A Dual Rumor Spreading Model with Consideration of Fans versus Ordinary People
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation and Preliminaries
- m: the coming rate of internet users;
- : the percentage of fans among internet users, where ;
- : the exit rate of each group;
- : the transmission rate from to ();
- : the cross-transmitted rate from to ;
- : the forgetting rate of ().
3. Existence of Equilibriums
4. Stability Analysis of the Rumor-Spreading Model
4.1. The Threshold Parameter
4.2. Stability at the Rumor-Demise Equilibrium
4.3. Stability at the Rumor-Permanence Equilibrium
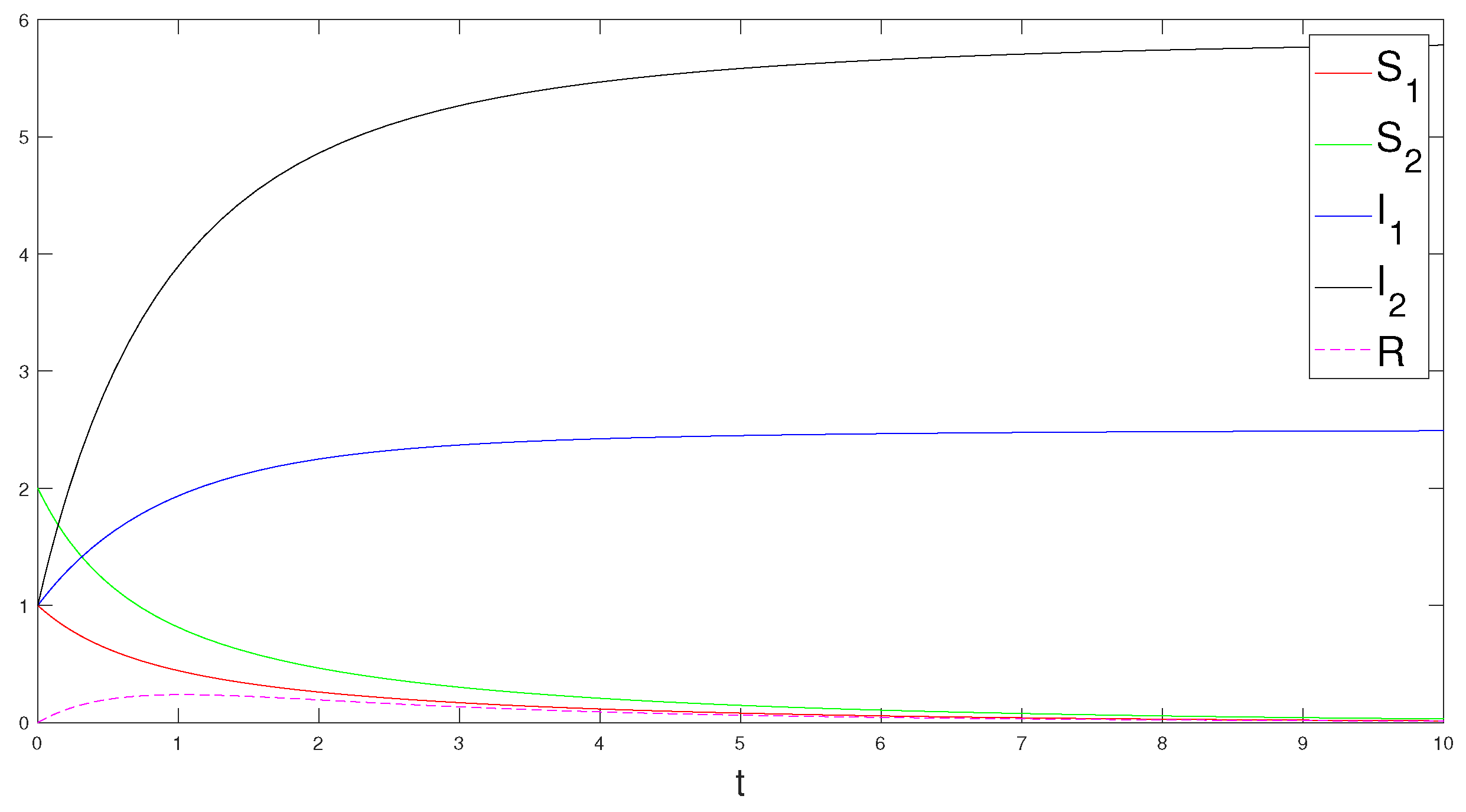
5. Numerical Simulations and Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Delay, D.; Kendall, D. Stochastic rumors. J. Inst. Math. Its Appl. 1965, 1, 42–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Guan, G.; Li, Y. Nonlinear dynamical analysis and control strategies of a network-based SIS epidemic model with time delay. Appl. Math. Model. 2019, 70, 512–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Ma, T.; Hu, C. Global dynamics of the multi-lingual SIR rumor spreading model with cross-transmitted mechanism. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2019, 126, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, K.A.; Kuga, K.; Tanimoto, J. Analysis of SIR epidemic model with information spreading of awareness. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2018, 119, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhu, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Loke, S.W. Rumor Source Detection in Networks Based on the SEIR Model. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 45240–45258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Huang, X.; Cai, X.; Zhu, X.; Lu, L. ILSR rumor spreading model with degree in complex network. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 531, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, H.; Yu, Z.; Hu, C. Dynamical analysis of rumor spreading model in homogeneous complex networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 2019, 359, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ren, N.; Jin, Z. An SICR rumor spreading model in heterogeneous networks. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst.-B 2020, 25, 1497–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Huang, X. SIS Model of Rumor Spreading in Social Network with Time Delay and Nonlinear Functions. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2020, 72, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekovee, M.; Moreno, Y.; Bianconi, G.; Marsili, M. Theory of rumour spreading in complex social networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2007, 374, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huo, L.; Chen, X. Near-optimal control of a stochastic rumor spreading model with Holling II functional response function and imprecise parameters. Chin. Phys. B 2021, 12, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhan, X.-X.; Zhang, Z.-K.; Sun, G.-Q.; Hui, P.M. How events determine spreading patterns: Information transmission via internal and external influences on social networks. New J. Phys. 2015, 17, 113045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Jia, W.; Niu, W.; Zhang, M.; Liu, S. SIR-IM: SIR rumor spreading model with influence mechanism in social networks. Soft Comput. 2020, 25, 13949–13958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, T.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Dong, J. Spreading dynamics of an online social rumor model with psychological factors on scale-free networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 525, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Li, W. Spreading dynamics of forget-remember mechanism. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95, 042306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, L. The influence of oblivion-recall mechanism and loss-interest mechanism on the spread of rumors in complex networks. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2019, 30, 1950075. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, B.; Han, S.-H.; Jin, Z. Modeling of knowledge transmission by considering the level of forgetfulness in complex networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2016, 451, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Xie, L. Simulating rumor spreading and rebuttal strategy with rebuttal forgetting: An agent-based modeling approach. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2023, 612, 128488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Q.; Yang, X.-Y.; Han, Y.-L.; Wang, X.-A. Rumor Spreading Model with Trust Mechanism in Complex Social Networks. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2013, 59, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Deng, X. Rumor spreading model with considering debunking behavior in emergencies. Appl. Math. Comput. 2019, 363, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Pan, Q.; Hou, W.; He, M. Rumor spreading model considering the proportion of wisemen in the crowd. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 505, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Song, N. Dynamical interplay between the dissemination of scientific knowledge and rumor spreading in emergency. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2016, 461, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trpevski, D.; Tang, W.; Kocarev, L. Model for rumor spread in gover networks. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Huang, R. 2SI2R rumor spreading model inhomogeneous networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2014, 413, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.; Liu, J.; Xiang, G. Anti-rumor dynamics and emergence of the timing threshold on complex network. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2014, 411, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, M.; Yu, S.; Ying, Z. Research on double rumor model in online social network. Comput. Technol. Dev. 2017, 27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zan, Y. DSIR double-rumors spreading model in complex networks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2018, 110, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieken, V. Producing Celebrity and The Economics of Attention, Celebrity Society; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Marwick, A. Instafame: Luxury selfies in the attention economy. Public Cult. 2015, 27, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tinkler, P. A fragmented picture: Reflections on the photographic practices of young people. Vis. Stud. 2008, 23, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieken, V. Imagined Community and Long-Distance Intimacy. Celebrity Society; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lipsman, A.; Mudd, G.; Rich, M.; Bruich, S. The Power of ”Like” How Brands Reach (and Influence) Fans Through Social-Media Marketing. J. Advert. Res. 2012, 1, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmatycki, L. Sports Arena vs. Crowd Psychology—A Psychosocial Analysis of Polish Football Fans’ Participation in UEFA EURO 2012. Balt. J. Health Phys. Act. 2013, 1, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wu, X.; Yang, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhong, S. Modeling cyber rumor spreading over mobile social networks: A compartment approach. Appl. Math. Comput. 2019, 343, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driessche, P.V.D.; Watmough, J. Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 2002, 180, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.Y. An Introduction to Mathematical Modeling of Infectious Diseases; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz, A. On the conditions under which an equation has only roots with negative real parts. Math. Annelen 1985, 46, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erawaty, N.; Kasbawati; Amir, A.K. Stability Analysis for Routh-Hurwitz Conditions Using Partial Pivot. J. Physics Conf. Ser. 2019, 1341, 062017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhao, Y. A Dual Rumor Spreading Model with Consideration of Fans versus Ordinary People. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2958. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132958
Xiao H, Li Z, Zhang Y, Lin H, Zhao Y. A Dual Rumor Spreading Model with Consideration of Fans versus Ordinary People. Mathematics. 2023; 11(13):2958. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132958
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Hongying, Zhaofeng Li, Yuanyuan Zhang, Hong Lin, and Yuxiao Zhao. 2023. "A Dual Rumor Spreading Model with Consideration of Fans versus Ordinary People" Mathematics 11, no. 13: 2958. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132958
APA StyleXiao, H., Li, Z., Zhang, Y., Lin, H., & Zhao, Y. (2023). A Dual Rumor Spreading Model with Consideration of Fans versus Ordinary People. Mathematics, 11(13), 2958. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132958





