A Cloud-Edge-End Collaboration Framework for Fixed-Time Distributed Optimization of Virtual Power Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A fixed-time consensus optimization algorithm is proposed to address the economic scheduling problem of VPPs. Unlike the approach in [20], the proposed algorithm not only exhibits a high convergence rate but also avoids dependence on the system’s initial values. In addition, it can be designed offline. Compared to [22], the proposed optimization algorithm incorporates more constraints, reflecting the actual conditions of the grid. Therefore, the algorithm presented in this paper is more practically significant.
- (2)
- A framework for cloud–edge–end collaborative control is proposed. Compared to the centralized framework [5], the proposed cloud–edge–end collaboration framework better protects user privacy, as the cloud server only requires aggregated regional information rather than individual agent data to solve the problem. At the edge server level, each agent only needs to exchange gradients with neighboring agents. Unlike the distributed framework [21], the cloud–edge–end collaboration framework allows for parallel computation of multiple distributed optimization algorithms, enhancing the speed of solving optimization problems.
2. Model and Preliminaries
2.1. VPP Cyber–Physical System Model
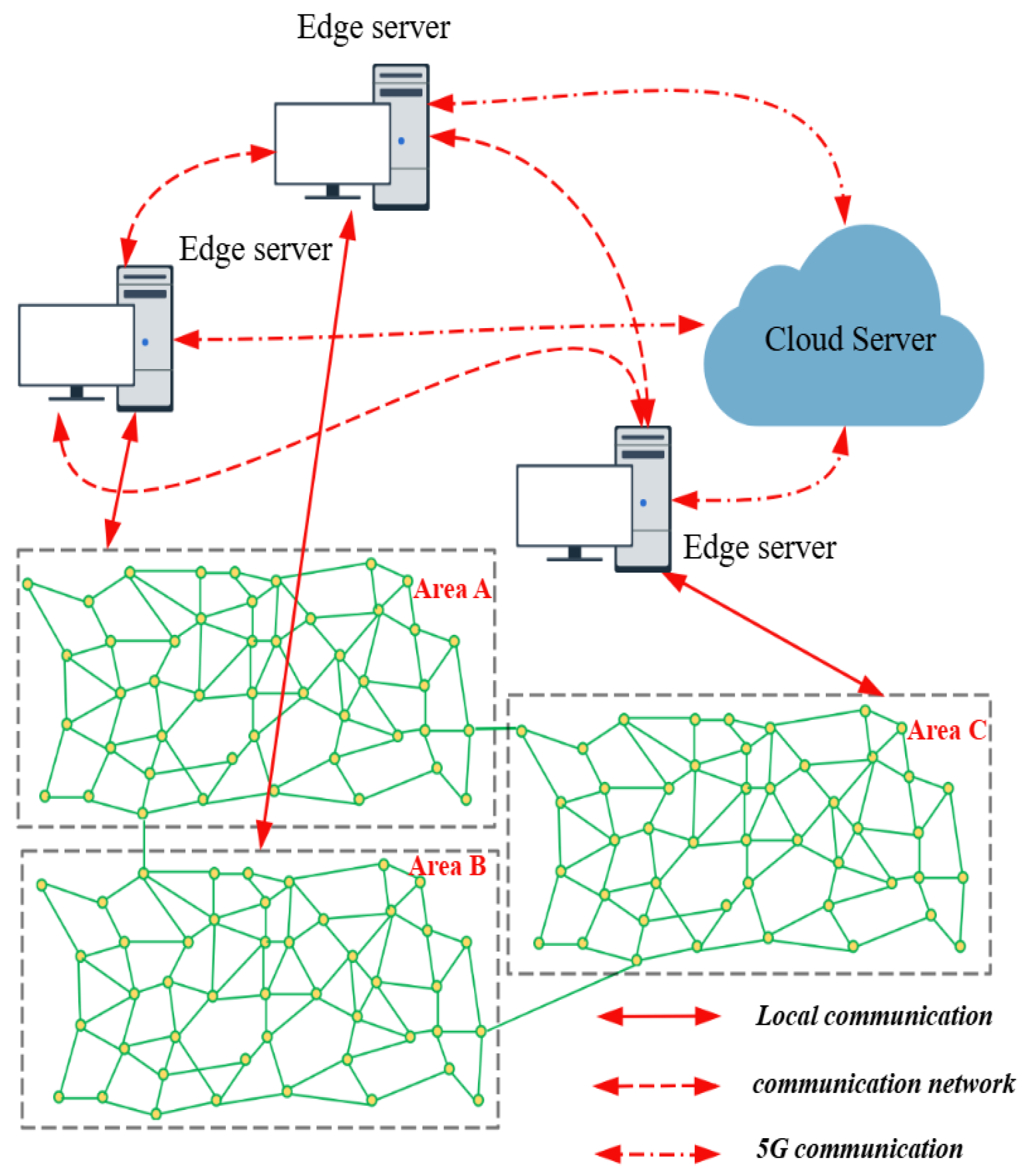
2.2. Cloud–Edge–End Collaboration Framework for VPPs
2.3. VPP Supply–Demand Model
- (1)
- Power Generation Unit
- (2)
- Power Controllable Load
- (3)
- Battery Energy Storage
- (4)
- Power balance and flow constraint
- (5)
- Problem Description
2.4. Definition and Some Lemmas
3. Main Results
3.1. Consensus Algorithm Design
3.2. Consensus Analysis
4. Numerical Simulations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, J.; Wen, Q.; Cheng, S.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X. Optimization of carbon emission reduction paths in the low-carbon power dispatching process. Renew. Energy 2022, 188, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, L.; Lv, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G.; Gan, W.; Fang, J. Data-driven two-stage robust optimization dispatching model and benefit allocation strategy for a novel virtual power plant considering carbon-green certificate equivalence conversion mechanism. Appl. Energy 2024, 362, 122974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, N.; Cobelo, I.; Oyarzabal, J. A direct load control model for virtual power plant management. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2009, 24, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, M.; Santos, S.F.; Lotfi, M.; Javadi, M.S.; Osório, G.J.; Ashraf, P.; Castro, R.; Catalão, J.P. Operation of a technical virtual power plant considering diverse distributed energy resources. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 2547–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Han, R.; Quan, X.; Wu, Z.; Tang, C.; Li, W.; Wang, W. Grid-forming inverter enabled virtual power plants with inertia support capability. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 13, 4134–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björk, J.; Johansson, K.H.; Dörfler, F. Dynamic virtual power plant design for fast frequency reserves: Coordinating hydro and wind. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2022, 10, 1266–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naina, P.; Swarup, K. Double-consensus-based distributed energy management in a virtual power plant. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 7047–7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, H. Blockchain-based decentralized energy management platform for residential distributed energy resources in a virtual power plant. Appl. Energy 2021, 294, 117026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Xin, H.; Jiang, X. A robust distributed economic dispatch strategy of virtual power plant under cyber-attacks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 4343–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zheng, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, H.; Xiao, J.; Wang, P. Distributed optimal control of dc microgrid considering balance of charge state. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 2162–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebbran, D.; Mhanna, S.; Chapman, A.C.; Verbič, G. Multiperiod der coordination using admm-based three-block distributed ac optimal power flow considering inverter volt-var control. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 12, 2874–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, B.; Wang, B.; Sun, S. Joint planning of distributed generations and energy storage in active distribution networks: A bilevel programming approach. Energy 2022, 245, 123226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Capitanescu, F. Three solution approaches to stochastic multi-period ac optimal power flow in active distribution systems. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2022, 14, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, S.M.; Qi, J. Optimal distributed control of ac microgrids with coordinated voltage regulation and reactive power sharing. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 13, 1789–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L. Distributed networked microgrids power flow. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2022, 38, 1405–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajanova, M.; Bracinik, P. Social welfare-based charging of electric vehicles in the microgrids fed by renewables. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 138, 107974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Liang, S.; Hong, Y. Distributed continuous-time algorithms for resource allocation problems over weight-balanced digraphs. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 48, 3116–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, V.S.; Abed, E.H. Local prediction for enhanced convergence of distributed optimization algorithms. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2017, 5, 1962–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necoara, I.; Nedelcu, V. On linear convergence of a distributed dual gradient algorithm for linearly constrained separable convex problems. Automatica 2015, 55, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Ren, W.; Farrell, J.A. Distributed continuous-time optimization: Nonuniform gradient gains, finite-time convergence, and convex constraint set. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2016, 62, 2239–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cao, J.; Rutkowski, L. A fixed-time distributed optimization algorithm based on event-triggered strategy. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Dong, Z.; Schultz, P.; Tang, Y.; Meng, K.; Dong, Z.Y.; Qian, F. A finite-time distributed optimization algorithm for economic dispatch in smart grids. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 51, 2068–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doostmohammadian, M.; Gabidullina, Z.R.; Rabiee, H.R. Momentum-based distributed resource scheduling optimization subject to sector-bound nonlinearity and latency. Syst. Control Lett. 2025, 199, 106062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, A. Nonlinear feedback design for fixed-time stabilization of linear control systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2012, 57, 2106–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Sun, Z. Multi-layer distributed multi-objective consensus algorithm for multi-objective economic dispatch of large-scale multi-area interconnected power systems. Appl. Energy 2021, 300, 117391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, G.H.; Littlewood, J.E.; Polya, G.; Polya, G.; Littlewood, D.E. Inequalities; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, Z.; Han, Q.L.; Ning, B.; Ge, X.; Zhang, X.M. An overview of recent advances in fixed-time cooperative control of multiagent systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 2322–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Guo, Z. Initialization-free distributed fixed-time convergent algorithms for optimal resource allocation. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2020, 52, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi-Sarvestani, S.; Jooshaki, M.; Fotuhi-Firuzabad, M.; Lehtonen, M. Incorporating direct load control demand response into active distribution system planning. Appl. Energy 2023, 339, 120897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doostmohammadian, M. Distributed energy resource management: All-time resource-demand feasibility, delay-tolerance, nonlinearity, and beyond. IEEE Control Syst. Lett. 2023, 7, 3423–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doostmohammadian, M.; Aghasi, A.; Rikos, A.L.; Grammenos, A.; Kalyvianaki, E.; Hadjicostis, C.N. Distributed anytime-feasible resource allocation subject to heterogeneous time-varying delays. IEEE Open J. Control Syst. 2022, 1, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, K.; Shi, N.; Zhang, K.; Cai, S.; Zhang, L.; Shao, X.; Shu, L.; Hu, R.; Wang, L. A Cloud-Edge-End Collaboration Framework for Fixed-Time Distributed Optimization of Virtual Power Plants. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111883
Kang K, Shi N, Zhang K, Cai S, Zhang L, Shao X, Shu L, Hu R, Wang L. A Cloud-Edge-End Collaboration Framework for Fixed-Time Distributed Optimization of Virtual Power Plants. Mathematics. 2025; 13(11):1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111883
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Kai, Nian Shi, Keqi Zhang, Si Cai, Liang Zhang, Xinan Shao, Lei Shu, Renjie Hu, and Leimin Wang. 2025. "A Cloud-Edge-End Collaboration Framework for Fixed-Time Distributed Optimization of Virtual Power Plants" Mathematics 13, no. 11: 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111883
APA StyleKang, K., Shi, N., Zhang, K., Cai, S., Zhang, L., Shao, X., Shu, L., Hu, R., & Wang, L. (2025). A Cloud-Edge-End Collaboration Framework for Fixed-Time Distributed Optimization of Virtual Power Plants. Mathematics, 13(11), 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111883







