Survival with Random Effect
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Main Concepts
2.2. Random Effect
3. Several Models with Random Effect
3.1. Gamma–Weibull Model
3.2. Gamma–Gompertz Model
3.3. Poisson-Gompertz Model
3.4. Geometric-Gompertz Model
3.5. Discrete-Weibull Model
4. Data and Model Fitness
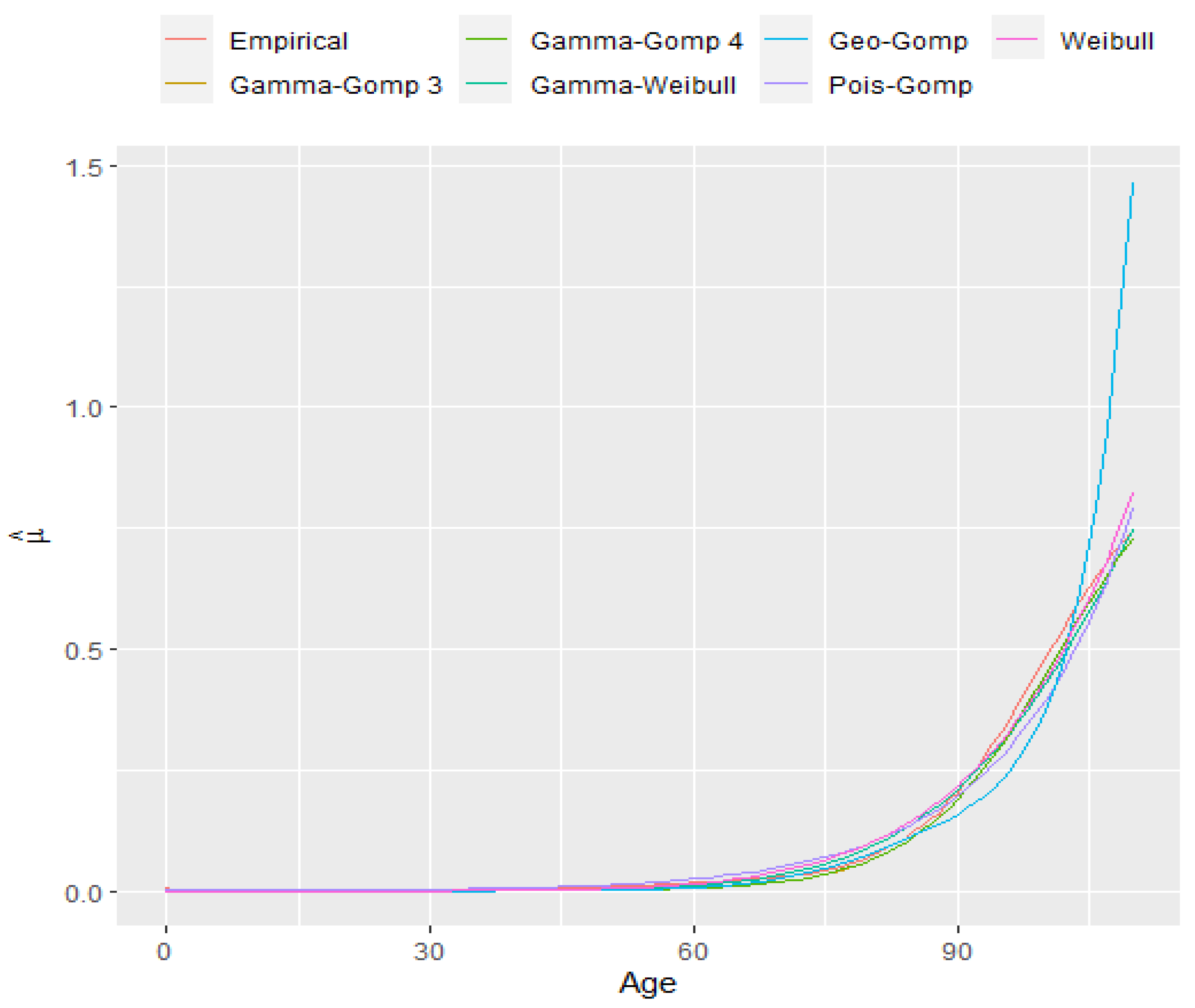
5. Data Analysis and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Juckett, D.A.; Rosenberg, B. Comparison of the Gompertz and Weibull functions as descriptions for human mortality distributions and their intersections. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1993, 69, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missov, T.I.; Lenart, A.; Nemeth, L.; Canudas-Romo, V.; Vaupel, J.W. The Gompertz force of mortality in terms of the modal age at death. Demog. Res. 2015, 32, 1031–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaupel, J.W. Inherited frailty and longevity. Demography 1988, 25, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.D. Constructions and applications of lifetime distributions. Appl. Stoch. Models Bus. Ind. 2013, 29, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienke, A. Frailty models. In MPIDR Working Paper WP 2003–2032; Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research: Rostock, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Manton, K.G.; Stallard, E.; Vaupel, J.W. Alternative Models for heterogeneity of mortality risks among the aged. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1986, 81, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manton, K.G. Changing concepts of morbidity and mortality in the elderly population. Milbank Mem. Fund Q. Health Soc. 1982, 60, 183–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashin, A.I.; Iachine, I.A.; Begun, A.Z.; Vaupel, J.W. Hidden frailty: Myths and reality. Doc. Trav. 2001, 34, 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Butt, Z.; Haberman, S. Application of frailty-based mortality models using generalized linear models. ASTIN Bull. 2004, 34, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moger, T.A.; Aalen, O.O. Regression models for infant mortality data in Norwegian siblings, using a compound Poisson frailty distribution with random scale. Biostatistics 2008, 3, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hougaard, P. Frailty models for survival data. Lifetime Data Anal. 1995, 1, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, M.S. Lifesaving explains mortality decline with time. Math. Biosci. 2005, 196, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitacco, E. From Halley to “frailty”: A review of survival models for actuarial calculations. Giornale dell’Istituto Italiano Degli Attuari. 2005. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=741586 (accessed on 18 February 2022).
- Pitacco, E. High age mortality and frailty. Some remarks and hints for actuarial modelling. In Working Paper 2016/2019; CEPAR: Kensington, Australia, 2016; Available online: https://www.cepar.edu.au/publications/working-papers/high-age-mortality-and-frailty-some-remarks-and-hints-actuarial-modeling (accessed on 18 February 2022).
- Spreeuw, J.; Nielsen, J.P.; Jarner, S.F. A nonparametric visual test of mixed hazard models. SORT 2013, 1, 153–174. [Google Scholar]
- Assabil, S.E. Forecasting maternal mortality with modified Gompertz model. J. Adv. Math. Comput. Sci. 2019, 32, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pitacco, E.; Denuit, M.; Haberman, S.; Olivieri, A. Modelling Longevity Dynamics for Pensions and Annuity Business; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilov, L.A.; Gavrilova, N.S. The reliability theory of aging and longevity. J. Theor. Biol. 2001, 213, 527–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henshaw, K.; Constantinescu, C.; Pamen, O.M. Stochastic mortality modelling for dependent coupled lives. Risks 2020, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Royden, H.L. Real Analysis; Macmillan Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Vaupel, J.M.; Manton, K.G.; Stallard, E. The impact of heterogeneity in individual frailty on the dynamics of mortality. Demography 1979, 6, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulla, S.; Laurent, J.P. Mortality Fluctuations Modelling with a Shared Frailty Approach. Working Paper. 2008. Available online: http://laurent.jeanpaul.free.fr/ (accessed on 18 February 2022).
- Tuljapurkar, S.; Edwards, R.D. Variance in death and its implications for modelling and forecasting mortality. Demogr. Res. 2011, 24, 497–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danilenko, S.; Šiaulys, J.; Stepanauskas, G. Closure properties of O-exponential distributions. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2018, 140, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragulina, O.; Šiaulys, J. Randomly stopped minima and maxima with exponential-type distributions. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control 2019, 24, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprindys, J.; Šiaulys, J. Regularly distributed randomly stopped sum, minimum, and maximum. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control 2020, 25, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamer, A.A.; Almulhim, A.S.; Alrashed, A.A.; Abraham, I. Mortality, severity, and hospital admission among COVID-19 patients with ACEI/ARB use: A meta-analysis stratifying countries based on response to the first wave of the pandemic. Healthcare 2021, 9, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-J.; Kuo, G.; Lee, T.H.; Yang, H.-Y.; Wu, H.H.; Tu, K.-H.; Tian, Y.-C. Incidence of mortality, acute kidney injury and graft loss in adult kidney transplant recipients with coronavirus disease 2019: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Izquierdo, M.; Pérez de Rojas, J.; Martínez-Ruiz, V.; Pérez-Gómez, B.; Sánchez, M.-J.; Khan, K.S.; Jiménez-Moleón, J.J. Obesity as a risk factor for prostate cancer mortality: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of 280,199 patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.; Burbanks, A.; Cerasuolo, M. Mathematical insights into neuroendocrine transdifferentiation of human prostate cancer cells. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control 2021, 5, 884–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.-P.; Turcotte, R. A longitudinal analysis of the impact of distance driven on the probability of car accidents. Risks 2020, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostiuc, S.; Diaconescu, I.; Rusu, M.C.; Negoi, I. Age estimation using the cameriere methods of open apices: A meta-analysis. Healthcare 2021, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, D. PQMLE of a partially linear, varying coefficient spatial autoregressive panel model with random effects. Symmetry 2021, 13, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroleva, E.; Jigeer, S.; Miao, A.; Skhvediani, A. Determinants affecting profitability of state-owned commercial banks: Case study of China. Risks 2021, 9, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Młynarczyk, D.; Armero, C.; Gómez-Rubio, V.; Puig, P. Bayesian analysis of population health data. Mathematics 2021, 9, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimon, G.; Appolloni, A.; Tarighi, H.; Shahmohammadi, S.; Daneshpou, E. Earnings management, related party transactions and corporate performance: The moderating role of internal control. Risks 2021, 9, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Dai, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, B. Remaining useful life prediction of cutting tools using an inverse Gaussian process model. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazonov, I.; Grebennikov, D.; Meyerhans, A.; Bocharov, G. Markov chain-based stochastic modelling of HIV-1 life cycle in a CD4 T cell. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klakattawi, H.S. The Weibull–Gamma distribution: Properties and applications. Entropy 2019, 21, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Missov, T.I.; Lenart, A. Gompertz-Makeham life expectancies: Expressions and applications. Theor. Pop. Biol. 2013, 90, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, O.; Missov, T.I. Evolutionary theory of ageing and the problem of correlated Gompertz parameters. J. Theor. Biol. 2016, 408, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotlačilová, P. Comparison of selected mortality models. In Proceedings of the 11th International Days of Statistics and Economics, Prague, Czech Republic, 14–16 September 2017; Vysoka Skola Ekonomicka: Prague, Czech Republic, 2017; pp. 324–337. [Google Scholar]
- Jarner, S.F.; Kryger, E.M. Modelling adult mortality in small populations: The SAINT model. ASTIN Bull. 2011, 41, 377–418. [Google Scholar]
- Saika, P.; Borah, M. A comparative study of parametric models of old-age mortality. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2014, 3, 406–410. [Google Scholar]
- Beard, R.E. Some aspects of theories of mortality, cause of death analysis, forecasting and stochastic processes. In Biological Aspects of Demography; Brass, W., Ed.; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 1971; pp. 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Pflaumer, P. Life table forecasting with Gompertz distribution. In JSM Proceedings, Social Statistics Section; American Statistical Association: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2007; pp. 3564–3571. [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi, S.; Ouellette, N.; Cheung, S.L.K.; Robine, J.M. Modal age at death: Lifespan indicator in the era of longevity extension. Vienna Yearb. Pop. Res. 2013, 11, 37–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rau, R.; Ebeling, M.; Peters, F.; Bohk-Ewald, C.; Missov, T.I. Where is the level of mortality plateau? In Living to 100, Society of Actuaries International Symposium; Society of Actuaries: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.E.; Bohk-Ewald, C.; Rau, R. Gompertz, Makeham and Siler models explain Taylor’s law in human mortality data. Demog. Res. 2018, 38, 773–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romo, V.C. The modal age of death and the shifting mortality hypothesis. Demog. Res. 2008, 19, 1179–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missov, T.I. Gamma-Gompertz life expectancy at birth. Demogr. Res. 2013, 28, 59–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.S.; Brown, R.L. A frailty model for projection of human mortality improvements. J. Actuar. Pract. 1998, 6, 1993–2006. [Google Scholar]
- Missov, T.I.; Vaupel, J.W. Mortality implications of morality plateaus. SIAM Rev. 2015, 57, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Estonia | Latvia | Lithuania | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||||
| 0 | 0.0045 | 1 | 0.0071 | 1 | 0.0058 | 1 |
| 1 | 0.0005 | 0.9954 | 0.0006 | 0.9929 | 0.0005 | 0.9942 |
| 2 | 0.0003 | 0.9949 | 0.0004 | 0.9923 | 0.0003 | 0.9936 |
| 3 | 0.0002 | 0.9946 | 0.0003 | 0.9918 | 0.0003 | 0.9933 |
| 4 | 0.0002 | 0.9944 | 0.0003 | 0.9915 | 0.0003 | 0.9930 |
| 5 | 0.0003 | 0.9941 | 0.0003 | 0.9912 | 0.0002 | 0.9927 |
| 6 | 0.0002 | 0.9938 | 0.0002 | 0.9909 | 0.0002 | 0.9925 |
| 7 | 0.0002 | 0.9936 | 0.0003 | 0.9906 | 0.0002 | 0.9923 |
| 8 | 0.0002 | 0.9934 | 0.0002 | 0.9904 | 0.0002 | 0.9920 |
| 9 | 0.0001 | 0.9933 | 0.0002 | 0.9901 | 0.0002 | 0.9918 |
| 10 | 0.0002 | 0.9931 | 0.0002 | 0.9899 | 0.0002 | 0.9916 |
| 11 | 0.0002 | 0.9930 | 0.0002 | 0.9897 | 0.0002 | 0.9915 |
| 12 | 0.0002 | 0.9928 | 0.0002 | 0.9895 | 0.0002 | 0.9913 |
| 13 | 0.0002 | 0.9926 | 0.0002 | 0.9892 | 0.0002 | 0.9911 |
| 14 | 0.0002 | 0.9924 | 0.0003 | 0.9890 | 0.0003 | 0.9908 |
| 15 | 0.0004 | 0.9922 | 0.0003 | 0.9887 | 0.0004 | 0.9905 |
| 16 | 0.0004 | 0.9918 | 0.0006 | 0.9884 | 0.0005 | 0.9901 |
| 17 | 0.0005 | 0.9914 | 0.0006 | 0.9878 | 0.0007 | 0.9896 |
| 18 | 0.0008 | 0.9909 | 0.0007 | 0.9873 | 0.0009 | 0.9889 |
| 19 | 0.0008 | 0.9901 | 0.0009 | 0.9866 | 0.0010 | 0.98802 |
| 20 | 0.0010 | 0.9893 | 0.001 | 0.9857 | 0.0011 | 0.9869 |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 50 | 0.0068 | 0.9172 | 0.0083 | 0.8972 | 0.0084 | 0.8950 |
| 51 | 0.0074 | 0.9109 | 0.0088 | 0.8897 | 0.0088 | 0.8875 |
| 52 | 0.0079 | 0.9042 | 0.0097 | 0.8819 | 0.0097 | 0.8797 |
| 53 | 0.0085 | 0.8971 | 0.0104 | 0.8734 | 0.0103 | 0.8711 |
| 54 | 0.0091 | 0.8895 | 0.0113 | 0.8643 | 0.0109 | 0.8622 |
| 55 | 0.0100 | 0.8815 | 0.0120 | 0.8546 | 0.0119 | 0.8529 |
| 56 | 0.0105 | 0.8727 | 0.0129 | 0.8444 | 0.0123 | 0.8428 |
| 57 | 0.0115 | 0.8636 | 0.0136 | 0.8336 | 0.0133 | 0.8325 |
| 58 | 0.0121 | 0.8538 | 0.0145 | 0.8223 | 0.0141 | 0.8215 |
| 59 | 0.0131 | 0.8435 | 0.0162 | 0.8105 | 0.0153 | 0.8099 |
| 60 | 0.0144 | 0.8326 | 0.0167 | 0.7975 | 0.0163 | 0.7977 |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 100 | 0.4641 | 0.0073 | 0.4873 | 0.0041 | 0.4799 | 0.0051 |
| 101 | 0.4966 | 0.0045 | 0.5187 | 0.0025 | 0.5109 | 0.0031 |
| 102 | 0.5291 | 0.0027 | 0.5500 | 0.0015 | 0.5414 | 0.0018 |
| 103 | 0.5614 | 0.0016 | 0.5808 | 0.0008 | 0.5711 | 0.0010 |
| 104 | 0.5932 | 0.0009 | 0.6110 | 0.0004 | 0.5998 | 0.0006 |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 110+ | 0.7613 | 0.00001 | 0.7670 | 0.000007 | 0.7422 | 0.00001 |
| Model | Mean Square Error (MSE) |
|---|---|
| Gamma-Gompertz with four parameters | 0.0001820656 |
| Gamma-Gompertz with three parameters | 0.0001824057 |
| Gamma-Weibull | 0.0003312705 |
| Weibull (discrete-Weibull with ) | 0.0003361133 |
| Poisson-Gompertz | 0.0008037022 |
| Geometric-Gompertz | 0.01091893 |
| Model | Mean Square Error (MSE) |
|---|---|
| Gamma-Gompertz with four parameters | 0.0001455127 |
| Gamma-Gompertz with three parameters | 0.0001830891 |
| Gamma-Weibull | 0.0002027425 |
| Weibull (discrete-Weibull with ) | 0.0002679813 |
| Poisson-Gompertz | 0.0007349811 |
| Geometric-Gompertz | 0.01031875 |
| Model | Mean Square Error (MSE) |
|---|---|
| Weibull (Discrete-Weibull with ) | 0.0001198733 |
| Gamma-Gompertz with three parameters | 0.0001817575 |
| Gamma-Gompertz with four parameters | 0.0001832729 |
| Gamma-Weibull | 0.0001985111 |
| Poisson-Gompertz | 0.0006680722 |
| Geometric-Gompertz | 0.01013277 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šiaulys, J.; Puišys, R. Survival with Random Effect. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10071097
Šiaulys J, Puišys R. Survival with Random Effect. Mathematics. 2022; 10(7):1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10071097
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠiaulys, Jonas, and Rokas Puišys. 2022. "Survival with Random Effect" Mathematics 10, no. 7: 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10071097
APA StyleŠiaulys, J., & Puišys, R. (2022). Survival with Random Effect. Mathematics, 10(7), 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10071097






