A New Efficient Method for Absolute Value Equations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Proposed Method
| Algorithm 1: NTS Method |
1: Choose . 2: For k, calculate 3: Using Step 2, calculate 4: If , then stop. Otherwise, go to step 2. |
3. Convergence
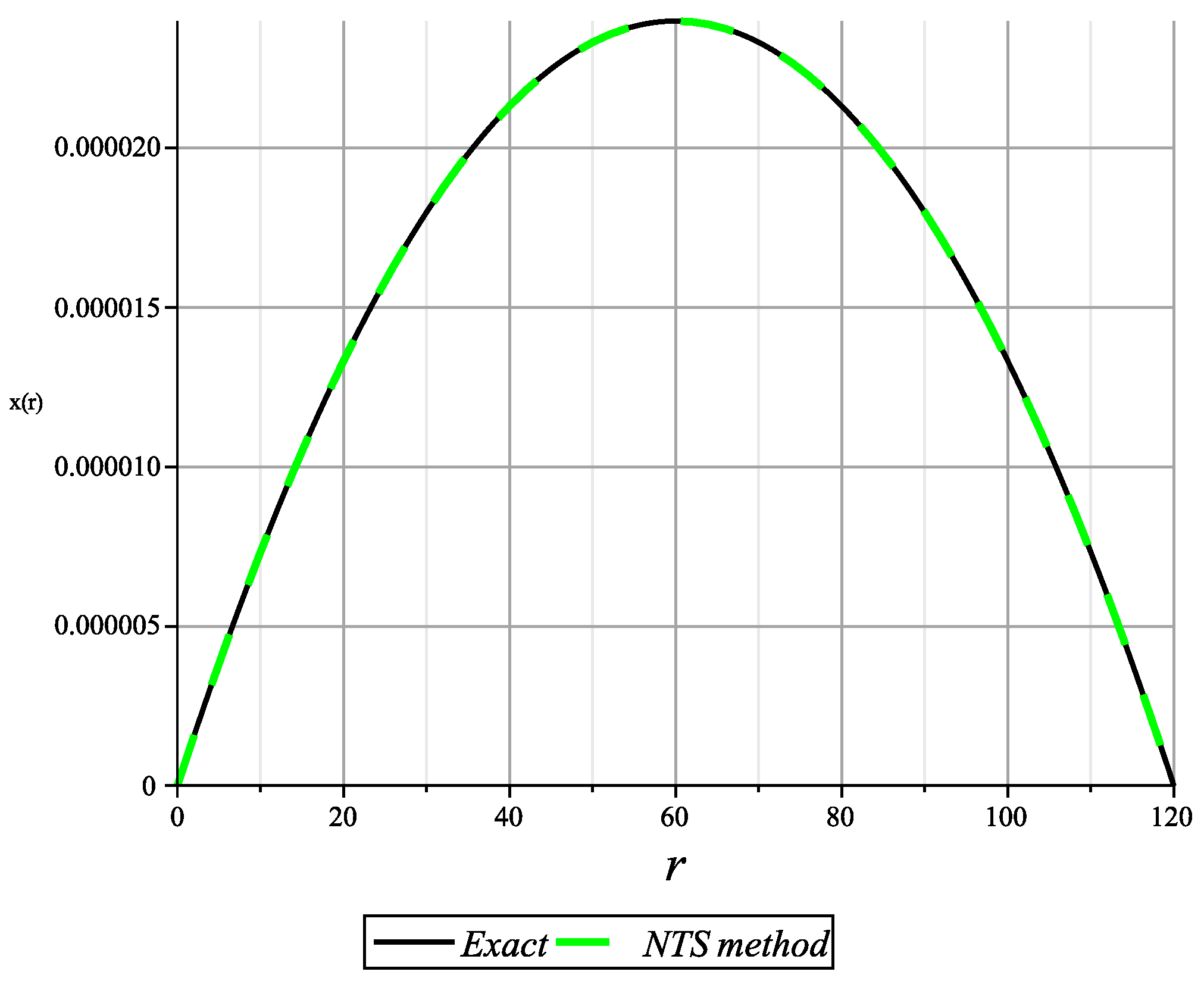
4. Numerical Result
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rohn, J. A theorem of the alternatives for the equation Ax + B|x| = b. Linear Multilinear Algebra 2004, 52, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangasarian, O.L.; Meyer, R.R. Absolute value equations. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 2006, 419, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoori, A.; Eshaghnezhad, M.; Effati, S. An efficient neural network model for solving the absolute value equations. IEEE Tran. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 2017, 65, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D.; Han, D. An inverse-free dynamical system for solving the absolute value equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 2021, 168, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairong, C.; Yu, D.; Han, D. Exact and inexact Douglas-Rachford splitting methods for solving large-scale sparse absolute value equations. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 2023, 43, 1036–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, R. Numerical solution of the absolute value equation using modified iteration methods. Comput. Math. Methods 2022, 2022, 2828457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Khan, I.; Ali, A.; Mohamed, A. Two new generalized iteration methods for solving absolute value equations using M-matrix. AIMS Math. 2022, 7, 8176–8187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edalatpour, V.; Hezari, D.; Salkuyeh, D.K. A generalization of the Gauss-Seidel iteration method for solving absolute value equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 2017, 293, 156–167. [Google Scholar]
- Haung, B.; Li, W. A modified SOR-like method for absolute value equations associated with second order cones. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2022, 400, 113745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoori, A.; Erfanian, M. A dynamic model to solve the absolute value equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2018, 333, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, M.A.; Iqbal, J.; Al-Said, E. Residual Iterative Method for Solving Absolute Value Equations. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2012, 2012, 406232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salkuyeh, D.K. The Picard-HSS iteration method for absolute value equations. Optim. Lett. 2014, 8, 2191–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, L.; Haddou, M.; Migot, T. Solving absolute value equation using complementarity and smoothing functions. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2018, 327, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, L.; Yuan, Y. A modified multivariate spectral gradient algorithm for solving absolute value equations. Appl. Math. Lett. 2021, 21, 107461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, D.; Yuan, Y. On the Alternative SOR-like Iteration Method for Solving Absolute Value Equations. Symmetry 2023, 15, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Liu, S. An improved generalized Newton method for absolute value equations. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Feng, J.; Liu, S. A new two-step iterative method for solving absolute value equations. J. Inequal. Appl. 2019, 2019, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Iqbal, J.; Akgul, A.; Ali, R.; Du, Y.; Hussain, A.; Nisar, K.S.; Vijayakumar, V. A Newton-type technique for solving absolute value equations. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 64, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Iqbal, J.; Arif, M.; Khan, A. A two-step Newton-type method for solving system of absolute value equations. Math. Prob. Eng. 2020, 2020, 2798080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, M.A.; Iqbal, J.; Khattri, S.; Al-Said, E. A new iterative method for solving absolute value equations. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2011, 6, 1793–1797. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Iqbal, J.; Raiz, F.; Arif, M. Gauss quadrature method for absolute value equations. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.-M.; Huang, T.-Z.; Li, H.-B.; Wang, S.-F.; Li, L. Two CSCS-based iteration methods for solving absolute value equations. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 2017, 7, 1336–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Mangasarian, O.L. A generalized Newton method for absolute value equations. Optim. Lett. 2009, 3, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyak, B.T. Introduction to Optimization; Optimization Software Inc., Publications Division: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Rockafellar, R.T. Convex Analysis; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, J.M.; Rheinboldt, W.C. Iterative Solution of Nonlinear Equations in Several Variables; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
| Method | s | 1000 | 2000 | 3000 | 4000 | 5000 | 6000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | 24 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | |
| RIM | CPU | 7.084206 | 54.430295 | 150.798374 | 321.604186 | 581.212038 | 912.840059 |
| RES | 7.6844 × 10 | 4.9891 × 10 | 6.3532 × 10 | 7.6121 × 10 | 8.8041 × 10 | 9.9454 × 10 | |
| K | 30 | 31 | 32 | 32 | 33 | 33 | |
| MSOR-Like | CPU | 0.0067390 | 0.0095621 | 0.0215634 | 0.0541456 | 0.0570134 | 0.0791257 |
| RES | 5.5241 × 10 | 7.0154 × 10 | 5.8684 × 10 | 9.0198 × 10 | 5.6562 × 10 | 7.4395 × 10 | |
| K | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| GNM | CPU | 0.0059651 | 0.007333 | 0.0115038 | 0.0330345 | 0.0551818 | 0.0783684 |
| RES | 3.1777 × 10 | 7.8326 × 10 | 2.6922 × 10 | 3.7473 × 10 | 8.3891 × 10 | 5.8502 × 10 | |
| K | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| NTS method | CPU | 0.001816 | 0.003410 | 0.018771 | 0.0326425 | 0.031539 | 0.069252 |
| RES | 9.6317 × 10 | 2.3697 × 10 | 4.1777 × 10 | 6.2756 × 10 | 8.20814 × 10 | 5.9998 × 10 |
| Method | s | 200 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| TSI | RES | 7.6320 × 10 | 9.0622 × 10 | 1.9329 × 10 | 4.0817 × 10 | 7.1917 × 10 |
| CPU | 0.031619 | 0.120520 | 0.32591 | 0.83649 | 1.00485 | |
| K | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| INM | RES | 2.1320 × 10 | 6.6512 × 10 | 3.0321 × 10 | 2.0629 × 10 | 8.0150 × 10 |
| CPU | 0.012851 | 0.098124 | 0.156810 | 0.638421 | 1 0.982314 | |
| K | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| GQ method | RES | 2.1415 × 10 | 4.4320 × 10 | 1.0515 × 10 | 1.9235 × 10 | 2.8104 × 10 |
| CPU | 0.013145 | 0.038734 | 0.162439 | 0.204578 | 0.276701 | |
| K | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| NTS method | RES | 1.0637 × 10 | 4.0165 × 10 | 1.0430 × 10 | 2.0644 × 10 | 2.1660 × 10 |
| CPU | 0.012832 | 0.071124 | 0.153001 | 0.201356 | 0.274165 |
| Methods | s | 1000 | 2000 | 3000 | 4000 | 5000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | |
| GGS | RES | 2.4156 × 10 | 2.7231 × 10 | 3.1872 × 10 | 3.2167 × 10 | 3.4538 × 10 |
| CPU | 0.514656 | 1.045221 | 1.153442 | 1.843198 | 5.652411 | |
| K | 7 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | |
| MGS | RES | 6.7056 × 10 | 7.30285 × 10 | 7.6382 × 10 | 9.57640 × 10 | 8.52425 × 10 |
| CPU | 0.215240 | 0.912429 | 0.916788 | 1.503518 | 4.514201 | |
| K | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| Method II | RES | 3.6218 × 10 | 5.1286 × 10 | 6.2720 × 10 | 7.2409 × 10 | 8.0154 × 10 |
| CPU | 0.238352 | 0.541264 | 0.961534 | 1.453189 | 2.109724 | |
| K | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| NTS method | RES | 4.9774 × 10 | 7.0304 × 10 | 8.6069 × 10 | 9.9363 × 10 | 1.1107 × 10 |
| CPU | 0.204974 | 0.321184 | 0.462869 | 0.819503 | 1.721235 |
| MMSGP | MM | NTS Method | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s | K | CPU | RES | K | CPU | RES | K | CPU | RES |
| 2 | 24 | 0.005129 | 5.6800 × 10 | 2 | 0.029965 | 1.2079 × 10 | 1 | 0.0032321 | 1.7763 × 10 |
| 4 | 37 | 0.008701 | 9.7485 × 10 | 4 | 0.027864 | 5.5011 × 10 | 1 | 0.008621 | 3.5527 × 10 |
| 8 | 45 | 0.009217 | 5.5254 × 10 | 6 | 0.045387 | 6.9779 × 10 | 1 | 0.004120 | 2.9296 × 10 |
| 16 | 66 | 0.012458 | 5.8865 × 10 | 7 | 0.356930 | 2.0736 × 10 | 1 | 0.006156 | 8.4072 × 10 |
| 32 | 55 | 0.031597 | 8.2514 × 10 | 8 | 0.033277 | 4.9218 × 10 | 1 | 0.005108 | 2.1645 × 10 |
| 64 | 86 | 0.085621 | 7.6463 × 10 | 9 | 0.185753 | 9.0520 × 10 | 1 | 0.008120 | 1.0088 × 10 |
| 128 | 90 | 0.521056 | 6.3326 × 10 | 9 | 0.452394 | 1.7912 × 10 | 1 | 0.362162 | 2.2822 × 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, P.; Iqbal, J.; Ghufran, S.M.; Arif, M.; Alhefthi, R.K.; Shi, L. A New Efficient Method for Absolute Value Equations. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3356. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11153356
Guo P, Iqbal J, Ghufran SM, Arif M, Alhefthi RK, Shi L. A New Efficient Method for Absolute Value Equations. Mathematics. 2023; 11(15):3356. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11153356
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Peng, Javed Iqbal, Syed Muhammad Ghufran, Muhammad Arif, Reem K. Alhefthi, and Lei Shi. 2023. "A New Efficient Method for Absolute Value Equations" Mathematics 11, no. 15: 3356. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11153356
APA StyleGuo, P., Iqbal, J., Ghufran, S. M., Arif, M., Alhefthi, R. K., & Shi, L. (2023). A New Efficient Method for Absolute Value Equations. Mathematics, 11(15), 3356. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11153356








