces a single discriminator with dual outputs to evaluate the fused image from different aspects. All of these methods have achieved promising performance across various benchmarks.
3. Methodology
In this section, we first provide an overview of the overall architecture of the proposed model. Then, we introduce the state-space-based feature extraction unit and fusion module in detail. Finally, we describe the loss functions used to optimize the model.
3.1. Overall Network Architecture
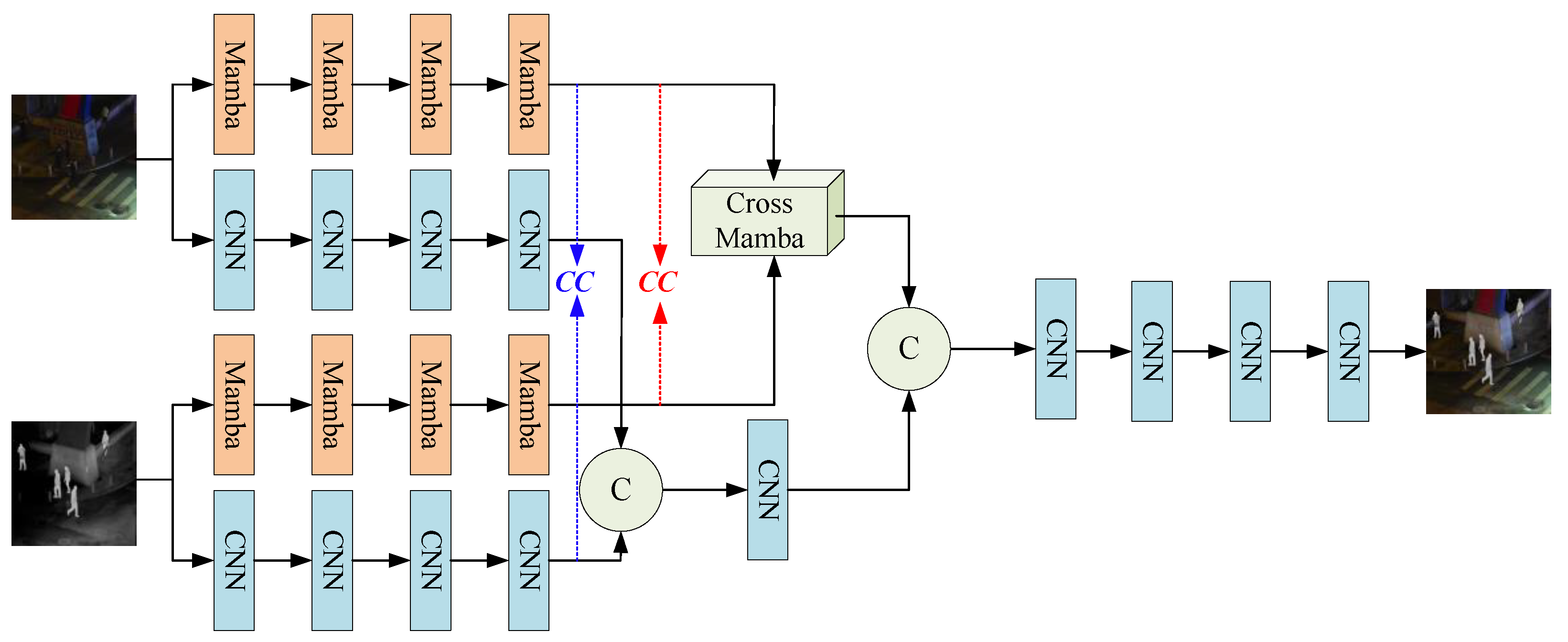
The proposed fusion network in this section consists of a generator and a discriminator. The generator is responsible for producing high-quality fused images, while the discriminator supervises the quality of the generated results. Through adversarial training, the classification accuracy of the discriminator and the generation quality of the generator are iteratively improved. Figure 1 illustrates the overall architecture of the generator. The generator is composed of two parallel branches: (1) a state-space model-based branch (Mamba), which is designed to extract global structural features from the input images; (2) a convolutional neural network (CNN)-based branch, which focuses on extracting local detail features. Since the infrared and visible images originate from the same scene but belong to different modalities, their structural information is largely similar. Therefore, the Mamba branch is used to extract common features shared across modalities. In contrast, modality-specific detail variations are captured by the CNN branch, which is responsible for learning differential features. Simple fusion strategies such as concatenation or element-wise addition are often insufficient for common features due to structural redundancy, potentially leading to information overload. To address this, we design a Cross-Mamba feature fusion module to effectively integrate the common features with reduced redundancy. On the other hand, differential features exhibit substantial modality-specific differences. Excessive processing of these features may lead to information loss and degrade the final fusion quality. Hence, we apply a minimal fusion strategy by directly concatenating the differential features along the channel dimension, followed by a CNN layer to reorganize the fused feature channels. Finally, the fused common and differential features are concatenated to form the final feature representation, which is passed through a CNN-based reconstruction module to generate the final fused image.
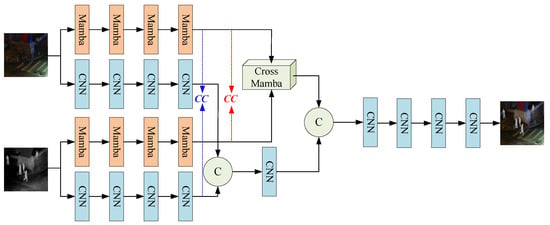
Figure 1.
Overall architecture of the generator.
To ensure that the generator can flexibly handle input images with varying resolutions, the spatial dimensions of the feature maps are preserved throughout both the feature extraction and image reconstruction stages, while the number of feature channels increases progressively. During feature extraction, the number of output channels in each layer is set to 16, 32, 64, and 128, respectively. In the image reconstruction stage, the number of output channels is reversed, set to 128, 64, 32, and 1, respectively.
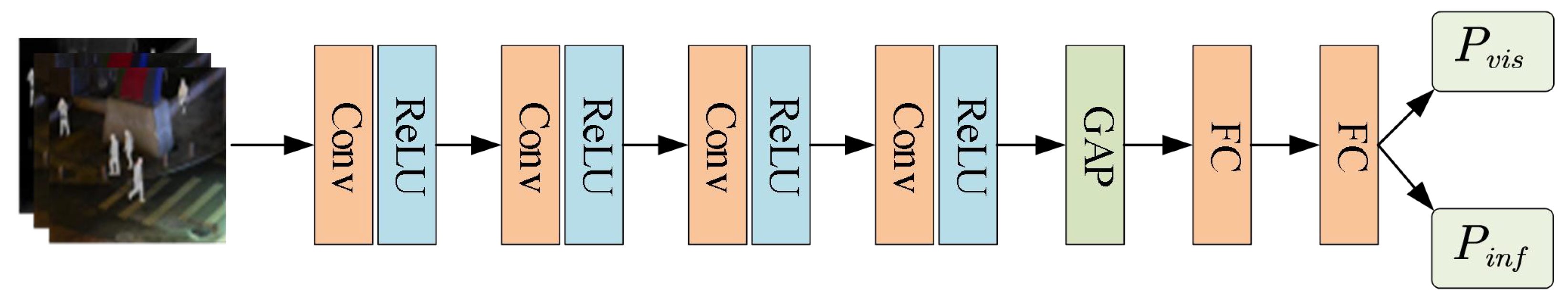
Figure 2 illustrates the overall architecture of the proposed discriminator. The discriminator takes an image as input and outputs the probabilities that the image belongs to the visible domain () and the infrared domain (). The input image is first processed by four consecutive convolutional and pooling layers for preliminary feature extraction. Then, a global average pooling (GAP) operation is applied to compress the feature maps into a feature vector. Finally, the feature vector is passed through two fully connected (FC) layers to compute the final classification probabilities.
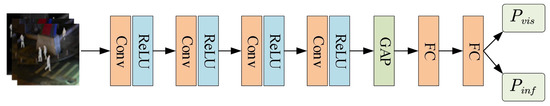
Figure 2.
Overall architecture of the discriminator.
In the feature extraction part of the discriminator, the number of output channels for each convolutional layer is set to 16, 32, 64, and 128, respectively. After the global average pooling (GAP) layer, the extracted features are compressed into a 128-dimensional vector. This vector is then passed through two consecutive fully connected (FC) layers, which reduce its dimensionality to 64 and finally to 2, yielding the final classification results.
3.2. Feature Extraction Unit Based on State-Space Model (Mamba)
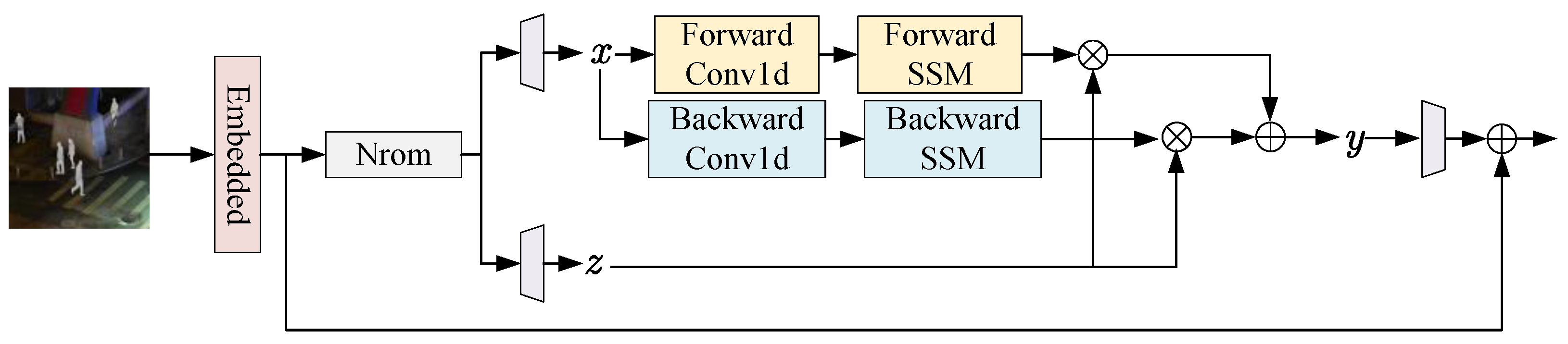
Figure 3 presents the overall structure of the feature extraction unit based on the state-space model used in this paper. First, the input features are serialized, and the serialized features are denoted as F. Then, the serialized features are fed into a layer normalization layer to eliminate the scale differences between different feature layers:
where represents layer normalization, and represents the feature after layer normalization. After that, the features are fed into two different linear layers to obtain the features x and z for state-space calculation:
where represents the linear layer for linear transformation. Immediately after, x is fed into the state-space model for calculation. Considering that the state-space model is quite sensitive to the order of the input vectors, in this paper, the linear features are fed into the state-space model from two different perspectives, forward and backward, to ensure that the features can be fully modeled. The processing procedure can be formulated as:
where represents the state-space model for forward-modeling the input linear features, and represents the state-space model for backward-modeling the input features. represents the output result of forward-modeling, and represents the output result of backward-modeling. To mitigate the potential information loss during the modeling process, in this paper, residual connections are used to correlate the features before and after modeling, and the results obtained from multi-directional modeling are aggregated. This process can be formulated as:
where ⊗ represents element–wise multiplication, and ⊕ represents element–wise addition. Finally, in this paper, a linear layer is used to perform a final transformation on the features, obtaining the output features:
where represents the features output from the proposed feature extraction unit. For the state-space model SSM involved in the modeling process, its input at time t is defined as , which is mapped to the output through an intermediate hidden variable . The process can be formulated as:
where A, B, C represent the system matrices, which are parameters to be solved. Through the above formulas, global modeling can be carried out for an input feature sequence, and the computational complexity remains at . Considering the discreteness of the input data, the ZOH (Zero-Order Hold) algorithm is used to discretize the parameters. The process can be formulated as:
where represents the time–scale parameter. Therefore, the discretized SSM process can be formulated as:
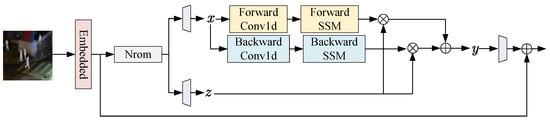
Figure 3.
Overall architecture of the feature extraction unit based on the state-space model (Mamba).
For the solution of SSM, it can be transformed into a problem of solving for A, B, C, and . Here, A is initialized as a learnable matrix parameter, and the acquisition methods for B, C, and can be formulated as:
where represents the linear layer. Therefore, the problem of solving SSM is transformed into a process of training three different linear layers. By updating the parameters of the linear layers with a large amount of data, SSM can achieve global structural modeling of the input features with linear complexity, thus ensuring that the fused images can possess sufficient texture structure information.
3.3. Fusion Module Based on Cross State-Space Model (Cross Mamba)
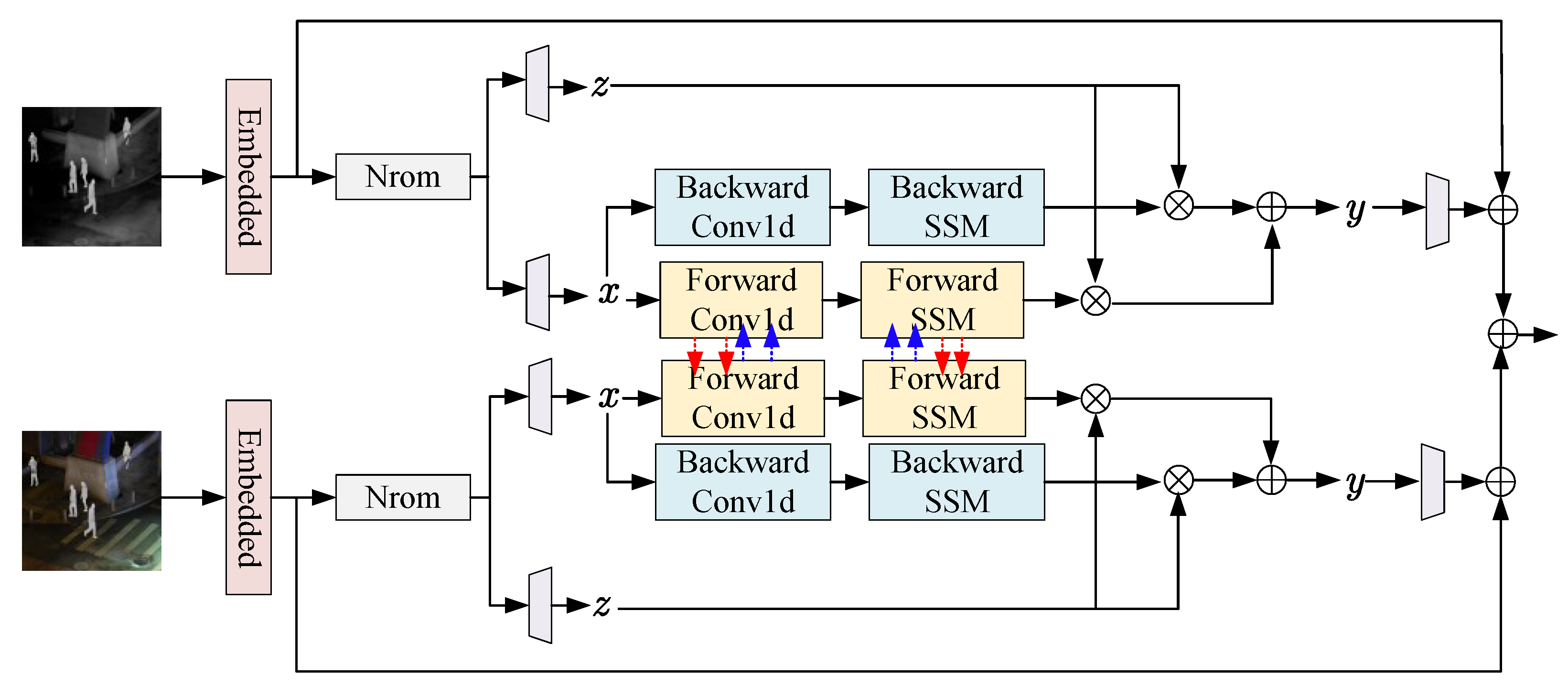
To ensure that multimodal common features can be fully fused, this paper designs a fusion module based on the cross state-space model to fully integrate the common features of different modalities. Figure 4 presents the overall structure of the proposed fusion module. First, similar to the feature extraction unit based on the state-space model, the input visible features and infrared features are first serialized. Let the serialized visible features and infrared features be and respectively. Then, they are fed into the layer normalization layer for processing, resulting in and . Next, through four independent linear layers, the visible features and infrared features are processed separately:
where represents the linear layer. Similar to the feature extraction unit based on the state-space model, the processed features are further fed into the cross state-space model for processing, obtaining the progressively fused features:
where represents the cross state-space model for forward-modeling the input linear features, and represents the cross state-space model for backward-modeling the input features. represents the output result of forward-modeling, and represents the output result of backward-modeling. Finally, the negative impact of information loss is eliminated through residual connections:
where ⊗ represents element–wise multiplication and ⊕ represents element-wise addition. Finally, a linear layer is used in this paper to perform a final transformation on the features, obtaining the output multimodal features:
where represents the progressively fused visible features, and represents the progressively fused infrared features. For the cross state-space model involved above, its inputs at time t are defined as and , which are mapped to the output through an intermediate hidden variable . The process can be formulated as
where A, B, C represent the system matrices, which are parameters to be solved. Similar to the calculation method of SSM described above, by introducing the time–scale parameter , it is ensured that CSSM can adapt to the discretized input. For the solution of CSSM, it is also transformed into a problem of solving for A, B, C, and . Here, A is initialized as a learnable matrix parameter, and the acquisition methods for B, C, and can be formulated as
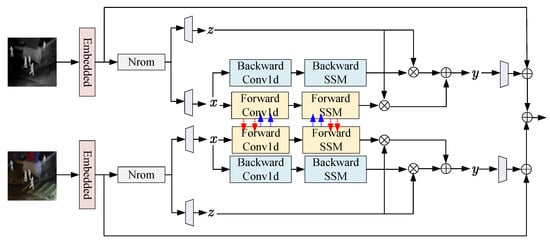
Figure 4.
Overall structure of the progressive fusion module based on the cross state-space model.
In this formula, this paper uses the additional modal input to realize the initialization of the parameters to be solved, thus achieving multimodal feature information interaction and ensuring that the multimodal common features can be effectively fused.
3.4. Design of Loss Function
The fusion network proposed in this paper is composed of a generator and a discriminator. This section will first introduce the loss for training the image generation network, and then introduce the loss for the image discrimination network.
3.4.1. Design of the Generator’s Loss Function
The goal of the image generation network is to generate a fused image with obvious texture and clear details. Based on this, first, it is necessary to ensure that the fused image contains all the texture and detail information from both the visible image and the infrared image. To this end, this paper designs a gradient loss to meet the above requirements:
where represents the gradient loss, represents the norm −1, represents using the Sobel operator to solve the edge information of the image, f represents the fused image, represents the visible image input into the network, and represents the infrared image input into the network. Through the gradient loss, it can be ensured that the fused image has as much edge information as possible, thereby ensuring that the fused image has more texture details.
Secondly, in order to make the fused image present a more natural fusion effect, this paper designs a pixel loss to further constrain the fused image. Considering that in the image fusion task, the background brightness of the infrared image is lower than that of the visible image, but the target information emitting heat radiation in the infrared image shows a relatively large brightness value. Therefore, this paper constructs a pixel loss by taking the maximum value of each pixel, as a supplement to the gradient loss. This process can be formulated as
The above two losses can ensure that the image generation network generates a fused image with a passable overall visual effect. However, both of these two losses are designed based on human judgment, which will cause the fused image to be unable to break through the limitations of human perception and thus generate a fused image with better fusion quality. Therefore, this paper uses an adversarial loss to force the image generation network to generate fused images with continuously improved visual effects through iterative methods. Specifically, this paper first uses a binary discriminator to generate the probability that the fused image belongs to visible and the probability that it belongs to infrared:
where and represent the probabilities that the fused image generated by the discriminator network belongs to visible and infrared respectively, and represents the discriminator. Then, the probabilities are used to constrain the fused image, ensuring that the generated fused image cannot be distinguished by the discriminator. In this way, the image generation network can obtain a fused image that is neither similar to visible nor infrared, thus obtaining a more natural, realistic fused image with continuously improved quality:
where represents the adversarial loss that uses the discriminator to constrain the generation network. The discriminator in this paper uses the Mamba branch to extract the common-mode information in multimodal images and the CNN branch to extract the differential-mode information in multimodal images. In order to separate different types of features as expected, this paper designs a decomposition loss to constrain the network during the training phase:
where represents the correlation coefficient of two features, represents the visible feature extracted by the Mamba branch, represents the infrared feature extracted by the Mamba branch, represents the visible feature extracted by the CNN branch, and represents the infrared feature extracted by the CNN branch. Through the above loss, the two features proposed by the Mamba branch are made as similar as possible, thus ensuring that the extracted features are the common-mode parts of the infrared and visible images. The two features obtained by the CNN branch are made as different as possible, thus ensuring that the two features are the differential-mode parts of different modalities. Finally, the four losses are combined with weights as the total loss of the image generation network:
where , , , represent the hyper-parameters used to combine the four losses, which are set in the experimental part.
3.4.2. Design of the Discriminator’s Loss
The purpose of the discriminator is to correctly determine the category of the input image. First, the most basic task of the discriminator is to correctly distinguish between visible images and infrared images. Therefore, the cross-entropy loss in the classification network scenario is used as the first term of the discriminator network loss:
where represents the discriminator classification loss, N represents the total number of categories in the classification network. In the task of this paper, N is set to 2. represents the category generated by the discriminator network, and represents the true category label. In this way, the discriminator network is able to distinguish different input images. For the fused image, it does not belong to either of the original image types, but contains most of the features of both visible and infrared images. Therefore, when the input is a fused image, the discriminator network considers it to belong to both visible and infrared images simultaneously. The fused-image discrimination loss is constructed as follows:
where represents the fused-image discrimination loss, and y represents the probability output when the input of the discriminator is a fused image. Finally, the two losses are weighted to obtain the total loss of the discriminator:
where represents the total loss of the discriminator network, and , represent the hyper-parameters used to combine the two losses, which are set in the experimental part.
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
The fusion network proposed in this section is implemented using Pytorch 1.12.0 and trained and tested on an Ubuntu system with a NVIDIA 3090 (NVIDIA Corporation, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The proposed algorithm is trained and tested using the MSRS dataset, and its generalization ability is verified on the TNO dataset and the LLVIP dataset. Since the MSRS dataset does not have enough data for the network to learn, the image pairs in the MSRS dataset are cropped into small patches of 128 × 128, and 20,000 pairs of infrared and visible images are obtained through rotation-based data augmentation.
During the training process, the hyper-parameters of the generator’s loss are set as: , , , . The hyper-parameters of the discriminator are set as , . The batch size for the generator during training is set to 128, the learning rate is set to 0.001, and the Adam optimizer is used for parameter updates. The batch size for the discriminator during loss calculation is set to 64, the learning rate is set to 0.0001, and the Adam optimizer is also used for parameter updates. The generator and the discriminator are trained alternately. One simultaneous training of the generator and the discriminator is regarded as one epoch, and the total number of epochs is set to 50.
To effectively compare the proposed method with existing approaches, several representative fusion models from different methodological categories are selected as baselines. Specifically, DenseFuse and RFN-Nest are chosen as autoencoder-based methods; UMF-CMGR represents convolutional neural network (CNN)-based approaches; CDDFuse is a Transformer-based method; FusionGAN and GANMcC are adversarial learning-based methods; and DDFM is a diffusion-based fusion model.
To quantitatively evaluate the performance of different fusion methods, six widely used evaluation metrics are adopted in this study: average gradient (AG), spatial frequency (SF), information entropy (EN), standard deviation (SD), mutual information (MI), and visual information fidelity (VIF). A higher AG and SF indicate that the fused image contains richer texture and detail information. A larger SD reflects more significant intensity variations, suggesting improved image contrast. A higher EN implies that the image carries more information content. A superior VIF score indicates that the image appears more natural and visually realistic. MI measures the amount of shared information between the fused image and the input images; a higher MI value reflects a stronger capability of the fusion model to integrate multimodal information.
4.2. Comparative Experiments
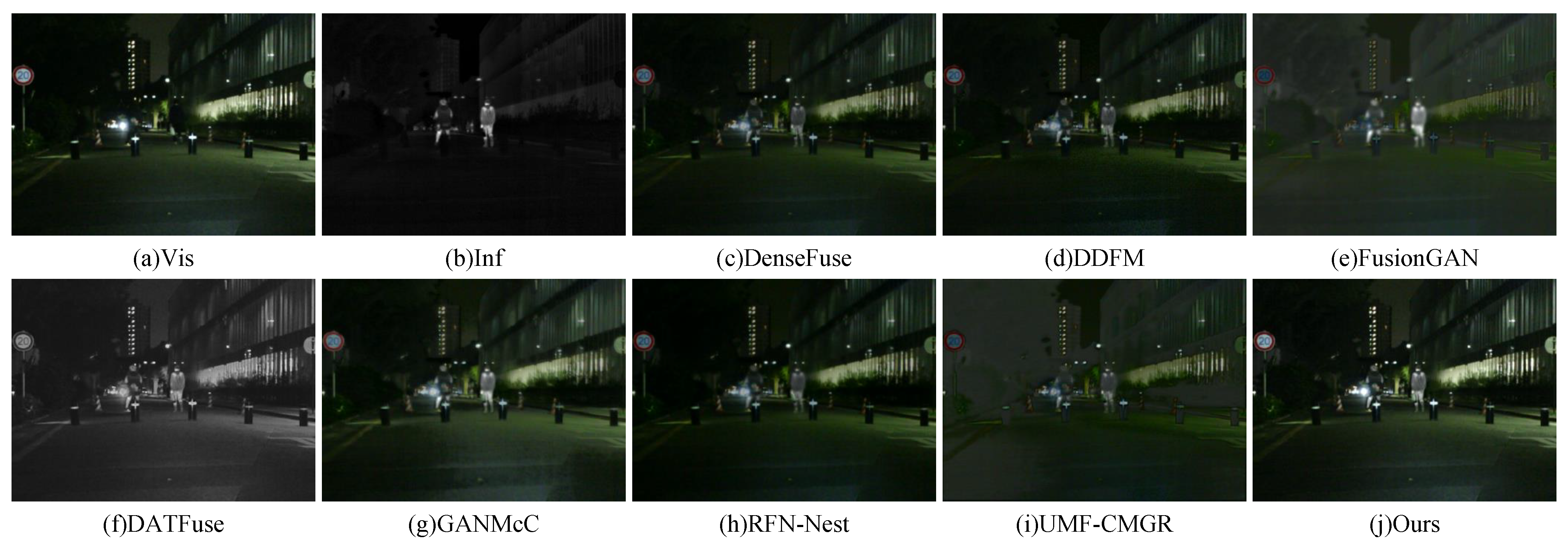
Figure 5 and Figure 6 present visual comparisons between the proposed method and several representative image fusion approaches on the MSRS dataset. In Figure 5, the visible image contains rich color information and clearly captures multiple lighting details. However, it fails to reveal pedestrians hidden in the dark. In contrast, the infrared image successfully highlights the pedestrians through thermal radiation but lacks background detail and color information. DenseFuse effectively integrates both infrared and visible features, but suffers from brightness degradation, which negatively impacts the overall visual quality. DDFM shows a similar issue, where the thermal targets are not prominent, and the background appears too dark. FusionGAN loses most of the visible information during fusion, resulting in an image that closely resembles the infrared input. CDDFuse fails to preserve color information during the fusion process. GANMcC achieves relatively good results overall, but the texture in glass facade regions appears blurred. RFN-Nest experiences severe brightness degradation, and UMF-CMGR exhibits similar visual issues. In contrast, the proposed method does not suffer from brightness degradation. It produces fused images that are visually clear, texture-rich, and preserve both the thermal radiation details from the infrared modality and the structural and color information from the visible modality, resulting in superior visual quality.

Figure 5.
Visual comparison of fusion results on the MSRS dataset (Example 1).

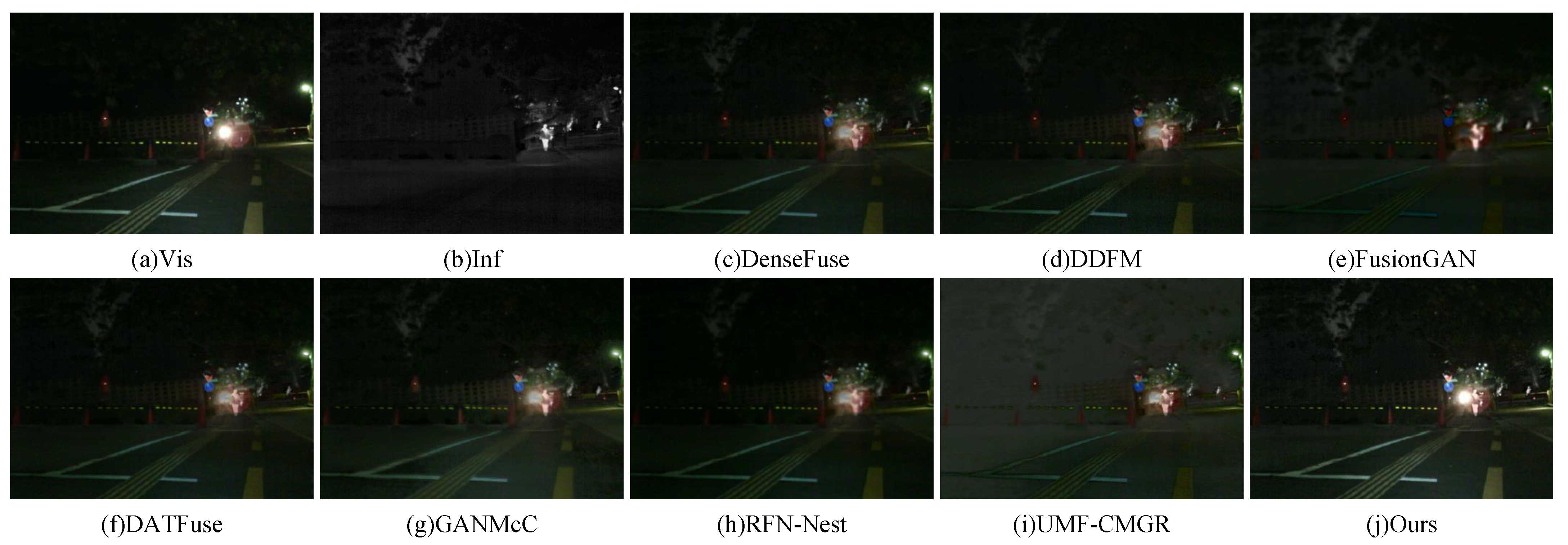
Figure 6.
Visual comparison of fusion results on the MSRS dataset (Example 2).
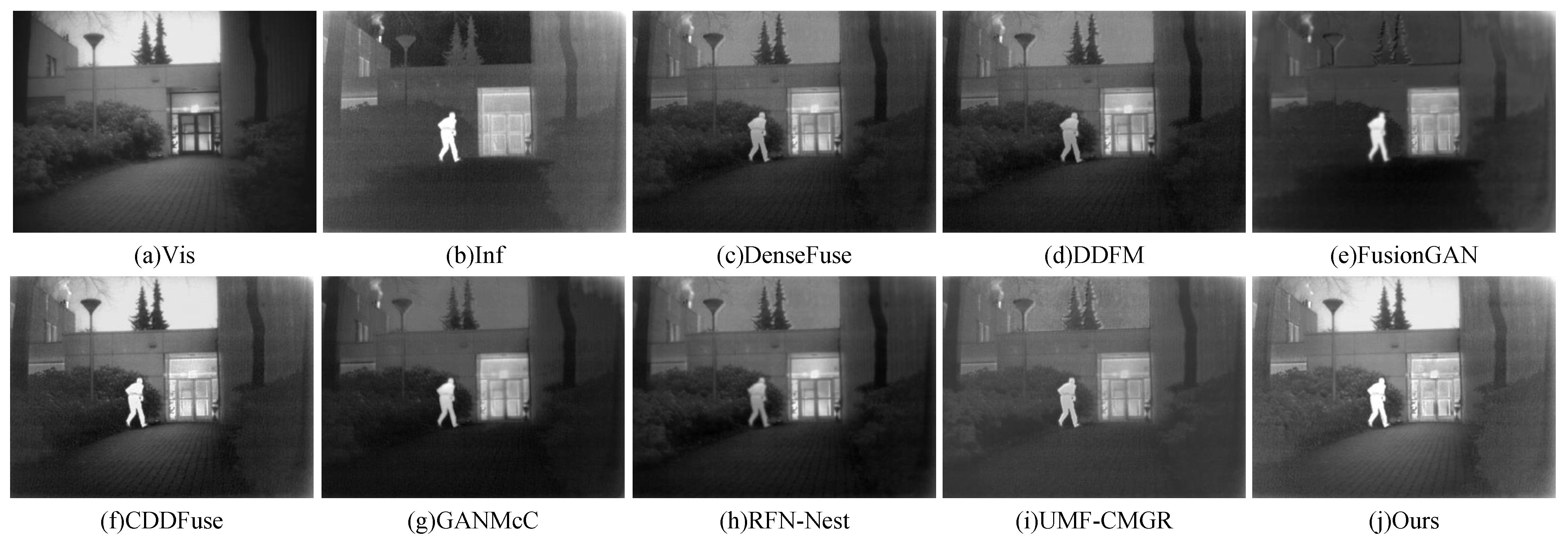
The visual comparison in Figure 6 shows similar results. The visible image clearly presents the lane markings, while the infrared image reveals pedestrians obscured by strong lighting. The fused results of DenseFuse and DDFM appear blurry, with noticeable loss of pedestrian information. FusionGAN effectively preserves pedestrian details but fails to retain the lane markings from the visible image. The result from CDDFuse is relatively dark and lacks visual clarity. GANMcC achieves better overall fusion performance, though a slight degradation in brightness is observed. RFN-Nest and UMF-CMGR produce generally blurred results, with insufficiently sharp pedestrian edges. In contrast, the proposed method maintains a balanced brightness level, clearly delineates the edges of infrared targets, and provides superior overall visual quality.
To quantitatively compare the proposed method with existing approaches, Table 1 presents the results of a quantitative evaluation conducted on the MSRS dataset. Across all evaluation metrics, the proposed model demonstrates outstanding performance, indicating its effectiveness in enhancing image clarity, structural fidelity, and overall visual quality. Moreover, it successfully preserves both spectral information and visual details in the fused images. In contrast, other methods such as FusionGAN and UMF-CMGR perform poorly on several metrics, particularly in terms of visual quality and information retention, which may lead to suboptimal fused results. Overall, the proposed image fusion method significantly outperforms existing approaches across multiple dimensions, showing a strong capability in improving fused image quality.

Table 1.
Quantitative comparison of evaluation metrics on the MSRS dataset.
4.3. Ablation Study
To further analyze the effectiveness of the proposed modules, ablation experiments were conducted on the MSRS dataset, focusing on the contributions of the adversarial loss and the progressive fusion module. The experimental results are presented in Table 2. As shown in the results, the proposed model outperforms the two comparison variants—one without the fusion module and the other without the discriminator—across all evaluation metrics. Specifically, the proposed method achieves the highest scores in spatial frequency, information entropy, and average gradient, indicating its superior capability in preserving structural details and maximizing information content. Overall, the ablation study demonstrates that the proposed approach, through effective feature fusion and denoising mechanisms, significantly enhances both the visual quality and the information fidelity of the fused images, showing stronger image quality improvement compared to the alternatives.

Table 2.
Results of the ablation study on the MSRS dataset.
4.4. Generalization Experiments
To further analyze the effectiveness of the proposed method, generalization experiments were conducted. In this part, the model trained on the MSRS dataset was directly evaluated on the TNO and LLVIP datasets using the same pretrained weights, in order to verify the model’s ability to adapt to fusion tasks under different scene conditions.
4.4.1. Generalization Experiments on the LLVIP Dataset
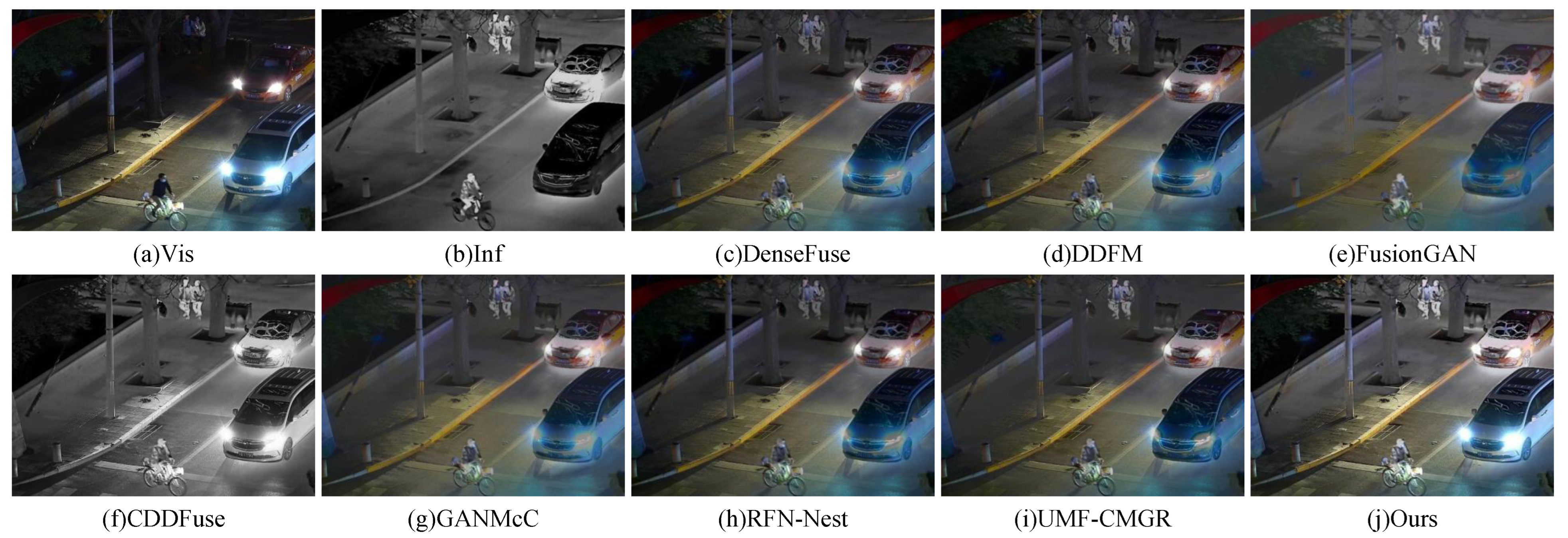
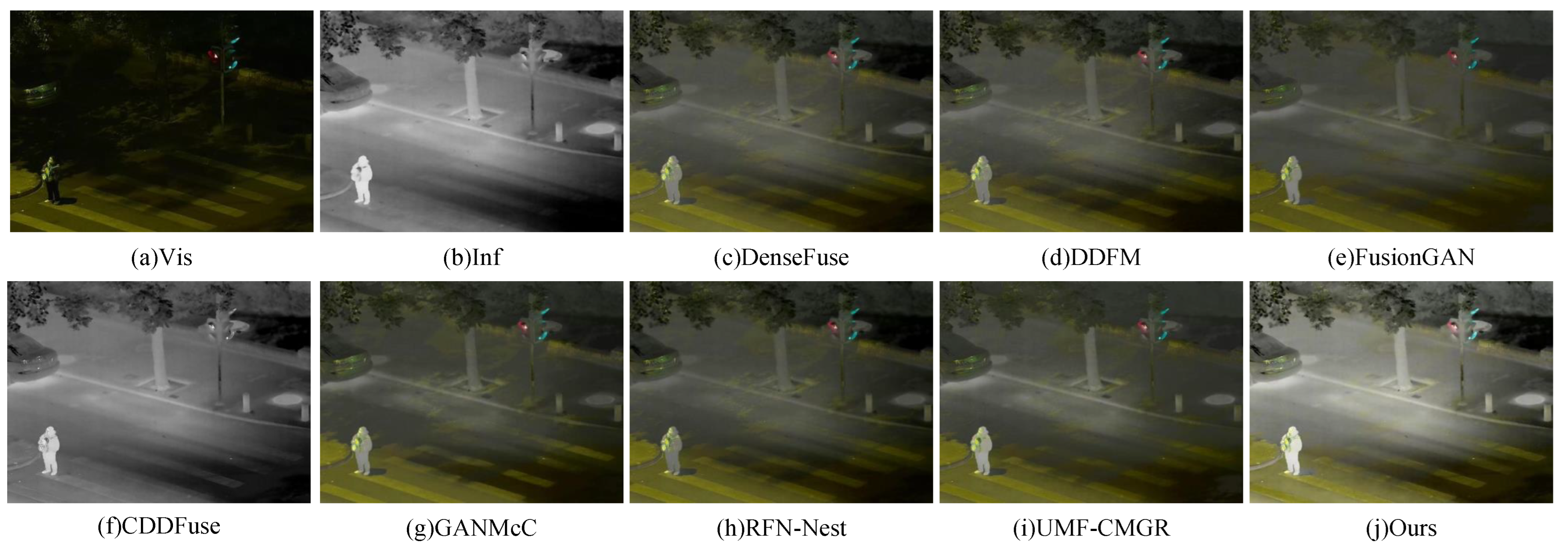
Two representative image pairs from the LLVIP dataset were selected to perform a visual comparison of fusion results. The outcomes are illustrated in Figure 7 and Figure 8. As shown in Figure 7, subfigures (a) and (b) represent the visible and infrared input images, respectively. The visible image provides rich color and texture information, while the infrared image effectively captures thermal signatures under low-light conditions. Subfigures (c) to (i) display the fused results obtained from several existing methods, including DenseFuse, DDFM, FusionGAN, CDDFuse, GANMcC, RFN-Nest, and UMF-CMGR. These methods exhibit varying performance in terms of detail preservation, target saliency, and overall visual quality. Specifically, DenseFuse and FusionGAN demonstrate limited capability in preserving fine details and achieving sufficient contrast. While CDDFuse and GANMcC enhance contrast, they introduce artifacts or color distortions. In contrast, the proposed method achieves superior performance in both target saliency and detail preservation. It clearly retains the thermal signals of key objects in the infrared image (e.g., pedestrians), while effectively incorporating the color and texture details from the visible image. The result is a high-quality fused image with natural appearance and balanced contrast. Figure 8 further confirms the effectiveness of the proposed method. The fused image successfully preserves critical visible information such as traffic lights and road markings (e.g., zebra crossings), while simultaneously maintaining the thermal radiation details of infrared targets like pedestrians.

Figure 7.
Visual comparison of fusion results on the LLVIP dataset (Pedestrians).

Figure 8.
Visual comparison of fusion results on the LLVIP dataset (Zebra crossings).
To further quantify the performance of the proposed method, Table 3 presents the results of a quantitative comparison conducted on the LLVIP dataset. The experimental results summarize the performance of various image fusion methods across multiple evaluation metrics. Compared to existing methods, the proposed approach achieves significant improvements across all metrics. Specifically, the method obtains a much higher average gradient, indicating enhanced detail clarity in the fused images. The superior information entropy suggests a richer amount of visual information. The higher spatial frequency reflects improved texture representation. The advantage in standard deviation indicates greater image contrast. Additionally, the improved VIF demonstrates better perceptual quality, while the mutual information highlights the effectiveness of integrating features from both infrared and visible images. Overall, the proposed method consistently outperforms competing methods across all evaluation metrics, with particularly strong performance in detail preservation, perceptual fidelity, and texture richness. These results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed fusion strategy in generating high-quality fused images and its potential for multimodal visual perception tasks in complex scenarios.

Table 3.
Quantitative comparison of evaluation metrics on the LLVIP dataset.
4.4.2. Generalization Experiments on the TNO Dataset
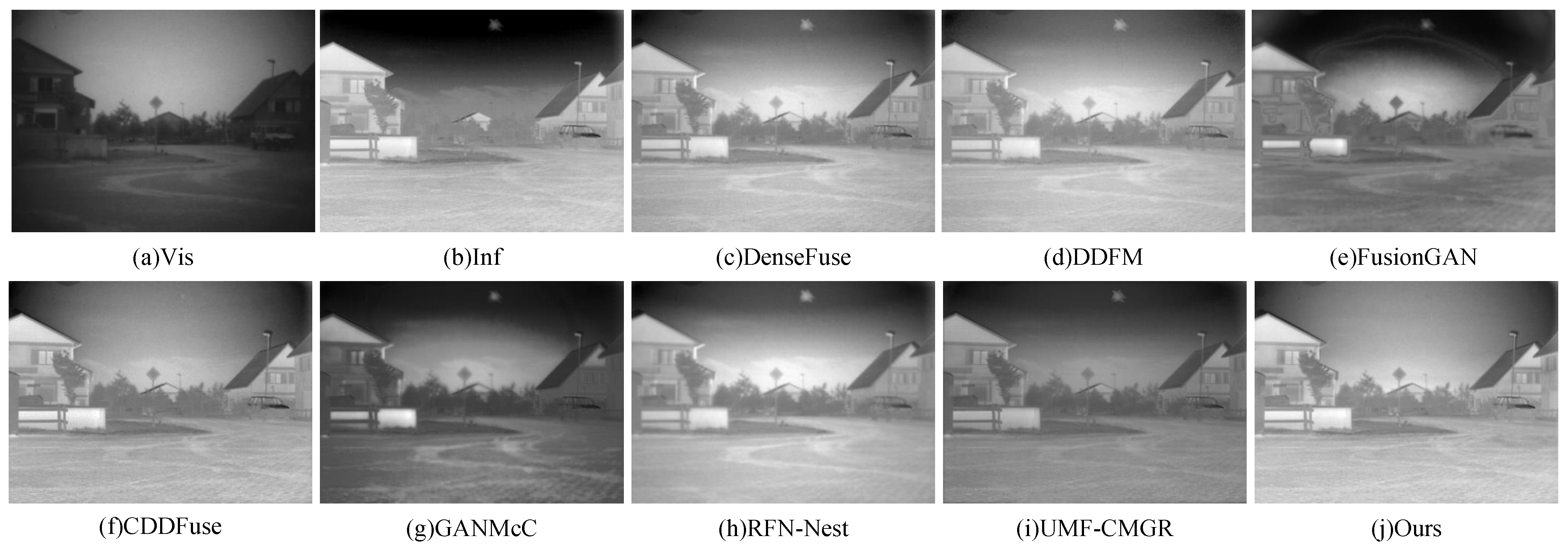
To further verify the generalization capability of the proposed method, two representative image pairs from the TNO dataset were selected for visual comparison, as shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10. In Figure 9, the visible image clearly presents background information such as grass, but fails to reveal the soldier hidden in the darkness. Conversely, the infrared image successfully highlights the soldier but lacks background detail. DenseFuse loses part of the thermal radiation information from the infrared image during fusion, resulting in a less prominent soldier. DDFM exhibits a similar issue. FusionGAN preserves thermal details effectively but sacrifices much of the background information present in the visible image. GANMcC and RFN-Nest fail to retain significant portions of both the infrared and visible information, with most visible features nearly lost. UMF-CMGR also produces blurry results. Although CDDFuse generates relatively clear images, the grass regions appear overly dark, leading to severe information loss. In contrast, the fused image produced by the proposed method exhibits sharp textures, preserves nearly all visible background information, and enhances the thermal signatures from the infrared image, resulting in superior visual quality. The visual comparison in Figure 10 further confirms the advantages of the proposed method in balancing structural detail, thermal information, and perceptual clarity.

Figure 9.
Visual comparison of fusion results on the TNO dataset (Example 1).

Figure 10.
Visual comparison of fusion results on the TNO dataset (Example 2).
To further quantify the performance of the proposed method compared to existing approaches, Table 4 presents the results of a quantitative evaluation conducted on the TNO dataset. The table summarizes the performance of different image fusion methods across six evaluation metrics. As shown in the results, the proposed method consistently outperforms all comparison methods across all metrics, demonstrating a clear advantage. In particular, it achieves superior performance in terms of detail preservation, information integration, and image contrast. These results validate the effectiveness of the proposed method in multimodal image fusion tasks, highlighting its capability to generate high-quality fused images from visible and infrared inputs and its suitability for visual perception in complex scenes.

Table 4.
Quantitative comparison of evaluation metrics (assumed context).
4.5. Model Complexity Analysis
This paper proposes an image fusion network based on the state space model, which enables global structure awareness with a lightweight computational burden. To comprehensively evaluate the model, we conducted statistics on the number of parameters (Parms) and the test time required to process a pair of images (Test time) on an NVIDIA 3090 using images with a resolution of 640 × 480. The results are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Quantitative comparison of model complexity.
DenseFuse uses DenseNet to extract features from multi-source images and fuses multimodal features using a norm-based approach. Since no learnable parameters are introduced in the multimodal feature fusion part, and DenseNet consists of only four convolutional layers, it exhibits a relatively low number of parameters and fast runtime.
Similarly, FusionGAN relies on consecutive convolutional layers for multimodal feature extraction and fusion. However, due to the large number of channels involved in the operations, more parameters are required for feature transformation, resulting in a higher number of parameters and computational burden than DenseFuse. GANMcC has a structure similar to FusionGAN, but the number of feature channels involved in the transformation is the same as DenseFuse, so its parameter count and computational burden are approximately equal to those of DenseFuse. RFN-Nest employs a multi-layer, multi-scale feature extraction backbone with extremely rich information flow. The backbone consists of numerous convolutional blocks, resulting in a large number of parameters. Nevertheless, since GPUs can efficiently handle parallel computation tasks, its test time is moderate. CDDFuse utilizes Transformer layers for input feature extraction and fusion. Due to the self-attention operations, it has more parameters than CNN-based models and a slightly worse test time performance. Among the methods listed in the table, UMF-CMGR and DDFM show abnormal performance in terms of parameter count and test time. UMF-CMGR consists of three stages: alignment, fusion, and reconstruction, which need to be executed sequentially, resulting in a longer computation time. DDFM is a diffusion-model-based image fusion algorithm that requires a progressive denoising process. Each denoising step involves predicting an accurate noise map, and the entire process includes 100 steps of continuous diffusion, leading to a significantly high test time.
In summary, our method runs slightly slower than CNN-based methods (e.g., DenseFuse) but is faster than Transformer-based methods (e.g., CDDFuse). In terms of parameter count, since the state space model only needs to predict a small number of parameter matrices, it remains at a relatively low level. Overall, the proposed method outperforms Transformer-based models in fusion quality while maintaining lower computational time and parameter count. Compared to CNN-based methods, our method shows only minor disadvantages in computational time and parameter count.
5. Discussion
5.1. Discussion and Comparative Analysis
The proposed method shows stable performance in terms of detail preservation and structural consistency across multiple fusion datasets. Compared with traditional multi-scale transform methods, it eliminates the need for hand-crafted fusion rules by using a state-space modelling mechanism for global feature representation. This offers a degree of adaptability, though its effectiveness depends on sufficient training data. In contrast to CNN- and autoencoder-based methods such as DenseFuse and RFN-Nest, the use of linear-complexity global modelling presents an alternative design, albeit with limited interpretability. Compared to adversarial approaches like FusionGAN and GANMcC, the multi-class discriminator focuses on maintaining modal balance rather than realism alone. While experimental results are competitive, adversarial training introduces tuning and stability challenges. Task-driven supervision could be explored to strengthen semantic alignment.
5.2. Limitations
The model’s performance relies on adequate training data and may degrade with limited or imbalanced samples. While the state-space design improves efficiency, it reduces transparency in feature interpretation. Adversarial optimisation introduces sensitivity to hyper-parameters and training dynamics. In addition, the current framework does not incorporate explicit semantic or task-level guidance, which could be considered in future extensions.
6. Conclusions and Future Work
This paper proposes a generative adversarial network based on a state-space model for infrared and visible image fusion, effectively addressing the challenges of environmental perception in complex scenes. First, a dual-branch architecture is designed to separately extract common features and modality-specific features from infrared and visible images. Second, a state-space model is introduced for the extraction and fusion of common features, enabling global feature modeling with linear computational complexity. Finally, adversarial loss is employed to continuously optimize the network, ensuring progressive improvement in the quality of the fused images.
Although the proposed method effectively addresses image fusion under typical conditions, it does not fully explore or analyze challenging scenarios such as low-light, rainy, or foggy environments. In future work, we plan to further investigate image fusion under adverse conditions and design an infrared–visible image fusion network that is adaptable to all-weather environments, thereby enhancing its practical applicability in fields such as autonomous driving and surveillance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.H.; Data Curation, Y.P.; Formal Analysis, Q.H.; Investigation, Q.H. and Y.P.; Methodology, Q.H.; Project Administration, K.U.; Resources, Q.H. and Y.P.; Software, Y.P. and S.Z.; Visualization, Q.H. and Y.P.; Writing—Original Draft, Q.H., Y.P. and K.U.; Writing—Review & Editing, Q.H., Y.P., K.U. and S.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used in this study are publicly available and can be accessed from the following repositories: the MSRS dataset is available on GitHub at https://github.com/Linfeng-Tang/MSRS (accessed on 18 May 2025) the TNO Image Fusion Dataset can be accessed on Figshare at https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/TNO_Image_Fusion_Dataset/1008029 (accessed on 18 May 2025), and the LLVIP dataset is available on GitHub at https://github.com/bupt-ai-cz/LLVIP (accessed on 18 May 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Yi, X.; Tang, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Ma, J. Diff-IF: Multi-modality image fusion via diffusion model with fusion knowledge prior. Inf. Fusion 2024, 110, 102450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, A.; Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X. SIMFusion: A semantic information-guided modality-specific fusion network for MR Images. Inf. Fusion 2024, 112, 102560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Xu, T.; Wu, X.J.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Tang, Z.; Kittler, J. TextFusion: Unveiling the power of textual semantics for controllable image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2025, 117, 102790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, B.; Liu, H.; Ding, Z. Multi-scene image fusion via memory aware synapses. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Huo, H.; Li, J.; Pang, S.; Zheng, B. A semantic-driven coupled network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2024, 108, 102352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Shi, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X. Improving RGB-infrared object detection with cascade alignment-guided transformer. Inf. Fusion 2024, 105, 102246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, C. CPIFuse: Toward realistic color and enhanced textures in color polarization image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2025, 120, 103111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Hu, S.; Ma, X. DGFD: A dual-graph convolutional network for image fusion and low-light object detection. Inf. Fusion 2025, 119, 103025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Jiang, Z.; Pan, D.; Yu, H.; Gui, G.; Gui, W. LFDT-Fusion: A latent feature-guided diffusion Transformer model for general image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2025, 113, 102639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Luo, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, T.; Chi, N.; Dai, Q. SMAE-Fusion: Integrating saliency-aware masked autoencoder with hybrid attention transformer for infrared–visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2025, 117, 102841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wu, X.j. KDFuse: A high-level vision task-driven infrared and visible image fusion method based on cross-domain knowledge distillation. Inf. Fusion 2025, 118, 102944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, G.; Wang, H.; Lu, Y.; Peng, Y. A comprehensive survey of visible and infrared imaging in complex environments: Principle, degradation and enhancement. Inf. Fusion 2025, 119, 103036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Dian, R.; Song, Z. DT-F Transformer: Dual transpose fusion transformer for polarization image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2024, 106, 102274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wu, S.; Ma, L. Adversarial attacks on GAN-based image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2024, 108, 102389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wu, G.; Jiang, Z.; Fan, W.; Xu, B.; Liu, J. Leveraging a self-adaptive mean teacher model for semi-supervised multi-exposure image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2024, 112, 102534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guan, Z.; Qian, W.; Cao, J.; Ma, R.; Bi, C. A degradation-aware guided fusion network for infrared and visible image. Inf. Fusion 2025, 118, 102931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Q.; Mian, A. Deep learning based infrared small object segmentation: Challenges and future directions. Inf. Fusion 2025, 118, 103007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Fang, Z.; Wang, L. SK-MMFMNet: A multi-dimensional fusion network of remote sensing images and EEG signals for multi-scale marine target recognition. Inf. Fusion 2024, 108, 102402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Yu, W.; Zhang, L. DF3Net: Dual frequency feature fusion network with hierarchical transformer for image inpainting. Inf. Fusion 2024, 111, 102487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Geng, S.; Wang, H.; Huang, J.; Zhou, T. FDiff-Fusion: Denoising diffusion fusion network based on fuzzy learning for 3D medical image segmentation. Inf. Fusion 2024, 112, 102540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Yan, C.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, T. A Cross-modal Fusion Method for Multispectral Small Ship Detection. In Proceedings of the 2024 27th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Venice, Italy, 8–11 July 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Ma, J. PIAFusion: A progressive infrared and visible image fusion network based on illumination aware. Inf. Fusion 2022, 83, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J.; Durrani, T. NestFuse: An infrared and visible image fusion architecture based on nest connection and spatial/channel attention models. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 9645–9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J. DenseFuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Liang, P.; Li, C.; Jiang, J. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, J.; Tian, X.; Ma, J. GAN-FM: Infrared and visible image fusion using GAN with full-scale skip connection and dual Markovian discriminators. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2021, 7, 1134–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Liu, G.; Qian, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiong, J. EgeFusion: Towards edge gradient enhancement in infrared and visible image fusion with multi-scale transform. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2024, 10, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, M. New insights into multi-focus image fusion: A fusion method based on multi-dictionary linear sparse representation and region fusion model. Inf. Fusion 2024, 105, 102230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, L.; Li, J.; Ren, X.; Fan, J. Optical and SAR image fusion based on complementary feature decomposition and visual saliency features. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5205315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ma, H.; Cheng, C.; Shen, Z.; Song, X.; Wu, X.J. Conti-Fuse: A novel continuous decomposition-based fusion framework for infrared and visible images. Inf. Fusion 2025, 117, 102839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Hong, X.; Zhang, B. A damage imaging method based on particle swarm optimization for composites nondestructive testing using ultrasonic guided waves. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 218, 109878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Guo, D.; Wang, N.; Qi, J.; Qiu, J. Subregional polarization fusion via Stokes parameters in passive millimeter-wave imaging. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 8585–8595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chi, N.; Dai, Q. WaveFusion: A Novel Wavelet Vision Transformer with Saliency-Guided Enhancement for Multimodal Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Hou, Z.; Wan, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lv, K. Multispectral and SAR image fusion for multiscale decomposition based on least squares optimization rolling guidance filtering. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yang, B. Progressive fusion of hyperspectral and multispectral images based on joint bilateral filtering. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2025, 145, 105676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aymaz, S.; Köse, C. A novel image decomposition-based hybrid technique with super-resolution method for multi-focus image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 45, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jiao, L.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Liu, F.; Yang, S. C-CNN: Contourlet convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 2636–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, L.; Zhang, P.; Gao, F. Combining two-layer semi-three-dimensional reconstruction and multi-wavelength image fusion for functional diffuse optical tomography. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2021, 7, 1055–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lv, M.; Jia, Z.; Jin, Q.; Liu, M.; Chen, L.; Ma, H. An effective infrared and visible image fusion approach via rolling guidance filtering and gradient saliency map. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Song, R.; Huang, C.; Tong, Q. Considering nonoverlapped bands construction: A general dictionary learning framework for hyperspectral and multispectral image fusion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5505215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dian, R.; Li, S.; Liu, H. SGFusion: A saliency guided deep-learning framework for pixel-level image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2023, 91, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Deep learning-based multi-focus image fusion: A survey and a comparative study. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 4819–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Newsam, S. Densenet for dense flow. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 17–20 September 2017; pp. 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2014, Proceedings of the 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part V 13; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J.; Kittler, J. RFN-Nest: An end-to-end residual fusion network for infrared and visible images. Inf. Fusion 2021, 73, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Ma, J. Image fusion in the loop of high-level vision tasks: A semantic-aware real-time infrared and visible image fusion network. Inf. Fusion 2022, 82, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, G. STDFusionNet: An infrared and visible image fusion network based on salient target detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 5009513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Zhou, M.; Huang, J.; Hou, J.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, F. Probing synergistic high-order interaction in infrared and visible image fusion. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 26384–26395. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Sun, D.; Gao, Q.; Wang, L.; Yan, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, E.; Wang, T. MLFFusion: Multi-level feature fusion network with region illumination retention for infrared and visible image fusion. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 134, 104916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, H.; Gong, M.; Ma, J. DIVFusion: Darkness-free infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2023, 91, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S. IAIFNet: An illumination-aware infrared and visible image fusion network. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2024, 31, 1374–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Shao, Z.; Liang, P.; Xu, H. GANMcC: A generative adversarial network with multiclassification constraints for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 5005014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Huang, Z.; Wu, G.; Liu, R.; Zhong, W.; Luo, Z. Target-aware dual adversarial learning and a multi-scenario multi-modality benchmark to fuse infrared and visible for object detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5802–5811. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Y.; Wu, D.; Han, M.; Wang, T.; Yang, Y.; Lei, T.; Zhou, C.; Bai, H.; Xing, L. AT-GAN: A generative adversarial network with attention and transition for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2023, 92, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).