Effect of Antiviral Therapy for HCV Treatment in the Presence of Hepatocyte Growth Factor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Compartmental Model of HCV
- a.
- All model variables and parameters are constants and positive.
- b.
- Only one route of transmission from viral interaction with uninfected cells is considered.
- c.
- The uninfected liver cell has constant production along with proliferation from the existing cells.
- d.
- The natural death rate is considered for all compartments.
3. Well-Posedness of the Model
3.1. Boundedness
3.2. Existence Condition
- (i)
- The infection-free equilibrium with
- (ii)
- The endemic equilibrium whereand is defined aswithIf and then has a unique positive root. The coefficient if and if and if
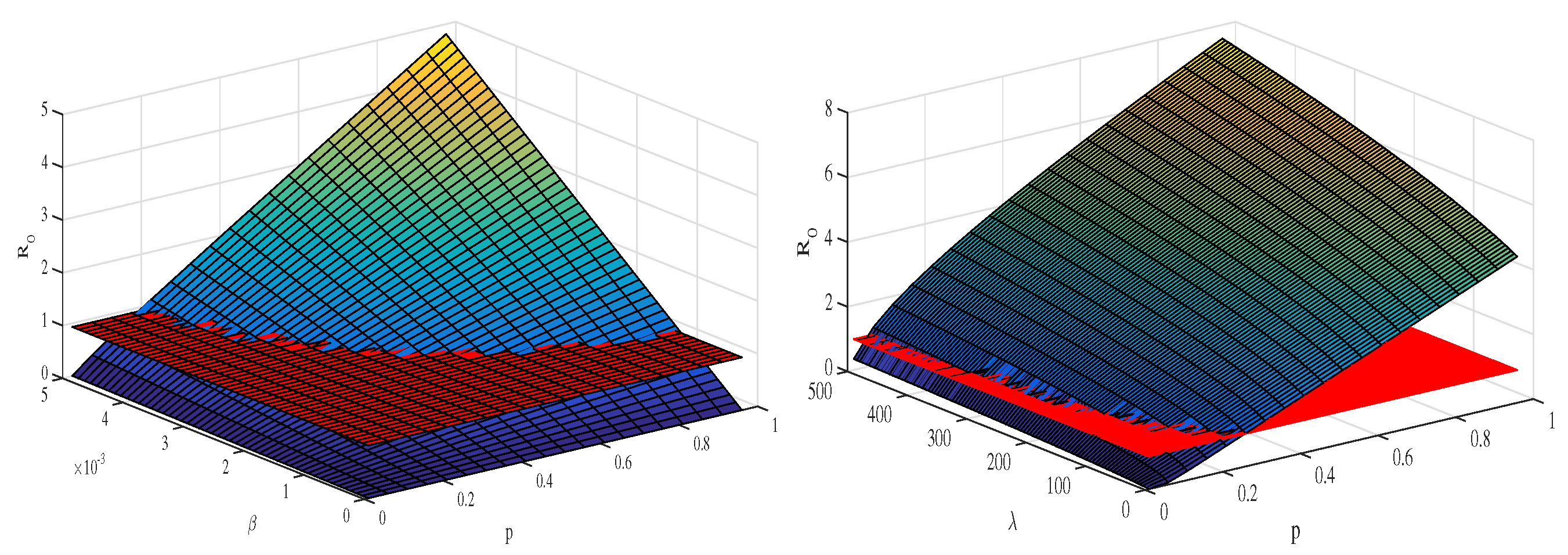
Basic Reproduction Number
- ;
- If , then ;
- for ;
- If , then for ;
- For the disease-free equilibrium (DFE) , the Jacobi matrix constrained to the subspace has all negative eigenvalues.
3.3. Stability of the System
3.4. Global Stability
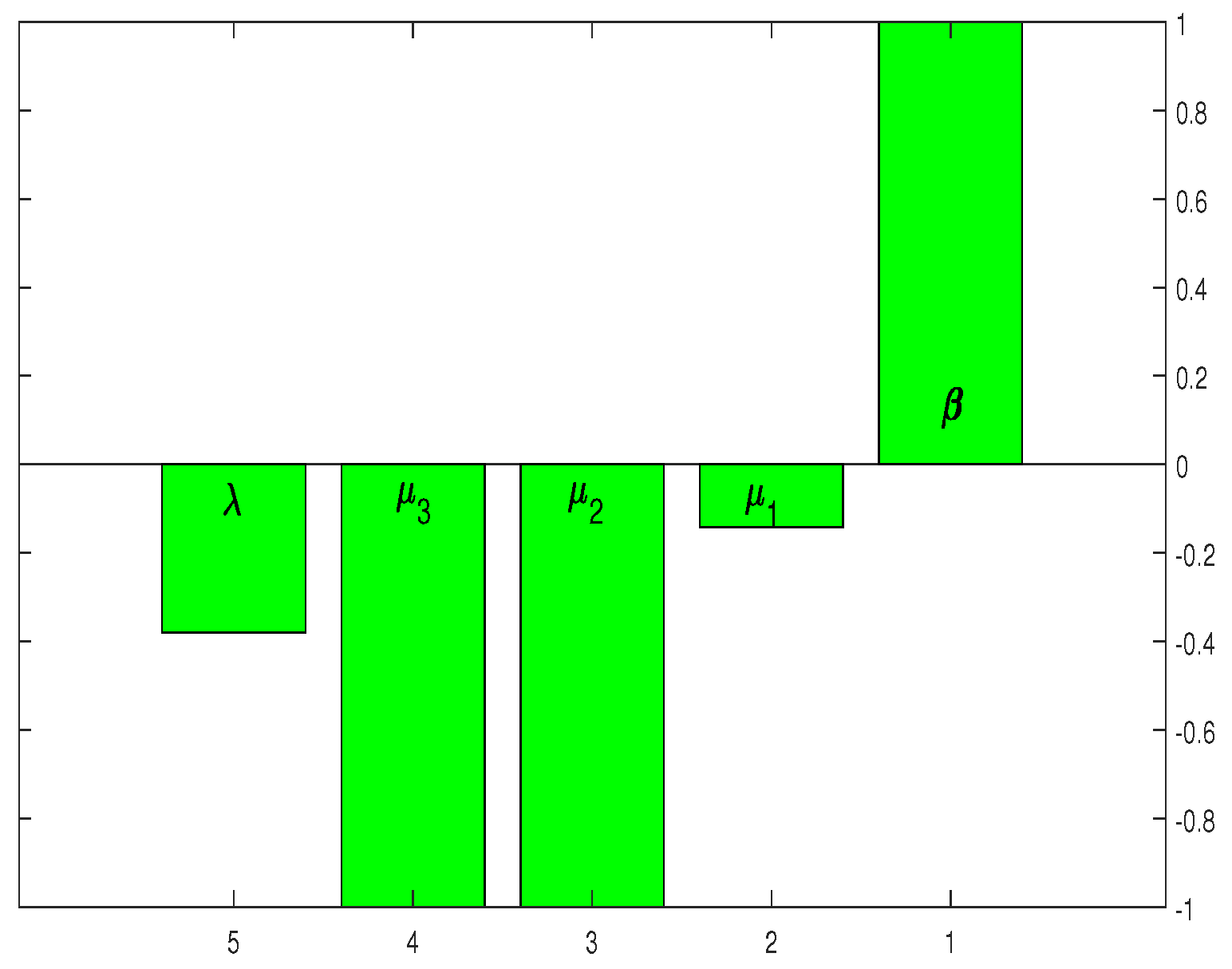
4. Sensitivity Analysis
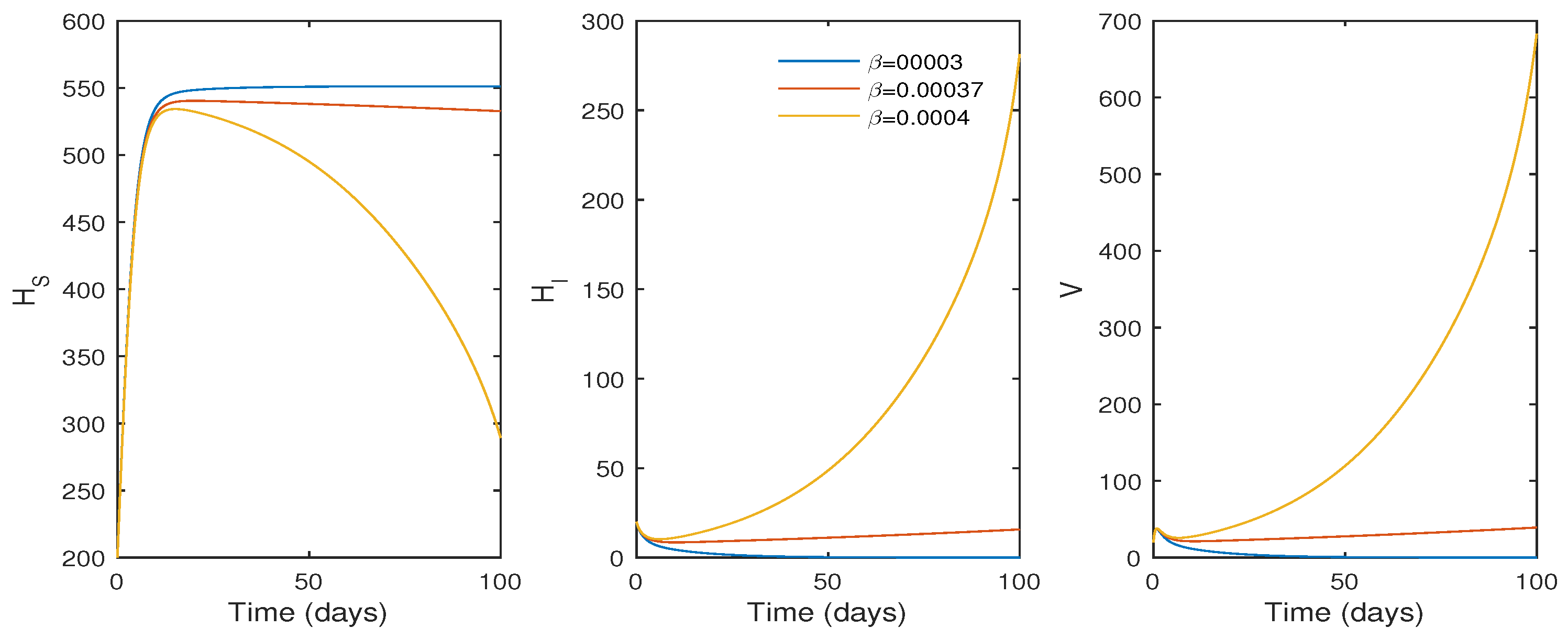
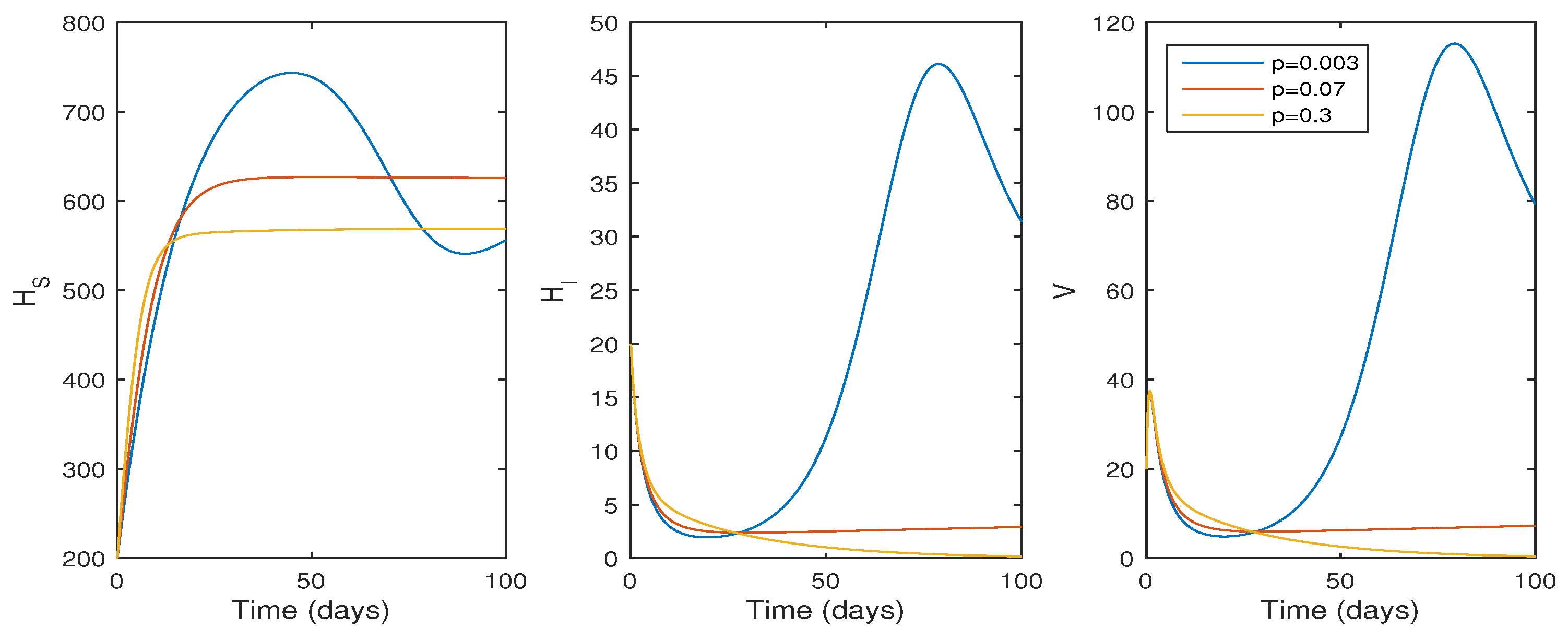
Numerical Findings of the System (1)
5. Optimal Control Problem
5.1. Methodology
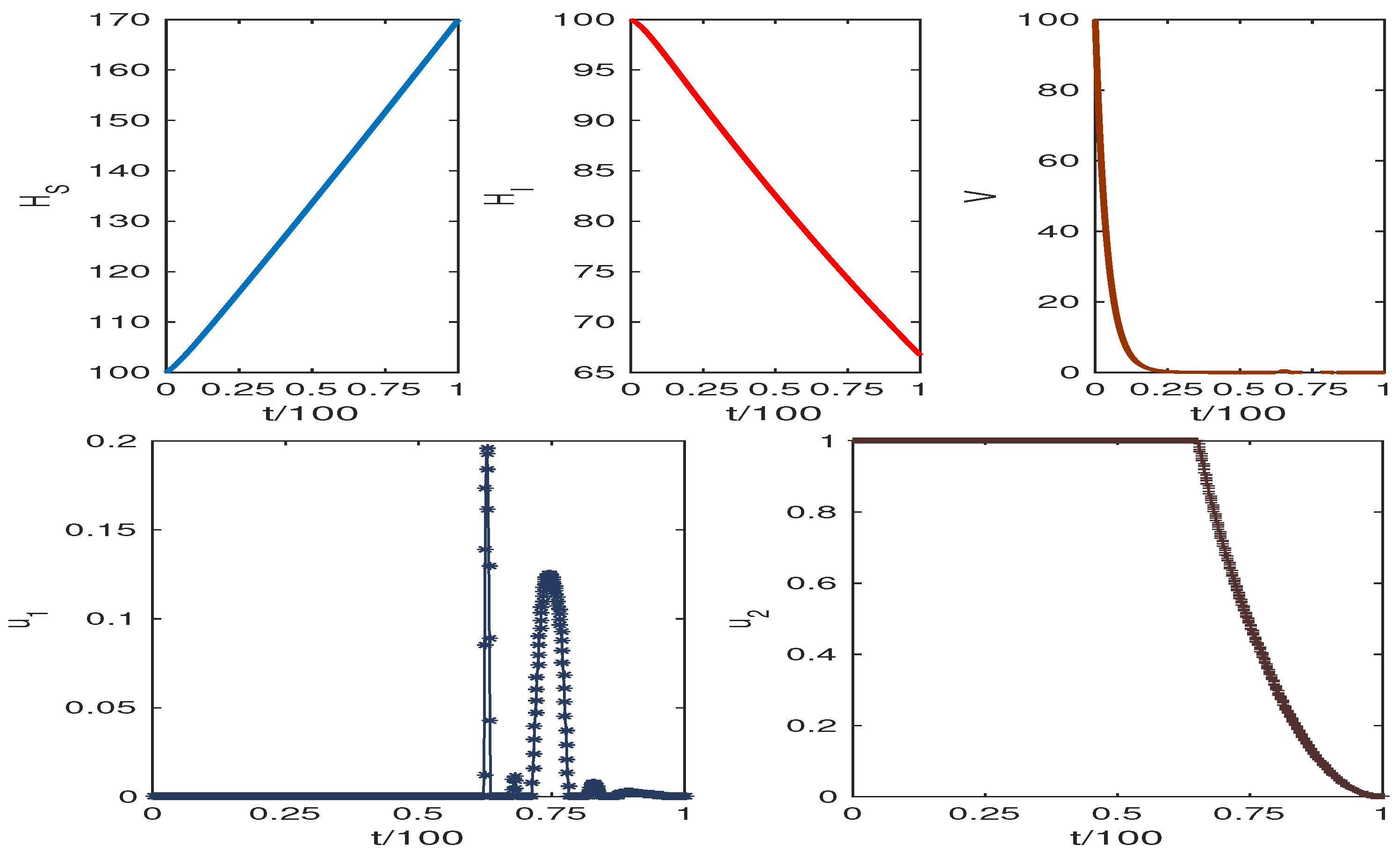
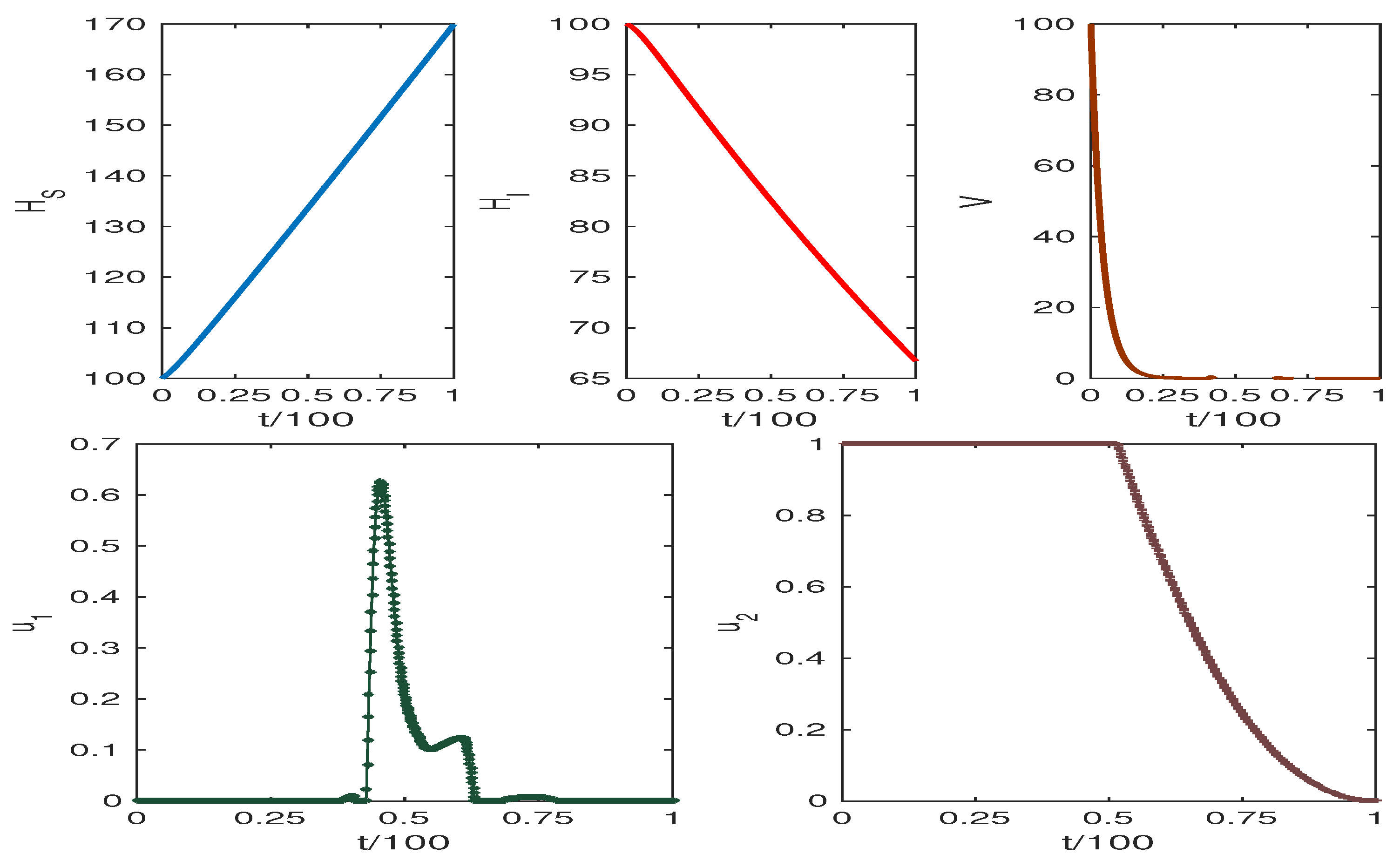
5.2. Numerical Findings of the Control System
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alvarez, F.; Berg, P.; Bianchi, F.B.; Bianchi, L.; Burroughs, A.; Cancado, E.L.; Chapman, R.; Cooksley, W.; Czaja, A.; Desmet, V.; et al. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Report: Review of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 1999, 31, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/24-06-2022-WHO-publishes-updated-guidance-on-hepatitis-C-infection (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- Sadki, M.; Danane, J.; Allali, K. Hepatitis C virus fractional-order model: Mathematical analysis. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitzmann, C.; Kaderali, L.; Perelson, A.S. Mathematical modeling of hepatitis C RNA replication, exosome secretion and virus release. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1008421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, A.N.; Roy, P.K. Anti-viral drug treatment along with immune activator IL-2: A control-based mathematical approach for HIV infection. Int. J. Control 2012, 85, 220–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.N.; Singh, M.K.; Kumar, B. The effect of immune responses in HCV disease progression. Eng. Math. Lett. 2019, 2019, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, M.A.; Bangham, C.R. Population dynamics of immune responses to persistent viruses. Science 1996, 272, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonhoeffer, S.; Coffin, J.M.; Nowak, M.A. Human immunodeficiency virus drug therapy and virus load. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 3275–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, A.U.; Lam, N.P.; Dahari, H.; Gretch, D.R.; Wiley, T.E.; Layden, T.J.; Perelson, A.S. Hepatitis C viral dynamics in vivo and the antiviral efficacy of interferon-α therapy. Science 1998, 282, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahari, H.; Lo, A.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Perelson, A.S. Modeling hepatitis C virus dynamics: Liver regeneration and critical drug efficacy. J. Theor. Biol. 2007, 247, 371–381. [Google Scholar]
- Avendano, R.; Esteva, L.; Flores, J.; Allen, J.F.; Gómez, G.; López-Estrada, J. A mathematical model for the dynamics of hepatitis C. J. Theor. Med. 2002, 4, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wodarz, D. Hepatitis C virus dynamics and pathology: The role of CTL and antibody responses. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, N.M.; Layden-Almer, J.E.; Layden, T.J.; Perelson, A.S. Modelling how ribavirin improves interferon response rates in hepatitis C virus infection. Nature 2004, 432, 922–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, Z. Global dynamics for a delayed hepatitis C virus infection model. Electron. J. Differ. Equ. 2014, 2014, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, A.N.; Al Basir, F. Role of immune effector responses during HCV infection: A mathematical study. Math. Anal. Infect. Dis. 2022, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.N.; Al Basir, F.; Takeuchi, Y. Effect of DAA therapy in hepatitis C treatment–an impulsive control approach. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 18, 1450–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, J.; Samui, P.; Chatterjee, A.N. Effect of SOF/VEL Antiviral Therapy for HCV Treatment. Lett. Biomath. 2021, 8, 191–213. [Google Scholar]
- Echevarria, D.; Gutfraind, A.; Boodram, B.; Major, M.; Del Valle, S.; Cotler, S.J.; Dahari, H. Mathematical modeling of hepatitis C prevalence reduction with antiviral treatment scale-up in persons who inject drugs in metropolitan Chicago. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, N.; McBryde, E.; Vickerman, P.; Martin, N.K.; Stone, J.; Drummer, H.; Hellard, M. The role of a hepatitis C virus vaccine: Modelling the benefits alongside direct-acting antiviral treatments. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Perelson, A.S. Mathematical analysis of multiscale models for hepatitis C virus dynamics under therapy with direct-acting antiviral agents. Math. Biosci. 2013, 245, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, X. Dynamic analysis and optimal control for a model of hepatitis C with treatment. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2017, 46, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattheij, R.; Molenaar, J. Ordinary Differential Equations in Theory and Practice; SIAM: Bangkok, Thailand, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, E.; El-Saka, H. On fractional order models for Hepatitis C. Nonlinear Biomed. Phys. 2010, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, J. Permanence and positive periodic solution for the single-species nonautonomous delay diffusive models. Comput. Math. Appl. 1996, 32, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedj, J.; Neumann, A. Understanding hepatitis C viral dynamics with direct-acting antiviral agents due to the interplay between intracellular replication and cellular infection dynamics. J. Theor. Biol. 2010, 267, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clercq, E. Current race in the development of DAAs (direct-acting antivirals) against HCV. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 89, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Pandya, M. Recent advancement of direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs) in hepatitis C therapy. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogalian, E.; German, P.; Kearney, B.P.; Yang, C.Y.; Brainard, D.; Link, J.; McNally, J.; Han, L.; Ling, J.; Mathias, A. Preclinical pharmacokinetics and first-in-human pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of velpatasvir, a pangenotypic hepatitis C virus NS5A inhibitor, in healthy subjects. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02084-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Driessche, P.; Watmough, J. Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 2002, 180, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawitz, E.J.; Dvory-Sobol, H.; Doehle, B.P.; Worth, A.S.; McNally, J.; Brainard, D.M.; Link, J.O.; Miller, M.D.; Mo, H. Clinical resistance to velpatasvir (GS-5816), a novel pan-genotypic inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus NS5A protein. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5368–5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Stepanova, M.; Feld, J.; Zeuzem, S.; Sulkowski, M.; Foster, G.R.; Mangia, A.; Charlton, M.; O’Leary, J.G.; Curry, M.P.; et al. Sofosbuvir and velpatasvir combination improves patient-reported outcomes for patients with HCV infection, without or with compensated or decompensated cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffernan, J.M.; Smith, R.J.; Wahl, L.M. Perspectives on the basic reproductive ratio. J. R. Soc. Interface 2005, 2, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Roy, P.; Grigorenko, N.; Khailov, E.; Grigorieva, E. Mathematical Modeling and Control of the Cell Dynamics in Leprosy. Comput. Math. Model. 2021, 32, 52–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukes, D.L. Differential Equations: Classical to Controlled; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Pontryagin, L.S. Mathematical Theory of Optimal Processes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
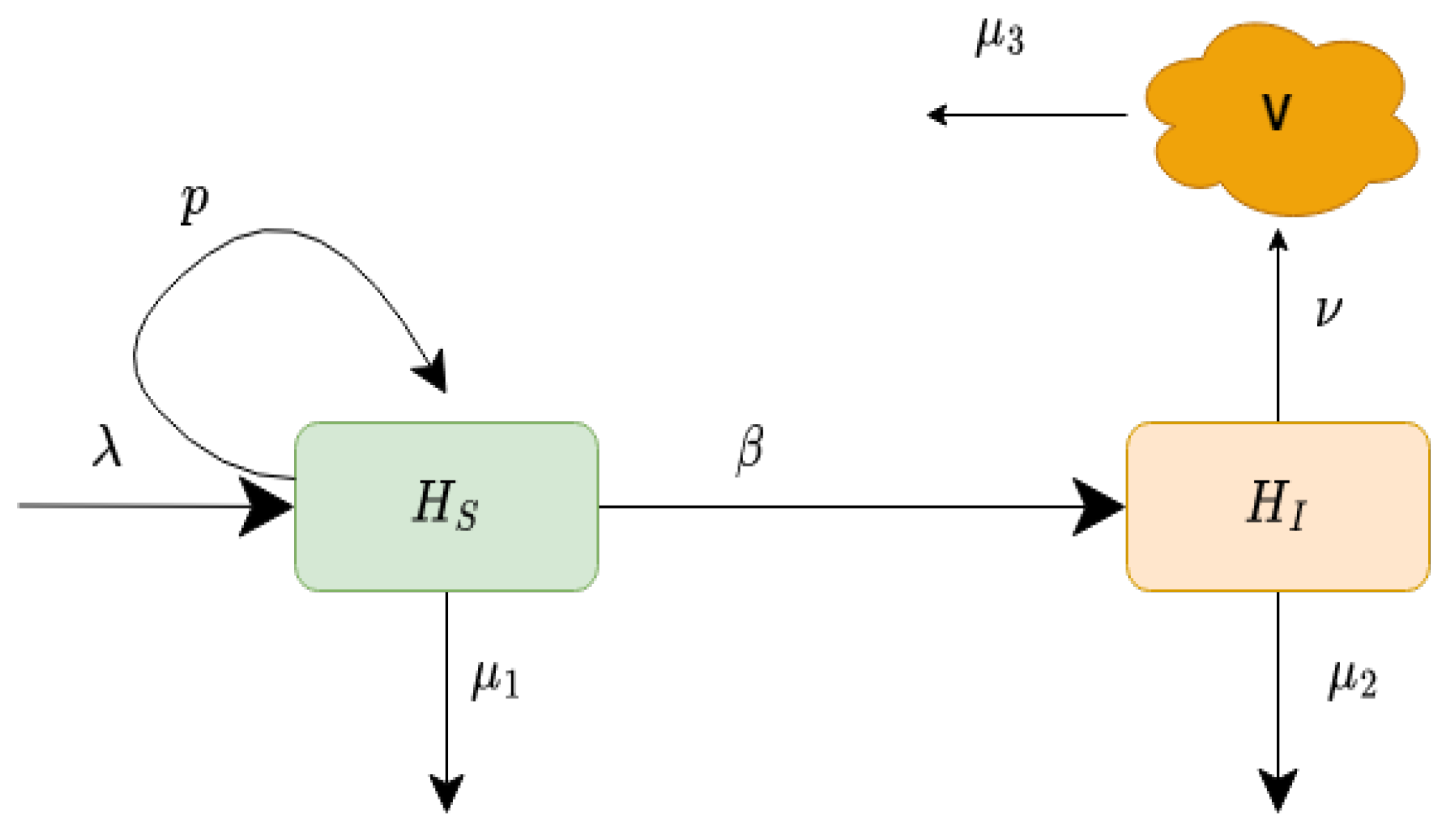
| Parameters | Short Description | Range of Value | Value Taken |
|---|---|---|---|
| Growth rate of Hepatocyte cells | 2–20 | 5 | |
| p | Proliferation rate | 0.1–0.6 | |
| Rate of infection | 0.00001–0.0019 | ||
| Natural death rate | 0.12–0.35 | ||
| uninfected Hepatocyte cells | |||
| Blanket death rate of | 0.10–0.41 | ||
| infected Hepatocyte cells | |||
| The simulation rate of virus | 10 -140 | 70 | |
| Virus clearance rate | 0.3–1 | ||
| Total Hepatocyte number | 100–1000 | 500 |
| Parameter | Indices | % Increase or Decrease | Impact of |
|---|---|---|---|
| −0.3125 | 10 | −3.125% | |
| +1 | 10 | 10% | |
| −0.1423 | 10 | −1.423% | |
| −1 | 10 | −10% | |
| −1 | 10 | −10% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, S.K.; Chatterjee, A.N.; Ahmad, B. Effect of Antiviral Therapy for HCV Treatment in the Presence of Hepatocyte Growth Factor. Mathematics 2023, 11, 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11030751
Sharma SK, Chatterjee AN, Ahmad B. Effect of Antiviral Therapy for HCV Treatment in the Presence of Hepatocyte Growth Factor. Mathematics. 2023; 11(3):751. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11030751
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Santosh Kumar, Amar Nath Chatterjee, and Bashir Ahmad. 2023. "Effect of Antiviral Therapy for HCV Treatment in the Presence of Hepatocyte Growth Factor" Mathematics 11, no. 3: 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11030751
APA StyleSharma, S. K., Chatterjee, A. N., & Ahmad, B. (2023). Effect of Antiviral Therapy for HCV Treatment in the Presence of Hepatocyte Growth Factor. Mathematics, 11(3), 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11030751








