High-Throughput Proteomic Approaches to the Elucidation of Potential Biomarkers of Chronic Allograft Injury (CAI)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Immunosuppressant—Induced Nephrotoxicity
3. Chronic Allograft Injury (CAI)
4. Proteomics
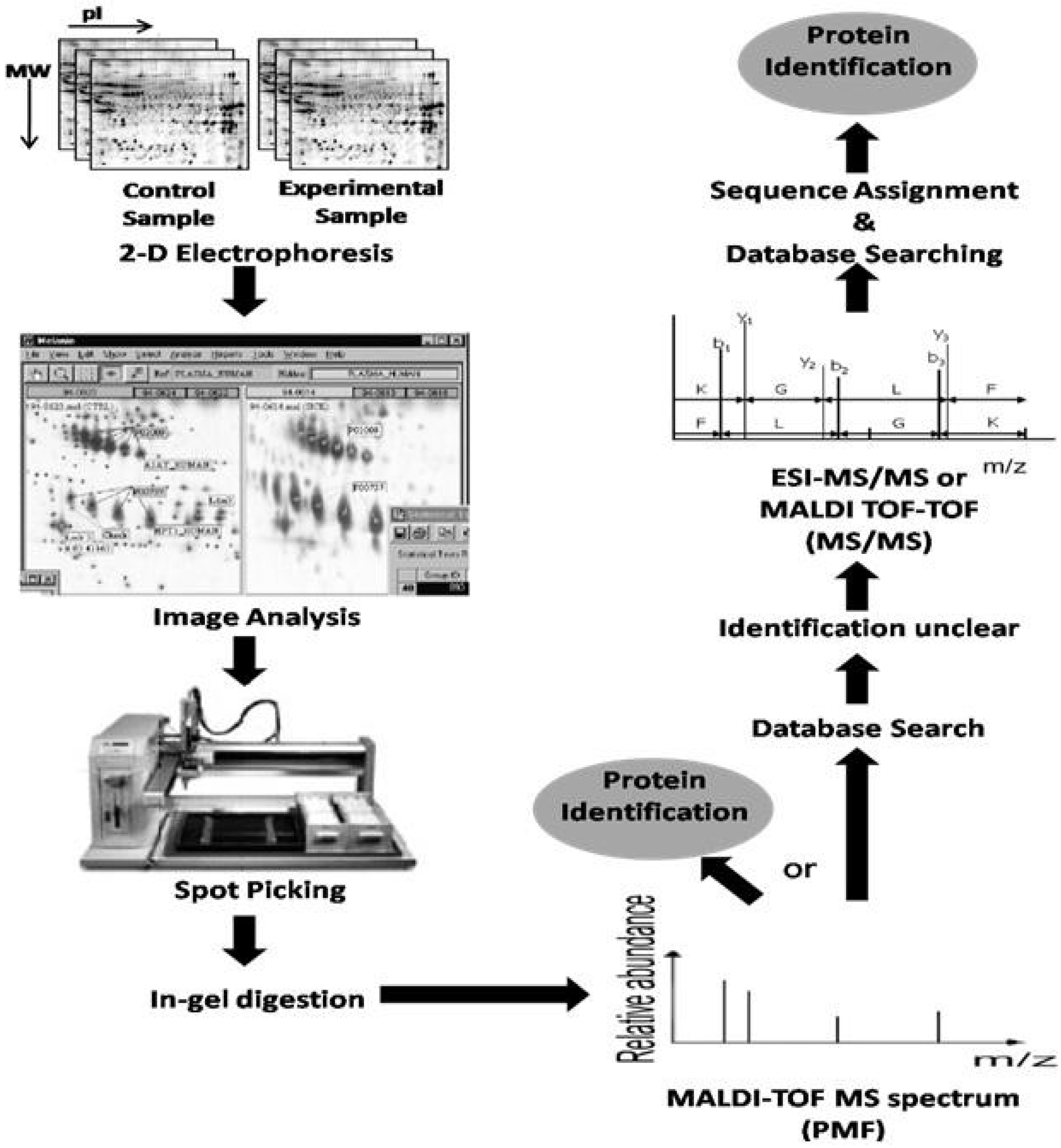
5. Clinical Proteomic Studies
5.1. Clinical Proteomics Using Tissue Biopsies for Biomarker Discovery
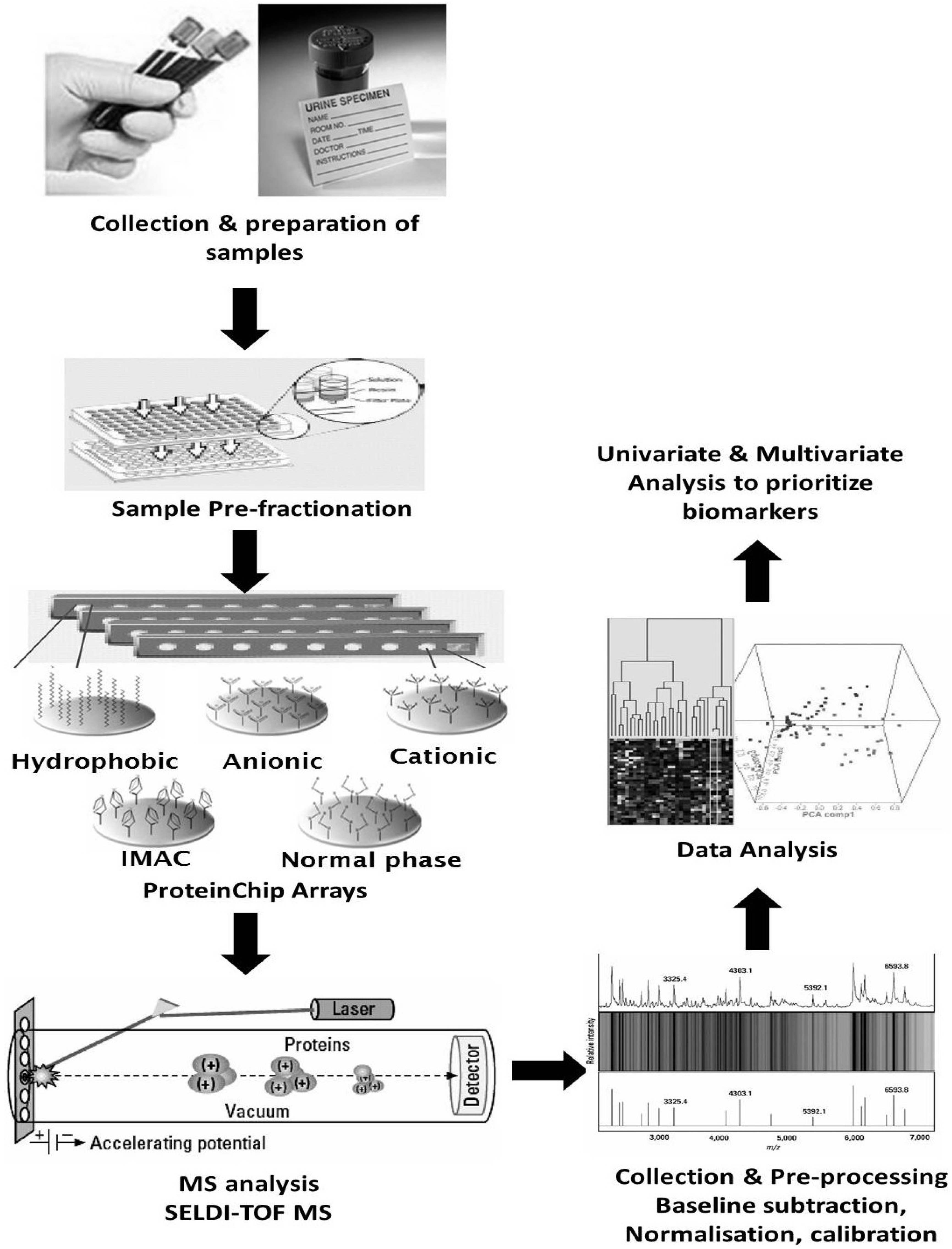
5.2. Clinical Proteomics Using Blood for Biomarker Discovery
5.3. Clinical Proteomics Using Urine for Biomarker Discovery
6. In Vivo Proteomic Studies

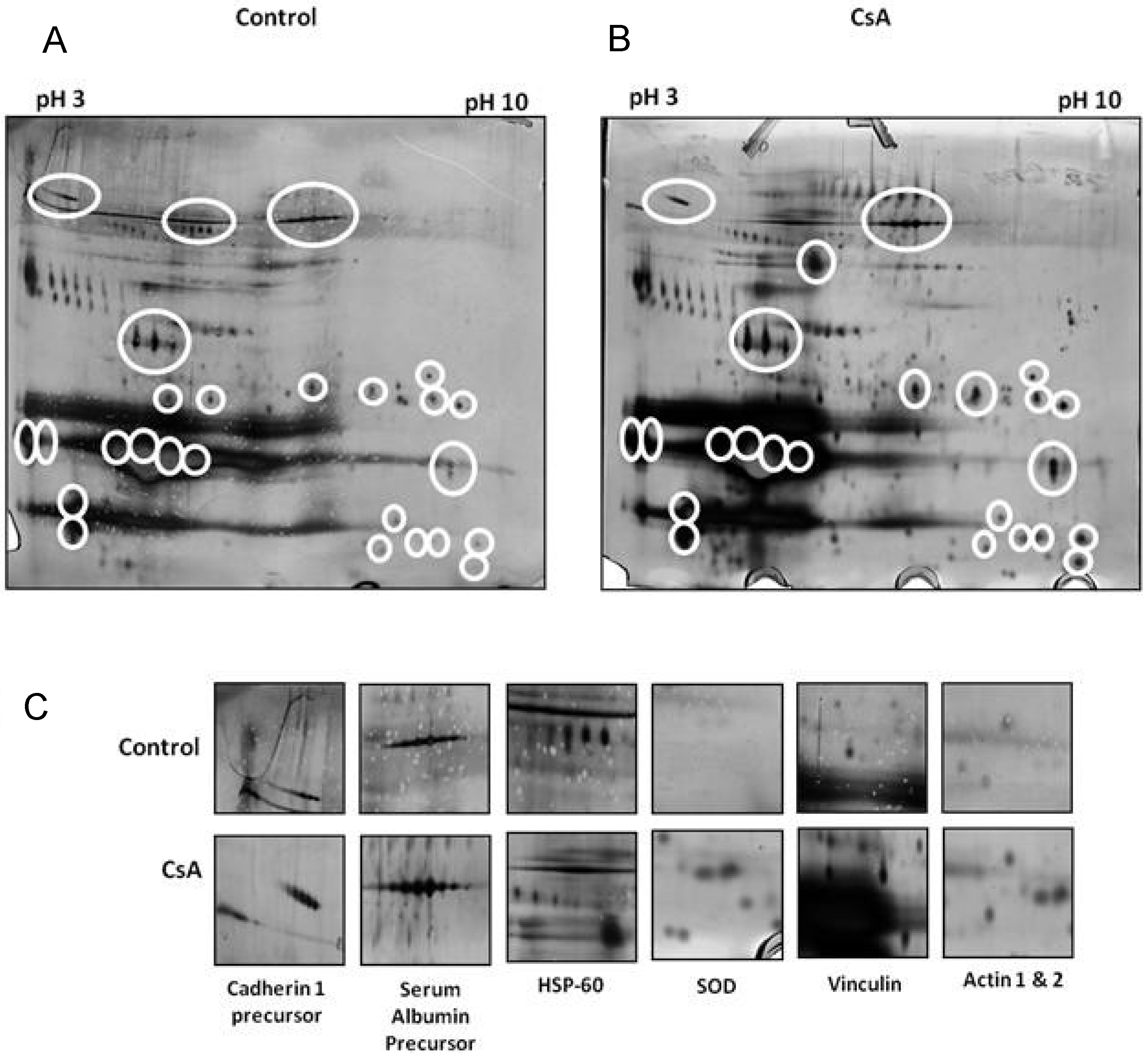
7. In Vitro Proteomic Studies
8. Discussion
9. The Future of Proteomics in CAI Biomarker Identification
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andoh, T.F.; Bennett, W.M. Chronic cyclosporine nephrotoxicity. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 1998, 7, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zoghby, Z.M.; Stegall, M.D.; Lager, D.J.; Kremers, W.K.; Amer, H.; Gloor, J.M.; Cosio, F.G. Identifying specific causes of kidney allograft loss. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, Y.; Sawada, T.; Kubota, K.; Fuchinoue, S.; Teraoka, S.; Shimizu, A. Loss of peritubular capillaries in the development of chronic allograft nephropathy. Transplant. Proc. 2005, 37, 981–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nankivell, B.J.; Chapman, J.R. Chronic allograft nephropathy: Current concepts and future directions. Transplantation 2006, 81, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akalin, E.; O’Connell, P.J. Genomics of chronic allograft injury. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2010, 119, S33–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, R.A.; Ashby, V.B.; Milford, E.L.; Ojo, A.O.; Ettenger, R.E.; Agodoa, L.Y.; Held, P.J.; Port, F.K. Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthanthiran, M.; Strom, T.B. Renal transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Textor, S.C.; Wiesner, R.; Wilson, D.J.; Porayko, M.; Romero, J.C.; Burnett, J.C., Jr.; Gores, G.; Hay, E.; Dickson, E.R.; Krom, R.A. Systemic and renal hemodynamic differences between FK506 and cyclosporine in liver transplant recipients. Transplantation 1993, 55, 1332–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lim, S.W.; Sun, B.K.; Yang, C.W. Chronic cyclosporine nephrotoxicity: New insights and preventive strategies. Yonsei Med. J. 2004, 45, 1004–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Clipstone, N.A.; Crabtree, G.R. Identification of calcineurin as a key signalling enzyme in T-lymphocyte activation. Nature 1992, 357, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepkowski, S.M. Molecular targets for existing and novel immunosuppressive drugs. In Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Remuzzi, G.; Perico, N. Cyclosporine-induced renal dysfunction in experimental animals and humans. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1995, 52, S70–S74. [Google Scholar]
- Shihab, F.S. Cyclosporine nephropathy: Pathophysiology and clinical impact. Semin. Nephrol. 1996, 16, 536–547. [Google Scholar]
- Mihatsch, M.J.; Thiel, G.; Ryffel, B. Histopathology of cyclosporine nephrotoxicity. Transplant. Proc. 1988, 20, 759–771. [Google Scholar]
- Young, B.A.; Burdmann, E.A.; Johnson, R.J.; Alpers, C.E.; Giachelli, C.M.; Eng, E.; Andoh, T.; Bennett, W.M.; Couser, W.G. Cellular proliferation and macrophage influx precede interstitial fibrosis in cyclosporine nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int. 1995, 48, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kino, T.; Inamura, N.; Sakai, F.; Nakahara, K.; Goto, T.; Okuhara, M.; Kohsaka, M.; Aoki, H.; Ochiai, T. Effect of FK-506 on human mixed lymphocyte reaction in vitro. Transplant. Proc. 1987, 19, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Starzl, T.E.; Todo, S.; Fung, J.; Demetris, A.J.; Venkataramman, R.; Jain, A. FK 506 for liver, kidney, and pancreas transplantation. Lancet 1989, 2, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas, M.E.; Zhu, D.; Heitman, J. Molecular mechanisms of immunosuppression by cyclosporine, FK506, and rapamycin. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 1995, 4, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmerman, L.A.; Clipstone, N.A.; Ho, S.N.; Northrop, J.P.; Crabtree, G.R. Rapid shuttling of NF-AT in discrimination of Ca2+ signals and immunosuppression. Nature 1996, 383, 837–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijpkens, Y.W.; Doxiadis, I.I.; van Kemenade, F.J.; Zwinderman, A.H.; de Fijter, J.W.; Claas, F.H.; Bruijn, J.A.; Paul, L.C. Chronic rejection with or without transplant vasculopathy. Clin. Transplant. 2003, 17, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwano, M.; Neilson, E.G. Mechanisms of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2004, 13, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. New insights into epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kidney fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, K.A. The tubulointerstitium in progressive renal disease. Kidney Int. 1998, 54, 992–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masszi, A.; Fan, L.; Rosivall, L.; McCulloch, C.A.; Rotstein, O.D; Mucsi, I.; Kapus, A. Integrity of cell-cell contacts is a critical regulator of TGF-beta 1-induced epithelial-to-myofibroblast transition: Role for beta-catenin. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 165, 1955–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.H.; Kanellis, J.; Hugo, C.; Truong, L.; Anderson, S.; Kerjaschki, D.; Schreiner, G.F.; Johnson, R.J. Role of the microvascular endothelium in progressive renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 806–816. [Google Scholar]
- Marcussen, N. Atubular glomeruli in chronic renal disease. Curr. Top. Pathol. 1995, 88, 145–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strutz, F.; Zeisberg, M.; Ziyadeh, F.N.; Yang, C.Q.; Kalluri, R.; Muller, G.A.; Neilson, E.G. Role of basic fibroblast growth factor-2 in epithelial-mesenchymal transformation. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 1714–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, A.A. Molecular insights into renal interstitial fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1996, 7, 2495–2508. [Google Scholar]
- Eddy, A.A. Progression in chronic kidney disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2005, 12, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solez, K.; Colvin, R.B.; Racusen, L.C.; Sis, B.; Halloran, P.F.; Birk, P.E.; Campbell, P.M.; Cascalho, M.; Collins, A.B.; Demetris, A.J.; et al. Banff '05 Meeting Report: Differential diagnosis of chronic allograft injury and elimination of chronic allograft nephropathy (“CAN”). Am. J. Transplant. 2007, 7, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Pasquali, C.; Appel, R.D.; Ou, O.; Golaz, O.; Sanchez, J.C.; Yan, J.X.; Gooley, A.A.; Hughes, G.; Humphery-Smith, I.; et al. From proteins to proteomes: Large scale protein identification by two-dimensional electrophoresis and amino acid analysis. Biotechnology (NY) 1996, 14, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Gygi, S.P. Proteomics: The move to mixtures. J. Mass Spectrom. 2001, 36, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naaby-Hansen, S.; Waterfield, M.D.; Cramer, R. Proteomics—Post-genomic cartography to understand gene function. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2001, 22, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knepper, M.A. Proteomics and the kidney. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 1398–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, E.S.; Linton, L.M.; Birren, B.; Nusbaum, C.; Zody, M.C.; Baldwin, J.; Devon, K.; Dewar, K.; Doyle, M.; FitzHugh, W.; et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001, 409, 860–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, R.E.; Dunn, M.J.; Hochstrasser, D.F.; Sanchez, J.C.; Blackstock, W.; Pappin, D.J.; Selby, P.J. Proteomics: New perspectives, new biomedical opportunities. Lancet 2000, 356, 1749–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteoliva, L.; Albar, J.P. Differential proteomics: An overview of gel and non-gel based approaches. Brief. Funct. Genomic Proteomic 2004, 3, 220–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.C.; Denny, R.; Dorschel, C.A.; Gorenstein, M.; Kass, I.J.; Li, G.Z.; McKenna, T.; Nold, M.J.; Richardson, K.; Young, P.; et al. Quantitative proteomic analysis by accurate mass retention time pairs. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 2187–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, K.; Mbeunkui, F.; Mitra, S.K.; Mentzel, T.; Goshe, M.B. Improving protein and proteome coverage through data-independent multiplexed peptide fragmentation. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3621–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakorchevsky, A.; Hewel, J.A.; Kurian, S.M.; Mondala, T.S.; Campbell, D.; Head, S.R.; Marsh, C.L.; Yates, J.R., 3rd.; Salomon, D.R. Molecular mechanisms of chronic kidney transplant rejection via large-scale proteogenomic analysis of tissue biopsies. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, S.M.; Heilman, R.; Mondala, T.S.; Nakorchevsky, A.; Hewel, J.A.; Campbell, D.; Robison, E.H.; Wang, L.; Lin, W.; Gaber, L.; et al. Biomarkers for early and late stage chronic allograft nephropathy by proteogenomic profiling of peripheral blood. PLoS One 2009, 4, e6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonyea, J.E.; Anderson, C.F. Weight change and serum lipoproteins in recipients of renal allografts. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1992, 67, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, V.; Navarro-Munoz, M.; Bayes, B.; Lauzurica, R.; Pastor, M.C.; Troya, M.; Bonet, J.; Ibernon, M.; Navarro, M.; Serra, A.; et al. Effect of low doses of atorvastatin on the urinary peptide profile of kidney transplant patients. Transplant. Proc. 2009, 41, 2111–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, V.; Navarro-Munoz, M.; Mas, S.; Bayes, B.; Pastor, M.C.; Martinez-Caceres, E.; Lauzurica, R.; Egido, J.; Romero, R. Proteomic approach to the study of statin pleiotropy in kidney transplant patients. Pharmacology 2011, 87, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongboonkerd, V.; McLeish, K.R.; Arthur, J.M.; Klein, J.B. Proteomic analysis of normal human urinary proteins isolated by acetone precipitation or ultracentrifugation. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieper, R.; Gatlin, C.L.; McGrath, A.M.; Makusky, A.J.; Mondal, M.; Seonarain, M.; Field, E.; Schatz, C.R.; Estock, M.A.; Ahmed, N.; et al. Characterization of the human urinary proteome: A method for high-resolution display of urinary proteins on two-dimensional electrophoresis gels with a yield of nearly 1,400 distinct protein spots. Proteomics 2004, 4, 1159–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, B.A.; Suzuki, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Tomino, Y.; Spasovski, G.; Novak, J. Sources of urinary proteins and their analysis by urinary proteomics for the detection of biomarkers of disease. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2009, 3, 1029–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroot, J.J.; Hendriks, J.C.; Laarakkers, C.M.; Klaver, S.M.; Kemna, E.H.; Tjalsma, H.; Swinkels, D.W. (Pre)analytical imprecision, between-subject variability, and daily variations in serum and urine hepcidin: Implications for clinical studies. Anal. Biochem. 2009, 389, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, E.; Bruschi, M.; Candiano, G.; Boccardi, C.; Citti, L.; Mangraviti, S.; Rosso, G.; Larti, A.; Rosati, A.; Ghiggeri, G.M.; et al. Posttransplant proteinuria associated with everolimus. Transplant. Proc. 2009, 41, 1216–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Riordan, E.; Orlova, T.N.; Mendelev, N.; Patschan, D.; Kemp, R.; Chander, P.N.; Hu, R.; Hao, G.; Gross, S.S.; Iozzo, R.V.; et al. Urinary proteomic analysis of chronic allograft nephropathy. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2008, 2, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, L.F.; Sole-Gonzalez, A.; Kalko, S.G.; Banon-Maneus, E.; Sole, M.; Diekmann, F.; Gutierrez-Dalmau, A.; Abian, J.; Campistol, J.M. Urine proteomics to detect biomarkers for chronic allograft dysfunction. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, L.F.; Campistol, J.M.; Alcolea, M.P.; Banon-Maneus, E.; Sol-Gonzalez, A.; Cutillas, P.R. Application of label-free quantitative peptidomics for the identification of urinary biomarkers of kidney chronic allograft dysfunction. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2009, 8, 1658–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banon-Maneus, E.; Diekmann, F.; Carrascal, M.; Quintana, L.F.; Moya-Rull, D.; Bescos, M.; Ramirez-Bajo, M.J.; Rovira, J.; Gutierrez-Dalmau, A.; Sole-Gonzalez, A.; et al. Two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis urinary proteomic profile in the search of nonimmune chronic allograft dysfunction biomarkers. Transplantation 2010, 89, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetaz, R.; Trocme, C.; Roustit, M.; Pinel, N.; Bayle, F.; Toussaint, B.; Zaoui, P. Predictive diagnostic of chronic allograft dysfunction using urinary proteomics analysis. Ann. Transplant. 2012, 17, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, M.; Eidelman, O.; Torosyan, Y.; Jozwik, C.; Mannon, R.B.; Pollard, H.B. Elevated expression levels of ANXA11, integrins beta3 and alpha3, and TNF-alpha contribute to a candidate proteomic signature in urine for kidney allograft rejection. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2011, 5, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
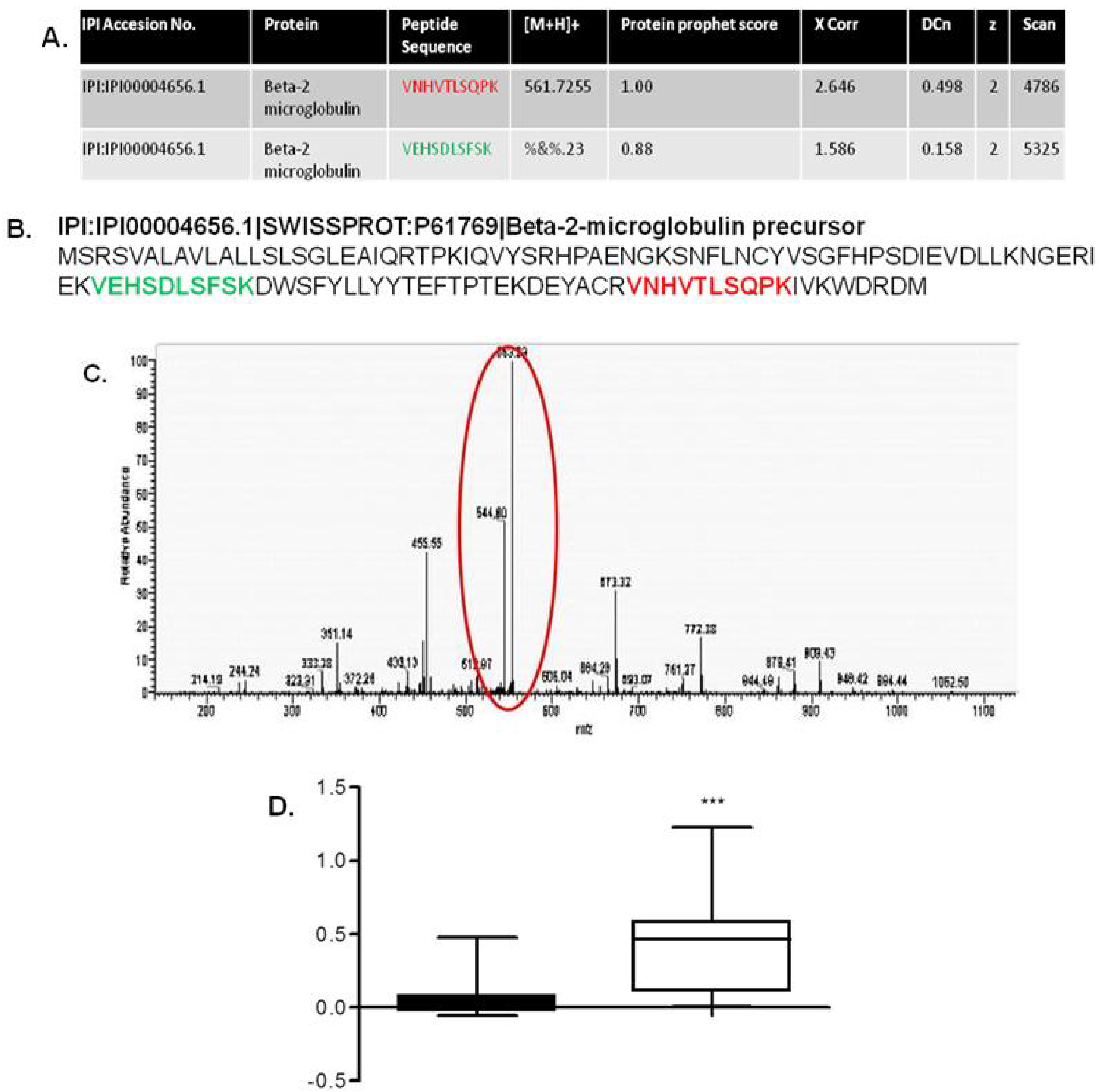
- Johnston, O.; Cassidy, H.; O’Connell, S.; O’Riordan, A.; Gallagher, W.; Maguire, P.B.; Wynne, K.; Cagney, G.; Ryan, M.P.; Conlon, P.J.; et al. Identification of beta2-microglobulin as a urinary biomarker for chronic allograft nephropathy using proteomic methods. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2011, 5, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, R.S.; Granger, G.A.; Brown, W.; Baker, P.; Jutila, J.; Holmes, B. Production of acute allogeneic disease in mice. Transplantation 1965, 3, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, E. Genetics. The geneticist’s best friend. Science 2007, 317, 1668–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyachieo, A.; Chai, D.C.; Deprest, J.; Mwenda, J.M.; D’Hooghe, T.M. The baboon as a research model for the study of endometrial biology, uterine receptivity and embryo implantation. Gynecol. Obstet. Invest. 2007, 64, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, J.A.; Zhang, Y.; Mangos, G.; Kelly, J.J. Species variability in cardiovascular research: The example of adrenocorticotrophin-induced hypertension. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 33, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; Reiermann, S.; Worner, R.; Schroter, R.; Edemir, B.; Buck, F.; Henning, S.; Peter-Katalinic, J.; Vollenbroker, B.; Amann, K.; et al. IF/TA-related metabolic changes—Proteome analysis of rat renal allografts. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 2492–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klawitter, J.; Kushner, E.; Jonscher, K.; Bendrick-Peart, J.; Leibfritz, D.; Christians, U.; Schmitz, V. Association of immunosuppressant-induced protein changes in the rat kidney with changes in urine metabolite patterns: A proteo-metabonomic study. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, S.; Slattery, C.; Ryan, M.P.; McMorrow, T. Identification of novel indicators of cyclosporine A nephrotoxicity in a CD-1 mouse model. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 252, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Lv, L.L.; Cao, Y.H.; Liu, H.; Ni, J.; Dai, H.Y.; Liu, D.; Lei, X.D.; Liu, B.C. A pilot trial assessing urinary gene expression profiling with an mRNA array for diabetic nephropathy. PLoS One 2012, 7, e34824. [Google Scholar]
- Ardaillou, R. Biology of glomerular cells in culture. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 1996, 12, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.D. In vitro methods in renal research. In Pediatric Nephrology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Schramek, H.; Willinger, C.C.; Gstraunthaler, G.; Pfaller, W. Endothelin-3 modulates glomerular filtration rate in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Ren. Physiol. Biochem. 1992, 15, 325–333. [Google Scholar]
- Ruegg, C.E.; Gandolfi, A.J.; Nagle, R.B.; Krumdieck, C.L.; Brendel, K. Preparation of positional renal slices for study of cell-specific toxicity. J. Pharmacol. Methods 1987, 17, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.H. The use of renal cortical slices from the Fischer 344 rat as an in vitro model to evaluate nephrotoxicity. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1988, 11, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruegg, C.E. Preparation of precision-cut renal slices and renal proximal tubular fragments for evaluating segment-specific nephrotoxicity. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 1994, 31, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potier, M.; L’Azou, B.; Cambar, J. Isolated glomeruli and cultured mesangial cells as in vitro models to study immunosuppressive agents. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 1996, 12, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaller, W.; Gstraunthaler, G. Nephrotoxicity testing in vitro—What we know and what we need to know. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106, 559–569. [Google Scholar]
- Lamoureux, F.; Mestre, E.; Essig, M.; Sauvage, F.L.; Marquet, P.; Gastinel, L.N. Quantitative proteomic analysis of cyclosporine-induced toxicity in a human kidney cell line and comparison with tacrolimus. J. Proteomics 2011, 75, 677–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Rahman, H.; Oellerich, M.; Asif, A.R. Differential proteome analysis of human embryonic kidney cell line (HEK-293) following mycophenolic acid treatment. Proteome Sci. 2011, 9, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puigmule, M.; Lopez-Hellin, J.; Sune, G.; Tornavaca, O.; Camano, S.; Tejedor, A.; Meseguer, A. Differential proteomic analysis of cyclosporine A-induced toxicity in renal proximal tubule cells. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 2672–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cassidy, H.; Slyne, J.; Frain, H.; Slattery, C.; Ryan, M.P.; McMorrow, T. High-Throughput Proteomic Approaches to the Elucidation of Potential Biomarkers of Chronic Allograft Injury (CAI). Proteomes 2013, 1, 159-179. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes1020159
Cassidy H, Slyne J, Frain H, Slattery C, Ryan MP, McMorrow T. High-Throughput Proteomic Approaches to the Elucidation of Potential Biomarkers of Chronic Allograft Injury (CAI). Proteomes. 2013; 1(2):159-179. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes1020159
Chicago/Turabian StyleCassidy, Hilary, Jennifer Slyne, Helena Frain, Craig Slattery, Michael P. Ryan, and Tara McMorrow. 2013. "High-Throughput Proteomic Approaches to the Elucidation of Potential Biomarkers of Chronic Allograft Injury (CAI)" Proteomes 1, no. 2: 159-179. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes1020159
APA StyleCassidy, H., Slyne, J., Frain, H., Slattery, C., Ryan, M. P., & McMorrow, T. (2013). High-Throughput Proteomic Approaches to the Elucidation of Potential Biomarkers of Chronic Allograft Injury (CAI). Proteomes, 1(2), 159-179. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes1020159





