Dynamic Behavior of an Interactive Mosquito Model under Stochastic Interference
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Development
3. The Solution of Stochastic System
3.1. The Global Unique Positive Solution of System
3.2. Stochastic Ultimate Boundedness
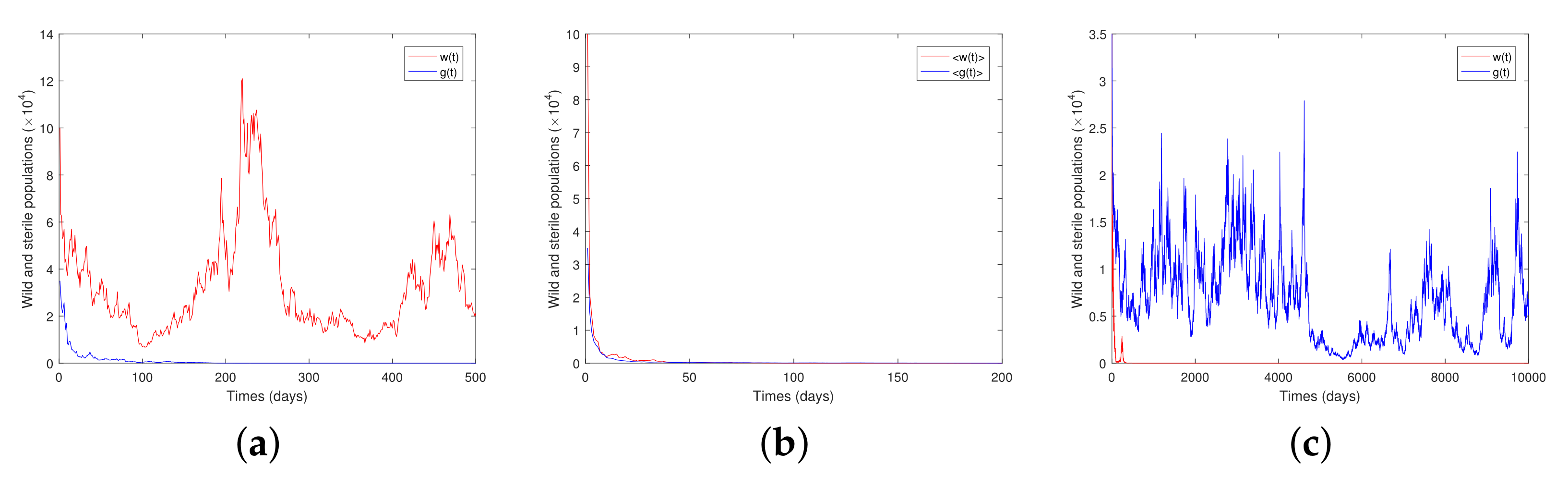
4. Persistence and Extinction
4.1. Wild Mosquitoes
4.2. Sterile Mosquitoes
5. Discussion
- (i)
- If then will go to extinction.
- (ii)
- If then will be stochastically non-persistent.
- (iii)
- If and then will be stochastically permanent.
- (iv)
- If then will go to extinction.
- (v)
- If then will be stochastically non-persistent.
- (vi)
- If and then will be stochastically permanent.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SIT | Sterile insect techniques |
| MBDs | Mosquito-borne diseases |
References
- Caraballo, H.; King, K. Emergency department management of mosquito-borne illness: Malaria, dengue, and west nile virus. Emerg. Med. Pract. 2014, 16, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bian, G.; Joshi, D.; Dong, Y.; Lu, P.; Zhou, G.; Pan, X.; Xu, Y.; Dimopoulos, G.; Xi, Z. Wolbachia invades anopheles stephensi populations and induces refractoriness to plasmodium infection. Science 2013, 340, 748–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutra, H.; Rocha, M.; Dias, F.; Mansur, S.B.; Caragata, E.P.; Moreira, L.A. Wolbachia blocks currently circulating Zika virus isolates in brazilian Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Epstein, P.R.; Diaz, H.F.; Elias, S.; Grabherr, G.; Graham, N.E.; Martens, W.J.; MosIey-Thompson, E.; Susskind, J. Biological and physical signs of climate change: Focus on mosquito-borne diseases. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1988, 79, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tolle, M.A. Mosquito-borne diseases. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2009, 39, 97–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chye, J.K.; Lim, C.T.; Ng, K.B.; Lim, J.M.; George, R.; Lam, S.K. Vertical transmission of dengue. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 25, 1374–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berg, H.V.D. Global status of DDT and its alternatives for use in vector control to prevent disease. Ciência Saúde Coletiva 2009, 117, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar]
- Lambrechts, L.; Ferguson, N.M.; Harris, E.; Holmes, E.C.; McGraw, E.A.; O’Neill, S.L.; Ooi, E.E.; Ritchie, S.A.; Ryan, P.A.; Scott, T.W.; et al. Assessing the epidemiological effect of Wolbachia for dengue control. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 15, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okumu, F.O.; Moore, S.J. Combining indoor residual spraying and insecticide-treated nets for malaria control in Africa: A review of possible outcomes and an outline of suggestions for the future. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J. Differential equations models for interacting wild and transgenic mosquito populations. J. Biol. Dyn. 2008, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barclay, H.J.; Mackuer, M. The sterile insect release method for pest control: A density dependent model. Environ. Entomol. 1980, 9, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, Y.; Tchuenche, J.M. Mathematical studies on the sterile insect technique for the Chikungunya disease and Aedes albopictus. J. Math. Biol. 2012, 65, 809–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyck, V.; Hendrichs, J.P.; Robinson, A.S. Sterile insect technique principles and practice in area-wide integrated pest management. New Agric. 2005, 1, 147–174. [Google Scholar]
- Esteva, L.; Yang, H.M. Mathematical model to assess the control of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes by the sterile insect technique. Math. Biosci. 2005, 198, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, J.; Ghosh, A.; Moreira, L.A.; Wilmmer, E.A.; Jacobs-Lorena, M. Transgenic anopheline mosquitoes impaired in transmission of a malria parasite. Nature 2002, 417, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafikov, M.; Bevilacqua, L.; Wyse, A. Optimal control strategy of malaria vector using genetically modified mosquitoes. J. Theor. Biol. 2009, 258, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thome, R.C.A.; Yang, H.M.; Esteva, L. Optimal control of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes by the sterile insect technique and insecticide. Math. Biosci. 2010, 223, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zheng, B. Modeling Wolbachia infection in mosquito population via discrete dynamical models. J. Differ. Equ. 2019, 25, 1549–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Ai, S.; Li, J. Dynamics of mosquitoes populations with different strategies for releasing sterile mosquitoes. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2014, 74, 1786–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.A.; Montgomery, B.L.; Popovici, J.; Iturbe-Ormaetxe, I.; Johnson, P.H.; Muzzi, F.; Greenfield, M.; Durkan, M.; Leong, Y.S.; Dong, Y.; et al. Successful establishment of Wolbachia in Aedes populations to suppress dengue transmission. Nature 2011, 476, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, P. Oviposition, dispersal, and survival in Aedes aegypti: Implications for the efficacy of control strategies. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2007, 7, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.; Johnson, P.H.; Moreira, L.A.; Iturbe-Ormaetxe, I.; Frentiu, F.D.; McMeniman, C.J.; Leong, Y.S.; Dong, Y.; Axford, J.; Kriesner, P.; et al. The wMel Wolbachia strain blocks dengue and invades caged Aedes aegypti populations. Nature 2011, 476, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, J. Global asymptotic stability in an interactive wild and sterile mosquito model. J. Differ. Equ. 2020, 7, 6193–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Wu, Y.; Liang, X.; Liang, Y.; Pan, X.; Hu, L.; Sun, Q.; et al. Incompatible and sterile insect techniques combined eliminate mosquitoes. Nature 2019, 572, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cai, L.; Li, Y. Stage-structured wild and sterile mosquito population models and their dynamics. J. Biol. Dyn. 2016, 11, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. New revised simple models for interactive wild and sterile mosquito populations and their dynamics. J. Biol. Dyn. 2017, 11, 316–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.; Song, X.; Li, J. Modeling and analysis of impulsive releases of sterile mosquitoes. J. Biol. Dyn. 2017, 11, 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, L.; Ai, S.; Fan, G. Dynamics of delayed mosquitoes populations models with two different strategies of releasing sterile mosquitoes. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2018, 15, 1181–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J. Modelling mosquito population suppression based on delay differential equations. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2018, 78, 3168–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, S.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Zheng, B. Stage-structured models for interactive wild and periodically and impulsively released sterile mosquitoes. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst.-B 2022, 27, 3039–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J. Existence and stability of a unique and exact two periodic orbits for an interactive wild and sterile mosquito model. J. Differ. Equ. 2020, 269, 10395–10415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, J. A delay suppression model with sterile mosquitoes release period equal to wild larvae maturation period. J. Math. Biol. 2022, 84, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Li, J.; Yu, J. Existence and stability of periodic solutions in a mosquito population suppression model with time delay. J. Differ. Equ. 2022, 315, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Li, J.; Yu, J. One discrete dynamical model on Wolbachia infection frequency in mosquito populations. Sci. China Math. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Yu, J.; Li, J. Modeling and analysis of the implementation of the Wolbachia incompatible and sterile insect technique for mosquito population suppression. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2021, 81, 718–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Yu, J. Existence and uniqueness of periodic orbits in a discrete model on Wolbachia infection frequency. Adv. Nonlinear Anal. 2022, 11, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Yu, J.; Xi, Z.; Tang, M. The annual abundance of dengue and Zika vector Aedes albopictus and its stubbornness to suppression. Ecol. Model. 2018, 387, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Liu, X.; Tang, M.; Xi, Z.; Yu, J. Use of age-stage structural models to seek optimal Wolbachia-infected male mosquito releases for mosquito-borne disease control. J. Theor. Biol. 2019, 472, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yao, C.; Lin, P.; Zhou, C. Studies on life table of the natural population of Aedes albopictus. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 1992, 31, 84–93. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Li, C.; Mai, W.; Wu, H.; Cao, H.; Zhang, F. Factors affecting the larval density index of Aedes albopictus in Guangzhou. J. Trop. Med. 2010, 10, 606–608. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Tang, S.; Cheke, R.A. Stage structured mosquito model incorporating effects of precipitation and daily temperature fluctuations. J. Theor. Biol. 2016, 411, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, K.; Yang, W. Long term behaviors of stochastic single-species growth models in a polluted environment. Appl. Math. Model. 2011, 35, 4438–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, K. Lobal stability of a nonlinear stochastic predator–prey system with Beddington–DeAngelis functional response. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2011, 16, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.J.; Zhang, Q.M.; Rong, L.B. A stochastic epidemic model with nonmonotone incidence rate: Sufficient and necessary conditions for near-optimality. Inf. Sci. 2018, 467, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazoua, A.; Wang, W. Analysis of mathematical model of prostate cancer with androgen deprivation therapy. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2019, 66, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higham, D.J. An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations. SIAM Rev. 2001, 43, 525–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, A.J.; Feng, Z.; Hoy, C.W.; James, R.L.; Naranjo, S.E.; Webb, S.E.; Welty, C. Instructional simulation: Sterile insect release method with spatial and random effects. Bull. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1987, 33, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Tan, Y.; Zheng, B. Dynamic Behavior of an Interactive Mosquito Model under Stochastic Interference. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10132284
Liu X, Tan Y, Zheng B. Dynamic Behavior of an Interactive Mosquito Model under Stochastic Interference. Mathematics. 2022; 10(13):2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10132284
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xingtong, Yuanshun Tan, and Bo Zheng. 2022. "Dynamic Behavior of an Interactive Mosquito Model under Stochastic Interference" Mathematics 10, no. 13: 2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10132284
APA StyleLiu, X., Tan, Y., & Zheng, B. (2022). Dynamic Behavior of an Interactive Mosquito Model under Stochastic Interference. Mathematics, 10(13), 2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10132284





