Leader-Following Consensus of Discrete-Time Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems with Asymmetric Saturation Impulsive Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- (2)
- (3)
- An asymmetric saturation impulsive control protocol is proposed to analyze the leader-following consensus of discrete-time nonlinear multi-agent systems, which can reduce energy consumption and damage to the equipment. Sufficient conditions are obtained for the leader-following consensus of nonlinear multi-agent systems, and the admissible region of the system is estimated.
2. Preliminaries and Problem Formulation
2.1. Notations
2.2. Algebraic Graph Theory
2.3. Problem Formulation
3. Main Results
| Algorithm 1 Leader-Following Consensus of Discrete-Time Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems Based on the Asymmetric Saturation Impulsive Control Strategy |
Input: Connection topology between agents, dynamic functions of agents, initial state of leader and followers for , and parameters . Output: Parameters P and C satisfying the conditions specified in the theorem and assumptions.
|
4. Numerical Simulation
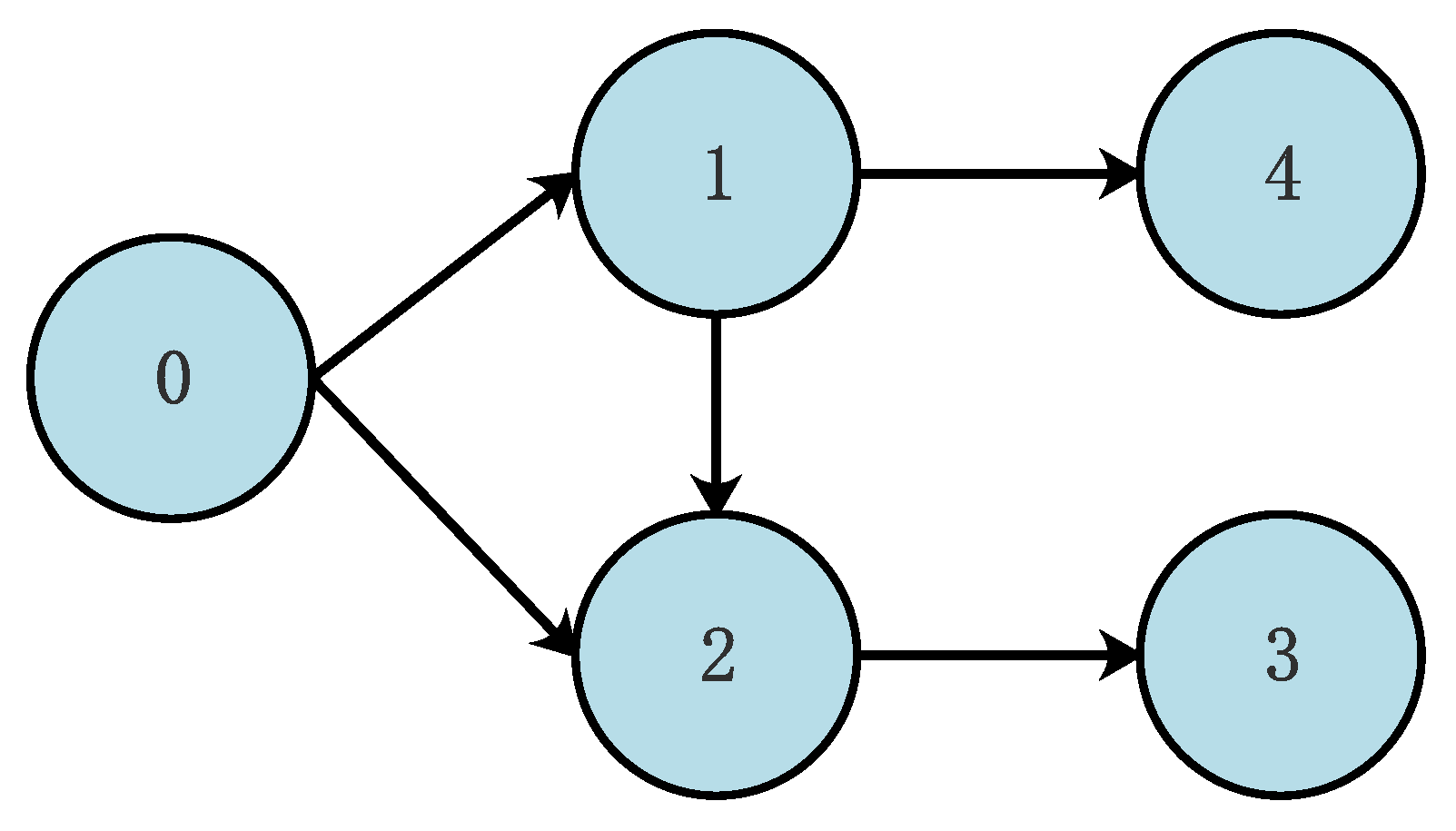
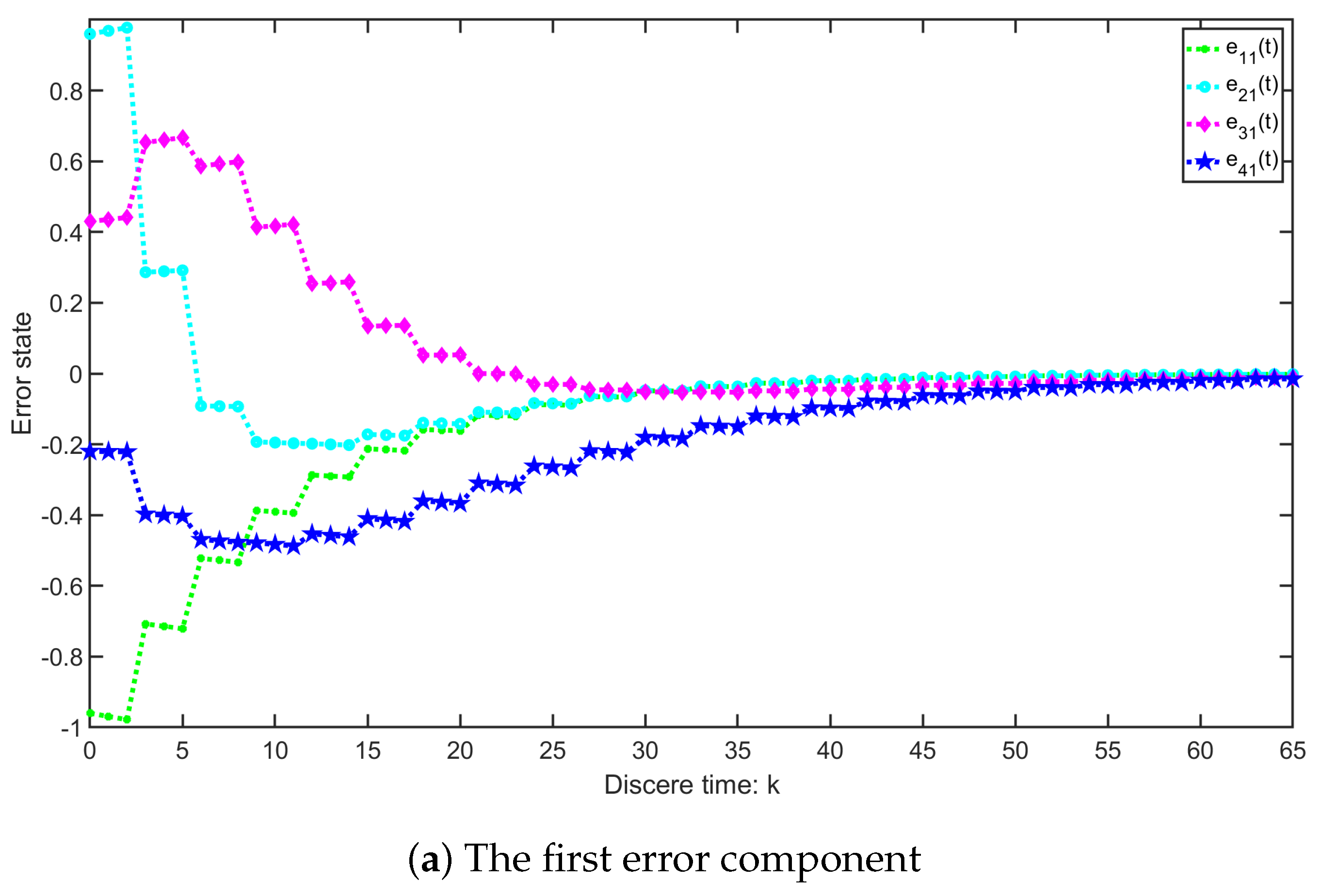
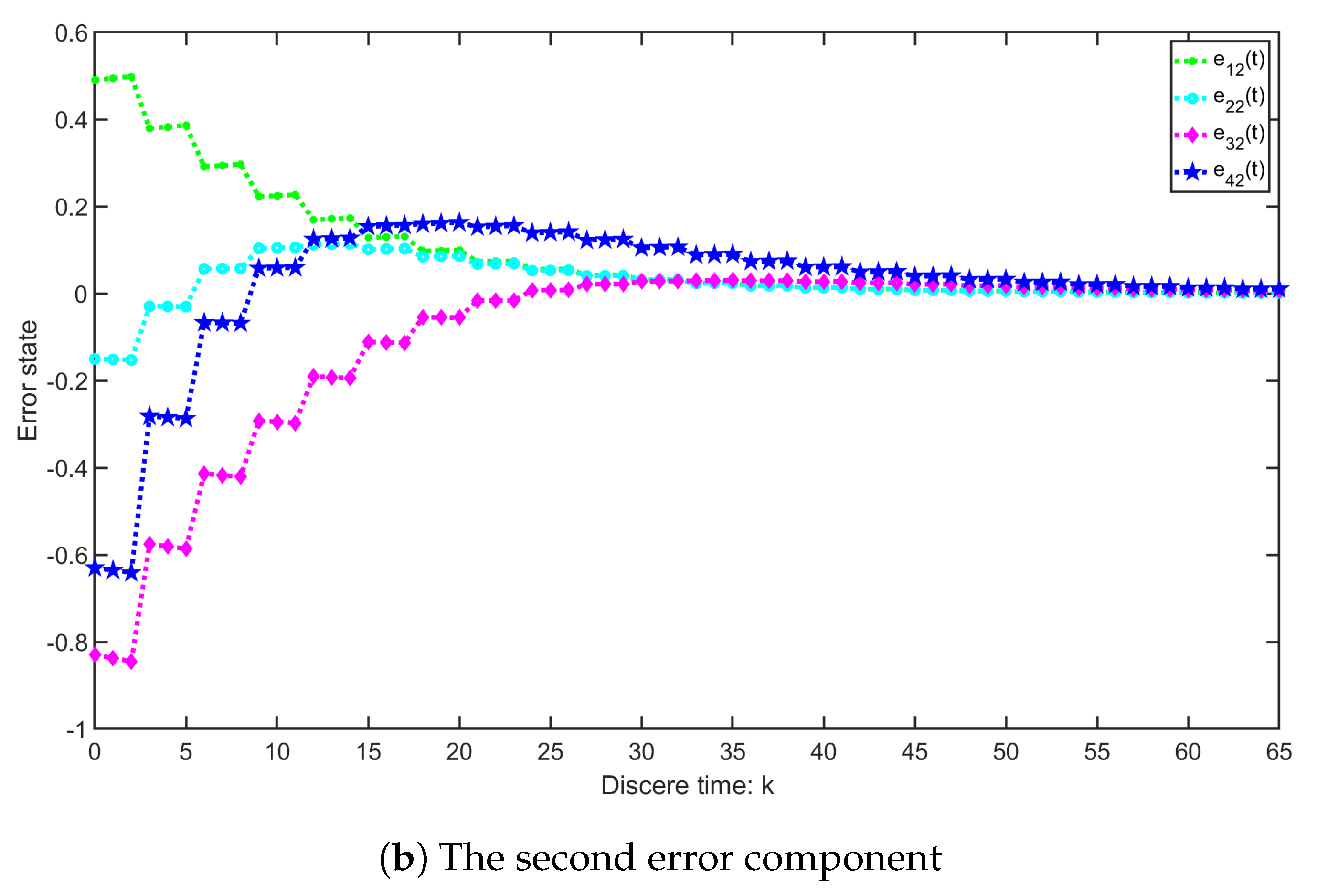
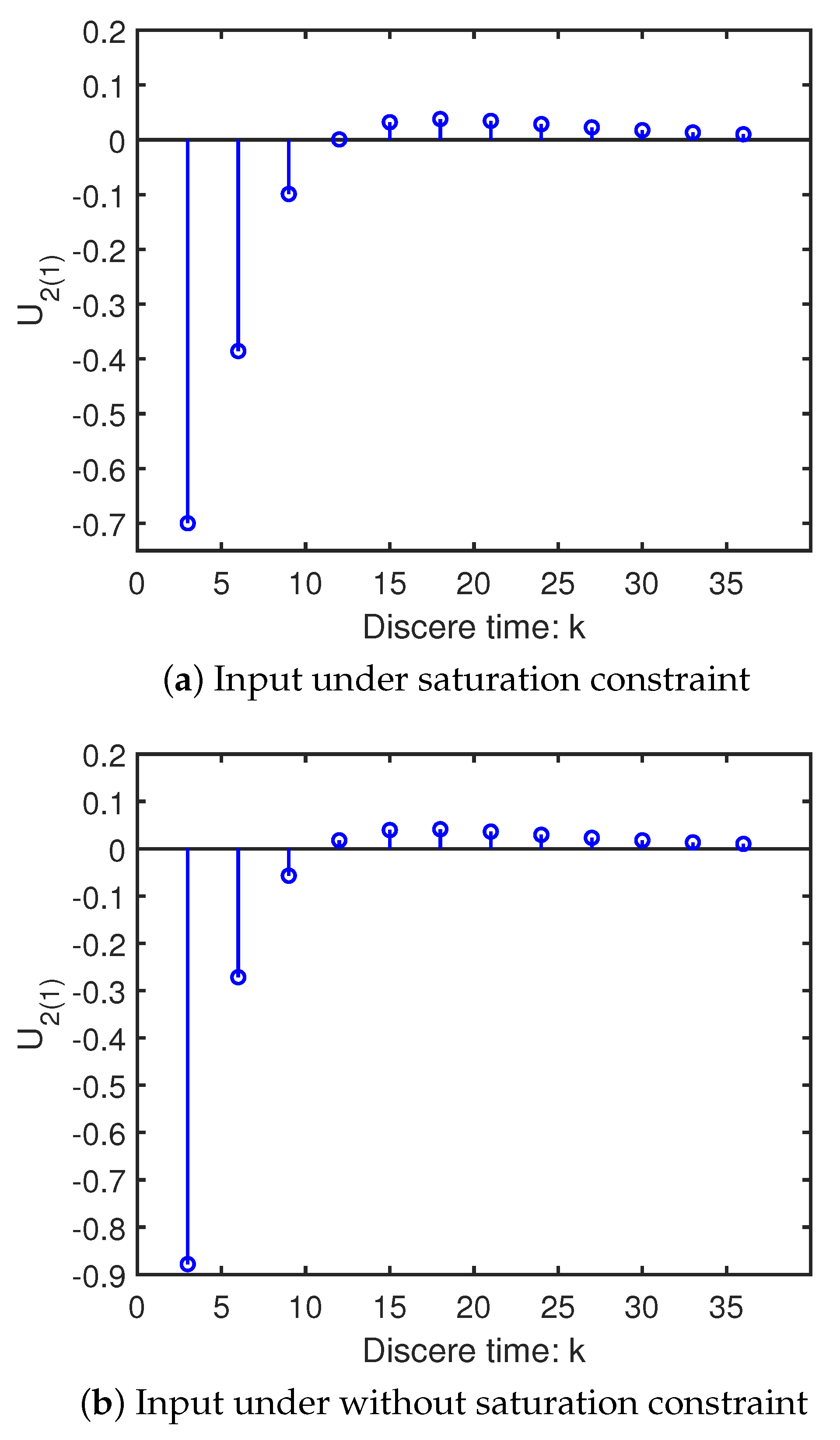
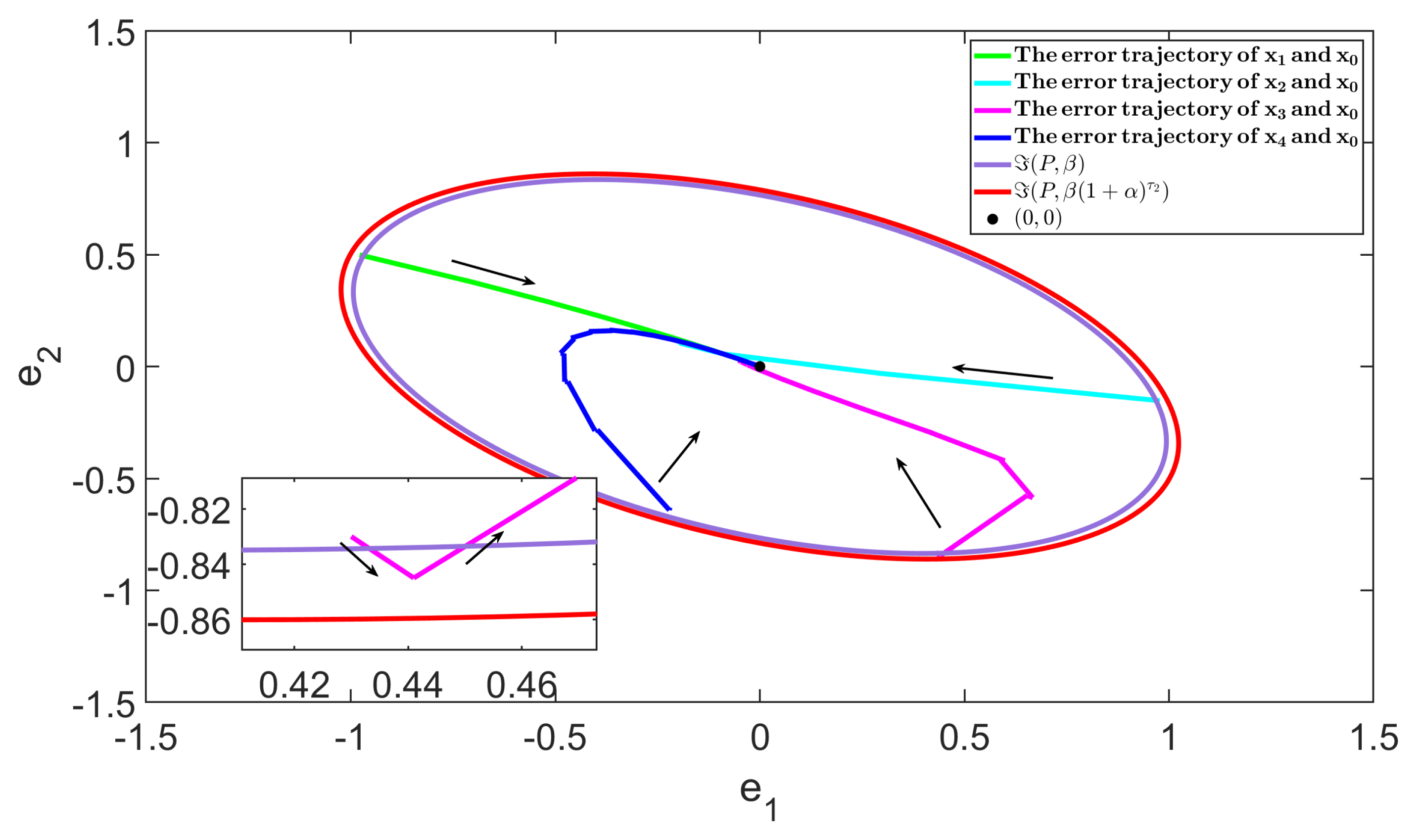
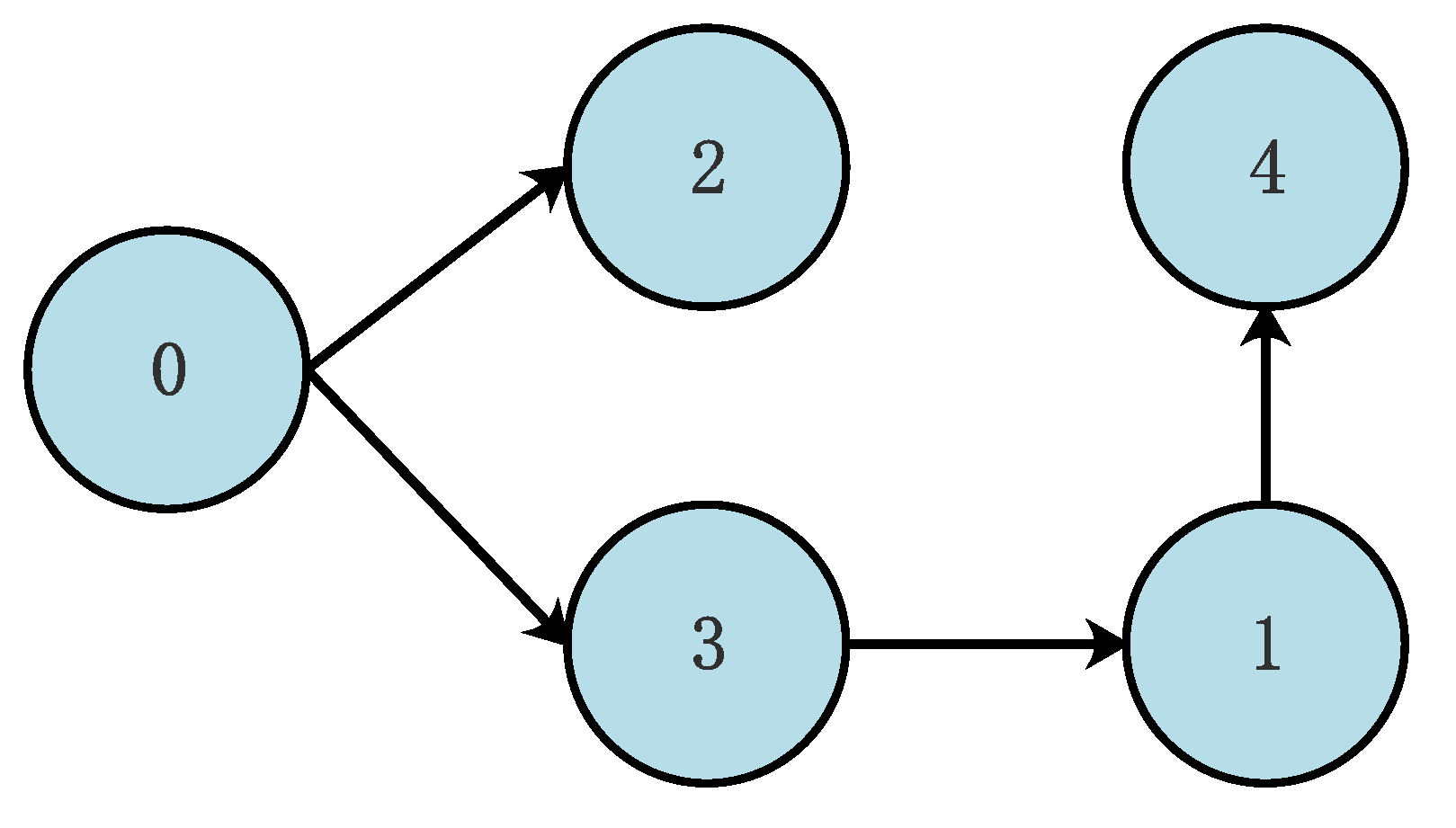
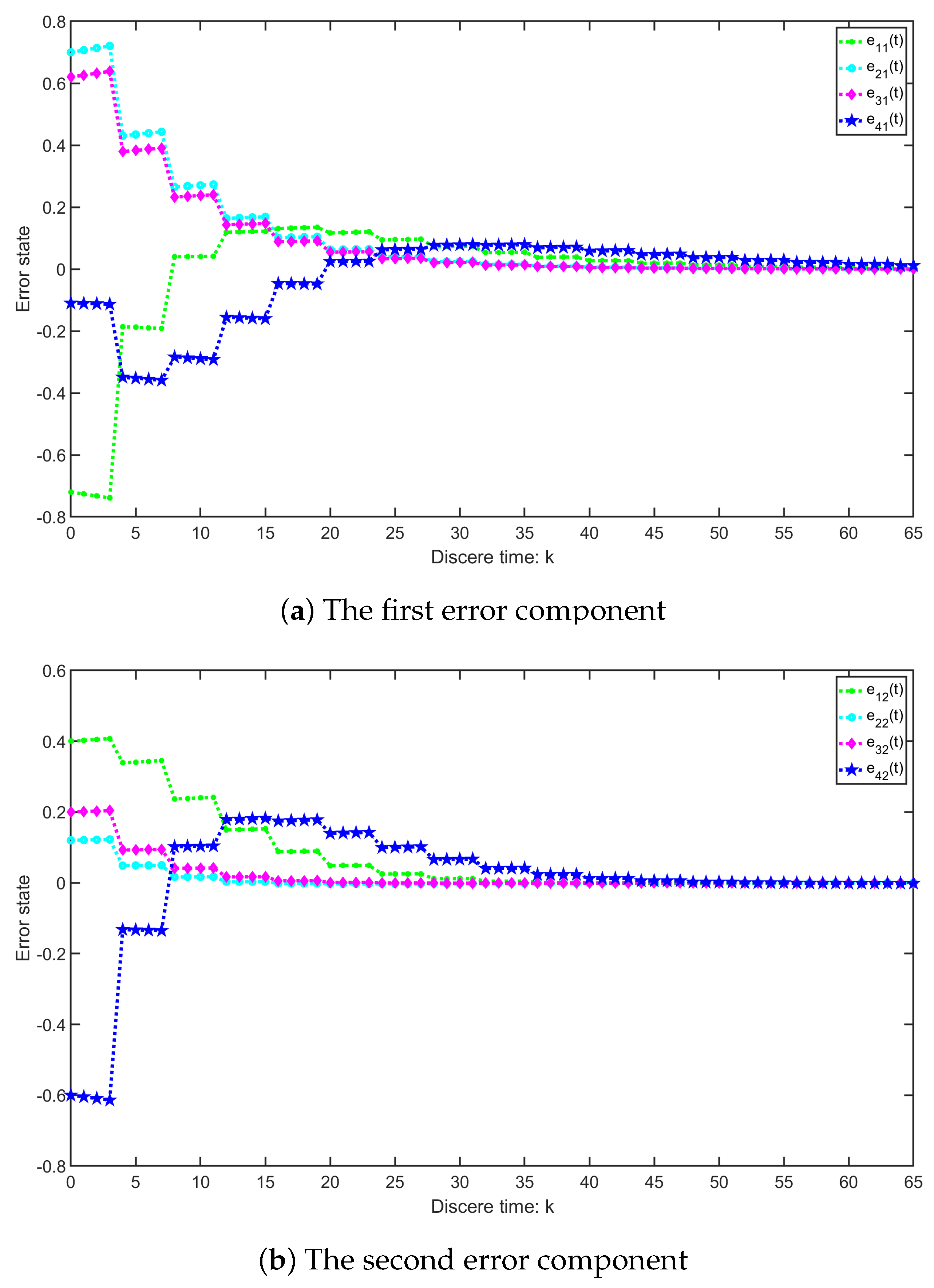
4.1. Example 1
4.2. Example 2
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El Romeh, A.; Mirjalili, S. Theoretical Framework and Practical Considerations for Achieving Superior Multi-Robot Exploration: Hybrid Cheetah Optimization with Intelligent Initial Configurations. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.; Chen, W.H.; Lu, X. Hierarchical Hybrid Control for Scaled Consensus and Its Application to Secondary Control for DC Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 53, 4446–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Chen, C.P.; Lai, G.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Y. Integrated nonholonomic multi-robot consensus tracking formation using neural-network-optimized distributed model predictive control strategy. Neurocomputing 2023, 518, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Su, H. Consensus of matrix-weighted hybrid multiagent systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 53, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Xia, K.; Zuo, Z.; Ding, Z. Distributed Interval Consensus of Multiagent Systems with a Pulse Width Modulation Protocol. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2023, 68, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Lewis, F.L.; Zeng, Z. Containment Control for Multiagent Systems Under Two Intermittent Control Schemes. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2019, 64, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Dong, X.; Li, Q.; Ren, Z. Time-varying formation tracking for high-order multi-agent systems with switching topologies and a leader of bounded unknown input. J. Frankl. Inst. 2018, 355, 2808–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olfati-Saber, R.; Fax, J.A.; Murray, R.M. Consensus and cooperation in networked multi-agent systems. Proc. IEEE 2007, 95, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zeng, Z. Asynchronous impulsive protocols with asymmetric feedback saturation on leader-based formation control of multiagent systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 52, 9931–9942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Jabbari, F.; Sun, X.M. Leader–Follower Consensus of Linear Multiagent Systems with Magnitude and Rate Saturation and an Active Leader. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2023, 68, 5584–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ji, Z. Dynamic event-triggered consensus of general linear multi-agent systems with adaptive strategy. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 3440–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lewis, F.L.; Sun, C. Observer-based resilient consensus control for heterogeneous multiagent systems against cyberattacks. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2022, 10, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Xu, Y.; Sun, J. Event-triggered predictive control for linear discrete-time multi-agent systems. Neurocomputing 2022, 505, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, J.L.; Wu, H.N.; Huang, T. Passivity-based finite-Time lag consensus for nonlinear multi-agent systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 69, 3224–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scola, I.R.; Carrillo, L.R.G.; Hespanha, J.P. Limbic System-Inspired Performance-Guaranteed Control for Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems with Uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 34, 4196–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Xie, L. Adaptive Neural Consensus of Unknown Non-Linear Multi-Agent Systems with Communication Noises under Markov Switching Topologies. Mathematics 2024, 12, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zheng, W.X.; Tang, Y.; Jin, X. Stability analysis for impulsive stochastic time-varying systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2022, 68, 2584–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Li, X.; Niu, S.; Lu, X. Input-to-state stability of positive delayed neural networks via impulsive control. Neural Netw. 2023, 164, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Mu, X. Event-Triggered Impulsive Control for Nonlinear Stochastic Systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 7805–7813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.P.; Tang, Z.; Park, J.H.; Feng, J. Impulsive time window based quasi-consensus on stochastic nonlinear multi-agent systems. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 3602–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Liu, X.; He, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, S. Hybrid Event-Triggered and Impulsive Control Strategy for Multiagent Systems with Switching Topologies. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 6283–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Peng, S.; Wang, Y. Leader-Following Consensus of Discrete-Time Stochastic Nonlinear Multiagent Systems under Fixed and Switching Topologies via Impulsive Control. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 16, 6021–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Peng, S.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T. Leader-following mean-square consensus of stochastic multiagent systems with ROUs and RONs via distributed event-triggered impulsive control. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 52, 1836–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.W.; Shi, Y.L.; Yan, H.; Han, B.X.; Guan, Z.H. Secure consensus of multiagent systems via impulsive control subject to deception attacks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 70, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ren, H. Output Consensus Problem for Linear Heterogeneous Multiagent Systems with Dynamic Event-Based Impulsive Control. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2022, 53, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasca, D.M. Pulse Power Failure Modes in Semiconductors. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1970, 17, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmanpour, Y.; Mehdi Arefi, M.; Khayatian, A.; Kaynak, O. Event-Triggered Fuzzy Adaptive Leader-Following Tracking Control of Nonaffine Multiagent Systems with Finite-Time Output Constraint and Input Saturation. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 30, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Zuo, W.; Gao, H.; Xu, S. Distributed robust semiglobal consensus with matched uncertainties and input saturation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 69, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Deng, F.; Wan, F.; Yu, P.; Sun, Y. Sampled-Data Stabilization for Stochastic Systems Subject to Input Saturation and Its Application to Synchronization of Two Chua’s Circuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 70, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Lin, Z. Control Systems with Actuator Saturation: Analysis and Design; Birkhäuser: Boston, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.; Tarbouriech, S. Antiwindup design with guaranteed regions of stability: An LMI-based approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2005, 50, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Su, H.; Zeng, Z. Output-Feedback Global Consensus of Discrete-Time Multiagent Systems Subject to Input Saturation via Q-Learning Method. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Z. Semiglobal Robust Consensus of Discrete-Time MASs Subject to Input Saturation and Additive Perturbations. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2023, 68, 7997–8004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Shi, P. Semiglobal Tracking Cooperative Control for Multiagent Systems with Input Saturation: A Multiple Saturation Levels Framework. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2021, 66, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.W. Distributed leaderless impulsive consensus of non-linear multi-agent systems with input saturation. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst. 2020, 36, 100855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, X.; Yan, H.; Huang, T. Distributed Edge Event-Triggered Control of Nonlinear Fuzzy Multiagent Systems with Saturation Constraint Hybrid Impulsive Protocols. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 30, 4142–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Jiang, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Yan, H.; Huang, T. Control for Nonlinear Fuzzy Time-delay Multi-agent Systems: Two Kinds of Distributed Saturation-constraint Impulsive Approach. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 31, 2861–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Huang, J. An Overview of Recent Advances in the Event-Triggered Consensus of Multi-Agent Systems with Actuator Saturations. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.J.; Liu, H.T. Semi-global stabilization of discrete-time linear systems with unsymmetrical saturation. ISA Trans. 2019, 92, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Feng, G.; Li, C. Stability Analysis on Discrete-Time Linear System with Asymmetric Saturation Impulsive Inputs. In Proceedings of the 2020 7th International Conference on Information, Cybernetics, and Computational Social Systems (ICCSS), Guangzhou, China, 13–15 November 2020; pp. 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wen, S.X.; Sun, X.M. Anti-Windup Synthesis for Linear Systems with Asymmetric Input Saturation: Application to Aircraft Engine Control. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 3214–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Chen, G.; Cao, M. Some necessary and sufficient conditions for second-order consensus in multi-agent dynamical systems. Automatica 2010, 46, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tanaka, K.; Griffin, M. An approach to fuzzy control of nonlinear systems: Stability and design issues. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 1996, 4, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Hua, C.; You, X.; Ahn, C.K. Leader-Following Consensus Control for Uncertain Feedforward Stochastic Nonlinear Multiagent Systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Q.; Chen, G.; Tian, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. Leader-Following Consensus of Discrete-Time Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems with Asymmetric Saturation Impulsive Control. Mathematics 2024, 12, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12030469
Yuan Q, Chen G, Tian Y, Yuan Y, Zhang Q, Wang X, Liu J. Leader-Following Consensus of Discrete-Time Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems with Asymmetric Saturation Impulsive Control. Mathematics. 2024; 12(3):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12030469
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Qiao, Guorong Chen, Yuan Tian, Yu Yuan, Qian Zhang, Xiaonan Wang, and Jingcheng Liu. 2024. "Leader-Following Consensus of Discrete-Time Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems with Asymmetric Saturation Impulsive Control" Mathematics 12, no. 3: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12030469
APA StyleYuan, Q., Chen, G., Tian, Y., Yuan, Y., Zhang, Q., Wang, X., & Liu, J. (2024). Leader-Following Consensus of Discrete-Time Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems with Asymmetric Saturation Impulsive Control. Mathematics, 12(3), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12030469





