Partial Eigenstructure Assignment for Linear Time-Invariant Systems via Dynamic Compensator
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Notations and Assumptions
3. Problem Description and Preliminary Results
3.1. Partial Eigenvector Matrices
3.2. Problem Statement
3.3. Preliminary Results
4. Parametric Solutions to Problem PEA
4.1. and Are Arbitrary
4.2. and Are Two Diagonal Matrices
5. Design Algorithm for Problem PEA
6. Utilizing the Degrees of Freedom in Parameters
- Low control gain
- Low compensation gain
7. An Illustrative Example
7.1. System Description
7.2. Non-Optimized Solution
7.3. Optimized Solution
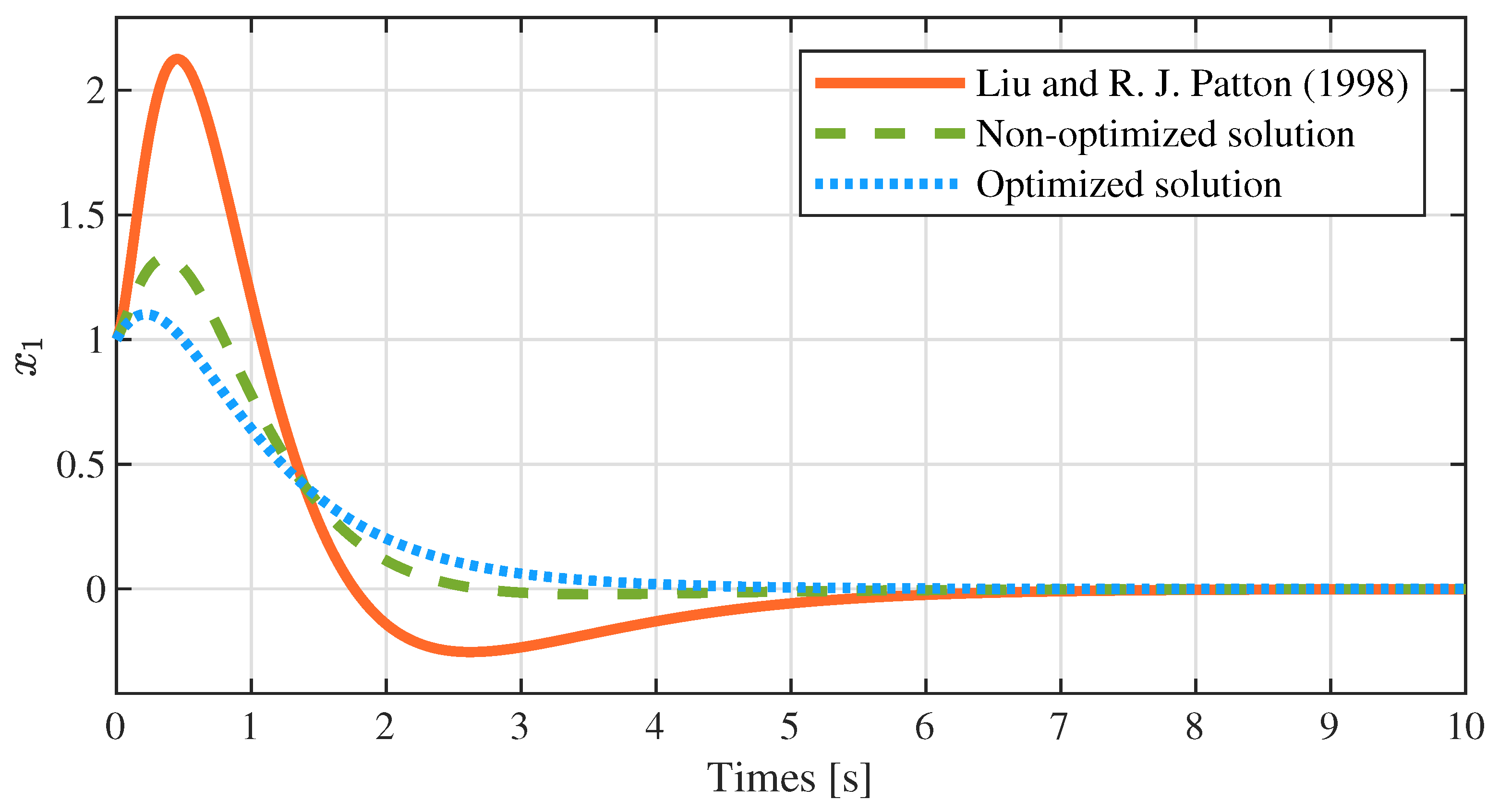
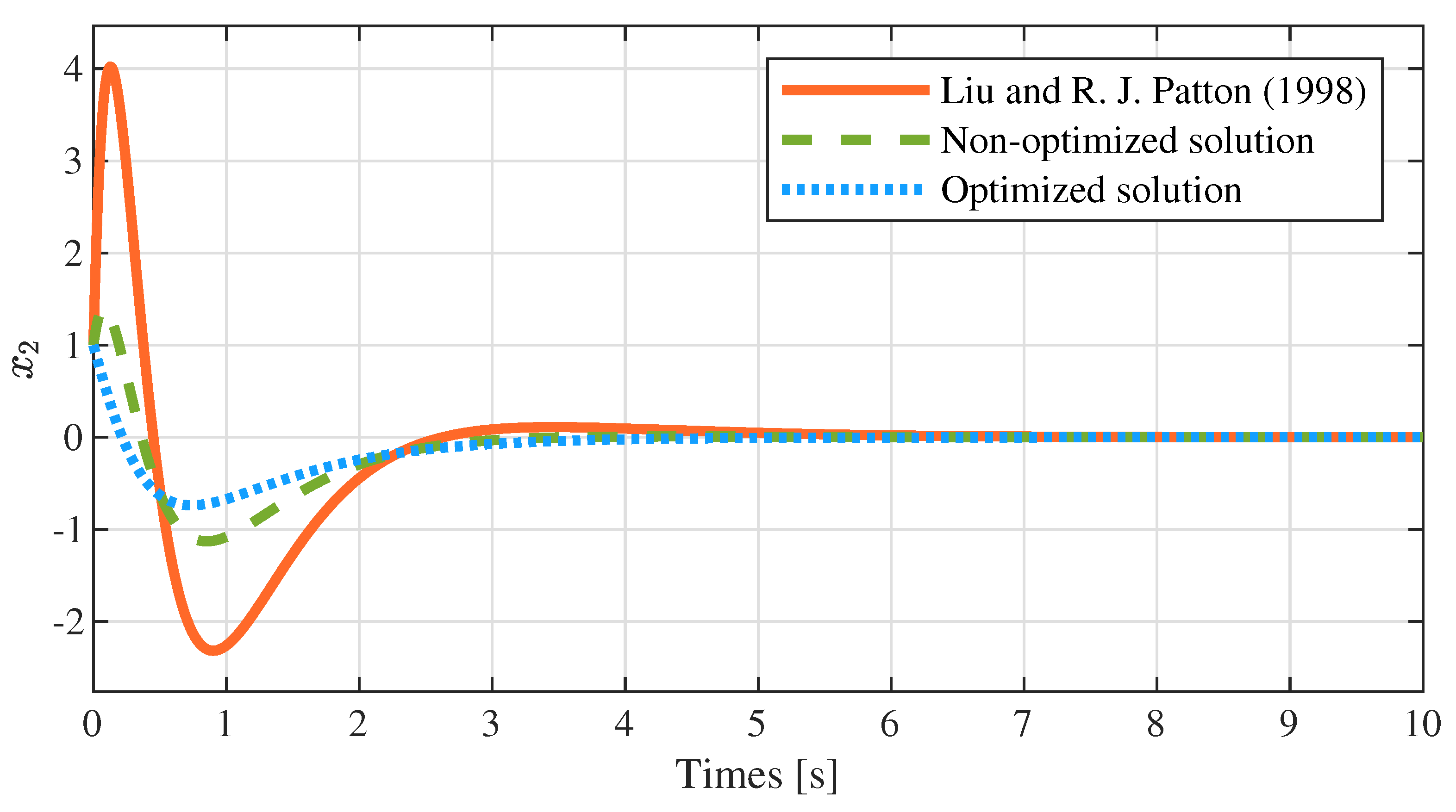
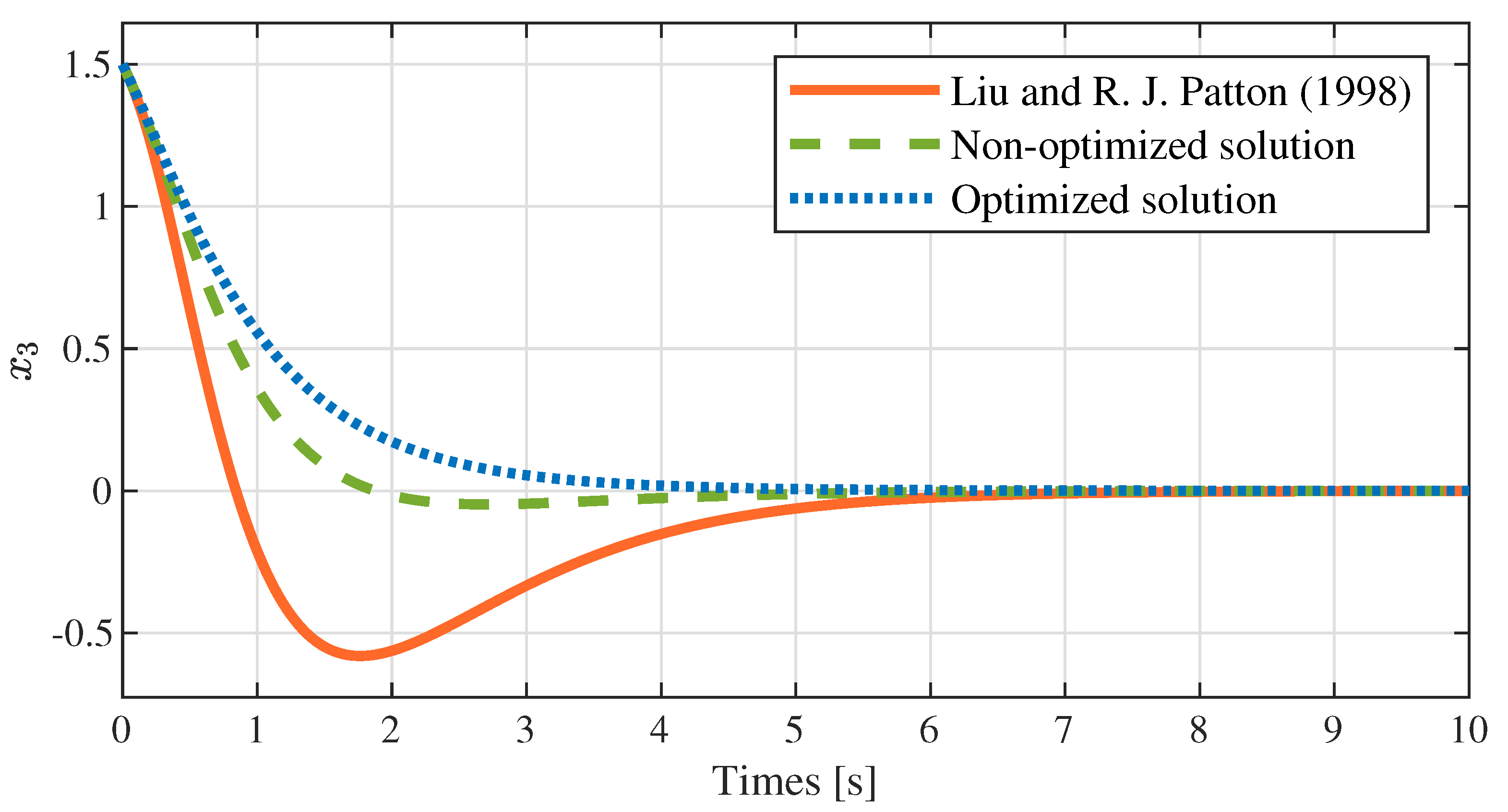
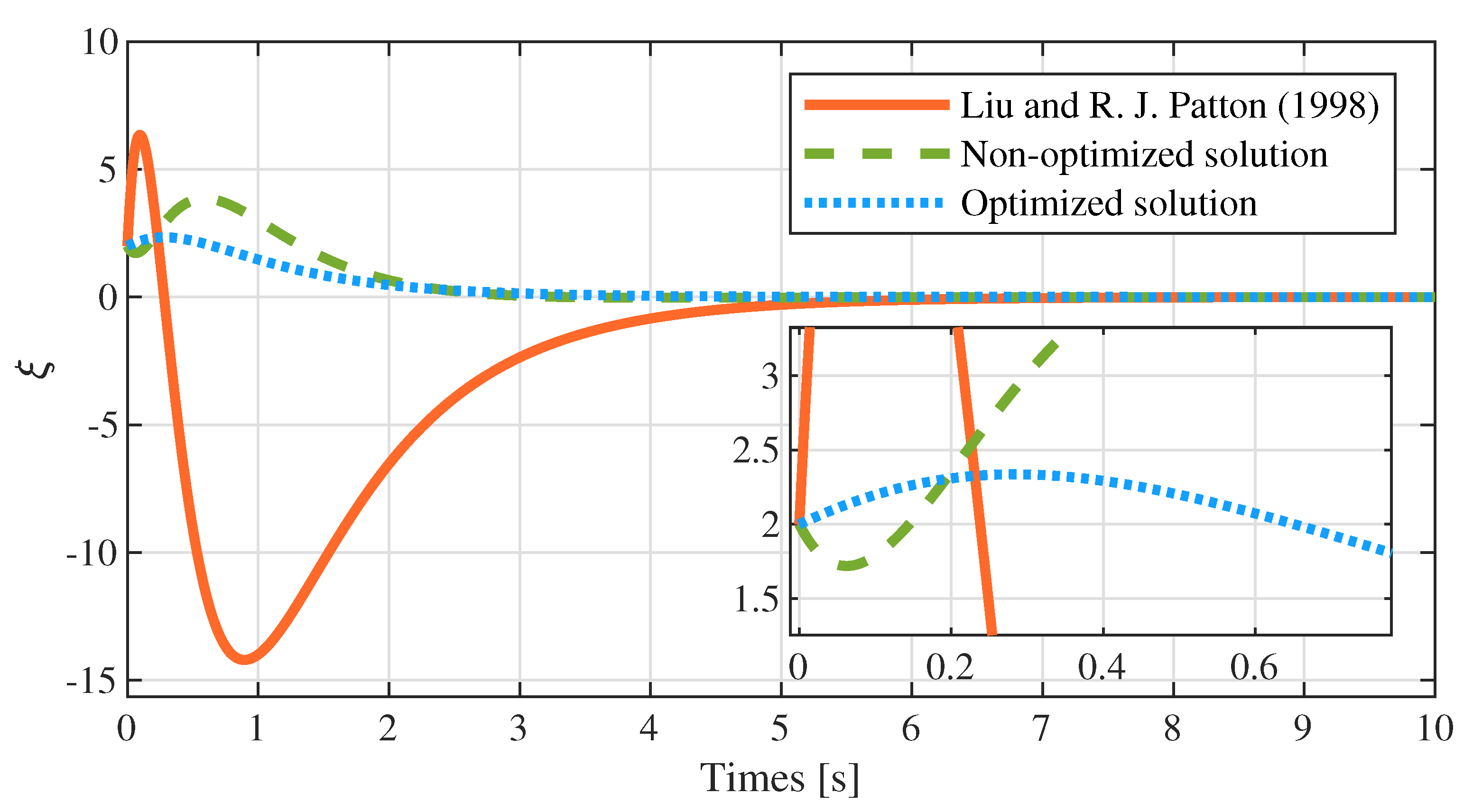
7.4. Simulation Results and Comparison
- It is not difficult to find from Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4 that the state variables of the closed-loop system tend to zero in both the optimized and non-optimized solutions, which indicates that the closed-loop system is stable and that the parametric method proposed in this paper is effective.
- Compared with Liu et al. in [32], the method presented in this paper greatly enhances the overall performance of the system. Specifically, Table 2 shows that the precision of the closed-loop system’s eigenvalues is improved, and Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5 illustrate that the object function, maximum amplitude and expected error are greatly reduced, respectively.
- The optimized dynamic compensator achieves superior control performance to Liu and the non-optimized dynamic compensator by utilizing the degrees of freedom offered in the parameter matrices (see Figure 5). Meanwhile, the optimized solution consumes less energy than the non-optimized solution and that of Liu (see control input in Figure 1).
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, G.R.; Liu, G.P. Complete parametric approach for eigenstructure assignment in a class of second-order linear systems. Automatica 2002, 38, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastgaar, M.; Ahmadian, M.; Southward, S. A review on eigenstructure assignment methods and orthogonal eigenstructure control of structural vibrations. Shock Vib. 2009, 16, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.S.; Liang, B.; Lv, Q.; Duan, G.R. Eigenstructure Assignment in Second-order Linear Systems: A Parametric Design Method. In Proceedings of the 2007 Chinese Control Conference, Zhangjiajie, China, 26–31 July 2007; pp. 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.K.; Zhao, D.J.; Liu, Y.D.; Fu, Y.M. Complete parametric approach for eigenstructure assignment in second-order systems using displacement-plus-acceleration feedback. In Proceedings of the 2016 22nd International Conference on Automation and Computing (ICAC), Colchester, UK, 7–8 September 2016; pp. 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, B. Eigenstructure assignment: A survey. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. P. J. Syst. Control 1995, 209, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H. Adjoint method for design sensitivity analysis of multiple eigenvalues and associated eigenvectors. AIAA J. 2007, 45, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhu, C. Robust Proportional-Differential Control via Eigenstructure Assignment for Active Magnetic Bearings-Rigid Rotor Systems. IEEE. Trans Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 6572–6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Bera, T. A Probabilistically Robust Eigenstructure Assignment Technique for Flight Control Design of UAVs. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Aerospace Conference (50100), Big Sky, MT, USA, 6–13 March 2021; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.K.; Zhang, D.W. Parametric control to a type of descriptor quasi-linear high-order systems via output feedback. Eur. J. Control 2021, 58, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddou, A.; Maarouf, H.; Benzaouia, A. Partial eigenstructure assignment problem and its application to the constrained linear problem. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2013, 44, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.R.; Irwin, G.W.; Liu, G.P. Partial eigenstructure assignment by state feedback: A complete parametric approach. In Proceedings of the 1999 European Control Conference (ECC), Karlsruhe, Germany, 31 August–3 September 1999; pp. 1890–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.R.; Wang, G.S. Partial eigenstructure assignment for descriptor linear systems: A complete parametric approach. In Proceedings of the 42nd IEEE International Conference on Decision and Control (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37475), Maui, HI, USA, 9–12 December 2003; Volume 4, pp. 3402–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.R. Circulation algorithm for partial eigenstructure assignment via state feedback. Eur. J. Control 2019, 50, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.K.; Wang, R.Y.; Liu, Y.D. A parametric approach of partial eigenstructure assignment for high-order linear systems via proportional plus derivative state feedback. AIMS Math. 2021, 6, 11139–11166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.K.; Duan, S.; Wang, R.Y.; Liu, Y.D. Parametric design method for partial eigenstructure assignment of second-order linear systems via observer-based state feedback. Eur. J. Control 2023, 71, 100801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.K.; Wang, R.Y.; Liu, Y.D. Partial eigenstructure assignment for descriptor high-order linear systems via proportional plus derivative state feedback: A parametric approach. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2023, 01423312221150295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ouyang, H.; Yang, J. Partial eigenstructure assignment for undamped vibration systems using acceleration and displacement feedback. J. Sound. Vib. 2014, 333, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ouyang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, J. Partial quadratic eigenvalue assignment in vibrating systems using acceleration and velocity feedback. Inverse. Probl. Sci. Eng. 2015, 23, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ye, J.; Ouyang, H. Static output feedback for partial eigenstructure assignment of undamped vibration systems. Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 2016, 68, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotti, R.; Richiedei, D.; Trevisani, A. Optimal design of vibrating systems through partial eigenstructure assignment. J. Mech. Des. 2016, 138, 071402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.J.; Datta, B.N.; Wang, J. Robust and minimum norm partial quadratic eigenvalue assignment in vibrating systems: A new optimization approach. Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 2010, 24, 766–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, F.; Wang, X. An algorithm of partial eigenstructure assignment for high-order systems. Math. Methods. Appl. Sci. 2018, 41, 6070–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P. Partial eigenstructure assignment problem for vibration system via feedback control. Asian. J. Control 2022, 24, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.K.; Zhang, D.W. Parametric control to second-order linear time-varying systems based on dynamic compensator and multi-objective optimization. Appl. Math. Comput. 2020, 365, 124681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.K.; Zhang, D.W. A parametric method to design dynamic compensator for high-order quasi-linear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 100, 1379–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.R. On a type of generalized sylvester equations. In Proceedings of the 2013 25th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Guiyang, China, 25–27 May 2013; pp. 1264–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.R. Generalized Sylvester Equations: Unified Parametric Solutions; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos, J.F.S.; Pellanda, P.C.; Simoes, A.M. Robust pole placement under structural constraints. Syst. Control Lett. 2018, 116, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.T.; Zhang, L. Partial eigenvalue assignment with time delay in high order system using the receptance. Linear Algebra. Appl. 2017, 523, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.R. Parametric eigenstructure assignment via output feedback based on singular value decompositions. IEEE. Int. Conf. Control. Autom. 2003, 150, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. Eigenstructure assignment for linear descriptor systems via output feedback. Asian. J. Control 2019, 21, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.P.; Patton, R. Eigenstructure Assignment for Control System Design; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Chiang, H.D.; Thorp, J.S. Partial eigenstructure assignment and its application to large scale systems. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control 1991, 36, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, A.; Sugimoto, K. Partial eigenstructure assignment approach for robust flight control. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2004, 27, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Notations | Definition |
|---|---|
| set of all real vectors of dimension n | |
| set of all complex vectors of dimension n | |
| the points on the left-half s-plane | |
| set of all real matrices of dimension | |
| the identity matrix with n dimensions | |
| the rank of the matrix A | |
| the determinant of the matrix A | |
| all eigenvalues of the matrix A | |
| the Spectral norm of matrix K | |
| the degree n of polynomial matrix | |
| the diagonal matrix with diagonal elements | |
| the imaginary part of |
| Solutions | Closed-Loop Eigenvalues |
|---|---|
| Liu et al. [32] | −0.99979784, −1.49975243, −3.00067144, −6.49977829 |
| Non-optimized solution | −1.00000000, −1.49999999, −3.00000000, −6.49999999 |
| Optimized solution | −0.99999999, −1.50000000, −2.99999999, −6.50000000 |
| Index | Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Liu et al. [32] | 111.0955 | 54.9084 | 166.0039 |
| Non-optimized solution | 39.7627 | 38.8143 | 78.5770 |
| Optimized solution | 19.6102 | 42.4929 | 62.1091 |
| Maximal Amplitude | Value(m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liu et al. [32] | 2.125 | 4.109 | 0.580 | 14.200 |
| Non-optimized solution | 1.327 | 1.127 | 0.048 | 3.853 |
| Optimized solution | 1.101 | 0.746 | ≈0 | 2.336 |
| Error | Value(s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liu et al. [32] | 9.248 | 9.123 | 9.374 | >10 |
| Non-optimized solution | 7.560 | 7.438 | 7.683 | 8.500 |
| Optimized solution | 6.693 | 6.699 | 6.693 | 7.534 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, D.-K.; Guo, Z.-J.; Wang, R.-Y.; Liu, Y.-D. Partial Eigenstructure Assignment for Linear Time-Invariant Systems via Dynamic Compensator. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2866. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132866
Gu D-K, Guo Z-J, Wang R-Y, Liu Y-D. Partial Eigenstructure Assignment for Linear Time-Invariant Systems via Dynamic Compensator. Mathematics. 2023; 11(13):2866. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132866
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Da-Ke, Zhi-Jing Guo, Rui-Yuan Wang, and Yin-Dong Liu. 2023. "Partial Eigenstructure Assignment for Linear Time-Invariant Systems via Dynamic Compensator" Mathematics 11, no. 13: 2866. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132866
APA StyleGu, D.-K., Guo, Z.-J., Wang, R.-Y., & Liu, Y.-D. (2023). Partial Eigenstructure Assignment for Linear Time-Invariant Systems via Dynamic Compensator. Mathematics, 11(13), 2866. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132866






