Shifted Brownian Fluctuation Game
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Shifted Brownian Fluctuation Game
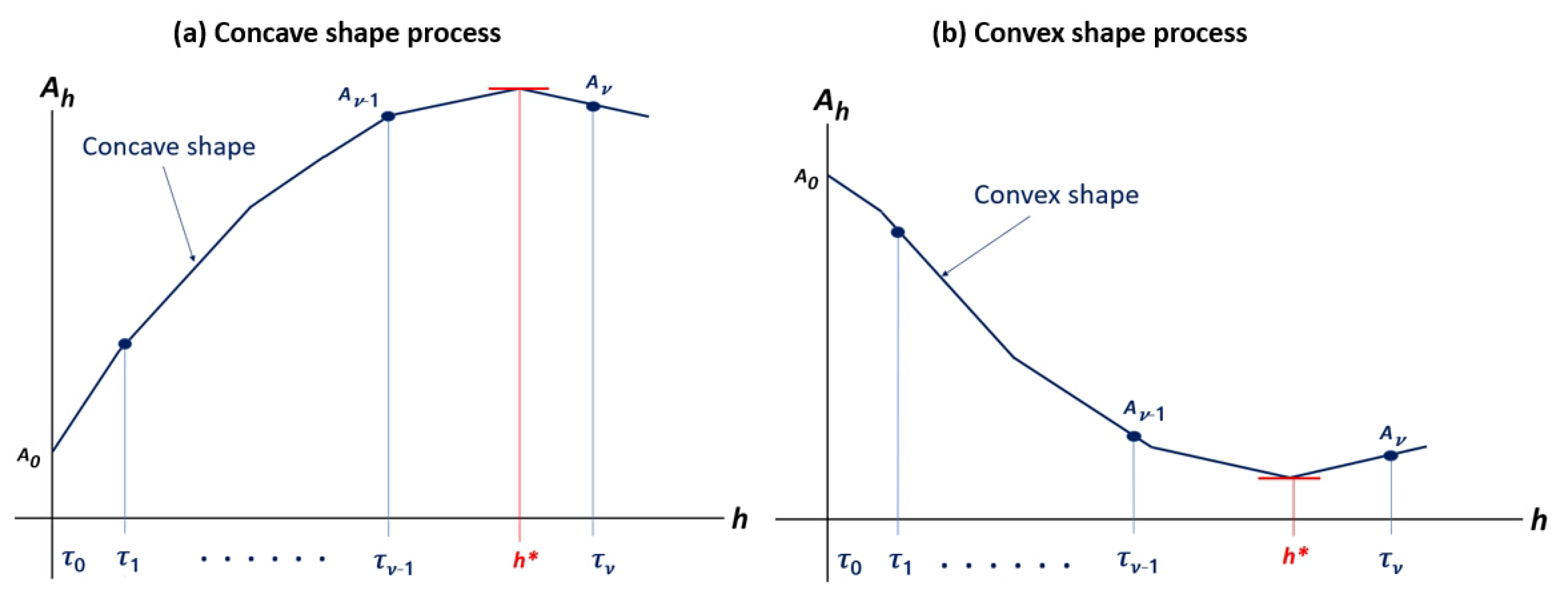
2.1. Shifted Brownian Fluctuation Process
2.2. Shifted Brownian Fluctuation Game
3. Special Case: Memoryless Observation Process
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Britannica. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/science/random-walk (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Dshalalow, J.H.; White, R.T. Current Trends in Random Walks on Random Lattices. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, E.S. On the fluctuations of sums of random variables. Math. Scand. 1953, 1, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, E.S. On the fluctuations of sums of random variables II. Math. Scand. 1954, 2, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takacs, L. On fluctuations of sums of random variables. In Studies in Probability and Ergodic Theory. Adv. Math. 1978, 2, 45–93. [Google Scholar]
- Takacs, L. Random walk on a finite group. Acta Sci. Math. 1983, 45, 395–408. [Google Scholar]
- Takacs, C. Biased random walks on directed trees. Probab. Theory Relat. Fields 1983, 111, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dshalalow, J.H.; Syski, R. Lajos Takacs and his work. J. Appl. Math. Stoch. Anal. 1994, 7, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van den Berg, M. Exit and Return of a Simple Random Walk. Potential Anal. 2005, 23, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, M.; Pucci, A.; Roma, V.; Siena, I. Itemrank: A random-walk based scoring algorithm for recommender engines. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Hyderabad, India, 6–12 January 2007; Volume 7, pp. 2766–2771. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, J.W.; Galla, T. Stochastic fluctuations and quasipattern formation in reaction-diffusion systems with anomalous transport. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 99, 052124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chanu, A.L.; Bhadana, J.; Singh, R.B. Stochastic fluctuations as a driving force to dissipative non-equilibrium states. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2020, 53, 425002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, M.; Pucci, A. Research paper recommender systems: A randomwalk based approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence, Hong Kong, China, 18–22 December 2006; pp. 778–781. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, F.; Liu, H.; Lee, I.; Cao, L. Scientific article recommendation: Exploiting common author relations and historical preferences. IEEE Trans. Big Data 2006, 2, 1010–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Yang, L.T. MVCWalker: Random walk-based most valuable collaborators recommendation exploiting academic factors. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2014, 2, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.; Moore, A. A tractable approach to finding closest truncatedcommute-time neighbors in large graphs. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1206.5259. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Du, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, X. Lazy random walks for superpixel segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meila, M.; Shi, J. A random walks view of spectral segmentation. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Key West, FL, USA, 4–7 January 2001; pp. 177–182. [Google Scholar]
- Gorelick, L.; Galun, M.; Sharon, E.; Basri, R.; Brandt, A. Shape representation and classification using the Poisson equation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 28, 1991–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grady, L. Random walks for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 1768–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grady, L. Multilabel random walker image segmentation using prior models. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 763–770. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, P.; Moore, A.W. Random walks in social networks and their applications: A survey. In Social Network Data Analytics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 43–77. [Google Scholar]
- de Arruda, H.F.; Silva, F.N.; Costa, L.D.F.; Amancio, D.R. Knowledge acquisition: A complex networks approach. Inf. Sci. 2017, 421, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lalle, S. Brownian Motion, Lecture Note. 2012. Available online: https://galton.uchicago.edu/~lalley/Courses/313/ (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Ermogenous, A. Brownian Motion and Its Applications in the Stock Market. In Undergraduate Mathematics Day: Proceedings and Other Materials; University of Dayton: Dayton, OH, USA, 2006; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- Shreve, S. Stochastic Calculus for Finance II Continuous Time Models; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Feynman, R. Lecture Notes on Physics. 1964. Available online: https://www.feynmanlectures.caltech.edu/I_41.html (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Metcalfe, G.; Speetjens, M.F.; Lester, D.R.; Clercx, H.J.H. Beyond Passive: Chaotic Transport in Stirred Fluids. Adv. Appl. Mech. 2012, 45, 109–188. [Google Scholar]
- Gensdarme, F. Methods of Detection and Characterization. Nanoengineering 2015, 55–84. [Google Scholar]
- Alili, L.; Chaumont, L.; Dony, R.A. On A Fluctuation Identity For Random walks and Levy Processes. Bull. Lond. Math. Soc. 2005, 37, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardoukhi, Y.; Jeon, J.H.; Chechkin, A.V.; Metzler, R. Fluctuations of random walks in critical random environments. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 20427–20438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietzonka, P.; Kleinbeck, K.; Seifert, U. Extreme fluctuations of active Brownian motion. New J. Phys. 2016, 18, 052001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dshalalow, J.H. First excess levels of vector processes. J. Appl. Math. Stoch. Anal. 1994, 7, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.-K. A Versatile Stochastic Duel Game. Mathematics 2020, 8, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K. Antagonistic One-To-N Stochastic Duel Game. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschini, G. Nash equilibrium in strictly competitive games: Live play in soccer. Econ. Lett. 2004, 85, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K. Blockchain Governance Game. Comp. Indust. Eng. 2019, 136, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.-K. Strategic Alliance For Blockchain Governance Game. Probab. Eng. Inf. Sci. 2022, 36, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dshalalow, J.H.; Ke, H.-J. Layers of noncooperative games. Nonlinear Anal. 2009, 71, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K. Multi-Layered Blockchain Governance Game. Axioms 2022, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, B. Discussion of Duel. Open Yale Courses. 2008. Available online: http://oyc.yale.edu/economics/econ-159/ (accessed on 1 May 2022).


| Up | Down | |
|---|---|---|
| Hold | ||
| Action |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-K. Shifted Brownian Fluctuation Game. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10101735
Kim S-K. Shifted Brownian Fluctuation Game. Mathematics. 2022; 10(10):1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10101735
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Song-Kyoo (Amang). 2022. "Shifted Brownian Fluctuation Game" Mathematics 10, no. 10: 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10101735
APA StyleKim, S.-K. (2022). Shifted Brownian Fluctuation Game. Mathematics, 10(10), 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10101735






