Topological Regularization for Representation Learning via Persistent Homology
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Related Works
1.2. Contribution
2. Topological Preliminaries
2.1. Simplicial Complex, Persistent Homology and Persistence Diagrams
2.2. DTM Function
3. Topological Regularization
3.1. Push-Forward Probability Measure and Generalization
3.2. Probability Mass Separation
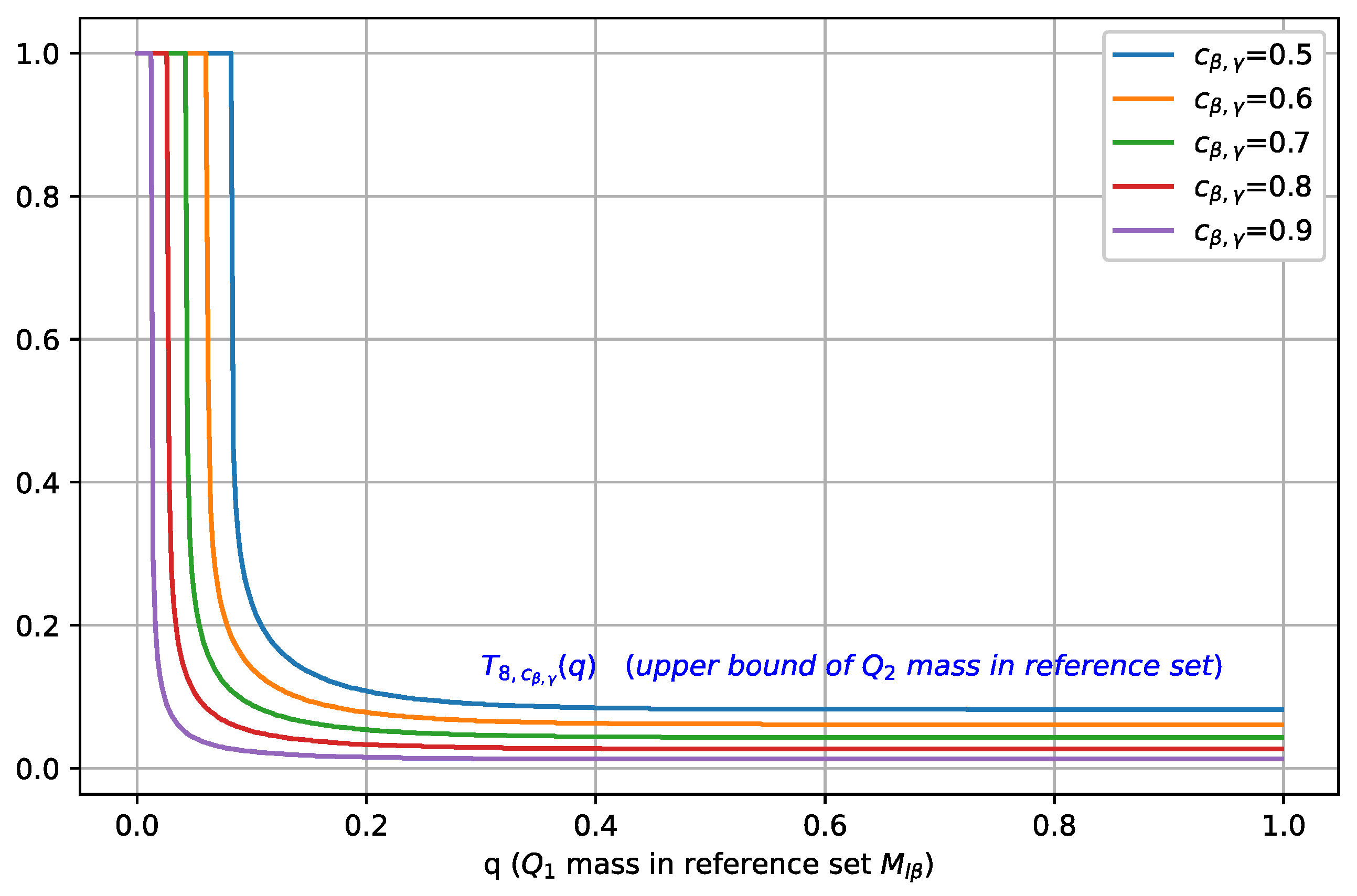
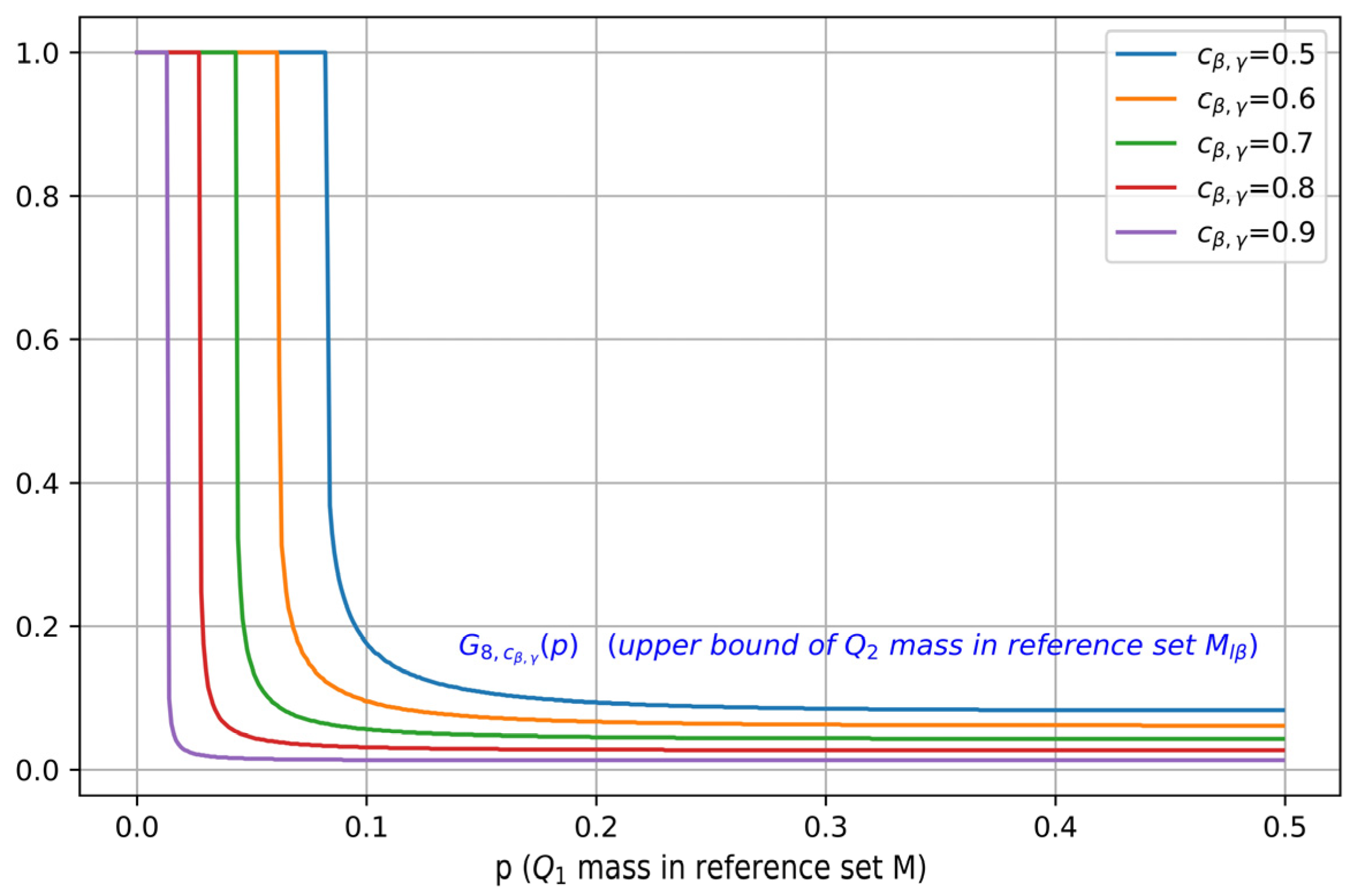
3.3. Ramifications of Theorem 1
3.4. Weighted Rips Filtration and Regularization
3.4.1. A Weight Function for Weighted Rips Filtration
3.4.2. Stability
3.4.3. Regularization via Persistent Homology
- Birth loss
- Margin loss
- Length loss
4. Experiments
4.1. Point Cloud Optimization
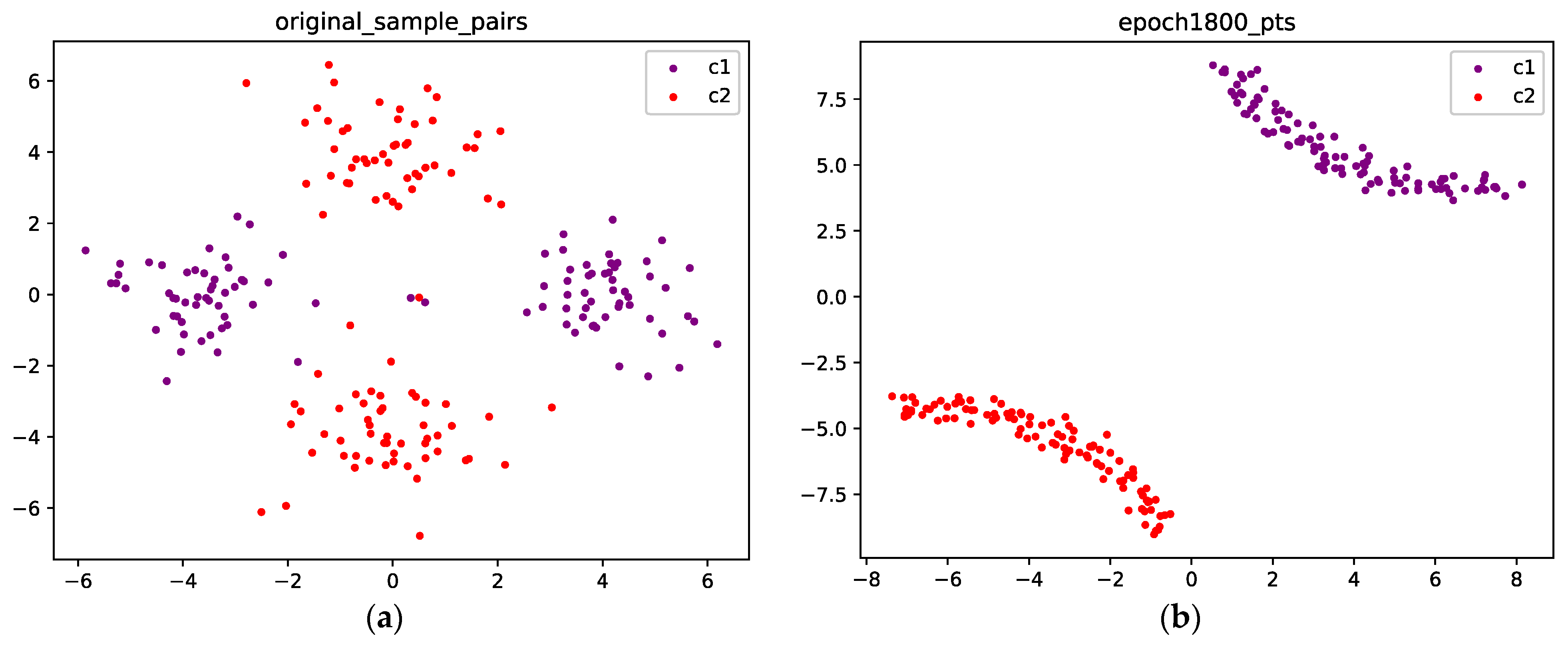
4.1.1. Gaussian Mixture with Two Components
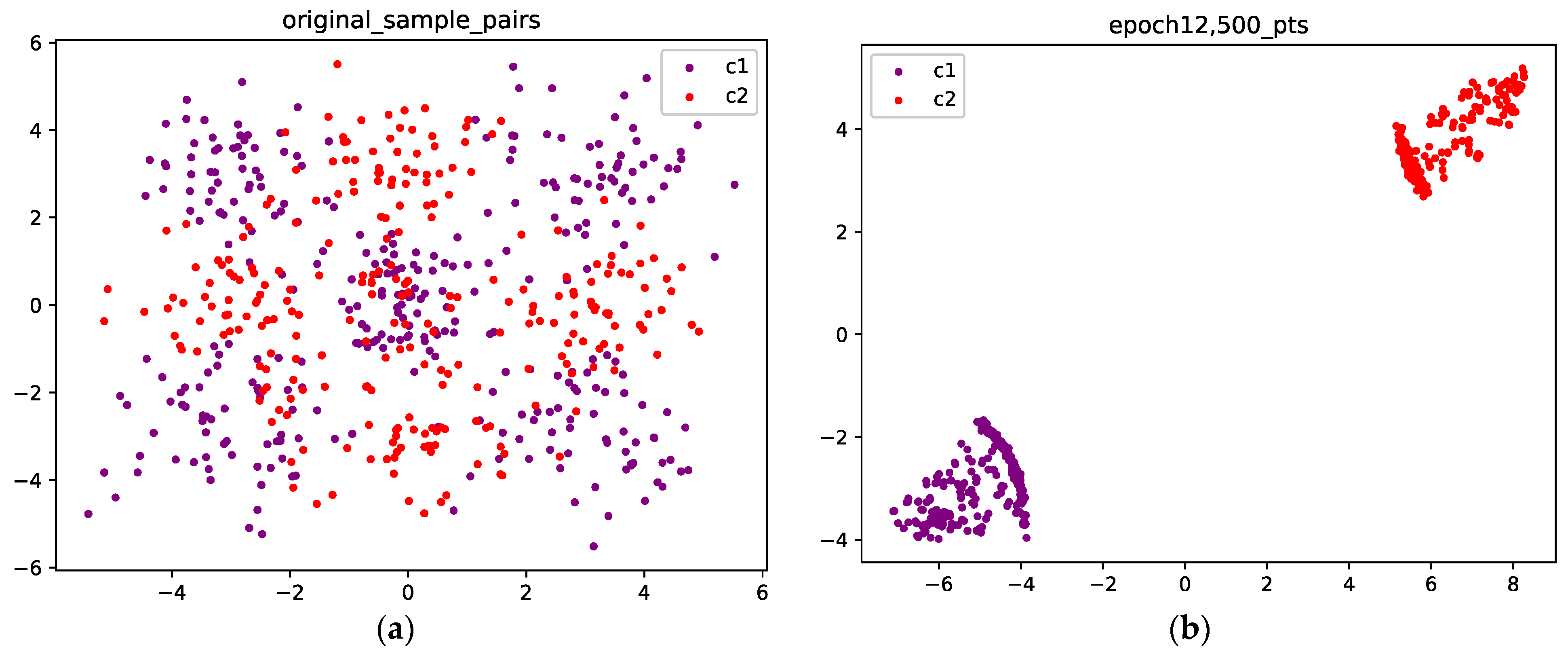
4.1.2. Gaussian Mixture with Four Components
4.1.3. Gaussian Mixture with Nine Components
4.2. Datasets
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cogswell, M.; Ahmed, F.; Girshick, R.; Zitnick, L.; Batra, D. Reducing Overfitting in Deep Networks by Decorrelating Representations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, San Juan, PR, USA, 2–4 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, D.; Rhee, W. Utilizing Class Information for Deep Network Representation Shaping. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Moor, M.; Horn, M.; Rieck, B.; Borgwardt, K. Topological Autoencoders. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 13–18 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Raghu, M.; Gilmer, J.; Yosinski, J.; Sohl-Dickstein, J. SVCCA: Singular Vector Canonical Correlation Analysis for Deep Learning Dynamics and Interpretability. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Littwin, E.; Wolf, L. Regularizing by the variance of the activations’ sample-variances. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2–8 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, T.Y.; Xu, K.; Dong, Y.P.; Du, C.; Chen, N.; Zhu, J. Rethinking Softmax Cross-Entropy Loss for Adversarial Robustness. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 26 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Qiu, Q.; Huang, J.; Calderbank, R.; Sapiro, G.; Daubechies, I. LDMNet: Low Dimensional Manifold Regularized Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson, G. Topology and Data. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 2009, 46, 255–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J.; Roberts, D.; Yaida, S. Robust Learning with Jacobian Regularization. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.02729. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Banff, AB, Canada, 14–16 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chazal, F.; Michel, B. An Introduction to Topological Data Analysis: Fundamental and Practical Aspects for Data Scientists. Front. Artif. Intell. 2017, 4, 667963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, E.; John, H. Computational Topology: An Introduction; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hensel, F.; Moor, M.; Rieck, B. A Survey of Topological Machine Learning Methods. Front. Artif. Intell. 2021, 4, 681108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüel-Gabrielsson, R.; Nelson, B.J.; Dwaraknath, A.; Skraba, P.; Guibas, L.J.; Carlsson, G. A topology layer for machine learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Online, 26–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Kim, J.; Zaheer, M.; Kim, J.S.; Chazal, F.; Wasserman, L. PLLay: Efficient Topological Layer Based on Persistence Landscapes. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Online, 6–12 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hajij, M.; Istvan, K. Topological Deep Learning: Classification Neural Networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.08354. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Dasarathy, G.; Ramamurthy, K.N.; Berisha, V. Finding the Homology of Decision Boundaries with Active Learning. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Online, 6–12 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Ni, X.; Bai, Q.; Wang, Y. A Topological Regularizer for Classifiers via Persistent Homology. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Naha, Japan, 16–18 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vandaele, R.; Kang, B.; Lijffijt, J.; De Bie, T.; Saeys, Y. Topologically Regularized Data Embeddings. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Online, 25–29 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hofer, C.; Kwitt, R.; Dixit, M.; Niethammer, M. Connectivity-Optimized Representation Learning via Persistent Homology. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Zheng, S.; Goswami, M.; Metaxas, D.; Chen, C. A Topological Filter for Learning with Label Noise. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Online, 6–12 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hofer, C.D.; Graf, F.; Niethammer, M.; Kwitt, R. Topologically Densified Distributions. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 13–18 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sizemore, A.E.; Phillips-Cremins, J.; Ghrist, R.; Bassett, D.S. The Importance of the Whole: Topological Data Analysis for the Network Neuroscientist. Netw. Neurosci. 2019, 3, 656–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chazal, F.; Cohen-Steiner, D.; Merigot, Q. Geometric Inference for Probability Measures. Found. Comput. Math. 2011, 11, 733–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anai, H.; Chazal, F.; Glisse, M.; Ike, Y.; Inakoshi, H.; Tinarrage, R.; Umeda, Y. DTM-Based Filtrations. In Proceedings of the 35th International Symposium on Computational Geometry, Portland, OR, USA, 18–21 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzer, Y.; Wang, T.; Coates, A.; Bissacco, A.; Wu, B.; Ng, A.Y. Reading Digits in Natural Images with Unsupervised Feature Learning. In Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Granada, Spain, 12–17 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A. Learning Multiple Layers of Features from Tiny Images; Technical Report; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Laine, S.; Aila, T. Temporal ensembling for semisupervised learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. SGDR: Stochastic Gradient Descent with Warm Restarts. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, H.; Xing, E.P.; Huang, D. Self-Challenging Improves Cross-Domain Generalization. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]








| Regularization | MNIST-250 | SVHN-250 | CIFAR10-500 | CIFAR10-1k |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vanilla | 7.1 ± 1.0 | 30.1 ± 2.9 | 39.4 ± 1.5 | 29.5 ± 0.8 |
| +Jac.-Reg [9] | 6.2 ± 0.8 | 33.1 ± 2.8 | 39.7 ± 2.0 | 29.8 ± 1.2 |
| +DeCov [1] | 6.5 ± 1.1 | 28.9 ± 2.2 | 38.2 ± 1.5 | 29.0 ± 0.6 |
| +VR [2] | 6.1 ± 0.5 | 28.2 ± 2.4 | 38.6 ± 1.4 | 29.3 ± 0.7 |
| +cw-CR [2] | 7.0 ± 0.6 | 28.8 ± 2.9 | 39.0 ± 1.9 | 29.1 ± 0.7 |
| +cw-VR [2] | 6.2 ± 0.8 | 28.4 ± 2.5 | 38.5 ± 1.6 | 29.0 ± 0.7 |
| +Sub-batches | 7.1 ± 0.5 | 27.5 ± 2.6 | 38.3 ± 3.0 | 28.9 ± 0.4 |
| +Sub-batches + Top.-Reg [22] | 5.6 ± 0.7 | 22.5 ± 2.0 | 36.5 ± 1.2 | 28.5 ± 0.6 |
| +Sub-batches + Top.-Reg [22] | 5.9 ± 0.3 | 23.3 ± 1.1 | 36.8 ± 0.3 | 28.8 ± 0.3 |
| +Sub-batches + Top.-Reg(Ours) | 4.3 ± 0.3 | 22.9 ± 1.3 | 35.2 ± 0.6 | 27.4 ± 0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, M.; Wang, D.; Feng, S.; Zhang, Y. Topological Regularization for Representation Learning via Persistent Homology. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11041008
Chen M, Wang D, Feng S, Zhang Y. Topological Regularization for Representation Learning via Persistent Homology. Mathematics. 2023; 11(4):1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11041008
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Muyi, Daling Wang, Shi Feng, and Yifei Zhang. 2023. "Topological Regularization for Representation Learning via Persistent Homology" Mathematics 11, no. 4: 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11041008
APA StyleChen, M., Wang, D., Feng, S., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Topological Regularization for Representation Learning via Persistent Homology. Mathematics, 11(4), 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11041008






