Abstract
The laminar movement in an expanding and contracting permeable pipe or surface has recently attracted the attention of many scholars owing to its application in engineering and biological processes. The objective of the current study is to examine the influence of chemical processes on magnetized nanofluid flow over extending or shrinking permeable pipes with a heat reservoir. The flow equations are renovated into first ODEs by introducing the new variable and then numerically solved by RK4 with a shooting procedure. The effect of emerging factors on the flow features is observed using graphs and elaborated in detail. From the analysis, the temperature is raised when the heat source is increased in both cases of wall expansion or contraction but declines in the case of heat sinks. In the case of a heat source, the temperature rises as the Hartmann and Prandtl numbers are enhanced, but in the case of a heat sink, the temperature falls. In the presence of heat sinks and injections, when the thermophoresis factor is increased, the concentration of nanoparticles is increased in both wall expansion and contractions. In both situations of wall extension or contraction, along with injection, the concentration of nanoparticles is a decreasing function of , while the concentration of nanoparticles is an increasing function in the case of a heat source. Additionally, for the confirmation of the RK4 code, the total average square residue error and average square residue error are also presented. For the stability analysis, the current work is compared with published work, and excellent agreement is established. The novelty of the present study is to investigate the effect of chemical reaction on magnetized nanofluid flow over extending and shrinking porous pipes with heat generation and absorption.
Keywords:
RK4 and HAM; expanding/contracting pipe; heat generation/absorption; total and average square residue errors; stability analysis; nanofluid flow; chemical reaction MSC:
76D05; 76-10
1. Introduction
The establishment of nanofluid innovation is a crucial field of research in physics, industry, mathematics, and chemical science. For the majority of applications with a practical purpose, designers and scientists work to successfully communicate sufficient knowledge of the heat transfer mechanism in nanofluids. Nanofluids are essential in a variety of applications, such as heat exchangers, freezers, hybrid-driven motors, food processing, and chips. The term “nanofluid” was originally used by Choi et al. [1]. Nanoparticles are now the subject of major scientific investigation because of their many applications in biological, optical, and electrical areas. They may be discovered in nanometals [2,3,4,5,6,7] and graphite, as well as oxides, carbides, nitrides, and metals such as copper and aluminum. Buongiorno investigated the diffusion of heat in nanofluids (NFs) [8]. Moreover, Buongiorno [9] concluded that Brownian and thermophoresis diffusion would be important when turbulent impacts are absent. The unsteady BLF over a flowing sheet was examined by Rosca et al. [10] using Buongiorno’s model. Kuznetsov et al. [11] studied the significance of bioconvection on MHD tangent hyperbolic nanofluid flow of irregular thickness across a slender elastic surface. The micropolar dusty fluid with coriolis force effects on dynamics of MHD rotating fluid when lorentz force is significant by Lou et al. [12]. The magnetic BLF toward an extended sheet, including nanoparticles, was examined analytically by Mustafa et al. [13] using HAM. Alsaedi et al. [14] have achieved an analytical solution for the SPF when the heat source passes via a convective sheet. Chamkha et al. [15] studied the convective BLF of NFs approaching a vertical sheet. Malvandi et al. [16] discussed NFFs (nanofluid flows) employing a vertical pipe, utilizing Buongiomo’s model (BM). Across a vertical tube, Akbari et al. [17] examined a fully evolved NFF. Ellahi [18] found a mathematical solution for the magnetic and changing viscosity viscous fluid within a pipe. An MHD NFF, incorporating the slip impact at the border, was seen by Uddin et al. [19] across the extended sheet. To explore the BLF traveling via a vertical stretched channel, Xu et al. [20] and Malik et al. [21] studied the BM and Casson nanofluids, respectively. The nonlinear movements of axisymmetric ternary hybrid nanofluids in a thermally radiated expanding or contracting permeable Darcy Walls with different shapes and densities using simple linear regression by Raju et al. [22]. Further examined were the Brownian and thermophoresis variables. Ramesh et al. [23] developed a flow of hybrid CNTs past a rotating sphere subjected to thermal radiation and thermophoretic particle deposition. Presently, Srinivas et al. [24] have researched the MHD flow of NFs in a permeability-expanding pipe. Hedayati et al. [25] very recently investigated titania water-related nanofluids across a ferromagnetic vertical cylindrical conduit. Malvandi et al. [26] also looked at a alumina water-based nanofluid across a vertical channel using the Lorentz force effect. Chemical engineering, metallurgy, radioactive nuclear safety, photovoltaic collectors, and other nanotechnology and scientific fields have been shown to significantly impact heat transport [27,28,29]. The impact of chemical efficiency on blood flow using Walter’s B model across a tapered artery was taken into consideration by Nadeem et al. [30]. Hayat et al.’s [31] examined Maxwell fluids’ biochemical processes. Abdul et al. [32] examined the chemical reactions taking place over a stretchy sheet that was saturated with nanofluids, utilizing the BLF. Kameswaran et al. [33] investigated uniform and heterogeneous chemical reactions across a porous stretching surface. The MHD laminar BLF, with a slip impact over a stretched permeable surface with chemical reactions, was numerically explored by Uddin et al. [34]. For free convection flow (FCF) across a horizontal surface containing nanofluids, an analytical solution was discovered [35]. Recently, Srinivas et al. [36] examined a viscoelastic fluid across a chemically stretched pipe. Uddin et al. [37] investigated the MHD FCBLF with NF chemical reactivity via a vertical surface. The laminar movement in an escalating or shrinking permeable pipe or surface has recently attracted the curiosity of many scholars owing to its application in engineering and biological developments, for example, in the transportation of natural fluids through stretching vessels, the synchronous rhythm of absorbent diaphragms, the respirational system, and the deterioration of the red-hot sheet in rock-solid engines [38,39,40]. The thermal flux and heat transfer have been studied by many researchers (see [41,42,43,44,45]). The unsteady fluid flow over semi-infinite stretching pipes with a heat source was examined by Boutros et al. [46] via the Lie group approach. Zeeshan [47] investigated the energy activation analysis for Maxwell fluid comprising molybdenum disulfide and graphene nanoparticles in engine-based fluid, enclosing the effect of isothermal wall temperature. Rasheed et al. [48] scrutinized the movement of micropolar fluid over an extended surface with thermal radiation influence. Zeeshan et al. [49] obtained the numerical solution for entropy generation by scrutinizing the second-order nanofluid’s thin film flow with error and stability analyses. Recently, the influence of heat and transfer analyses of nanofluids over a horizontal surface with thermal and magnetic field effects was investigated by Zeeshan et al. [50]. Raza et al. [51] investigated the movement of MHD Casson liquid over a porous sheet with extended and stationary walls. Khan et al. [52] obtained the exact solution of a Casson model movement situated with dust particles through a stretching surface enclosing the Lorentz forces. Similarly, Chabani et al. [53] numerically investigated a magnetized hybrid nanofluid over a porous trapezoidal inclusion.
The above study reveals that no effort towards the influence of chemical processes on magnetohydrodynamic NFFs over a stretchable permeable pipe enclosing the effect of a heat reservoir has been scrutinized so far. Such deliberation has a significant value in science and engineering study, including chips, refrigerators, hybrid powered motors, food improvement, heat exchangers, and so on. Keeping the overhead observations in view, the purpose of the recent study is to observe the inspiration of chemical processes on magnetized nanofluid flows over extending or shrinking permeable pipes with a heat reservoir. The flow characteristics are renovated into first ODEs by introducing the new variable and then numerically elucidated using the Runge–Kutta fourth-order method with a shooting technique [54]. The effect of emerging parameters on the flow features is observed using graphs and elaborated in detail. Additionally, the confirmation of RK4 is compared with HAM. For the stability analysis, the current work is likened to the available literature, and exceptional correlation is established.
2. Formulation of the Problem
The unsteady NFF of an electrically conducting fluid in a semi-infinite length over an equally porous pipe is considered. The pipe has at a radius, . The wall is the function of time that is expanding and shrinking with time. Figure 1 demonstrates the geometry of the present problem, in which its origin is taken at the center of the pipe, where -axis is parallel to the wall and is normal to the wall.
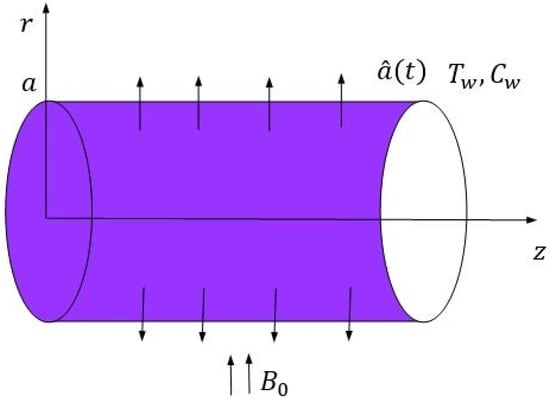
Figure 1.
Geometrical presentation of the problem.
The central equations are under these presumptions [16,17,18,19,20,21,22]:
where and represent directions, and , represent the components of the velocity. The fluid density is , thermal diffusivity is , time is , kinematic viscosity is , dimensional pressure is , magnetic field strength is , and electrical conductivity is , represents the specific heat, the average (mean) temperature is , Brownian and thermophoretic diffusion coefficients are and , respectively, and and stand for temperature and nanoparticle concentration, respectively; , while represents the first-order chemical reaction rate ( for a generative reaction (GR), for a destructive reaction (DR), and for no reaction).
The pertinent boundary constraints are
The wall permeability is represented by the A (injection/suction coefficient) in Equation (6), where, are the wall’s temperature and concentration, respectively.
Add a stream function that meets the continuity requirement in Equation (1)
where the dimensionless radial location is represented by . You can write the radial and axial velocity components as
One may obtain this by replacing Equation (10) with Equations (2) and (3) after removing pressure.
where is the Hartmann number (HN), and is the viscosity. The non-dimensional wall dilation rate is defined as , being positive for extension and negative for shrinkage. The associated boundary constraints from Equations (6) through (8) convert into
defines the permeation Reynolds number (PRN) as follows: is positive for inoculation but negative for suction, as you can see. By separately applying the transformations outlined by Si et al. [9] and Uchida and Aoki [7], a comparable solution with regard to both time and space may be created. It follows that for constant and To fulfil this requirement, the expansion ratio’s value must be determined by the beginning value.
where , define the initial radius and growth rate correspondingly. By integrating Equation (13) with regard to time, the temporal similarity transformation may be accomplished. The outcome is
It is demonstrated that the injection coefficient is constant since may be used to calculate an equation for the injection velocity. It is evident from Equations (13) and (14),
These boundary constraints are
One can normalize Equations (10), (16), and (17) by inputting Equation (18) and ignoring the “*”; we get
It should be noticed that Equation (19) describes the situation that Majdalani et al. [13] have outlined when and exist. The relationship between the temperature and the concentration in the pipe is as follows:
where and are the reference temperatures and concentrations of nanoparticles at the center. From Equation (21), the dimensionless temperature and nanoparticle concentration are
Equation (21) is substituted into Equations (4) and (5) to get
with the boundary constraints
Here , and represent the Prandtl number, Brownian motion, the thermophoresis factor, the Lewis number, the sink/heat source (i.e., for a heat sink and for a heat source), and the chemical reaction factor, respectively, and
3. Numerical Procedure and Convergence
The scheme of Equations (23)–(25) is solved by RK4. For this solution, Equations (23) and (25) are first transformed to the conventional first ODEs by introducing new variables and then solved numerically by keeping step size and obtaining the convergence criteria up to 10−5. For endorsement of the consequences, the HAM is also functional, and brilliant settlement is originated as shown in (Figure 2). The procedure of the numerical method is given in (Figure 3). Detailed information on this method is given in [31]. Additionally, the current effort is likened to the previous and brilliant settlement originated, as revealed in Table 1 and Table 2.
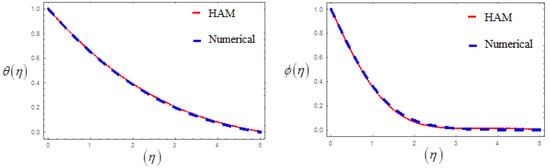
Figure 2.
Assessment of RK4 and HAM for .
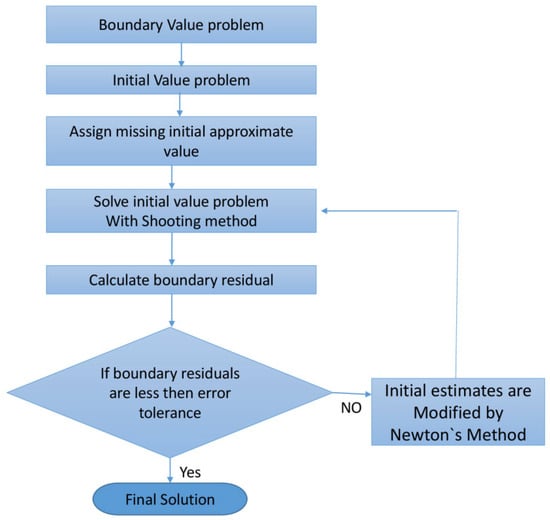
Figure 3.
Flow chart of the numerical algorithm.

Table 1.
Variation of radial velocity in the suction case for the viscous fluid; .

Table 2.
Variation of radial velocity in the suction case for the viscous fluid; .
4. Stability Analysis
The numerical solution has been obtained for the nonlinear differential equation for the temperature and concentration profiles. For the stability analysis of the mathematical problem, the present work is compared with the published work. Table 1 and Table 2 show that for up to 25 orders of approximation, the comparison of the present work and the published work reported by Srinivas et al. [49] shows excellent agreement.
5. Error Explanation
For most linear first-order differential equations, the RK4 approach yields solutions that are typically trustworthy. Significant errors are quite improbable, but that is because the conclusions are based on computer sampling and error calculations. Examining results using a solution that is derived with working precision that is higher than the Machine Precise standard is often helpful. The RK4 method is used to compute the answer to the issue with the usual work precision, and the same method is used to calculate the error with working precision-22. As errors are often rather small, it is useful to evaluate them on a logarithmic scale. The following graphs show the incorrect solutions we generated for the various physical parameters utilized in the model.
We initially conducted an error evaluation to check the validity of the process before establishing any physical predictions. This is the purpose for the creation of Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7. The minimum mistake 10−30 of the RK4 program is corrected during the solution by using the ND-Solve Mathematica package to reduce the overall average squared residual error (ASRE). We initially modified the thermal radiation factor and fixed and to observe the error for numerous orders of approximation. The greatest ASRE at various interpolation orders is shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5.
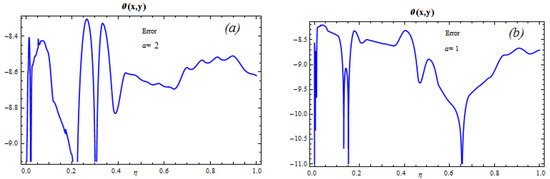
Figure 4.
Temperature error analysis for physical parameters (a) and (b) .
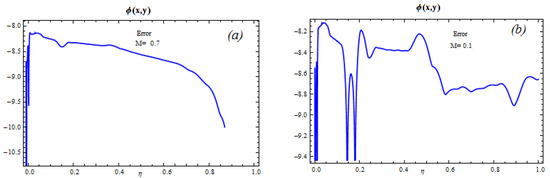
Figure 5.
Concentration error analysis for physical parameters (a) and (b) .
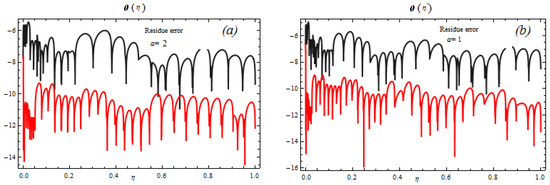
Figure 6.
Residue error for temperature for physical parameters (a) and (b) .
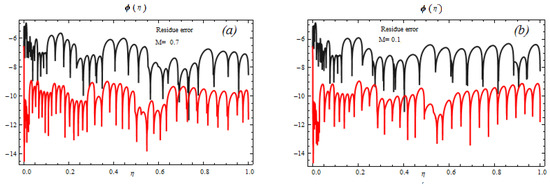
Figure 7.
Residue error for concentration for physical parameters (a) and (b) .
In Figure 4, it is seen that for , total ASRE and ASRE are decreasing as the order of approximation increases. Additionally, for , the error is streakily decreasing compared to the cases for , as exposed in Figure 5. By changing the magnetic parameter of and setting similarly distinct plots are given in Figure 6 and Figure 7, respectively. Averaged squared residual errors and total averaged squared residual errors both decrease for and as the order of approximation increases. It is also observed that for the error streakily reduces, as related to the cases for and and shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7.
6. Analysis and Discussion
This section examines the consequence of several physical factors on the flow characteristics, such as the Nusselt number, Sherwood number, non-dimensional temperature, and nanoparticle concentration. Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13, Figure 14, Figure 15, Figure 16, Figure 17, Figure 18, Figure 19, Figure 20 and Figure 21 provide a graphic representation of the outcomes against . The effect of numerous factors such as the thermophoresis factor , the heat source/sink factor , the wall extension ratio, the Hartmann number , the Prandtl number , the Brownian motion factor and the permeation parameter , the Lewis number , and the chemical reaction parameter are discussed in detail. For a better understanding of the physical interpretation of the physical parameters, we chose and . It should be emphasized that the variables and describe the magnitudes of Brownian movement and thermophoresis impacts, respectively. The greater quantities of and have stronger consequences. Hence, and can have any value between . Figure 8a, Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14b illustrate the influence of various parameters, including the sink parameter or heat source, the Brownian motion factor, the thermophoresis factor, the ratio of the wall extension, the Hartmann number, the permeation Reynolds factor, and the Prandtl number, on the temperature field. The effects of the Brownian factor on the temperature field for both situations of injection, including wall extension and shrinking, are exposed in Figure 8a,b. It is noted that the temperature rises in injection with wall expansion and contraction by enhancing for . In the injection situation, the concentration of nanoparticles migrates from the wall to the liquid, which causes a considerable rise in the temperature field. For , the opposite behavior is observed. Figure 9a,b illustrates how the heat source/sink parameter affects the temperature in the circumstances of both injections, combined with wall shrinking and expansion. It is observed that the heat source raises the temperature in both situations of injection, along with wall contraction and moderation, but a heat sink lowers it. The influence of the thermophoresis factor on energy is depicted in Figure 10a,b for the injection situation, along with wall extension and contraction. For a certain rise in , it is observed that the temperature is enhanced. Figure 11a,b show the relationship between temperature and the wall expansion ratio. In the event of wall extension, regardless of injection or suction, if it increases in the presence of a heat generation (i.e., ), then the temperature increases; if grows in the case of wall shrinkage, then the temperature decreases. However, in the event of a heat source, the behavior is the opposite (for ). The influence of the Harmann number (HN) on the temperature field is shown in Figure 12a,b. It has been noted that nanofluids exhibit similar properties to ordinary fluids in terms of temperature regarding the Harmann number. As grows, the temperature rises in the existence of a heat source for both the expansion and contraction of the wall. In a heat sink, the reverse observation is observed. Figure 13a,b explore the effect of the Prandtl number on the temperature. It is essential to remember that the Prandtl number describes liquid metals and oils. Larger values of are associated with high viscosity oils, whereas smaller values of define liquid metals with low viscosity and thermal conductivity. Here, , and corresponds to water, water at 4 °C, and human blood, individually. It is clear that in both scenarios of wall expansion and contraction associated with inoculation, the temperature falls as grows (i.e., rising thermal diffusivity) in the existence of a heat sink, but it improves in the context of a heat source. The relationship between the permeation Reynolds number and the temperature is seen in Figure 14a,b. It has been found that the boundary layer thickness reduces with increasing injection, and as a consequence, the temperature declines in both scenarios of injection, together with wall extension and contraction. The reverse effect is observed in the case of suction, along with wall extension and contraction.
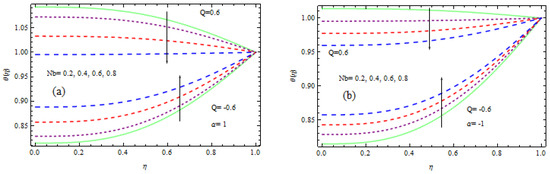
Figure 8.
(a,b) Influence of Brownian factor on temperature.
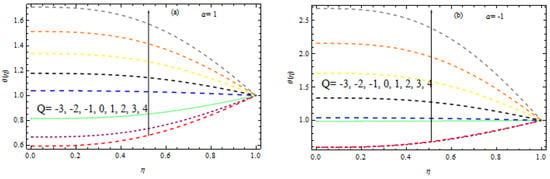
Figure 9.
(a,b) Influence of heat source factor on temperature.
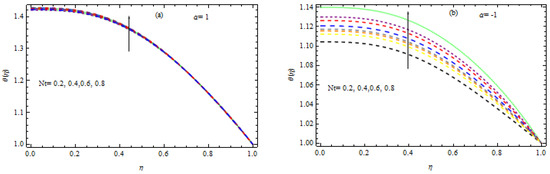
Figure 10.
(a,b) Influence of Nt on temperature.
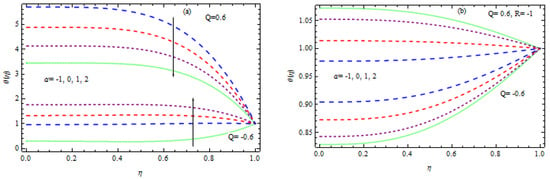
Figure 11.
(a,b) Influence of wall on temperature.
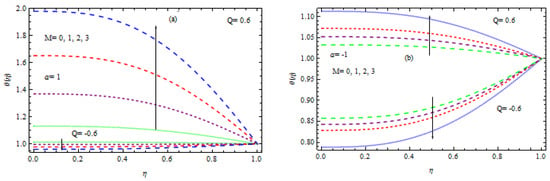
Figure 12.
(a,b) Influence of on temperature.
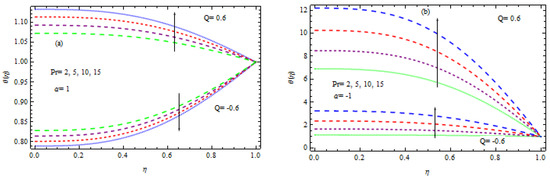
Figure 13.
(a,b) Influence of Pr on temperature.
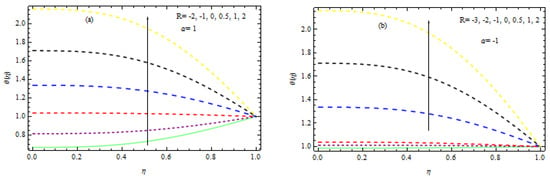
Figure 14.
(a,b) Influence of R on temperature.
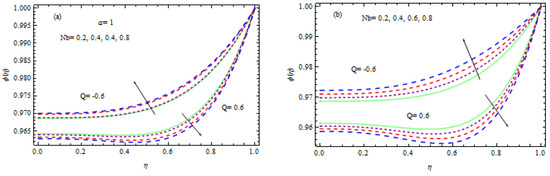
Figure 15.
(a,b) Influence of Nb on temperature.
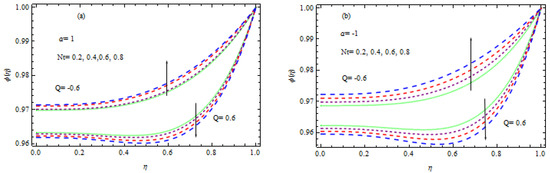
Figure 16.
(a,b) Influence of Nt on temperature.
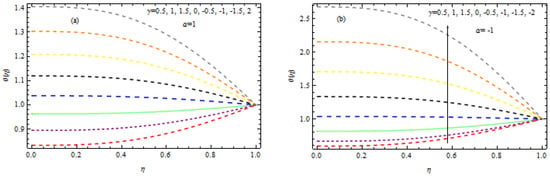
Figure 17.
(a,b) Influence of on temperature.
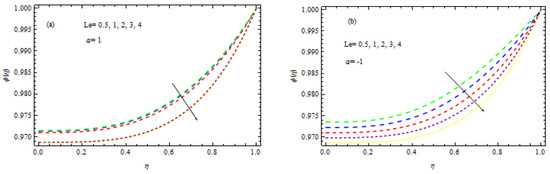
Figure 18.
(a,b) Influence of on concentration.
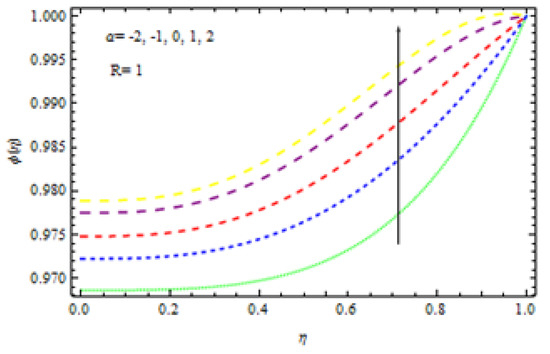
Figure 19.
Influence of on concentration.
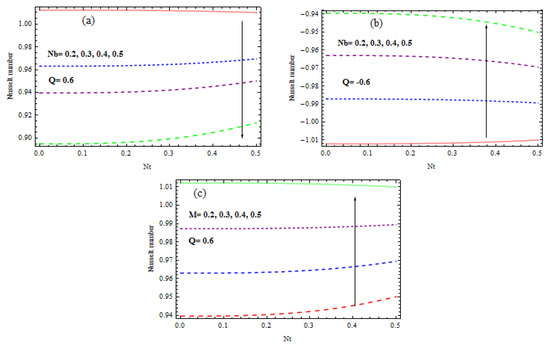
Figure 20.
(a–c) Variation of Nusselt number for (a) Nb when Q = 0.6, (b) Nb when Q = −0.6, (c) M.
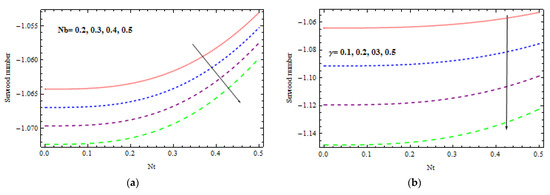
Figure 21.
Variation of Sherwood number by (a) Nb, (b)
Figure 15a,b, Figure 16, Figure 17 and Figure 18 show the influence of the Lewis number, the wall expansion ratio, thermophoresis, Brownian motion, and the chemical factor on the concentration of nanoparticles. Figure 15a,b demonstrate that the concentration field declines with the growing amount of in the occurrence of a heat sink, but the opposite trend is observed in the existence of heat generation and destruction for wall extension and shrinkage. The consequence of the thermophoresis factor on the concentration of nanoparticles is shown in Figure 16a,b. It is evident that for both developments of wall extension and shrinkage with injection, nanoparticle concentration is increased with increasing in the existence of a heat sink. From a physical standpoint, a larger mass flux is produced by a rise in the thermophoresis parameter due to the temperature difference; as a consequence, the concentration enhances. In the manifestation of a heat source, the reverse behavior is examined in the same figure. Figure 17a,b exhibit the influence of a chemical factor, , on the concentration field, where the parameter is negative for a generative reaction and positive for a destructive reaction. It is noted that for an increment in , there is a drop in nanoparticle concentration in the case of the destructive chemical process parameter (). Additionally, in the event of a generative chemical process (), the behavior is the opposite. Figure 18a,b show how the Lewis quantity effects . It is obvious that the function is a shrinking function of . When the values of the Lewis number are increased, the concentration of mass transfer is increased, which lowers nanoparticle concentration. The effect of the wall extension ratio on is seen in Figure 19. When increases, the nanoparticle concentration enhances for wall expansion in the occurrence of injection, although for the situation of wall contraction, it decreases as increases.
Figure 20a–c shows the influence of the Brownian and thermophoresis factors on the Nusselt number against . The at the pipe wall is found to be an increasing function of . It is evident from Figure 20a that rises when rises near the wall for but falls in situation (Figure 20b). It is also analyzed from Figure 20c that rises for a given rise in at the surface of the wall. Figure 21a,b are plotted to check the inspiration of the thermophoresis and the Brownian factors versus the Sherwood number It is obvious that the rises as at the surface of the wall increases. Figure 21a witnesses that that reduces as enhances at the wall. Figure 21b shows that declines for a specified growth in near the wall.
7. Key Notes
In this study, we investigate the influence of chemical reactions and heat reservoirs on MHD nanofluid flow in a porous expanding or contracting pipe. The characteristics equation of the flow cylinder coordinates is transformed to an ordinary differential equation and converted by using suitable transformation and then solved numerically by using the RK4 method. For the stability analysis, the present work is compared with the previous work. For the confirmation of the mathematical modeling, the error estimation and the residue error are also calculated, and it is found that the error is too small, which validates our solution. The novelty of the present study is to investigate the effect of chemical reactions on magnetized nanofluid flow over an extending and shrinking porous pipe with heat generation and absorption; in limiting cases, the present work is compared with the published work, and outstanding agreement is found.
The following summarizes the key conclusions:
- It is observed that for both situations of wall extension or contraction with injection, the temperature is the increasing function of the thermophoresis and Brownian motion factors.
- It is analyzed that the temperature is raised when the heat source is increased in both cases of wall expansion or contraction but declines in the case of a heat sink.
- In the case of a heat source, the temperature rises as the Hartmann and Prandtl numbers are enhanced, but in the case of a heat sink, the temperature falls.
- In the presence of heat sinks and injections when the thermophoresis factor is increased, the concentration of nanoparticles is increased in both wall expansion and contraction.
- In both situations of wall expansion or contraction, along with injection, the concentration of nanoparticles is a decreasing function of , while the concentration of nanoparticles is an increasing function in the case of a heat source.
- It is also observed that is increased for and decreased for.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z., N.A.S. and J.D.C.; Methodology, Z., J.D.C. and A.; Software, N.A.A.; Validation, N.A.A. and N.A.S.; Formal analysis, Z., J.D.C. and A.; Resources, N.A.S.; Writing—original draft, Z., N.A.S., J.D.C. and A.; Writing—review & editing, N.A.A. and A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work received no external fund.
Data Availability Statement
All the data is available within the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Technology Innovation Program (20018869, Development of Waste Heat and Waste Cold Recovery Bus Air-conditioning System to Reduce Heating and Cooling Load by 10%), funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE, Korea).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Nomenclature
| radius of the pipe | ||
| the injection/suction coefficient | ||
| applied magnetic field | ||
| dimensional nanoparticle concentration | ||
| reference nanoparticle concentration at the center | ||
| specific heat at constant pressure | ||
| nanoparticle concentration at the wall | ||
| first-order chemical reaction rate | ||
| Lewis number | ||
| Hartmann number | ||
| thermophoresis parameter | ||
| Brownian motion parameter | ||
| Prandtl number | ||
| heat source/sink parameter | ||
| dimensional cylindrical coordinates | ||
| dimensional temperature | ||
| reference temperature at the center | ||
| mean temperature | ||
| mean fluid temperature | ||
| temperature near the wall | ||
| velocity components along ^r and ^z directions respectively | ||
| injection/suction velocity | ||
| density of the base fluid | ||
| electrical conductivity | ||
| thermal diffusivity | ||
| dimensionless temperature | ||
| heat capacity of the nanoparticle | ||
| dimensionless concentration |
References
- Choi, S.U.S. Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticle. In Developments and Applications of Non-Newtonian Flows; Siginer, D.A., Wang, H.P., Eds.; FED-V.231/MDV. 66; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.-Q.; Mujumdar, A.S. A review on nanofluids. Part I: Theoretical and numerical investigations. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 25, 613–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.U.S. Nanofluids: A new field of scientific research and innovative applications. Heat Transf. Eng. 2008, 29, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.A.; Pop, I. Boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 53, 2477–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.D.; Raju, C.; Sajjan, K.; El-Zahar, E.R.; Shah, N.A. Linear and quadratic convection on 3D flow with transpiration and hybrid nanoparticles. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 134, 105995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abderrahmane, A.; Qasem, N.A.A.; Younis, O.; Marzouki, R.; Mourad, A.; Shah, N.A.; Chung, J.D. MHD Hybrid Nanofluid Mixed Convection Heat Transfer and Entropy Generation in a 3-D Triangular Porous Cavity with Zigzag Wall and Rotating Cylinder. Mathematics 2022, 10, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.A.; Wakif, A.; El-Zahar, E.R.; Thumma, T.; Yook, S.-J. Heat transfers thermodynamic activity of a second-grade ternary nanofluid flow over a vertical plate with Atangana-Baleanu time-fractional integral. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 10045–10053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buongiorno, J. Convective heat transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 2006, 128, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roşca, N.C.; Pop, I. Unsteady boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a moving surface in an external uniform free stream using Buongiorno’s model. Comput. Fluids 2014, 95, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, A.V.; Nield, D.A. Natural convective boundarylayer flow of a nanofluid past a vertical plate. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2010, 49, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.Z.; Rehman, S.U.; Farid, S.; Hussein, A.K.; Ali, B.; Shah, N.A.; Weera, W. Insight into significance of bioconvection on MHD tangent hyperbolic nanofluid flow of irregular thickness across a slender elastic surface. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Q.; Ali, B.; Rehman, S.U.; Habib, D.; Abdal, S.; Shah, N.A.; Chung, J.D. Micropolar dusty fluid: Coriolis force effects on dynamics of MHD rotating fluid when lorentz force is significant. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.; Nawaz, M.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A. MHD boundary layer flow of second grade nanofluid over a stretching sheet with convective boundary conditions. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2014, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaedi, A.; Awais, M.; Hayat, T. Effect of heat generation/ absorption on stagnation point flow of nanofluid over a surface with convective boundary conditions. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2012, 17, 4210–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkha, J.; Rashad, A.M.; Aly, A.M. Transient natural convection flow of a nanofluid over a vertical cylinder. Meccanica 2012, 48, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvandi, A.; Moshizi, S.; Soltani, E.; Ganji, D. Modified Buongiorno’s model for fully developed mixed convection flow of nanofluids in a vertical annular pipe. Comput. Fluids 2014, 89, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Behzadmehr, A.; Shahraki, F. Fully developed mixed convection inhorizontal and inclined tubes with uniform heat flux using nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellahi, R. The effects of MHD and temperature dependent viscosity on the flow of non-Newtonian nanofluid in a pipe: Analytical solutions. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 37, 1451–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Bég, O.A.; Amin, N. Hydromagnetic transport phenomena from a stretching or shrinking nonlinear nanomaterial sheet with Navier slip and convective heating: A model for bio-nano-materials processing. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 368, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Fan, T.; Pop, I. Analysis of mixed convection flow of a nanofluid in vertical a channel with Buongiorno mathematical model. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 44, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.; Naseer, M.; Nadeem, S.; Rehman, A. The boundary layer flow of Casson nanofluid over a vertical exponentially stretching cylinder. Appl. Nanosci. 2014, 4, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, C.S.K.; Ameer, N.A.; Kiran, S.; Nehad, A.S.; Se-jin, Y.; Dinesh, M.K. Nonlinear movements of axisymmetric ternary hybrid nanofluids in a thermally radiated expanding or contracting permeable Darcy Walls with different shapes and densities: Simple linear regression. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 2022, 135, 106110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, G.; Madhukesh, J.; Shah, N.A.; Yook, S.-J. Flow of hybrid CNTs past a rotating sphere subjected to thermal radiation and thermophoretic particle deposition. Alexandria Eng. J. 2022, 64, 969–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, S.; Vijayalakshmi, A.; Ramamohan, T.; Reddy, A.S. Hydromagnetic flow of a nanofluid in a porous channel with expanding or contracting walls. J. Porous Media 2014, 17, 953–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, F.; Domairry, G. Effects of nanoparticle migration and asymmetric heating on mixed convection of TiO2-H2O nanofluid inside a vertical micro channel. Powder Technol. 2015, 272, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvandi, A.; Safaei, M.; Kaffash, M.; Ganji, D. MHD mixed convection in a vertical annulus filled with Al2O3-water nanofluid considering nanoparticle migration. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 382, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajravelu, K.; Prasad, K.; Rao, N.P. Diffusion of a chemically reactive species of a power-law fluid past a stretching surface. Comput. Math. Appl. 2011, 62, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, W.; Tlili, I.; Siddique, I. Maxwell fluid flow between vertical plates with damped shear and thermal flux: Free convection. Chin. J. Phys. 2020, 65, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahsud, Y.; Vieru, D. Influence of time-fractional derivatives on the boundary layer flow of Maxwell fluids. Chin. J. Phys. 2017, 55, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, S.; Akbar, N. Influence of heat and chemical reactions on Walter’s B fluid model for blood flow through a tapered artery. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2011, 42, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Abbas, Z. Channel flow of a Maxwell fluid with chemical reaction. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 2008, 59, 124–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Kahar, R.; Kandasamy, R. Muhaimin, Scaling group transformation for boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a porous vertical streching surface in the presence of chemical reaction with heat radiation. Comput. Fluids 2011, 52, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameswaran, P.; Shaw, S.; Sibanda, P.; Murthy, P. Homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions in a nanofluid due to a porous stretching sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 57, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Khan, W.; Ismail, A. Lie group analysis and numerical solutions for magneto convective slip flow along a moving chemically reacting radiating plate in porous media with variable mass diffusivity. Heat Transf.-Asian Res. 2014, 45, 239–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, M.; Momoniat, E.; Ferdows, M.; Basiriparsa, A. Lie group solution for free convective flow of a nanofluid past a chemically reacting horizontal plate in porous media. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, S.; Reddy, A.S.; Ramamohan, T. Mass transfer effects on viscous flow in an expanding or contracting porous pipe with chemical reaction. Heat Transf.-Asian Res. 2015, 44, 552–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Beg, O.; Aziz, A.; Ismail, A. Group analysis of free convection flow of a magnetic nanofluid with chemical reaction. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, S.; Aoki, H. Unsteady flows in a semi-infinite contracting or expanding pipe. J. Fluid Mech. 1977, 82, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, M.; Uchida, S. Unsteady flows in a semi-infinite contracting or expanding pipe with a porous wall. Theor. Appl. Mech. 1991, 40, 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Majdalani, J.; Zhou, C. Moderate-to-large injection and suction driven channel flows with expanding or contracting walls. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 2003, 83, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.A.; Zafar, A.A.; Akhtar, S. General solution for MHD-free convection flow over a vertical plate with ramped wall temperature and chemical reaction. Arab. J. Math. 2018, 7, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdalani, J.; Flandro, G.L. The oscillatory pipe flow with arbitrary injection. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 2002, 458, 1621–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Shah, N.A.; Dennis, L.C.C. A scientific report on heat transfer analysis in mixed convection flow of Maxwell fluid over an oscillating vertical plate. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep40147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrill, R.; Thomas, P. Spiral flow in a porous pipe. Phys. Fluids 1973, 16, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjan, K.; Ahammad, N.; Raju, C.; Kumar, M.; Weera, W. Nonlinear Boussinesq and Rosseland approximations on 3D flow in an interruption of Ternary nanoparticles with various shapes of densities and conductivity properties. AIMS Math. 2022, 7, 18416–18449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutros, Y.; Abd-El-Malek, M.; Badran, N.; Hassan, H. Lie-group method for unsteady flows in a semi-infinite expanding or contracting pipe with injection or suction through a porous wall. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2006, 197, 465–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeshan. Heat enhancement analysis of Maxwell fluid containing molybdenum disulfide and graphene nanoparticles in engine oil base fluid with isothermal wall temperature conditions. Waves Random Complex Media 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeshan; Ahammad, N.A.; Rasheed, H.; El-Deeb, A.A.; Almarri, B.; Shah, N.A. Numerical Intuition of Activation Energy in Transient Micropolar Nanofluid Flow Configured by an Exponentially Extended Plat Surface with Thermal Radiation Effects. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeshan; Attaullah; Ahammad, N.A.; Shah, N.A.; Chung, J.D. A Numerical Framework for Entropy Generation Using Second-Order Nanofluid Thin Film Flow over an Expanding Sheet: Error Estimation and Stability Analysis. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeshan; Ahammad, N.A.; Shah, N.A.; Chung, J.D.; Attaullah; Rasheed, H.U. Analysis of Error and Stability of Nanofluid over Horizontal Channel with Heat/Mass Transfer and Nonlinear Thermal Conductivity. Mathematics 2023, 11, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, J.; Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Lund, L. The flow of magnetised convective Casson liquid via a porous channel with shrinking and stationary walls. Pramana 2022, 96, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.; Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Zaib, A.; Ishak, A.; Abu Bakar, S.; Sherif, E.-S.M.; Baleanu, D. An exact solution of a Casson fluid flow induced by dust particles with hybrid nanofluid over a stretching sheet subject to Lorentz forces. Wave Random Complex 2022, 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabani, I.; Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Vaidya, H.; Ismail, A.I. Numerical analysis of magnetic hybrid nano-fluid natural convective flow in an adjusted porous trapezoidal enclosure. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 564, 170142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.J. Beyond Perturbation: Introduction to Homotopy Analysis Method; CRC Press; Chapman and Hall: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).