Quality-Enhancing Techniques for Model-Based Reconstruction in Magnetic Particle Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Signal Encoding
2.2. MPI Core Operator and Reconstruction Formulae
3. Algorithmic Framework and Numerical Realization
3.1. Model-Based Reconstruction Framework
3.2. Discretization and Numerical Realization
4. Model-Based Reconstruction for Combining Multiple Scans
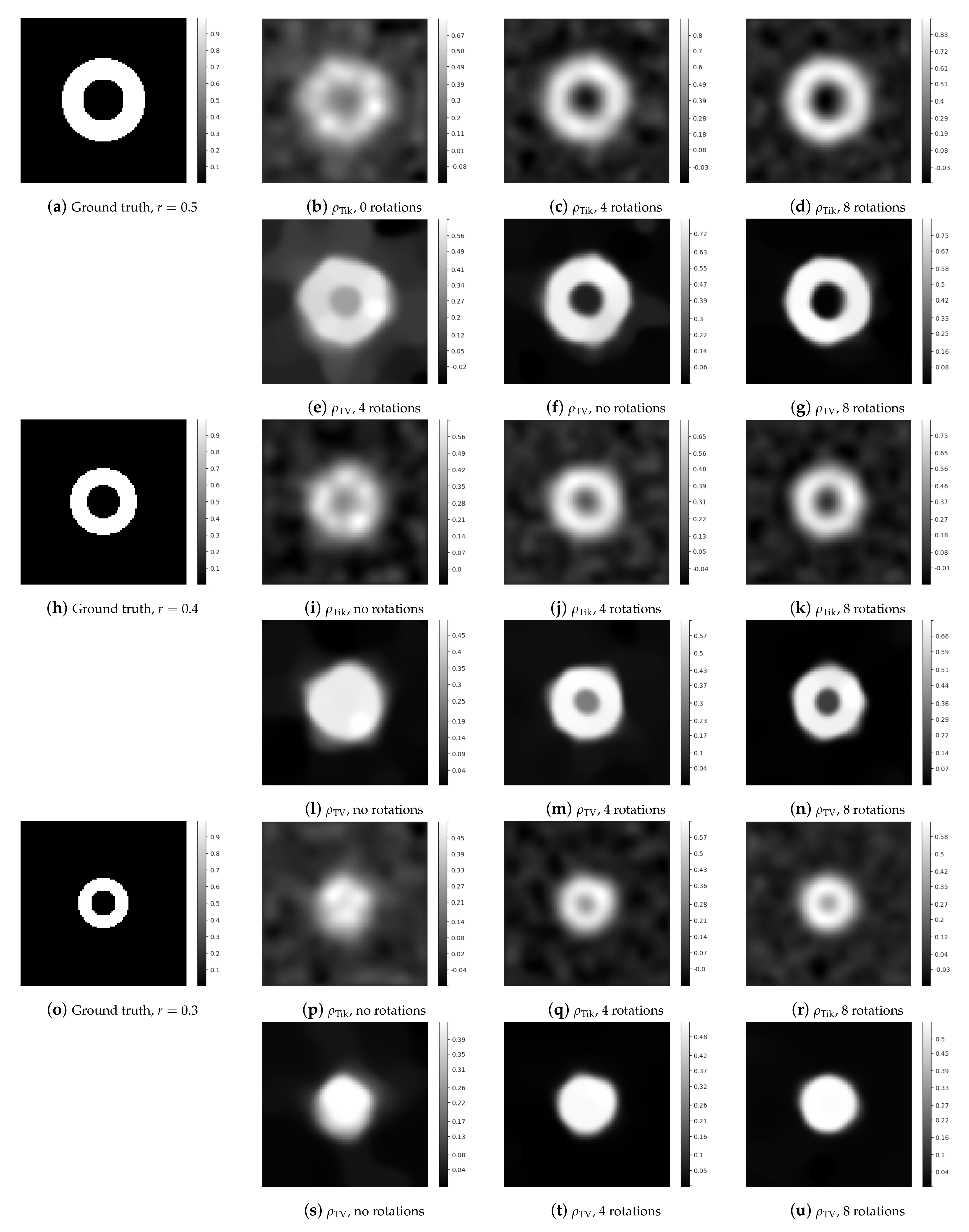
5. Numerical Experiments
5.1. Experimental Setup
5.2. Experimental Results
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gleich, B.; Weizenecker, J. Tomographic imaging using the nonlinear response of magnetic particles. Nature 2005, 435, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopp, T.; Buzug, T.M. Magnetic Particle Imaging: An Introduction to Imaging Principles and Scanner Instrumentation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.; Vazin, T.; Yang, W.; Goodwill, P.; Saritas, E.; Croft, L.; Schaffer, D.; Conolly, S. Quantitative stem cell imaging with magnetic particle imaging. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Magnetic Particle Imaging, Berkeley, CA, USA, 23–24 March 2013; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Graeser, M.; Thieben, F.; Szwargulski, P.; Werner, F.; Gdaniec, N.; Boberg, M.; Griese, F.; Möddel, M.; Ludewig, P.; van de Ven, D.; et al. Human-sized magnetic particle imaging for brain applications. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ter-Pogossian, M.; Phelps, M.; Hoffman, E.; Mullani, N. A positron-emission transaxial tomograph for nuclear imaging (PETT). Radiology 1975, 114, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhl, D.; Edwards, R. Image separation radioisotope scanning. Radiology 1963, 80, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, T.; Biederer, S.; Sattel, T.; Erbe, M.; Buzug, T. Prediction of the spatial resolution of magnetic particle imaging using the modulation transfer function of the imaging process. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2011, 30, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weizenecker, J.; Borgert, J.; Gleich, B. A simulation study on the resolution and sensitivity of Magnetic Particle Imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007, 52, 6363–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmer, J.; Weizenecker, J.; Gleich, B.; Borgert, J. Analysis of a 3-D system function measured for Magnetic Particle Imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2012, 31, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampe, J.; Bassoy, C.; Rahmer, J.; Weizenecker, J.; Voss, H.; Gleich, B.; Borgert, J. Fast reconstruction in Magnetic Particle Imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 1113–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, T.; Rahmer, J.; Sattel, T.; Biederer, S.; Weizenecker, J.; Gleich, B.; Borgert, J.; Buzug, T. Weighted iterative reconstruction for magnetic particle imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storath, M.; Brandt, C.; Hofmann, M.; Knopp, T.; Salamon, J.; Weber, A.; Weinmann, A. Edge preserving and noise reducing reconstruction for Magnetic Particle Imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 36, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwargulski, P.; Möddel, M.; Gdaniec, N.; Knopp, T. Efficient joint image reconstruction of multi-patch data reusing a single system matrix in magnetic particle imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 38, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gdaniec, N.; Boberg, M.; Möddel, M.; Szwargulski, P.; Knopp, T. Suppression of motion artifacts caused by temporally recurring tracer distributions in multi-patch magnetic particle imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 3548–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmer, J.; Weizenecker, J.; Gleich, B.; Borgert, J. Signal encoding in Magnetic Particle Imaging: Properties of the system function. BMC Med. Imaging 2009, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopp, T.; Sattel, T.F.; Biederer, S.; Rahmer, J.; Weizenecker, J.; Gleich, B.; Borgert, J.; Buzug, T.M. Model-Based Reconstruction for Magnetic Particle Imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schomberg, H. Magnetic Particle Imaging: Model and reconstruction. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 14–17 April 2010; pp. 992–995. [Google Scholar]
- Goodwill, P.; Conolly, S.M. The X-Space Formulation of the Magnetic Particle Imaging Process: 1-D Signal, Resolution, Bandwidth, SNR, SAR, and Magnetostimulation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1851–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwill, P.; Conolly, S.M. Multidimensional X-Space Magnetic Particle Imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2011, 30, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grüttner, M.; Knopp, T.; Franke, J.; Heidenreich, M.; Rahmer, J.; Halkola, A.; Kaethner, C.; Borgert, J.; Buzug, T.M. On the Formulation of the Image Reconstruction Problem in Magnetic Particle Imaging. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 58, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringout, G.; Erb, W.; Frikel, J. A new 3D model for magnetic particle imaging using realistic magnetic field topologies for algebraic reconstruction. Inverse Probl. 2020, 36, 124002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- März, T.; Weinmann, A. Model-based reconstruction for Magnetic Particle Imaging in 2D and 3D. Inverse Probl. Imaging 2016, 10, 1087–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- März, T.; Gapyak, V.; Weinmann, A. A two-stage Model-Based Regularized Reconstruction Approach for Magnetic Particle Imaging. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, submitted.
- Bertero, M.; Boccacci, P.; De Mol, C. Introduction to Inverse Problems in Imaging; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch, A. An Introduction to the Mathematical Theory of Inverse Problems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 120. [Google Scholar]
- Knopp, T.; Szwargulski, P.; Griese, F.; Gräser, M. OpenMPIData: An initiative for freely accessible Magnetic Particle Imaging data. Data Brief 2020, 28, 104971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikazumi, S.; Charap, S. Physics of Magnetism; Krieger Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Jiles, D. Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, C.R.; Oman, M.E. Iterative methods for total variation denoising. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 1996, 17, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, C.R.; Oman, M.E. Fast, robust total variation-based reconstruction of noisy, blurred images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1998, 7, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golub, G.H.; Van Loan, C.F. Matrix Computations; JHU Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
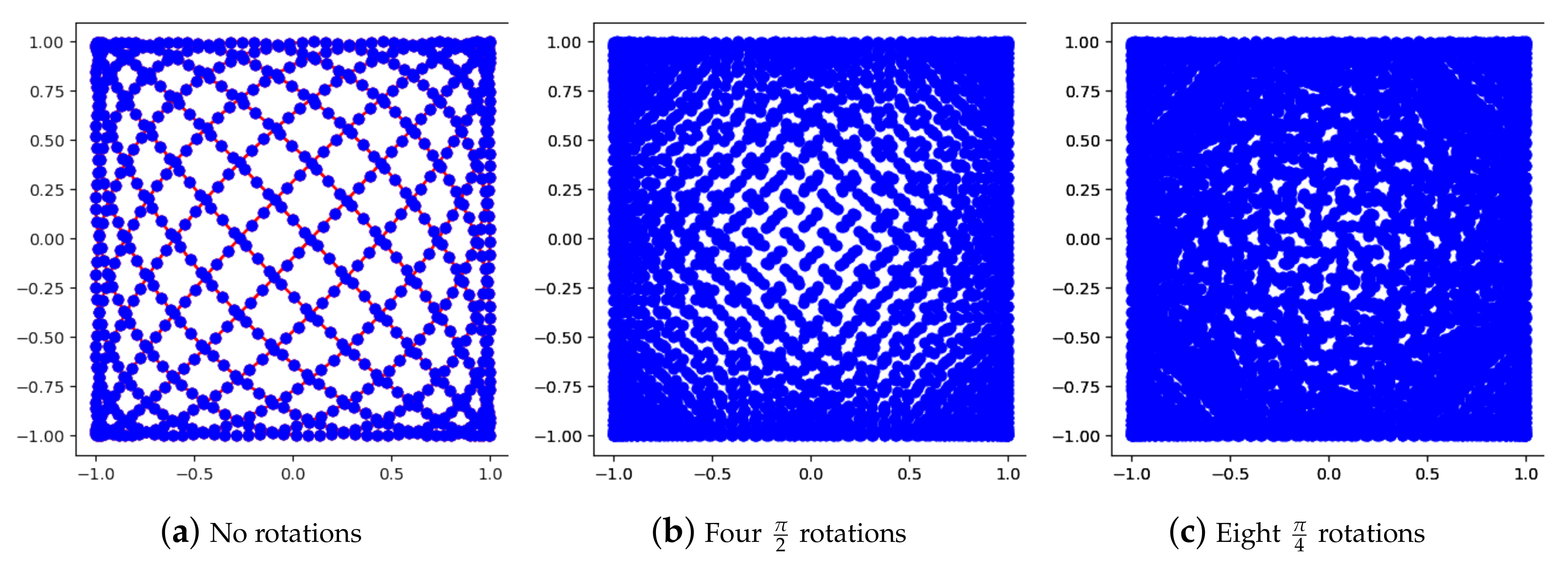
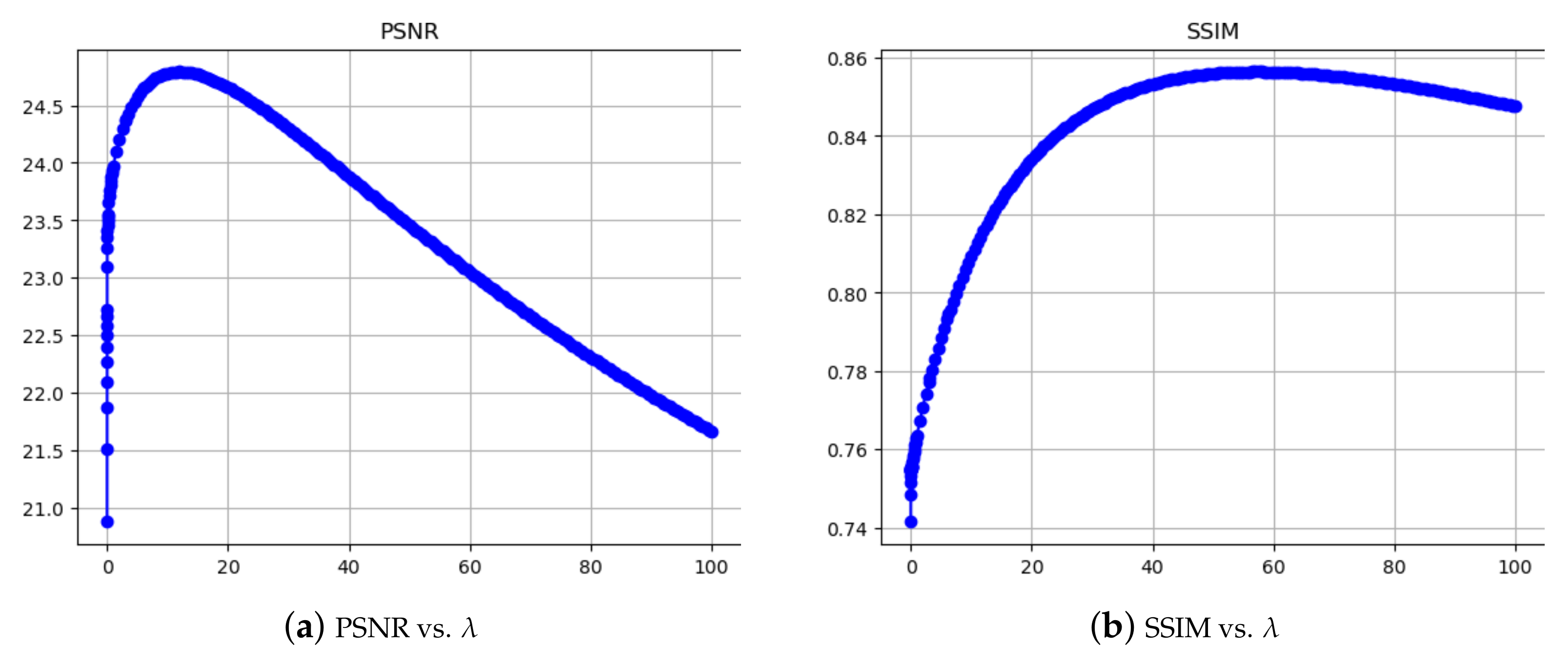
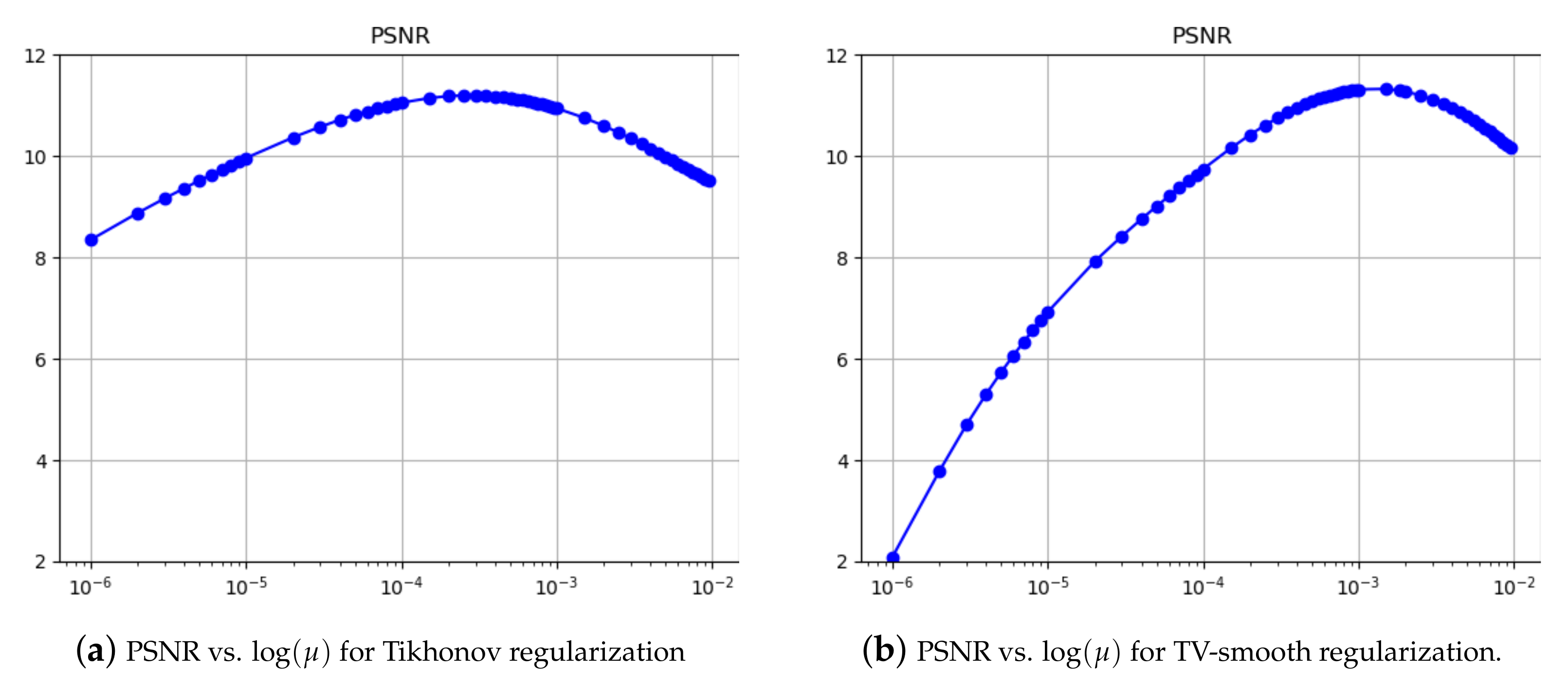
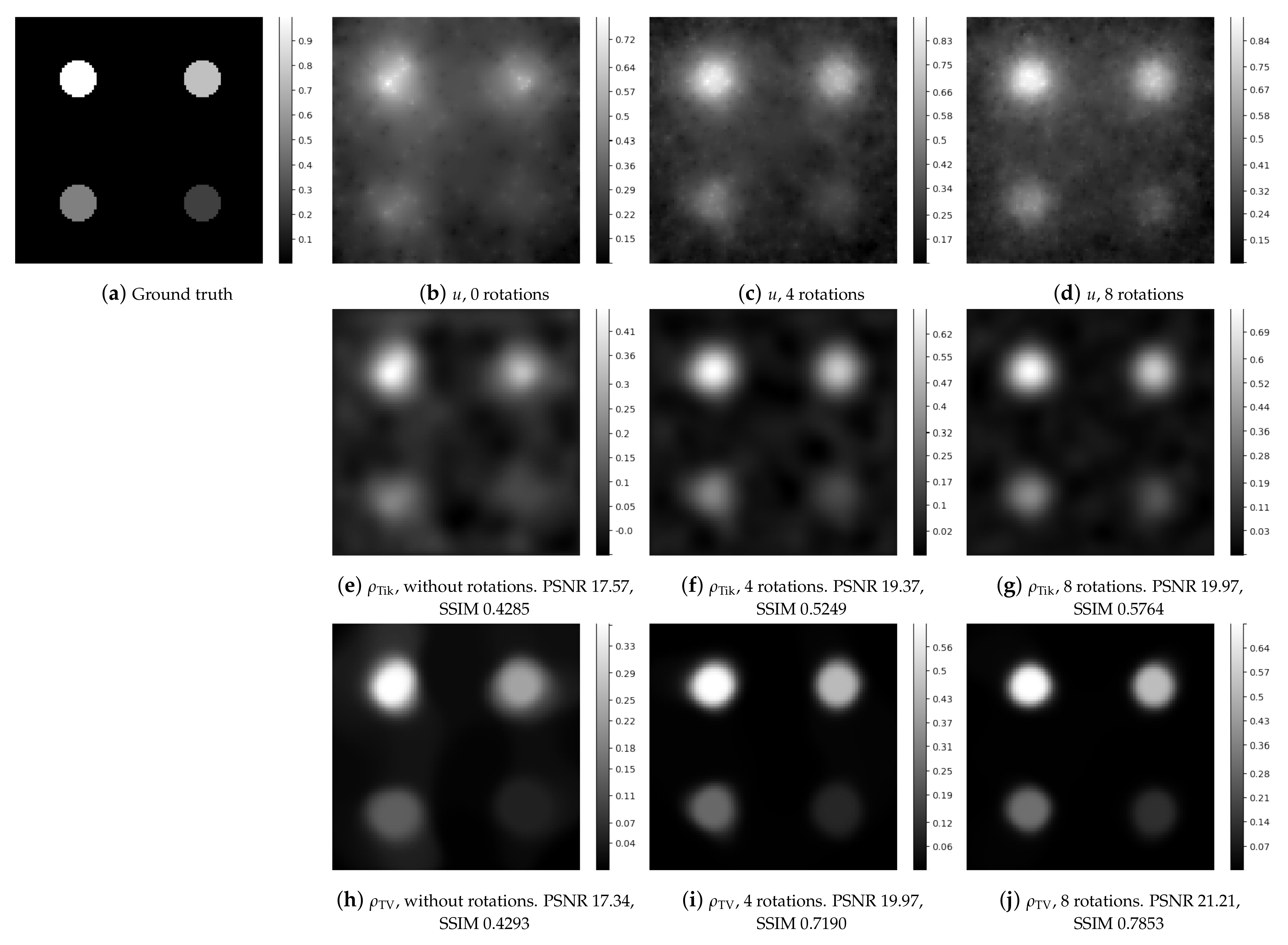

| nRot | Total Concentration of the Ground Truth | Total Concentration, Tikhonov Reconstruction in Stage 2 | Total Concentration, TV Smooth Reconstruction in Stage 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.177 | 0.191236 | 0.181551 |
| 4 | 0.177 | 0.203939 | 0.178848 |
| 8 | 0.177 | 0.202336 | 0.178237 |
| nRot | Tikhonov | TV Smooth | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| Figure 4 | 1 | 17.57 | 0.4285 | 17.34 | 0.4293 |
| 4 | 19.37 | 0.5249 | 19.97 | 0.7190 | |
| 8 | 19.97 | 0.5764 | 21.21 | 0.7853 | |
| Figure 5a | 1 | 12.85 | 0.2238 | 12.84 | 0.2933 |
| 4 | 14.88 | 0.3303 | 15.61 | 0.5964 | |
| 8 | 15.84 | 0.3764 | 17.26 | 0.7256 | |
| Figure 5h | 1 | 14.08 | 0.3358 | 13.75 | 0.4886 |
| 4 | 15.53 | 0.3894 | 15.58 | 0.6891 | |
| 8 | 16.15 | 0.4071 | 16.68 | 0.7931 | |
| Figure 5o | 1 | 15.52 | 0.4314 | 15.82 | 0.5516 |
| 4 | 16.70 | 0.4650 | 16.53 | 0.8134 | |
| 8 | 16.98 | 0.4977 | 16.87 | 0.8179 | |
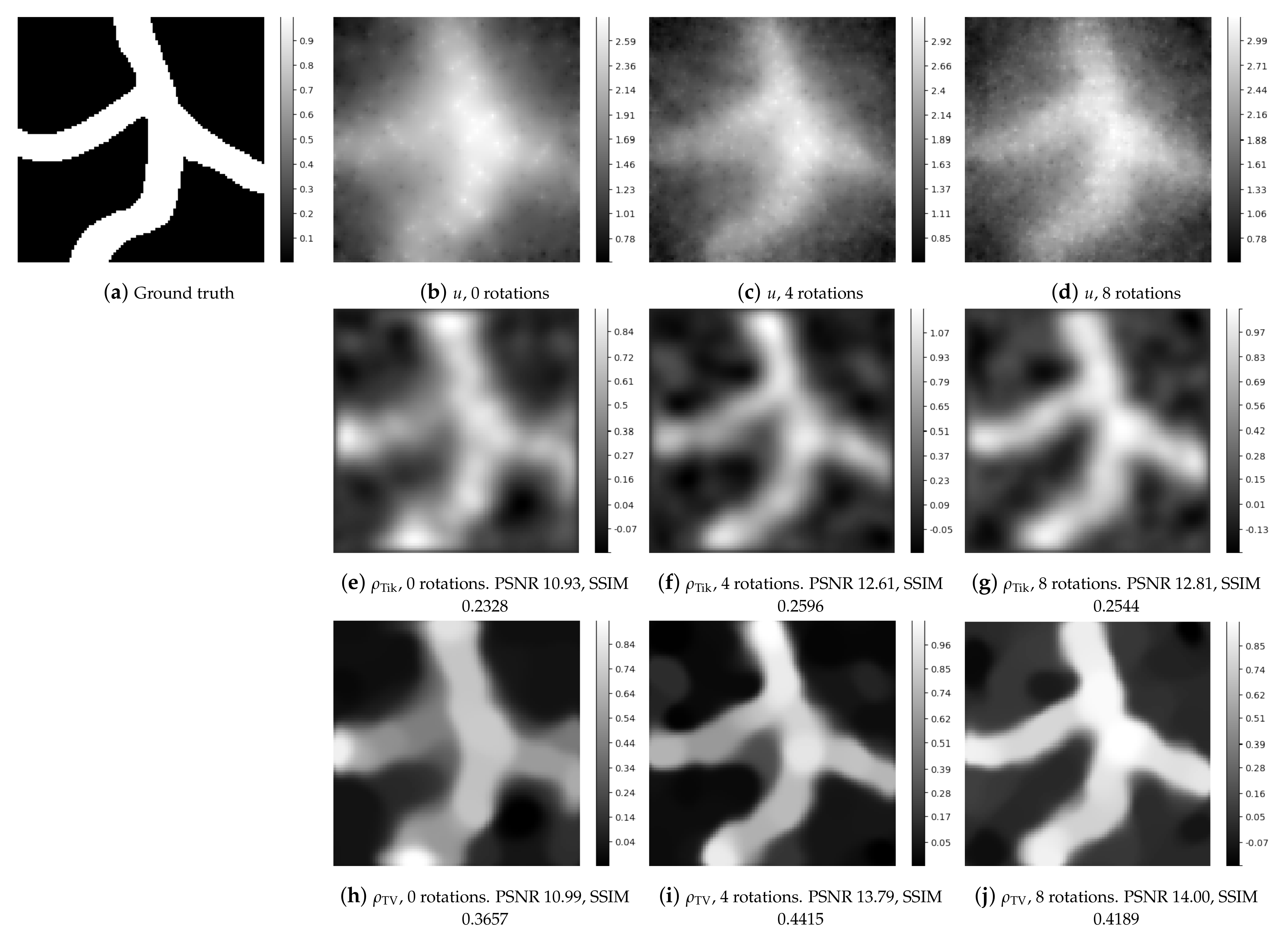
| Figure 6 | 1 | 10.93 | 0.2328 | 10.99 | 0.3657 |
| 4 | 12.61 | 0.2596 | 13.79 | 0.4415 | |
| 8 | 12.81 | 0.2544 | 14.00 | 0.4189 | |
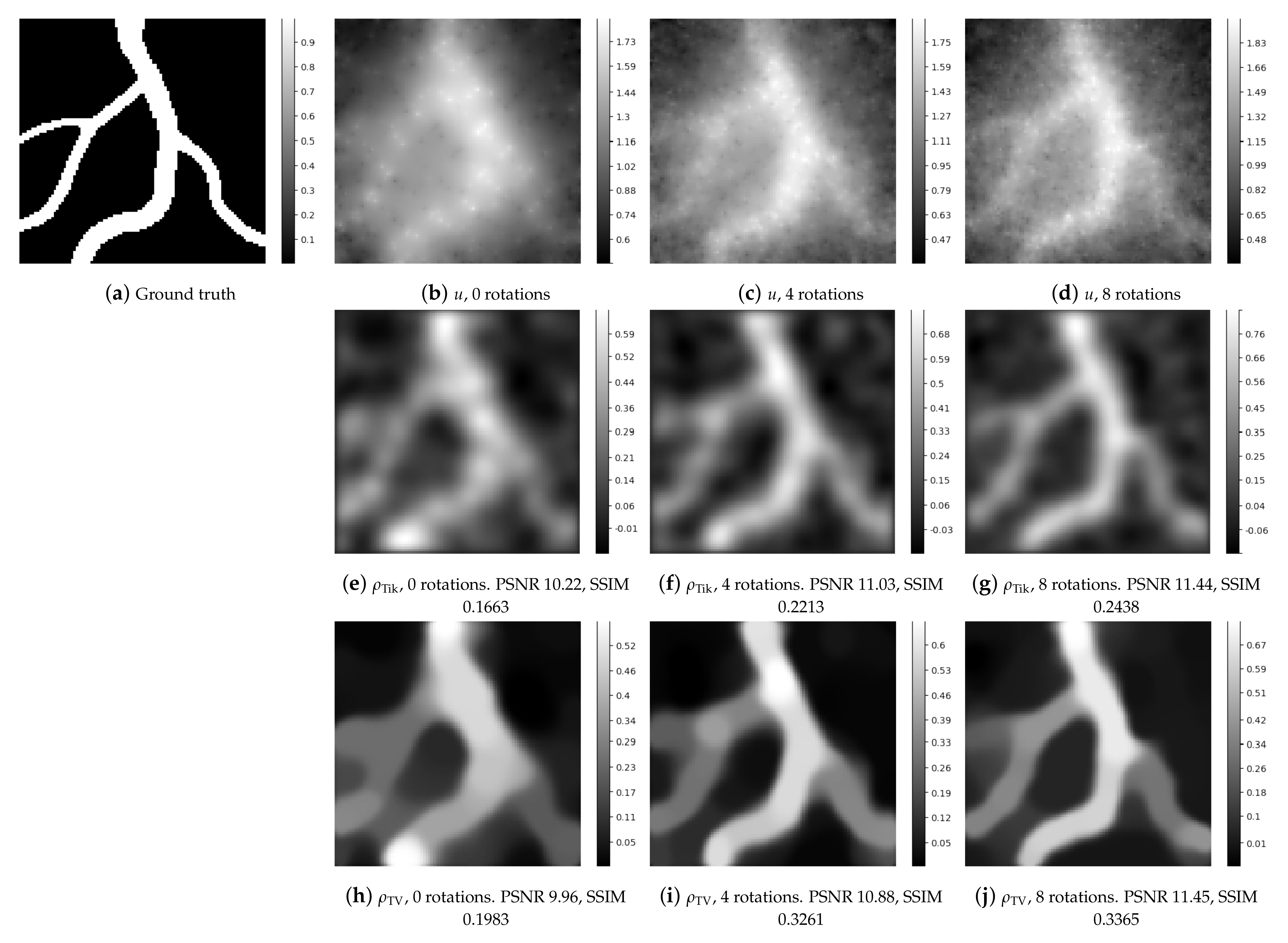
| Figure 7 | 1 | 10.22 | 0.1663 | 9.96 | 0.1983 |
| 4 | 11.03 | 0.2213 | 10.88 | 0.3261 | |
| 8 | 11.44 | 0.2438 | 11.45 | 0.3365 | |
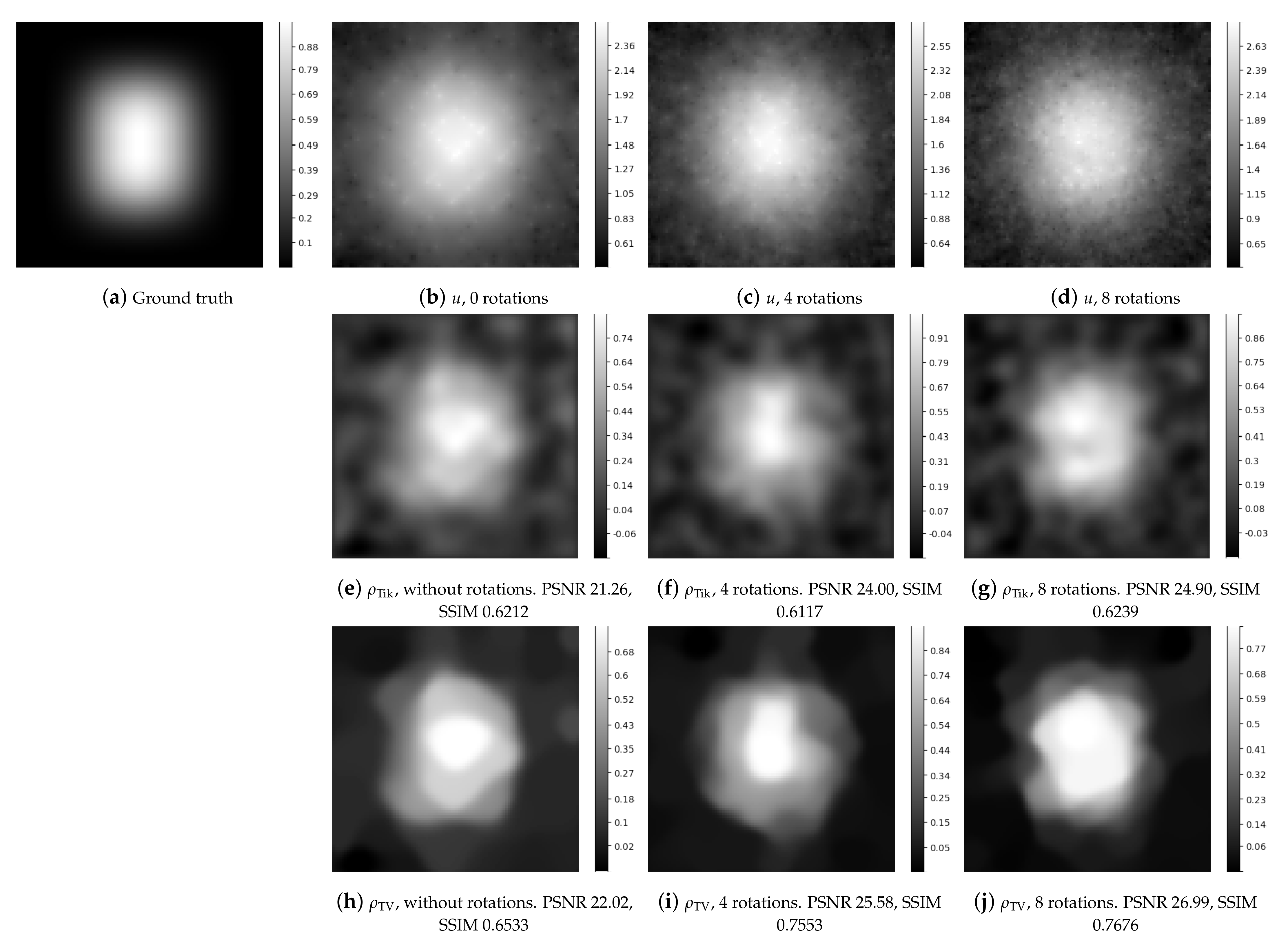
| Figure 8 | 1 | 21.26 | 0.6212 | 22.02 | 0.6533 |
| 4 | 24.00 | 0.6117 | 25.58 | 0.7553 | |
| 8 | 24.90 | 0.6239 | 26.99 | 0.7676 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gapyak, V.; März, T.; Weinmann, A. Quality-Enhancing Techniques for Model-Based Reconstruction in Magnetic Particle Imaging. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3278. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10183278
Gapyak V, März T, Weinmann A. Quality-Enhancing Techniques for Model-Based Reconstruction in Magnetic Particle Imaging. Mathematics. 2022; 10(18):3278. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10183278
Chicago/Turabian StyleGapyak, Vladyslav, Thomas März, and Andreas Weinmann. 2022. "Quality-Enhancing Techniques for Model-Based Reconstruction in Magnetic Particle Imaging" Mathematics 10, no. 18: 3278. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10183278
APA StyleGapyak, V., März, T., & Weinmann, A. (2022). Quality-Enhancing Techniques for Model-Based Reconstruction in Magnetic Particle Imaging. Mathematics, 10(18), 3278. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10183278







