Top-Down Proteomics and Farm Animal and Aquatic Sciences
Abstract
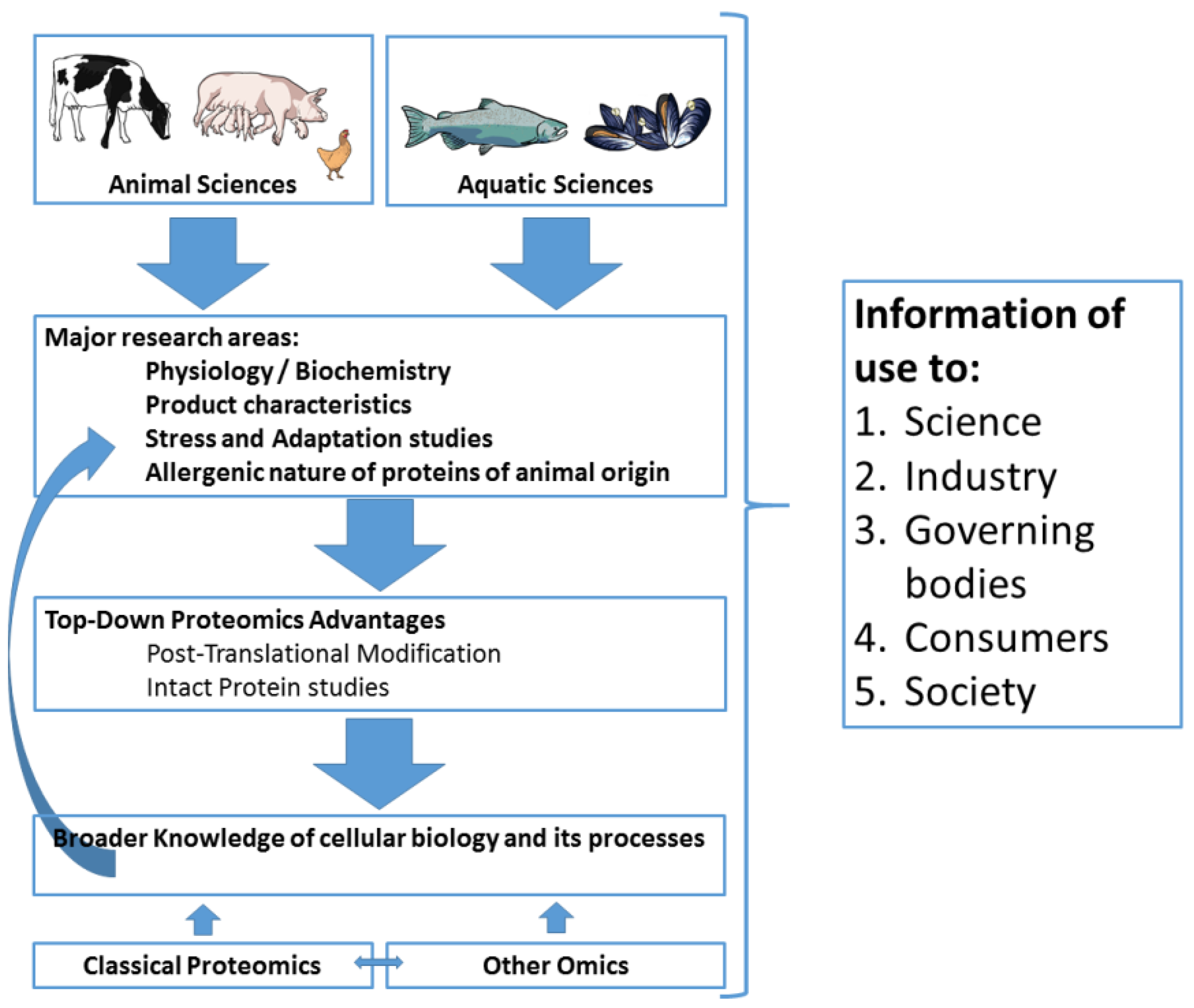
:1. Introduction
2. Basis of Top-Down Proteomics
3. Top-Down Proteomics in Animal Sciences
4. Top-Down Proteomics in Aquatic Sciences
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eckersall, P.D.; Miller, I.; de Almeida, A.M. Proteomics, a new tool for farm animal science. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 4187–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, A.M.; Bassols, A.; Bendixen, E.; Bhide, M.; Ceciliani, F.; Cristobal, S.; Eckersall, P.D.; Hollung, K.; Lisacek, F.; Mazzucchelli, G.; et al. Animal board invited review: Advances in proteomics for animal and food sciences. Animal 2015, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredi, G.; Raboni, S.; Bendixen, E.; de Almeida, A.M.; Mozzarelli, A. “Muscle to meat” molecular events and technological transformations: The proteomics insight. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 4275–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredi, G.; Sentandreu, M.A.; Mozzarelli, A.; Fadda, S.; Hollung, K.; de Almeida, A.M. Muscle and meat: New horizons and applications for proteomics on a farm to fork perspective. J. Proteom. 2013, 88, 58–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Castellano, L.E.; Almeida, A.M.; Castro, N.; Arguello, A. The colostrum proteome, ruminant nutrition and immunity: A review. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. Neth. 2014, 15, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelino, I.; de Almeida, A.M.; Ventosa, M.; Pruneau, L.; Meyer, D.F.; Martinez, D.; Lefrançois, T.; Vachiéry, N.; Coelho, A.V. Tick-borne diseases in cattle: Applications of proteomics to develop new generation vaccines. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 4232–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marco-Ramell, A.; de Almeida, A.M.; Cristobal, S.; Rodrigues, P.; Roncada, P.; Bassols, A. Proteomics and the search for welfare and stress biomarkers in animal production in the one-health context. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 2024–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, P.M.; Silva, T.S.; Dias, J.; Jessen, F. Proteomics in aquaculture: Applications and trends. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 4325–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, A.; Tedesco, S.; Vasconcelos, V.; Cristobal, S. Proteomic research in bivalves. Towards the identification of molecular markers of aquatic pollution. J. Proteom. 2012, 4346–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, R.; Franco, C.; Pires, E.; Ventosa, M.; Palhinhas, R.; Koci, K.; Martinho de Almeida, A.; Varela Coelho, A. Mass spectrometry and animal science: Protein identification strategies and particularities of farm animal species. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 4190–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Bislev, S.L.; Bendixen, E.; Almeida, A.M. The mammary gland in domestic ruminants: A systems biology perspective. J. Proteom. 2013, 94, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Almeida, A.M.; Bendixen, E. Pig proteomics: A review of a species in the crossroad between biomedical and food sciences. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 4296–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassols, A.; Costa, C.; Eckersall, P.D.; Osada, J.; Sabrià, J.; Tibau, J. The pig as an animal model for human pathologies: A proteomics perspective. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2014, 8, 715–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, I.; Rogel-Gaillard, C.; Spina, D.; Fontanesi, L.; de Almeida, A.M. The rabbit as an experimental and production animal: From genomics to proteomics. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2014, 15, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, A.M.; Campos, A.; Francisco, R.; Van Harten, S.; Cardoso, L.A.; Coelho, A.V. Proteomic investigation of the effects of weight loss in the gastrocnemius muscle of wild and NZW rabbits via 2D-electrophoresis and MALDI-TOF MS. Anim. Genet. 2010, 41, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puerto, M.; Campos, A.; Prieto, A.; Cameán, A.; Almeida, A.M.; Coelho, A.V.; Vasconcelos, V. Differential protein expression in two bivalve species; Mytilus galloprovincialis and Corbicula fluminea; exposed to Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii cells. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlizza, E.; Campos, A.; Neagu, A.; Cuoghi, A.; Bellei, E.; Monari, E.; Dondi, F.; Almeida, A.M.; Isani, G. The effect of chronic kidney disease on the urine proteome in the domestic cat (Felis catus). Vet. J. 2015, 204, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Castellano, L.E.; Almeida, A.M.; Renaut, J.; Argüello, A.; Castro, N. A proteomics study of colostrum and milk from the two major small ruminant dairy breeds from the Canary Islands: A bovine milk comparison perspective. J. Dairy Res. 2016, 83, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.B.; Lonergan, S.M.; Grubbs, J.K.; Cruzen, S.M.; Fritchen, A.N.; della Malva, A.; Marino, R.; Huff-Lonergan, E. Effect of low voltage electrical stimulation on protein and quality changes in bovine muscles during postmortem aging. Meat Sci. 2013, 94, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittig, I.; Braun, H.-P.; Schägger, H. Blue native PAGE. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cugno, G.; Parreira, J.R.; Ferlizza, E.; Hernández-Castellano, L.E.; Carneiro, M.; Renaut, J.; Castro, N.; Arguello, A.; Capote, J.; Campos, A.M.; et al. The Goat (Capra hircus) mammary gland mitochondrial proteome: A study on the effect of weight loss using blue-native page and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, A.M.; Plowman, J.E.; Harland, D.P.; Thomas, A.; Kilminster, T.; Scanlon, T.; Milton, J.; Greeff, J.; Oldham, C.; Clerens, S. Influence of feed restriction on the wool proteome: A combined iTRAQ and fiber structural study. J. Proteom. 2014, 103, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Castellano, L.E.; Argüello, A.; Almeida, A.M.; Castro, N.; Bendixen, E. Colostrum protein uptake in neonatal lambs examined by descriptive and quantitative liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Castellano, L.E.; Ferreira, A.M.; Nanni, P.; Grossmann, J.; Argüello, A.; Capote, J.; Cai, G.; Lippolis, J.; Castro, N.; de Almeida, A.M. The goat (Capra hircus) mammary gland secretory tissue proteome as influenced by weight loss: A study using label free proteomics. J. Proteom. 2016, 145, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, A.; Danielsson, G.; Farinha, A.P.; Kuruvilla, J.; Warholm, P.; Cristobal, S. Shotgun proteomics to unravel marine mussel (Mytilus edulis) response to long-term exposure to low salinity and propranolol in a Baltic Sea microcosm. J. Proteom. 2016, 137, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskay, Ü.A.; Lobas, A.A.; Srzentić, K.; Gorshkov, M.V.; Tsybin, Y.O. Proteome digestion specificity analysis for rational design of extended bottom-up and middle-down proteomics experiments. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 5558–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siuti, N.; Kelleher, N.L. Decoding protein modifications using top-down mass spectrometry. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanov, B.; Smith, R.D. Proteomics by fticr mass spectrometry: Top down and bottom up. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2005, 24, 168–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macek, B.; Waanders, L.F.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. Top-down Protein Sequencing and MS3 on a Hybrid Linear Quadrupole Ion Trap-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2006, 5, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubarev, R.A.; Horn, D.M.; Fridriksson, E.K.; Kelleher, N.L.; Kruger, N.A.; Lewis, M.A.; Carpenter, B.K.; McLafferty, F.W. Electron capture dissociation for structural characterization of multiply charged protein cations. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syka, J.E.P.; Coon, J.J.; Schroeder, M.J.; Shabanowitz, J.; Hunt, D.F. Peptide and protein sequence analysis by electron transfer dissociation mass spectrometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9528–9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ge, Y. Comprehensive analysis of protein modifications by top-down mass spectrometry. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2011, 4, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelleher, R.L.; Zubarev, R.A.; Bush, K.; Furie, B.; Furie, B.C.; McLafferty, F.W.; Walsh, C.T. Localization of labile posttranslational modifications by electron capture dissociation: The case of γ-carboxyglutamic acid. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 4250–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G.K.; Kim, Y.B.; Forbes, A.J.; Meng, F.; McCarthy, R.; Kelleher, N.L. Web and database software for identification of intact proteins using “top down” mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 4081–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, J.C.; Zamdborg, L.; Ahlf, D.R.; Lee, J.E.; Catherman, A.D.; Durbin, K.R.; Tipton, J.D.; Vellaichamy, A.; Kellie, J.F.; Li, M.; et al. Mapping intact protein isoforms in discovery mode using top-down proteomics. Nature 2011, 480, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Guner, H.; Gregorich, Z.R.; Chen, A.J.; Ayaz-Guner, S.; Peng, Y.; Valeja, S.G.; Liu, X.; Ge, Y. MASH Suite Pro: A Comprehensive Software Tool for Top-Down Proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2016, 15, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durbin, K.R.; Fellers, R.T.; Ntai, I.; Kelleher, N.L.; Compton, P.D. Autopilot: An online data acquisition control system for the enhanced high-throughput characterization of intact proteins. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Simpson, D.C.; Tolić, N.; Jaitly, N.; Mayampurath, A.M.; Smith, R.D.; Pasa-Tolić, L. Proteomic profiling of intact proteins using WAX-RPLC 2-D separations and FTICR mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Johnston, M.V. Protein profiling by capillary isoelectric focusing, reversed-phase liquid chromatography, and mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, B.E.; Yan, F.; Lubman, D.M.; Miller, F.R. Chromatofocusing nonporous reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry of proteins from human breast cancer whole cell lysates: A novel two-dimensional liquid chromatography/mass spectrome. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2001, 15, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durbin, K.R.; Fornelli, L.; Fellers, R.T.; Doubleday, P.F.; Narita, M.; Kelleher, N.L. Quantitation and Identification of Thousands of Human Proteoforms below 30 kDa. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, B.M.; Coorssen, J.R.; Martins-de-Souza, D. 2DE: The Phoenix of Proteomics. J. Proteom. 2014, 104, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzatto, K.R.; Kim, K.; Ntai, I.; Paludo, G.P.; Camargo De Lima, J.; Thomas, P.M.; Kelleher, N.L.; Ferreira, H.B. Top down proteomics reveals mature proteoforms expressed in subcellular fractions of the Echinococcus granulosus preadult stage. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 4805–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregorich, Z.R.; Ge, Y. Top-down proteomics in health and disease: Challenges and opportunities. Proteom. 2014, 14, 1195–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesavento, J.J.; Mizzen, C.A.; Kelleher, N.L. Quantitative analysis of modified proteins and their positional isomers by tandem mass spectrometry: Human histone H4. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4271–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhu, G.; Dovichi, N.J. Coupling capillary zone electrophoresis to a Q Exactive HF mass spectrometer for top-down proteomics: 580 Proteoform identifications from yeast. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 3679–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Gregorich, Z.R.; Valeja, S.G.; Zhang, H.; Cai, W.; Chen, Y.C.; Guner, H.; Chen, A.J.; Schwahn, D.J.; Hacker, T.A.; et al. Top-down proteomics reveals concerted reductions in myofilament and Z-disc protein phosphorylation after acute myocardial infarction. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 2752–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Peng, Y.; Lin, Z.; Chen, Y.C.; Wei, L.; Hacker, T.A.; Larsson, L.; Ge, Y. Comprehensive analysis of tropomyosin isoforms in skeletal muscles by top-down proteomics. J. Muscle Res. Cell. Motil. 2016, 37, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, M.T.B.; Shah, D.J.; Thulin, C.D.; Graves, S.W. Tissue proteomics of the low-molecular weight proteome using an integrated cLC-ESI-QTOFMS approach. Proteomics 2013, 13, 1400–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labas, V.; Spina, L.; Belleannee, C.; Teixeira-Gomes, A.P.; Gargaros, A.; Dacheux, F.; Dacheux, J.L. Analysis of epididymal sperm maturation by maldi profiling and top-down mass spectrometry. J. Proteom. 2015, 113, 226–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler, L.; Labas, V.; Thélie, A.; Grasseau, I.; Teixeira-Gomes, A.P.; Blesbois, E. Intact cell MALDI-TOF MS on sperm: A molecular test for male fertility diagnosis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2016, 15, 1998–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, I.R.; Nagler, J.J.; Swanson, P.; Wunschel, D.; Skillman, A.D.; Burnett, V.; Smith, D.; Barry, R. Toxicokinetic, toxicodynamic, and toxicoproteomic aspects of short-term exposure to trenbolone in female fish. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 136, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsen, O.A.; Bjørneklett, S.; Berg, K.; Brattås, M.; Bohne-Kjersem, A.; Grøsvik, B.E.; Goksøyr, A. Integrative Environmental Genomics of Cod (Gadus morhua): The Proteomics Approach. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2011, 74, 494–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampel, M.; Alonso, E.; Aparicio, I.; Santos, J.L.; Leaver, M. Hepatic proteome analysis of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) after exposure to environmental concentrations of human pharmaceuticals. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talakhun, W.; Phaonakrop, N.; Roytrakul, S.; Klinbunga, S.; Menasveta, P.; Khamnamtong, B. Proteomic analysis of ovarian proteins and characterization of thymosin-β and RAC-GTPase activating protein 1 of the giant tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D Genom. Proteom. 2014, 11, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinbunga, S.; Petkorn, S.; Kittisenachai, S.; Phaonakrop, N.; Roytrakul, S.; Khamnamtong, B.; Menasveta, P. Identification of reproduction-related proteins and characterization of proteasome alpha 3 and proteasome beta 6 cDNAs in testes of the giant tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 355, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie, B.; Zanella-Cléon, I.; Guichard, N.; Becchi, M.; Marin, F. Novel Proteins from the Calcifying Shell Matrix of the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provan, F.; Jensen, L.B.; Uleberg, K.E.; Larssen, E.; Rajalahti, T.; Mullins, J.; Obach, A. Proteomic analysis of epidermal mucus from sea lice-infected Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. J. Fish. Dis. 2013, 36, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braceland, M.; Bickerdike, R.; Tinsley, J.; Cockerill, D.; Mcloughlin, M.F.; Graham, D.A.; Burchmore, R.J.; Weir, W.; Wallace, C.; Eckersall, P.D. The serum proteome of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar, during pancreas disease (PD) following infection with salmonid alphavirus subtype 3 (SAV3). J. Proteom. 2013, 94, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, M.; Zhao, J.; Li, T.; Tafalla, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Gong, X.; Shen, Z.; Li, A. Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of splenic immune mechanisms of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) infected by Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida. J. Proteom. 2015, 122, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, A.; Apraiz, I.; Fonseca, R.R.; Cristobal, S. Shotgun analysis of the marine mussel Mytilus edulis haemolymph proteome and mapping the innate immunity elements. Proteomics 2015, 15, 4021–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrera, M.; Cañas, B.; Gallardo, J.M. Proteomics for the assessment of quality and safety of fishery products. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, S.; Mullen, W.; Cristobal, S. High-throughput proteomics: A new tool for quality and safety in fishery products. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2014, 15, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J.; Grøsvik, B.E.; Rodríguez-Ariza, A.; Goksøyr, A.; López-Barea, J. Changes in protein expression profiles in bivalve molluscs (Chamaelea gallina) exposed to four model environmental pollutants. Proteomics 2003, 3, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chora, S.; Starita-Geribaldi, M.; Guigonis, J.M.; Samson, M.; Roméo, M.; Bebianno, M.J. Effect of cadmium in the clam Ruditapes decussatus assessed by proteomic analysis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 94, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.C.; Wang, H.C.; Leu, J.H.; Kou, G.H.; Wang, A.H.J.; Lo, C.F. Protein expression profiling of the shrimp cellular response to white spot syndrome virus infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2007, 31, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, A.; Fuentes, J.; Comesaña, P.; Casas, S.M.; Villalba, A. A proteomic approach envisaged to analyse the bases of oyster tolerance/resistance to bonamiosis. Aquaculture 2009, 295, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.J.; Lin, Y.F.; Chiang, B.L.; Chow, L.P. Proteomics and Immunological Analysis of a Novel Shrimp Allergen, Pen m 2. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, R.; Satoh, R.; Nakajima, Y.; Kawasaki, N.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sawada, J.; Nagoya, H.; Teshima, R. Comparative study of GH-transgenic and non-transgenic amago salmon (Oncorhynchus masou ishikawae) allergenicity and proteomic analysis of amago salmon allergens. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 55, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñeiro, C.; Vázquez, J.; Marina, A.I.; Barros-Velézquez, J.; Gallardo, J.M. Characterization and partial sequencing of species-specific sarcoplasmic polypeptides from commercial hake species by mass spectrometry following two-dimensional electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2001, 22, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, M.; Cañas, B.; Piñeiro, C.; Vázquez, J.; Gallardo, J.M. Identification of commercial hake and grenadier species by proteomic analysis of the parvalbumin fraction. Proteomics 2006, 6, 5278–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrini, A.; Tepedino, V.; Borromeo, V.; Secchi, C. Identification of freshwater fish commercially labelled “perch” by isoelectric focusing and two-dimensional electrophoresis. Food Chem. 2006, 96, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.C.; Campos, A.; Osório, H.; da Fonseca, R.; Vasconcelos, V. Proteomic profiling of cytosolic glutathione transferases from three bivalve species: Corbicula fluminea, Mytilus galloprovincialis and Anodonta cygnea. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 1887–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, C.C.; Guzmán-Guillén, R.; Martins, J.C.; Osório, H.; Vasconcelos, V.; da Fonseca, R.R.; Campos, A. Proteomic profiling of gill GSTs in Mytilus galloprovincialis from the North of Portugal and Galicia evidences variations at protein isoform level with a possible relation with water quality. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 110, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, M.; Reis, B.; Azevedo, J.; Campos, A.; Osório, H.; Vasconcelos, V.; Martins, J.C. Glutathione transferases responses induced by microcystin-LR in the gills and hepatopancreas of the clam Venerupis philippinarum. Toxins 2015, 7, 2096–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, P.T.Y.; Park, T.J.; Wang, Y.; Che, C.M.; Leung, K.M.Y. Isoform-specific responses of metallothioneins in a marine pollution biomonitor, the green-lipped mussel Perna viridis, towards different stress stimulations. Proteomics 2014, 14, 1796–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, T.; Koyanagi, R.; Gyoja, F.; Kanda, M.; Hisata, K.; Fujie, M.; Goto, H.; Yamasaki, S.; Nagai, K.; Morino, Y.; et al. Bivalve-specific gene expansion in the pearl oyster genome: Implications of adaptation to a sessile lifestyle. Zool. Lett. 2016, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, H.; Endo, H.; Hashimoto, N.; Limura, K.; Isowa, Y.; Kinoshita, S.; Kotaki, T.; Masaoka, T.; Miki, T.; Nakayama, S.; et al. The diversity of shell matrix proteins: Genome-wide investigation of the pearl oyster, Pinctada fucata. Zool. Sci. 2013, 30, 801–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lelong, C.; Jouaux, A. Immune and stress responses in oysters with insights on adaptation. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 46, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Shiomi, K. Fish allergy in patients with parvalbumin-specific immunoglobulin E depends on parvalbumin content rather than molecular differences in the protein among fish species. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 2018–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, S.D.; Rahman, A.M.A.; Komoda, T.; Lopata, A.L. Impact of heat processing on the detection of the major shellfish allergen tropomyosin in crustaceans and molluscs using specific monoclonal antibodies. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 4031–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrera, M.; Cañas, B.; Vázquez, J.; Gallardo, J.M. Extensive de Novo sequencing of new parvalbumin isoforms using a novel combination of bottom-up proteomics, accurate molecular mass measurement by FTICR-MS, and selected MS/MS ion monitoring. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 4393–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piovesana, S.; Capriotti, A.L.; Caruso, G.; Cavaliere, C.; La Barbera, G.; Zenezini Chiozzi, R.; Laganà, A. Labeling and label free shotgun proteomics approaches to characterize muscle tissue from farmed and wild gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1428, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, H.; Kobayashi, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Shiomi, K.; Hamada-Sato, N. Reduction in IgE reactivity of Pacific mackerel parvalbumin by heat treatment. Food Chem. 2016, 206, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasekan, A.O.; Nayak, B. Effects of buffer additives and thermal processing methods on the solubility of shrimp (Penaeus monodon) proteins and the immunoreactivity of its major allergen. Food Chem. 2016, 200, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campos, A.M.O.; De Almeida, A.M. Top-Down Proteomics and Farm Animal and Aquatic Sciences. Proteomes 2016, 4, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes4040038
Campos AMO, De Almeida AM. Top-Down Proteomics and Farm Animal and Aquatic Sciences. Proteomes. 2016; 4(4):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes4040038
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampos, Alexandre M.O., and André M. De Almeida. 2016. "Top-Down Proteomics and Farm Animal and Aquatic Sciences" Proteomes 4, no. 4: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes4040038
APA StyleCampos, A. M. O., & De Almeida, A. M. (2016). Top-Down Proteomics and Farm Animal and Aquatic Sciences. Proteomes, 4(4), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes4040038





