Natural Gas Scarcity Risk in the Belt and Road Economies Based on Complex Network and Multi-Regional Input-Output Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Multi-Regional Input-Output Model (MRIO)
2.2. Natural Gas Scarcity Risk (GSR)
2.2.1. Initial Natural Gas Scarcity Risk (IGSR)
2.2.2. Embodied Natural Gas Scarcity Risk (EGSR)
2.3. EGSR Transmission Network Construction and Analysis
2.3.1. Small-World Nature
2.3.2. Degree and Strength Analysis
2.3.3. Centrality
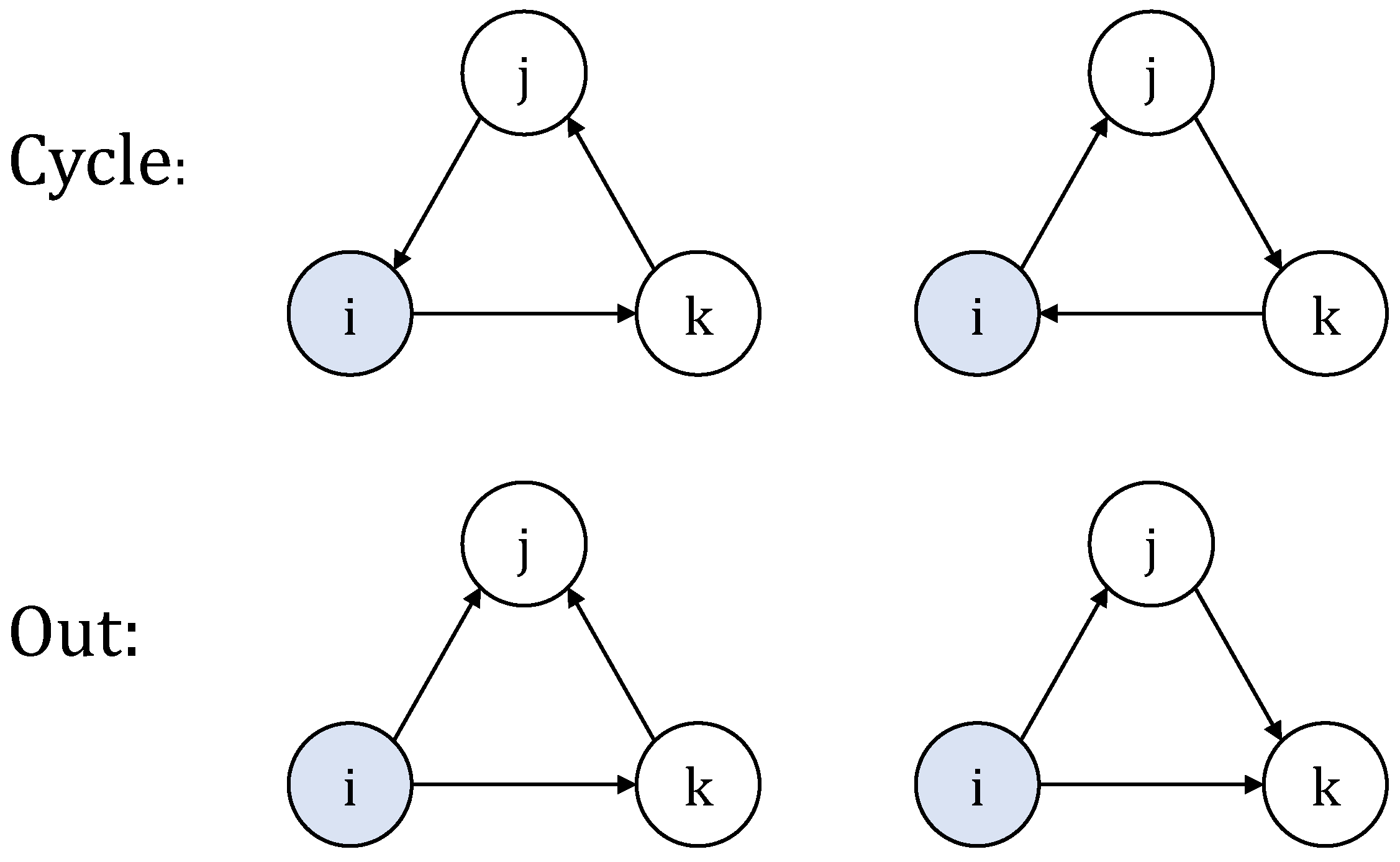
2.3.4. The Weighted and Directed Clustering Coefficients
2.3.5. Communities
2.4. Data Sources
3. Results
3.1. Small-World Nature
3.2. Major EGSR Flows
3.3. Roles of Countries
3.4. Communities
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Country | Code | Continent | Country | Code | Continent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | AFG | Asia | Lithuania | LTU | Europe |
| Albania | ALB | Europe | Malaysia | MYS | Asia |
| Armenia | ARM | Asia | Moldova | MDA | Europe |
| Azerbaijan | AZE | Asia | Myanmar | MMR | Asia |
| Bahrain | BHR | Asia | Oman | OMN | Asia |
| Bangladesh | BGD | Asia | Pakistan | PAK | Asia |
| Belarus | BLR | Europe | Philippines | PHL | Asia |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | BIH | Europe | Poland | POL | Europe |
| Brunei | BRN | Asia | Qatar | QAT | Asia |
| Bulgaria | BGR | Europe | Romania | ROU | Europe |
| China | CHN | Asia | Russia | RUS | Europe |
| Croatia | HRV | Europe | Saudi Arabia | SAU | Asia |
| Czech Republic | CZE | Europe | Serbia | SRB | Europe |
| Egypt | EGY | Arica | Singapore | SGP | Asia |
| Estonia | EST | Europe | Slovakia | SVK | Europe |
| Georgia | GEO | Asia | Slovenia | SVN | Europe |
| Hungary | HUN | Europe | Syria | SYR | Asia |
| India | IND | Asia | Tajikistan | TJK | Asia |
| Indonesia | IDN | Asia | TFYR Macedonia | MKD | Europe |
| Iran | IRN | Asia | Thailand | THA | Asia |
| Iraq | IRQ | Asia | Turkey | TUR | Asia |
| Israel | ISR | Asia | Turkmenistan | TKM | Asia |
| Jordan | JOR | Asia | UAE | ARE | Asia |
| Kazakhstan | KAZ | Asia | Ukraine | UKR | Europe |
| Kuwait | KWT | Asia | Uzbekistan | UZB | Asia |
| Kyrgyzstan | KGZ | Asia | Viet Nam | VNM | Asia |
| Latvia | LVA | Europe | Yemen | YEM | Asia |
| Lebanon | LBN | Asia |
References
- Sasse, T.; Rutter, J.; Norris, E.; Shepheard, M. Net Zero: How Government Can Meet Its Climate Change Target; Institute for Government: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Fu, J.; Pu, Z. A study of the petroleum trade network of countries along “The Belt and Road Initiative”. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Ge, Y. Energy relations between China and the countries along the Belt and Road: An analysis of the distribution of energy resources and interdependence relationships. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 107, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bompard, E.; Corgnati, S.; Grosso, D.; Huang, T.; Mietti, G.; Profumo, F. Multidimensional assessment of the energy sustainability and carbon pricing impacts along the Belt and Road Initiative. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 154, 111741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheshmehzangi, A.; Xie, L.; Tan-Mullins, M. Pioneering a Green Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) alignment between China and other members: Mapping BRI’s sustainability plan. Blue-Green Syst. 2021, 3, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, S.; Chen, B.; Wu, X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G. Natural gas overview for world economy: From primary supply to final demand via global supply chains. Energy Policy 2019, 124, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BP Statistical Review of World Energy. 2020. Available online: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/natural-gas.html (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Acquaye, A.; Feng, K.; Oppon, E.; Salhi, S.; Ibn-Mohammed, T.; Genovese, A.; Hubacek, K. Measuring the environmental sustainability performance of global supply chains: A multi-regional input-output analysis for carbon, sulphur oxide and water footprints. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 187, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, R.; Rodrigues, J.F.; Behrens, P. Impact of non-fossil electricity on the carbon emissions embodied in China’s exports. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 192, 582–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pan, L.; Fu, F.; Liu, P.; Ma, L.; Amorelli, A. China’s regional disparities in energy consumption: An input–output analysis. Energy 2014, 78, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, B.R.; Hawkins, T.R.; Wiedmann, T.O.; Galli, A.; Ercin, A.E.; Weinzettel, J.; Steen-Olsen, K. Integrating ecological and water footprint accounting in a multi-regional input–output framework. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Wu, S.; Lei, Y.; Li, S. Interprovincial transfer of embodied energy between the Jing-Jin-Ji area and other provinces in China: A quantification using interprovincial input-output model. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, D.J.; Feng, K.; Sun, L.; Hubacek, K. A hydro-economic MRIO analysis of the Haihe River Basin’s water footprint and water stress. Ecol. Model. 2015, 318, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Pfister, S.; Bhaduri, A. Accounting for a scarce resource: Virtual water and water footprint in the global water system. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, A.Y. Water scarcity challenges to business. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 318–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushforth, R.R.; Ruddell, B.L. The vulnerability and resilience of a city’s water footprint: The case of Flagstaff, Arizona, USA. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 2698–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, S.; Liang, S.; Konar, M.; Zhu, Z.; Chiu, A.S.; Jia, X.; Xu, M. Virtual water scarcity risk to the global trade system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Qu, S.; Guo, S.; Zhao, H.; Liang, S.; Xu, M. Virtual water scarcity risk to global trade under climate change. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qu, S.; Liu, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhao, H.; Chiu, A.C.; Liang, S.; Zou, J.P.; Xu, M. Virtual water scarcity risk in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 160, 104886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, T.; Wang, J.; Wei, Y. The embodied CO2 transfer across sectors of cities in Jing-Jin-Ji region: Combining multi-regional input–output analysis with complex network analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 44249–44263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Fan, F.; Li, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, H. Inter-provincial sectoral embodied CO2 net-transfer analysis in China based on hypothetical extraction method and complex network analysis. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 786, 147211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, G.; Fan, J.; Shekhtman, L.M.; Shai, S.; Du, R.; Tian, L.; Chen, X.; Stanley, H.E.; Havlin, S. Resilience of networks with community structure behaves as if under an external field. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6911–6915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Sanhedrai, H.; Dong, G.; Shekhtman, L.M.; Wang, F.; Buldyrev, S.V.; Havlin, S. Efficient network immunization under limited knowledge. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwaa229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, G.; Wang, F.; Shekhtman, L.M.; Danziger, M.M.; Fan, J.; Du, R.; Liu, J.; Tian, L.; Stanley, H.E.; Havlin, S. Optimal resilience of modular interacting networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e1922831118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zareie, A.; Sheikhahmadi, A. A hierarchical approach for influential node ranking in complex social networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 93, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raducha, T.; Gubiec, T. Coevolving complex networks in the model of social interactions. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2017, 471, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, R.; Dong, G.; Tian, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Vilela, A.L.; Stanley, H.E. Identifying the peak point of systemic risk in international crude oil importing trade. Energy 2019, 176, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Wang, Y.; Dong, G.; Tian, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Fang, G. A complex network perspective on interrelations and evolution features of international oil trade, 2002–2013. Appl. Energy 2017, 196, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; An, H.; Gao, X.; Liu, S.; Xi, X. Factors driving global carbon emissions: A complex network perspective. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 146, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Meng, J.; Ashkenazy, Y.; Havlin, S.; Schellnhuber, H.J. Network analysis reveals strongly localized impacts of El Niño. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7543–7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shanmukhappa, T.; Ho, I.W.H.; Tse, C.K. Spatial analysis of bus transport networks using network theory. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 502, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Chen, B. Energy–water nexus of international energy trade of China. Appl. Energy 2017, 194, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; An, H.; Gao, X.; Jia, X.; Liu, X. Indirect energy flow between industrial sectors in China: A complex network approach. Energy 2016, 94, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Yang, X.; Yan, F.; Li, Z. Exploring global embodied metal flows in international trade based combination of multi-regional input-output analysis and complex network analysis. Resour. Policy 2020, 67, 101661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yao, M.; Li, J.; Ge, J.; Wei, W.; Wu, B.; Zhang, M. Global embodied rare earths flows and the outflow paths of China’s embodied rare earths: Combining multi-regional input-output analysis with the complex network approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 216, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Lu, F.; Wu, L.; Xu, C. Social network analysis of virtual water trade among major countries in the world. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 142043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, B. Water-energy scarcity nexus risk in the national trade system based on multiregional input-output and network environ analyses. Appl. Energy 2020, 268, 114974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fan, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, B. Spillover risk analysis of virtual water trade based on multi-regional input-output model-A case study. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 275, 111242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manresa, A.; Sancho, F. A follow-up note on the plausibility of the Leontief and Ghosh closed models. Econ. Syst. Res. 2020, 32, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulu, M.M.; Hou, R.; Younas, T. Identifying influential nodes based on community structure to speed up the dissemination of information in complex network. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 7390–7401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G. Structure of small world innovation network and learning performance. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 860216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buldú, J.M.; Busquets, J.; Martínez, J.H.; Herrera-Diestra, J.L.; Echegoyen, I.; Galeano, J.; Luque, J. Using network science to analyse football passing networks: Dynamics, space, time, and the multilayer nature of the game. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, M.; Gao, X.; Guan, Q.; Hao, X.; An, F. The structural roles of sectors and their contributions to global carbon emissions: A complex network perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Satorras, R.; Castellano, C. Eigenvector localization in real networks and its implications for epidemic spreading. J. Stat. Phys. 2018, 173, 1110–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clemente, G.P.; Grassi, R. Directed clustering in weighted networks: A new perspective. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2018, 107, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyu, D.; Wang, B.; Zhang, W. Large-Scale Complex Network Community Detection Combined with Local Search and Genetic Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzen, M.; Kanemoto, K.; Moran, D.; Geschke, A. Mapping the structure of the world economy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8374–8381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenzen, M.; Moran, D.; Kanemoto, K.; Geschke, A. Building Eora: A global multi-region input–output database at high country and sector resolution. Econ. Syst. Res. 2013, 25, 20–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Central Intelligence Agency. 2020. Available online: https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/ (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Zhang, Q.; Zeng, Q. Analyzing the shipping network of the maritime silk road (MSR) based on a complex network. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 98, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Topic | Methods | Scope | Main Focus | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virtual transfers of water/ energy/metal | MRIO | Global | Assessment and tracking of global embodied natural gas flows | [6] |
| MRIO | Global | Ecological and water footprint accounting | [11] | |
| MRIO | China | Quantitative estimation of the embodied energy transfer | [12] | |
| MRIO Complex network | Global | Calculating the global embodied energy flows; uncovering the structure of embodied energy flow network | [33] | |
| MRIO Complex network | Global | Calculating the embodied metal flows; structural characteristics analysis of the global embodied metal flow network | [34] | |
| Resource scarcity risk transmission | MRIO | Global | Measuring the local water scarcity risk and international virtual water scarcity risk in the global trade system | [17] |
| MRIO | China | Quantifying the local water scarcity risk and international virtual water scarcity risk in China | [19] | |
| MRIO Network environs analysis | Global | Assessment and tracking the transmission of water-energy scarcity risk | [37] | |
| MRIO Complex network | B&R economies | Quantifying the natural gas scarcity risk; revealing the structural feature of the EGSR transmission network | Our work |
| Intermediate Use | Final Use | Total Output | ||||
| Economy 1 | ⋯ | Economy n | ||||
| Economy 1 | ||||||
| Intermediate input | ⋯ | |||||
| Economy n | ||||||
| Value added | ||||||
| Total input | ||||||
| Source | Target | |
|---|---|---|
| Turkey | → | Turkmenistan |
| Turkey | → | Georgia |
| Turkey | → | Albania |
| Turkey | → | TFYR Macedonia |
| Bulgaria | → | TFYR Macedonia |
| China | → | Viet Nam |
| China | → | Singapore |
| Turkey | → | Azerbaijan |
| Turkey | → | Israel |
| Ukraine | → | Turkmenistan |
| Source | Target | |
|---|---|---|
| Turkey—Petroleum, Chemical and Non-Metallic Mineral Products | → | Turkmenistan—Petroleum, Chemical and Non-Metallic Mineral Products |
| Turkey—Petroleum, Chemical and Non-Metallic Mineral Products | → | Georgia—Petroleum, Chemical and Non-Metallic Mineral Products |
| Turkey—Petroleum, Chemical and Non-Metallic Mineral Products | → | Albania—Petroleum, Chemical and Non-Metallic Mineral Products |
| Turkey—Petroleum, Chemical and Non-Metallic Mineral Products | → | Turkmenistan—Electricity, Gas and Water |
| Bulgaria—Petroleum, Chemical and Non-Metallic Mineral Products | → | TFYR Macedonia—Re-export and Re-import |
| Ukraine—Metal Products | → | Turkey—Other Manufacturing |
| Turkey—Petroleum, Chemical and Non-Metallic Mineral Products | → | Turkmenistan—Fishing |
| Turkey—Petroleum, Chemical and Non-Metallic Mineral Products | → | Tajikistan—Petroleum, Chemical and Non-Metallic Mineral Products |
| Ukraine—Metal Products | → | Lithuania—Metal Products |
| China—Electrical and Machinery | → | Hungary—Electrical and Machinery |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, R.; Wu, Q.; Nan, Z.; Dong, G.; Tian, L.; Wu, F. Natural Gas Scarcity Risk in the Belt and Road Economies Based on Complex Network and Multi-Regional Input-Output Analysis. Mathematics 2022, 10, 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10050788
Du R, Wu Q, Nan Z, Dong G, Tian L, Wu F. Natural Gas Scarcity Risk in the Belt and Road Economies Based on Complex Network and Multi-Regional Input-Output Analysis. Mathematics. 2022; 10(5):788. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10050788
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Ruijin, Qi Wu, Ziwei Nan, Gaogao Dong, Lixin Tian, and Feifan Wu. 2022. "Natural Gas Scarcity Risk in the Belt and Road Economies Based on Complex Network and Multi-Regional Input-Output Analysis" Mathematics 10, no. 5: 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10050788
APA StyleDu, R., Wu, Q., Nan, Z., Dong, G., Tian, L., & Wu, F. (2022). Natural Gas Scarcity Risk in the Belt and Road Economies Based on Complex Network and Multi-Regional Input-Output Analysis. Mathematics, 10(5), 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10050788








