Tracking Contaminant Transport Backwards with an Operator-Splitting Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Formulation of the Forward Problem
2.2. Operator-Splitting Method
2.3. Formulation of the Backward Problem
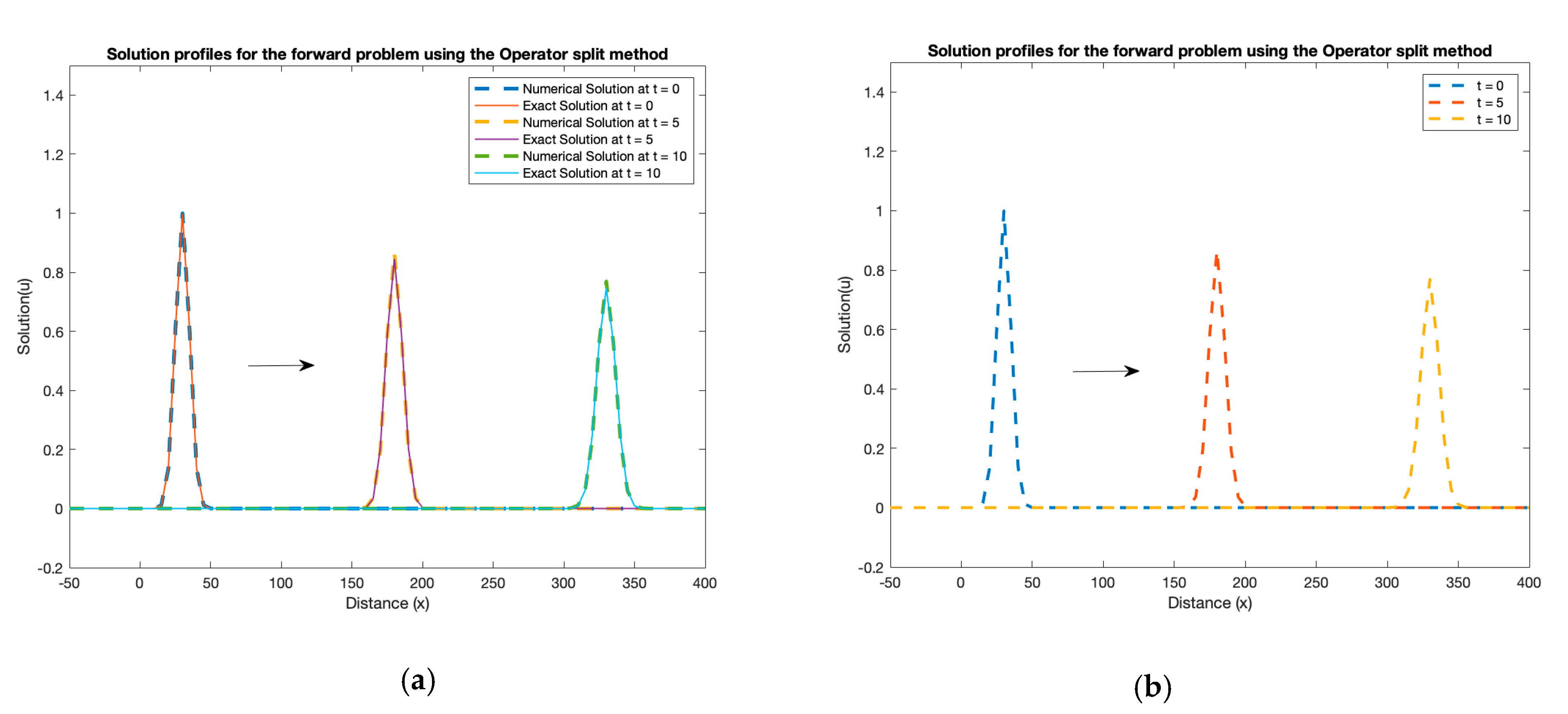
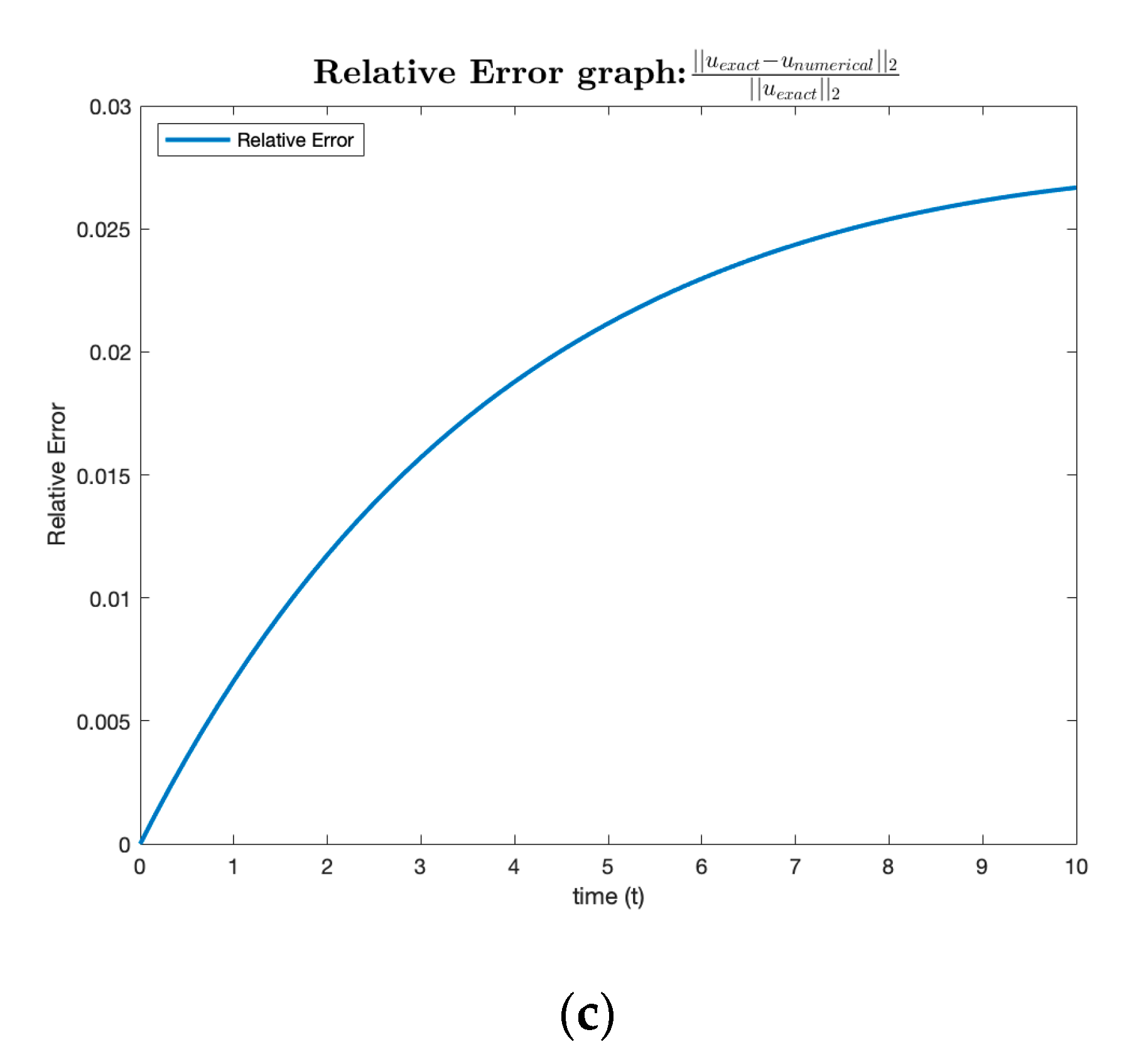
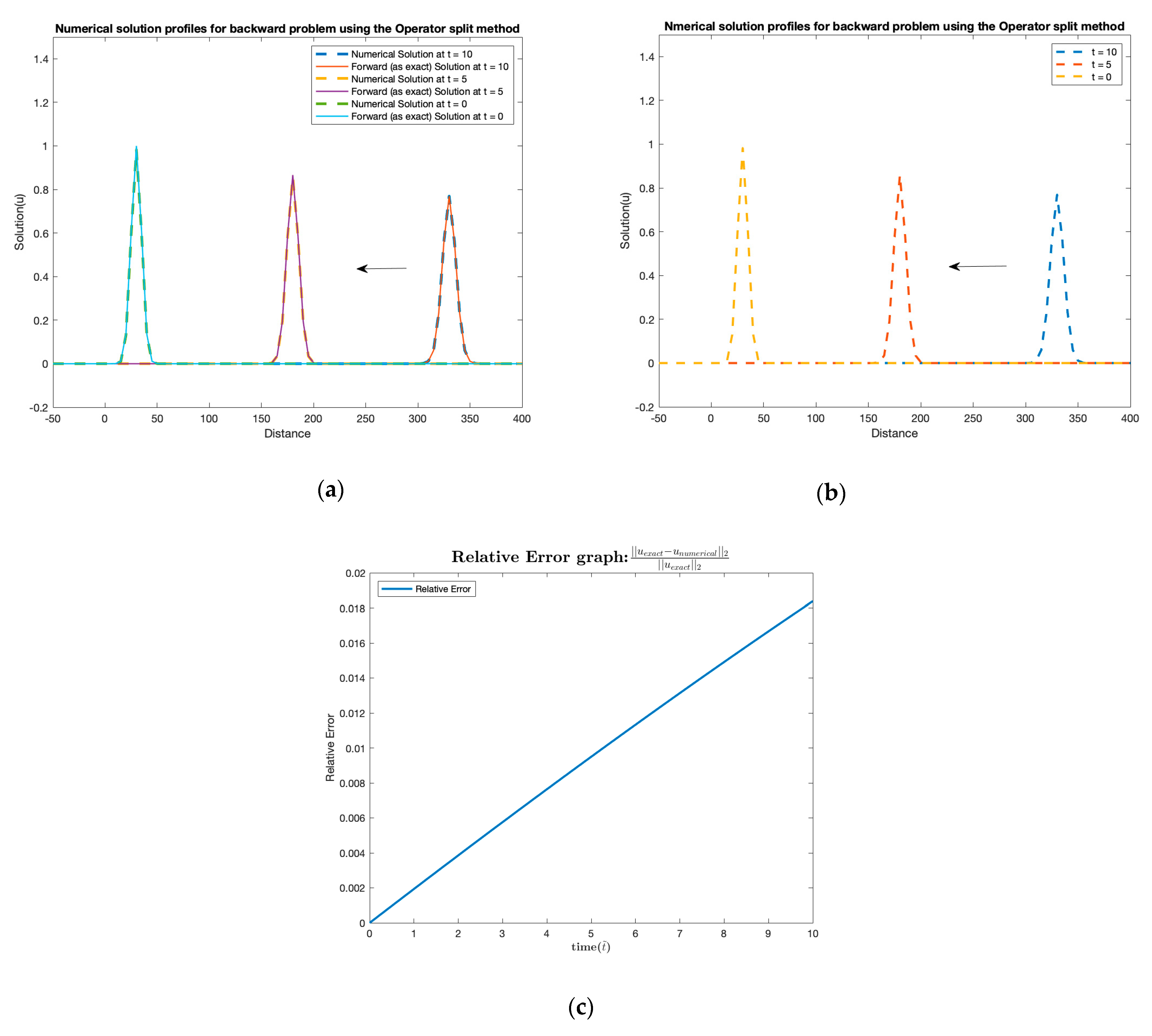
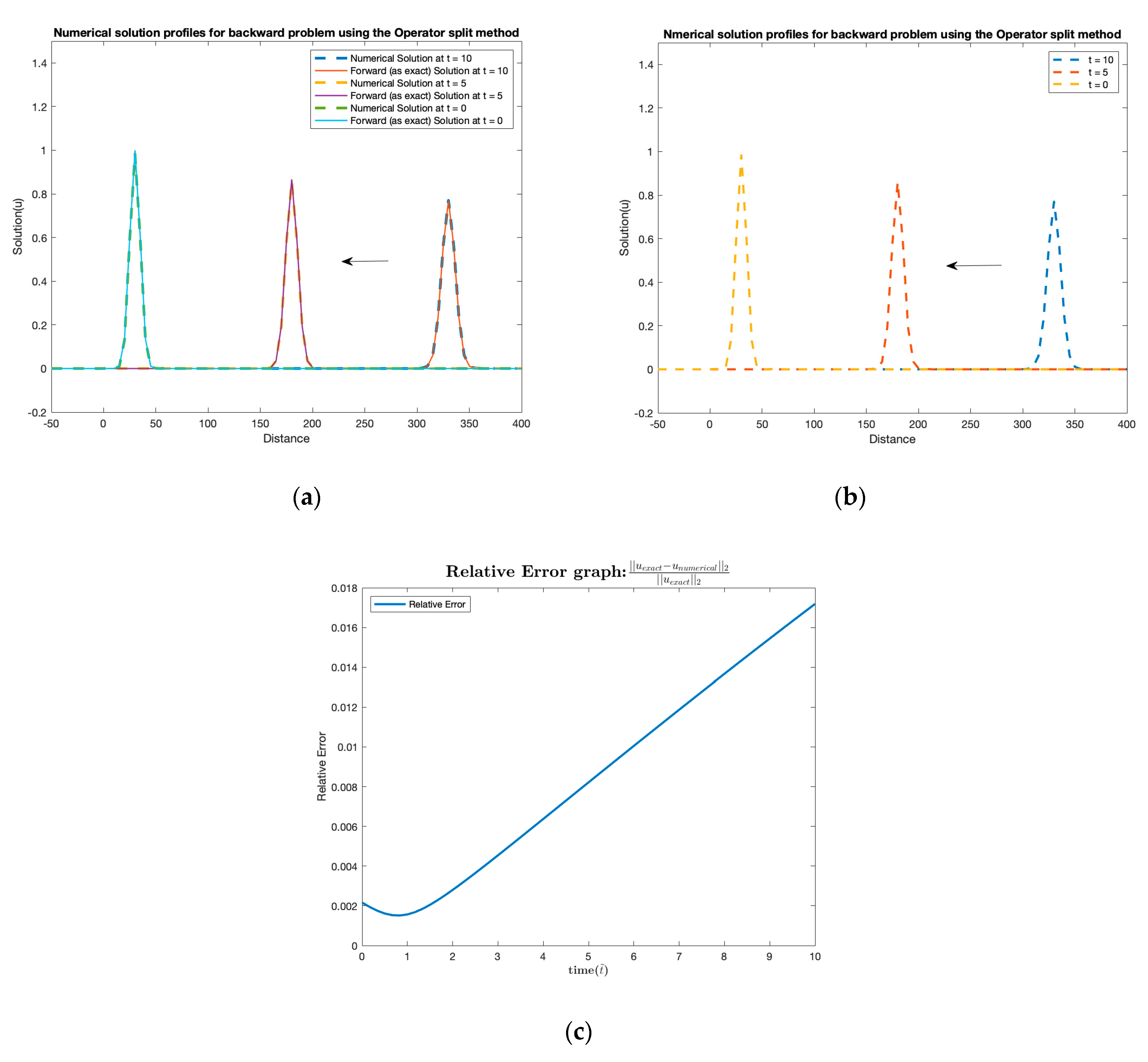
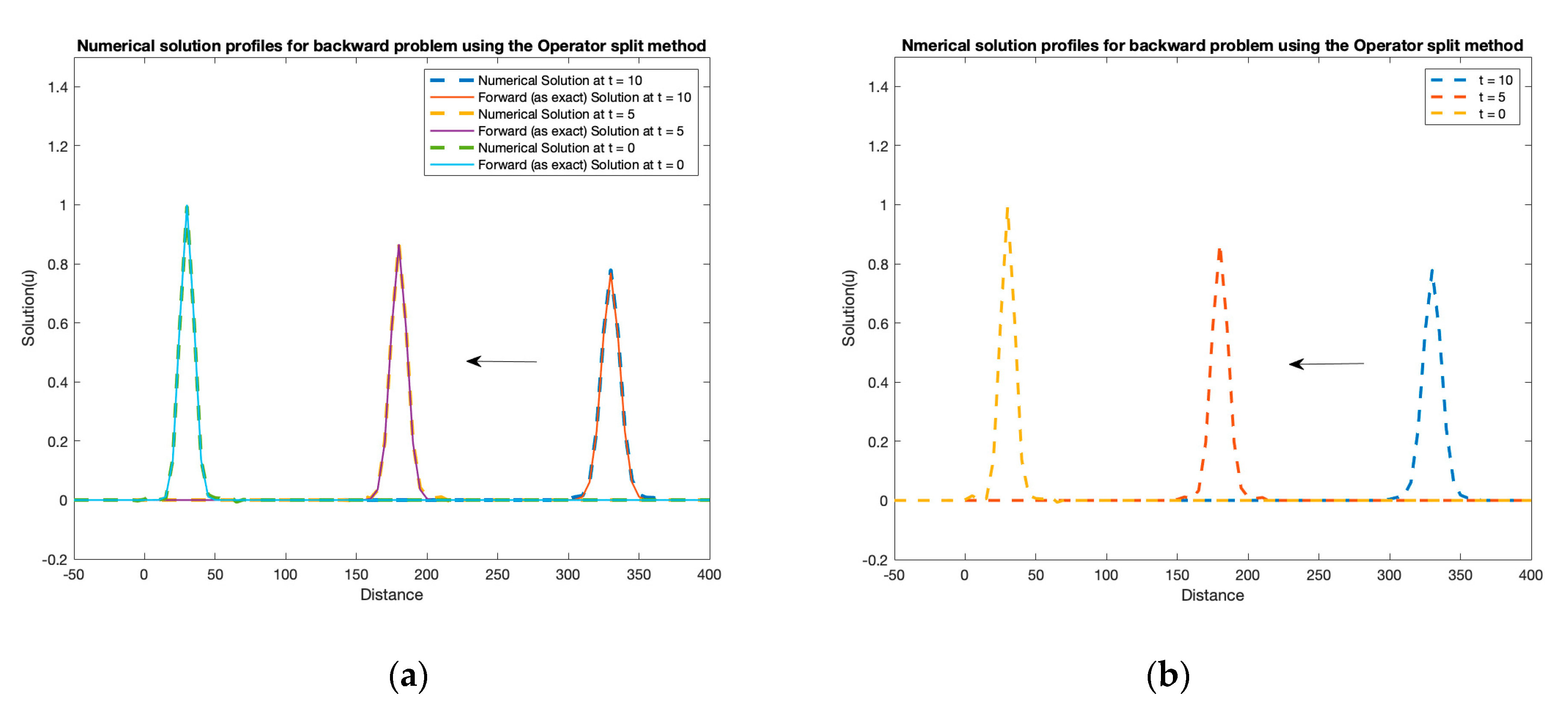
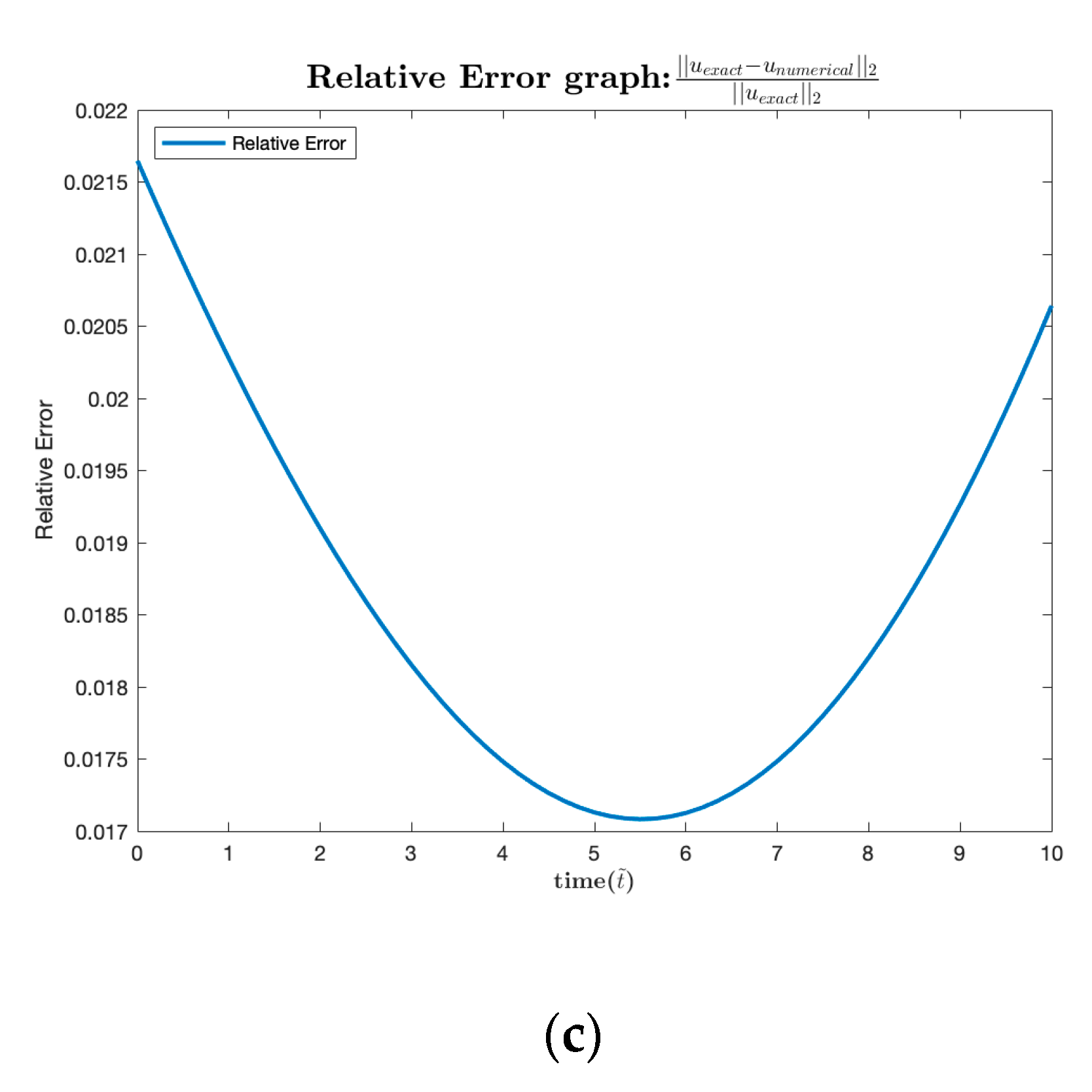
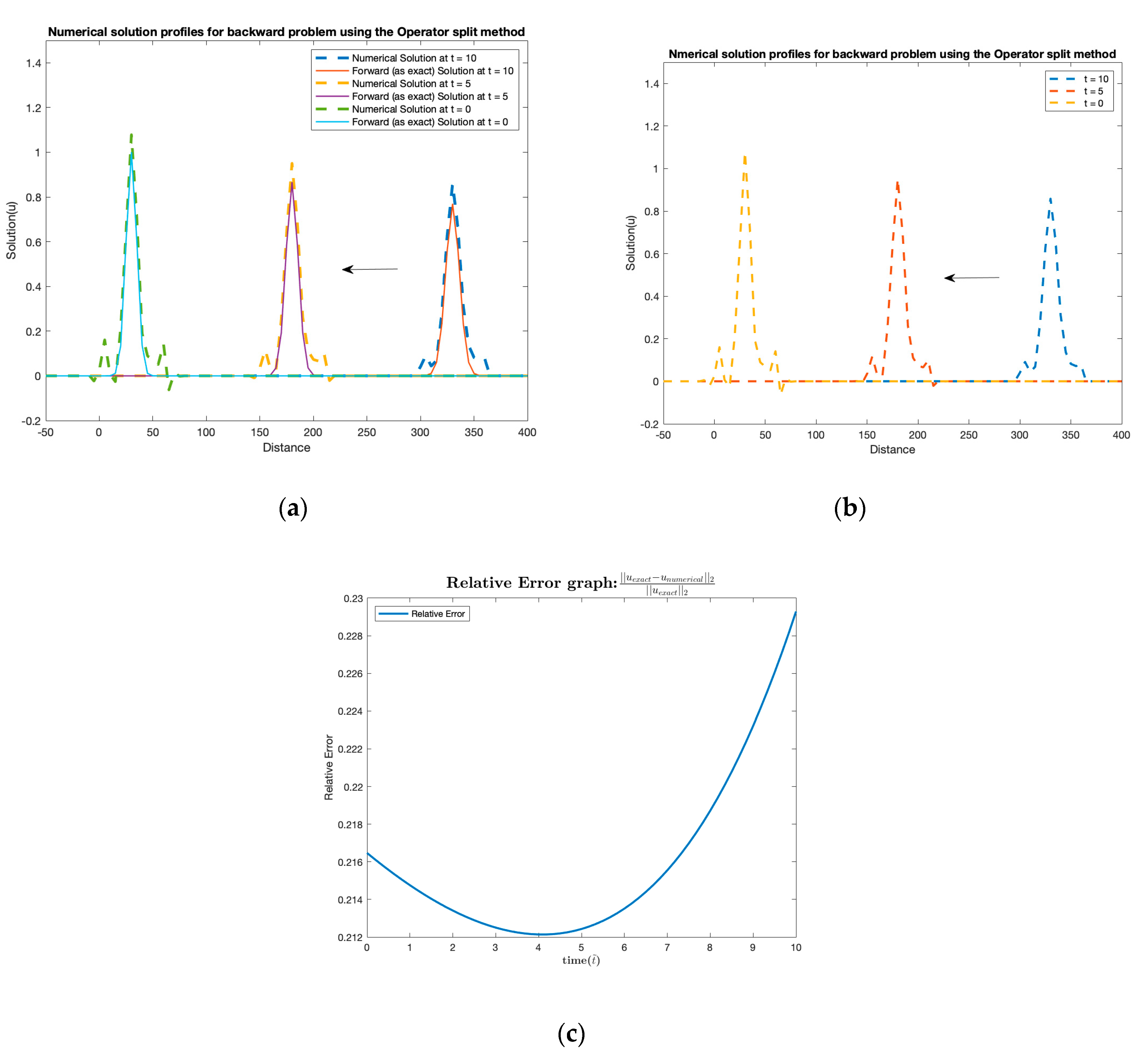
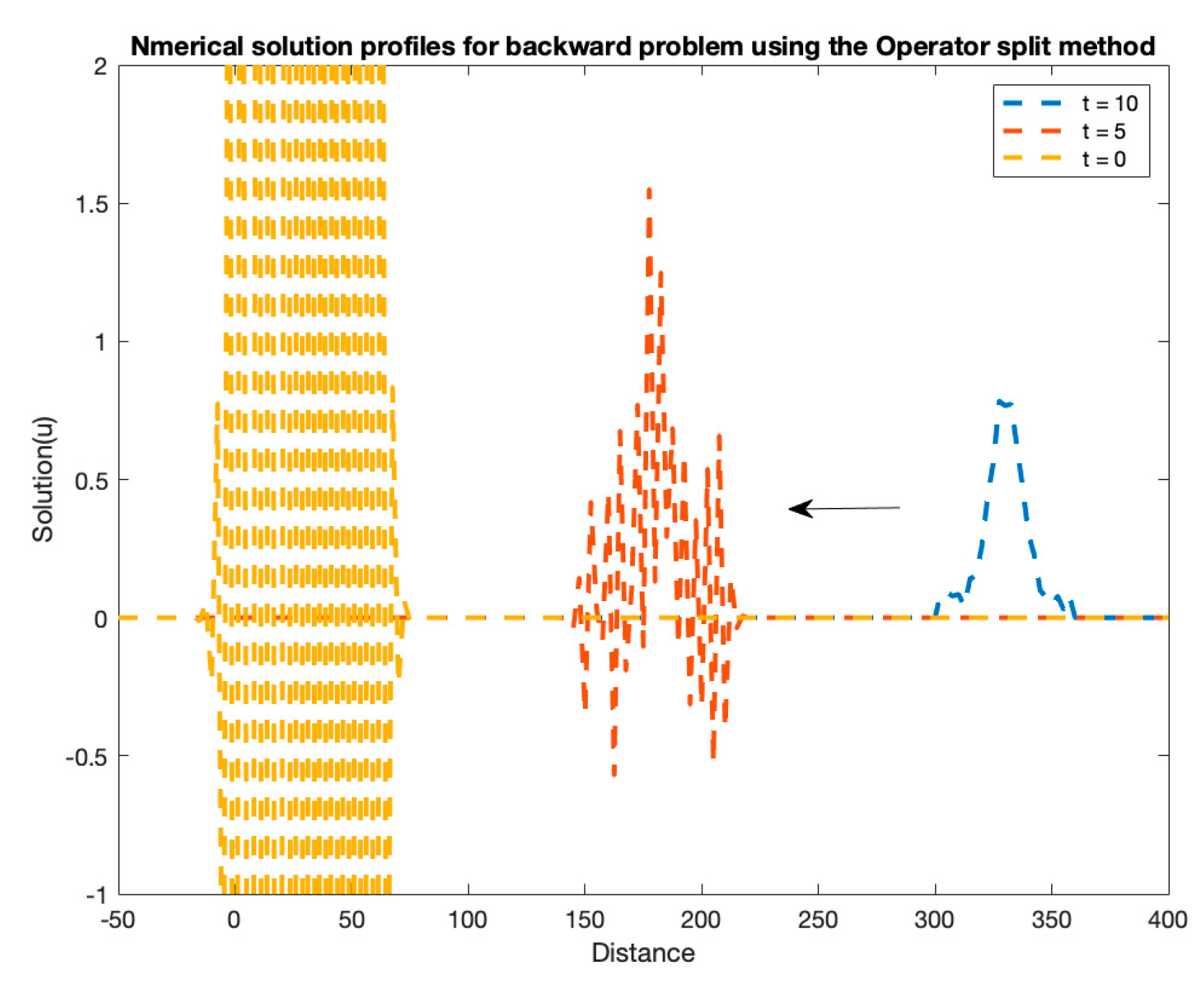
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manoranjan, V.S. Analytic solutions for contaminant transport under nonequilibrium conditions. Appl. Sci. Res. 1995, 55, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoranjan, V.S.; Stauffer, T.B. Exact solution for contaminant transport with kinetic Langmuir sorption. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoranjan, V.S.; Stauffer, T.B. Analytical solution for solute transport with Freundlich sorption. Dyn. Contin. Discret. Impuls. Syst.-Ser. A-Math. Anal. 2003, 10, 851–861. [Google Scholar]
- Gorelick, S.M.; Evans, B.; Remson, I. Identifying Sources of Groundwater Pollution: An Optimization Approach. Water Resour. Res. 1983, 19, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Ground Water Models: Scientific and Regulatory Applications; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaggs, T.H.; Kabala, Z.J. Recovering the release history of a groundwater contaminant. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ball, W.P. Application of inverse methods to contaminant source identification from aquitard diffusion profiles. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 1975–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupauer, R.M.; Borchers, B.; Wilson, J.L. Comparison of inverse methods for reconstructing the release history of a groundwater contamination source. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 2469–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, J.B.; Gauthier, T.D. Estimation of residual dense NAPL mass by inverse modeling. Ground Water 1994, 32, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alapati, S.; Kabala, Z.J. Recovering the release history of a groundwater contaminant using a non-linear least-squares method. Hydrol. Process. 2000, 14, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmadja, J.; Bagtzoglou, A.C. Pollution source identification in heterogeneous porous media. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 2113–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagtzoglou, A.C.; Atmadja, J. Marching-jury backward beam equation and quasi-reversibility methods for hydrologic inversion: Application to contaminant plume spatial distribution recovery. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaggs, T.H.; Kabala, Z.J. Recovering the history of a groundwater contaminant plume: Method of quasi-reversibility. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 2669–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.F.; Chen, Q. Identification of contaminant sources in enclosed environments by inverse CFD modeling. Indoor Air 2007, 17, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugat, M. Contamination source determination in water distribution networks. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2012, 72, 1772–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, B.; Beegle, J.E.; Kavvas, M.L.; Orlob, G.T. Development of an Expert System Embedding Pattern Recognition Techniques for Pollution Source Identification; National Technical Information Service: Springfield, VA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Bagtzoglou, A.C.; Dougherty, D.E.; Tompson, A.F.B. Application of particle methods to reliable identification of groundwater pollution sources. Water Resour. Manag. 1992, 6, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snodgrass, M.F.; Kitanidis, P.K. A geostatistical approach to contaminant source identification. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, A.M.; Kitanidis, P.K. Application of Bayesian inference methods to inverse modeling for contaminant source identification. Comput. Methods Water Resour. 2002, XIV, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Michalak, A.M.; Kitanidis, P.K. ; Kitanidis, P.K. A method for enforcing parameter nonnegativity in Bayesian inverse problems with an application to contaminant source identification. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, A.M.; Kitanidis, P.K. Application of geostatistical inverse modeling to contaminant source identification. J. Hydraul. Res. 2004, 42, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, A.M.; Kitanidis, P.K. Estimation of historical groundwater contaminant distribution using the adjoint state method applied to geostatistical inverse modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, W08302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupauer, R.M.; Wilson, J.L. Adjoint method for obtaining backward in-time location and travel time probabilities of a conservative groundwater contaminant. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 3389–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodbury, A.D.; Ulrych, T.J. Minimum relative entropy inversion: Theory and application to recovering the release history of a groundwater contaminant. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 2671–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodbury, A.D.; Sudicky, E.A.; Ludwig, R.; Ulrych, T.J. Three-dimensional plume source reconstruction using minimum relative entropy inversion. J. Cont. Hydrol. 1998, 32, 131–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barajas-Solano David, A.; Alexander Francis, J.; Anghel, M.; Tartakovsky Daniel, M. Efficient gHMC Reconstruction of Contaminant Release History. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Xia, H. Lookback option pricing models based on the uncertain fractional-order differential equation with Caputo type. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2023, 14, 6435–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Feiz, A.-A.; Singh, S.K.; Ngae, P.; Turbelin, G. Reconstruction of an atmospheric tracer source in an urban like environment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 12589–12604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesselinov, V.V.; Alexandrov, B.S.; O’Malley, D. Contaminant source identification using semi-supervised machine learning. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 212, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesselinov, V.V.; Alexandrov, B.S.; O’Malley, D. Nonnegative tensor factorization for contaminant source identification. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2019, 220, 66–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanev, V.G.; Iliev, F.L.; Hansen, S.; Vesselinov, V.V.; Alexandrov, B.S. Identification of release sources in advection-diffusion system by machine learning combined with Green’s function inverse method. Appl. Math. Model. 2018, 60, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangi, M.S.F.; Kwon, J.S. Deep hybrid modeling of chemical process: Application to hydraulic fracturing. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2020, 34, 106696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwood, R.C.; Manoranjan, V.S.; Edwards, D.B. Lead-Acid Battery Model Under Discharge with a Fast Splitting Method. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2011, 26, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, K.W.; Mayers, D.F. Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations: An Introduction; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X.-T.; Fu, C.-L.; Qian, Z. Two numerical methods for solving a backward heat conduction problem. Appl. Math. Comput. 2005, 179, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzbee, B.L.; Carasso, A. On the Numerical Computation of Parabolic Problems for Preceding Times. Math. Comput. 1973, 27, 237–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Relative Error | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| at | at | at | at | at | at | Relative Error Bound | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rao, P.; Manoranjan, V.S. Tracking Contaminant Transport Backwards with an Operator-Splitting Method. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2828. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132828
Rao P, Manoranjan VS. Tracking Contaminant Transport Backwards with an Operator-Splitting Method. Mathematics. 2023; 11(13):2828. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132828
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, Priyanka, and Valipuram S. Manoranjan. 2023. "Tracking Contaminant Transport Backwards with an Operator-Splitting Method" Mathematics 11, no. 13: 2828. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132828
APA StyleRao, P., & Manoranjan, V. S. (2023). Tracking Contaminant Transport Backwards with an Operator-Splitting Method. Mathematics, 11(13), 2828. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132828





