Advanced Drone Swarm Security by Using Blockchain Governance Game
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Stochastic Game for Smart Drone Network Framework
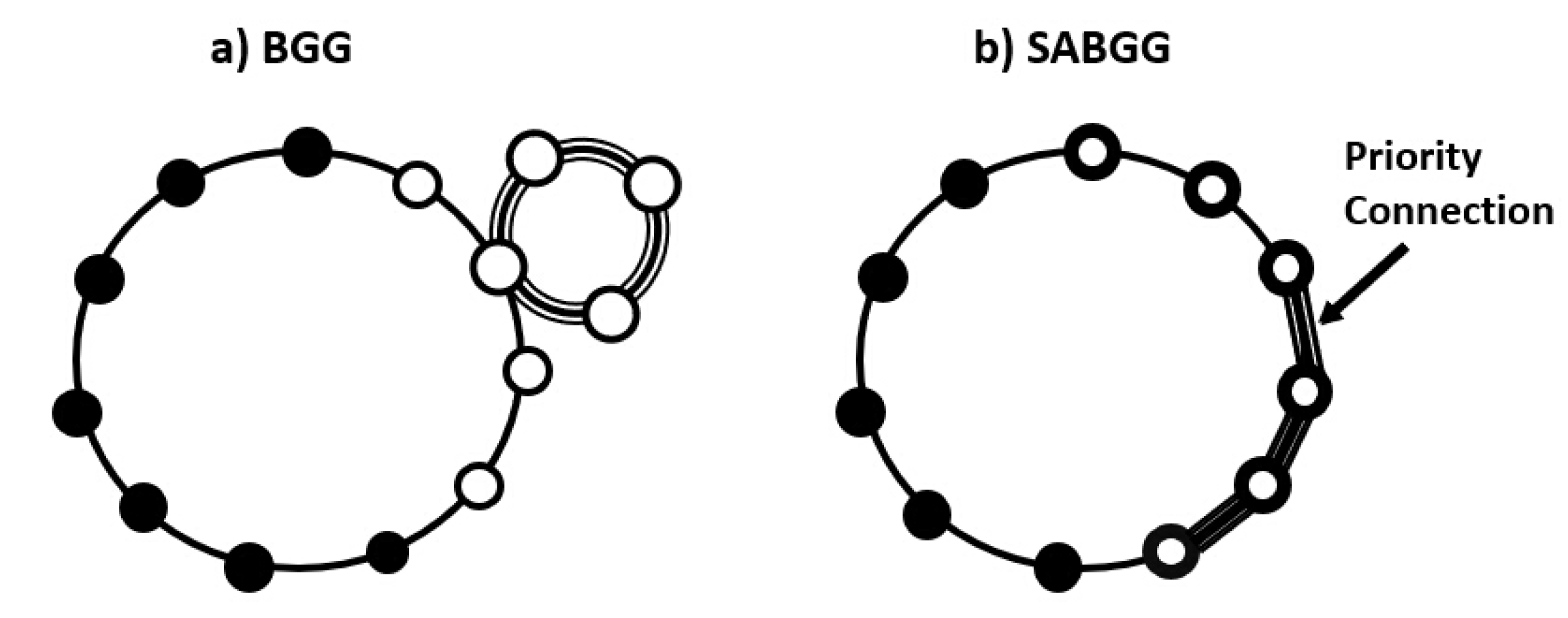
2.1. Advanced Blockchain-Based Secured Smart Drone Swarm Network Structure
2.2. SABGG Models for Advanced Blockchain-Based Secured Smart Drone Swarm Network
2.3. Mixed Strategy Game Design for SABGG
3. The Optimization Practice for SABGG-Based Drone Security
3.1. Special Case for Advanced Drone Swarm Security
3.2. Linear Programming Practice
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vergouw, B.; Nagel, H.; Bondt, G.; Custers, B. Drone technology: Types, payloads, applications, frequency spectrum issues and future developments. In The Future of Drone Use; TMC Asser Press: Hague, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 21–45. [Google Scholar]
- Shahmoradi, J.; Talebi, E.; Roghanchi, P.; Hassanalian, M. A Comprehensive Review of Applications of Drone Technology in the Mining Industry. Drones 2020, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.; Kim, J.; Duguma, D.G.; Astillo, P.V.; You, I.; Pau, G. Drone Secure Communication Protocol for Future Sensitive Applications in Military Zone. Sensors 2021, 21, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliusar, N.; Filkin, T.; Huber-Humer, M.; Ritzkowski, M. Drone technology in municipal solid waste management and landfilling: A comprehensive review. Waste Manag. 2022, 139, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intel. Drone100 Performed by Ars Electronica Futurelab. 2015. Available online: https://inteldronelightshows.com/ (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Hambling, D. What Are Drone Swarms and Why Does Every Military Suddenly Want One? Forbes 2021. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/davidhambling/2021/03/01/what-are-drone-swarms-and-why-does-everyone-suddenly-want-one/ (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Kallenborn, Z. Israel’s Drone Swarm over Gaza Should Worry Everyone. 2021. Available online: https://www.defenseone.com/ideas/2021/07/israels-drone-swarm-over-gaza-should-worry-everyone/183156/ (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- DOD; Department of Defense Announces Successful Micro-Drone Demonstration. US Dep. of Defense; 9 January 2017. Available online: https://www.defense.gov/ (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Naqvi, S.A.; Hassan, S.A.; Pervaiz, H.; Ni, Q. Drone-Aided communication as a key enabler for 5G and resilient public safety networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallenborn, Z. Meet the future weapon of mass destruction, the drone swarm. Bull. At. Sci. 2021. Available online: https://thebulletin.org/2021/04/meet-the-future-weapon-of-mass-destruction-the-drone-swarm/ (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Choudhary, G.; Sharma, V.; You, I. Sustainable and secure trajectories for the military Internet of Drones (IoD) through an efficient Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2019, 74, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Chan, S.; Guizani, M. Communication security of unmanned aerial vehicles. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2016, 24, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, S. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. 2008. Available online: https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Wood, G. Ethereum: A Secure Decentralised Generalised Transaction Ledger. Ethereum Project Yellow Paper. 2014. Available online: http://gavwood.com/paper.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Strobel, V.; Ferrer, E.C.; Dorigo, M. Managing Byzantine Robots via Blockchain Technology in a Swarm Robotics Collective Decision Making Scenario. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi Agent Systems, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 541–549. [Google Scholar]
- Strobel, V.; Ferrer, E.C.; Dorigo, M. Blockchain Technology Secures Robot Swarms: A Comparison of Consensus Protocols and Their Resilience to Byzantine Robots. Front. Robot. AI. 2020, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millard, A.G.; Timmis, J.; Winfield, A.F.T. Towards Exogenous Fault Detection in Swarm Robotic Systems. In Proceedings of the 14th Annual Conference, TAROS 2013, Oxford, UK, 28–30 August 2013; pp. 429–430. [Google Scholar]
- Restuccia, F. Blockchain for the Internet of Things: Present and Future. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.07448. [Google Scholar]
- Jesus, E.F.; Chicarino, V.R.L.; de Albuquerque, C.V.N.; Rocha, A.A.D.A. Survey of How to Use Blockchain to Secure Internet of Things and the Stalker Attack. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2018, 2018, 9675050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazid, M.; Bera, B.; Mitra, A.; Das, A.K.; Ali, R. Private blockchain-envisioned security framework for AI-enabled IoT-based drone-aided healthcare services. In Proceedings of the 2020 DroneCom, London, UK, 25 September 2020; pp. 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Cheema, M.A.; Shehzad, M.K.; Qureshi, H.K.; Hassan, S.A.; Jung, H. A Drone-Aided Blockchain-Based Smart Vehicular Network. IEEE Trans. Intel. Trans. Sys. 2021, 22, 4160–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buterin, V. A Next-Generation Smart Contract and Decentralized Application Platform. Ethereum Project White Paper. 2014. Available online: https://github.com/ethereum/wiki/wiki/White-Paper (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Pinciroli, C.; Trianni, V.; O’Grady, R.; Pini, G.; Brutschy, A.; Brambilla, M.; Mathews, N.; Ferrante, E.; Di Caro, G.; Ducatelle, F.; et al. ARGoS: A modular, parallel, multi-engine simulator for multi-robot systems. Swarm Intell. 2012, 6, 271–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.-K. Blockchain Governance Game. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 136, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K. Strategic Alliance for Blockchain Governance Game. Probab. Eng. Inf. Sci. 2020, 36, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K. Enhanced IoV Security Network by Using Blockchain Governance Game. Mathematics 2021, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micali, S.; Rabin, M.O.; Vadhan, S.P. Verifiable random functions. In Proceedings of the 40th IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, New York, NY, USA, 17–18 October 1999; pp. 120–130. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, S.; Reyzin, L.; Papadopoulos, D.; Vcelak, J. Verifiable Random Functions. IETF. 2022. Available online: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-irtf-cfrg-vrf/ (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Guerrero-Bonilla, L.; Prorok, A.; Kumar, V. Formations for resilient robot teams. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 741–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldana, D.; Prorok, A.; Sundaram, S.; Campos, M.F.; Kumar, V. Resilient consensus for time-varying networks of dynamic agents. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 24–26 May 2017; pp. 252–258. [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc, H.J.; Zhang, H.; Koutsoukos, X.; Sundaram, S. Resilient asymptotic consensus in robust networks. IEEE J. Select. Areas Commun. 2013, 31, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulnier, K.; Saldana, D.; Prorok, A.; Pappas, G.J.; Kumar, V. Resilien flocking for mobile robot teams. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dshalalow, J.H. First Excess Level Process, Advances in Queueing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995; pp. 244–261. [Google Scholar]



| NotBurst | Burst | |
|---|---|---|
| Regular | 0 | V |
| Safety |
| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| M | 20 (drones) | Total number of the nodes in the drone swarm |
| V | 1500 (USD) | Total value of a blockchain-enabled drone |
| (USD) | Cost for reserving nodes to avoid attacks per each car | |
| 3 (trial) | Average number of the observation until the attacker governs the smart drone swarm | |
| C | (drone) | Random number of accepted drones at |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-K. Advanced Drone Swarm Security by Using Blockchain Governance Game. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10183338
Kim S-K. Advanced Drone Swarm Security by Using Blockchain Governance Game. Mathematics. 2022; 10(18):3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10183338
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Song-Kyoo (Amang). 2022. "Advanced Drone Swarm Security by Using Blockchain Governance Game" Mathematics 10, no. 18: 3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10183338
APA StyleKim, S.-K. (2022). Advanced Drone Swarm Security by Using Blockchain Governance Game. Mathematics, 10(18), 3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10183338