Numerical Method for a Perturbed Risk Model with Proportional Investment
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- How do the perturbations affect the dividend payments and ruin probability?
- (2)
- How does proportional investment affect the dividend payments and ruin probability?
- (3)
- If the explicit solutions are not easy to find, do the numerical solutions of the related actuarial quantities exist?
2. Literature Review
3. The Model
4. Integro-Differential Equations
4.1. Integro-Differential Equations for
4.2. Integro-Differential Equations for
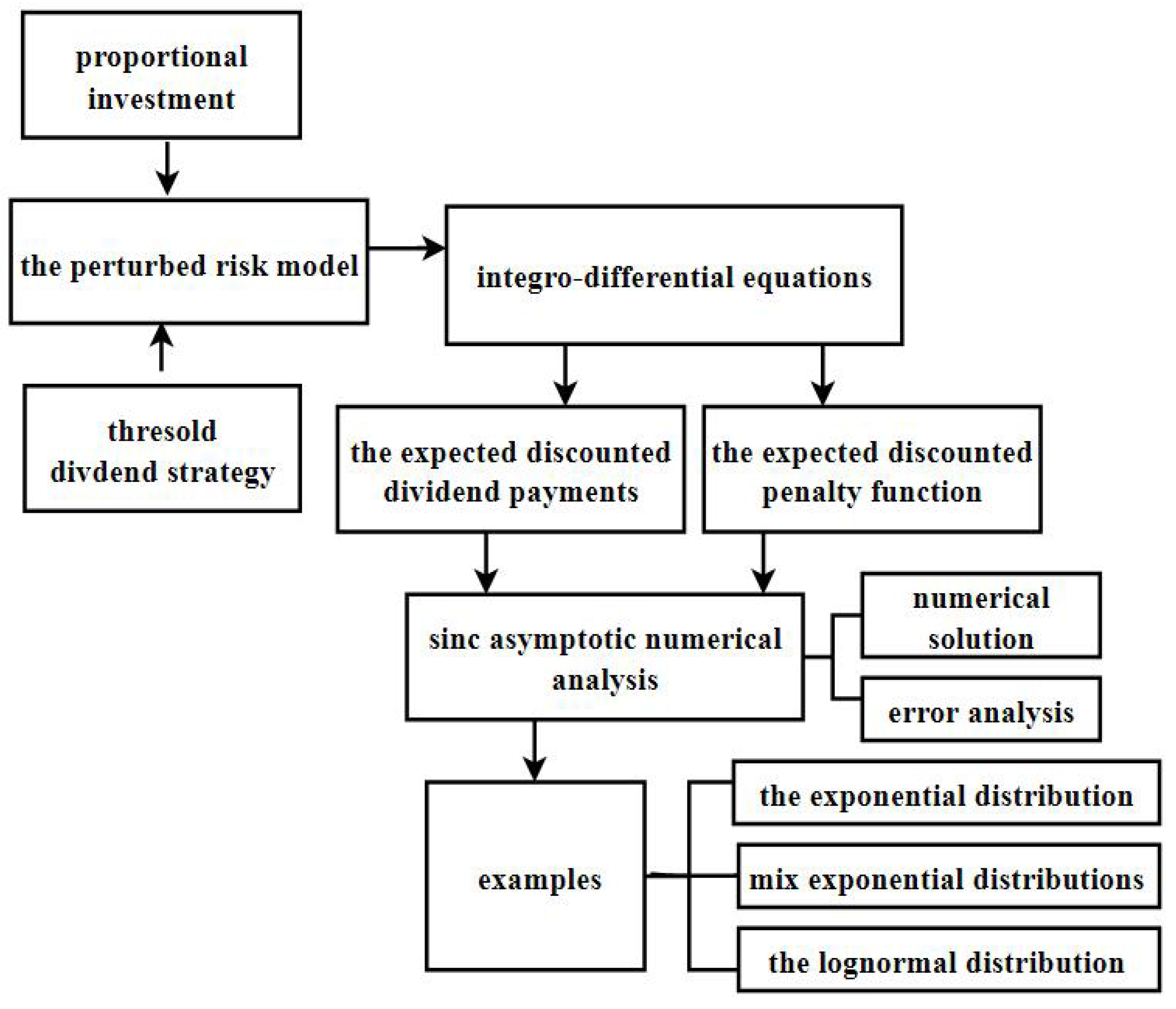
5. Sinc Asymptotic Numerical Analysis
5.1. Sinc Function Preliminaries
5.2. Numerical Solutions of the Expected Discounted Dividend Payments
5.3. Numerical Solutions of the Expected Discounted Penalty Function
5.4. Error Analysis
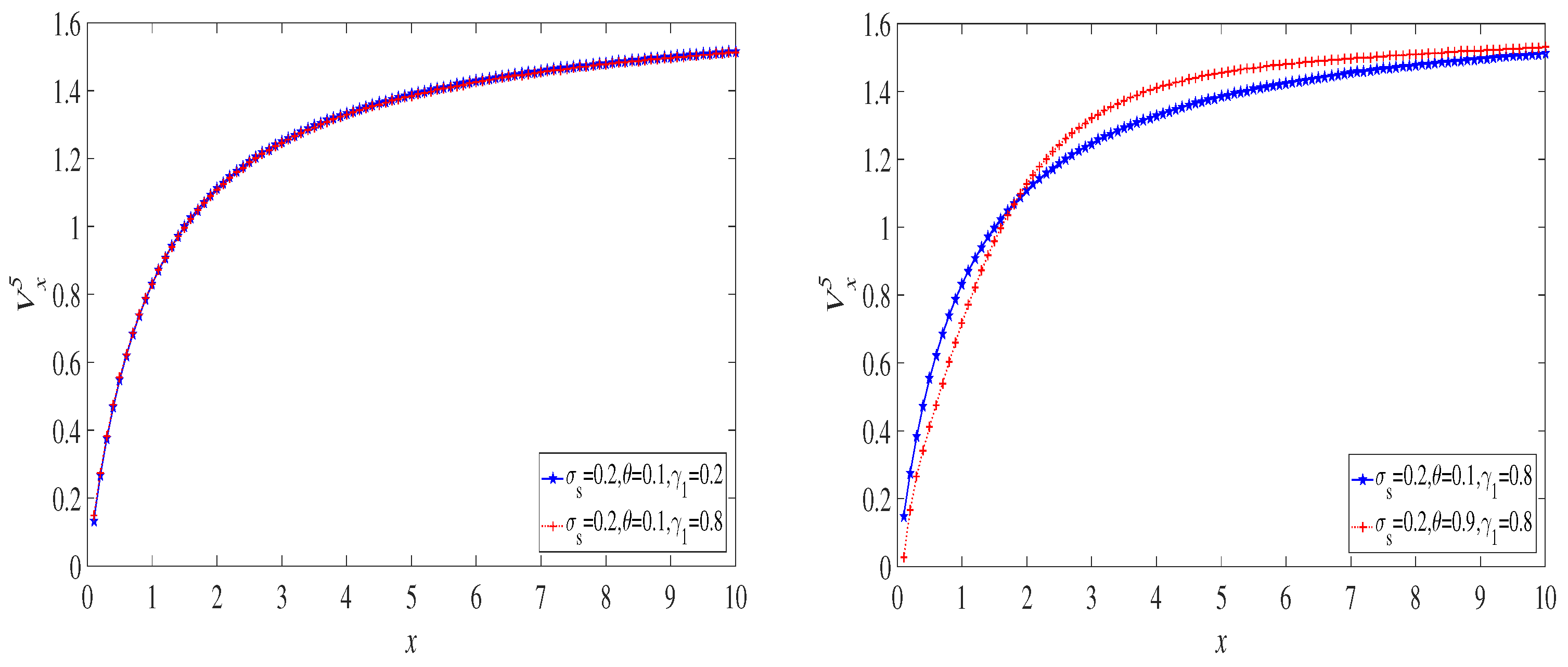
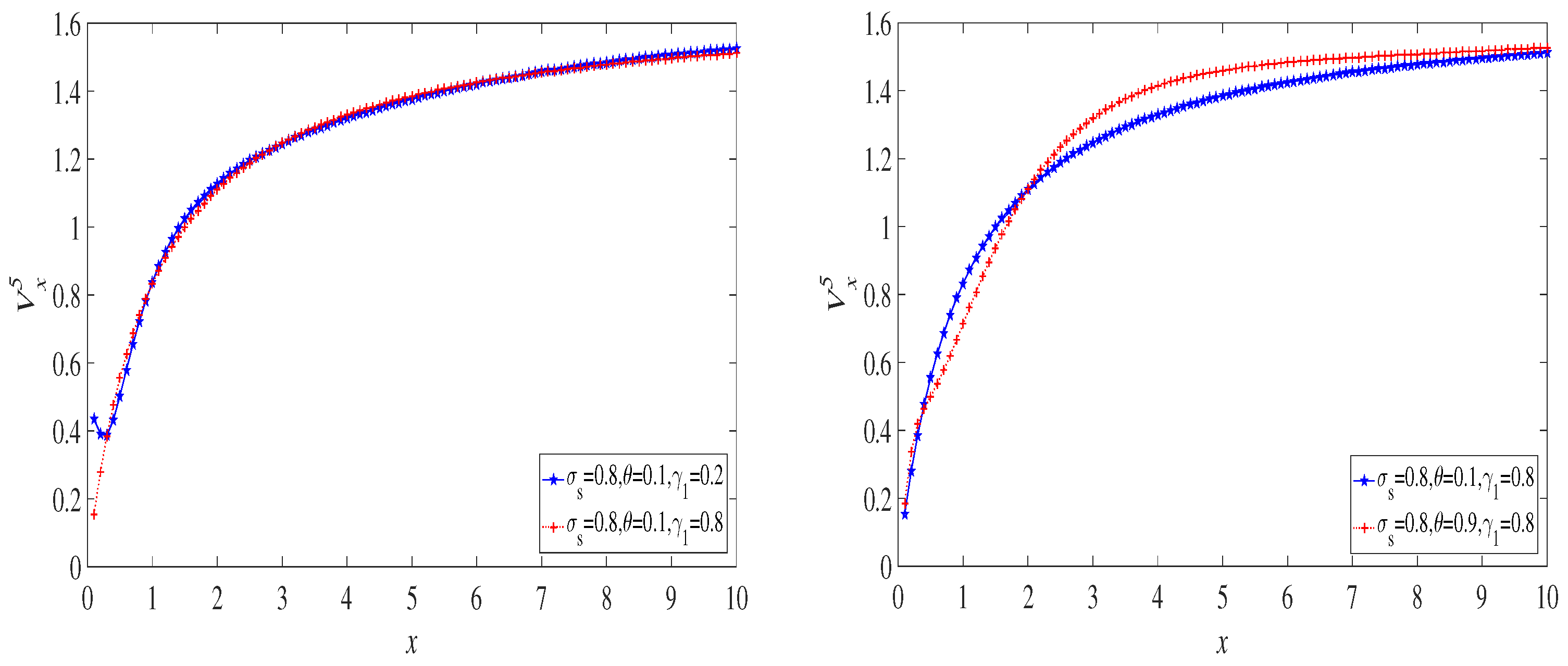
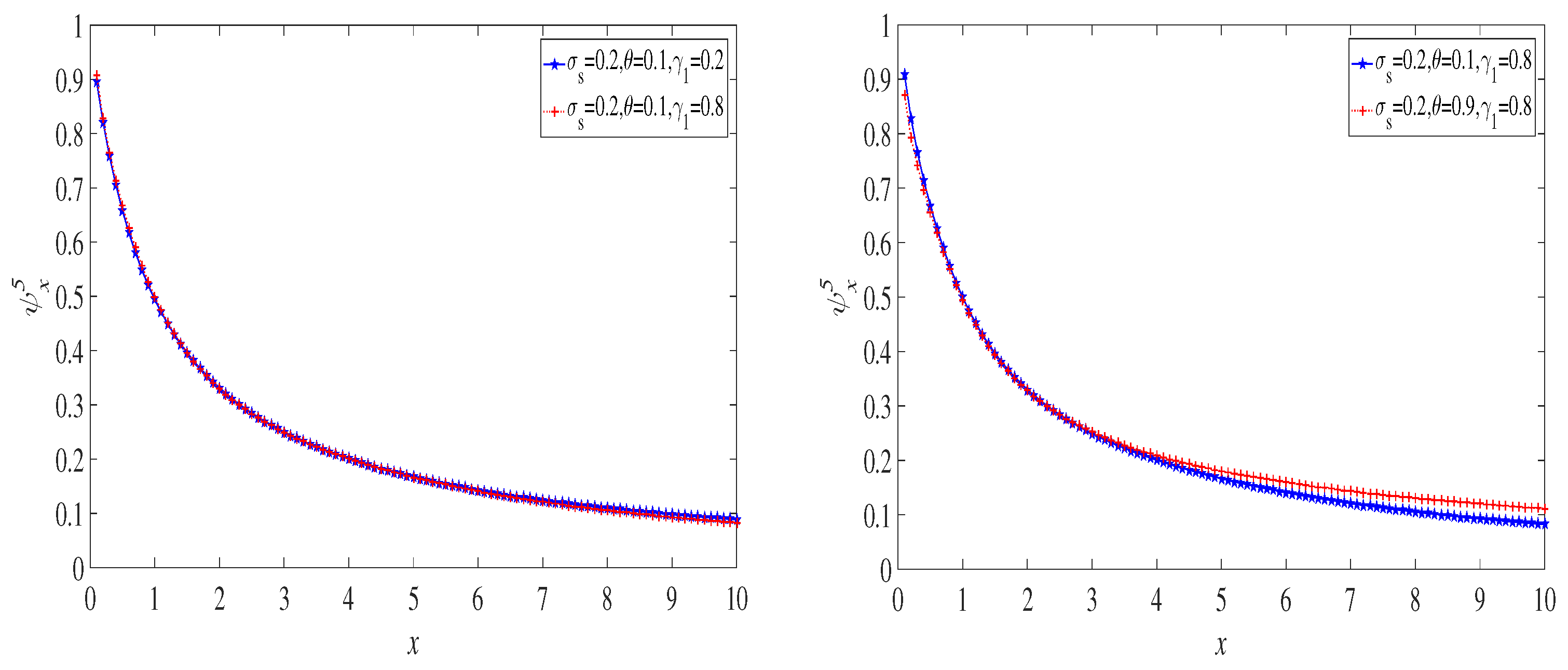
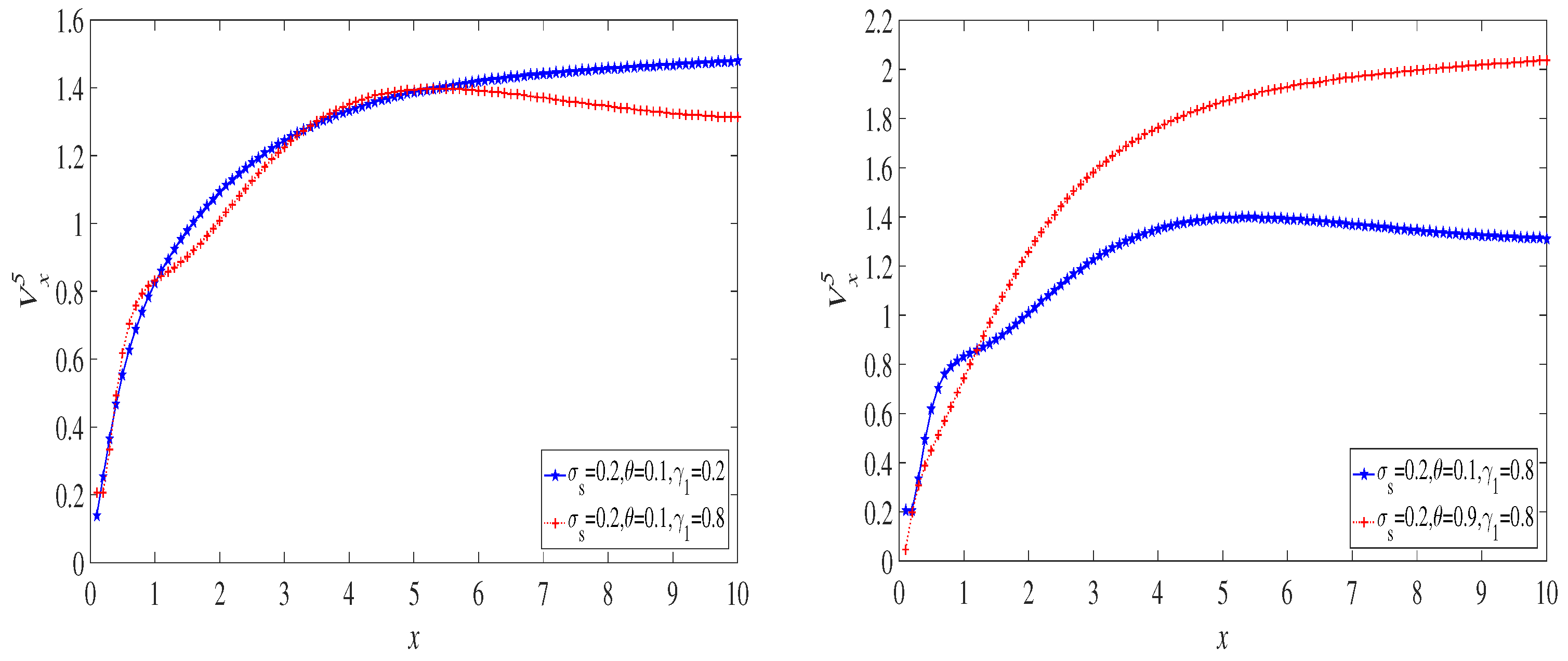
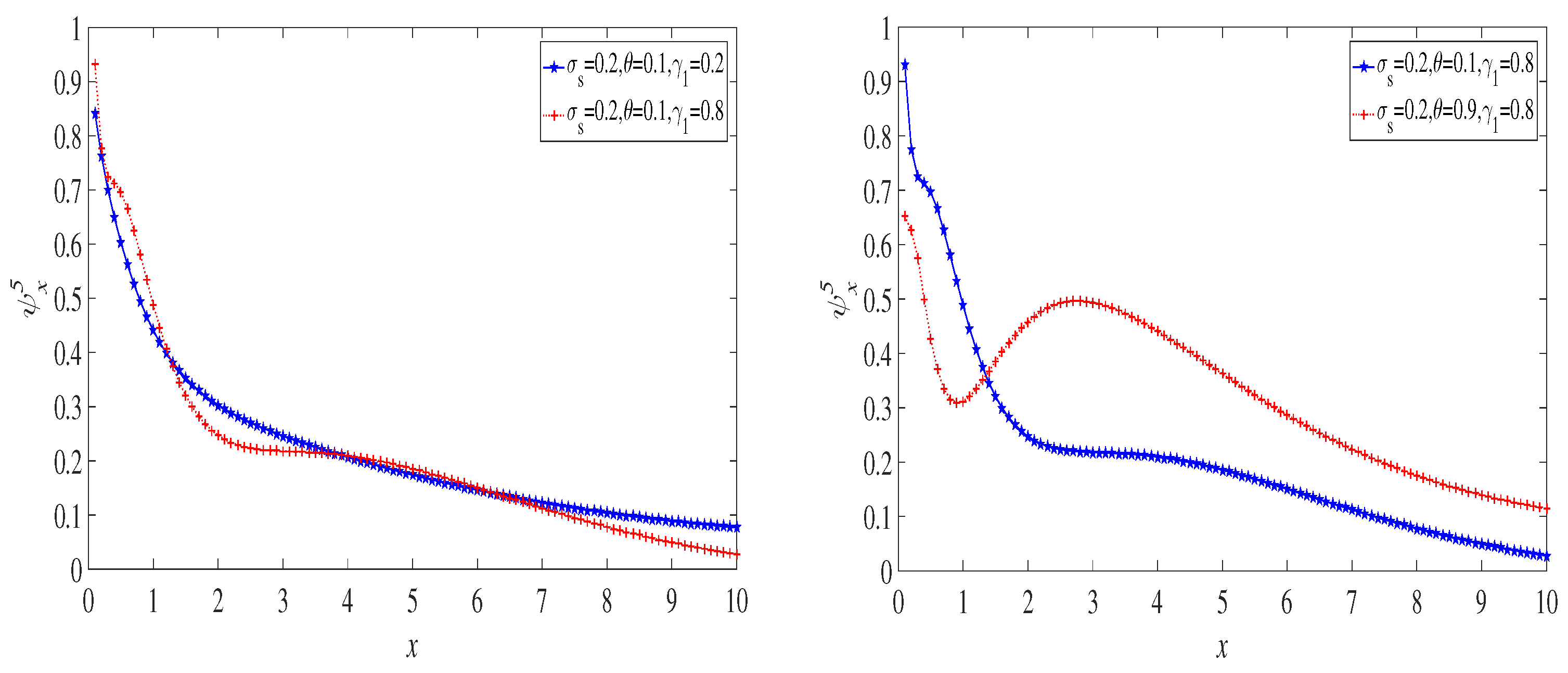
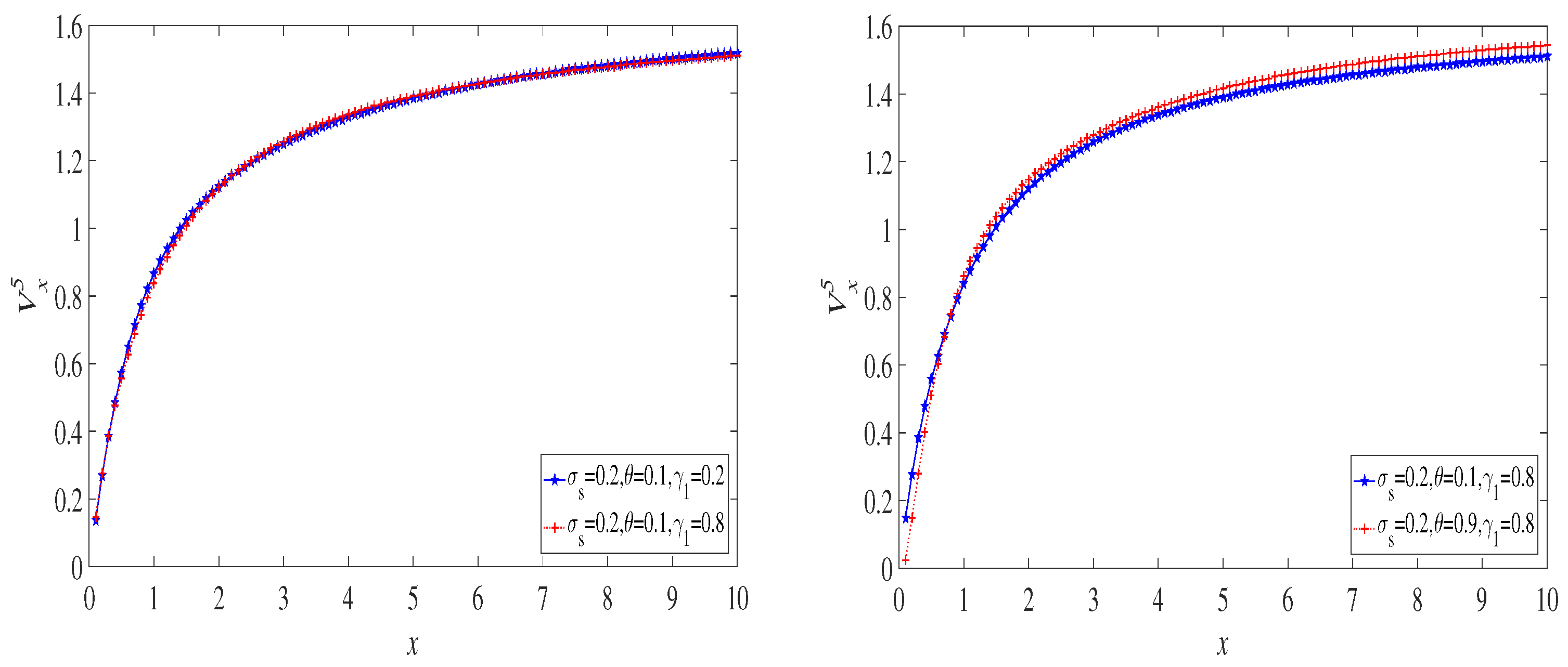
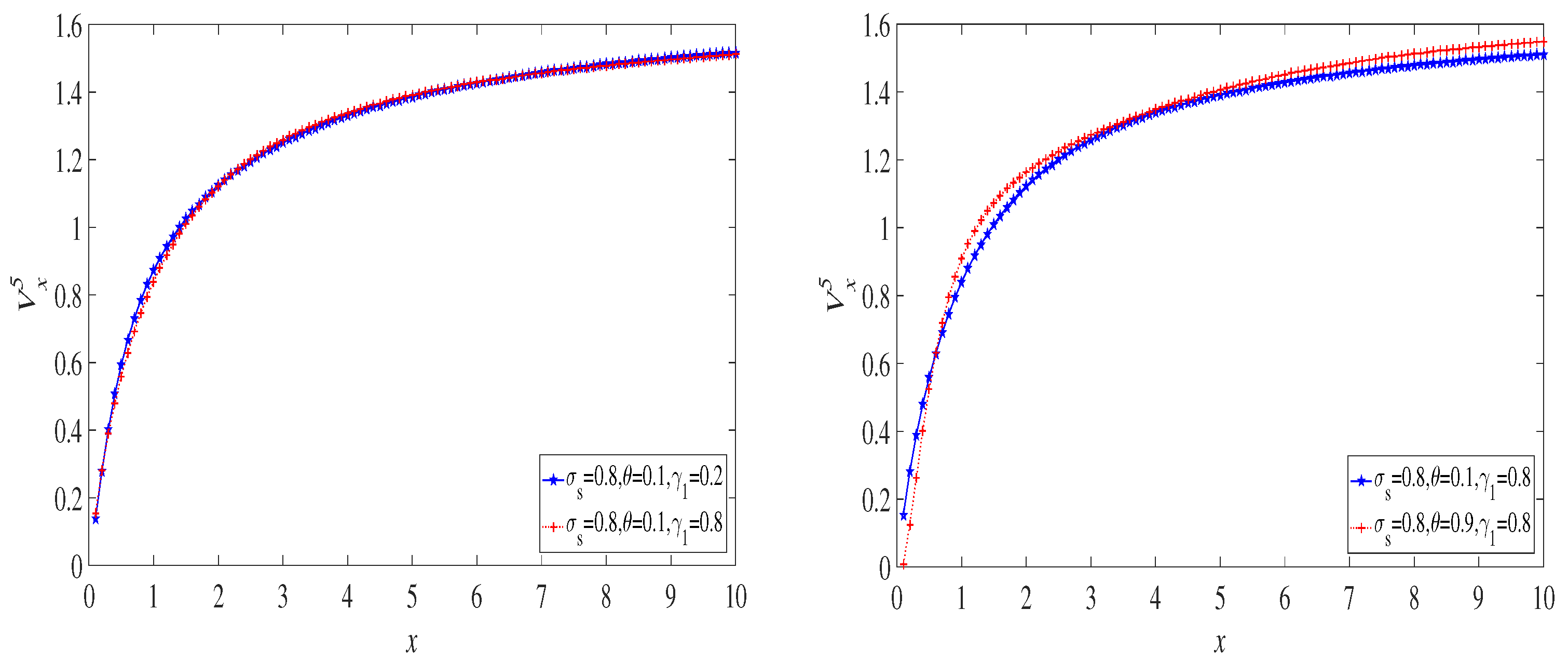
6. Examples
6.1. The Exponential Distribution Case
6.2. The Case of a Mixture of Two Exponential Distributions
6.3. The Lognormal Distribution Case
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Ou, H. A compound Poisson risk model with proportional investment. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2013, 242, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Rong, X.; Zhao, H. Optimal investment strategies for an insurer and a reinsurer with a jump-diffusion risk process under the CEV model. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2018, 328, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.H.; Li, Y.F. Dividend payments in a perturbed compound Poisson model with stochastic investment and debit interest. Ukr. Math. J. 2019, 71, 718–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Ruin probability of the renewal model with risky investment and large claims. Sci. China 2009, 52, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar]
- Rachev, S.T.; Stoyanov, S.V.; Fabozzi, F.J. Financial markets with no riskless (safe) asset. Int. J. Theor. Appl. Fin. 2017, 20, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wang, D. Uniform asymptotics for ruin probabilities in a dependent renewal risk model with stochastic return on investments. Stochastics 2018, 90, 432–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellanskaya, A.; Kabanov, Y. On ruin probabilities with risky investments in a stock with stochastic volatility. Extremes 2021, 24, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberlein, E.; Kabanov, Y.; Schmidt, T. Ruin probabilities for a Sparre Andersen model with investments. Stoch. Proc. Appl. 2022, 144, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Finetti, B. Su un’impostauione alternativa della teoria collectiva del rischio. In Transactions XVth International Congress of Actuaries; Actuarial Society of America: New York, NY, USA, 1957; Volume 2, pp. 433–443. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, C.; Zhou, J.; Deng, Y. The Gerber-Shiu discounted penalty function in a delayed renewal risk model with multi-layer dividend strategy. Stat. Probabil. Lett. 2012, 82, 1648–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecher, H.; Azcue, P.; Muler, N. Optimal dividend strategies for two collaborating insurance companies. Adv. Appl. Probab. 2017, 49, 515–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierkötter, M.; Schmidli, H. On optimal dividends with exponential and linear penalty payments. Insur. Math. Econ. 2017, 72, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, N. Dividend payments with a threshold strategy in the compound Poisson risk model perturbed by diffusion. Insur. Math. Econ. 2007, 40, 509–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Sendova, K.P.; Li, Z. Parisian ruin with a threshold dividend strategy under the dual Lévy risk model. Insur. Math. Econ. 2020, 90, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xiao, T.; Yang, X. A Markov-Modulated jump-diffusion risk model with randomized observation periods and threshold dividend strategy. Insur. Math. Econ. 2014, 54, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenger, F. Numerical Methods Based on Sinc and Analytic Functions; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Rashidinia, J.; Zarebnia, M. The numerical solution of integro-differential equation by means of the sinc method. Appl. Math. Comput. 2007, 188, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, A.; Araghi, M.A.F.; Rashidinia, J.; Jalalvand, M. Numerical solution of Volterra partial integro-differential equations based on sinc-collocation method. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2017, 362–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhuo, W. Dividends under threshold dividend strategy with randomized observation periods and capital-exchange agreement. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2020, 366, 112426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenger, F. Handbook of Sinc Numerical Methods; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Yu, W. Estimating ruin probability in an insurance risk model with stochastic premium income based on the CFS method. Mathematics 2021, 9, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, S. Time-Consistent investment and reinsurance strategies for Mean-Variance insurers under stochastic interest rate and stochastic volatility. Mathematics 2020, 8, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, W.; Yang, H.; Chen, X. Expected discounted penalty function for a phase-type risk model with stochastic return on investment and random observation periods. Kybernetes 2018, 47, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarebnia, M.; Abadi, M.G.A. A numerical sinc method for systems of integro-differential equations. Phys. Scr. 2010, 82, 055011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatmandi, A.; Dehghan, M. The use of sinc-collocation method for solving multi-point boundary value problems. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 2012, 17, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gamel, M. Sinc-collocation method for solving linear and nonlinear system of second-order boundary value problems. Appl. Math. 2012, 3, 1627–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambrah, P.S.N.; Pirvu, T.A. Risk measures and portfolio optimization. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2014, 90, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanti, D.; Najmia, M.; Lesmana, E.; Napitupulu, H.; Supian, S.; Putra, A.S. Analysis of stock investment selection based on CAPM using covariance and genetic algorithm approach. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 332, 012046. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, S.G. A jump-diffusion model for option pricing. Manag. Sci. 2002, 48, 1086–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y. Analysis of the expected discounted penalty function for a general jump-diffusion risk model and applications in finance. Insur. Math. Econ. 2010, 46, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liang, Z. Portfolio optimization for jump-diffusion a risky asset with common shock dependence and state dependent risk aversion. Optim. Contr. Appl. Methods 2017, 38, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gao, Z.; Wang, B. Omega model for a jump-diffusion process with a two-step premium rate. J. Korean Stat. Soc. 2019, 48, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Kan, X.; Shu, H. Optimal investment and reinsurance problem with jump-diffusion model. Commun. Stat.-Theor. Methods 2019, 50, 1082–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, L.; Bowers, K.L. Sinc Methods for Quadrature and Differential Equations; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Saadatmandi, A.; Dehghana, M. The numerical solution of third-order boundary value problems using sinc-collocation method. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2007, 366, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghana, M.; Saadatmandi, A. The numerical solution of a nonlinear system of second-order boundary value problems using the sinc-collocation method. Math. Comput. Model. 2007, 46, 1434–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sababheh, M.S.; Nusayr, A.M.; Khaled, K.A. Some convergence results on Sinc interpolation. J. Inequal. Pure Appl. Math. 2003, 4, 32–48. [Google Scholar]
- Stenger, F. Summary of sinc numerical methods. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2000, 21, 379–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhang, Z. Finite-time dividend problems in a Lévy risk model under periodic observation. Appl. Math. Comput. 2021, 398, 125981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Approximating the density of the time to ruin via fourier-cosine series expansion. Astin Bull. 2017, 47, 169–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Su, W.; Zhang, Z. Estimating the discounted density of the deficit at ruin by fourier cosine series expansion. Stat. Probabil. Lett. 2018, 146, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



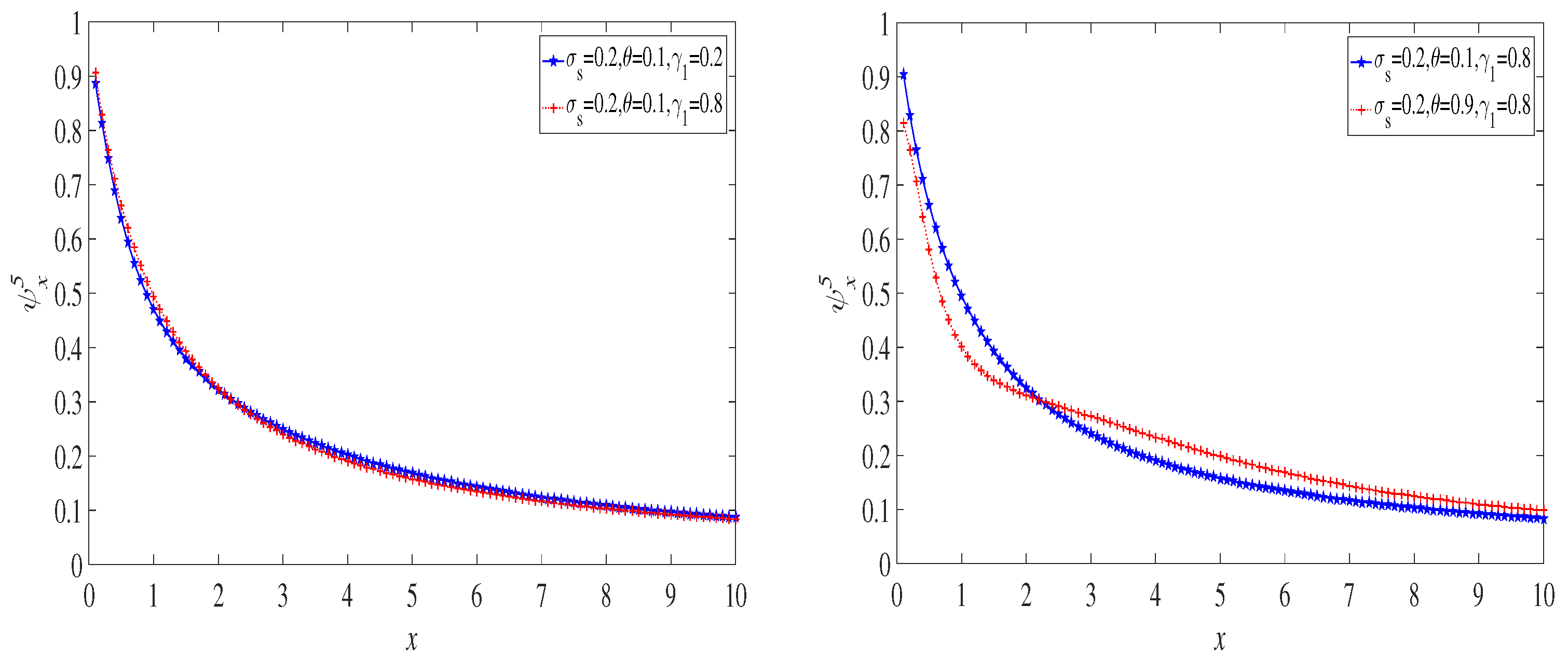
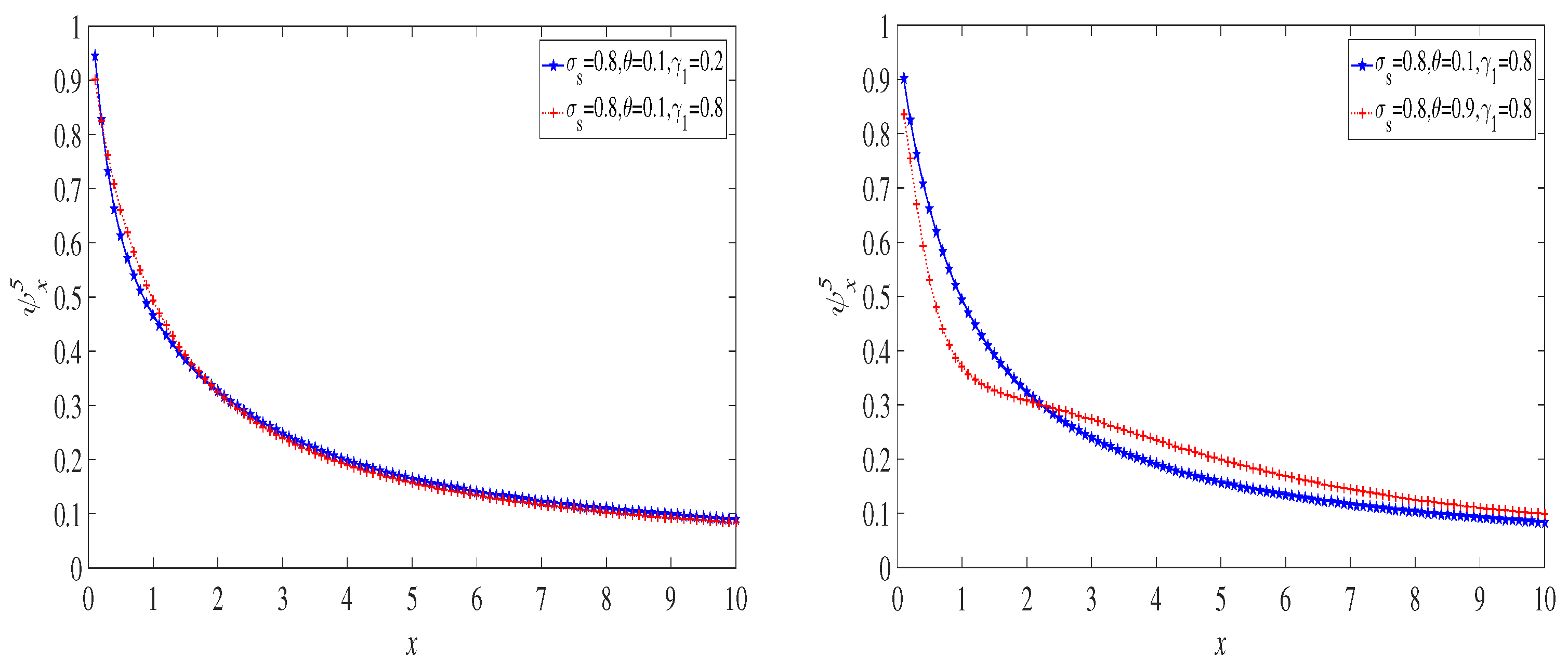
| Research Paper | Risk Model | Sinc | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perturbation | Risk-Free Asset | Risky Asset | Dividend | ||
| Chen and Ou [1] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Wang et al. [2] | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Lu and Li [3] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Li [4] | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Rachev et al. [5] | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Peng and Wang [6] | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Ellanskaya and Kabanov [7] | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Matthias and Hanspeter [12] | ✓ | ||||
| Wan [13] | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Yang et al. [14] | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Zhuo et al. [23] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Chen et al. [15] | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Our work | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 0.2208 | 0.2210 | 0.2211 | 0.2213 | 0.2215 | |
| 0.2216 | 0.2217 | 0.2211 | 0.2209 | 0.2207 |
| N | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.90414 | 0.66493 | 0.55286 | 0.41320 | 0.34186 | 0.32426 | 0.30654 | 0.27845 |
| 15 | 0.89749 | 0.66212 | 0.55084 | 0.40922 | 0.28676 | 0.21566 | 0.17488 | 0.13788 |
| 20 | 0.89998 | 0.66256 | 0.54823 | 0.41337 | 0.26072 | 0.17699 | 0.15013 | 0.12781 |
| 25 | 0.89946 | 0.66333 | 0.54786 | 0.41336 | 0.25838 | 0.18303 | 0.15359 | 0.12053 |
| 0.3080 | 0.3096 | 0.3109 | 0.3129 | 0.3136 | |
| 0.3140 | 0.3157 | 0.3169 | 0.3176 | 0.3135 |
| N | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.90866 | 0.51823 | 0.43358 | 0.33938 | 0.22602 | 0.15149 | 0.11418 | 0.08409 |
| 15 | 0.90094 | 0.45252 | 0.37632 | 0.32218 | 0.21997 | 0.14668 | 0.11099 | 0.08109 |
| 20 | 0.90104 | 0.41090 | 0.33789 | 0.31887 | 0.21558 | 0.14314 | 0.10882 | 0.07916 |
| 25 | 0.88713 | 0.38654 | 0.30848 | 0.31715 | 0.21273 | 0.14064 | 0.10799 | 0.07911 |
| 0.1517 | 0.1518 | 0.1519 | 0.1520 | 0.1522 | |
| 0.1524 | 0.1526 | 0.1527 | 0.1517 | 0.1514 |
| N | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.90362 | 0.66308 | 0.55190 | 0.39376 | 0.24356 | 0.16124 | 0.11965 | 0.08539 |
| 15 | 0.89681 | 0.65951 | 0.54863 | 0.38461 | 0.22964 | 0.14846 | 0.10803 | 0.07444 |
| 20 | 0.89424 | 0.64789 | 0.53217 | 0.39517 | 0.30584 | 0.23360 | 0.17522 | 0.12216 |
| 25 | 0.89341 | 0.64702 | 0.53349 | 0.38471 | 0.25032 | 0.16928 | 0.12426 | 0.08682 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Deng, N.; Shen, S. Numerical Method for a Perturbed Risk Model with Proportional Investment. Mathematics 2023, 11, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11010043
Wang C, Deng N, Shen S. Numerical Method for a Perturbed Risk Model with Proportional Investment. Mathematics. 2023; 11(1):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11010043
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chunwei, Naidan Deng, and Silian Shen. 2023. "Numerical Method for a Perturbed Risk Model with Proportional Investment" Mathematics 11, no. 1: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11010043
APA StyleWang, C., Deng, N., & Shen, S. (2023). Numerical Method for a Perturbed Risk Model with Proportional Investment. Mathematics, 11(1), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11010043







