Information–Theoretic Analysis of Visibility Graph Properties of Extremes in Time Series Generated by a Nonlinear Langevin Equation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Model
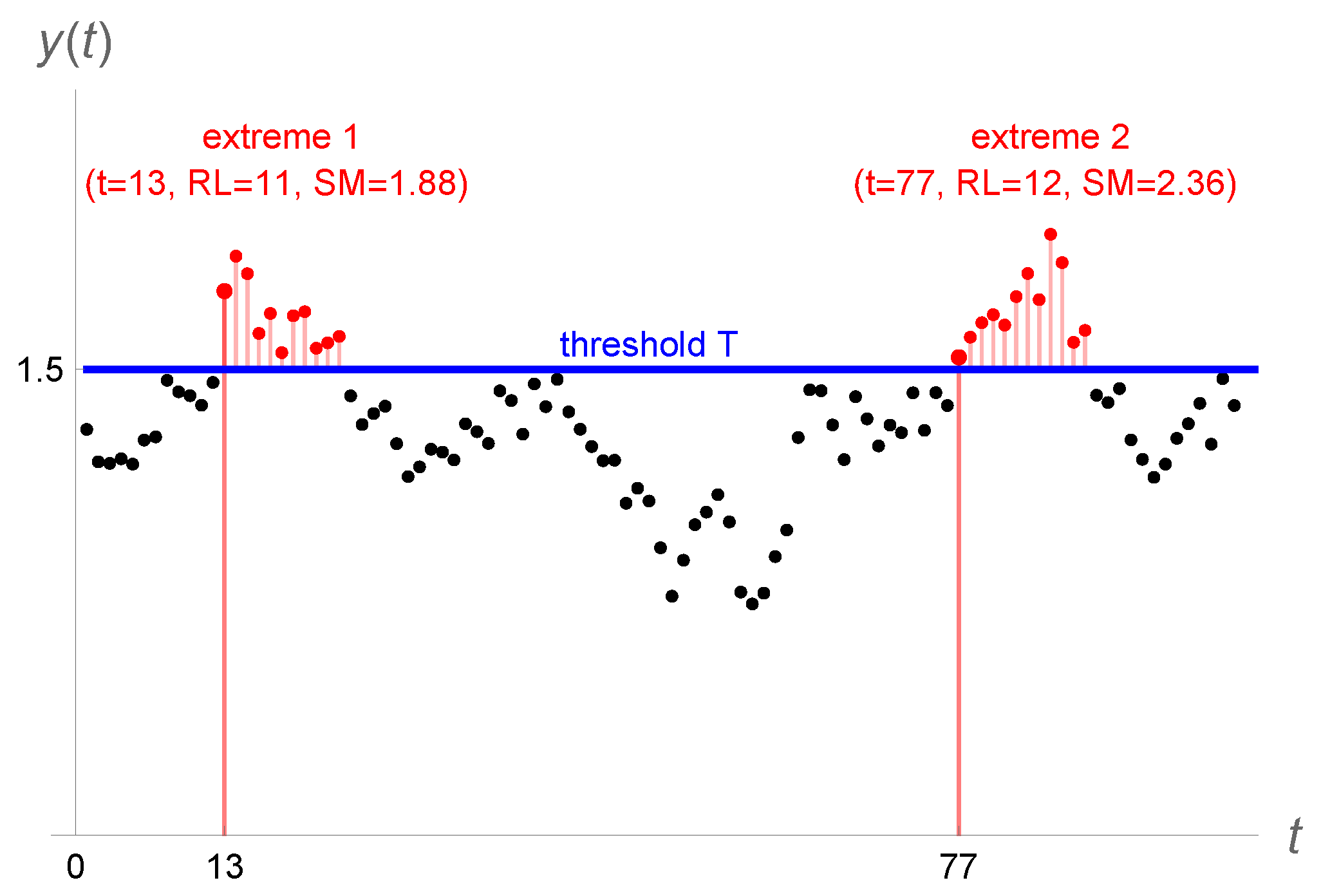
3. Definition of Extremes
4. The Fisher–Shannon Information Plane
5. The Visibility Graph
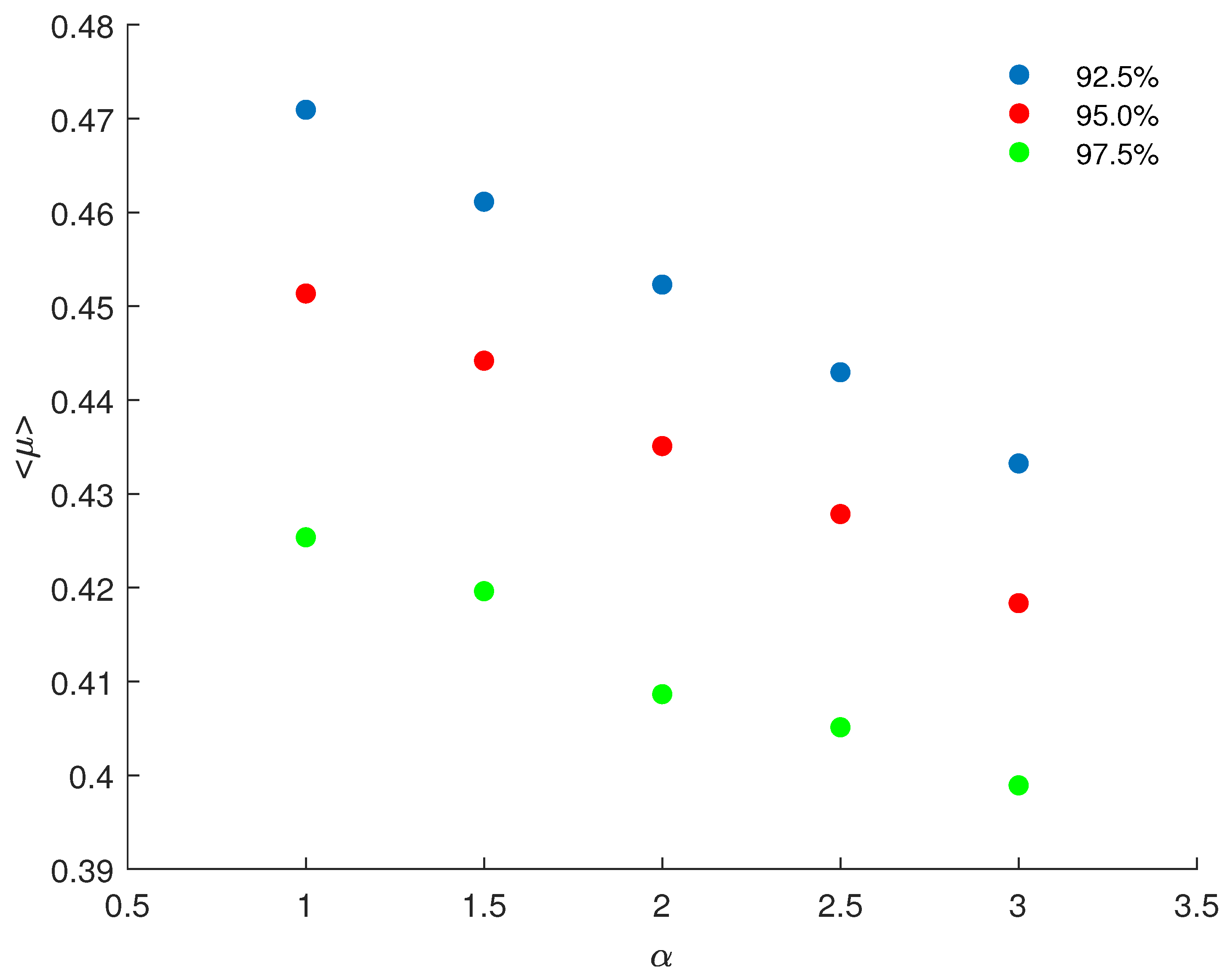
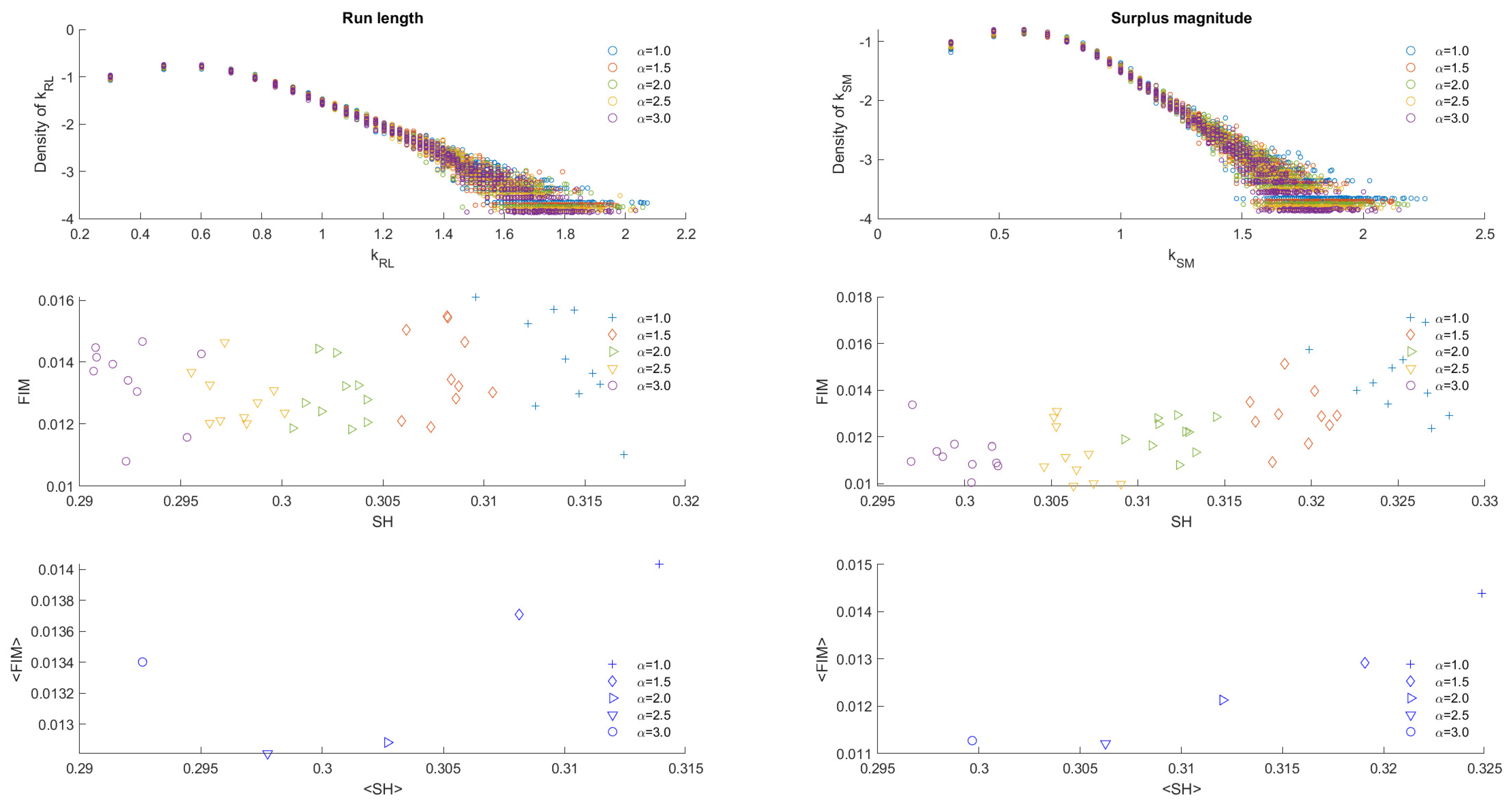
6. Results
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leadbetter, M.R.; Lindgren, G.; Rootzen, H. Extremes and Related Properties of Random Sequences and Processes; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Embrechts, P.; Kluppelberg, C.; Mikosch, T. Modelling Extremal Events for Insurance and Finance; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Blender, R.; Fraedrich, K.; Sienz, F. Extreme event return times in long-term memory processes near 1/f. Nonlinear Processes Geophys. 2008, 15, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhanam, M.S.; Kantz, H. Return interval distribution of extreme events and long-term memory. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 78, 051113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, S.O. Mathematical Analysis of Random Noise. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1945, 24, 46–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratonovich, R.L. Topics in the Theory of Random Noise, Volume II; Gordon and Breach: London, UK, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, H.; Leadbetter, M.R. Stationary and Related Stochastic Processes Sample Function Properties and Their Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Nordin, C.F.; Rosbjerg, D.M. Applications of crossing theory in hydrology. Bull. Int. Assoc. Sci. Hydrol. 1970, 15, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavliotis, G.A. Stochastic Processes and Application; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Small, M. Complex network from pseudoperiodic time series: Topology versus dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 238701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Small, M. Superfamily phenomena and motifs of networks induced from time series. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19601–19605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, B. An approach to Hang Seng index in Hong Kong stock market based on network topological statistics. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, B.H. Extracting hidden fluctuation patterns of Hang Seng stock index from network topologies. Phys. A 2007, 378, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donner, R.V.; Zou, Y.; Donges, J.F.; Marwan, N.; Kurths, J. Recurrence networks—A novel paradigm for nonlinear time series analysis. New J. Phys. 2010, 12, 033025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donner, R.V.; Small, M.; Donges, J.F.; Marwan, N.; Zou, Y.; Xiang, R.; Kurths, J. Recurrence-based time series analysis by means of complex network methods. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2011, 21, 1019–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Jin, N. Complex network from time series based on phase space reconstruction. Chaos 2009, 19, 033137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhou, W.X. Superfamily classification of nonstationary time series based on DFA scaling exponents. J. Phys. Math. Theor. 2010, 43, 495005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sinatra, R.; Condorelli, D.; Latora, V. Networks of motifs from sequences of symbols. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 178702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacasa, L.; Luque, B.; Ballesteros, F.; Luque, J.; Nuno, J.C. From time series to complex networks: The visibility graph. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4972–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ashuri, B.; Shyr, Y.; Deng, Y. Forecasting construction cost index based on visibility graph: A network approach. Phys. A 2018, 493, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y. Visibility graph network analysis of gold price time series. Phys. A 2013, 392, 3374–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, D.; Wang, Q. Visibility graph analysis on quarterly macroeconomic series of China based on complex network theory. Phys. A 2012, 391, 6543–6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wei, B.; Zhan, J.; Xie, C.; Zhou, D. A visibility graph power averaging aggregation operator: A methodology based on network analysis. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2016, 101, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hu, Y.; Mahadevan, S.; Deng, Y. A visibility graph averaging aggregation operator. Phys. A 2014, 403, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Hillebrand, A.; Gouw, A.A.; Stam, C.J. Horizontal visibility graph transfer entropy (HVG-TE): A novel metric to characterize directed connectivity in large-scale brain networks. NeuroImage 2017, 156, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, L.; Lovallo, M.; Pierini, J.O. Visibility graph approach to the analysis of ocean tidal records. Chaos Solit. Fractals 2012, 45, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, L.; Lovallo, M.; Aggarwal, S.K.; Khan, P.K.; Rastogi, B.K. Visibility graph analysis of 2003–2012 earthquake sequence in Kachchh region, Western India. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2016, 173, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnevis, N.; Taborda, R.; Azizzadeh-Roodpish, S.; Telesca, L. Analysis of the 2005–2016 earthquake sequence in Northern Iran using the visibility graph method. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2017, 174, 4003–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizzadeh-Roodpish, S.; Cramer, C.H. Visibility graph analysis of Alaska crustal and Aleutian subduction zone seismicity: An investigation of the correlation between b value and k–M slope. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2018, 175, 4241–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Oregon, J.; Lovallo, M.; Telesca, L. Visibility graph analysis of synthetic earthquakes generated by the Olami–Feder–Christensen spring-block model. Chaos 2020, 30, 093111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, L.; Thai, A.T.; Lovallo, M.; Cao, D.T.; Nguyen, L.M. Shannon Entropy Analysis of Reservoir-Triggered Seis-micity at Song Tranh 2 Hydropower Plant, Vietnam. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Luo, G.; Liu, M. The K-M Slope: A Potential Supplement for b-Value. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2023, 94, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, G. Topological pattern recognition for point cloud data. Acta Numer. 2014, 23, 289–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley-Boevey, W. Decomposition of pointwise finite-dimensional persistence modules. J. Algebra Its Appl. 2015, 14, 1550066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea, J.A.; Harer, J. Sliding windows and persistence: An application of topological methods to signal analysis. Found. Comput. Math. 2015, 15, 799–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea, J.A. Topological time series analysis. N. Am. Math. Soc. 2019, 66, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksendal, B. Stochastic Differential Equations: An Introduction with Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, R.; Peinke, J.; Sahimi, M.; Reza Rahimi Tabar, M. Approaching complexity by stochastic methods: From biological systems to turbulence. Phys. Rep. 2011, 506, 87–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, E. Modelling with Ito Stochastic Differential Equations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Coffey, W.; Kalmykov, Y. The Langevin Equation: With Applications to Stochastic Problems in Physics, Chemistry, and Electrical Engineering; World Scientific: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Grasman, J.; van Herwaarden, O.A. Asymptotic Methods for the Fokker-Planck Equation and the Exit Problem in Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rümelin, W. Numerical treatment of stochastic differential equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 1982, 19, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczyk, K. Stochastic Differential Equations with Applications to Physics and Engineering; Kluwer Academic Publishers B. V.: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- May, R.M. Stability in random fluctuating versus deterministic environments. Am. Nat. 1973, 107, 621–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guterrez, R.; Gutierrez-Sanchez, R.; Nafidi, A.; Ramos, E. A diffusion model with cubic drift: Statistical and computational aspects and applications to modelling of the global CO2 emission in Spain. Environmetrics 2007, 18, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, L.; Czechowski, Z.; Lovallo, M. Multifractal analysis of time series generated by discrete Ito equations. Chaos 2015, 25, 063113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero-Campos, C.; Bernaola-Galván, P.; Ivanov, P.C.; Carpena, P. Phase transitions in the first-passage time of scale-invariant correlated processes. Phys. Rev. E—Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2012, 85, 011139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Ramirez, I.; Guzman-Vargas, L. Scaling properties of excursions in heartbeat dynamics. Europhys. Lett. 2010, 89, 38008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martius, O.; Pfahl, S.; Chevalier, C. A global quantification of compound precipitation and wind extremes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 7709–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froidevaux, P.; Schwanbeck, J.; Weingartner, R.; Chevalier, C.; Martius, O. Flood triggering in switzerland: The role of daily to monthly preceding precipitation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 3903–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klawa, M.; Ulbrich, U. A model for the estimation of storm losses and the identification of severe winter storms in Germany. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2003, 3, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignat, C.; Bercher, J. Analysis of signals in the Fisher–Shannon information plane. Phys. Lett. A 2003, 312, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravetti, M.; Carpi, L.; Gonçalves, B.; Frery, A.; Rosso, O. Distinguishing noise from chaos: Objective versus subjective criteria using horizontal visibility graph. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosso, O.; Olivares, F.; Zunino, L.; De Micco, L.; Aquino, A.; Plastino, A.; Larrondo, H. Characterization of chaotic maps using the permutation Bandt-Pompe probability distribution. Eur. Phys. J. B 2013, 86, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, F.; Plastino, A.; Rosso, O. Contrasting chaos with noise via local versus global information quantifiers. Phys. Lett. A 2012, 376, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, B.A.; Carpi, L.; Rosso, O.A.; Ravetti, M.G. Time series characterization via horizontal visibility graph and Information Theory. Phys. A 2016, 464, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R. On the Mathematical Foundations of Theoretical Statistics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1922, 222, 309–368. [Google Scholar]
- Frieden, B. Science from Fisher Information: A Unification; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Frieden, B.R. Physics from Fisher Information: A Unification; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Moreno, P.; Yañéz, R.; Dehesa, J. Discrete Densities and Fisher Information. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Difference Equations and Applications, Estoril, Portugal, 19–23 October 2009; pp. 291–298. [Google Scholar]
- Telesca, L.; Czechowski, Z. Fisher-Shannon Investigation of the Effect of Nonlinearity of Discrete Langevin Model on Behavior of Extremes in Generated Time Series. Entropy 2023, 25, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czechowski, Z.; Telesca, L. Effect of Nonlinearity of Discrete Langevin Model on Behavior of Extremes in Generated Time Series. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 183, 114927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
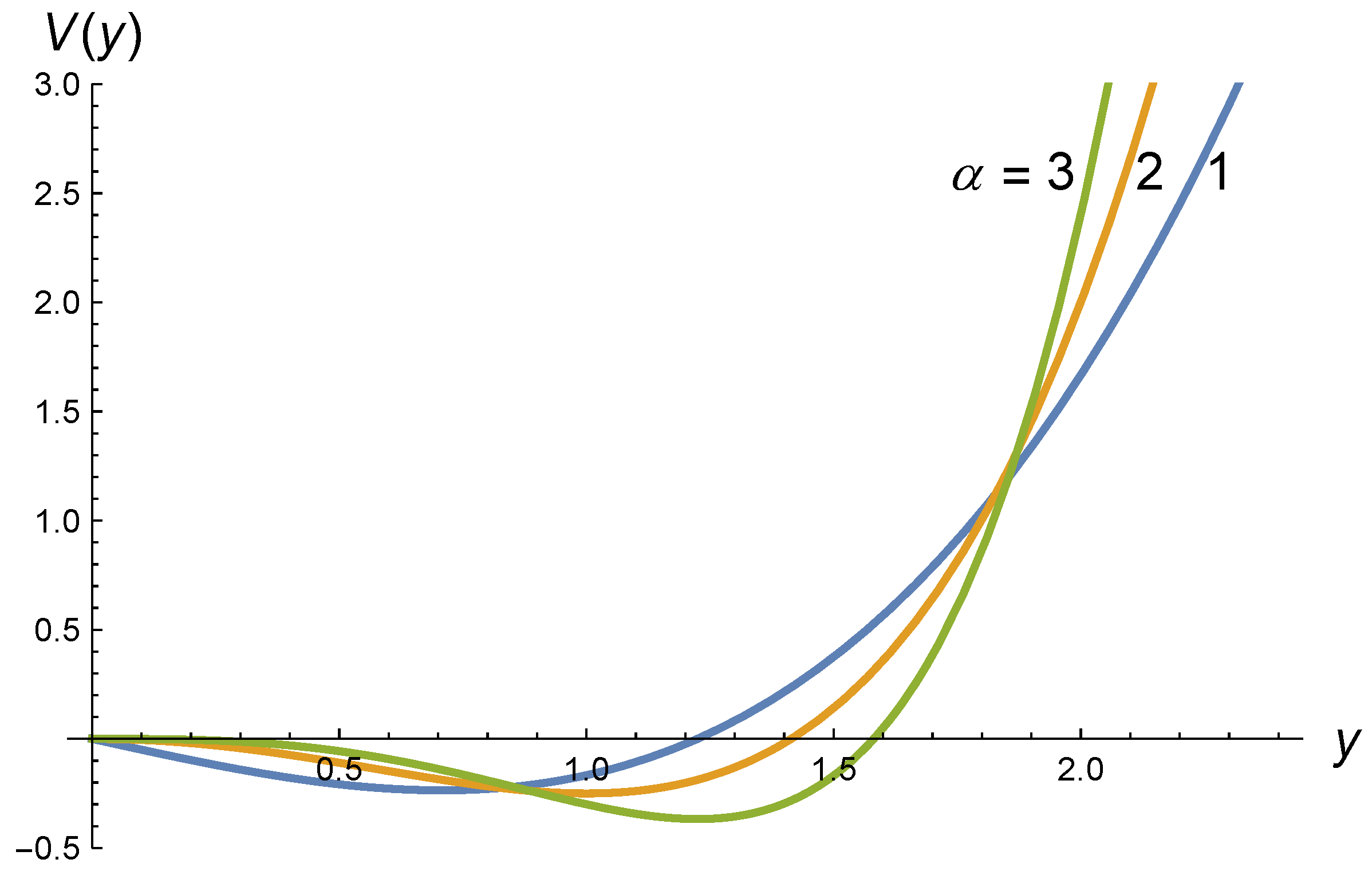





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Telesca, L.; Czechowski, Z. Information–Theoretic Analysis of Visibility Graph Properties of Extremes in Time Series Generated by a Nonlinear Langevin Equation. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3197. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12203197
Telesca L, Czechowski Z. Information–Theoretic Analysis of Visibility Graph Properties of Extremes in Time Series Generated by a Nonlinear Langevin Equation. Mathematics. 2024; 12(20):3197. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12203197
Chicago/Turabian StyleTelesca, Luciano, and Zbigniew Czechowski. 2024. "Information–Theoretic Analysis of Visibility Graph Properties of Extremes in Time Series Generated by a Nonlinear Langevin Equation" Mathematics 12, no. 20: 3197. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12203197
APA StyleTelesca, L., & Czechowski, Z. (2024). Information–Theoretic Analysis of Visibility Graph Properties of Extremes in Time Series Generated by a Nonlinear Langevin Equation. Mathematics, 12(20), 3197. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12203197






