Abstract
The moisture diffusion behaviors of 3D woven composites exhibit non-Fickian properties when they are exposed to a hydrothermal environment. Although some experimental works have been undertaken to investigate this phenomenon, very few mathematical works on non-Fickian moisture diffusion predictions of 3D woven composites are available in the literature. To capture the non-Fickian behavior of moisture diffusion in 3D woven composites, this study first utilized a time fractional diffusion equation to derive the percentage of moisture content of a homogeneous material under hydrothermal conditions. A two-stage moisture diffusion model was subsequently developed based on the moisture diffusion mechanics of both neat resin and 3D woven composites, which describes the initial fast diffusion and the long-term slow diffusion stages. Notably, the model incorporated fractional order parameters to account for the nonlinear property of moisture diffusion in composites. Finally, the weight gain curves of neat resin and the 3D woven composite were calculated to verify the fractional diffusion model, and the predicted moisture uptake curves were all in good agreement with the experimental results. It is important to note that when the fractional order parameter α < 1, the initial moisture uptake will become larger with a later slow down process. This phenomenon can better describe non-Fickian behavior caused by initial voids or complicated structures.
Keywords:
time-fractional diffusion equation; non-Fickian behaviors; hygrothermal aging; 3D woven composite MSC:
26A33
1. Introduction
3D woven composites have gained widespread application in various industries, such as aerospace, automotive, and civil engineering, owing to their high strength-to-weight ratio [1,2]. Nevertheless, these composites exhibit a critical drawback of water absorption when exposed to hygrothermal environments, which significantly deteriorates their performance [3]. Considering that carbon or glass fibers possess a relatively low water absorption rate [4], it is imperative to comprehend the moisture diffusion mechanics of void, mesostructure, and neat matrix to enhance the long-term performance of 3D woven composites [5,6].
Regarding the polymer matrix, both Fickian [7] and non-Fickian [8] behaviors resulting from moisture diffusion in hygrothermal environments have been observed. The commonly recognized mechanism of moisture transport in polymers involves two distinct stages of diffusion: the initial fast diffusion stage and the long-term slow diffusion stage [9,10]. The initial fast diffusion stage is mainly driven by the concentration gradient, which leads to Fickian diffusion. In contrast, the long-term slow diffusion stage is regulated by the slow relaxation process, resulting in non-Fickian diffusion [11,12]. For long-term diffusion, the stress relaxation phenomenon occurs in polymer chains due to the penetration of water molecules after hydrothermal aging. Since the motion of polymer chains demonstrates a trend of rescinding stress, the chains will experience a slow re-orientation and translation process. Therefore, the distances between the molecules will increase, leading to additional absorption. Obviously, the relaxation process is much slower than the diffusion controlled by the concentration gradient.
Unlike in unidirectional composites, where weight gains in fast diffusion generally follow a linear trend [13], the initial fast moisture uptake in woven composites does not always exhibit a similar behavior. In fact, the moisture uptake of woven composites has been observed to increase rather rapidly at first and then to quickly slow down [14], which indicates a non-linear trend. This behavior could be attributed to the diffusion in cure-induced voids and cracks that are present in the woven composites. In contrast, the initial fast moisture uptake of unidirectional composites has been found to follow a Fickian behavior. After the initial fast diffusion controlled by voids and cracks, the diffusion will be dominated by the micro-structure of woven composites. In contrast with a unidirectional composite, the resin pockets and wave shape structures in woven composites can provide an easier path for moisture diffusion [15]. In contrast to short-term behavior, the weight gain of woven composites in long-term diffusion shows a linear function, indicating the dominance of structural relaxation of the matrix in slow diffusion. Additionally, the weight gain of woven composites caused by cracks has been observed to increase due to hygrothermal aging after more than one year [16].
Non-Fickan diffusion is actually an anomalous diffusion. For example, aging effects diffusion [17], chemistry, physics [18], fluid flow in porous media [19], and state-dependent diffusion [20]. The motion of particles exhibits different behaviors, e.g., fractional Brownian motions [21,22], non-Gaussian [23,24], as well as normal yet non-Gaussian diffusion [25]. Normal diffusion can be described as a Markov process where the current is independent of both the space and the history. In contrast, anomalous diffusion is characterized by a non-Markov process, where the current is related to the concentration values across the entire space, and is dependent on both the previous history and even the initial conditions [26].
In contrast to the integer diffusion model, the advantage of a time fractional model is that the memory or history effects can be easily described. The anomalous diffusion observed in 3D woven composites is a result of the time-dependent moisture absorption, which leads to a memory or history effect of the concentration. Therefore, this effect needs to be taken into consideration when modelling the diffusion behavior [27]. In contrast to other models, the level of nonlinearity in the moisture diffusion of composites can be represented using fractional order parameters within a fractional model. These parameters enable the description of memory or history effects during different physical processes [28]. The specific analytical moisture diffusion models of 3D woven composites are seldom found in references.
The main objective of this paper is to develop the moisture diffusion model of neat resin and 3D woven composites in a hydrothermal aging environment. The outline of this paper is as follows. In Section 2, the moisture uptake experiment of neat resin and 3D woven composites was carried out. In Section 3, an analytical solution for the time fractional diffusion equation was developed to describe the nonlinear moisture uptake of 3D woven composites during hygrothermal aging. The total weight gain of both the neat resin and 3D woven composite was then calculated by summing the weight gains from the initial fast diffusion stage and the subsequent slow diffusion stage. In Section 4, the findings were summarized and conclusions were drawn based on the results obtained from the model.
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
Epoxy resin (E51) is used as the resin matrix for preparing the composites specimen. The glass fiber reinforced 3D woven composites, which are composed of glass fiber tows and an epoxy matrix, were supplied by the Nanjing Research Institute on Simulation Technique (NRIST), and some details of the 3D woven composite are shown in Figure 1. Figure 1a shows the diagram of the meso 3D woven structure. Weft tows (green) are straight tows, and orthogonal warp tows (yellow) go through different weft layers as a wave shape to interlock each other as a whole reinforcement. Figure 1b,c illustrates two cross sections of 3D woven composite along different directions, captured by an optical microscope. Figure 1d gives a picture of the specimen for the hydrothermal aging experiment, and there are three test pieces of the 3D woven composite. The dimensions of the 3D woven composite and pure resin are listed in Table 1.
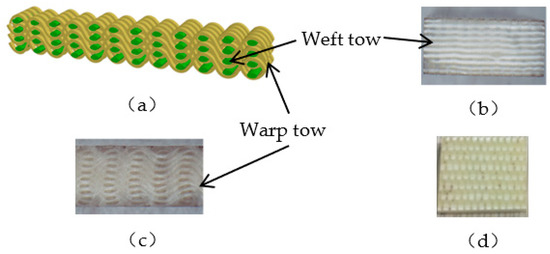
Figure 1.
3D woven composite. (a) 3D woven structure; (b) Cross section of weft tow; (c) Cross section of warp tow; (d) Specimen.

Table 1.
The dimensions of resin and 3D woven composite.
2.2. Moisture Uptake Experiment
To investigate the moisture uptake behavior of the pure resin and 3D woven composites, a standard protocol was followed. The specimens were initially dried in a constant temperature drying oven at 60 °C for 24 h to eliminate any residual moisture. Afterwards, the specimens were prepared by coating their four lateral sides with a waterproof layer to ensure that water could only diffuse along the thickness direction. The moisture uptake of the specimens was determined using an electronic balance (Mettler Toledo al-105), and the initial mass (W0) of the dried specimens was recorded. The specimens were subsequently placed in an environmental box at 60 °C and 100% relative humidity, and were taken out at specific time intervals. The specimens were wiped and dried with a test paper, and their weight gains (Wt) were measured and recorded until the moisture uptake reached a saturation point. The moisture absorption (Mt) of the material was calculated using the following equation:
The diffusivity can be shown as:
The diffusivity is denoted by D, and h represents the thickness of the specimen. Additionally, the slope of the linear portion of the moisture absorption Mt plotted against the square root of time t (i.e., the t0.5 curve) is represented by the parameter k. M∞ is its maximum moisture uptake in an equilibrium state.
3. Theory
3.1. Time Fractional Diffusion Equation
The following problem was investigated. One dimensional moisture uptake of a homogeneous material through thickness direction exposed to a hydrothermal environment was considered, as is shown in Figure 2, where h is the thickness of the material. The primary aim of this study is to establish a relationship between the percentage of moisture content (i.e., percent weight gain) of the material and time. In order to achieve this, we consider the temperature and diffusivity to be constant within the material, leading to a description of the problem through the time fractional diffusion equation. By utilizing this equation, we can effectively capture the history effect and nonlinear property of moisture diffusion.
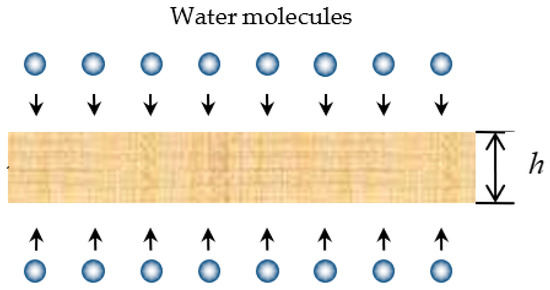
Figure 2.
Time fractional diffusion equation for moisture uptake of the material.
The time fractional moisture diffusion equation is [29]:
The moisture concentration of the material is represented by C(x,t), where x is the position coordinate and t is the time. The diffusivity of the material in the direction normal to the surface is denoted by D, while α represents the fractional order parameter. It is important to note that the time-fractional derivative is intended in the Caputo sense, as specified by previous literature [30]:
For α = 1, the diffusion equation reduces to the classical or integral-order diffusion equation:
The initial and boundary conditions are:
The details of the derivation process are listed in Appendix A. The solution of the time fractional moisture diffusion equation (Equation (3)) is:
where , is generalized Mittag-Leffler function,
The total moisture weight gain of the material can be derived by integrating Equation (7) over the thickness of the plate:
where ρw and ρm are the density of water and material, respectively. M∞ is the maximum moisture uptake of the material.
3.2. The Two-Stage Time Fractional Diffusion Model
During the hygrothermal aging process of the neat resin and composites, two distinct stages of moisture uptake can be observed: initial fast diffusion and long-term slow diffusion. The fast diffusion in neat resin follows a Fickian behavior, whereas the fast diffusion in 3D woven composite exhibits non-Fickian behavior. On the other hand, both neat resin and 3D woven composites display non-Fickian behavior during long-term slow diffusion. Since the initial fast diffusion is primarily controlled by the concentration gradient, while long-term diffusion is related to a slow relaxation process, a two-stage fractional model has been developed to accurately describe the weight gain of the material during hygrothermal aging:
The weight gain during hygrothermal aging can be described by the sum of the initial fast moisture uptake and the long-term slow weight gain. The total weight gain is denoted as Mt(t), while Mf (α, Df, Mf, t) and Ms (γ, Ds, Ms, t) represent the initial fast moisture uptake and the long-term slow weight gain, respectively. The fast diffusivity is represented by Df, while the slow diffusivity is denoted as Ds. The fractional order parameters, α and γ, are used to account for the history effect and the nonlinearity of moisture diffusion. The equilibrium moisture uptake of the fast and slow diffusion processes is represented by Mf and Ms, respectively.
4. Result and Discussion
4.1. The Results of the Time-Fractional Diffusion Equation
The moisture uptake results calculated by Equation (9) are shown in Figure 3 for the case where the aging time is 40 min and the saturated moisture content is 1%. Figure 3a,b indicate the calculated moisture uptake (during 0 ≤ t ≤ 40 min,) when the diffusivities of the material is 0.02 cm2/min and 0.05 cm2/min, respectively. It is found that if α = 1, the diffusion follows a Fickian behavior. However, when α = 0.25, 0.5 and 0.75, the moisture absorptions do not follow Fick’s law, exhibiting non-linear properties. The moisture uptake rapidly increases at first, and then develops slowly compared to Fickian diffusion. The initial moisture uptake becomes quicker when α is smaller. It is worth noting that the intersection points of the curves (α = 0.25, 0.5 and 0.75) and the Fickian diffusion become larger with the increase in diffusivities.
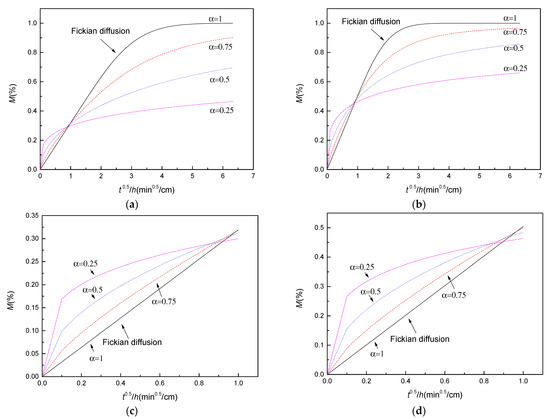
Figure 3.
The moisture uptake calculated by time fractional moisture diffusion Equation (9) for four cases. (a) D = 0.02 cm2/min, 0 ≤ t ≤ 40 min; (b) D = 0.05 cm2/min, 0 ≤ t ≤ 40 min; (c) D = 0.02 cm2/min, 0 ≤ t≤1 min; and (d) D = 0.05 cm2/min, 0 ≤ t ≤ 1 min. The solid lines are Fickian diffusion (black, α = 1). The dash (red), dot (blue) and dash dot(magenta) lines are α = 0.75, 0.5 and 0.25, respectively.
To clearly observe the initial moisture uptake, we also give the moisture absorption curves when 0 ≤ t ≤ 1 min, as shown in Figure 3c,d. It was observed that the initial moisture uptake quickly grows when α = 0.25 compared to other parameters. In addition, the values of diffusivities also significantly affect the speed of initial moisture uptake, which is about 1.5 times the difference of the initial values observed between Figure 3c,d.
4.2. Moisture Uptake of Resin
Figure 4 illustrates the weight gain for resin under 60 °C at 100%RH. Several features are found in Figure 4. Firstly, the weight gain initially increases linearly as expected following Fick’s law. Secondly, the weight gain continues to increase with a slow process over an extended time scale. However, no equilibrium moisture uptake is reached. Obviously, the hygrothermal aging process cannot be described by Fickian diffusion.
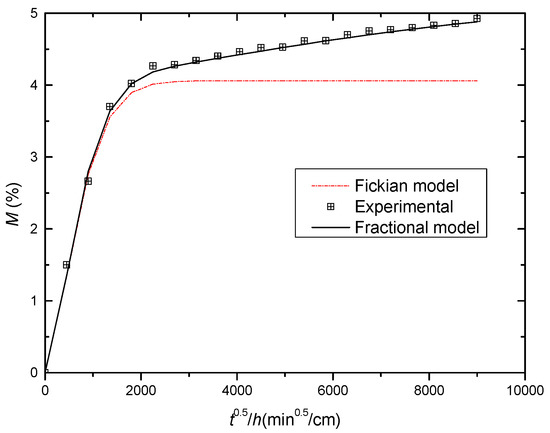
Figure 4.
The comparison between experimental results and the fractional model by Equation (10) of the weight gain curve of resin during hygrothermal aging at 60 °C and 100%RH. The dash dot line is Fickian diffusion.
The hygrothermal aging diffusion is explained by fractional diffusion Equation (10), and the analytical results achieve a good agreement with the experimental results. Table 2 is the summary of parameters used in Equation (10). Since the fast diffusion obeys Fick’s law, thus α = 1. The observed long-term diffusion of resin increases linearly, therefore, γ = 1. Because the long-term diffusion induces a very slow diffusivity, no equilibrium moisture uptake is reached.

Table 2.
Parameters in time-fractional diffusion equation for neat resin.
4.3. Moisture Uptake of 3D Woven Composite
Figure 5 presents an analysis of the moisture diffusion behavior of 3D woven composite during hygrothermal aging at 60 °C and 100% RH. The investigation reveals that the rapid diffusion of the 3D woven composite cannot be satisfactorily explained by Fick’s law, unlike the behavior of neat resin, as demonstrated in Figure 5a. Specifically, the initial moisture uptake shows nonlinearity, in contrast to the linear increase in weight gain predicted by Fick’s law. Additionally, the moisture uptake increases rather quickly during the initial period, but subsequently decelerates.
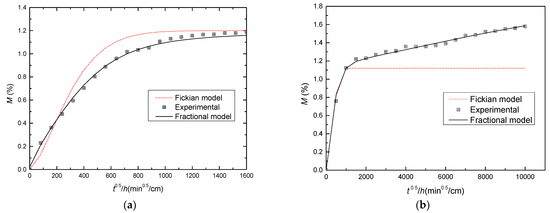
Figure 5.
The comparison between experimental results and the fractional model by Equation (10) of the weight gain curve of a 3D woven composite during hygrothermal aging at 60 °C and 100%RH. The dash dot lines are Fickian diffusion. (a) Short-term moisture diffusion. (b) Long-term moisture diffusion.
A time fractional moisture diffusion equation has been derived to capture the nonlinear moisture diffusion behavior of 3D woven composites during the fast diffusion stage. The value of α = 0.83, which was obtained through fitting, characterizes the nonlinear property of non-Fickian diffusion, and is associated with the presence of voids and cracks. A decrease in α leads to an increase in the nonlinearity of non-Fickian diffusion, resulting in a more rapid initial moisture uptake. Due to the non-constant nature of the diffusivity of 3D woven composites, the average diffusivity was selected to fit the weight gain curve. The theoretical and experimental results demonstrate good agreement.
Figure 5b illustrates the long-term moisture diffusion behavior of the 3D woven composite subjected to hygrothermal aging at 60 °C and 100% RH. Notably, a linear trend was observed in the weight gain curve during the one-year aging period. This trend led to the determination of the fractional order parameter γ as 1, which is consistent with the experimental results. It can be inferred that the developed fractional diffusion model can be applied to both neat resin and 3D woven composite, since the model’s outcome was in good agreement with the experimental observations. Furthermore, the specific parameters used in the model are reported in Table 3.

Table 3.
Moisture diffusion parameters for 3D woven composite.
5. Conclusions
This paper presents a two-stage time fractional moisture diffusion equation for the non-Fickian diffusion of a 3D woven composite. The present study conducted moisture absorption experiments on both neat resin and 3D woven composite to validate the analytical method. The main findings of the study are outlined as follows:
(1) The analytical solution of the time fractional moisture diffusion equation was given by Equation (9), and the effects of fractional order parameter α and diffusivities D are discussed.
- (a)
- when α < 1, the moisture absorptions do not follow Fick’s law, exhibiting nonlinear properties. The moisture uptake rapidly increases at first, then develops slowly compared to Fickian diffusion.
- (b)
- The initial moisture uptake becomes quicker while α is smaller. It is worth noting that the intersection points of the curves (α = 0.25, 0.5 and 0.75) and the Fickian diffusion become larger with the increase of diffusivities D.
(2) The moisture absorption behaviors of neat resin and the 3D woven composite are successfully described by a two stage time fractional diffusion equation, i.e., Equation (10).
- (a)
- For neat resin, since the fast diffusion obeys Fick’s law, thus α = 1. The observed long-term diffusion of resin increases linearly, therefore, γ = 1.
- (b)
- However, for the 3D woven composite, α = 0.83 related to the voids and cracks, is fitted to represent the nonlinear property during non-Fickian diffusion. A linear tendency is found from the experimental observation during long-term hydrothermal aging, leading to γ = 1 for the 3D woven composite.
(3) Compared with other references, the method used in this paper can better describe the non-linear properties caused by initial voids or cracks. The tendency of moisture increase obtained by the time fractional diffusion equation is also shown to be a function of fractional parameters and diffusivities. The calculated curves demonstrate that this method has potential applications for other anomalous diffusion problems of different materials.
(4) The major limitation of this paper is that the direct mathematical relationship between fractional parameter α and the anomalous diffusion influence factor (such as the volume fraction of initial voids or cracks) is not clear. We will work on this problem in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Y.; methodology, C.Z.; software, Y.M.; validation, S.L.; formal analysis, H.L.; investigation, Y.L.; resources, Y.N.; data curation, L.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, H.Y.; writing—review and editing, H.Y.; visualization, H.Y.; supervision, L.Y.; project administration, L.Y.; funding acquisition, Y.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 52105153, the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province under Grants BK20221378, in part by the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China under Grants 22KJB130010, 22KJA540001, 21KJB570009, 21KJA490001, and 20KJA540001, in part by Projects from Nantong city Grant MS22022103, MS12021005, MS22021003, MS22021022, JB2022004, JC2021041 and JC2021060, in part by Undergraduate Innovation Training Program 202210304064Z.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
To solve the above initial value problem under the hydrothermal boundary condition, the moisture concentration turns out to be:
It is easy to prove that g(x,t) is satisfied with Equation (A1), and we can obtain:
Therefore, the relative initial and boundary conditions are:
Using the variable separation approach allows the required solution to be obtained as:
Therefore, the following equation can be obtained from Equation (A2):
It is easy to verify λ ≠ 0, otherwise, the equation does not have any meaning. Furthermore, we get:
From the second formula in Equation (A6), we obtain:
From the boundary conditions in Equation (A3), we note the relation:
For t > 0, Equation (A8) is tenable, so we can obtain . Then, from Equation (A7) we obtain:
Therefore, λ = (kπ/h)2, where k = 0, 1, 2…. The solution of Equation (A7) is:
The fractional derivative equation in Equation (A6) is:
The property of the Laplace transform in the Caputo sense is:
The application of the Laplace transform to Equation (A11) leads to the following equation:
From which we obtain:
Recalling the Laplace transform pair:
Now, according to the inversion formula:
The solution of Equation (A4) can then be written as:
If t = 0, we can obtain Eα,1(Atα) = 1. Especially when α = 1, E1,1(At) = eAt is the solution of the integral order diffusion equation.
By using the boundary conditions:
Hence,
Then,
If k is even, Ck = 0; If k is odd, Ck = −4C∞/kπ.
Therefore, the solution of Equation (A4) is:
References
- Gereke, T.; Cherif, C. A review of numerical models for 3D woven composite reinforcements. Compos. Struct. 2019, 209, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielhorski, Y.; Mendoza, A.; Rubino, M.; Roux, S. Numerical modeling of 3D woven composite reinforcements: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 154, 106729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, E.J.; Bednarcyk, B.A.; Ricks, T.M.; Farrokh, B.; Jackson, W. Multiscale failure analysis of a 3D woven composite containing manufacturing induced voids and disbonds. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 156, 106844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Lucas, J.P. Hygrothermal effects of epoxy resin. Part I: The nature of water in epoxy. Polymer 1999, 40, 5505–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apicella, A.; Nicolais, L.; Astarita, G.; Drioli, E. Effect of thermal history on water sorption, elastic properties and the glass transition of epoxy resins. Polymer 1979, 20, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yao, L.; Ma, Y.; Hou, Z.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Ni, Y. The Moisture Diffusion Equation for Moisture Absorption of Multiphase Symmetrical Sandwich Structures. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijović, J.; Lin, K.F. The effect of hygrothermal fatigue on physical/mechanical properties and morphology of neat epoxy resin and graphite/epoxy composite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1985, 30, 2527–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.; Broutman, L. Moisture diffusion in epoxy resins Part I. Non-Fickian sorption processes. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1985, 25, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berens, A.; Hopfenberg, H. Diffusion and relaxation in glassy polymer powders: 2. Separation of diffusion and relaxation parameters. Polymer 1978, 19, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, I.M.; Berens, A.R. Effects of annealing and prior history on enthalpy relaxation in glassy polymers. 2. Mathematical modeling. Macromolecules 1982, 15, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Miranda, J.; Sue, H.-J. Hygrothermal diffusion behavior in bismaleimide resin. Polymer 2001, 42, 7791–7799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.-R.; Yee, A.F.; Lee, C.Y.-C. Moisture absorption and hygrothermal aging in a bismaleimide resin. Polymer 2001, 42, 7327–7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.-R.; Yee, A.F. Moisture diffusion and hygrothermal aging in bismaleimide matrix carbon fiber composites—Part I: Uni-weave composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 2099–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.-R.; Yee, A.F. Moisture diffusion and hygrothermal aging in bismaleimide matrix carbon fiber composites: Part II--woven and hybrid composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Whitcomb, J.D.; Li, Y.; Sue, H.-J. Micromechanics modeling of moisture diffusion in woven composites. Composites Science and Technology 2005, 65, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, C.; Hassoune-Rhabbour, B.; Poncin-Epaillard, F.; Tchalla, T.; Nassiet, V. Contributions of atmospheric plasma treatment on a hygrothermal aged carbon/epoxy 3D woven composite material. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 202, 110023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherstvy, A.G.; Chechkin, A.V.; Metzler, R. Ageing and confinement in non-ergodic heterogeneous diffusion processes. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2014, 47, 485002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlichter, J.; Friedrich, J.; Herenyi, L.; Fidy, J. Protein dynamics at low temperatures. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 112, 3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerschaert, M.M.; Tadjeran, C. Finite difference approximations for fractional advection–dispersion flow equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2004, 172, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.W.; Lubensky, T.C. State-dependent diffusion: Thermodynamic consistency and its path integral formulation. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 76, 011123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumarie, G. New results on Fokker–Planck equations of fractional order. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2001, 12, 1873–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherstvy, A.G.; Wang, W.; Metzler, R.; Sokolov, I.M. Inertia triggers nonergodicity of fractional Brownian motion. Phys. Rev. E 2021, 104, 024115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chechkin, A.V.; Seno, F.; Metzler, R.; Sokolov, I.M. Brownian yet non-Gaussian diffusion: From superstatistics to subordination of diffusing diffusivities. Phys. Rev. X 2017, 7, 021002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, N.A.; Saad-Roy, C.M.; Cherstvy, A.G.; Wagner, C.E. Distributed medium viscosity yields quasi-exponential step-size probability distributions in heterogeneous media. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 8572–8581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chubynsky, M.V.; Slater, G.W. Diffusing diffusivity: A model for anomalous, yet Brownian, diffusion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 098302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoy, S.; García-Colín, L. Mesoscopic diffusion as a non-Markov process. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 1998, 258, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorenflo, R.; Mainardi, F.; Vivoli, A. Continuous-time random walk and parametric subordination in fractional diffusion. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2007, 34, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcerek, M.; Burnecki, K.; Thapa, S.; Wyłomańska, A.; Chechkin, A. Fractional Brownian motion with random Hurst exponent: Accelerating diffusion and persistence transitions. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2022, 32, 093114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muliana, A. Deformation in viscoelastic sandwich composites subject to moisture diffusion. Compos. Struct. 2010, 92, 254–264. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, F.F.; Hon, Y.C. Kernel-based approximation for Cauchy problem of the time-fractional diffusion equation. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2012, 36, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).